Abstract
The current state of the study of different liquid crystalline (LC) systems doped with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is discussed. An attempt is endeavored to outline the state-of-the-art technology that has emerged after two past decades. Systematization and analysis are presented for the integration of single- and multi-walled carbon nanotubes in thermotropic (nematic, smectic, cholesteric, ferroelectric, etc.) and lyotropic LCs. Special attention is paid to the effects of alignment and supramolecular organization resulting from orientational coupling between CNTs and the LC matrix. The effects of the specific inter-molecular and inter-particle interactions and intriguing microstructural, electromagnetic, percolation, optical, and electro-optical properties are also discussed.
1. Introduction
Liquid crystal (LC) colloids constantly attract great attention from researchers. The early historical account of the problem was presented in [1]. One can also mention the recent reviews on metal oxide nanoparticles (MgO, ZnO, Fe2O3, Al2O3, Cu2O3, NiO, SiO2, ZrO2, and TiO2) [2], semiconducting quantum dots/rods [3], and metal (Ag, Au, and Pt) nanoparticles [4,5] dispersed in LCs. The effects of the LC’s material alignment induced or enhanced by incorporated nanoparticles and the methodology of developing new innovative devices based on this alignment process were recently discussed [6]. The effects of LC phase transitions on the topological defects (defect morphogenesis) induced by the colloidal particles dispersed in LCs were also recently reviewed [7].
Note that LCs may serve as a special type of host for anisotropically shaped nanoparticles such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), as well as graphene-derived or inorganic nano-platelets [8]. These composites exhibit many intriguing properties related to the anisotropy of individual particles and self-assembled LC systems [9]. LCs can assist in the aligning of such nanoparticles, resulting in the formation of anisotropic systems with enhanced functional properties. Moreover, in such systems, the inverse alignment effects of anisometric particles on the LC’s ordering can be very important. In previous years, the composites based on LCs doped with anisotropically shaped nanoparticles attracted great attention. These composites can be used for creating multifunctional devices with exceptional electronic performance.
This review aims to provide an overview as well as the authors’ personal account of the studies of LC materials doped with CNTs and their applications. A comprehensive overview of the “state-of-the-art” technology in the field, developments, and advantages for the recent 20–25 years is given. The critical analysis of CNTs self-assembling in LC media and the effects of CNTs on LC ordering is presented. The review starts with brief discussions of different classes of LCs and the main properties of CNTs. A short presentation of the existing reviews in the field is presented in the table. The different properties of thermotropic and lyotropic LCs doped with CNTs, particularly phase transitions, microstructural, electromagnetic, percolation, optical, electro-optical properties, and issues related to the material stability, are given. Finally, the conclusions and future perspectives of this rapidly emerging field are provided.
2. Types of Liquid Crystals
The liquid-crystalline state of matter (mesomorphic state, or mesophase) is intermediate between the crystalline and liquid states, simultaneously showing some of the anisotropic properties of solids and the fluidity of liquids [10]. In this state, materials demonstrate a tendency to flow like liquids and have some properties similar to solids. LCs may be divided into two main classes, named thermotropics and lyotropics [2,6,11]. Amphotropic LCs that show both thermotropic and lyotropic phases were also identified [12,13]. For example, exhibition of amphotropic LC properties has been reported for many amino acid, peptide, phospho- and glycolipid-based LCs, with a special attention to the LC-like structure of cell membranes [14,15,16]. The properties of polymeric and elastomeric LC phases were also discussed [17,18,19,20]. These materials combine polymer network properties with LC anisotropy, and they are good candidates for stimuli-responsive reversible shape memory materials [21]. The different polymer-modified LCs (e.g., a continuous polymer matrix with the inclusion of LC droplets or a bicontinuous system of a polymer network dispersed in an LC host) also represent a great interest for different practical applications [22].
For the completeness, we can also refer to important classes of unconventional LCs. The two main categories related to supermolecular and supramolecular systems were highlighted (for a recent review, see [23]). The different types of ionic LC versatile materials (dendrimeric thermotropic, polymeric, lyotropic, zwitterionic, and mesoionic) were also identified [24,25].
2.1. Thermotropic Liquid Crystals
Thermotropic LCs demonstrate the presence of LC phases in a certain temperature range between the crystalline solid and isotropic liquid. Therefore, in these materials, the mesomorphic state formation depends on temperature. These substances with anisotropically shaped molecules demonstrate the dual characteristics of solids and liquids. They have some sort of positional or orientational order and may flow like a liquid. This duality can lead to anisotropy in optical, viscoelastic, electrical, and magnetic properties. On the basis of molecular shape, the LCs can be classified as calamitic (rod-like molecules), discotic (disc-like molecules), and bent-core (banana-shaped molecules with bent cores and flexible tails) types; other more exotic types (e.g., bowlic) have also been reported. Nowadays, huge quantities of thermotropic LC substances (more than 70,000) with different chemical compositions and phase transition temperatures have been discovered [26,27].
The main thermotropic LC phases are nematics, smectics, and cholesterics [28,29,30]. In the simplest nematic LCs, the molecules are preferentially oriented along a single director axis, but they have no positional order. In the smectic LCs phases with positional layered order, the molecules have a long-range orientational order and are organized positionally in smectic layers. In smectic A and smectic C phases, the molecules are oriented along the layer normally and at an oblique angle to the normal angle, respectively. There also exist many other types of smectic arrangements (B, D, E, F, etc.) with more complex self-organization. In the cholesteric (chiral nematic) LC phase, the director shows a helical structure and the molecules are arranged along a director axis with continuous changes of their directions in the form of a helix [28]. The helical period is typically in the range from 0.1 to 100 microns, with characteristics optimal for applications observed in more narrow ranges (10–20 μm in most cases). The more complex LC phases such as chiral nematic, chiral smectic, blue phases, and twist grain boundary phases were also identified [13], as well as most novel twist-bend and ferroelectric nematics [31,32]. The phase transitions between various LC phases can be first order, second order, or weakly first order.
2.2. Lyotropic Liquid Crystals
In lyotropic LCs, the phase transitions are induced by changes in the temperature and concentration of dissolved amphiphilic molecules (including the hydrophobic and hydrophilic blocks) in suitable solvents. In an aqueous environment, such molecules can be self-organized in different phases depending on their molecular structure [33,34]. At temperatures above Krafft point, boundaries called CMC curves between the unimer and aggregate solution (micellar, vesicle, or microemulsions) phases appear. Typically, lyotropic LCs demonstrate the different types of long-range periodicity, with amphiphilic molecules arranged in the nematic, hexagonal, lamellar, and different intermediate (e.g., cubic) phases [35]. In a lamellar phase, bilayers with hydrophilic head groups oriented to water are formed. In a hexagonal phase, the amphiphilic molecules are arranged as infinite cylindrical structures on a hexagonal lattice. A cubic phase may exist between the lamellar and hexagonal LC phases; in this phase, the arrangement is in the form of a lipid sphere in a dense cubic lattice. These LCs can be used as efficient systems in drug delivery [36]. Water-based lyotropic LCs are common in biological and living systems [37]. The phase diagrams for many surfactant/water systems can be found in the review [34]. The anisotropic colloidal particles (rod-like, plate-like, or their hybrids) can also form lyotropic LC phases. These structures are called nanomesogen lyotropic LCs [38].
3. Carbon Nanotubes
The tribute to the first publication on carbon nanotubes is usually paid to Iijima, who seems to be the first to have had them synthesized [39]. (However, as always, every discovery finds its predecessors, and we mention here the work where CNTs were, in fact, obtained, but not fully understood and advertised by the authors [40]). CNTs represent elongated cylindrical graphene sheets, and there exist single-walled (SWCNTs) and multi-walled (MWCNTs) carbon nanotubes. CNTs can have extremely high aspect ratios, ε ≈ 100–1000 (ε = L/d is the length to diameter ratio). Examples of microscopy images of MWCNTs are shown in Figure 1.
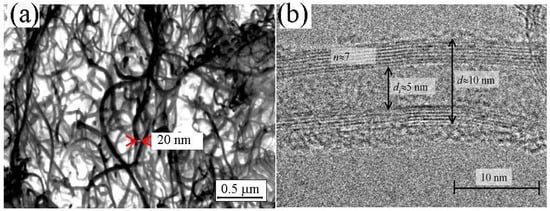
Figure 1.
Scanning electron microscopy (a) and high-resolution electron microscopy (b) images of MWCNTs. Here, the inner and outer diameters are denoted as di and d, respectively, while n is a number of MWCNT walls. ((a) was reprinted with permission from Ref. [41]. Copyright 2009 IOP Publishing; (b) was reprinted with permission from Ref. [42]. Copyright 2014 Elsevier).
Typically, MWCNTs display very good mechanical properties and very high electrical (metallic) and thermal conductivity. The combination of these attractive properties allows a wide range of their applications in different sensors, field emitters, energy-storage, energy-conversion, and gas storage devices.
The length of CNTs can vary from hundreds of nanometers to centimeters. Their diameter can also vary between about one and two nanometers (SWCNTs) and tens of nanometers (MWCNTs). Moreover, the shape of CNTs is not straight and they are rather tortuous [43].
4. Liquid Crystalline Composites with CNT Dopants
Historically, the behavior of elongated particles suspended in an LC was discussed for the first time some 50 years ago [44]. In such systems, the particle axis is locked and directed parallelly to the nematic axis. A similar analysis was performed for magnetic platelets introduced into a nematic LC [45].
About 20–25 years ago, CNTs started to be used as the dopants in different thermotropic and lyotropic LC systems. It seems that the dispersions of CNTs in nematic LCs were first analyzed with the aim of improving the characteristics of LC optical gratings [46,47]. In pioneering works, the properties of CNTs in orientationally ordered LC matrixes were also studied [48,49]. The existing reviews on previous works are collected in Table 1.

Table 1.
Short description of some reviews of the behavior of LCs doped with anisotropically shaped nanoparticles (mainly with CNTs).
4.1. Thermotropic Liquid Crystals
In thermotropic LCs, anisotropic interactions between the CNTs and media can drastically change the alignments and physical properties of the mixtures. In these systems, the macroscopic organization resulting from mutual interactions between CNTs and LCs can be very pronounced [78]. The great interest in such systems can be explained by a variety of intriguing effects that can be of great practical importance. In LC electro-optical cells doped with CNTs, the response times became shorter, and the driving voltage was lowered. This was also accompanied by the suppression of image sticking and parasitic backflow [79,80,81,82]. Various non-trivial effects were reported for LC + CNT composites, such as super-elongation [83], electromechanical memory [84], ultra-low percolation thresholds [41,85], electrokinetic dispersion [86], etc. One should especially note the electro-optical memory effects [57].
Dielectric anisotropy of SWCNT–nematic LC (E7) composites in microwave range was studied [87]. It was shown that the dielectric anisotropy can be increased; this is a promising result for creating tunable dielectric materials. In recent works, the effects of ionic impurities on properties of LC nano-colloids were intensively discussed [88,89,90]. The presence of CNTs can significantly affect the behavior of ions in LCs [62]. Observed non-monotonous behavior of electrical properties at different concentrations of nanoparticles was explained by the peculiarities of the adsorption/desorption processes. It was demonstrated that the adding of quantum dots (QDs) may generate the ionic contamination of the LC [91,92]. The intriguing effects in the electro-physical properties and electro-optical responses in LC cells doped with semiconductor QDs (CdSe/ZnS) have been reported [91,92]. The concentration of QDs significantly affected the response and relaxation time. The effects of the application of a unipolar rectangular electric field to an LC cell were also discussed.
4.1.1. Nematic Liquid Crystals
Thermotropic LCs have been frequently applied as suitable nematic hosts for the alignment of nanotubes, and many of the previously reported works were devoted to studies of the CNT–nematic LC dispersions. SWCNTs and MWCNTs dispersed in nematic LCs 5CB (nematic range 24–35 °C), and E7 (nematic range −10 to +60 °C) demonstrated the presence of orientational ordering in the nematic matrix [48]. It was shown that CNT alignment results from orientational coupling to the nematic matrix. Spontaneous parallel alignment of CNTs in LCs along the director with a high level of orientational order parameter (S ≈ 0.9) was explained by elastic interactions (so-called anchoring forces) of elongated particles with the nematic LC host [93,94].
The behavior of electrical conductivity as a function of the applied voltage for the CNT–LC composites and their possible practical applications in electrically controlled light-steered switches and wavelength-dependent sensors were discussed [94]. The effect of MWCNTs on phase transitions of nematic LCs (E7) has been investigated by means of polarizing optical microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry [95]. Observed enhancement of the isotropic–nematic phase transition temperature in a very narrow range of CNT concentration (0.1–0.2% wt) was attributed to anisotropic alignment of LC molecules along the CN bundles. For LCs with a biphenyl molecular core structure, the importance of π-stacking interactions between CNTs and LC molecules was justified using polarized Raman spectroscopy [96,97]. The mutual self-organizational effects in CNT and LC subsystems results in the manifestation of versatile properties of these functional mixtures [98].
The mixtures of MWCNTs (0.01–0.15% wt) and nematic media with different signs of dielectric anisotropy ZhK-1282 (Δε > 0) and ZhK-440 (Δε < 0) have been studied by means of optical transmission and electric conductivity measurements [99,100,101]. The obtained data suggested the existence of supra-molecular organization in the studied CNT–LC mixtures. The presence of strong anisotropic interactions between CNTs and orientationally ordered LC matrixes was supposed.
The joint orientationally ordered arrangements for Δε > 0 and Δε < 0 are schematically shown in Figure 2. The nanotubes in an LC environment are shown as “cell”-forming elements. Here, the orientation of “large” anisotropic particles is restricted by the orientational order imposed by the nematic matrix, whereas these particles also perturb the ordering inside matrix. The different supra-molecular organizations in orientationally ordered LC + CNTs systems with different signs of Δε reflect the diversity in strong anisotropic interactions between components in these systems. This diversity results in different properties of such composites. In particular, for a fixed concentration of MWCNTs, the electrical conductivity in ZhK-1282 (Δε > 0) was several times high than that in ZhK-440 (Δε < 0) since, in the latter case, the LC environment does not favor NT orientation along the electric field.
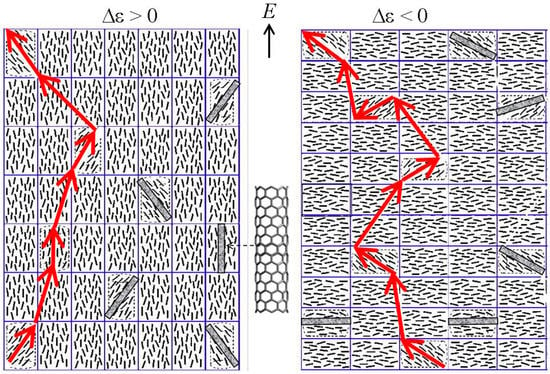
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the supra-molecular organization in CNT–LC mixtures for nematic media with different signs of dielectric anisotropy Δε. Arrows correspond to the local preferred orientation of CNTs inside the LC host (based on the model discussed in [99]).
It has been shown that the optical transmission taken at a certain wavelength well above the eventual absorption or selective reflection bands showed a dramatic increase at the N–I transition. The magnitude of this “transmission jump” was substantially increased in the presence of dispersed CNTs. This increase obviously reflected the effects of the spatial organization of CNTs in the orientationally ordered nematic medium. In this respect, the studied LC–CNT composites were essentially similar to the LC systems with non-mesogenic dopants, which are generally considered homogeneous at the microscopic level.
The behaviors of composites of MWCNTs (0.01–0.15% wt) in nematic hosts with dielectric anisotropy of different signs 5CB (Δε > 0), ZhK-1282 (Δε > 0) and ZhK-440 (Δε < 0), 1:1 MBBA + EBBA mixture (weakly negative Δε) have been compared [99,102]. The complex electrical conductivity versus the applied voltage dependencies (Figure 3) in these mixtures were explained by the different impact of an LC environment on the preferred orientation of CNTs inside the hosts. The addition of CNT dopants improved the functional properties of LC composites and resulted in an increasing threshold voltage and in the suppression of electro-hydrodynamic instability in nematics.
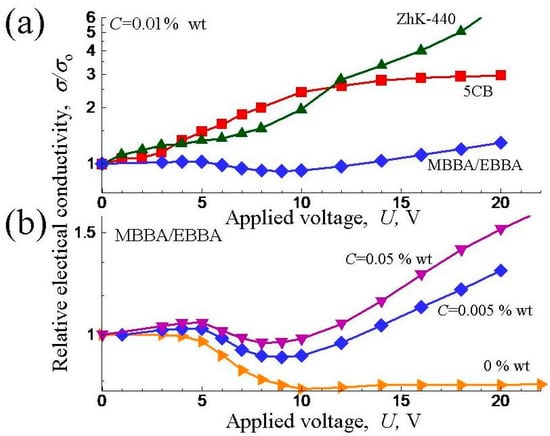
Figure 3.
Relative changes in electrical conductivity on application of DC voltage for MWCNTs in different LCs at fixed concentration C = 0.01% wt (a) and in MBBA/EBBA LC mixtures at different values of C (b). (Based on the experimental data presented in [102]).
With nematic LCs of other chemical classes, the transmission jump was similar to that of cyanobiphenyls, while it was obviously less pronounced with that of cyclohexylcyclohexanes [103], probably due to the absence of aromatic rings and, respectively, weaker interactions with CNTs. It is also clear that the transmission jump becomes more pronounced with higher concentration of CNTs, monotonously increasing from ~0.01% wt to 0.1% wt.
The phase transitions and intermolecular interactions in the CNT–LC (EBBA) composites were experimentally studied by means of DSC and FTIR spectroscopy, measurement of electrical conductivity, optical transmittance, and analysis of microstructure [41,85,104]. The effect of a positive temperature coefficient was observed at CNT concentrations above 0.05–0.1% wt. Observed heating–cooling hysteretic behavior was explained by strong agglomeration and rearrangement of nanotubes during the thermal incubation. The time lag of the solidification process was shown to be dependent upon a supercooling temperature in accordance with the classical heterogeneous nucleation law [41]. In this process, the CNTs played the role of solidification centers in LC media. Observed nonlinear dependences of electrical conductivity on the applied voltage and frequency were explained by the existence of the field-enhanced charge transport through hopping junctions in the LC gaps between CNTs.
The CNT–LC composites studied in various papers were, in most cases, non-equilibrium systems because of the tendency of CNTs to aggregate. For CNT concentrations in the 0.01–0.1% wt range, the composites represent a sort of “quasi-equilibrium” system. For these systems, quite reasonable and seemingly reproducible results can only be obtained for a sufficiently short time after the preparation of samples.
The effects of CNT aggregation on the optical transmission jump at the nematic-isotropic transition were discussed [41] (Figure 4). The measurements were carried out just after ultrasonication of CNTs in the nematic host and after certain periods of time. It was shown that, at CNT concentrations of 0.05–0.1% wt, the transmission jump noticeably decreased after several hours of incubation. This can be explained by aggregation processes. In subsequent studies, these experiments were repeated with different nematic matrices, CNTs with different aspect ratios and concentrations, different temperatures, etc. [70,105,106,107,108]. It can be argued that the proposed method could be used as a convenient way to monitor the CNTs’ aggregation, thus allowing optimization of CNT–LC systems as promising nanomaterials.
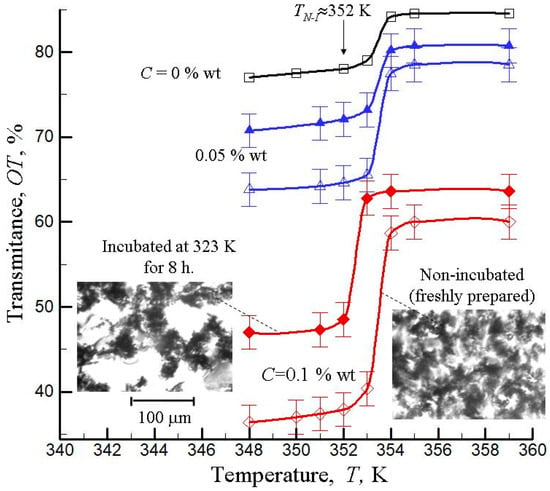
Figure 4.
The “optical transmittance jumps” in MWCNTs + EBBA composites. The data are presented near the transition temperature from the nematic to isotropic phase (TNI = 352 K). Open and closed symbols denote non-incubated and incubated (at 323 K for 8 h) samples, respectively. The microphotographs were obtained for 0.1% wt composites. (Based on the experimental data presented in [41]).
The electro-optical responses in CNTs dispersed in different nematic LCs with positive (5CB) and negative (EBBA and MLC6608) dielectric anisotropy were investigated [109,110,111,112]. The electro-optical memory effects have been discovered and described in detail. In such LC systems placed between two crossed polarizers, the optical transmittance of the suspension layer substantially increased after the application of an electric field, and this state was very long-lasting (persisted over months). The observed effects were most significant after the formation of an interconnected network of CNTs in LCs. The memory effects were explained by the incomplete relaxation of LC molecules from a planar to an initial homeotropic state after the electric field switch-off.
Relationships between electro-optical responses, optical singularities, and electrical conductivity behavior of mixtures of MWCNTs and nematic LC (5CB) have been discussed [113,114,115,116,117]. The self-organization of CNTs, formation of fractal aggregates, and spanning CNT networks was accompanied by the generation of optical singularities. The effects were explained by optical effects related to the formation of micron-sized perturbed interfacial LC shells covering the CNT clusters. The inversion wall topological structures were observed for CNT–LC composites at threshold values of the applied field in the vicinity of Freedericksz transition [116,117]. In particular, the effects of time incubation on induced optical singularities, inversion walls, and electrophysical and thermodynamic characteristics of CNT–LC (5CB) composites have been investigated [118]. The different incubation stages included the initial stage of formation of loose aggregates of CNTs, the formation of aggregates with ramified fractal borders, and the compactization of aggregates.
The factors affecting the efficient dispersion of CNTs in thermotropic LCs and the stability of these systems were discussed in detail [58,105,106,119,120,121]. The different methods for characterizing equilibrium CNT–LC composite materials have been discussed and compared [120]. The formation of aggregates in mixtures of CNTs (0.025–1% wt) in nematic LC (5CB) during the aging (incubation) processes was monitored [105,106,119,121]. The observations included changes in microstructure, birefringent structure of LC cladding around CNT aggregates and induced optical singularities, and measurements of the temperature and concentration dependences of light transmissions, DSC, and electrical conductivity patterns. In the initial state, after intensive homogenization via ultrasonication, the CNTs were more or less homogeneously dispersed in the nematic matrix and aligned along the nematic director. The time incubation (several hours or days) resulted in the formation of micron-sized aggregates consisting of inner skeletons with trapped shells of adjacent nematic molecules [119] (Figure 5). Light shells near the surface of MWCNT aggregates initiated by the applied electric field have been explained by the strong anchoring of 5CB molecules to the surface of MWCNTs [106].
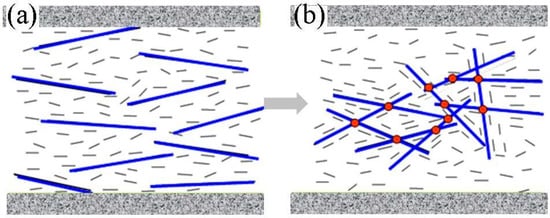
Figure 5.
A simplified model of the aging of CNTs dispersed in nematic LCs. The nanotubes are initially dispersed homogeneously via intensive ultrasonication (a), and time incubation (several hours or days) resulted in formation of ramified aggregates with trapped nematic shells incorporated into the CNT skeleton (b). (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [119]. Copyright 2011 Elsevier).
Analysis of the voltage dependence on the relative integral intensity of images, I/Io, (here, Io is the integral intensity at U = 0 V) showed the presence of a strong dependence of the thickness of birefringent interfacial shells upon the applied voltage U (Figure 6). The value of I/Io increased noticeably for voltages above some threshold value of Uth = 3–4 V because of the Freedericksz transition. The “fresh” composites also displayed a higher saturation level of I/Io at large U > 8–10 V as compared with incubated composites. Observed aging behavior was explained by the transition from loose aggregates (L-aggregates) in the “fresh” composite to the compacted aggregates (C-aggregates) in the “incubated” composite.
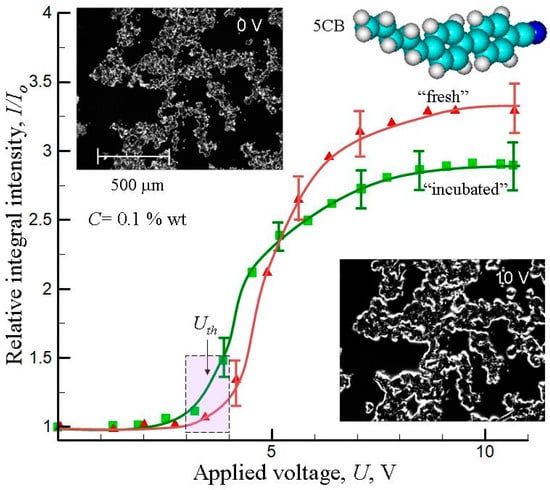
Figure 6.
Relative integral intensity of images, I/Io, as function of the applied voltage U. The data are presented “fresh” or “incubated” (during 1 week) 5CB + MWCNT (0.1% wt) composites at temperature 298 K. Microphotographs of the “fresh” composites at U = 0 V and 10 V are shown in the inserts. (Based on the experimental data presented in [106]).
The values of I/Io increased noticeably for voltages above some threshold value of Uth = 3–4 V (Freedericksz transition inside 5CB). At large voltages (U > 8–10 V), the saturation level of I/Io was smaller for the “incubated” composites. It can reflect compactization of the initially formed loose aggregates into the more compact aggregates during the incubation time of one week [106].
The effects of applied electric fields on the alignment of CNTs in LCs have been intensively discussed in many recent theoretical and experimental studies [122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131].
In particular, the structural changes in CNT–nematic LC (6CHBT) composites in applied electric and magnetic fields have been studied using the attenuation measurement of surface acoustic wave (SAW) propagating techniques [125]. The studied CNTs were MWCNT and magnetically functionalized MWCNT/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The applied acoustic method is useful for the characterization of elastic and viscous parameters of composites near phase transitions. Obtained data evidence the presence of orientational coupling between MWCNTs and LC molecules. The results show that the combination of electric and magnetic fields can be used to control the orientation of LC molecules in doped samples.
The dynamic behavior of CNT–nematic LC composites in the electric and magnetic fields has been analyzed both theoretically and experimentally [124,127,128,129,130,131]. A theoretical model based on elastic continuum theory allowed the evaluation of the relaxation times [124]. Experimental studies of CNT–nematic (5CB) composites revealed significant effects of CNT doping on the relaxation time. The relaxation time was shorter when the field was switched off immediately after application and longer when the field was applied for at least one hour. Recently, the impact of dispersed CNTs on the Freedericksz transition threshold was discussed [129].
Flexoelectric effects (appearance of electric polarization due to the strain gradient in a dielectric material) in CNT–nematic LC composites have been evaluated using the Helfrich theory for weak and hard anchoring conditions [123]. The calculations were performed assuming the absence of aggregation of the CNTs in a nematic host. The flexoelectric coefficients’ increase up to 5-fold was predicted near the phase transition temperature.
For strong anchoring of nematogens over the surfaces of CNTs, the theory predicts that the application of an electric field can change the phase behavior, and it influences the ordering of both LC molecules and CNTs [122]. The effect of an electric field and LC media on the alignment and order parameters of CNTs was examined analytically. The influence of CNT aspect ratio (length-to-diameter ratio) on CNT and LC alignments have also been analyzed [126]. The CNT and LC order parameters increased with the increasing of the electric fields, and the electric field acted as a stimulus. It was demonstrated that the CNT alignment can be improved and controlled by adjusting the LC anchoring strength.
Several experimental techniques (DSC, low-temperature photoluminescence, measurement of electrical conductivity) were used to study low-temperature phase transformations in CNT–LC (5CB) mixtures [132,133]. The introduction of CNTs resulted in partial elimination of the low-temperature metastable states of 5CB, and several anomalies in the temperature dependences of electrical conductivity were revealed. The effects were explained by the influence of phase transformations of 5CB in the interfacial layers on the transport of charge carriers between CNTs [132]. The observed temperature transformation of the luminescent and thermal properties of LC and CNT–LC mixtures in the temperature interval 10–297 K were explained by the intra-crystalline transitions in 5CB medium [133].
The formation of interconnected percolation networks with ultra-low percolation thresholds at some critical concentrations of CNTs (0.05–0.1% wt) was discussed in many early works [41,57,85,100,101,102,104,106,108,114]. Note that the percolation behavior is a complex phenomenon that can depend upon the degree of aggregation, shape of the measuring cell, and distance between electrodes. The different regimes of electrical conductivity behavior in CNT–LC composites (tunneling–hopping, percolation, and multiple-contacts) placed between two electrodes have been revealed [115]. The different modes of sample preparation in cells between two electrodes were used [134]. It was demonstrated that typical capillary filling techniques may introduce some inaccuracies when the size of CNT aggregates is comparable with the thickness of the cell. The more accurate filling technique was based on pressing the drop of dispersion between two electrodes with a fixed distance of 250 μm. The measured concentration dependencies of electrical conductivity clearly revealed the two-step percolation transitions at concentrations 10−4% wt and 10−1% wt. This behavior was explained using the mean-field theory, assuming a core–shell structure of CNTs. Two types of cell geometries were used in studies of structural evolution and dielectric properties of CNTs (10−5–2.5% wt) in nematic LC (5CB) mixtures. The two sandwich-type cells with the electric field applied along (OP cells) and perpendicularly (IP cells) to the LC layers were fabricated. The data revealed different stages of structural evolution with the increasing of concentration of CNTs related to the dispersion of individual CNTs (at low concentrations, <3 × 10−4% wt), formation of branched aggregates with non-compact structures (3 × 10−4–5 × 10−3% wt), percolation of non-compact aggregates (5 × 10−3–10−1% wt), and formation of dense networks (>10−1% wt). Observed two-step percolation thresholds at ≈0.004% wt and ≈0.5% wt were explained by the formation of non-compact and dense CNT networks.
A similar two-step percolation behavior was observed for aggregating suspension of CNTs in isotropic liquid (decane) [135]. A planar filtration-compression conductometric cell was used for mechanical de-liquoring of the suspension. The first percolation threshold was explained by the interpenetration of loose CNT aggregates, and the second one was attributed to percolation across the compact conducting aggregates. The Monte Carlo simulation-based core–shell structure particles also revealed the presence of two smoothed percolation transitions though the shells and cores.
Comparative studies of optical transmission and dielectric properties of SWCNTs and MWCNTs in nematic LC (5CB) were reported [136,137]. The studies revealed violations of the Beer–Lambert–Bouguer (BLB) law both in cell thickness and concentration dependencies. This is illustrated in Figure 7, where optical density D versus the CNT concentration in LC (5CB) is presented. In the isotropic phase (T = 310 K), the optical density changed rather closely to the BLB law for both SWCNT- and MWCNT-doped systems. On the other hand, in the nematic phase (at T = 301 K), the obtained D(C) dependencies were nonlinear, and this effect was more pronounced for SWCNTs.
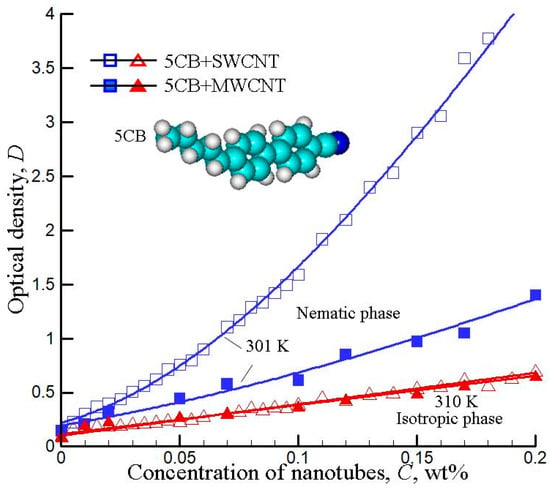
Figure 7.
Optical density D versus the concentration of CNTs (SWCNTs and MWCNTs) in 5CB. The data are shown for two different temperatures in the nematic (301 K) and isotropic (310 K). (Based on the experimental data presented in [137]).
The quite different optical transmission behavior for SWCNTs and MWCNTs was discussed, accounting for the differences in the specific surface area of CNT species, formation of CNT coils, their aggregation, and perturbations of the nematic state inside the coils [137]. This conclusion was confirmed by the data of Monte Carlo calculations for the systems with different degrees of aggregation. The more detailed Monte Carlo studies of optical transmission of anisotropic suspensions filled by aggregates of absorbing cylindrical particles were also reported [138]. The deviations from the Beer–Lambert–Bouguer law were analyzed for the systems with different aspect ratios (i.e., ratio of length and diameter), aggregation degree, and order parameters.
Theoretical descriptions of CNT–LC composites have been also developed in many works (for example, see [139,140,141,142,143]). In particular, different models proposed for the description of phase behavior, structural ordering, and alignment (para-nematic and nematic) of CNTs in LC media have been reviewed. The phase behavior and orientational properties were discussed as influenced by temperatures, volume fraction of CNTs, and coupling strength.
4.1.2. Smectic Liquid Crystals
The behavior of CNT–smectic LC composites was discussed in many recent works. A SWCNT thin plate was prepared using a smectic LC (40-hexyloxy-biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid ethyl ester) template [144]. The induced structure in the CNT plate was attributed to π–π stacking interactions in the hexagonal rings of the CNT wall and aromatic moieties in the LC. The effects of MWCNTs on the phase transitions in smectic LC (8CB, octyl-cyanobiphenyl) have been reported [145]. The observed effects were explained by the interaction of CNTs with LC molecules and the elastic coupling between the CNTs and LC. The electro-optical behavior of the MWCNTs and smectic LC (8S5, 4-n-pentylphenylthiol-4′-n-octyloxybenzoate) mixture has been studied [146]. The CNTs with inherent surface chirality were used. In these systems, a pronounced electroclinic effect (the tilt of the optical axis of an LC in the plane perpendicular to an applied electric field) was observed. The effect was explained by the interactions between the LC and the chiral surface of the CNTs. The phase transitions in MWCNTs and smectic LC (9OO4, alkoxyphenylbenzoate) mixtures have been studied [147]. The impact of CNTs on phase transitions was discussed, accounting for the LC–CNT surface coupling interactions. The properties of the smectic C LCs (4,n-heptyloxybenzoic acid, 7OBA) on oriented SWCNTs were analyzed using microtexture and polarized Raman spectroscopy [148]. The memorization strength of the LC system was estimated, and it was explained by the trapping of LC bulk charges by the CNTs.
The optical, thermodynamic, and microstructural properties and electrical conductivity of MWCNTs and smectogenic LC (BBBA, 4-butoxybenzylidene-4′-butylaniline) composites have been studied [108]. A fuzzy-type percolation behavior with multiple thresholds in these composites was observed. The observed behavior was explained by the perturbations of the BBBA mesogenic structure in the interfacial layers near the surface of CNT aggregates. The electrical conductivity σ of MWCNT-BBBA dispersions versus the temperature dependencies are shown in Figure 8 [108].
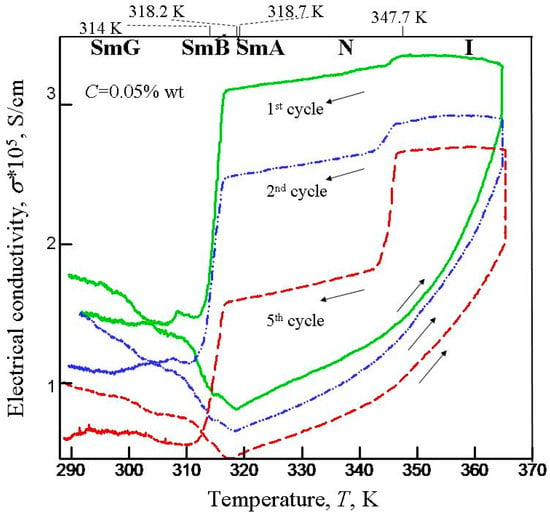
Figure 8.
Electrical conductivity σ versus temperature T dependencies in MWCNT (0.05% wt)–LC (BBBA) composites for multiple cycles of heating and cooling. (Based on the experimental data presented in [108]).
Such dependencies were obtained using multiple heating–cooling cycles. The σ(T) plots gradually moved down in successive cycles. Near the isotropic-nematic transition temperature, the step-like drop of σ became more clearly expressed. Thus, transition to a more ordered phase was accompanied by the decrease in electric conductivity, which can reflect the restricted mobility of ionic impurities and the effects of LC ordering on the alignment of the dispersed CNTs. The effect of multiple heating–cooling cycles was explained by changes in the microstructure of the studied composites and transformations from loose, spatially distributed aggregates to more compact and isolated aggregates.
The behavior of SWCNTs dispersed in mixtures of smectic LC (MHPOBC, 4′-Octyloxy-biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid 4-(1-methyl-heptyloxycarbonyl)-phenyl ester) and nematic E7 was reported [78]. The MHPOBC has very complicated phase behavior and demonstrates many smectic phases. The mixtures MHPOBC + E7 allowed for the improvement of the CNT dispersion in higher-ordered smectic phases. The effects of carboxyl group (–COOH) functionalized MWCNTs on physical properties (electro-optical, thermo-optical, dielectric anisotropy, electrical conductivity anisotropy, threshold voltage, and rotational viscosity) of a highly polar smectic LC (8CB, octyl cyanobiphenyl) composite have been studied [149]. Inclusion of CNTs substantially decreased phase transition temperatures, affected the optical relaxation processes, and increased the rotational viscosity. The effects were attributed to the strong elastic interaction between CNTs and 8CB molecules.
The dielectric, optical microscopy, elastic, and X-ray diffraction studies of SWCNTs and smectic LCs (a mixture of the hexyloxy (6OCB)- and octyloxy-(8OCB) cyanobiphenyl) have been performed [150,151]. The doping a small of amount of CNTs led to self-assembly of the layered smectic phase. The introduction of CNTs significantly enriched the phase diagram and enhanced the thermal range of the layered smectic phase. The MWCNT–smectic LC (8CB, octylcyanobiphenyl) composites have been studied using high-resolution optical birefringence measurements [152]. Inclusion of CNTs substantially decreased both the Ne-I and the Ne-Sm A transition temperatures. However, the nature of the nematic and smectic fluctuations remained essentially bulk-like for the studied composites.
SWCNT—smectic A (4-nitrophenyl-4′-decyloxybenzoic acid) composites have been studied using dielectric techniques [153]. Observed decreases in the order parameter and clearing temperature were explained by the inclusion of a part of the SWCNTs into the gap between the smectic layers. The changes in electrical conductivity were attributed to the percolation effect and the predominance of the hopping electronic conductivity over the ionic one.
4.1.3. Cholesteric Liquid Crystals
One of the first studies of MWCNT–cholesteric LC (CLC) composites involved three cholesteric mixtures: (1) an induced cholesteric mixture (70% wt of nematic ZhK-1282 and 30% wt of chiral dopant CB-15); (2) a mixture of steroid cholesterics (80% wt of cholesteryl oleyl carbonate and 20% wt of cholesteryl chloride, COC/CC); and (3) a cholesterol ester mixture exhibiting helix unwinding at temperatures close to cholesteric-smectic A phase transition (60% wt of cholesteryl nonanoate, 20% wt of cholesteryl caprynate and 20% wt of cholesteryl caprylate) [103]. With the first two types, no noticeable effects of MWCNTs on the selective reflection spectra were observed. For the third type, changes in helical pitch were noted, which were related to suppression of the smectic phase. The optical transmission above the selective reflection band sharply increased at the temperature of isotropic phase transition in a similar way as that in nematics, and the “transmission jump” was substantially smaller with non-aromatic cholesterol esters as compared with systems with chiral dopants. Similar behavior was also noted in [154], where changes in helical pitch were attributed to the effects of CNTs on the mesophase temperature range. The addition of chiral dopants to the nematic matrix improved the stability of CNT dispersions.
The temperature dependencies of selective reflection spectra in MWCNT-COC/CC (4(COC)/1(CC)), and MWCNT-COC/CC + 5CB) cholesteric mixtures were also compared [155]. In these studies, the pure cholesteric with ratio Ch = COC/CC = 4/1 and the cholesteric–nematic mixture with ratio Ch/5CB = 7/3 were used. Figure 9 presents examples of selective reflection spectra for undoped and doped mixtures (a) and temperature dependencies of the wavelength of selective reflection maximum λm (b). For the pure cholesteric mixture with ratio Ch = COC/CC = 4/1, the temperature T = 308 K was rather close to the transition temperature into the isotropic phase (Ti ≈ 313 K). The data evidenced that the incorporation of MWCNTs resulted in lowering the optical transmission and bordering of the selective reflection peaks. Moreover, at lower temperature T = 303 K, the peak became even more smeared and two separate peaks appeared. This can be explained by the effects on nanotubes on helical arrangement in the host.
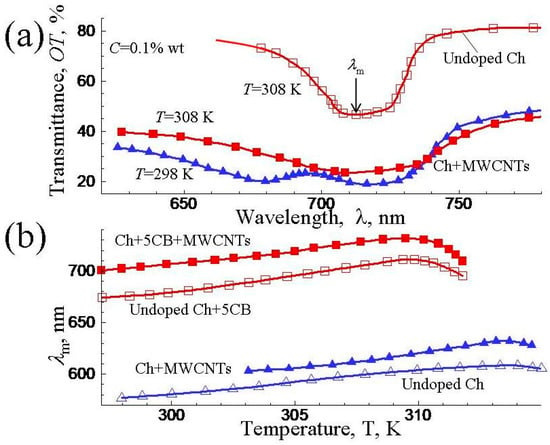
Figure 9.
Examples of selective reflection spectra undoped and doped pure cholesteric Ch(COC/CC) mixtures (a) and temperature dependencies of the wavelength of the selective reflection maximum λm for MWCNT–Ch (pure cholesteric), and MWCNT–Ch/5CB (cholesteric/nematic) mixtures (b). The concentration of MWCNTs in doped mixtures was C = 0.1% wt. (Based on the experimental data presented in [155]).
Analysis of temperature dependencies of the selective reflection maximums λmax for both MWCNT–Ch and MWCNT–Ch/5CB cholesteric mixtures evidenced that the introduction of nanotubes resulted in increasing values of λm, but the transition temperatures into the isotropic phase were practically unaffected (Figure 9b).
The slower aggregation of MWCNTs in cholesteric matrices as compared with that in nematic matrices was explained by the higher effective viscosity of cholesterics [155]. A similar stabilizing effect of helical twisting, explained by the suppression of CNT aggregate formation in helically twisted quasi-nematic layers, was noted in [107]. Minor effects of CNTs on helical twisting in cholesteric mixtures were also noted in [156]. Several interesting works can be noted where carbon nanotubes possessing intrinsic chirality could induce weak but observable helical twisting in nematic matrices [157,158].
The optical and electro-optical properties, microstructure, phase transitions, and electrical conductivity behavior of MWCNTs dispersed in the nematic 5CB (“bad” solvent), cholesteryl oleyl carbonate, COC (“good” solvent), and their mixtures have been studied [159]. Here, the terms “good” and “bad “ refer to the high and low solubility in terms of the Hansen solubility parameters [160]. The 5CB and COC LC solvents have close temperatures of the transitions to the isotropic state (Ti = 308–309 K for 5CB and Ti ≈ 309 K for COC) and different temperatures of solid-LC transitions (Ts ≈ 296 K for 5CB and Ts < 273 K for COC). The pronounced agglomeration of CNTs was observed in nematic 5CB (“bad” solvent), and the high-quality dispersion, exfoliation, and stabilization of the CNTs were observed in COC solvent (“good” solvent). The similar agglomeration behavior was also observed for MWCNT dispersions in 1-cyclohexyl-2-pyrrolidone (“good” solvent) and in water (“bad” solvent) [161].
Figure 10 presents electrical conductivity heating–cooling hysteresis loops for MWCNTs (0.1% wt) in pure 5CB and in COC/5CB = 3/1 mixture. The significant changes in electrical conductivity in these LC solvents, effects of thermal pre-history, and hysteretic behaviors were observed. Such effects were explained by possible strengthening of electric contacts between adjacent nanotubes due to intense Brownian motion in the high-temperature isotropic phase. The 5CB-COC mixtures were found to be promising for fine regulation of chiral and electro-physical properties of CNT–LC composites.
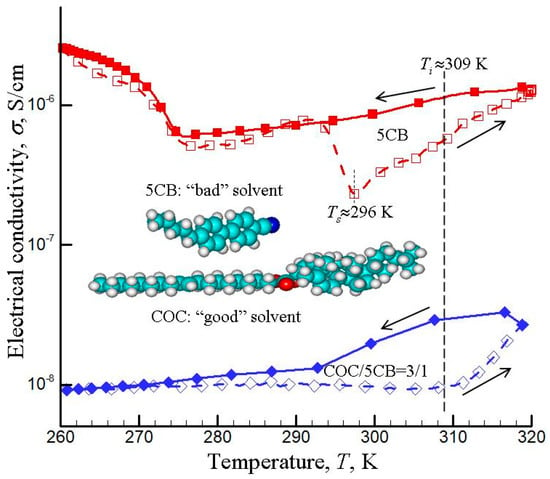
Figure 10.
Electrical conductivity σ versus the temperature T for heating–cooling cycles for MWCNT (0.1% wt)–CL (5CB and COC/5CB = 3/1) composites. Here, Ti ≈ 309 K is temperature of the transitions to the isotropic state (for both the 5CB and COC) and Ts ≈ 296 K is the temperature of solid-LC transition for 5CB. (Based on the experimental data presented in [159]).
As the use of CLC for vapor detection is one of their promising practical applications, it was natural to increase the sensitivity and selectivity of such sensor materials by doping cholesteric mixtures with CNTs [162,163,164]. A promising way to create an efficient gas sensor with a wide dynamic range on the base of cholesteric mixtures doped with CNTs was discussed [162]. Incorporation of CNT networks into the helically twisted cholesteric structure ensured a strong response to the absorbed gas molecules, with optical and electrical properties showing easily recordable changes in low and high gas concentration range, respectively.
The presence of strong interactions between CNTs and LC director nematic E7 with ZLI-811 chiral dopant was clearly evidenced [165]. The doping resulted in considerable changes in the electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of composites. The effects of CNT doping on viscoelastic and rheological properties of cholesterics have been also discussed [166,167,168], which are related to the potential application of cholesterics as lubricants.
CNT–cholesteric LC composites displayed interesting non-linear and even non-monotonous dependences of optical density versus CNT concentration, with a minimum observed at a certain point [136,169,170]. Such behavior was observed only in the presence of chiral components—with the same nematics and without chiral dopants, these dependences are close to linearity. An explanation could be based either on the formation of CNT aggregates of stacking type, or by preferential positioning of the dispersed CNTs at topological defects of the cholesteric texture. A similar study was carried out in [171], where carbon nanotubes were added to cholesteryl nonanoate; however, since the authors used only two discrete concentrations of CNTs, they could not notice anything particular.
The optical density, microstructure, and electrical conductivity in SWCNT cholesteric (the mixtures of ZhK440, 5CB with chiral M5) composites have been studied [169]. The optical density as a function of CNT concentration was not only non-linear, but non-monotonous, with pronounced extremums on the D(Cn) plots. Several tentative explanations were proposed for such unusual behavior, including the formation of stacking-type CNT aggregates, interaction between cholesteric structural defects (oily streaks) and CNT networks, localization of nanotubes on the defects, etc. Since the azoxy nematic ZhK-440 can reversibly change its molecular conformation under UV irradiation, the radiation-induced effects in such systems were also studied.
The various memory effects considered promising for electro-optical applications have been reported [172], with various subsequent developments [173,174]. Further efforts showed the ways for various CLC-based materials, where doping with CNT allowed temperature- and irradiation-induced writing and erasing effects [175]. Carbon nanotubes were also reported to stabilize the “blue phase” as a promising phase state observed in cholesterics close to the isotropic transition [176]. Additionally, just to be mentioned—there are several reports of CNTs in more exotic media possessing cholesteric-like structures of molecular arrangements, such as DNA [177] or cellulose LCs [178].
4.1.4. Ferro- and Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystals
Ferroelectric LCs have been receiving scientific attention for about fifty years, starting from the discovery of the ferroelectric chiral smectic phases [179]. Ferroelectricity reflects a spontaneous electric polarization of LC material which can be reversed by the application of an electric field [180,181]. In these materials, the dipoles all point in the same direction. In contrast, in anti-ferroelectric LC materials, the adjacent dipoles are oriented in opposite (anti-parallel) directions. These LC materials can exhibit distinctive ferroelectric or anti-ferroelectric, dielectric, and electro-optical properties, the presence of spontaneous polarization, a high contrast ratio, and excellent switching characteristics. Such materials have shown a wide area of application for improved quality of LC display, and they were found to be useful for applications in fast-switching, low power consumption, in high resolution and high contrast devices, spatial light modulators, holographic storage, and other photonic devices [182].
Intensive studies of such LC materials doped with CNTs were started approximately 15 years ago. In particular, the compositions of SWCNTs with anti-ferroelectric chiral smectic LCs have been studied [183]. In these experiments, CNTs were introduced in the nematic LC and then mixed with an anti-ferroelectric chiral smectic compound. The doping at very small concentrations of CNTs (0.002% wt) in the phase sequence significantly affected the phase sequence of the studied LC systems.
The dielectric and electro-optical properties of different ferroelectric LC materials doped with CNTs have been studied in many works. The fastening of the electro-optical switching response in ferroelectric LC (LAHS7) due to the trapping of ions by CNTs was observed [184,185,186,187]. For MWCNTs in LC mixtures (LAHS7) with SmC* and SmC* phases, the significant changes in the performance of the LC cells were explained by the trapping of ions through the CNTs [184]. The doping with MWCNTs greatly affected the performance of cells, and significant changes in the spontaneous polarization, rise time, and dielectric permittivity were observed [185]. The effects were explained by the impact of CNTs on the screening and trapping of the ionic impurities. The fastness of the response in MWCNT–deformed helix ferroelectric LC composites has been attributed to the decrease in rotational viscosity and increase in anchoring energy [186]. A substantial difference in tilt angles of pure and doped samples below a certain threshold voltage of around 2 V and the increase in conductance in doped cells were also observed. The dielectric and electro-optical properties in mixtures of chiral SWCNT ferroelectric LC (eutectic multi-component mixture LAHS2, LNTS1, and LNTS2) have been studied. The different properties (electro-optical response, spontaneous polarization, rotational viscosity, dielectric permittivity, dielectric loss factor, and electrical conductivity) of MWCNT–ferroelectric LC (LAHS 18) composites have been studied [187]. Non-zero spontaneous polarization in the para-electric phase has been attributed to the effects of surface anchoring and ionic impurities.
Dielectrical, electro-optical, and thermo-optical studies of MWCNT–LC mixtures (ZLI-3654 and KCFLC10R) were performed [82,188]. A reduction in permittivity and electrical conductivity with increasing MWCNT concentrations was reported. Improvements in electro-optical responses, increased contrast ratio, and low threshold voltage in doped cells were also observed. The increase in spontaneous polarization and decrease in response time was explained by changes in ionic concentration in doped samples.
The changes in dielectric and electro-optic responses in MWCNT–ferroelectric LC composites were reported [189,190]. A switchable grating based on chiral SWCNT–ferroelectric LC (Felix 17/100) composites was studied [191]. It was assumed that the decrease in ferroelectric domain periodicity and optical activity of the SWCNTs could explain the observed increases in diffraction efficiency.
In series of works the dielectric and electro-optical properties of SWCNT–ferroelectric LC (Felix 17–100, 16–100) composites were studied [192,193,194]. The comparative studies of spontaneous polarization, response time, rotational viscosity, dielectric permittivity, and loss factor allowed the explanation of observed effects by the presence of strong π–π electron stacking between SWCNT and LC molecules. The dielectric and electro-optical properties of MWCNT–ferroelectric LC composites were also discussed [195,196,197]. The effects of cell thickness and anchoring energy on bistability were also discussed. Observed changes were explained by the strong coupling between the MWCNTs and LC molecules (the strong π–π interactions), and changes in anchoring energy, rotational viscosity, and charge transfer mechanism. In particular, the effect of applied voltage on the mesomorphic and electro-optical behavior has been established [197]. The doping with CNTs (0.03% wt) strongly affected the optical contrast, birefringence, transmission and contrast ratio, led to the generation of new colors, and effectively reduced the driving voltage. The fastening of the switching time was also detected.
Effects of the alignment of SWCNTs with ferroelectric LC (3M2CPNOB) have been studied using SEM, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopy techniques [198]. The SEM images have shown the presence of good alignment of SWCNTs along the LC smectic layers. The studies also evidenced the presence of charge transfer processes and strong π−π stacking interactions between CNTs and aromatic rings of the LC molecules.
The effect of MWCNTs on the dielectric properties of a short pitch and high spontaneous polarization deformed helix ferroelectric LC mixture (DHFLC) in different chiral phases (SmC*, SmA*) has been studied [199]. Observed changes were attributed to the increase in elastic constant and dilution of chiral content.
The dielectric and electro-optical properties of MWCNT–ferroelectric LC (LAHS 22) mixtures have been studied [200]. The native and gold-decorated nanoparticles were used for doping. The effects of decoration on improvement in the dielectric and electro-optical properties were discussed. The decoration also changed the phase transition temperature (ferro to para) of LAHS 22.
The dielectric spectra MWCNT–ferroelectric LC (KCFLC10S) mixtures at different bias voltages have been studied [201]. The observed distortion in the Cole–Cole plots was explained by the overlapping of Goldstone and low-frequency relaxation modes. The doping of mixtures by MWCNTs enhanced the effect of the bias.
The changes in dielectric properties (dielectric permittivity, strength, and conductivity) in CNT–ferroelectric LC (KCFLC10R) systems was discussed [202]. Microstructure and dielectric studies of MWCNT–ferroelectric LC ((S-(-)-4-(2-n-hexylpropionyloxy) biphenyl-4′-(3-methyl-4-decyloxy) benzoate) mixtures have been studied [203]. In order to increase the stability of MWCNTs in the LC medium, they were functionalized with carboxyl groups (–COOH). The dielectric permittivity of the ferroelectric phase was enhanced with the addition of MWCNTs. In another work, the effect of the functionalization of MWCNTs (with –COOH, –OH, and –NH2 groups) on dielectric, electro-optical, and photoluminescence properties of ferroelectric LC (LAHS-IN) composites has been studied [204]. A strong dependence of the studied properties on the functional groups of MWCNTs was observed. Fictionalization resulted in remarkable modification of the dielectric properties and enhancement of the photoluminescence intensity.
The dielectric and electro-optic MWCNT–ferroelectric LC (Felix M4851/050) mixtures have been studied at different MWCNT concentrations (0.005–0.04% wt) [205]. The behaviors of the tilt angle, spontaneous polarization, response time, and Goldstone mode relaxation strength and frequency were attributed to a possible dipole moment due to the presence of the MWCNTs and increase in rotational viscosity.
The impact of different methods of MWCNT–antiferroelectric LC (MHPOBC) mixture preparation on phase behavior has been studied [206]. In first method, the MWCNTs were initially dispersed in nematic E7 and then mixed with MHPOBC, and in the second method the dry MWCNT powder was dispersed directly in MHPOBC. The preparation method affected the clearing transition, which was explained by differences in the dispersion and aggregation of MWCNTs.
The microstructure, dielectric, and electro-optical properties of MWCNT–ferroelectric (W206E) LC mixtures have been studied [207]. The optical micrographs revealed some topological defects. The doping resulted in a decrease in the spontaneous polarization, dielectric permittivity, and conductivity. These decrements were attributed to the trapping of mobile ion MWCNTs.
The dielectric and electro-optical properties of MWCNT–high tilt anti-ferroelectric LC (DM1) composites were studied [208]. The doping affected the transition temperatures (the stability of SmA* and SmC* phases increased, whereas that of the SmCA* phase decreased). The changes in different properties (pitch of the helicoidal structure, absorption strength and critical frequency of the anti-phase antiferroelectric mode, and switching time) were discussed and explained. In particular, the decrease in response time in the doped system was attributed to the decrease in the rotational viscosity.
The theoretical description of the CNTs on the structure of ferroelectric and antiferroelectric LC mixtures was provided on the base of a combination of Flory-Huggins theory and Landau theory [209,210]. In particular, the changes in polarization, tilt angle and dielectric susceptibility, and transition temperature with the increase in the concentration of CNTs were discussed.
Structural, thermal, optical, and electrical properties in MWCNT–hydrogen bonded ferroelectric LC (cholesteryl stearate and 4-dodecyloxybenzoic acid) mixtures have been studied [211]. The effect of optical modulation in doped mixtures was observed. It was assumed that the introduction of MWCNTs in these LC mixtures can substantially improve the characteristics relevant to possible applications of these composites. Recently, the effects of doping with SWCNTs and MWCNTs of fluorinated ferroelectric LC mixtures have been studied [212]. The differences observed for SWCNTs and MWCNTs were explained by the different dimensions and surface area of the nanotubes. It was concluded that the trapping of the mobile ions by CNTs can minimize many negative effects such as high switching time, high operating voltage, image sticking, image flickering, and non-uniformity of the images.
4.1.5. Discotic Liquid Crystals
Discotic LCs represent mesophases formed from the disc-shaped molecules. These mesophases are commonly called columnar phases. The composites on the base of acid-purified SWNTs dispersed in columnar LC (triphenylene-based) have been studied [213]. The SWCNTs were chemically functionalized by hexaalkoxytriphenylene mesogens; good integration of SWCNTs into the columnar matrix occupying the space between the disc columns was confirmed. In other work from the same group, the octadecylamine (ODA)-functionalized SWCNTs were also used to prepare dispersions in columnar phases of triphenylene- and rufigallol-based discotic monomers and polymers [214]. Mesophase behavior of these composites was studied using polarizing optical microscopy, DSC, and X-ray diffractometric methods. The doping resulted in a decrease in the isotropic transition temperature. The well-dispersed composites of SWCNTs in imidazolium ion-appended LC triphenylene derivatives have been prepared [215]. It was demonstrated that in such composites, the shear-induced orientation of SWCNTs may be maintained for a very long time (more than half a year). The structure and properties of different CNT–discotic LC composites and their possible practical applications were recently reviewed [216,217].
4.2. Lyotropic Liquid Crystals
In many works, lyotropic LCs have been also used as solvents for the alignment of CNTs [37]. Integration of nanoparticle guests inside lyotropic LCs may be defined by the sort of nanoparticles, details of the interactions between nanoparticles and LC molecules, and the concentration of components and temperature. The incorporation of CNTs in different lyotropic LC hosts has been intensively discussed for two decades. The structure of SWCNT–lyotropic (Triton X-100/water) mixtures was studied using light microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering techniques [218]. The experimental data provided evidence of the integration of SWNTs within the cylinders of the hexagonal LCs and on the alignment of SWCNTs along the LC director. Similar trends in SWCNT concentration depending on the supramolecular (d-spacing) and macroscopic (viscosity) properties were observed. Similar findings have been reported for MWCNT–lyotropic (ethylammonium nitrate/water) mixtures [219]. The MWCNTs were well-dispersed and integrated within the cylinders of the hexagonal LCs. The studied composites demonstrated special tribological behavior. The spontaneous alignment of SWCNTs along the director in lyotropic (sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)/water) LC mixtures was verified by means of resonant Raman spectroscopy [220,221,222].
Spontaneous alignment of SWCNTs in more complex lyotropic hosts, combining cationic and anionic surfactants in a hexagonal columnar LC phase, was studied [223]. The applied two-step preparation procedure includes initial dispersion of nanotubes in a low-concentration solution of anionic surfactant followed by the formation of the LC phase with the addition of cationic surfactant. This approach allowed achieving heavily loaded systems with controlled orientation of nanotubes. The possibility of fractionalization of the SWCNTs according their chirality on the base of the proposed approach was mentioned. Later on, the same group incorporated the SWCNT suspension prepared below the Krafft temperature into a very low-surfactant concentration lyotropic host formed by charge combination of cationic and anionic surfactants [224] (see [225] for more discussion of this technique).
Phase behavior and shear alignment in SWNT–surfactant (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB) aqueous mixtures have been studied using small-angle X-ray scattering and cryogenic transmission electron microscopy techniques [226]. At high CTAB concentrations, the SWCNTs were integrated into the ordered lyotropic LCs while preserving the native d-spacing in the LC phase. The mechanism of carbon nanotubes’ incorporation in lyotropic LCs has been discussed [227,228,229]. The percolation-like transition to aligned and quasi-infinite micelles stabilized by chains of nanotubes and the filament formation triggered by nanotubes were supposed.
The technique of incorporation of SWCNTs into lyotropic LCs is via phase separation in the presence of polyelectrolytes [230]. The lyotropic phases of anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in the presence of an anionic polyelectrolyte poly(sodium styrenesulfonate) (PSS) and of cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) in the presence of a cationic polyelectrolyte poly(diallydimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC) were studied using polarized optical microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering techniques. The SWCNTs were well-dispersed in the lyotropic LCs, and the obtained SWCNTs/LLC hybrids showed considerable thermal stability. A similar approach was applied for the incorporation of SWCNTs into lyotropic LCs, which formed n-dodecyl octaoxyethene monoether (C12E6) via separation in the presence of a hydrophilic polymer poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). In these systems, by varying the ratio of PEG to C12E6, the transition from hexagonal phase to lamellar phase was observed. Th proposed approach allowed obtaining highly concentrated carbon nanotube LC systems.
The integration of MWCNTs into lyotropic LC phases formed in binary mixtures of 1-tetradecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride/ethylammonium nitrate has been studied using polarized optical microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering techniques [231]. The incorporation of MWCNTs did not break the structure of hexagonal lyotropic LC phase and resulted in an increase in the viscosity of this phase.
The rheological properties of SWCNT–lyotropic LC (sodium deoxycholate, NaDC) mixtures have been studied [232,233]. The enhanced rheological properties at high NaDC concentration (30% wt) allowed the shear-induced filament formation. In these filaments (fibrous long aggregates), the nanotubes were aligned along the shear direction.
The elastic properties of SWCNT–lyotropic LC composites have been studied [234]. A nematic solvent was prepared in a nonconventional mixture of sodium dodecyl sulfate, decanol, and water. Observed elastic behavior was interpreted accounting for the entanglement between nanotubes dispersed in the nematic matrix.
The dispersion and alignment of SWCNTs in chromonic LCs (Di-sodium cromoglycate, DSCG) have been investigated usings polarizing microscopy, Raman, and photoluminescence spectroscopy techniques [235]. Chromonic LCs are formed by the self-organization of aromatic compounds with ionic or hydrophilic groups in aqueous solutions. The high level of individual nanotube alignment in the DSCG nematic phase (with an order parameter of approximately 0.9) was observed.
Self-assembled ordering of SWCNTs in a lyotropic LC (25% wt cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) in water) system has been studied using small-angle X-ray scattering, optical birefringence, and electrical conductivity measurement techniques [236]. This lyotropic material shows nematic, hexagonal, and isotropic phases on heating. The MWCNTs exhibited 2-D hexagonal ordering in nematic, hexagonal phases and 1-D ordering in the crystalline and isotropic phases.
The electrical conductivity of SWCNTs in lyotropic LC (50% wt of Triton X-100 in water) as a function of magnetic field and temperature has been studied [237]. This lyotropic material shows hexagonal and isotropic phases on heating. The temperature dependence of electrical conductivity exhibited a discontinuous change at the hexagonal to isotropic transition temperature. With the increasing of the magnetic field, the transition from spherical to hook-like SWCNT aggregates was observed.
Novel ionic LC/MWCNT composites for electrocatalytic treatment have been synthesized [238]. MWCNTs were decorated with nano-nickel oxide (NiO). These composites are shown to be useful for the treatment of urea-contaminated water. In several works, the behavior of carbon nanotubes impregnated into the more complex lyotropic gels [239,240,241,242] and the lyotropic polymers [243,244,245,246,247] was also discussed.
4.3. Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals
Polymer-dispersed LCs can be obtained by embedding submicron-sized LC droplets into polymer matrices. These composites have many promising optoelectronic applications [248]. Recently, the functionalized CNTs were integrated into the polymer-dispersed LC in order to improve functionality of a gas (NO2) sensor device [249]. Developed composites were shown to be promising candidates for use in different sensing devices. A new technique for the preparation of polymer-dispersed LC doped with CNTs has been reported [250]. The obtained films were characterized using different experimental techniques. The doped LC materials demonstrated improved electro-optical characteristics. The electro-optical properties and frequency response of polymer-dispersed LC doped with MWCNTs have been reported [251]. Diffusion of MWCNTs into the LC regions was observed during the polymerization. The ways for improving the diffraction efficiency and threshold voltage of the prepared switchable grating devices were also discussed.
5. Conclusions
Studies of self-assembling in different types of thermotropic and lyotropic LC materials doped with SWCNTs and MWCNTs performed in the past two decades have significantly advanced our knowledge in the field. The discovered LC materials are based on variety of molecular structures and exhibit many phase states with different spatial and orientational arrangements. In LCs doped with CNTs, the mutual influences of LC-ordering on the organization of CNTs and of the integration of CNTs on molecular arrangements in LCs are typically observed. For each type of LC (thermotropic, lyotropic, etc.), the interaction of anisometric CNTs with an LC host results in the manifestation of exciting and exceptional structural, electro-magnetic, optical, thermal, and rheological properties.
Nowadays, developed theoretical and experimental approaches are being widely used in different engineering applications, and LC materials doped with CNTs have unequivocally shown great potential to contribute to the creation of new electronics, electro-optics, sensors, optical memories, and display devices. In many cases, the LC dispersions doped with nanoparticles of different types, particularly organo-modified clay platelets, various metal oxides, polymers, graphene, luminescent quantum dots, and composite nanoparticles (e.g., CNTs + clay platelets composite) also display attractive properties. Current challenges include problems related to the study of complex and synergic effects in complex composite LC materials. These effects can depend upon the type of LC media, the nature of composite dopants, and the presence of external fields. Therefore, further and multidisciplinary efforts are well worth it in this field to resolve existing problems and gaps, and we are confident that this research will produce some very exciting results over the next few years.
Author Contributions
All the authors participated in the collection of data from the literature, analysis of the data, and drafting the manuscript. The final publication was prepared with contributions from all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (projects No 6541230 (1230) and No 0122U002636), and by the Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv (projects No 23BF05101).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| CNTs | Carbon nanotubes |
| SWCNTs | Single-walled carbon nanotubes |
| MWCNTs | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| LCs | Liquid crystals |
References
- Stark, H. Physics of Colloidal Dispersions in Nematic Liquid Crystals. Phys. Rep. 2001, 351, 387–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Khan, S.; Chauhan, S.; Biradar, A.M. Metal Oxide-Nanoparticles and Liquid Crystal Composites: A Review of Recent Progress. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Fisch, M.; Kumar, S. Emissivity and Electrooptical Properties of Semiconducting Quantum Dots/Rods and Liquid Crystal Composites: A Review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 56502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Singh, G.; Biradar, A.M. Advances in Gold Nanoparticle—Liquid Crystal Composites. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7743–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Luqman, M.; Jamil, M. Advances in the Metal Nanoparticles (MNPs) Doped Liquid Crystals and Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC) Composites and Their Applications—A Review. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2021, 731, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Kumar, A.; Chauhan, S. Aligning Liquid Crystal Materials through Nanoparticles: A Review of Recent Progress. Liquids 2022, 2, 50–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhail, K.P.; Humar, M.; Dhara, S. Effect of Phase Transitions on Liquid Crystal Colloids: A Short Review. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2020, 8, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, J.; Srivastava, R. Liquid Crystals with Nano/Micro Particles and Their Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, Q.; Banin, U. Introduction: Anisotropic Nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 3325–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Uchida, J.; Ichikawa, T.; Sakamoto, T. Functional Liquid Crystals towards the next Generation of Materials. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4355–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudimalla, A.; Lavrič, M.; Trček, M.; Harkai, S.; Rožič, B.; Cordoyiannis, G.; Thomas, S.; Pal, K.; Kutnjak, Z.; Kralj, S. Nanoparticle-Stabilized Lattices of Topological Defects in Liquid Crystals. Int. J. Thermophys. 2020, 41, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C. Amphotropic Liquid Crystals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, L.S.; Awasthi, K.S. General Observation about Liquid Crystals: A Review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Manag. Technol. 2015, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shanker, G.; Paul, B.; Ganjiwale, A. Amino Acid and Peptide-Based Liquid Crystals: An Overview. Curr. Org. Synth. 2021, 18, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Vashchenko, O.V.; Kasian, N.A.; Sviechnikova, L.V. Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Phases of Phospholipids as Model Tools in Molecular Biophysics and Pharmacology. In Soft Matter Systems for Biomedical Applications; Bulavin, L., Lebovka, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Takeuchi, R.; Ichikawa, T. Amphotropic Liquid-Crystalline Behaviour of Glycolipids in Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinpoor, M. Review of Liquid Crystal Elastomers. In Fundamentals of Smart Materials; Shahinpoor, M., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020; pp. 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ula, S.W.; Traugutt, N.A.; Volpe, R.H.; Patel, R.R.; Yu, K.; Yakacki, C.M. Liquid Crystal Elastomers: An Introduction and Review of Emerging Technologies. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2018, 6, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, P.; Njuguna, J.; Kandasubramanian, B. Exploration of Elastomeric and Polymeric Liquid Crystals with Photothermal Actuation: A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 121, 109287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Zhong, X.; Shi, X.; Dang, J.; Gu, J. Liquid Crystal Epoxy Resins with High Intrinsic Thermal Conductivities and Their Composites: A Mini-Review. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 20, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Yang, K.; Raquez, J.-M. A Review on Liquid Crystal Polymers in Free-Standing Reversible Shape Memory Materials. Molecules 2020, 25, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierking, I. Polymer—Modified Liquid Crystals; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yuvaraj, A.R.; Lee, W.; Kumar, S. Unconventional Liquid Crystals: Chemical Aspects. In Unconventional Liquid Crystals and Their Applications; Lee, W., Kumar, S., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 109–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Li, Q. Liquid Crystals: Versatile Self-Organized Smart Soft Materials. Chem. Rev. 2021, 122, 4887–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, K.; Lava, K.; Bielawski, C.W.; Binnemans, K. Ionic Liquid Crystals: Versatile Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4643–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vill, V.; Sajus, H.; Thiemann, T. LiqCryst 2.1: Database and Scientific Tool. In Liquid Crystals: Physics, Technology, and Applications; Rutkowska, J., Klosowicz, S.J., Zielinski, J., Zmija, J., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Volume 3318, pp. 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Goodby, J.W.; Collings, P.J.; Kato, T.; Tschierske, C.; Gleeson, H.; Raynes, P.; Vill, V. Handbook of Liquid Crystals, 8 Volume Set; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, I.-C. Liquid Crystals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- DiLisi, G.A.; DeLuca, J.J. An Introduction to Liquid Crystals; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oswald, P.; Pieranski, P. Liquid Crystals: Concepts and Physical Properties Illustrated by Experiments; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kasian, N.A.; Lisetski, L.N.; Gvozdovskyy, I.A. Twist-Bend Nematics and Heliconical Cholesterics: A Physico-Chemical Analysis of Phase Transitions and Related Specific Properties. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, K.G.; Kasian, N.A.; Minenko, S.S.; Samoilov, O.M.; Nazarenko, V.G.; Lisetski, L.N.; Gvozdovskyy, I.A. Chiral Ferronematic Liquid Crystals: A Physico-Chemical Analysis of Phase Transitions and Induced Helical Twisting. Liq. Cryst. 2023, 50, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamley, I.W. Introduction to Soft Matter: Synthetic and Biological Self-Assembling Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, E.; Silva, B. Surfactants, Phase Behavior. In Encyclopedia of Colloid and Interface Science; Tadros, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1290–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, S.; Huang, J.; Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Chu, X. Characterization of Lipid-Based Lyotropic Liquid Crystal and Effects of Guest Molecules on Its Microstructure: A Systematic Review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2023–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Jahn, A.; Cho, S.-J.; Kim, J.S.; Ki, M.-H.; Kim, D.-D. Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Systems in Drug Delivery: A Review. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Martins Figueiredo Neto, A. Novel Trends in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2020, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamade, F.; Amit, S.K.; Woods, M.B.; Davis, V.A. The Effects of Size and Shape Dispersity on the Phase Behavior of Nanomesogen Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2020, 10, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radushkevich, L.V.; Lukyanovich, V.M. On the Structure of Carbon Formed under Thermal Treatment of Carbon Oxide on Iron. Zhurnal Fiz. Khimii 1952, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Goncharuk, A.I.; Lebovka, N.I.; Lisetski, L.N.; Minenko, S.S. Aggregation, Percolation and Phase Transitions in Nematic Liquid Crystal EBBA Doped with Carbon Nanotubes. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 165411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilo, M.; Lebovka, N.; Barany, S. Characterization of the Electric Double Layers of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Laponite and Nanotube-Laponite Hybrids in Aqueous Suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 462, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Yun, C.H. Translational and Rotational Diffusions of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes with Static Bending. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10653–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochard, F.; De Gennes, P.G. Theory of Magnetic Suspensions in Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. 1970, 31, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.F. Magnetic Platelets in a Nematic Liquid Crystal. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1976, 36, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Chiu, C.-S. Observation of Self-Diffraction by Gratings in Nematic Liquid Crystals Doped with Carbon Nanotubes. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yeh, S.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Lee, C.-C. Beam Coupling in Nanotube-Doped Nematic Liquid-Crystal Films. Opt. Express 2001, 9, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.; Patrick, D.L. Organizing Carbon Nanotubes with Liquid Crystals. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Crawford, G.; Gao, Y.; Hurt, R.; Jian, K.; Li, H.; Sheldon, B.; Sousa, M.; Yang, N. Liquid Crystal Engineering of Carbon Nanofibers and Nanotubes. Carbon N. Y. 2005, 43, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakri, C.; Poulin, P. Phase Behavior of Nanotube Suspensions: From Attraction Induced Percolation to Liquid Crystalline Phases. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 4095–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakri, C. Carbon Nanotubes and Liquid Crystalline Phases. Liq. Cryst. Today 2007, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegmann, T.; Qi, H.; Marx, V.M. Nanoparticles in Liquid Crystals: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, Defect Formation and Potential Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2007, 17, 483–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G. Carbon Nanotubes in Liquid Crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Hegmann, T. Impact of Nanoscale Particles and Carbon Nanotubes on Current and Future Generations of Liquid Crystal Displays. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Lee, W. Scientific Duo of Carbon Nanotubes and Nematic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 63001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.C. Nonlinear Optics of Liquid Crystalline Materials. Phys. Rep. 2009, 471, 221–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, L.; Kovalchuk, O.; Lebovka, N.; Tomylko, S.; Yaroshchuk, O. Liquid Crystal Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes: Dielectric, Electro-Optical and Structural Peculiarities. In Carbon Nanotubes; Marulanda, J.M., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schymura, S.; Kühnast, M.; Lutz, V.; Jagiella, S.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Roth, S.; Giesselmann, F.; Tschierske, C.; Scalia, G.; Lagerwall, J. Towards Efficient Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Thermotropic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, G. Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes in Thermotropic and Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y.A.; Glushchenko, A. V Liquid Crystalline Colloids of Nanoparticles: Preparation, Properties, and Applications. Solid State Phys. 2010, 62, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y.; Glushchenko, I. Nano-Objects and Ions in Liquid Crystals: Ion Trapping Effect and Related Phenomena. Crystals 2015, 5, 501–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Conventional and Unconventional Ionic Phenomena in Tunable Soft Materials Made of Liquid Crystals and Nanoparticles. Nano Express 2021, 2, 12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Kumar, S. Liquid-Crystal Nanoscience: An Emerging Avenue of Soft Self-Assembly. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatoiu, O.; Mirzaei, J.; Feng, X.; Hegmann, T. Nanoparticles in Liquid Crystals and Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles. In Liquid Crystals; Tschierske, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 318, pp. 331–393. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama, A. Phase Separations in Mixtures of a Nanoparticle and a Liquid Crystal. In Smart Nanoparticles Technology; Hashim, A.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 241–268. [Google Scholar]
- Scalia, G. Liquid Crystals of Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Nanotubes in Liquid Crystals. In Liquid Crystals Beyond Displays: Chemistry, Physics, and Applications; Li, Q., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 341–378. [Google Scholar]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G. A New Era for Liquid Crystal Research: Applications of Liquid Crystals in Soft Matter Nano-, Bio-and Microtechnology. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 1387–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymura, S.; Scalia, G. On the Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on Properties of Liquid Crystals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 371, 20120261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, C.; Coursault, D.; Lacaze, E. Ordering Nano-and Microparticles Assemblies with Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2013, 1, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.; Soskin, M.; Lebovka, N. Chapter 10: Carbon Nanotubes in Liquid Crystals: Fundamental Properties and Applications. In Physics of Liquid Matter: Modern Problems; Bulavin, L., Lebovka, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 171, pp. 243–298. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.P.; Singh, S. Carbon Nanotube Dispersion in Nematic Liquid Crystals: An Overview. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 80, 38–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymura, S.; Park, J.H.; Dierking, I.; Scalia, G. Carbon Nanotubes in Thermotropic Low Molar Mass Liquid Crystals. In Liquid Crystals with Nano and Microparticles; Lagerwall, J.P.F., Scalia, G., Eds.; Soft Condensed Matter; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017; pp. 603–630. [Google Scholar]
- Dierking, I. From Colloids in Liquid Crystals to Colloidal Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 2057–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Dierking, I. Perspectives in Liquid-Crystal-Aided Nanotechnology and Nanoscience. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draude, A.P.; Dierking, I. Thermotropic Liquid Crystals with Low-Dimensional Carbon Allotropes. Nano Express 2021, 2, 12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowczan, A.; Hebda, E.; Pielichowski, K. The Influence of Nanoparticles on Phase Formation and Stability of Liquid Crystals and Liquid Crystalline Polymers. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadian, S.; Dalir, N. Thermotropic Liquid Crystalline/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposites. In Liquid Crystal Polymer Nanocomposites; Visakh, P.M., Semkin, A., Özdemir, Z.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski, M.; Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G. Nanotube Networks in Liquid Crystals. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9769, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Hu, C.-Y.; Pan, H.-C.; Lo, K.-Y. Electrooptical Responses of Carbon Nanotube-Doped Liquid Crystal Devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Shin, S.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, K.J. Effects of Carbon Nanotubes on Electro-Optical Characteristics of Liquid Crystal Cell Driven by in-Plane Field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 121901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Chen, H.-Y.; Shih, Y.-C. Reduced Dc Offset and Faster Dynamic Response in a Carbon-Nanotube-Impregnated Liquid-Crystal Display. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2008, 16, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Mehra, R.; Raina, K.K. Electro-Optic, Thermo-Optic and Dielectric Responses of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Thin Films. J. Mol. Liq. 2012, 165, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Park, K.A.; Jeong, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; An, K.H.; Nah, C.W.; Pribat, D.; Lee, S.H.; Lee Sr, Y.H. Electroactive Superelongation of Carbon Nanotube Aggregates in Liquid Crystal Medium. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2178–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, R.; Iannacchione, G.S. Carbon Nanotube Dispersed Liquid Crystal: A Nano Electromechanical System. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 183105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovka, N.; Dadakova, T.; Lysetskiy, L.; Melezhyk, O.; Puchkovska, G.; Gavrilko, T.; Baran, J.; Drozd, M. Phase Transitions, Intermolecular Interactions and Electrical Conductivity Behavior in Carbon Multiwalled Nanotubes/Nematic Liquid Crystal Composites. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 887, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Jeong, S.J.; Kim, M.; Jo, E.M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.H. Anomalous Electrokinetic Dispersion of Carbon Nanotube Clusters in Liquid Crystal under Electric Field. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 4741–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushkevych, O.; Gölden, F.; Pivnenko, M.; Xu, H.; Collings, N.; Crossland, W.A.; Müller, S.; Jakoby, R. Dielectric Anisotropy of Nematic Liquid Crystals Loaded with Carbon Nanotubes in Microwave Range. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Electrical Properties of Liquid Crystal Nano-Colloids Analysed from Perspectives of the Ionic Purity of Nano-Dopants. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Adsorption/Desorption of Ions in Liquid Crystal Nanocolloids: The Applicability of the Langmuir Isotherm, Impact of High Electric Fields and Effects of the Nanoparticle’s Size. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbovskiy, Y. Impact of Contaminated Nanoparticles on the Non-Monotonous Change in the Concentration of Mobile Ions in Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konshina, E.A.; Galin, I.F.; Shcherbinin, D.P.; Gavrish, E.O. Study of Dynamics and Relaxation Optical Response of Nematic Liquid Crystals Doped with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbinin, D.P.; Konshina, E.A. Ionic Impurities in Nematic Liquid Crystal Doped with Quantum Dots CdSe/ZnS. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Scalia, G.; Morales, P.; LeClere, D. Aligning and Reorienting Carbon Nanotubes with Nematic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Scalia, G.; Morales, P. Liquid Crystal—Carbon Nanotube Dispersions. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 44309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, H.; Gazdecki, B.; Yamashita, A.; Kyu, T. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on Phase Transitions of Nematic Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 32, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, G.; Haluska, M.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Giesselmann, F.; Roth, S. Polarized Raman Spectroscopy Study of SWCNT Orientational Order in an Aligning Liquid Crystalline Matrix. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2005; Volume 786, pp. 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Scalia, G.; Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Haluska, M.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Giesselmann, F.; Roth, S. Effect of Phenyl Rings in Liquid Crystal Molecules on SWCNTs Studied by Raman Spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi 2006, 243, 3238–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, G.; Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Schymura, S.; Haluska, M.; Giesselmann, F.; Roth, S. Carbon Nanotubes in Liquid Crystals as Versatile Functional Materials. Phys. Status Solidi 2007, 244, 4212–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoryako, A.P.; Lebovka, N.I.; Lisetski, L.N.; Melezhyk, O.V.; Shtifanyuk, P.P. Anisotropic Organic Media as Model Bioequvalent Systems. 1. Liquid Crystals Containing Dispersed Multiwall Nanotubes under Aspects of Anisotropic Intermolecular Interactions. Biophys. Bull. 2007, 18, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Sidletsky, O.T.; Panikarskaya, V.D.; Kasian, N.A.; Kositsyn, S.S.; Lisunova, M.O.; Melezhyk, O. V Spectrophotometry and Electrical Conductivity Studies of Multiwall Nanotubes Dispersed in Nematic Liquid Crystals. Funct. Mater. 2007, 14, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Lysetskiy, L.; Panikarskaya, V.; Sidletskiy, O.; Kasian, N.; Kositsyn, S.; Shtifanyuk, P.; Lebovka, N.; Lisunova, M.; Melezhyk, O. Optical Transmission and Conductivity of Nematic Liquid Crystals Containing Dispersed Multiwall Nanotubes. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2007, 478, 127–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Fedoryako, A.P.; Lebovka, N.I. Dispersions of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Different Nematic Mesogens: The Study of Optical Transmittance and Electrical Conductivity. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2009, 41, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Zhukov, A.V.; Shtifanyuk, P.P.; Lebovka, N.I. Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes in Cholesteric Liquid Crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 510, 43–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovka, N.I.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Boyko, Y.P.; Lisetsky, L.; Puchkovska, G.A.; Gavrilko, T.; Baran, J. Interface Interaction and Electrical Conductivity in Composites Carbon Nanotubes/Liquid Crystal. Nanosyst. Nanomater. Nanotehnologies 2009, 7, 701–715. [Google Scholar]
- Minenko, S.S.; Lisetski, L.N.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Lebovka, N.I.; Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Soskin, M.S. Aggregates of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Nematic Liquid Crystal Dispersions: Experimental Evidence and a Physical Picture. Funct. Mater. 2010, 17, 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Soskin, M.S.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Lebovka, N.I. Microstructure and Incubation Processes in Composite Liquid Crystalline Material (5CB) Filled with Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Materwiss. Werksttech. 2011, 42, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Fedoryako, A.P.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes in Cholesteric Liquid Crystals: Features of Aggregate Formation. Funct. Mater. 2013, 20, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovka, N.I.; Lisetski, L.N.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Minenko, S.S.; Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Soskin, M.S. Phase Transitions in Smectogenic Liquid Crystal 4-Butoxybenzylidene-4′-Butylaniline (BBBA) Doped by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Phase Transit. 2013, 86, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, L.; Yaroshchuk, O.; Lebovka, M. Effect of Electro-Optical Memory in Liquid Crystals Doped with Carbon Nanotubes. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 496, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, L.; Yaroshchuk, O.; Lebovka, N. Structure and Electrooptic Response of Liquid Crystal with Negative Dielectric Anisotropy, Doped Carbon Nanotubes. Nanosyst. Nanomater. Nanotehnol. 2008, 6, 625–633. [Google Scholar]
- Dolgov, L.A.; Lebovka, N.I.; Yaroshchuk, O. V Effect of Electrooptical Memory in Suspensions of Carbon Nanotubes in Liquid Crystals. Colloid J. 2009, 71, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, L.; Yaroshchuk, O.; Tomylko, S.; Lebovka, N. Electro-Optical Memory of a Nematic Liquid Crystal Doped by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 15, 33401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Vasil’Ev, V.I.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Self-Organized Composites of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and Nematic Liquid Crystal 5CB: Optical Singularities and Percolation Behavior in Electrical Conductivity. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Correlation Optics, Chernivtsi, Ukraine, 20–24 September 2009; Volume 7388, p. 738802. [Google Scholar]
- Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Vasil’ev, V.I.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Cluster Self-Organization of Nanotubes in a Nematic Phase: The Percolation Behavior and Appearance of Optical Singularities. JETP Lett. 2010, 91, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponevchinsky, V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Vasil’ev, V.I.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Optical Singularities Induced in a Nematic-Cell by Carbon Nanotubes. In Proceedings of the Complex Light and Optical Forces IV, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–28 January 2010; Volume 7613, p. 761306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Naydenov, S.V.; Lisetski, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Complex Light with Optical Singularities Induced by Nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the Complex Light and Optical Forces V, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 January 2011; Volume 7950, p. 79500A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Minenko, S.S.; Lisetski, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Incubation Processes in Nematic 5CB + Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Composites: Induced Optical Singularities and Inversion Walls, Percolation Phenomena. Nonlinear Opt. Quantum Opt. 2012, 43, 281–302. [Google Scholar]
- Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Minenko, S.S.; Lisetskii, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Fine Topological Structure of Coherent Complex Light Created by Carbon Nanocomposites in LC. In Proceedings of the Complex Light and Optical Forces VI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 21–26 January 2012; Volume 8274, pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Naydenov, S.V.; Soskin, M.S. Dispersions of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Liquid Crystals: A Physical Picture of Aggregation. J. Mol. Liq. 2011, 164, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushkevych, O.; Collings, N.; Hasan, T.; Scardaci, V.; Ferrari, A.C.; Wilkinson, T.D.; Crossland, W.A.; Milne, W.I.; Geng, J.; Johnson, B.F.G.; et al. Characterization of Carbon Nanotube—Thermotropic Nematic Liquid Crystal Composites. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 125106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Chepikov, A.M.; Minenko, S.S.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S. Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes in Nematic Liquid Crystals: Effects of Nanotube Geometry. Funct. Mater. 2011, 18, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri, T.; Pushkar, S.K.; Poddar, P. Theoretical Study on the Effect of Electric Field for Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Nematic Liquid Crystal. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 588, 412177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadas, F.; Poursamad, J.B.; Sahrai, M.; Emdadi, M. Flexoelectric Coefficients Enhancement via Doping Carbon Nanotubes in Nematic Liquid Crystal Host. Eur. Phys. J. E 2019, 42, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, E.; Cirtoaje, C. Dynamic Behavior of a Nematic Liquid Crystal with Added Carbon Nanotubes in an Electric Field. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veveričík, M.; Bury, P.; Kopčansky, P.; Timko, M.; Mitróová, Z. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on Liquid Crystal Behavior in Electric and Magnetic Fields Studied by SAW. Procedia Eng. 2017, 192, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumandra, S.B.; Mahendra, B.; Nugroho, F.; Yusuf, Y. Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes under the Influences of Nematic Liquid Crystals and Electric Fields—An Analytical Study. Int. J. Comput. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 11, 2150033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirtoaje, C.; Petrescu, E. The Influence of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on the Dynamic Properties of Nematic Liquid Crystals in Magnetic Field. Materials 2019, 12, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîrtoaje, C.; Petrescu, E.; Moţoc, C. Electric Field Effects in Nematic Liquid Crystals Doped with Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2013, 54, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, E.; Cirtoaje, C. Electric Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Liquid Crystals and Their Influence on Freedericksz Transitions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîrtoaje, C.; Stoian, V.; Petrescu, E.; Moţoc, C. Relaxation Phenomena in Nematic Liquid Crystals with Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Adding. In Proceedings of the Smart Sensors, Actuators, and MEMS VII; and Cyber Physical Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 4–6 May 2015; Volume 9517, pp. 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Cirtoaje, C.; Petrescu, E. Measurement of Magnetic Anisotropy of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Nematic Host. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2016, 84, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovka, N.; Melnyk, V.; Mamunya, Y.; Klishevich, G.; Goncharuk, A.; Pivovarova, N. Low Temperature Phase Transformations in 4-Cyano-4′-Pentylbiphenyl (5CB) Filled by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2013, 52, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klishevich, G.V.; Curmei, N.D.; Lebovka, N.I.; Melnik, V.I. Conformational Effects and Photoluminescence Spectra of Nanocomposites 5CB Liquid Crystals-Carbon Nanotubes. Ukr. J. Phys. 2016, 61, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, O.; Tomylko, S.; Lebovka, N. Two-Step Electrical Percolation in Nematic Liquid Crystal Filled by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2015, 92, 12502. [Google Scholar]
- Lebovka, N.; Bulavin, L.; Kovalchuk, V.; Melnyk, I.; Repnin, K. Two Step Percolation in Aggregating Systems. Condens. Matter Phys. 2017, 20, 13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilov, A.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Lisetski, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Soskin, M.S.; Torgova, S.I. Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes in Cholesteric Liquid Crystals with Photoactive Components. Funct. Mater. 2014, 21, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Fedoryako, A.P.; Samoilov, A.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Soskin, M.S.; Lebovka, N.I. Optical Transmission of Nematic Liquid Crystal 5CB Doped by Single-Walled and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Eur. Phys. J. E 2014, 37, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovka, N.I.; Vygornitskii, N.V.; Bulavin, L.A.; Mazur, L.O.; Lisetski, L.N. Monte Carlo Studies of Optical Transmission of Anisotropic Suspensions. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Schoot, P.; Popa-Nita, V.; Kralj, S. Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes in Nematic Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 4512–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa-Nita, V.; Kralj, S. Liquid Crystal-Carbon Nanotubes Mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 24902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Nita, V.; Buček, S. Length Bidisperse Carbon Nanotubes Dispersions in Thermotropic Liquid Crystals. Phys. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 750890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Nita, V. The Phase Behavior of Rigid Rods in an Anisotropic Mean Field with Applications to Carbon Nanotubes in Nematic Liquid Crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 94901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Nita, V.; Repnik, R. Binary Mixture Composed of Nematic Liquid Crystal and Carbon Nanotubes: A Theoretical Description. In Liquid Crystals-Self-Organized Soft Functional Materials for Advanced Applications; Carlescu, I., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.S.; Ko, Y.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoon, D.K.; Jung, H.-T. Self Assembled Plate-like Structures of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Non-Covalent Hybridization with Smectic Liquid Crystals. Carbon 2010, 48, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, K.P.; Iannacchione, G.S. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on the Isotropic to Nematic and the Nematic to Smectic-A Phase Transitions in Liquid Crystal and Carbon Nanotubes Composites. Eur. Phys. J. E 2011, 34, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Petschek, R.G.; Rosenblatt, C. Nematic Electroclinic Effect in a Carbon-Nanotube-Doped Achiral Liquid Crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 41707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalakonda, P.; Basu, R.; Nemitz, I.R.; Rosenblatt, C.; Iannacchione, G.S. Studies of Nanocomposites of Carbon Nanotubes and a Negative Dielectric Anisotropy Liquid Crystal. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, M.; Katranchev, B.; Rafailov, P.M.; Naradikian, H.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Keskinova, E. Smectic C Liquid Crystal Growth and Memory Effect through Surface Orientation by Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 180, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, M.C.; Yildiz, S.; Ozbek, H. The Effect Of-COOH Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Doping on Electro-Optical, Thermo-Optical and Elastic Properties of a Highly Polar Smectic Liquid Crystal. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshini, G.V.; Shankar Rao, D.S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Krishna Prasad, S. Nanophase Segregation of Nanostructures: Induction of Smectic A and Re-Entrance in a Carbon Nanotube/Nematic Liquid Crystal Composite. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 10774–10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshini, G.V.; Rao, D.S.S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Prasad, S.K. Suppression of the Reentrant Nematic and Stabilization of the Smectic Phases by Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.; Cetinkaya, M.C.; Ozbek, H. The Influence of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Doping on Liquid Crystalline Phase Transitions of a Smectogen Octylcyanobiphenyl: A High-Resolution Birefringence Study. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2019, 495, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, T.D. Reduction of the Order Parameter and High Electric Conductivity of SWCNT Doped Smectic a Liquid Crystal. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2021, 29, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J. An introduction to the physics of liquid crystals. In Fluids, Colloids and Soft Materials: An Introduction to Soft Matter Physics; Nieves, A.F., Puertas, A.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepikov, A.M.; Minenko, S.S.; Lisetski, L.N.; Lebovka, N.I.; Usol’tseva, N.V.; Soskin, M.S. Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes and Organomodified Clay Platelets in Cholesteric Liquid Crystals. Funct. Mater. 2012, 19, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lebovka, N.I.; Lisetski, L.N.; Nesterenko, M.I.; Panikarskaya, V.D.; Kasian, N.A.; Minenko, S.S.; Soskin, M.S. Anomalous Selective Reflection in Cholesteryl Oleyl Carbonate—Nematic 5CB Mixtures and Effects of Their Doping by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Boccuzzi, K.; Ferjani, S.; Lemieux, R.; Petschek, R.; Rosenblatt, C. Carbon Nanotube-Induced Chirality and Macroscopic Helical Twist in Achiral Liquid Crystals. In Proceedings of the APS March Meeting Abstracts, Boston, MA, USA, 27 February–2 March 2012; Volume 2012, pp. C1–C120. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, R.; Chen, C.-L.; Rosenblatt, C. Carbon Nanotube-Induced Macroscopic Helical Twist in an Achiral Nematic Liquid Crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 83518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponevchinsky, V.V.; Goncharuk, A.I.; Denisenko, V.G.; Lebovka, N.I.; Lisetski, L.N.; Nesterenko, M.I.; Panikarskaya, V.D.; Soskin, M.S. LC Nanocomposites: Induced Optical Singularities, Managed Nano/Micro Structure, and Electrical Conductivity. In Proceedings of the Complex Light and Optical Forces VII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2013; Volume 8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Deriabina, O.; Lebovka, N.; Bulavin, L.; Goncharuk, A. Regulation of Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Binary Water+ 1-Cyclohexyl-2-Pyrrolidone Mixtures. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2014, 59, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-K.; Chiu, S.-W.; Kuo, H.-L.; Tang, K.-T. Cholesteric Liquid Crystal-Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Architectures for Gas Detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 43501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryshak, V.; Mikityuk, Z.; Vistak, M.; Gotra, Z.; Akhmetova, A.; Wójcik, W.; Assembay, A. Highly Sensitive Active Medium of Primary Converter SO2 Sensors Based on Cholesteric-Nematic Mixtures, Doped by Carbon Nanotubes. Prz. Elektrotech 2017, 1, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykytyuk, Z.M.; Vistak, M.V.; Kogut, I.T.; Petryshak, V.S. Highly Sensitive Active Medium of Sensor NO2, Based on Cholesteric Nematic Mixture with Impurities of Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. Chem. Solid State 2021, 22, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köysal, O. Conductivity and Dielectric Properties of Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Doped with Single Wall Carbon Nanotube. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usol’tseva, N.V.; Smirnova, M.V.; Sotsky, V.V.; Smirnova, A.I. Physical Properties of Cholesteric Liquid Crystals-Carbon Nanotube Dispersions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 558, 12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usol’tseva, N.V.; Smirnova, M.V.; Kazak, A.V.; Smirnova, A.I.; Bumbina, N.V.; Ilyin, S.O.; Rozhkova, N.N. Rheological Characteristics of Different Carbon Nanoparticles in Cholesteric Mesogen Dispersions as Lubricant Coolant Additives. J. Frict. Wear 2015, 36, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, E.V.; Godlevskiy, V.A.; Usol’Tseva, N. V Investigation of Cholesteric Liquid Crystals and Carbon Nanotubes Additives on Mineral Oil Antifrictional and Rheological Characteristics. Procedia Eng. 2016, 150, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisetski, L.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Samoilov, A.N.; Lebovka, N.I. Optical Density and Microstructure-Related Properties of Photoactive Nematic and Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Colloids with Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 235, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilov, A.N.; Minenko, S.S.; Lisetski, L.N.; Soskin, M.S.; Torgova, S.I.; Lebovka, N.I. Anomalous Optical Properties of Photoactive Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Doped with Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharde, R.A.; Thakare, S.Y. Effects of Concentration of Multiwall Carbon Nanotube on Cholesteric Liquid Crystal. Int. J. Chem. Phys. Sci. 2015, 4, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Yaroshchuk, O.; Tomylko, S.; Gvozdovskyy, I.; Yamaguchi, R. Cholesteric Liquid Crystal—Carbon Nanotube Composites with Photo-Settable Reversible and Memory Electro-Optic Modes. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, E53–E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middha, M.; Kumar, R.; Raina, K.K. Memory Effects in Chiral Nematic Liquid Crystals Doped with Functionalised Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middha, M.; Kumar, R.; Raina, K.K. Improved Electro-Optical Response of Induced Chiral Nematic Liquid Crystal Doped with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Ferroelectrics 2016, 495, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, D. An Electrically and Thermally Erasable Liquid Crystal Film Containing NIR Absorbent Carbon Nanotube. Molecules 2022, 27, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draude, A.P.; Kalavalapalli, T.Y.; Iliut, M.; McConnell, B.; Dierking, I. Stabilization of Liquid Crystal Blue Phases by Carbon Nanoparticles of Varying Dimensionality. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2404–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, G.; Nepal, D.; Aono, M.; Davis, V.A. Cholesteric and Nematic Liquid Crystalline Phase Behavior of Double-Stranded DNA Stabilized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Dispersions. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, L. Cholesteric Cellulose Liquid Crystals with Multifunctional Structural Colors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2107242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.B.; Liebert, L.; Strzelecki, L.; Keller, P. Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. J. Phys. Lett. 1975, 36, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, P.J. Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals: The 2004 Benjamin Franklin Medal in Physics Presented to Robert B. Meyer of Brandeis University. J. Frankl. Inst. 2005, 342, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, S.T. Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystals; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH.: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; ISBN 3-527-2983-1-2. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Yan, K.; Chigrinov, V.; Zhao, H.; Tribelsky, M. Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals: Physics and Applications. Crystals 2019, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Dabrowski, R.; Scalia, G. Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystals with Induced Intermediate Polar Phases and the Effects of Doping with Carbon Nanotubes. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 4411–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Mikulko, A.; Podgornov, F.; Haase, W. Dielectric and Electro-Optic Properties of New Ferroelectric Liquid Crystalline Mixture Doped with Carbon Nanotubes. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2009, 502, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornov, F.V.; Suvorova, A.M.; Lapanik, A.V.; Haase, W. Electrooptic and Dielectric Properties of Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal/Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersions Confined in Thin Cells. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 479, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Choudhary, A.; Mehta, D.S.; Biradar, A.M. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on Response Time of Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, T.; Mehta, D.S.; Biradar, A.M.; Haase, W. Spontaneous Polarization in Smectic A Phase of Carbon Nanotubes Doped Deformed Helix Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 541, 166–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Raina, K.K. Dielectric Studies of Carbon Nanotube Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Films. Asian J. Chem. 2009, 21, S095–S098. [Google Scholar]
- Neeraj; Kumar, P.; Raina, K.K. Analysis of Dielectric and Electro-Optic Responses of Nanomaterials Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Mixture. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeraj; Raina, K.K. Dynamic Responses of Dispersed Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Composite Materials. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2011, 125, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Pozhidaev, E.P.; Chigrinov, V.G.; Manohar, R. Single Walled Carbon Nano-Tube, Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Composites: Excellent Diffractive Tool. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 201106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Manohar, R. Modification in Dielectric Properties of SWCNT Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Singh, D.P.; Manohar, R. SWCNT Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal: The Electro-Optical Properties with Enhanced Dipolar Contribution. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Singh, D.P.; Manohar, R. Enhancement of Dielectric and Electro-Optical Properties in SWCNT Dispersed Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Ferroelectrics 2014, 468, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Raina, K.K.; Hamplová, V.; Kašpar, M.; Bubnov, A. Dielectric Behaviour of the Composite System: Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal. Phase Transit. 2011, 84, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Chaudhary, A.; Bubnov, A.; Raina, K.K. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes-Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Nanocomposites: Effect of Cell Thickness and Dopant Concentration on Electro-Optic and Dielectric Behaviour. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Chaudhary, A.; Bubnov, A.; Hamplova, V.; Raina, K.K. Electrically Switchable Birefringent Self-Assembled Nanocomposites: Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Doped with the Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y. Alignment of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16694–16699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N.; Khosla, S.; Singh, D.; Bawa, S.S. Dielectric Investigations of Pure and Carbon Nanotube-Doped Deformed Helix Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 39, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Prakash, J.; Chandran, A.; Joshi, T.; Kumar, A.; Dhar, A.; Biradar, A.M. Enhanced Dielectric and Electro-Optical Properties of a Newly Synthesised Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Material by Doping Gold Nanoparticle-Decorated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, S.; Sharma, A. Dielectric Behavior of Carbon-Nanotube-Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Mixture. J. Inf. Disp. 2013, 14, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushboo; Jayoti, D.; Malik, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Mehra, R.; Raina, K.K. Properties of Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Doped Composite. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2014, 158, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, K.K. Others Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Composites: A Study of Modified Electrical Behavior. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2014, 434, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, P.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, S.; Haranath, D.; Biradar, A.M. Effect of Functionalisation of Carbon Nanotubes on the Dielectric and Electro-Optical Properties of Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakemseva, M.; Dierking, I.; Kapernaum, N.; Usoltseva, N.; Giesselmann, F. Dispersions of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes in Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Eur. Phys. J. E 2014, 37, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.; Scalia, G. The Effects of Carbon Nanotubes on the Clearing Transition of the Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystal MHPOBC. Ferroelectrics 2016, 495, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sinha, A. Electro-Optical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Doped Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2018, 186, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, K.C.; Mandal, P.K. Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on Dielectric and Electro-Optic Properties of a High Tilt Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystal. Phase Transit. 2019, 92, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K. Influence of Carbon Nanotubes in Antiferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Soft Mater. 2019, 17, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes in Ferroelectric Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhasri, P.; Balasubramanian, V.; Vasanthi, T.; Balamuralikrishnan, S.; Jayaprakasam, R.; Vijayakumar, V.N. Optical Modulation Studies of Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Dispersed in Hydrogen Bonded Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Mixture for Electro-Optic Devices. Ferroelectrics 2020, 558, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.; Mandal, P.K. Influence of Carbon Nanotubes on the Dielectric and Electro-Optical Properties of a Proto-Type Ferroelectric Mixture Used in Display Devices. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 117653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bisoyi, H.K. Aligned Carbon Nanotubes in the Supramolecular Order of Discotic Liquid Crystals. Angew. Chemie 2007, 119, 1523–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Kumar, S. Carbon Nanotubes in Triphenylene and Rufigallol-Based Room Temperature Monomeric and Polymeric Discotic Liquid Crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3032–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Yamaguchi, A.; Alam, M.A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Kato, K.; Takata, M.; Fujita, N.; Aida, T. Discotic Ionic Liquid Crystals of Triphenylene as Dispersants for Orienting Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Angew. Chemie 2012, 124, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Nanoparticles in Discotic Liquid Crystals. In Liquid Crystals with Nano and Microparticles; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017; pp. 461–496. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S. Investigations on Discotic Liquid Crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, V.; Thiruvengadathan, R.; Regev, O. Preparation and Characterization of a Carbon Nanotube- Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Composite. Langmuir 2006, 22, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, B.; Liu, W.; Hao, J. Carbon Nanotubes Incorporated within Lyotropic Hexagonal Liquid Crystal Formed in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8549–8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Scalia, G.; Haluska, M.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Giesselmann, F.; Roth, S. Simultaneous Alignment and Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes with Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Phys. Status Solidi 2006, 243, 3046–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.; Scalia, G.; Haluska, M.; Dettlaff-Weglikowska, U.; Roth, S.; Giesselmann, F. Nanotube Alignment Using Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F. Three Facets of Modern Liquid Crystal Science. Ph.D. Thesis, Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultat IIder Martin-Luther-Universit¨at Halle-Wittenberg, Halle, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Scalia, G.; von Bühler, C.; Hägele, C.; Roth, S.; Giesselmann, F.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Spontaneous Macroscopic Carbon Nanotube Alignment via Colloidal Suspension in Hexagonal Columnar Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.R.; Yamamoto, J.; Lagerwall, J.; Scalia, G. Effects of Carbon Nanotubes on a Very Low Surfactant Concentration Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Host. In Proceedings of the Emerging Liquid Crystal Technologies IX, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5 February 2014; Volume 9004, pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Dölle, S.; Park, J.H.; Schymura, S.; Jo, H.; Scalia, G.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Nanoparticle Guests in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. In Liquid Crystals with Nano and Microparticles; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017; pp. 695–722. [Google Scholar]
- Nativ-Roth, E.; Yerushalmi-Rozen, R.; Regev, O. Phase Behavior and Shear Alignment in SWNT-Surfactant Dispersions. Small 2008, 4, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymura, S.; Enz, E.; Roth, S.; Scalia, G.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Macroscopic-Scale Carbon Nanotube Alignment via Self-Assembly in Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 2177–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymura, S.; Dölle, S.; Yamamoto, J.; Lagerwall, J. Filament Formation in Carbon Nanotube-Doped Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2663–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymura, S. Liquid Crystalline Carbon Nanotube Suspensions: From Unique Challenges to Unique Properties/von Stefan Schymura. Doctoral Dissertation, Universitäts-und Landesbibliothek Sachsen-Anhalt, Halle, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.; Li, H.; Kalwarczyk, E.; Kelm, A.; Fiałkowski, M.; Gorecka, E.; Pociecha, D.; Hołyst, R. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Hybrid Materials Fabricated by a Phase Separation Method in the Presence of Polyelectrolyte. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8821–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L. Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phases Formed in Binary Mixture of 1-Tetradecyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride/Ethylammonium Nitrate and Its Application in the Dispersion of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 369, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Tan, Z.; Kondo, A.; Naito, M. Direct Filament Formation of Biological Carbon Nanotube Suspensions. Addit. Pap. Present. 2012, 2012, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Tan, Z.; Kondo, A.; Naito, M. Filament Formation in Biological Carbon Nanotube Suspensions. Trans. Join. Weld. Res. Inst. 2012, 41, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardani, F.; La Mesa, C. Elasticity of Dispersions Based on Carbon Nanotubes Dissolved in a Lyotropic Nematic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9424–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ould-Moussa, N.; Blanc, C.; Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Maugey, M.; Poulin, P.; Anglaret, E.; Nobili, M. Dispersion and Alignment of Individual Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes in a Chromonic Liquid Crystal. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 40, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, D. Self-Assembled Ordering of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in a Lyotropic Liquid Crystal System. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, D.; Mishra, J.; Thejas, R. Magnetic Field Dependence of the Hexagonal to Isotropic Transition Temperature of a Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed Lyotropic Liquid Crystal. Phase Transit. 2019, 92, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srour, H.K.; Atta, N.F.; Khalil, M.W.; Galal, A. Ionic Liquid Crystals/Nano-Nickel Oxide-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes Composite for Electrocatalytic Treatment of Urea-Contaminated Water. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.F.; Alsayed, A.M.; Dogic, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lubensky, T.C.; Yodh, A.G. Nematic Nanotube Gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 88303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.F.; Nobili, M.; Ye, F.; Lubensky, T.C.; Yodh, A.G. Cracks and Topological Defects in Lyotropic Nematic Gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 148301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, L.A.; Islam, M.F.; Hammouda, B.; Yodh, A.G.; Heiney, P.A. Structure of Semidilute Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube Suspensions and Gels. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Ohara, S.; Naito, M.; Abe, H. Supramolecular Hydrogel of Bile Salts Triggered by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4053–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuer, S.; Braun, L.; Zentel, R. Solubilisation of Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes by $α$-Pyrene Functionalised PMMA and Their Liquid Crystalline Self-Organisation. Chem. Commun. 2008, 27, 3166–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; You, W.; Barman, S.; Hellstrom, S.; LeMieux, M.C.; Oh, J.H.; Liu, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Wang, W.M.; Chen, B.; et al. Lyotropic Liquid-Crystalline Solutions of High-Concentration Dispersions of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Conjugated Polymers. Small 2009, 5, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, H.; Chang, J.Y. Preparation of Polymeric SWNT- Liquid Crystal Composites Using a Polymerizable Surfactant. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 5376–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Do, C.; Lee, M.-J.; Choi, S.-M. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Induced Re-Entrant Hexagonal Phases in a Pluronic Block Copolymer System. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3050–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xin, X.; Guo, K.; Yang, M.; Ma, X.; Yuan, J.; Shen, J.; Yuan, S. Ordered Carbon Nanotubes-n-Dodecyl Tetraethylene Monoether Liquid Crystal Composites through Phase Separation Induced by Poly (Ethylene Glycol). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14771–14780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Miao, Z.; Shen, W. Development of Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals: From Mode Innovation to Applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 163, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagidi, S.; Pasupuleti, K.S.; Reddeppa, M.; Ahn, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, M.-D.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, M.Y. Resistive Type NO2 Gas Sensing in Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals with Functionalized-Carbon Nanotubes Dopant at Room Temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 370, 132482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mănăilă-Maximean, D.; Cîrcu, V.; Ganea, P.; Bărar, A.; Danila, O.; Staicu, T.; Loiko, V.A.; Konkolovich, A.V.; Miskevich, A.A. Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystals Films Doped with Carbon Nanotubes: Preparation Methods. In Proceedings of the Advanced Topics in Optoelectronics, Microelectronics, and Nanotechnologies IX, Constanta, Romania, 23–26 August 2018; Volume 10977, p. 1097702. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Shen, T.; Zheng, J.; Zhuang, S. Electro-Optical Properties and Frequency Response of Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystal Gratings Doped with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 12660–12670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).