Lactic Acid Bacteria-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles: A Smart Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates and Growth Conditions
2.1.1. Isolation of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) from Raw Milk
2.1.2. Pathogenic Isolates
2.2. Production and Recovery of Purified Nano Selenium
2.3. Characterization of Se-NPs
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity of Se-NPs and MIC Determination
2.5. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
2.6. Cytotoxicity of Biogenic Se-NPs
2.7. Drug Combination Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Isolation of Lactic Acid Bacteria
3.2. Identification of the Pathogenic Isolates
3.3. Production and Recovery of Purified Nano Selenium
3.4. Characterization of Se-NPs
3.4.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.4.2. EDEX
3.4.3. UV Results
3.4.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
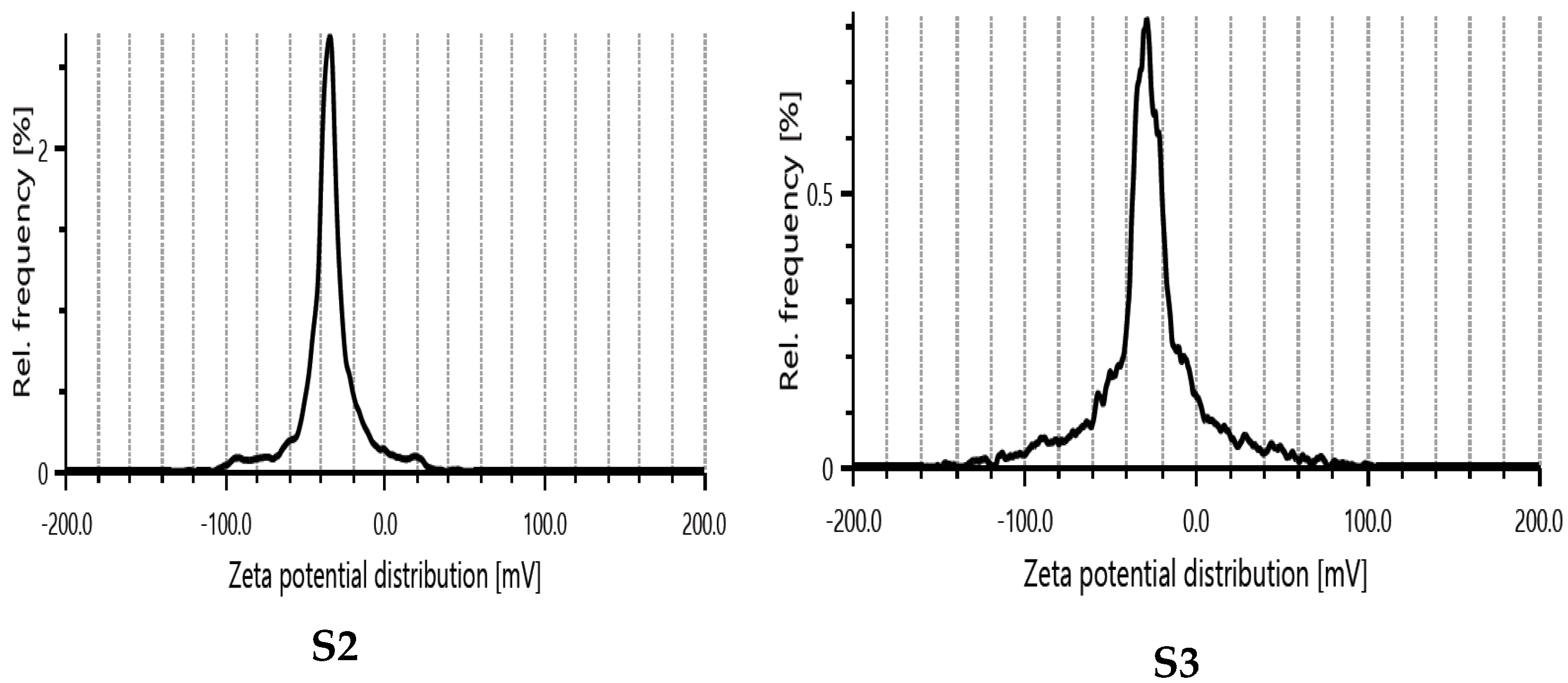
3.5. Zeta Potential Measurements
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity and MIC of Se-NPs
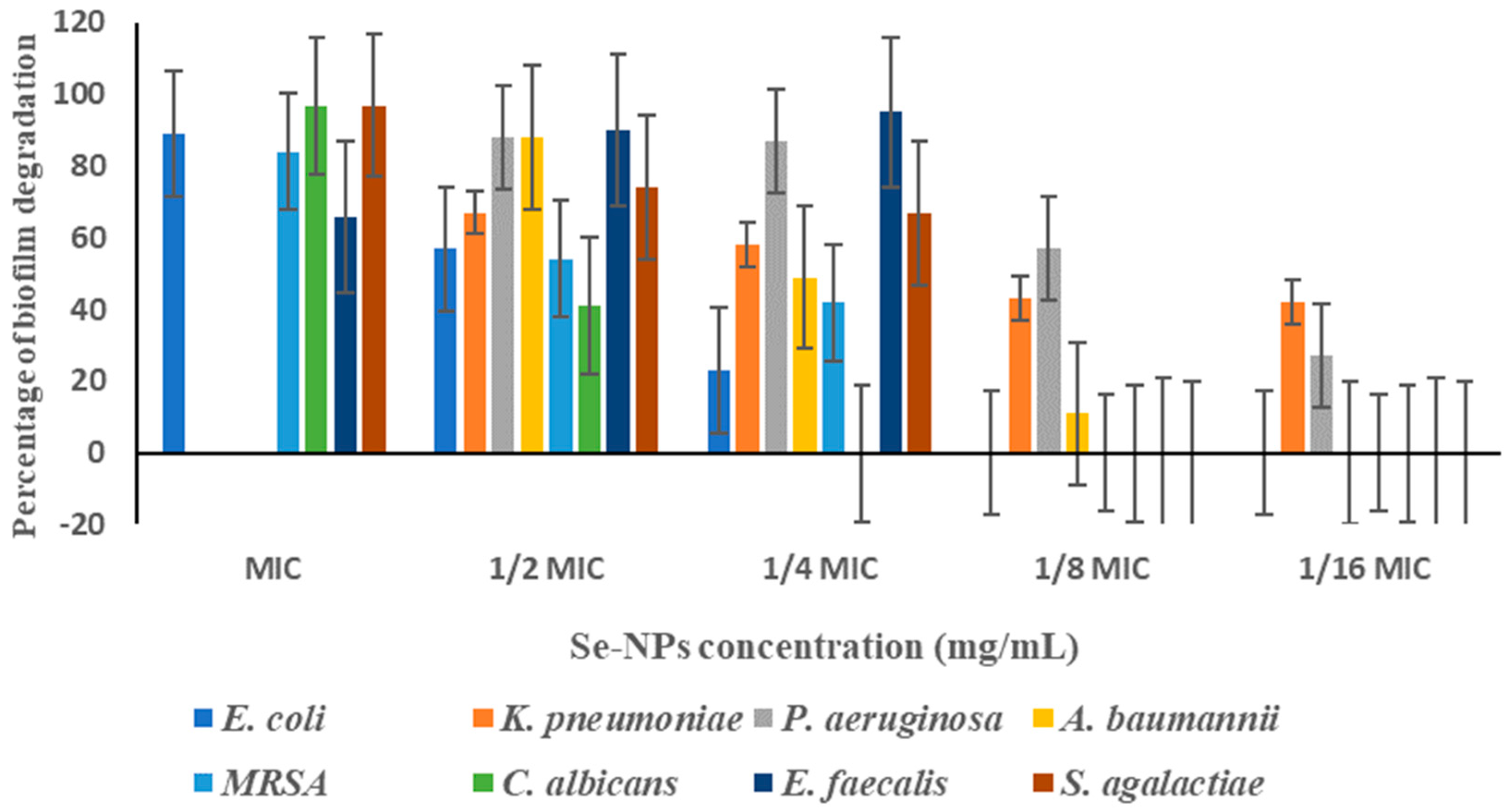
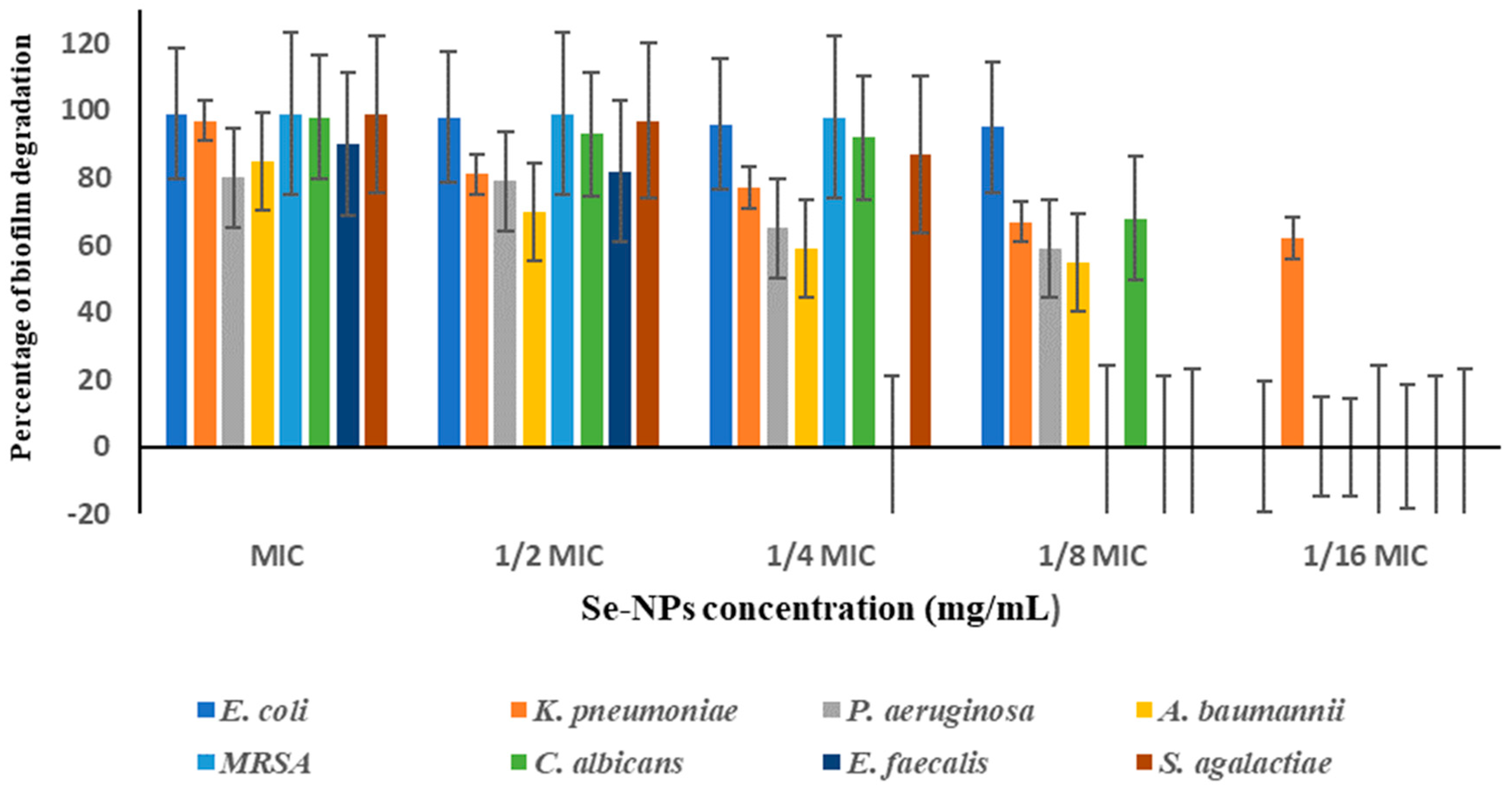
3.7. Biofilm Inhibition
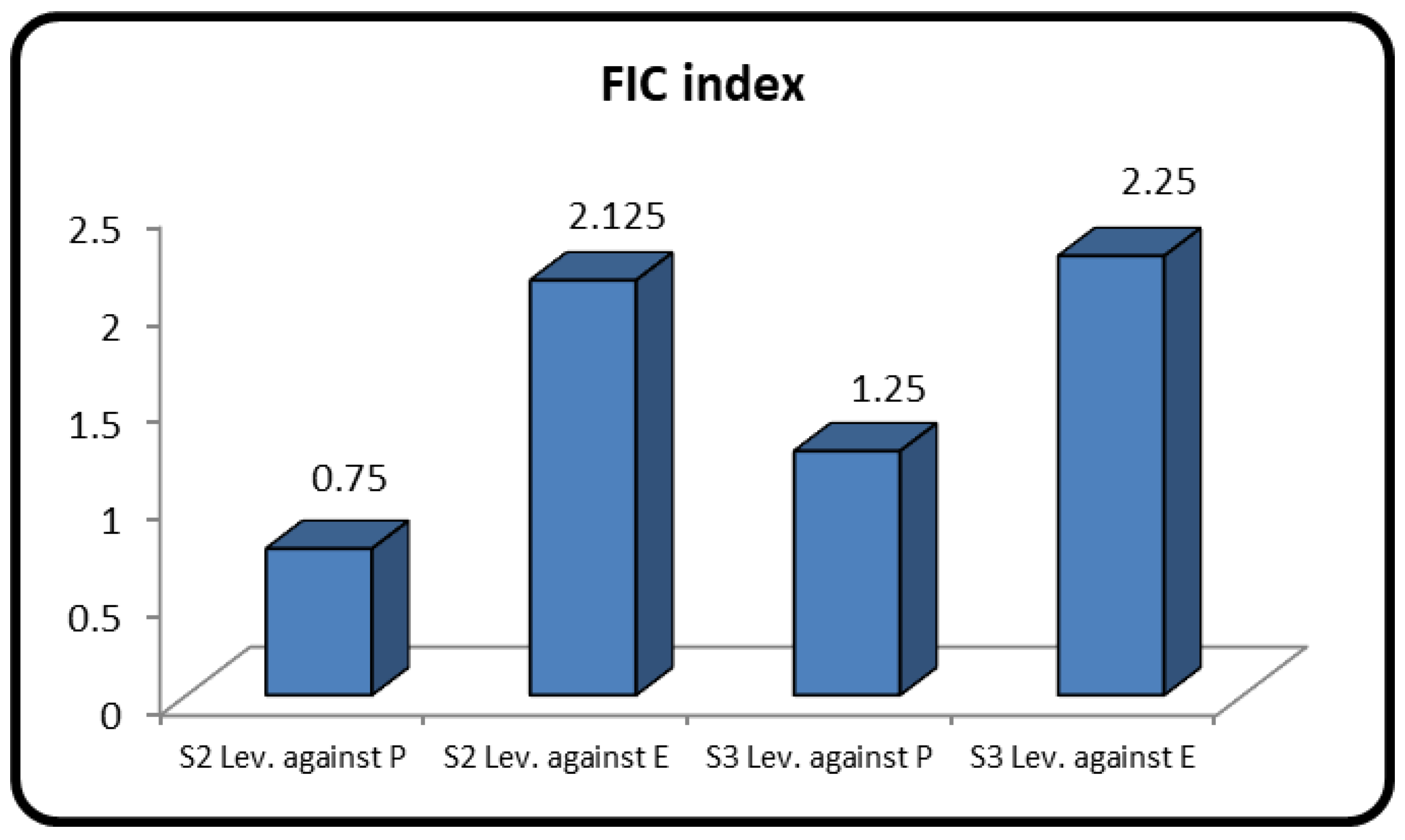
3.8. Drug Combination Assay
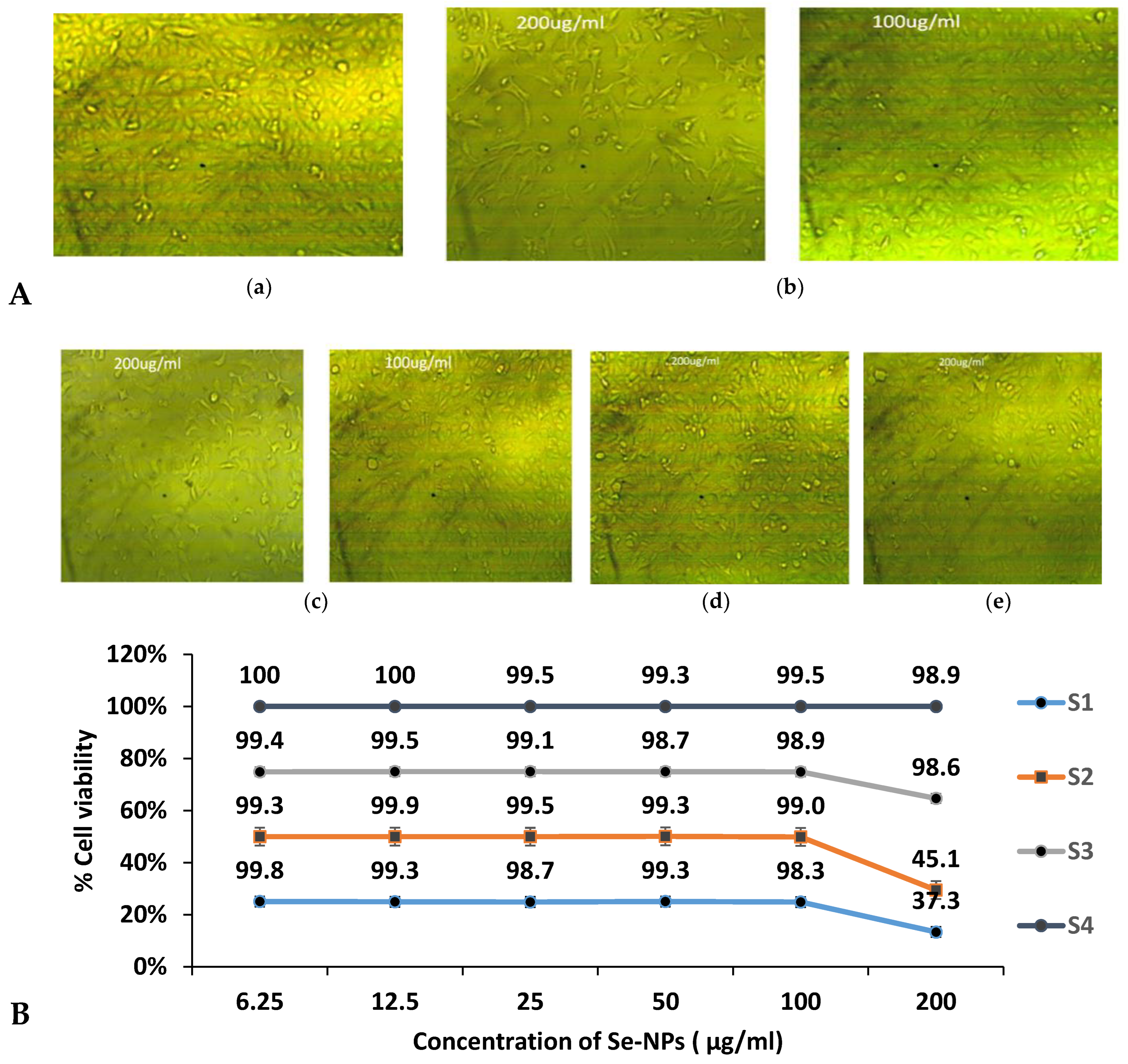
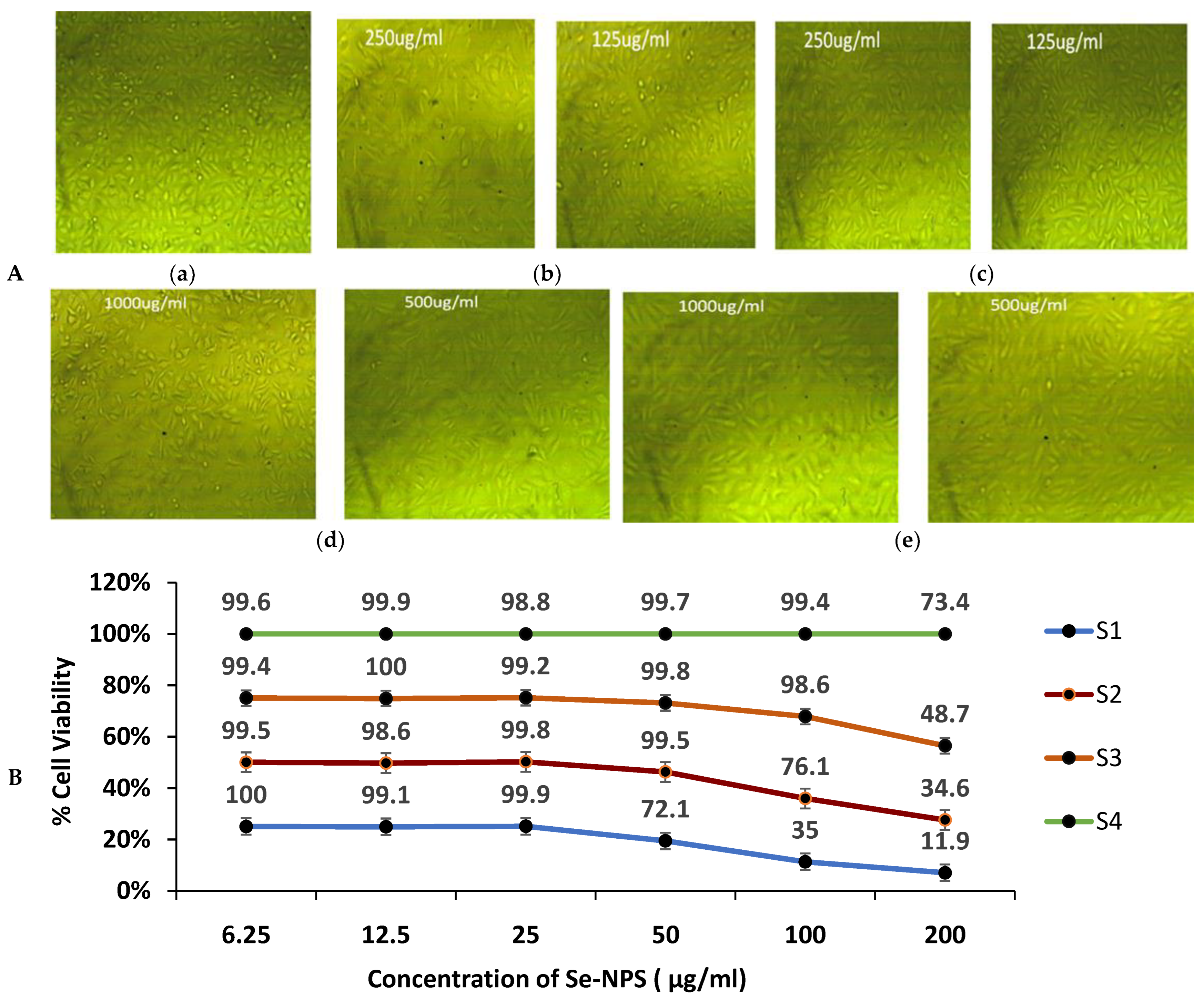
3.9. Cytotoxicity of Biogenic Se-NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| EDX | Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FIC | Fractional Inhibitory Concentration |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MRS | de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| OD | Optical density |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Se-NPs | Selenium nanoparticles |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| UV-vis | UV-Visible absorption spectra |
| 16s rRNA | 6S ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
References
- Bhushan, B. Introduction to nanotechnology. In Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Basuini, M.F.E.; Yilmaz, S.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Kari, Z.A.; Abdul Razab, M.K.A.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alagawany, M.; Gewaily, M.S. Selenium nanoparticles as a natural antioxidant and metabolic regulator in aquaculture: A review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, J.; McClements, D.J. Standardization of nanoparticle characterization: Methods for testing properties, stability; functionality of edible nanoparticles. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1334–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Vaghari, H.; Mohammad-Jafari, R.; Najian, Y.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities assessment of fabricated selenium nanoparticles using Pelargonium zonale leaf extract. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhira, D.; Aruna, A.; Manikandan, K.; Albeshr, M.F.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Vinayagam, R.; Kathirvel, A.; Priyan, S.R.; Kumar, G.S.; Srinivasan, R. Antimicrobial and Photocatalytic Activities of Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized from Elaeagnus indica Leaf Extract. Processes 2023, 11, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Bao, Y.; Broadley, M.R.; Collings, R.; Ford, D.; Hesketh, J.E.; Hurst, R. Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1337–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.M. Nanobiohybrids: A new concept for metal nanoparticles synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9583–9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husen, A.; Siddiqi, K.S. Phytosynthesis of nanoparticles: Concept, controversy and application. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Yin, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, B.; Mirani, Z.A.; Xu, B.; Chan, M.W.H.; Ali, A.; Usman, M.; Ali, N. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles (via Bacillus subtilis BSN313); their isolation, characterization; bioactivities. Molecules 2021, 26, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabnikova, O.; Khonkiv, M.; Kovshar, I. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles by lactic acid bacteria and areas of their possible applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscola, V.; Albuquerque, M.A.C.; Nunes, T.P.; Vieira, A.D.S.; Franco, D.G.M. Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Functional Approach, 1st ed.; Albuquerque, M.A.C., LeBlanc, A.M., LeBlanc, J.G., Bedani, R., Eds.; CRC Press (Taylor and Francis Group): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; p. 292. [Google Scholar]
- Sahli, C.; Moya, S.E.; Lomas, J.S.; Gravier-Pelletier, C.; Briandet, R.; Hémadi, M. Recent advances in nanotechnology for eradicating bacterial biofilm. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2383–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, G.; Ivanova, K.; Ivanov, I.; Tzanov, T. Nanomaterials and Coatings for Managing Antibiotic-Resistant Biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Manzano, L.A.; Vázquez-Villegas, P.; Prado-Cervantes, L.V.; Franco-Gómez, K.X.; Carbajal-Ocaña, S.; Sotelo-Cortés, D.L.; Atehortúa-Benítez, V.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Membrillo-Hernández, J. Advances in Material Modification with Smart Functional Polymers for Combating Biofilms in Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavenne, E.; Mounier, J.; Déniel, F.; Barbier, G.; Le Blay, G. Biodiversity of antifungal lactic acid bacteria isolated from raw milk samples from cow, ewe and goat over one-year period. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 155, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davati, N.; Yazdi, F.T.; Zibaee, S.; Shahidi, F.; Edalatian, M.R. Study of lactic acid bacteria community from raw milk of Iranian one humped camel and evaluation of their probiotic properties. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e16750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eszenyi, P.; Sztrik, A.; Babka, B.; Prokisch, J. Elemental, nano-sized (100–500 nm) selenium production by probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Biosci. Biochem. Bioinform. 2011, 1, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, M.; Rudayni, H.A.; Assiri, R.A.; Bepari, A.; Basavarajappa, D.S.; Nagaraja, S.K.; Chakraborty, B.; Swamy, P.S.; Agadi, S.N.; Niazi, S.K. Plumeria alba-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Exhibits Antimicrobial Effect and Anti-Oncogenic Activity against Glioblastoma U118 MG Cancer Cell Line. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, M.M.; Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Allam, A.A.; Shaheen, T.I. Antibacterial, cytotoxicity and larvicidal activity of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles using Penicillium corylophilum. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, N.; Ušjak, D.; Milenković, M.T.; Zheng, K.; Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Stevanović, M.M. Comparative study of the antimicrobial activity of selenium nanoparticles with different surface chemistry and structure. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 624621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Mishra, P. Thymoquinone inhibits biofilm formation and has selective antibacterial activity due to ROS generation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soflaei, S.; Dalimi, A.; Abdoli, A.; Kamali, M.; Nasiri, V.; Shakibaie, M.; Tat, M. Anti-leishmanial activities of selenium nanoparticles and selenium dioxide on Leishmania infantum. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 23, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaytah, A.; Farajallah, A.; Abualhaijaa, A.; Al-Balas, Q. A3, a scorpion venom derived peptide analogue with potent antimicrobial and potential antibiofilm activity against clinical isolates of multi-drug resistant gram positive bacteria. Molecules 2018, 23, E1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinicovscaia, I. Use of Bacteria and Microalgae in Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Chem. J. Mold. 2021, 7, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Kaudal, T.; Sharma, A. Probiotic mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles: Characterization and biofilm scavenging analysis. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2018, 4, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.; Khatoon, N.; Khan, M.A.; Husain, S.A.; Saravanan, M.; Sardar, M. Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus and their enhanced antimicrobial activity against resistant bacteria. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Taha, T.F.; Najjar, A.A.; Zabermawi, N.M.; Nader, M.M.; AbuQamar, S.F.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Salama, A. Selenium nanoparticles from Lactobacillus paracasei HM1 capable of antagonizing animal pathogenic fungi as a new source from human breast milk. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6782–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Guo, Y.; Qiao, L.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Y.; Roman, A. Biogenic synthesis of novel functionalized selenium nanoparticles by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 and its protective effects on intestinal barrier dysfunction caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-deeb, B.A.; Asem, E.; Mohammed, K. Biosynthesis and Optimization of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Streptomyces sp. Sohag J. Sci. 2023, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, S.; Kumaran, S.; Suresh, G.; Ramesh, M.; Thangamani, V.; Pugazhvendan, S.; Sathiyamurthy, K. Extracellular synthesis of nanoselenium from fresh water bacteria Bacillus sp.; its validation of antibacterial and cytotoxic potential. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, C.; Wang, P.; Fan, S.; Yu, B.; Qu, Y. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Providencia sp. DCX. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes: Comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, A.; Blinov, A.; Kravtsov, A.; Nagdalian, A.; Rekhman, Z.; Gvozdenko, A.; Kolodkin, M.; Filippov, D.; Askerova, A.; Golik, A.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and potential antimicrobial activity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized with cetyltrimethylammonium chloride. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, A.A.; Hawwa, M.T.; Baraka, D.M.; El-Shora, H.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Al-Hazmi, N.E.; Hassan, M.G. Understanding antimicrobial activity of biogenic selenium nanoparticles and selenium/chitosan nano-incorporates via studying their inhibition activity against key metabolic enzymes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 72, 126981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Mirani, Z.A.; Binbin, S.; Wang, F.; Chan, M.W.H.; Aslam, S.; Yonghong, L.; Hasan, N.; Naveed, M.; Hussain, S.; et al. An elucidative study of the anti-biofilm effect of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) on selected biofilm producing pathogenic bacteria: A disintegrating effect of SeNPs on bacteria. Process Biochem. 2023, 126, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonini, E.; Zonaro, E.; Donini, M.; Lampis, S.; Boaretti, M.; Dusi, S.; Melotti, P.; Lleo, M.M.; Vallini, G. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: Characterization, antimicrobial activity and effects on human dendritic cells and fibroblasts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Badawy, M.S.E.M.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Arishi, A.A.; Elkady, F.M.; Hashem, A.H. Green Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Orange Peel Waste: Characterization, Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Life 2022, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Chen, T.; Yu, B.; Wong, K.-H. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells by surface-capping selenium nanoparticles: An effect enhanced by polysaccharide-protein complexes from Polyporus rhinocerus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9859–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Mu, J.; Wang, F.; Chan, M.W.H.; Yin, X.; Liao, Y.; Mirani, Z.A.; Sebt-e-Hassan, S.; Aslam, S.; Naveed, M. Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles and Their Anticancer Effects Pertaining to Probiotic Bacteria—A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.G.; Hawwa, M.T.; Baraka, D.M. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles and selenium/chitosan-Nanoconjugate biosynthesized by Streptomyces parvulus MAR4 with antimicrobial and anticancer potential. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.; Florindo, H.F.; Santos, H.A. Selenium Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: From Development and Characterization to Therapeutics. Adv. Health Mater. 2021, 10, 2100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, R.; Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M. Structural parameters of nanoparticles affecting their toxicity for biomedical applications: A review. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2023, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
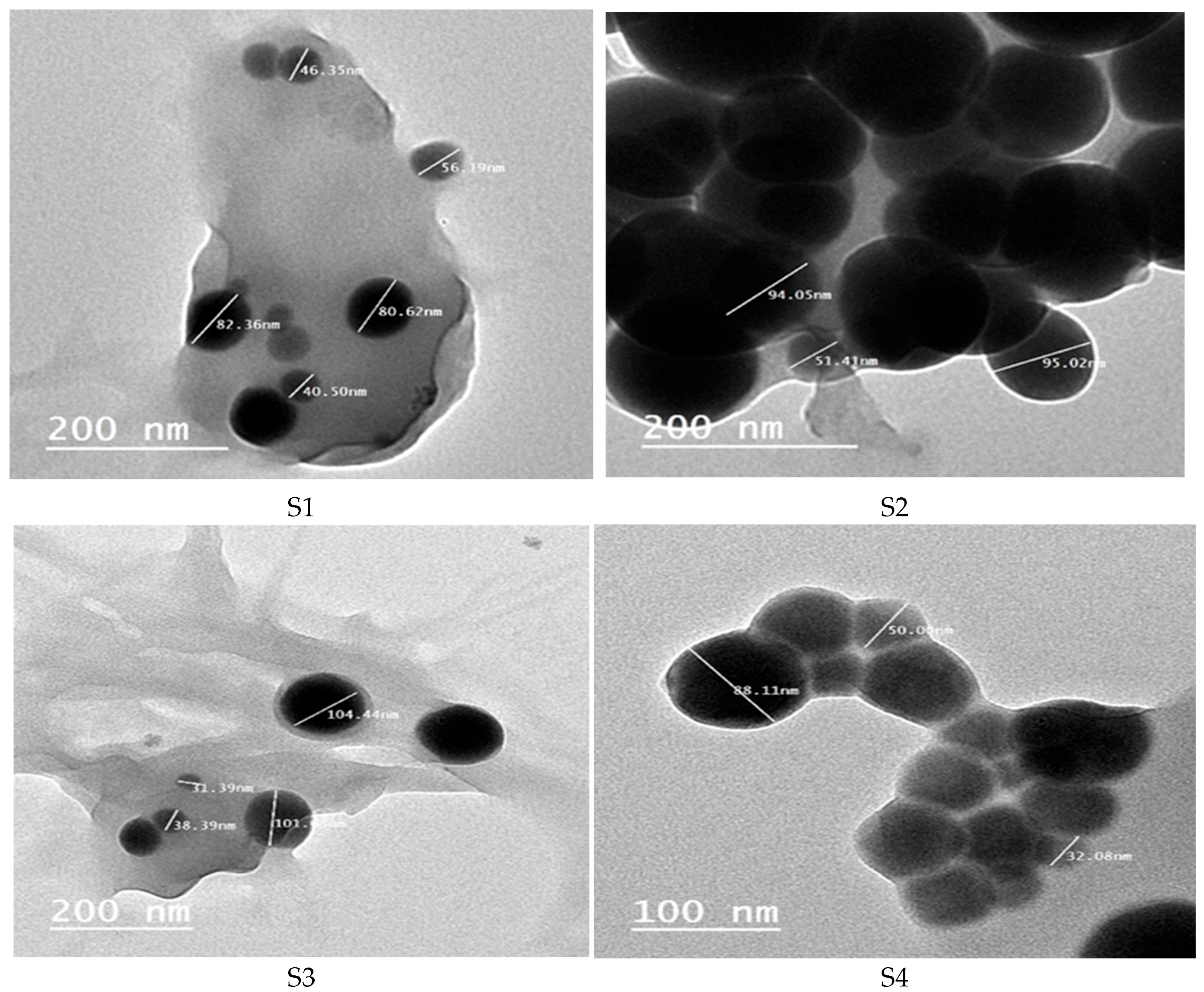
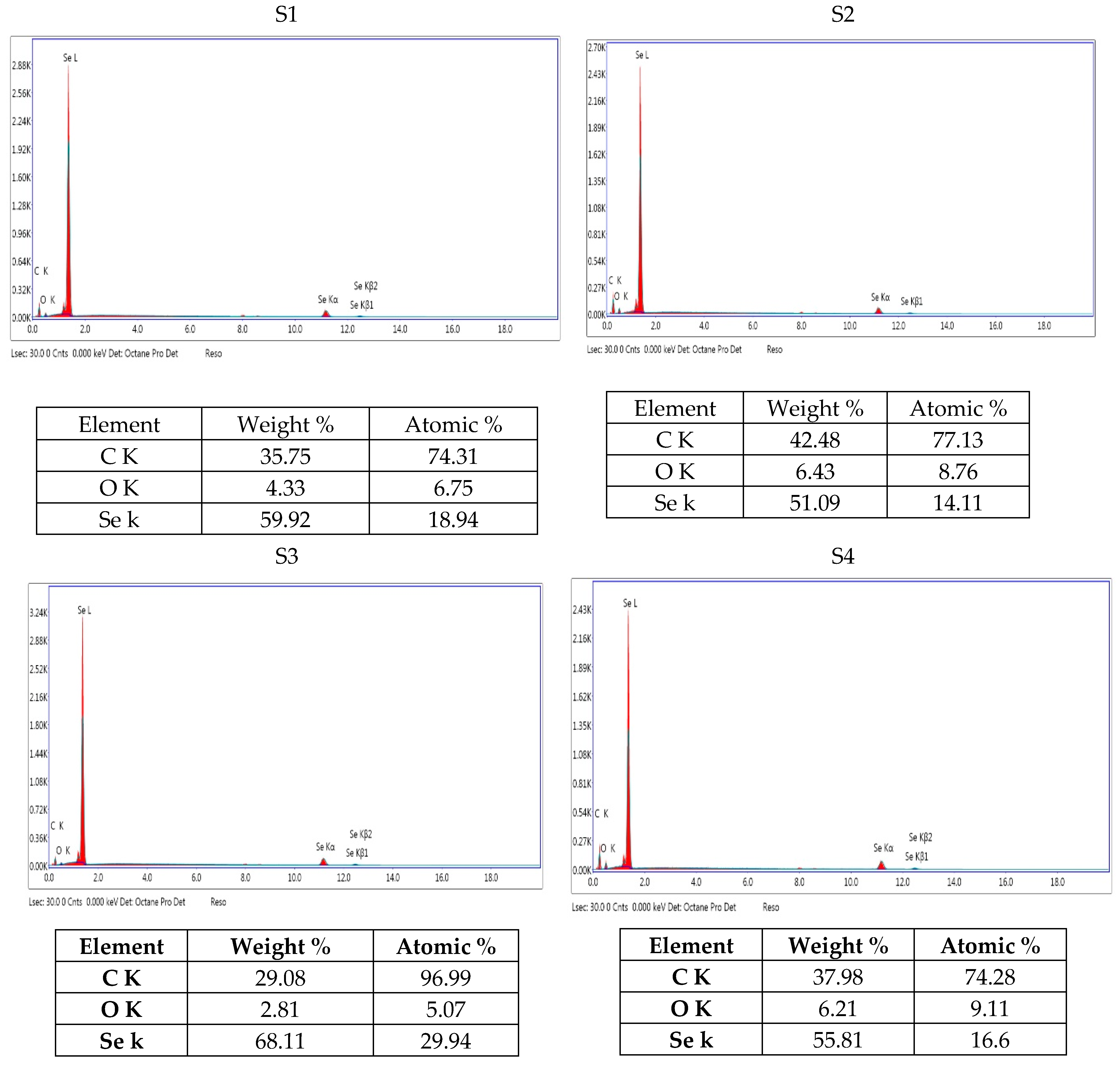






| Isolate Code | Identification | Similarity % |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | Lactiplantibacillus pentosus | 96.87 |
| S2 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | 97.51 |
| S3 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | 98.41 |
| S4 | Lactobacillus acidophilus | 95.36 |
| Gram Negative Isolates | Gram Positive Isolates | Fungi |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | MRSA | Candida albicans |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Enterococcus faecalis | |
| Acinetobcter baumannii | Streptococcus agalactiae | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||
| Proteus mirabilis |
| Sample | Electrophoretic Mobility μm * cm/Vs | Av. Zeta Potential, mV | Transmittance % | Conductivity mS/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2 | −2.1542 | −34.8 | 0.2 | 0.123 |
| S3 | −2.7123 | −27.6 | 0.0 | 0.057 |
| Human Pathogen | S1 MIC (mg/mL) | S2 MIC (mg/mL) | S3 MIC (mg/mL) | S4 MIC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram negative bacteria | ||||
| Escherichia coli | 8.12 ± 1.7 | 1.07 ± 3.5 | 1.125 ± 1.8 | 0.625 ± 1.03 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 16.25 ± 1.7 | 3.15 ± 3.5 | 18 ± 1.8 | 1.25 ± 1.03 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 8.12 ± 1.7 | 1.07 ± 3.5 | 9 ± 1.8 | 5 ± 1.03 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 8.12 ± 1.7 | 0.62 ± 3.5 | 4.5 ± 1.8 | 1.25 ± 1.03 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 1.015 ± 1.7 | 0.62 ± 3.5 | 0.562 ± 1.8 | 0.625 ± 1.03 |
| Gram positive bacteria | ||||
| MRSA | 4.06 ± 1.7 | 25 ± 3.5 | 9 ± 1.8 | 1.25 ± 1.03 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 4.06 ± 1.7 | 1.07 ± 3.5 | 2.25 ± 1.8 | 0.625 ± 1.03 |
| Eenterococcus faecalis | 8.12 ± 1.7 | 25 ± 3.5 | 9 ± 1.8 | 2.5 ± 1.03 |
| Fungus | ||||
| Candida albicans | 16.25 ± 1.7 | 1.07 ± 3.5 | 2.25 ± 1.8 | 10 ± 1.03 |
| Test Item | FIC Index | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| S2 Se-NPs + Lev. against P | 0.75 | Synergism |
| S2 Se-NPs + Lev. against E | 2.125 | Antagonism |
| S3 Se-NPs + Lev. against P | 1.25 | Addition |
| S3 Se-NPs + Lev. against E | 2.25 | Antagonism |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadel, N.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Gebreel, H.; Zendo, T.; Youssef, H. Lactic Acid Bacteria-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles: A Smart Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040121
Fadel N, Abu-Elghait M, Gebreel H, Zendo T, Youssef H. Lactic Acid Bacteria-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles: A Smart Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Applied Microbiology. 2025; 5(4):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040121
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadel, Nahla, Mohammed Abu-Elghait, Hassan Gebreel, Takeshi Zendo, and HebatAllah Youssef. 2025. "Lactic Acid Bacteria-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles: A Smart Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens" Applied Microbiology 5, no. 4: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040121
APA StyleFadel, N., Abu-Elghait, M., Gebreel, H., Zendo, T., & Youssef, H. (2025). Lactic Acid Bacteria-Mediated Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles: A Smart Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Applied Microbiology, 5(4), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040121






