Seasonal Variation in Bacterial Load and Genetic Diversity in Groundwater from Aïn Tawjdate, Morocco
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Design and Field Procedures
2.3. Bacteriological Analyses: Overview and Rationale
2.4. Membrane Filtration and Culture Conditions
2.5. Indicator Organisms: Methods and Reporting
2.6. Target Organisms: Selective Detection
2.7. Isolation, Purification, and Biochemical Identification
2.8. Expression of Results and Data Management
2.9. ERIC-PCR Typing of Enterobacter cloacae
2.10. Quality Assurance and Biosafety
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. Ethical and Administrative Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Indicator Bacteria
3.2. Cultivable Pathogenic and Opportunistic Bacteria
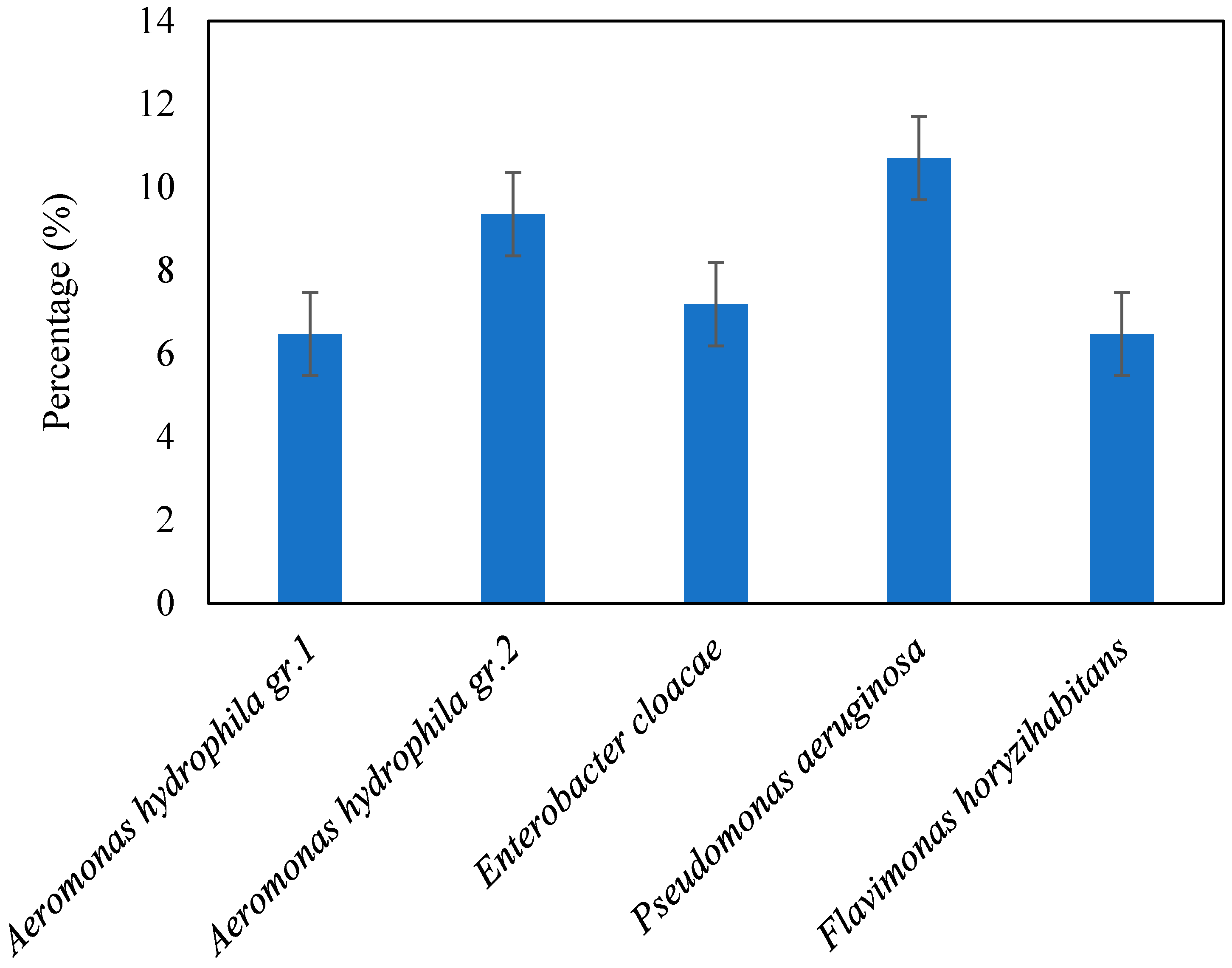
3.3. Frequency of the Most Abundant Taxa
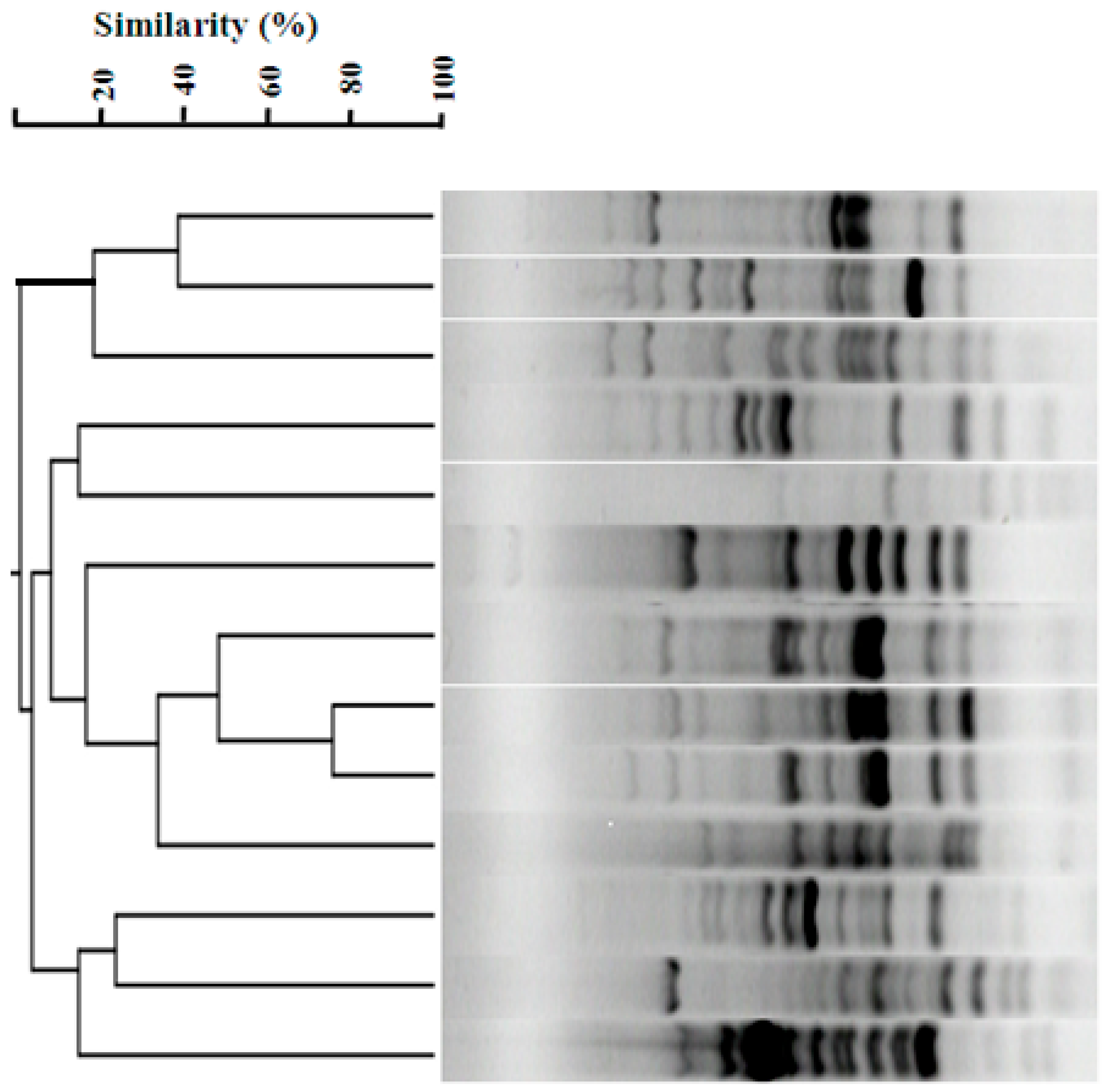
3.4. ERIC-PCR Profiles of Enterobacter cloacae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nahar, N.; Das, T.K.; Sadia, L.; Khatun, A.; Farzana, F.; Sarwar, S.; Shaibur, M.R. Hydrogeochemical evaluation and health implications of groundwater in Magura sadar upazila, Bangladesh: Application of GIS and Multivariate statistics. J. Chem. 2025, 2025, 8012445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouafae, K.; Aouragh, M.H.; Hmaidi, A.E.; Ragragui, H.; Ouali, A.E. Integrated multi-index, GIS and multivariate statistical approaches for groundwater quality assessment in the Saïss Basin, Morocco. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2025, 10, 4217–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgettafi, M.; Rochdane, S.; Elmandour, A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Himi, M.; Casas, A. Br-Li and stable isotopes to induce groundwater salinity in crystalline and detrital aquifers: Oriental Haouz Morocco. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echogdali, F.Z.; Boutaleb, S.; Tariq, A.; Hamidi, M.; El Mekkaoui, M.; Ikirri, M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Uddin, G.; Akhtar, N.; Bendarma, A.; et al. Exploring groundwater patterns in Souss-Massa Mountainous Basin, Morocco: A fusion of fractal analysis and machine learning techniques on gravity data. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 54, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzoun, O.; Iharzi, C.; Kassou, A.; Essahlaoui, A.; Khrabcha, A. Lineament mapping using sig and optical and radar remote sensing: The case of the Tafilalet plain (Southeastern Morocco). In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Ulis, France, 2025; Volume 607, p. 02007. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Jha, M.K.; Kim, K.W.; Pacheco, F.A. Groundwater resources: Challenges and future opportunities. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, V. Water quality, air pollution, and climate change: Investigating the environmental impacts of industrialization and urbanization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, A.; Tsur, Y. The Economics of Water Resources: A Comprehensive Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marzouki, H.; Nordine, N.; Azzirgue, E.M.; Silva, J.C.E.D.; Cherif, E.K. From Contamination to Conservation: A Hydrochemical and Isotopic Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in the Semi-Arid Guire Basin (Morocco). Water 2025, 17, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Ariza, B.; Piña, A.; Donado, L.D. Assessment of groundwater quality for human consumption and its health risks in the Middle Magdalena Valley, Colombia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Deng, J.; Yan, W.; Qin, C.; Du, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Burden and trends of infectious disease mortality attributed to air pollution, unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene, and non-optimal temperature globally and in different socio-demographic index regions. Glob. Health Res. Policy 2024, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, B.V.; Mapoma, H.W.T.; Thole, B. Investigating Antibiotic Susceptibility of Pathogenic Micro-Organisms in Groundwater from Boreholes and Shallow Wells in T/A Makhwira, Chikwawa. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousouis, A.; Bouabdli, A.; Ayach, M.; Lazar, H.; Ravung, L.; Valles, V.; Barbiero, L. Discrimination of Spatial and Temporal Variabilities in the Analysis of Groundwater Databases: Application to the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Region, France. Water 2025, 17, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Yi, H.; Ye, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cui, J. Seasonal variations in groundwater chemistry and quality and associated health risks from domestic wells and crucial constraints in the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2025, 27, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagordo, F.; Brigida, S.; Grassi, T.; Caputo, M.C.; Apollonio, F.; De Carlo, L.; Savino, A.F.; Triggiano, F.; Turturro, A.C.; De Donno, A.; et al. Factors influencing microbial contamination of groundwater: A systematic review of field-scale studies. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueroui, Y.; Bousbia, A.; Boudalia, S.; Touati, H.; Benaissa, M.; Maoui, A. Groundwater quality and hydrochemical characteristics in the upper Seybouse sub-basin, Northeast Algeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 26628–26645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruța, N.L.; Sur, I.M.; Rusu, T.A.; Gabor, T.; Rusu, T. Integrated assessment of groundwater vulnerability and drinking water quality in rural wells: Case study from Ceanu Mare Commune, Northern Transylvanian Basin, Romania. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Chaudhary, S.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, P. Water pollution in rural areas: Primary sources, associated health issues, and remedies. Water Resour. Manag. Rural. Dev. 2024, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauloup, A.; Cébron, A. Development of a device to trap soil bacteria capable of degrading organic contaminants such as alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 491, 137690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobnicka-Kupiec, A.; Gołofit-Szymczak, M.; Cyprowski, M.; Górny, R.L. Monitoring of enteropathogenic gram-negative bacteria in wastewater treatment plants: A multimethod approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 37229–37244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petculescu, I.; Hynds, P.; Brown, R.S.; Boudou, M.; McDermott, K.; Majury, A. Development of a “big data” groundwater microbial contamination index and spatial comparisons with enteric infection rates in southern Ontario. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuvo, R.M.; Chowdhury, R.R.; Chakroborty, S.; Das, A.; Kafy, A.A.; Altuwaijri, H.A.; Rahman, M.T. Geospatially Informed Water Pricing for Sustainability: A Mixed Methods Approach to the Increasing Block Tariff Model for Groundwater Management in Arid Regions of Northwest Bangladesh. Water 2024, 16, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.R.; Oh, J.; Choi, J.; Park, S.; Yun, S.T. Predicting leachate impact on groundwater using electrical conductivity and oxidation–reduction potential measurements: An empirical and theoretical approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.; Malik, A. Geospatial mapping and cluster analysis of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in drinking water of semi-arid areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.C.; Siciliano, S.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Wosnick, N.; Rincon, G.; Roges, E.M.; Festivo, M.L.; Rodrigues, D.D.P.; Silva, J.L. Nunes An enteric microbiota assessment in sharks and rays from the Brazilian Amazon Coast. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2025, 108, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odewade, L.O.; Imam, A.A.; Adesakin, T.A.; Odewade, J.O. Assessment of human faecal contamination on groundwater quality and reporting consequent waterborne diseases in Funtua Metropolis, Katsina State, Nigeria. Front. Water 2025, 7, 1561777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashir, N.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.; Song, X. Co-occurrence of microplastics, PFASs, antibiotics, and antibiotic resistance genes in groundwater and their composite impacts on indigenous microbial communities: A field study. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 961, 178373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, G.; Uçar, F.; Telli, O.; Lima, N.; Boiu-Sicuia, O.A. Fungal contaminants in Turkish bottled water and their mycotoxin-producing potential. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 2025, 20, Doc41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Debassi, B.; Allaoua, N.; Ghanem, N.; Hafid, H.; Benacherine, M.; Chenchouni, H. Assessment of water quality of groundwater, surface water, and wastewater using physicochemical parameters and microbiological indicators. Sci. Prog. 2025, 108, 00368504251348544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 9308-1:2014; Water Quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria. Part 1: Membrane Filtration Method for Waters with Low Bacterial Background Flora. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 7899-2:2000; Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Intestinal Enterococci. Part 2: Membrane Filtration Method. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- ISO 6222:1999; Water Quality—Enumeration of Culturable Micro-Organisms—Colony Count by Inoculation in a Nutrient Agar Culture Medium. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Koujalagi, T.; Ruhal, R. Mitigating Health Risks Through Environmental Tracking of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr. Microbiol. 2025, 82, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çaktü Güler, K.; Göktürk, I.; Yılmaz, F.; Araz, A.; Denizli, A. Plasmonic nanosensors for environmental pollutants sensing: Recent advances and perspectives. Essent. Chem. 2024, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tong, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y. Pathogen contamination of groundwater systems and health risks. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 54, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleni, U.; Morare, R.; Masunga, G.S.; Magwaza, N.; Saasa, V.; Madito, M.J.; Managa, M. Recent developments in waterborne pathogen detection technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, J.S.; Marciales, K.P.M. Microbiological identification of pathogens in water from educational centers in Norte de Santander. Rev. Cuid. 2025, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, L.J.; LaSala, P.R.; Whittier, S. Rapid devices and instruments for the identification of aerobic bacteria. In Manual of Commercial Methods in Clinical Microbiology, International ed., 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, A.; Sato, K.; Tamamura, S.; Murakami, T.; Inomata, H.; Tamazawa, S.; Igarashi, T. Gaoshiqia hydrogeniformans sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2025, 75, 006802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluym, T.; Waegenaar, F.; Dejaeger, K.; Dhoore, M.; Mestdagh, E.; Cornelissen, E.; De Gusseme, B. Membrane filtration reduces nutrient availability and invasion potential in drinking water systems, without affecting mature biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1622038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sraphet, S.; Tharasawatpipat, C.; Choo-In, S.; Kayee, P.; Namwong, S.; Budsabun, T.; Javadi, B. Comparative genomic analysis of cassava rhizospheric Bacillus subtilis using integrated in vitro and in Silico approaches with enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC) sequences. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louws, F.J.; Schneider, M.; de Bruijn, F.J. Assessing Genetic Diversity of Microbes Using Repetitive SequenceBased PCR (rep-PCR). In Environmental Applications of Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 63–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, D.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yang, D.; Jin, M. Landscape of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial communities in groundwater on the Tibetan Plateau, and distinguishing their difference with low-altitude counterparts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versalovic, J.; Koeuth, T.; Lupski, R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to finerpriting of bacterial enomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 6823–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Le, K.K.; Gleeson, L.J.; Stenos, J.; Graves, S.R.; Day, N.P.J. Assessing the evidence for effective biosafety risk management in Coxiella burnetii research. One Health 2025, 21, 101159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybraniec, C.; Cournoyer, B.; Moussard, C.; Beaupère, M.; Lusurier, L.; Leriche, F.; Galia, W. Occurrence of 40 sanitary indicators in French digestates derived from different anaerobic digestion processes and raw organic wastes from agricultural and urban origin. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1346715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Song, W. Effect of coal mining subsidence on soil microbial communities in mining areas with high groundwater levels. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likando, N.M.; Chipandwe, M.S. Statistical investigation of climate and landfill age impacts on Kupferberg landfill leachate composition: One-way ANOVA analysis. Discov. Water 2024, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Sun, M.; Li, Q.; Fan, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, R. Improvement of soil structure and bacterial composition by long-term application of seaweed fertilizer. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5122–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, H.; Maheshwari, B.; Mohapatra, S.; Sood, S.; Dhawan, B.; Kapil, A.; Tezpur, B. Clonal relationship among Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from different clinical specimens by ERIC-PCR. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 116, S18–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baroudi, H.; Ouazzani, C.; Moustaghfir, A.; Er-Ramly, A.; Essebbahi, I.; El Baroudi, Y.; Balouch, L. Evaluation of drinking water quality and potential health risks on the population in Morocco. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. Hydrogeochemical and anthropogenic controls on quality and quantitative source-specific risks of groundwater in a resource-based area with intensive industrial and agricultural activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 140911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkacem, A.; Chahlaoui, A.; Soulaymani, A.; Rhazi-Filali, F.; Benali, D. Etude comparative de la qualité bactériologique des eaux des oueds Boufekrane et Ouislane à la traversée de la ville de Meknès (Maroc). Rev. Microbiol. Ind. San. Environ. 2007, 1, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Petculescu, I.; Hynds, P.; Brown, R.S.; Mcdermott, K.; Majury, A. An investigation of microbial groundwater contamination seasonality and extreme weather event interruptions using “big data”, time-series analyses, and unsupervised machine learning. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.G.; Reinecke, R.; Copty, N.K.; Barry, D.A.; Heggy, E.; Labat, D.; Roggero, P.P.; Borchardt, D.; Rode, M.; Gómez-Hernández, J.J.; et al. Multi-decadal groundwater observations reveal surprisingly stable levels in southwestern Europe. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtak, K.; Marzec-Grządziel, A. Microbial Hazard in Cultivated Soils Located in the Floodplains of the Vistula River Valley, Poland—Preliminary Research. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M. A group with emerging potential in the clinical and public health realms: The genus Providencia. Infect. Dis. 2025, 57, 699–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V.; Mickelsen, P.A.; Murray, B.E.; Persing, D.H.; Swaminathan, B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Mtewa, A.G.; Chiutula, C.; Mvula, R.L.S.; Maluwa, A.; Eregno, F.E.; Njalam’mano, J. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Bacteria in Manure, Soil, and Vegetables in Urban Blantyre, Malawi, from a Farm-to-Fork Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sarma, K. Tracing the land use specific impacts on groundwater quality: A chemometric, information entropy WQI and health risk assessment study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 30519–30542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çallı, K.Ö.; Chiogna, G.; Bittner, D.; Sivelle, V.; Labat, D.; Richieri, B.; Hartmann, A. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of solute transport modeling approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2025, 63, e2023RG000811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waegenaar, F.; Pluym, T.; Vermeulen, E.; De Gusseme, B.; Boon, N. Impact of flushing procedures on drinking water biostability and invasion susceptibility in distribution systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0068625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tuan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Stigter, T.; Zhou, Y. Understanding groundwater use and vulnerability of rural communities in the Mekong Delta: The case of Tra Vinh province, Vietnam. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarc, A.; Kosel, J.; Stopar, D.; Oder, M.; Dular, M. Removal of bacteria Legionella pneumophila, Escherichia coli, and Bacillus subtilis by (super) cavitation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.P.; Pradhan, A.K.; Patel, J. Persistence of foodborne bacterial pathogens on microgreens and soil irrigated with contaminated water. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Beretsou, V.G.; Iakovides, I.C.; Karaolia, P.; Michael, C.; Benmarhnia, T.; Chefetz, B.; Donner, E.; Gawlik, B.M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Sustainable wastewater reuse for agriculture. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganisms Sought | Analysis Method | Culture Medium | Incubation | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total coliforms and fecal coliforms | Filtration of 100 mL | Tergitol-7 agar | 48 h at 44 °C | NM 03.07.003 (ISO 9308-1) [30] |
| Intestinal enterococci | Filtration of 100 mL | Slanetz and Bartley | 48 h at 37 °C | NM 03.7.006 (ISO 7899-2) [31] |
| Revivable microorganisms at 22 °C | Deep seeding of 1 mL | Nutrient agar | 72 h at 22 °C | NM 03.07.005 (ISO 6222) [32] |
| Microorganisms Sought | Amount of Water Filtered | Culture Medium | Incubation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 250 mL | Cetrimide | 48 h at 37 °C |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 250 mL | RYAN base agar | 24 h at 37 °C |
| Salmonella spp. | 250 mL | Buffered peptone water + Tween 80 | 24 h at 37 °C (pre-enrichment) |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 250 mL | MacConkey | 24 h at 37 °C |
| Aerobic mesophilic bacteria | 250 mL | Plate Count Agar (PCA) | 24 h at 37 °C |
| API Gallery | Strains | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 20E | Enterobacteriaceae and other Gram-negative rods | Galerie d’identification API-Diagnostic Clinique, bioMérieux France. |
| 20NE | non-enteric Gram-negative rods | Galerie d’identification API-Diagnostic Clinique, bioMérieux France. |
| API Rapid 20E | Rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae in 4 h. | Galerie d’identification API-Diagnostic Clinique, bioMérieux France. |
| API Listeria | Listeria | Galerie d’identification API-Diagnostic Clinique, bioMérieux France. |
| Target | Primer | Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Fragment Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERIC loci | ERIC-2 | AAGTAAGTGACTGGGGTGAGCG | Variable | Versalovic et al., 1991 [44] |
| ERIC loci | ERIC-1R | ATGTAAGCTCCTGGGGATTCAC | Variable | Versalovic et al., 1991 [44] |
| Microorganisms Sought | Unit | Spring (Maximum Reported) | Summer (Maximum Reported) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total coliforms | CFU/100 mL | 158 | 303 |
| Intestinal enterococci | CFU/100 mL | 80 | 103 |
| Fecal coliforms | CFU/100 mL | 90 | 205 |
| Revivable microorganisms (at 37 °C) | CFU/mL | 145 | 276 |
| Well | Spring (Species Identified) | Summer (Species Identified) |
|---|---|---|
| Well 1 | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Citrobacter freundii; Comamonas testosteroni | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Citrobacter freundii; Enterobacter amnigenus 2; Serratia odorifera |
| Well 2 | Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Enterobacter cloacae; Escherichia coli (type 1); Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Flavimonas horyzihabitans; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Citrobacter freundii; Comamonas testosteroni; Enterobacter amnigenus 2; Klebsiella ornithinolytica; Photobacterium damsela; Serratia liquefaciens; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Pseudomonas alcaligenes | Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Enterobacter cloacae; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Flavimonas horyzihabitans; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Citrobacter freundii; Comamonas testosteroni; Klebsiella ornithinolytica; Photobacterium damsela; Serratia liquefaciens; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Hafnia alvei; Klebsiella oxytoca; Pasteurella pneumotropica; Pseudomonas stutzeri |
| Well 3 | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Escherichia coli (type 1); Pseudomonas fluorescens; Citrobacter freundii; Comamonas testosteroni; Proteus mirabilis | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Enterobacter cloacae; Escherichia coli (type 1); Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Flavimonas horyzihabitans; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Comamonas testosteroni; Enterobacter amnigenus 2; Klebsiella ornithinolytica; Photobacterium damsela; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Acinetobacter cloacae; Ochrobactrum anthropi |
| Well 4 | Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Flavimonas horyzihabitans; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Enterobacter amnigenus 2; Klebsiella ornithinolytica; Photobacterium damsela; Serratia liquefaciens; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Acinetobacter baumannii; Enterobacter sakazakii; Providencia rettgeri; Pseudomonas horyzihabitans | Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Enterobacter cloacae; Escherichia coli (type 1); Flavimonas horyzihabitans; Enterobacter amnigenus 2; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Citrobacter freundii; Comamonas testosteroni; Klebsiella ornithinolytica; Photobacterium damsela; Serratia liquefaciens; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Aeromonas salmonicida; Enterobacter aerogenes; Raoultella ornithinolytica; Serratia marcescens |
| Well 5 | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Escherichia coli (type 1); Citrobacter freundii; Serratia liquefaciens; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Escherichia coli (type 1); Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Citrobacter freundii; Pantoea spp. 4; Pseudomonas luteola; Vibrio parahaemolyticus |
| Well 6 | Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Bordetella sp.; Vibrio hollisae | Aeromonas hydrophila gr.1; Aeromonas hydrophila gr.2; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Comamonas testosteroni; Klebsiella ornithinolytica; Eikenella corrodens |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aboulkacem, A.; Zaki, H.; Aboulkacem, A.; Ainane, T.; Isemin, R.; Mohamed Abdoul-Latif, F.; Ainane, A. Seasonal Variation in Bacterial Load and Genetic Diversity in Groundwater from Aïn Tawjdate, Morocco. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040136
Aboulkacem A, Zaki H, Aboulkacem A, Ainane T, Isemin R, Mohamed Abdoul-Latif F, Ainane A. Seasonal Variation in Bacterial Load and Genetic Diversity in Groundwater from Aïn Tawjdate, Morocco. Applied Microbiology. 2025; 5(4):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboulkacem, Asmae, Hanane Zaki, Amina Aboulkacem, Tarik Ainane, Rafail Isemin, Fatouma Mohamed Abdoul-Latif, and Ayoub Ainane. 2025. "Seasonal Variation in Bacterial Load and Genetic Diversity in Groundwater from Aïn Tawjdate, Morocco" Applied Microbiology 5, no. 4: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040136
APA StyleAboulkacem, A., Zaki, H., Aboulkacem, A., Ainane, T., Isemin, R., Mohamed Abdoul-Latif, F., & Ainane, A. (2025). Seasonal Variation in Bacterial Load and Genetic Diversity in Groundwater from Aïn Tawjdate, Morocco. Applied Microbiology, 5(4), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040136







