Black Soldier Fly Gut Microbiota Resists Invasion by Bacillus subtilis 168 and Pseudomonas putida KT2440
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of 6-Day-Old Larvae
2.2. Substrate Preparation
2.3. Bioassay
2.4. Intrinsic Parameters
2.5. Gut Removal and DNA Extraction
2.6. q-PCR
2.7. High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) on Bacterial Community
2.8. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth, Development Time, and Survival of Larvae
3.2. Bacillus spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Abundance
3.3. Gut Bacterial Microbiome Diversity and Community Structure
3.4. Dominant Bacterial Genera Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSF | Black Soldier Fly |
| CF | Larvae Fed Chicken Feed |
| CFB | Larvae Fed Chicken Feed + Bacillus subtilis |
| CFP | Larvae Fed Chicken Feed + Pseudomonas putida |
References
- Mertenat, A.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C. Black Soldier Fly Biowaste Treatment—Assessment of Global Warming Potential. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, H. Material Flow Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment of Food Waste Bioconversion by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, H.M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Lambert, B.D.; Kattes, D. Development of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae Fed Dairy Manure. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, R.; Saija, G.; Mondello, G.; Giannetto, A.; Fasulo, S.; Savastano, D. Environmental Impact of Food Waste Bioconversion by Insects: Application of Life Cycle Assessment to Process Using Hermetia illucens. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Magri, M.E.; Zurbrügg, C.; Lindström, A.; Vinnerås, B. Faecal Sludge Management with the Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens)—From a Hygiene Aspect. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Vinnerås, B. Effects of Feedstock on Larval Development and Process Efficiency in Waste Treatment with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klammsteiner, T.; Walter, A.; Bogataj, T.; Heussler, C.D.; Stres, B.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Arthofer, W.; Insam, H. The Core Gut Microbiome of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Raised on Low-Bioburden Diets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoc, B.; Genva, M.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Lognay, G.; Francis, F.; Caparros Megido, R. About Lipid Metabolism in Hermetia illucens (L. 1758): On the Origin of Fatty Acids in Prepupae. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoc, B.; Tomson, T.; Malumba, P.; Blecker, C.; Jijakli, M.H.; Purcaro, G.; Francis, F.; Caparros Megido, R. Production of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Using Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Prepupae-Based Formulations with Differentiated Fatty Acid Profiles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-W.; Mohd-Noor, S.-N.; Wong, C.-Y.; Lam, M.-K.; Goh, P.-S.; Beniers, J.J.A.; Oh, W.-D.; Jumbri, K.; Ghani, N.A. Palatability of Black Soldier Fly Larvae in Valorizing Mixed Waste Coconut Endosperm and Soybean Curd Residue into Larval Lipid and Protein Sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, J.; Abenaim, L.; Luttenschlager, H.; Dessauvages, K.; Liu, Y.; Samoah, P.; Francis, F.; Caparros Megido, R. Microorganism Contribution to Mass-Reared Edible Insects: Opportunities and Challenges. Insects 2024, 15, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.E.; Ricigliano, V.A.; Mott, B.M.; Copeland, D.C.; Floyd, A.S.; Maes, P. The Queen’s Gut Refines with Age: Longevity Phenotypes in a Social Insect Model. Microbiome 2018, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The Gut Microbiota of Insects—Diversity in Structure and Function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Kikuchi, Y. Impact of the Insect Gut Microbiota on Ecology, Evolution, and Industry. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 41, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varotto Boccazzi, I.; Ottoboni, M.; Martin, E.; Comandatore, F.; Vallone, L.; Spranghers, T.; Eeckhout, M.; Mereghetti, V.; Pinotti, L.; Epis, S. A Survey of the Mycobiota Associated with Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared for Feed Production. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; De Filippis, F.; Di Lelio, I.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M.; Ercolini, D.; Caccia, S. The Intestinal Microbiota of Hermetia Illucens Larvae Is Affected by Diet and Shows a Diverse Composition in the Different Midgut Regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01864-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Crauwels, S.; Verreth, C.; De Smet, J.; Sandrock, C.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Van Schelt, J.; Depraetere, S.; Lievens, B.; et al. Assessing the Microbiota of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Organic Waste Streams on Four Different Locations at Laboratory and Large Scale. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Yan, M.; Yang, S.; Ji, L.; Han, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, K.; Zou, L. Bacillus and Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculation to Transform Kitchen Waste Using Hermetia illucens. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Supeanu, A.; Jansson, A.; Boqvist, S.; Vagsholm, I.; SLU, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Department of Biomedical Sciences and Veterinary Public Health, Sweden. Novel Foods: A Risk Profile for the House Cricket (Acheta Domesticus). EFSA J. 2018, 16, e16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.C.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security. Food Agric. Organ. United Nations 2013, 171, xiv+187. [Google Scholar]
- Mufungwe, J.; Namukonde, N.; Mwaanga, P.; Johnson, T.; Siamujompa, M.; Mwango, N.C.; Ngoma, J.; Hang’ombe, B.M. Critical Safety Concerns in the Production of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae in Africa. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hil, E.F.H.; Meijer, N.P.; Rozen, K.V.; Elissen, H.; van Wikselaar, P.G.; Brust, H.; Loeke, N.A.J.M.T.; de Rijk, T.; Tienstra, M.; van de Schans, M.G.M.; et al. Safety of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Reared on Waste Streams of Animal and Vegetal Origin and Manure. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 10, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomila, M.; Peña, A.; Mulet, M.; Lalucat, J.; García-Valdés, E. Phylogenomics and Systematics in Pseudomonas. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, J.; Tian, H.; Ji, M. Bacillus Species as Versatile Weapons for Plant Pathogens: A Review. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2017, 31, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, E.; Calteau, A.; Danchin, A.; Harwood, C.; Helmann, J.D.; Médigue, C.; Palsson, B.O.; Sekowska, A.; Vallenet, D.; Zuniga, A.; et al. A Model Industrial Workhorse: Bacillus subtilis Strain 168 and Its Genome after a Quarter of a Century. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 1203–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.F.; Rokana, N.; Gulhane, R.D.; Sharma, C.; Panwar, H. Bacillus As Potential Probiotics: Status, Concerns, and Future Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lorenzo, V.; Pérez-Pantoja, D.; Nikel, P.I. Pseudomonas putida KT2440: The Long Journey of a Soil-Dweller to Become a Synthetic Biology Chassis. J. Bacteriol. 2024, 206, e00136-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, S.; Spampinato, G.; Macavei, L.I.; Lugli, L.; Candeliere, F.; Rossi, M.; Maistrello, L.; Amaretti, A. Effect of Rearing Temperature on Growth and Microbiota Composition of Hermetia illucens. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.C.; Islam, M.; Sheppard, C.; Liao, J.; Doyle, M.P. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica Serovar enteritidis in Chicken Manure by Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrens, E.; Van Looveren, N.; Van Moll, L.; Vandeweyer, D.; Lachi, D.; De Smet, J.; Van Campenhout, L. Staphylococcus aureus in Substrates for Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) and Its Dynamics during Rearing. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e02183-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyet, M.; Morrill, H.; Espinal, D.L.; Bernard, E.; Alyokhin, A. Early Growth Patterns of Bacillus cereus on Potato Substrate in the Presence of Low Densities of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kessel, K.; Castelijn, G.; van der Voort, M.; Meijer, N. Investigation of Bacillus cereus Growth and Sporulation during Hermetia illucens Larval Rearing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoc, B.; Noël, G.; Carpentier, J.; Francis, F.; Caparros Megido, R. Optimization of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Artificial Reproduction. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A Comprehensive Online Resource for Quality Checked and Aligned Ribosomal RNA Sequence Data Compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Dillon, M.R.; Bolyen, E.; Kaehler, B.D.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Q2-Sample-Classifier: Machine-Learning Tools for Microbiome Classification and Regression. J. Open Res. Softw. 2018, 30, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstahler, P.; Bjerrum, S.S.; Friis-Møller, A.; la Cour, M.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Westh, H.; Pamp, S.J. Genomics-Based Identification of Microorganisms in Human Ocular Body Fluid. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhan, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, L.; Feng, T.; Chen, M.; Wu, T.; Hu, E.; et al. MicrobiotaProcess: A Comprehensive R Package for Deep Mining Microbiome. Innovation 2023, 4, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Fang, H.; Zhang, D. Bacillus subtilis: A Universal Cell Factory for Industry, Agriculture, Biomaterials and Medicine. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Mazza, L.; Yu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, J.; van Huis, A.; Yu, Z.; Fasulo, S.; et al. Efficient Co-Conversion Process of Chicken Manure into Protein Feed and Organic Fertilizer by Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae and Functional Bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-H.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Xu, Z.-M.; Peng, D.-H.; Yu, G.-H.; Shao, M.-W. Using Kin Discrimination to Construct Synthetic Microbial Communities of Bacillus subtilis Strains Impacts the Growth of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 1943–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Ren, L. Enhancing Food Waste Reduction Efficiency and High-Value Biomass Production in Hermetia illucens Rearing through Bioaugmentation with Gut Bacterial Agent. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, H.; Müller, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Gutzeit, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Nutritional Immunology: Diversification and Diet-Dependent Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhan, S.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Huang, D.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Dual Oxidase Duox and Toll-like Receptor 3 TLR3 in the Toll Pathway Suppress Zoonotic Pathogens through Regulating the Intestinal Bacterial Community Homeostasis in Hermetia illucens L. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, T.J.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Jaffe, S.P.; Fierer, N. Caterpillars Lack a Resident Gut Microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9641–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Jeong, G.; Lee, S.-B.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.-J. The Intestinal Bacterial Community in the Food Waste-Reducing Larvae of Hermetia illucens. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-L.; Jin, W.-Z.; Tao, X.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.-Y.; Xu, X.-H.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.-J. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Strengthen the Metabolic Function of Food Waste Biodegradation by Gut Microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Significantly Change the Microbial Community in Chicken Manure. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Brady, J.A.; Sanford, M.R.; Yu, Z. Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae Reduce Escherichia Coli in Dairy Manure. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauvry, E.; Mathot, A.-G.; Couvert, O.; Leguérinel, I.; Coroller, L. Effects of Temperature, pH and Water Activity on the Growth and the Sporulation Abilities of Bacillus subtilis BSB1. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada-Uribe, L.F.; Romero-Tabarez, M.; Villegas-Escobar, V. Effect of Medium Components and Culture Conditions in Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0575 Spore Production. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belperio, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Nannoni, E.; Sardi, L.; Martelli, G.; Dabbou, S.; Meneguz, M. Assessing Substrate Utilization and Bioconversion Efficiency of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae: Effect of Diet Composition on Growth and Development Temperature. Animals 2024, 14, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecherskii, M.V.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Khairullin, D.R.; Chaporov, I.A.; Bastrakov, A.I.; Ushakova, N.A. Feeding Impact on the Gut Microbiome of Hermetia illucens Larvae. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2025, 61, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Relationship of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) Gut Microbiota and Bioconversion Efficiency with Properties of Substrates. Waste Manag. 2024, 180, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J. Ecological Role of Lactobacilli in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Implications for Fundamental and Biomedical Research. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4985–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somroo, A.A.; ur Rehman, K.; Zheng, L.; Cai, M.; Xiao, X.; Hu, S.; Mathys, A.; Gold, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of Lactobacillus Buchneri on Soybean Curd Residue Co-Conversion by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) for Food and Feedstock Production. Waste Manag. 2019, 86, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Nil, C.; He, G.; Zhou, L.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, P. Isolation and identification of bacteria producing enzymes from gut and skin of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Front. Microbiol. 2010, 47, 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Wattiau, P.; Renard, M.-E.; Ledent, P.; Debois, V.; Blackman, G.; Agathos, S. A PCR Test to Identify Bacillus subtilis and Closely Related Species and Its Application to the Monitoring of Wastewater Biotreatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Development of a Semiquantitative Degenerate Real-Time PCR-Based Assay for Estimation of Numbers of Butyryl-Coenzyme A (CoA) CoA Transferase Genes in Complex Bacterial Samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

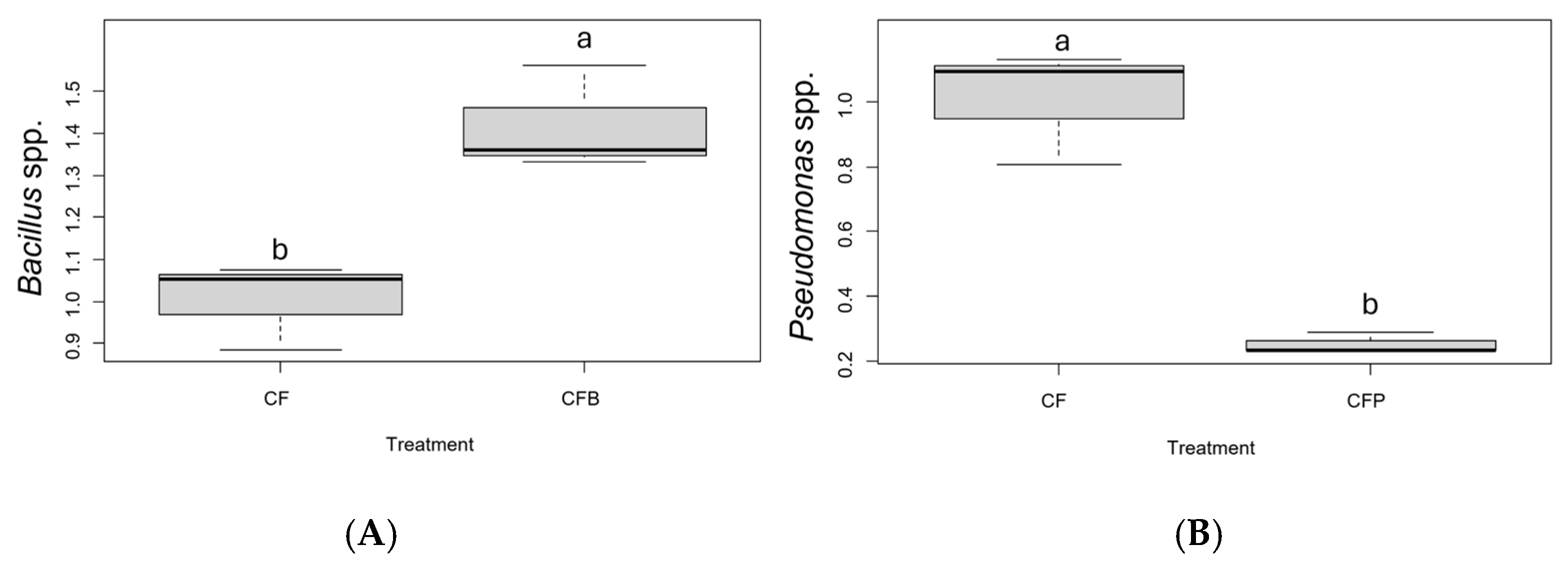

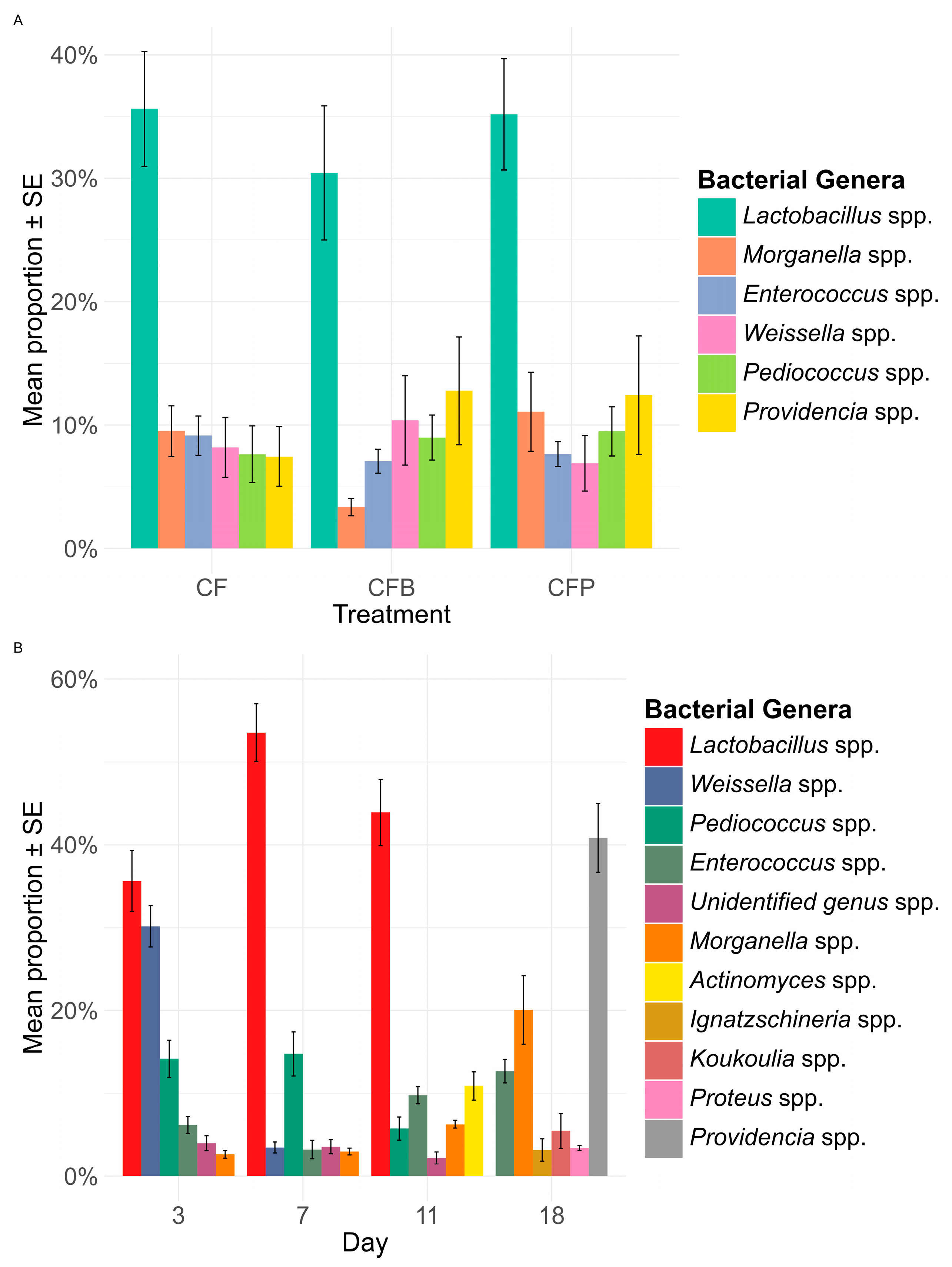
| Treatments | Development Time (days ± SD) | Survival Rate (% ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| CF | 17.8 ± 1.11 a | 93.00 ± 2.67 a |
| CFB | 18.3 ± 0.78 a | 91.33 ± 1.77 a |
| CFP | 17.8 ± 0.89 a | 91.67 ± 1.11 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpentier, J.; Noël, G.; Li, B.; Francis, F.; Caparros Megido, R. Black Soldier Fly Gut Microbiota Resists Invasion by Bacillus subtilis 168 and Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030082
Carpentier J, Noël G, Li B, Francis F, Caparros Megido R. Black Soldier Fly Gut Microbiota Resists Invasion by Bacillus subtilis 168 and Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Applied Microbiology. 2025; 5(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpentier, Joachim, Grégoire Noël, Bo Li, Frédéric Francis, and Rudy Caparros Megido. 2025. "Black Soldier Fly Gut Microbiota Resists Invasion by Bacillus subtilis 168 and Pseudomonas putida KT2440" Applied Microbiology 5, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030082
APA StyleCarpentier, J., Noël, G., Li, B., Francis, F., & Caparros Megido, R. (2025). Black Soldier Fly Gut Microbiota Resists Invasion by Bacillus subtilis 168 and Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Applied Microbiology, 5(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5030082








