Surface Display of Human GM-CSF in Methylotrophic Yeasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular-Biology Techniques
2.2. Plasmids and Strains
2.3. Cultivation Condition of Engineered K. phaffii and O. parapolymorpha
2.4. Biochemical Methods
2.5. Purification
2.6. Immunofluorescent Assay
2.7. Bioactivity of GM-CSF
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
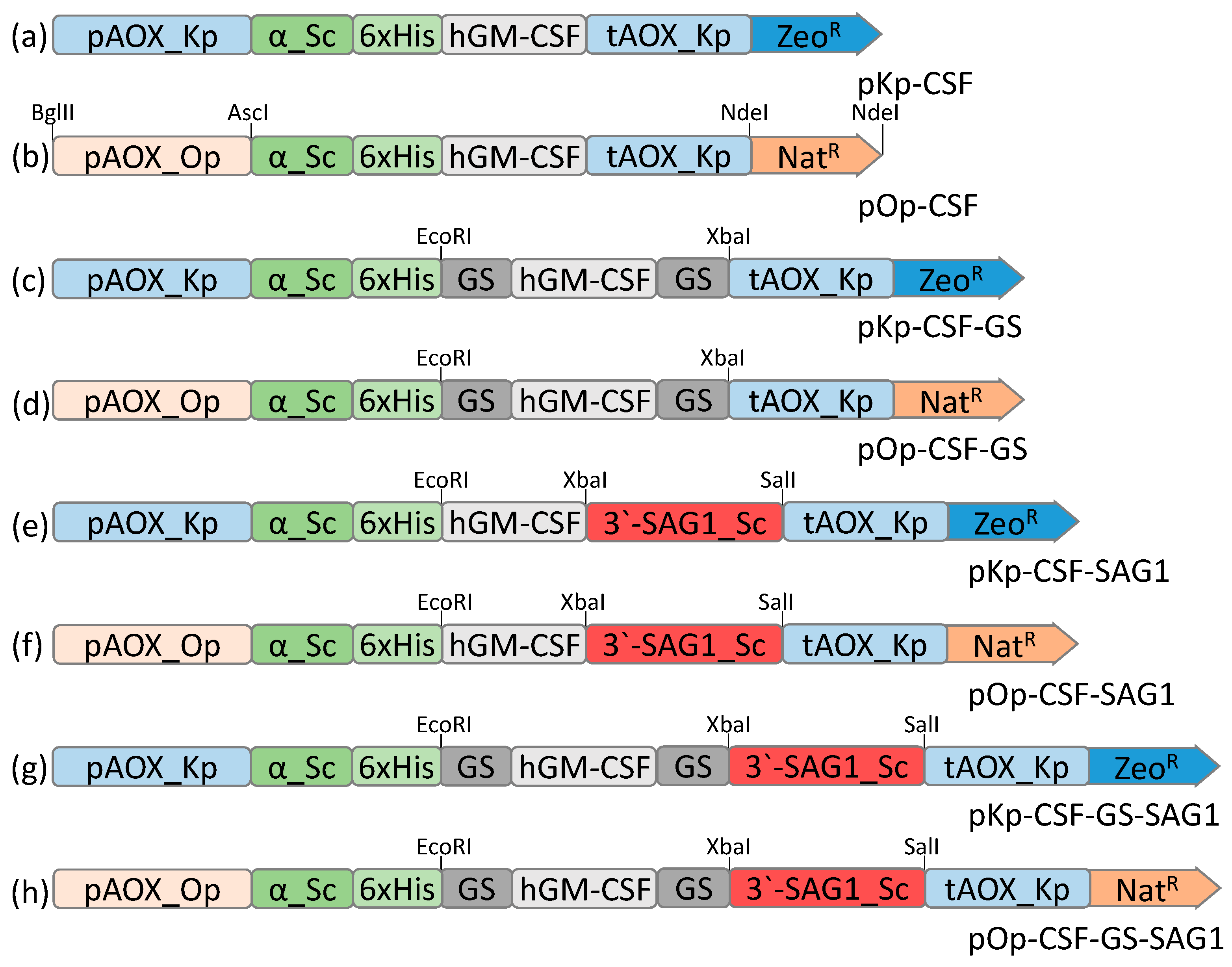
3.1. Design of GM-CSF Expression Vectors and Generation of Recombinant Yeast Strains
3.2. GM-CSF Secretion by Engineered Yeast Strains
3.3. Purification and Analysis of Secreted GM-CSF
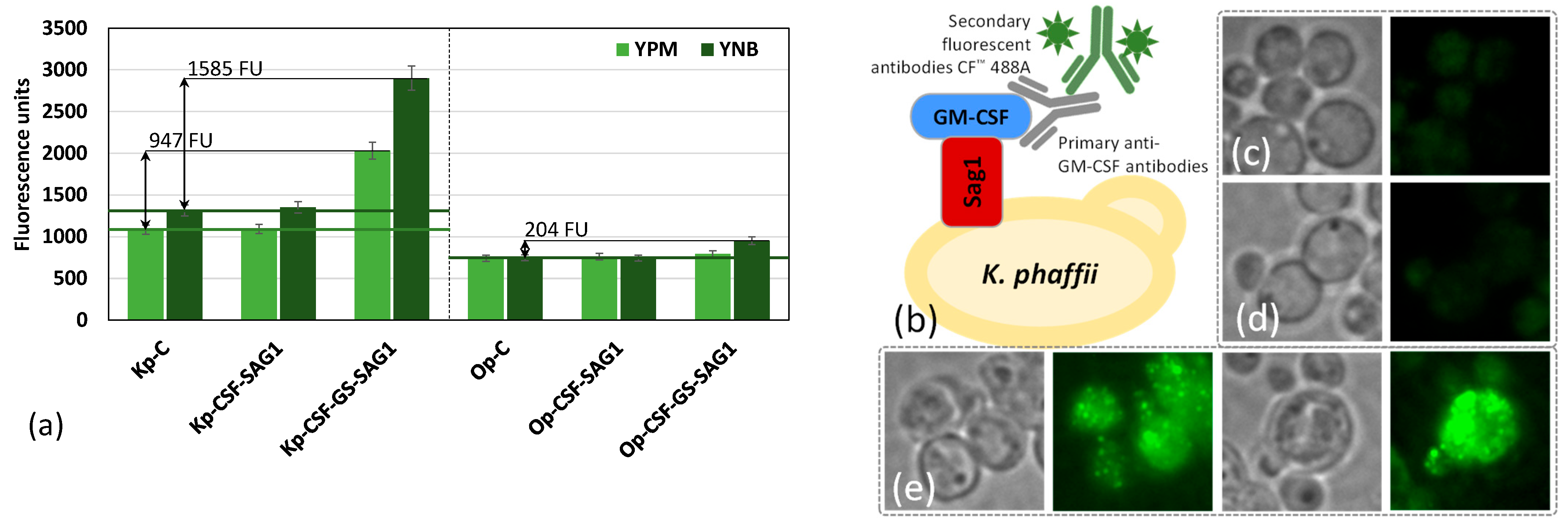
3.4. Surface Display of GM-CSF
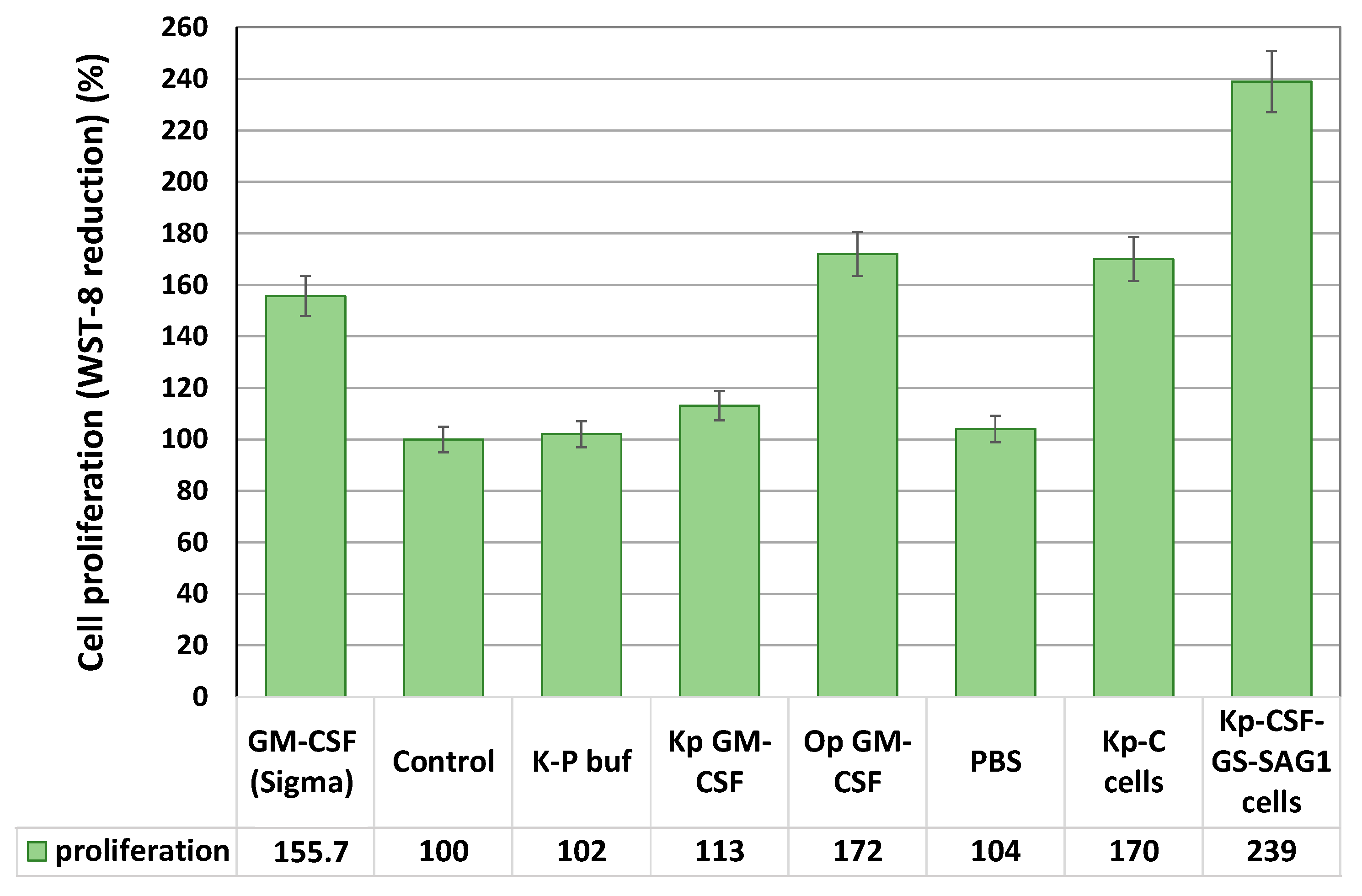
3.5. Biological Activity of Secreted and Surface-Displayed GM-CSF
3.6. Implications and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behm, B.; Babilas, P.; Landthaler, M.; Schreml, S. Cytokines, chemokines and growth factors in wound healing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnici, L.; Suleiman, S.; Schembri-Wismayer, P.; Cassar, A. Targeting signalling pathways in chronic wound healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidova-Rice, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Herman, I.M. Acute and impaired wound healing: Pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 2: Role of growth factors in normal and pathological wound healing: Therapeutic potential and methods of delivery. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2012, 25, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerty, C.C.; Jeschke, M.G.; Herndon, D.N.; Gamelli, R.; Gibran, N.; Klein, M.; Silver, G.; Arnoldo, B.; Remick, D.; Tompkins, R.G.; et al. Temporal cytokine profiles in severely burned patients: A comparison of adults and children. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Sappino, A.P.; Gabbiani, G. Locally applied GM-CSF induces the accumulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin containing myofibroblasts. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. Incl. Mol. Pathol. 1991, 60, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.H.; Allen, M.H.; Groves, R.W.; Barker, J.N. Effect of granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor on Langerhans cells in normal and healthy atopic subjects. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 139, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.; Breuhahn, K.; Schirmacher, P.; Blessing, M. Keratinocyte-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor accelerates wound healing: Stimulation of keratinocyte proliferation, granulation tissue formation, and vascularization. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Walsh, G.; Guido, L.S.; Meyn, P.; Burkhardt, R.A.; Abalos, R.M.; Barker, J.; Frindt, P.A.; Fajardo, T.T.; Celona, R. Novel responses of human skin to intradermal recombinant granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor: Langerhans cell recruitment, keratinocyte growth, and enhanced wound healing. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carral, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Martín, G.; Martínez, J.; Sanz, G.; Jarque, I.; Sempere, A.; Soler, M.A.; Marty, M.L.; Sanz, M.A. Factors influencing hematopoietic recovery after autologous blood stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia and with non-myeloid malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002, 29, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Gong, S.J.; Xu, Y.H.; Hambly, B.D.; Bao, S. Impaired cutaneous wound healing in granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor knockout mice. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, K.; Ishii, G.; Ochiai, A.; Esumi, H. Improvement of the breaking strength of wound by combined treatment with recombinant human G-CSF, recombinant human M-CSF, and a TGF-beta1 receptor kinase inhibitor in rat skin. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Shen, J.; Yao, M.; Beagley, K.W.; Hambly, B.D.; Bao, S. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances wound healing in diabetes via upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forno, G.; Bollati Fogolin, M.; Oggero, M.; Kratje, R.; Etcheverrigaray, M.; Conradt, H.S.; Nimtz, M. N- and O-linked carbohydrates and glycosylation site occupancy in recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor secreted by a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Babu, K.; Muthukumaran, T.; Antony, A.; Prem Singh Samuel, S.D.; Balamurali, M.; Murugan, V.; Meenakshisundaram, S. Single step intein-mediated purification of hGMCSF expressed in salt-inducible E. coli. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, E.A.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Reeves, R.; Shin, J.H.; Magnuson, N.S.; Lee, J.M. Production and characterization of biologically active human GM-CSF secreted by genetically modified plant cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 2000, 19, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.J.; Wu, M.C. Expression of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. FEBS Lett. 1990, 259, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, R.T. Clinical properties of yeast-derived versus Escherichia coli-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin. Ther. 1993, 15, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bergès, H.; Joseph-Liauzun, E.; Fayet, O. Combined effects of the signal sequence and the major chaperone proteins on the export of human cytokines in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasa, Y.P.; Khushoo, A.; Tapryal, S.; Mukherjee, K.J. Optimization of human granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expression using asparaginase and xylanase gene’s signal sequences in Escherichia coli. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahdev, S.; Khattar, S.K.; Saini, K.S. Production of active eukaryotic proteins through bacterial expression systems: A review of the existing biotechnology strategies. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 307, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLamarter, J.F.; Mermod, J.J.; Liang, C.M.; Eliason, J.F.; Thatcher, D.R. Recombinant murine GM-CSF from E. coli has biological activity and is neutralized by a specific antiserum. EMBO J. 1985, 4, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, N.; Lassoued, R.; Ayed, A.; Tréton, B.; Chevret, D.; Nicaud, J.M.; Kallel, H. Production and characterization of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expressed in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, C.T.; Huynh-Thi, X.M.; Nguyen, C.T.; Trinh, M.T.; Tran, L.T.; Cartwright, S.P.; Bill, R.M.; Tran-Van, H. Pichia pastoris versus Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A case study on the recombinant production of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pykhtina, M.; Miroshnichenko, S.; Romanov, V.; Grazhdantseva, A.; Kochneva, G.; Beklemishev, A. Construction of recombinant human GM-CSF and GM-CSF-ApoA-I fusion protein and evaluation of their biological activity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, Y.; Khushoo, A.; Mukherjee, K.J. Process optimization of constitutive human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expression in Pichia pastoris fed-batch culture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 69, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.; Fischer, J.E.; Hyden, P.; Wasmayer, R.; Sturmberger, L.; Glieder, A. Orthologous promoters from related methylotrophic yeasts surpass expression of endogenous promoters of Pichia pastoris. AMB Express 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Cai, M. Advancing recombinant protein expression in Komagataella phaffii: Opportunities and challenges. FEMS Yeast Res. 2025, 25, foaf010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besleaga, M.; Ebner, K.; Glieder, A.; Spadiut, O.; Kopp, J. Chances and drawbacks of derepressed recombinant enzyme production in continuous cultivations with Komagataella phaffii. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1523037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.R.; Gerngross, T.U. Glycosylation engineering in yeast: The advent of fully humanized yeast. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonekamp, F.J.; Knibbe, E.; Vieira-Lara, M.A.; Wijsman, M.; Luttik, M.A.H.; van Eunen, K.; Ridder, M.D.; Bron, R.; Almonacid Suarez, A.M.; van Rijn, P.; et al. Full humanization of the glycolytic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 111010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, S.A.; Kim, H.; Oh, D.B.; Kwon, O.; Kang, H.A. Remodeling of the glycosylation pathway in the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha to produce human hybrid-type N-glycans. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Taxis, C.; Knop, M. System of centromeric, episomal, and integrative vectors based on drug resistance markers for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechniques 2006, 40, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, K.N.; Haima, P.; Harder, W.; Veenhuis, M.; Ab, G. Highly-efficient electrotransformation of the yeast Hansenula polymorpha. Curr. Genet. 1994, 25, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baerends, R.J.; Faber, K.N.; Kram, A.M.; Kiel, J.A.; van der Klei, I.J.; Veenhuis, M. A stretch of positively charged amino acids at the N terminus of Hansenula polymorpha Pex3p is involved in incorporation of the protein into the peroxisomal membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9986–9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyhse-Andersen, J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: A simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1984, 10, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delic, M.; Valli, M.; Graf, A.B.; Pfeffer, M.; Mattanovich, D.; Gasser, B. The secretory pathway: Exploring yeast diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 872–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.R.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, K.H.; Park, B.R.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, S.O. Parabiotic immunomodulatory activity of yeast cell wall polysaccharides from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and S. boulardii. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 123, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.S.; Oh, H.J.; Jang, Y.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, A.; Song, J.A.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, J. Synthetic pro-peptide design to enhance the secretion of heterologous proteins by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiologyopen 2022, 11, e1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Khalilzadeh, R.; Mohammadian, J.; Farahani, E.V.; Masoumian, M.R. Prevention of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor protein aggregation in recombinant Pichia pastoris fed-batch fermentation using additives. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2009, 52, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.L.; Xue, C.; Xiong, X.H.; Yao, X.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, H.P.; Liu, Z.M. Enhanced secretion of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris following overexpression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chaperone proteins. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dmytruk, O.; Finiuk, N.; Stoika, R.; Sibirny, A.; Dmytruk, K. Surface Display of Human GM-CSF in Methylotrophic Yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030098
Dmytruk O, Finiuk N, Stoika R, Sibirny A, Dmytruk K. Surface Display of Human GM-CSF in Methylotrophic Yeasts. Applied Microbiology. 2025; 5(3):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030098
Chicago/Turabian StyleDmytruk, Olena, Nataliya Finiuk, Rostyslav Stoika, Andriy Sibirny, and Kostyantyn Dmytruk. 2025. "Surface Display of Human GM-CSF in Methylotrophic Yeasts" Applied Microbiology 5, no. 3: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030098
APA StyleDmytruk, O., Finiuk, N., Stoika, R., Sibirny, A., & Dmytruk, K. (2025). Surface Display of Human GM-CSF in Methylotrophic Yeasts. Applied Microbiology, 5(3), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030098








