Bacterial Pigment Prodigiosin as Multifaceted Compound for Medical and Industrial Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prodigiosin for Biomedical Application
2.1. Antibacterial Activity of Prodigiosin
2.2. Prodigiosin in Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy (APDT)
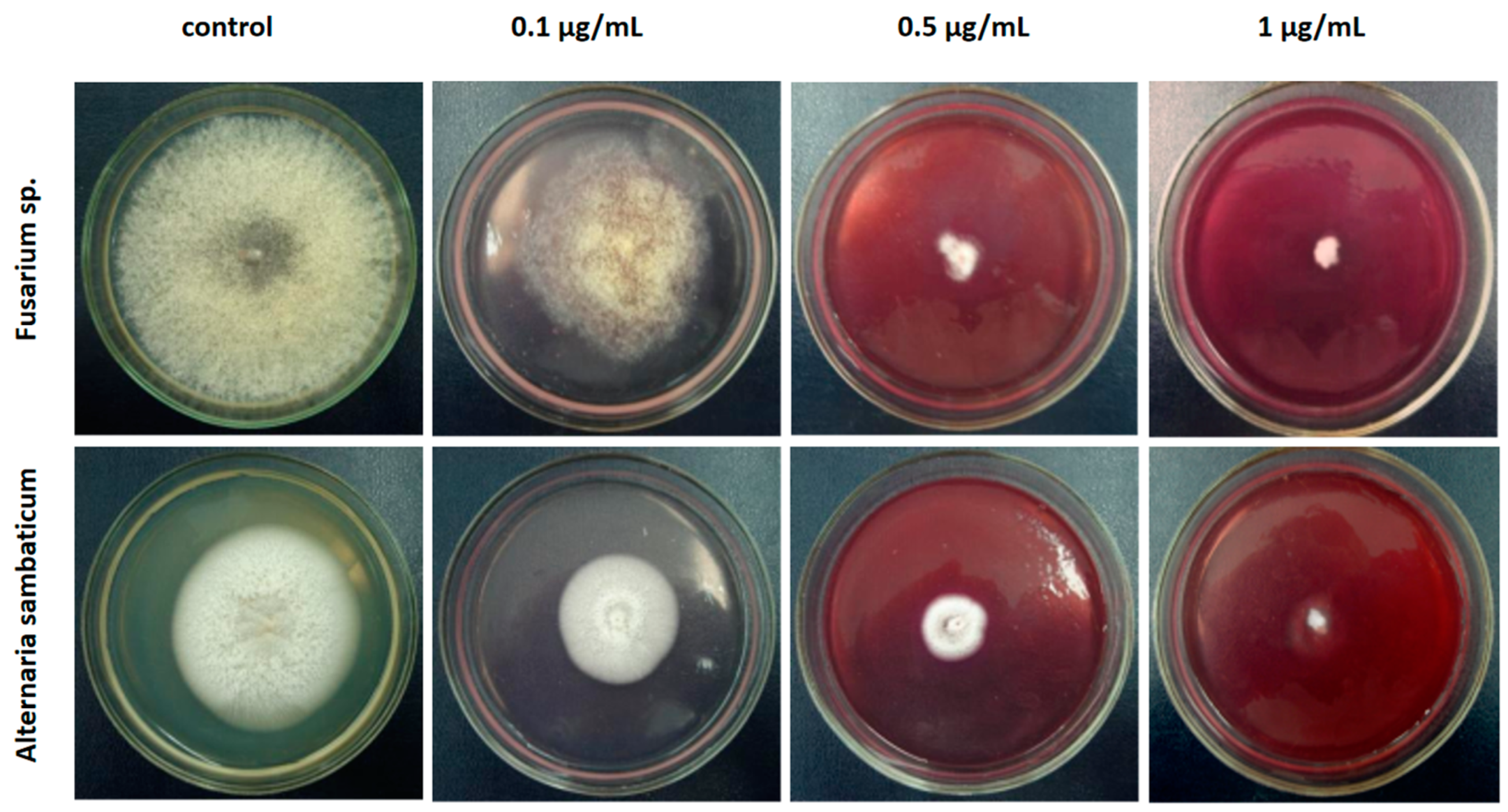
2.3. Antifungal Activity of Prodigiosin
2.4. Antiparasitic Activity of Prodigiosin
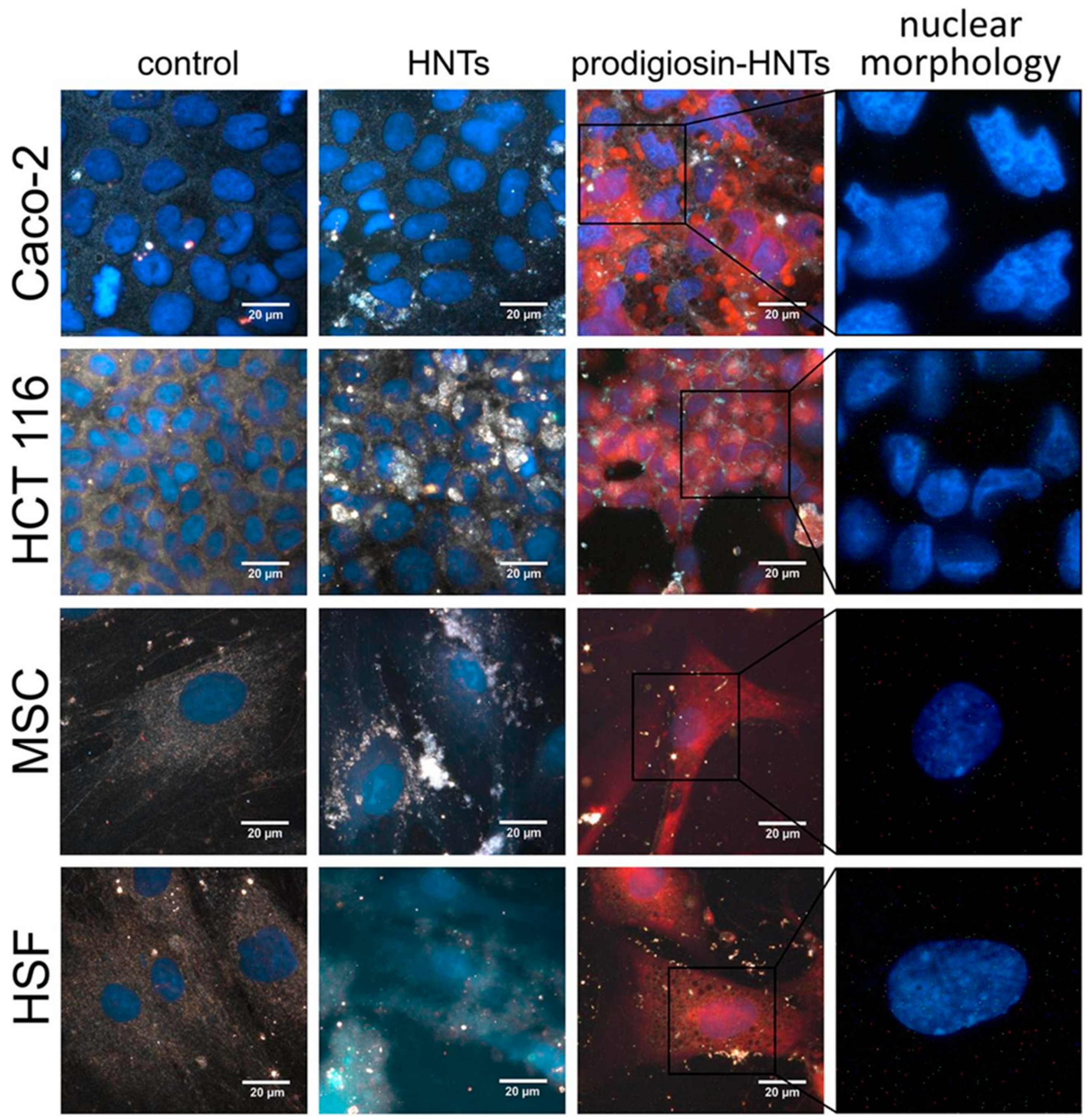
2.5. Prodigiosin as an Anticancer Drug: Mechanisms of Action and Prospects
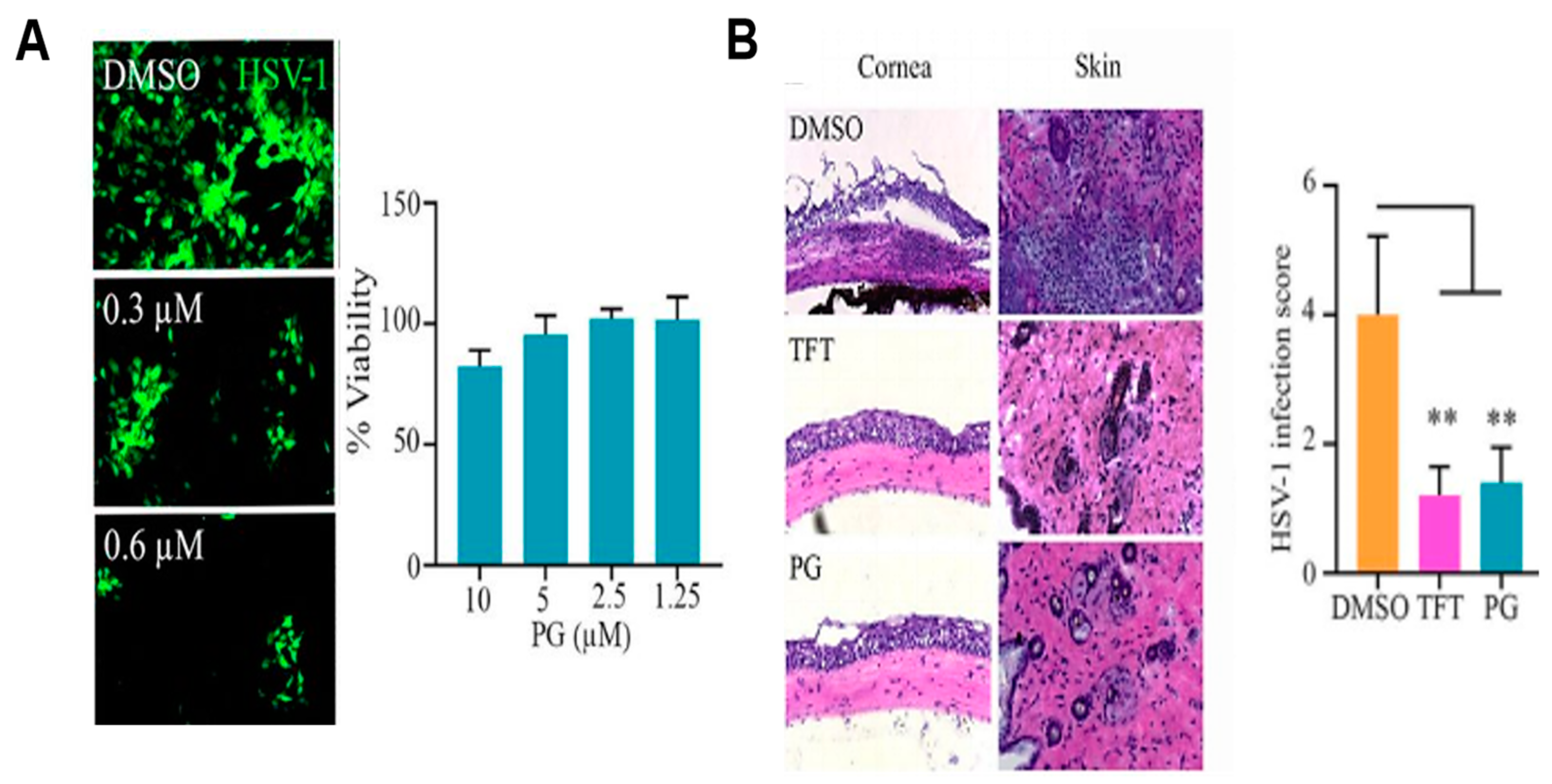
2.6. Antiviral Activity of PG
3. Prodigiosin for Industrial Biotechnology
3.1. Prodigiosin as Industrial Colorant and Antibacterial Agent for Plastic, Textile and Cellulose Materials
3.2. Prodigiosin in Cosmetics
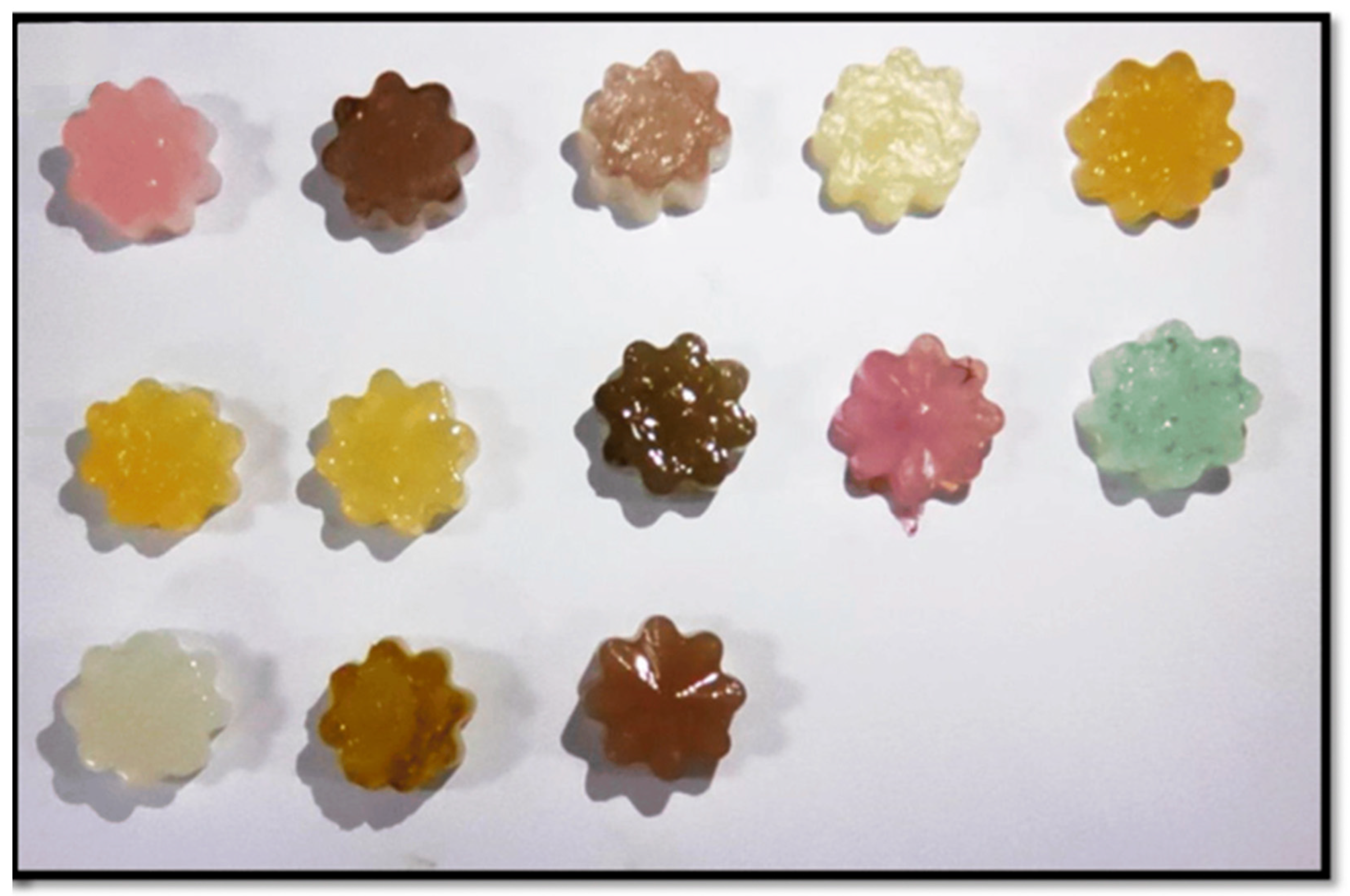
3.3. Prodigiosin in the Food Industry
3.3.1. Prodigiosin as Food Colorant
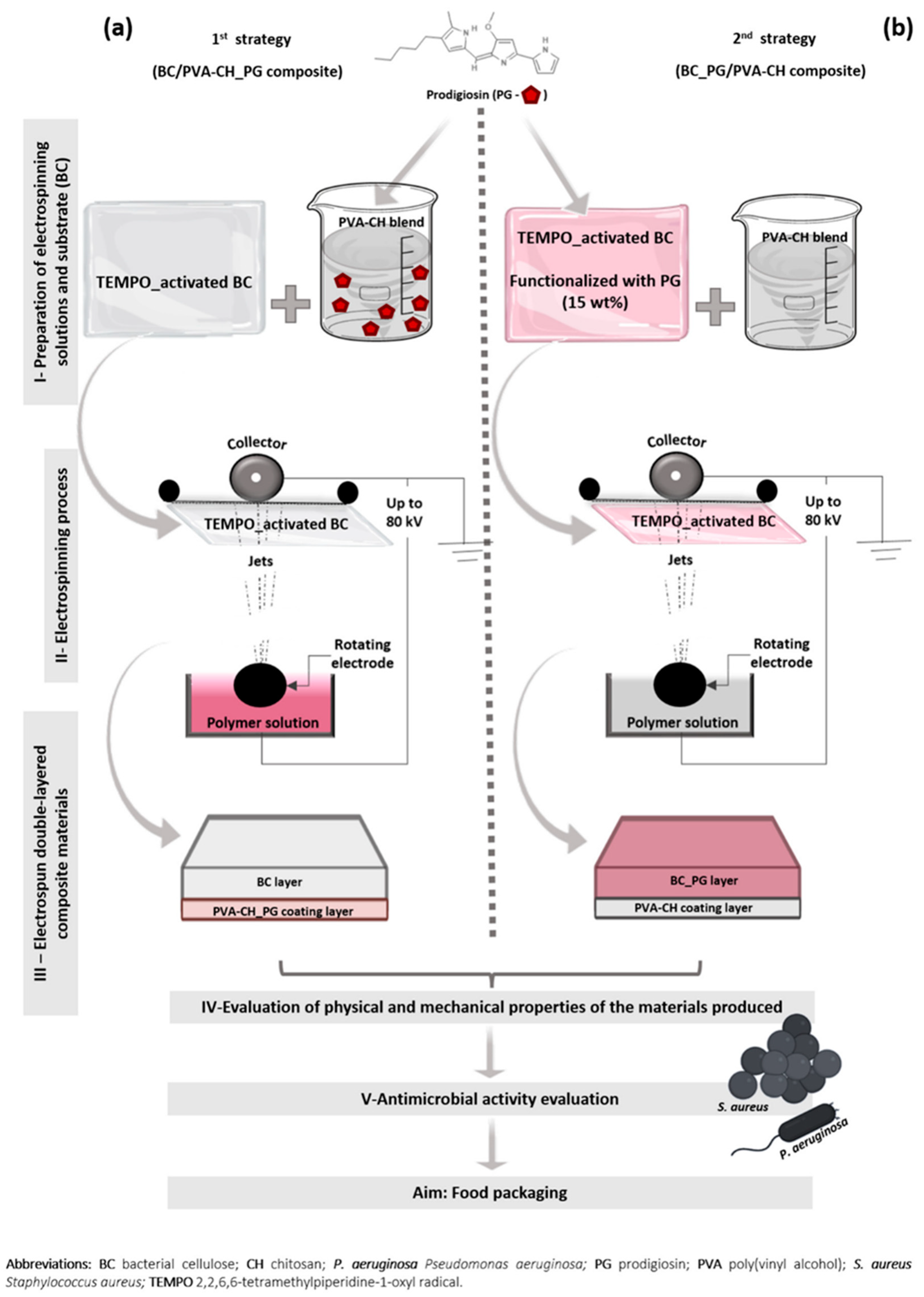
3.3.2. Prodigiosin as a Functional Additive for Food Packaging
3.4. Prodigiosin as Antifouling Agent
3.5. Prodigiosin as a Component of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
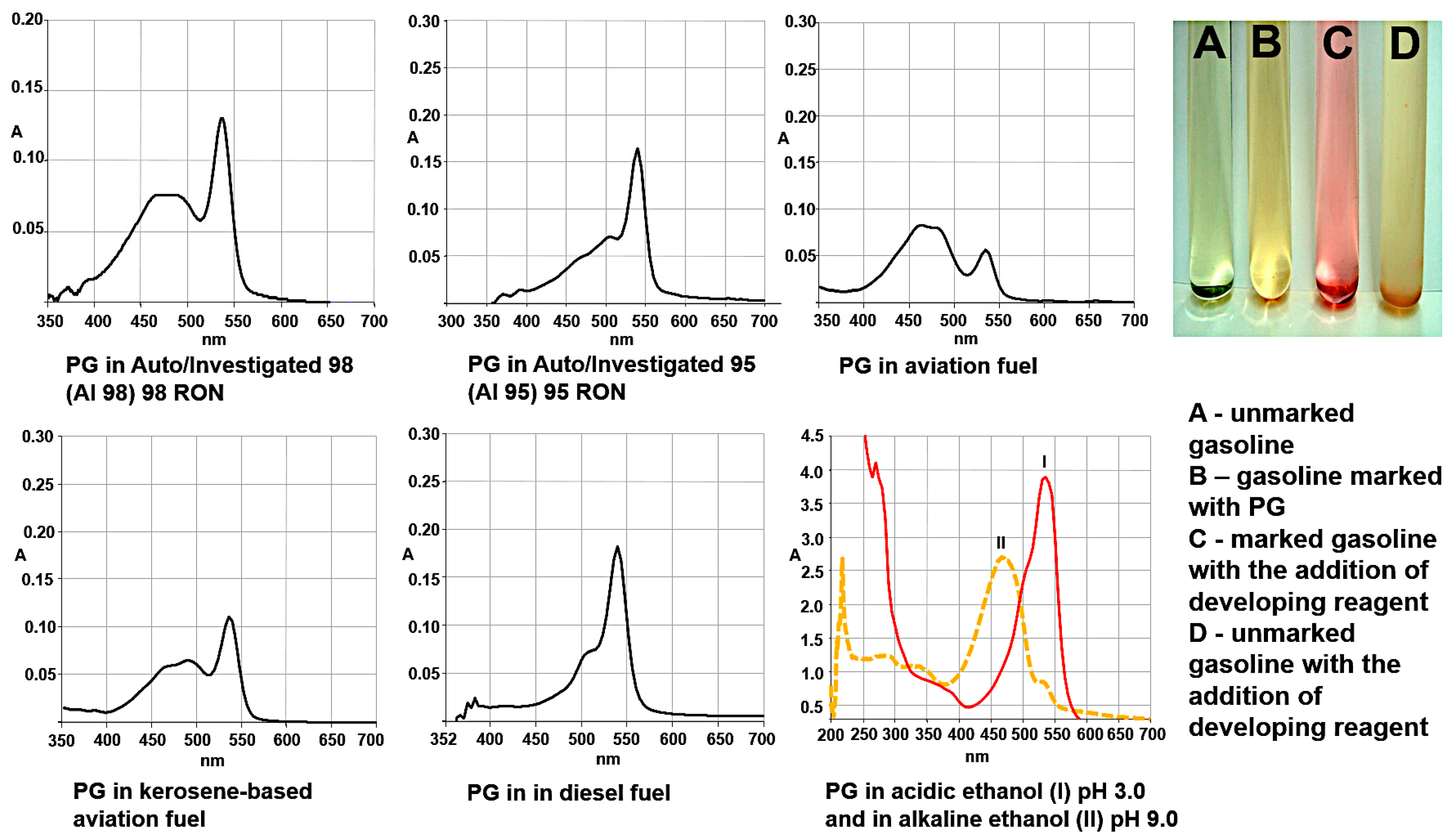
3.6. Prodigiosin as Fuel Marker
4. Future Perspectives and Challenges of Prodigiosin Using
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guryanov, I.D.; Karamova, N.S.; Yusupova, D.V.; Gnezdilov, O.I.; Koshkarova, L.A. Bacterial pigment prodigiosin and its genotoxic effect. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2013, 39, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Anishetty, S.; Pennathur, G. Molecular dynamics of the membrane interaction and localisation of prodigiosin. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2020, 98, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Kong, D.; Du, W.; Li, H.; Hse, C.-Y.; Shupe, T.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, K. Biological Potential and Mechanism of Prodigiosin from Serratia marcescens subsp. lawsoniana in Human Choriocarcinoma and Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, N.R.; Fineran, P.C.; Gristwood, T.; Chawrai, S.R.; Leeper, F.J.; Salmond, G.P.C. Anticancer and immunosuppressive properties of bacterial prodiginines. Future Microbiol. 2007, 2, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, N.; Radulovic, V.; Petkovic, M.; Vuckovic, I.; Jadranin, M.; Vasiljevic, B.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Streptomyces sp. JS520 Produces Exceptionally High Quantities of Undecylprodigiosin with Antibacterial, Antioxidative, and UV-Protective Properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, L.; Yu, S.; Su, Z.; Song, J.; Sun, Q.; Sha, O.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; et al. Prodigiosin inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exerts anticancer activity in breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13150–13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaner, B.; Castillo-Avila, W.; Martinell, M.; Ollinger, R.; Aymami, J.; Giralt, E.; Pérez-Tomás, R. DNA interaction and dual topoisomerase I and II inhibition properties of the anti-tumor drug prodigiosin. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 85, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelic, L.; Skaro Bogojevic, S.; Andrejević, T.P.; Pantović, B.V.; Marković, V.R.; Ašanin, D.P.; Milanović, Ž.; Ilic-Tomic, T.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Glišić, B.Đ.; et al. Copper(II) and Zinc(II) Complexes with Bacterial Prodigiosin Are Targeting Site III of Bovine Serum Albumin and Acting as DNA Minor Groove Binders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei-Heidari, H.R.; Partovifar, M.; Memarpoor-Yazdi, M. Evaluation of the Bioactive Potential of Secondary Metabolites Produced by a New Marine Micrococcus Species Isolated from the Persian Gulf. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2020, 12, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Greer, Y.; Lipkowitz, S.; Takebe, N. Novel Apoptosis-Inducing Agents for the Treatment of Cancer, a New Arsenal in the Toolbox. Cancers 2019, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, M.L.; Sartini, M.; Spagnolo, A.M. Serratia marcescens Infections in Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamble, K.D.; Hiwarale, V.D. Prodigiosin production from Serratia marcescens strains obtained from farm soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 631–638. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, E.; Graevenitz, A.V. Nonpigmented Serratia marcescens. JAMA 1966, 197, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, K.; Satheesh, S.; Ashokkumar, B.; Varalakshmi, P.; Selvakumar, G.; Sivakumar, N. Antifouling Activity of Prodigiosin from Estuarine Isolate of Serratia marcescens CMST 07. In Microbiological Research in Agroecosystem Management; Velu, R., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Le-Trilling, V.T.K.; Wang, K.; Mennerich, D.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Deng, Y.; Katschinski, B.; Xu, S.; et al. Obatoclax inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry by altered endosomal acidification and impaired cathepsin and furin activity in vitro. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, A.; Padalia, U. Optimization of prodigiosin biosynthesis by Serratia marcescens using unconventional bioresources. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Luo, H.; Song, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Su, X.; Ma, X. Prodigiosin found in Serratia marcescens y2 initiates phototoxicity in the cytomembrane. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, Y.; Copeland, A.; Hagemeister, F.; Fayad, L.E.; Fanale, M.; Romaguera, J.; Younes, A. Experience with obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070), a small molecule pan-Bcl-2 family antagonist in patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2012, 119, 2171–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglani, K.; Singh, S.; Singh, D.P.; Krishania, M. Sustainable production of prodigiosin from rice straw derived xylose by using isolated Serratia marcescens (CMS 2): Statistical optimization, characterization, encapsulation & cost analysis. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Patents. Prodigiosin. Available online: https://patents.google.com/?q=(prodigiosin)&oq=prodigiosin (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- PubMed Databases. Prodigiosin. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=prodigiosin (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Danevčič, T.; Borić, V.M.; Tabor, M.; Zorec, M.; Stopar, D. Prodigiosin induces autolysins in actively grown Bacillus subtilis cells. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, C.L.; Chauvet, S.; Andrès, E.; Aurouze, M.; Vallet, I.; Michel, G.P.; Uh, M.; Celli, J.; Filloux, A.; De Bentzmann, S.; et al. Virulence factors of the human opportunistic pathogen Serratia marcescens identified by in vivo screening. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, G. Biocidal agents used for disinfection can enhance antibiotic resistance in Gram-Negative species. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzade, M.; Yahya, N.A.; Shayesteh, F.; Usup, G.; Ahmad, A. Influence of Culture Conditions and Medium Composition on the Production of Antibacterial Compounds by Marine Serratia sp. WPRA3. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Yan, J.; Nie, H.; Yin, Q. Prodigiosin as an Antibiofilm Agent against the Bacterial Biofilm-Associated Infection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pathogens 2024, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.S.; van Woudenbergh, E.; Overheul, G.J.; Eleveld, M.J.; Kurver, L.; van Heerbeek, N.; van Laarhoven, A.; Miesen, P.; den Hartog, G.; de Jonge, M.I.; et al. Berberine and Obatoclax Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells In Vitro. Viruses 2021, 13, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darshan, N.; Manonmani, H.K. Prodigiosin Inhibits Motility and Activates Bacterial Cell Death Revealing Molecular Biomarkers of Programmed Cell Death. AMB Express 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapenda, J.C.; Silva, P.A.; Vicalvi, M.C.; Sena, K.; Nascimento, S.C. Antimicrobial Activity of Prodigiosin Isolated from Serratia marcescens UFPEDA 398. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Toliba, A.O.; Akl, B.A. Sensory evaluation, antioxidant, antimicrobial activities and colour of strawberry nectar enriched with prodigiosin pigment produced from Serratia marcescens. Pak. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 16, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallath, N.; Johnson, S.; Paul, E.; TA, R. Prodigiosin pigment from Serratia marcescens mbm-17 from facial acne as antimicrobial agent. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2023, 33, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimyon, Ö.; Das, T.; Ibugo, A.I.; Kutty, S.K.; Ho, K.K.; Tebben, J.; Kumar, N.; Manefield, M. Serratia Secondary Metabolite Prodigiosin Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Development by Producing Reactive Oxygen Species that Damage Biological Molecules. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai-Kawada, F.E.; Ip, C.G.; Hagiwara, K.A.; Awaya, J.D. Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Prodiginine Analogs in Marine Bacteria, Pseudoalteromonas: A Mini Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; You, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yun, Y.; Zhang, J. Transcriptomic analysis of cell envelope inhibition by prodigiosin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1333526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herráez, R.; Mur, A.; Merlos, A.; Viñas, M.; Vinuesa, T. Using prodigiosin against some gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 25, e20190001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, M.S.; Jeong, S.K.; Lee, S.J. Transcriptomic analysis of the antimicrobial activity of prodigiosin against Cutibacterium acnes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, T.; Ibrahim, D.; Zakaria, N.; Jalil, M. Effect of physical parameters in enhancing prodigiosin production and anti-mrsa activity of marine bacterium, Serratia marcescens ibrl usm84. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2023, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage-Hülsmann, J.; Grünberger, A.; Thies, S.; Santiago-Schübel, B.; Klein, A.S.; Pietruszka, J.; Binder, D.; Hilgers, F.; Domröse, A.; Drepper, T.; et al. Natural Biocide Cocktails: Combinatorial Antibiotic Effects of Prodigiosin and Biosurfactants. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boby, F.; Bhuiyan, N.H.; Saha, B.K.; Dey, S.S.; Saha, A.K.; Islam, J.; Al Bashera, M.; Moulick, S.P.; Jahan, F.; Zaman, A.U.; et al. In silico exploration of Serratia sp. brl41 genome for detecting prodigiosin biosynthetic gene cluster (bgc) and in vitro antimicrobial activity assessment of secreted prodigiosin. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danevčič, T.; Borić-Vezjak, M.; Zorec, M.; Stopar, D. Prodigiosin-A multifaceted Escherichia coli antimicrobial agent. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.H.; Mahalingam, S.; Wan, K.L.; Nathan, S. Prodigiosin inhibits bacterial growth and virulence factors as a potential physiological response to interspecies competition. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yin, Q.; Nie, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, X.R.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H. Prodigiosin as an antibiofilm agent against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biofouling 2023, 39, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tomás, R.; Montaner, B.; Llagostera, E.; Soto-Cerrato, V. The prodigiosins, proapoptotic drugs with anticancer properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, J.; Rahban, D.; Aghamiri, S.; Teymouri, A.; Bahador, A. Photosensitizers in antibacterial photodynamic therapy: An overview. Laser Ther. 2018, 27, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borić, M.; Danevčič, T.; Stopar, D. Prodigiosin from Vibrio sp. DSM 14379; a new UV-protective pigment. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Velasco, P.; Morales-Atilano, I.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.; Rodríguez-Delgado, J.M.; Luna-Moreno, D.; Ávalos-Alanís, F.G.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F. Photoelectric evaluation of dye-sensitized solar cells based on prodigiosin pigment derived from Serratia marcescens 11E. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 177, 108278–108287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, N.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Singh, V. Synergistic bactericidal profiling of prodigiosin extracted from Serratia marcescens in combination with antibiotics against pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, G.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z. Cationization-enhanced type i and type ii ros generation for photodynamic treatment of drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9130–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiniforush, N.; Pourhajibagher, M.; Shahabi, S.; Kosarieh, E.; Bahador, A. Can antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (apdt) enhance the endodontic treatment? J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 7, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Shi, J. A nanozyme-reinforced injectable photodynamic hydrogel for combating biofilm infection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 10108–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, W.; Wan, L.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Yuwen, L.; Dong, H.; Mou, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, L. Potentiating hypoxic microenvironment for antibiotic activation by photodynamic therapy to combat bacterial biofilm infections. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prażmo, E.J.; Godlewska, R.; Mielczarek, A. Effectiveness of repeated photodynamic therapy in the elimination of intracanal Enterococcus faecalis biofilm: An in vitro study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, C.; Mohana, P.D.; Swarnalatha, S.; Dinesh, M.G.; Sekaran, G. Production of prodigiosin using tannery fleshing and evaluating its pharmacological effects. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 290327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Sato, Z.; Sato, M.; Koiso, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Isaka, M. Identification of antibiotic red pigments of Serratia marcescens F-1-1, a biocontrol agent of damping-off of cucumber, and antimicrobial activity against other plant pathogens. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1998, 64, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, Z.; Amini, J.; Ashengroph, M.; Bahramnejad, B. Antifungal Activity of Serratia rubidaea Mar61-01 Purified Prodigiosin Against Colletotrichum nymphaeae, the Causal Agent of Strawberry Anthracnose. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhams, D.C.; LaBumbard, B.C.; Barnhart, K.L.; Becker, M.H.; Bletz, M.C.; Escobar, L.A.; Flechas, S.V.; Forman, M.E.; Iannetta, A.A.; Joyce, M.D.; et al. Prodigiosin, violacein, and volatile organic compounds produced by widespread cutaneous bacteria of amphibians can inhibit two Batrachochytrium fungal pathogens. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.J. Antimalarial activity of prodigiosin. Nature 1967, 213, 903–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papireddy, K.; Smilkstein, M.; Kelly, J.X.; Shweta; Salem, S.M.; Alhamadsheh, M.; Haynes, S.W.; Challis, G.L.; Reynolds, K.A. Antimalarial activity of natural and synthetic prodiginines. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 5296–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, J.E.; Nitcheu, J.; Predicala, R.Z.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Nesslany, F.; Marzin, D.; Concepcion, G.P.; Diquet, B. Heptyl prodigiosin, a bacterial metabolite, is antimalarial in vivo and non-mutagenic in vitro. J. Nat. Toxins 2002, 11, 367–377. [Google Scholar]
- Kancharla, P.; Li, Y.; Yeluguri, M.; Dodean, R.A.; Reynolds, K.A.; Kelly, J.X. Total Synthesis and Antimalarial Activity of 2-(p-Hydroxybenzyl)-prodigiosins, Isoheptylprodigiosin, and Geometric Isomers of Tambjamine MYP1 Isolated from Marine Bacteria. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8739–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkaufer, G.; Li, P.; Stebbins, E.E.; Kangussu-Marcolino, M.M.; Debnath, A.; White, C.V.; Moser, M.S.; DeRisi, J.; Gisselberg, J.; Yeh, E.; et al. Identification of anisomycin, prodigiosin and obatoclax as compounds with broad-spectrum anti-parasitic activity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitsch, D. Drug Resistance in the Microaerophilic Parasite Giardia lamblia. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2015, 2, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Suresh, S.; Solow-Cordero, D.; Singh, U. High-Throughput Screening of Entamoeba Identifies Compounds Which Target Both Life Cycle Stages and Which Are Effective Against Metronidazole Resistant Parasites. Front Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, S.; Chandrashekhar, P.; Hemant, B.; Chandrakant, N.; Laxmikant, S.; Satish, P. Nematicidal activity of microbial pigment from Serratia marcescens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgado, P.; Manna, D.; Singh, U. Recent advances in Entamoeba biology: RNA interference, drug discovery, and gut microbiome. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, M.M.; Albanese, C.; Hamdy, N.M.; Sultan, A.S. Rise of the natural red pigment ‘prodigiosin’ as an immunomodulator in cancer. Cancer Cell. Int. 2022, 22, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guryanov, I.; Naumenko, E.; Akhatova, F.; Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Nigamatzyanova, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Selective Cytotoxic Activity of Prodigiosin@halloysite Nanoformulation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Kantarjian, H.; Schimmer, A.; Walsh, W.; Asatiani, E.; El-Shami, K.; Winton, E.; Verstovsek, S. Phase II Study of Obatoclax Mesylate (GX15-070), a Small-Molecule BCL-2 Family Antagonist, for Patients with Myelofibrosis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2010, 10, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, R.; Pérez-Tomás, R.; Gimènez-Bonafé, P.; Soto-Cerrato, V.; Giménez-Xavier, P.; Ambrosio, S. Mechanisms of prodigiosin cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 572, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaner, B.; Pérez-Tomás, R. The cytotoxic prodigiosin induces phosphorylation of p38-MAPK but not of SAPK/JNK. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 129, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Prabhu, V.V.; Zhang, S.; van den Heuvel, A.P.; Dicker, D.T.; Kopelovich, L.; El-Deiry, W.S. Prodigiosin rescues deficient p53 signaling and antitumor effects via upregulating p73 and disrupting its interaction with mutant p53. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.C.; Pontes, C.A.; Rezende-Teixeira, P.; Amengual-Rigo, P.; Alves-Fernandes, D.K.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; da Silva, A.B.; Pessoa, O.D.L.; Jimenez, P.C.; Mollasalehi, N.; et al. Survivin modulation in the antimelanoma activity of prodiginines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 888, 173465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y. Prodigiosin from Serratia Marcescens in Cockroach Inhibits the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Molecules 2022, 27, 7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassankhani, R.; Sam, M.R.; Esmaeilou, M.; Ahangar, P. Prodigiosin isolated from cell wall of Serratia marcescens alters expression of apoptosis-related genes and increases apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2014, 32, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, D.; Jiang, R.; Li, Z.; Gao, X. Prodigiosin: Unveiling the crimson wonder—A comprehensive journey from diverse bioactivity to synthesis and yield enhancement. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1412776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, M.M.; Shalaby, M.; Embaby, A.M.; Saeed, H.; Agwa, M.M.; Hussein, A. Prodigiosin/PU-H71 as a novel potential combined therapy for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): Preclinical insights. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zeng, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Bai, W.; Liu, X.; Xiang, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Antiviral activity and specific modes of action of bacterial prodigiosin against Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus in vitro. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 100, 3979–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawanshi, R.K.; Koujah, L.; Patil, C.D.; Ames, J.M.; Agelidis, A.; Yadavalli, T.; Patil, S.V.; Shukla, D. Bacterial Pigment Prodigiosin Demonstrates a Unique Antiherpesvirus Activity That Is Mediated through Inhibition of Prosurvival Signal Transducers. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00251-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Shekhar, P.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, H.; Jayasena, V. Microbial pigments: Sources, current status, future challenges in cosmetics and therapeutic applications. J. Basic Microbiol. 2024, 64, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.F.A.; Yip, C.W.; Nor, N.S.M. In silico and in vitro antiviral activity evaluation of prodigiosin from Serratia marcescens against enterovirus 71. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2022, 51, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.S.; Rausalu, K.; Hakanen, M.; Saul, S.; Kümmerer, B.M.; Susi, P.; Merits, A.; Ahola, T. Obatoclax Inhibits Alphavirus Membrane Fusion by Neutralizing the Acidic Environment of Endocytic Compartments. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02227-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L. Biodegradation of synthetic dyes: A mycoremediation approach for degradation/decolourization of textile dyes and effluents. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 3, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berradi, M.; Hsissou, R.; Khudhair, M.; Assouag, M.; Cherkaoui, O.; El Bachiri, A.; El Harfi, A. Textile Finishing Dyes and Their Impact on Aquatic Environs. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.; King, M. Natural dye extracted from Chinese gall–the application of color and antibacterial activity to wool fabric. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Bajpai, S.; Mishra, A.; Kohli, I.; Varma, A.; Fouillaud, M.; Dufossé, L.; Joshi, N.C. Bacterial Pigments and Their Multifaceted Roles in Contemporary Biotechnology and Pharmacological Applications. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, C.; Vinithkumar, N.V.; Kirubagaran, R.; Venil, C.K.; Dufossé, L. Applications of Prodigiosin Extracted from Marine Red Pigmented Bacteria Zooshikella sp. and Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawanshi, R.K.; Patil, C.D.; Borase, H.P.; Narkhede, C.P.; Stevenson, A.; Hallsworth, J.E.; Patil, S.V. Towards an understanding of bacterial metabolites prodigiosin and violacein and their potential for use in commercial sunscreens. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.A.R.; dos Santos, R.A.; Mendonça, R.d.S.; Sá, A.V.P.; Andrade, R.F.d.S.; Rodríguez, D.M.; Campos-Takaki, G.M. Cost-effective production of stable prodigiosin by Serratia marcescens UCP 1549 and application in soap coloring. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e9711427078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Fu, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Lou, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Dyeing and functional properties of polyester fabric dyed with prodigiosins nanomicelles produced by microbial fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, J.G.; Jacob, A.; Kurian, P.; Elyas, K.K.; Chandrasekaran, M. Marine Bacterial Prodigiosin as Dye for Rubber Latex, Polymethyl Methacrylate Sheets and Paper. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 2266–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Ryazantseva, I.; Andreyeva, I. Application of prodigiosin as a colorant for polyolefines. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2014, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivizhivendhan, K.V.; Mahesh, M.; Boopathy, R.; Swarnalatha, S.; Regina Mary, R.; Sekaran, G. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of bioactive prodigiosin produces from Serratia marcescens using agricultural waste as a substrate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenconi, E.; Guichard, P.; Motte, P.; Matagne, A.; Rigali, S. Use of red autofluorescence for monitoring prodiginine biosynthesis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 93, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouro, C.; Gomes, A.P.; Costa, R.V.; Moghtader, F.; Gouveia, I.C. The Sustainable Bioactive Dyeing of Textiles: A Novel Strategy Using Bacterial Pigments, Natural Antibacterial Ingredients, and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Gels 2023, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zhong, M. Method for Dyeing Wool Fabric by Using Bacterial Dye of Prodigiosin. CN102493228B, 7 October 2013. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN102493228B/en (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Fu, R.; Zhang, J.; Fang, K.; Liu, X. Antibacterial dyeing of silk with prodigiosins suspention produced by liquid fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Fu, R.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, X. Dyeing and antibacterial properties of cotton dyed with prodigiosins nanomicelles produced by microbial fermentation. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 138, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, R.A.; El Sikaily, A.; El-Sersy, N.A.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Sabry, S.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Textile Fabrics Dyed with Prodigiosin Pigment Extracted from Marine Serratia rubidaea RAM_Alex Bacteria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 47, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivuselvam, R.; Dera, A.A.; Parween Ali, S.; Alraey, Y.; Saif, A.; Hani, U.; Arumugam Ramakrishnan, S.; Azeeze, M.S.T.A.; Rajeshkumar, R.; Susil, A.; et al. Isolation, Identification, and Antibacterial Properties of Prodigiosin, a Bioactive Product Produced by a New Serratia marcescens JSSCPM1 Strain: Exploring the Biosynthetic Gene Clusters of Serratia Species for Biological Applications. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.S.; Seabra, S.H.; Albuquerque-Cunha, J.M.; Castro, D.P.; Genta, F.A.; de Souza, W.; Brazil, R.P.; Garcia, E.S.; Azambuja, P. Prodigiosin is not a determinant factor in lysis of Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis after interaction with Serratia marcescens D-mannose sensitive fimbriae. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 122, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihosseini, F.; Ju, K.S.; Lango, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Sun, G. Antibacterial colorants: Characterization of prodiginines and their applications on textile materials. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, I.N.; Ogorodnikova, T.I. Pigmentation of Serratia marcescens and spectral properties of prodigiosin. Mikrobiologiia 2015, 84, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drink, E.; Dugourd, P.; Dumont, E.; Aronssohn, N.; Antoine, R.; Loison, C. Optical properties of prodigiosin and obatoclax: Action spectroscopy and theoretical calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 25946–25955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Oyervides, L.; Oliveira, J.; Sousa-Gallagher, M.; Méndez-Zavala, A.; Montañez, J.C. Assessment of the Dyeing Properties of the Pigments Produced by Talaromyces spp. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, S.; Kumar, S.D.; Murugan, A. Dyeing of Jute Fabrics with Prodigiosin Produced from Sago Waste and their Applications. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 16, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venil, C.K.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Ahmad, W.A. Bacterial pigments and their applications. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.-J.; Lee, M.-H.; Ryu, S.; Choi, J.M.; Oh, T.-K.; Yoon, J.-H. Exceptional Production of both Prodigiosin and Cycloprodigiosin as Major Metabolic Constituents by a Novel Marine Bacterium, Zooshikella rubidus S1-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivizhivendhan, K.V.; Boopathy, R.; Maharaja, P.; Regina Mary, R.; Sekaran, G. Bioactive Prodigiosin-Impregnated Cellulose Matrix for the Removal of Pathogenic Bacteria from Aqueous Solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68621–68631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivizhivendhan, K.V.; Mahesh, M.; Murali, R.; Mary, R.R.; Thanikaivelan, P.; Sekaran, G. Prodigiosin–Iron-Oxide–Carbon Matrix for Efficient Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Disinfection of Contaminated Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3164–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, L.F.A.; Fangueiro, R.; Gouveia, I.C. Characterization of Bioactive Colored Materials Produced from Bacterial Cellulose and Bacterial Pigments. Materials 2022, 15, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diken-Gür, S. Investigation of anti-adherence and antimicrobial properties of prodigiosin-functionalized bacterial cellulose membrane for biomedical applications. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 385, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidwai, S. Cosmetic Pigments Market Size, Share, and Trends 2024 to 2034. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/cosmetic-pigments-market (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Balwierz, R.; Biernat, P.; Jasińska-Balwierz, A.; Siodłak, D.; Kusakiewicz-Dawid, A.; Kurek-Górecka, A.; Olczyk, P.; Ochędzan-Siodłak, W. Potential Carcinogens in Makeup Cosmetics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, F.J.; Paniz, F.P.; Batista, B.L.; Nardocci, A.C.; Olympio, K.P.K. Potentially Toxic Elements in Costume Cosmetics Used by Children and Adults Are Associated with Cancer Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehrei, F.M. Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms associated with high-quality and low-quality cosmetics from different brands in Mecca region-Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Lobato, C.; Vázquez, L.; Mayo, B.; Flórez, A.B. Prodigiosin-Producing Serratia marcescens as the Causal Agent of a Red Colour Defect in a Blue Cheese. Foods 2023, 12, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Thavasi, T.R.; Jayalakshmi, S. Phenazine Pigments from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Their Application as Antibacterial Agent and Food Colourants. Res. J. Microbiol. 2008, 3, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmaraj, S.; Ashokkumar, B.; Dhevendaran, K. Food-Grade Pigments from Streptomyces sp. Isolated from the Marine Sponge Callyspongia diffusa. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Chaudhary, R.; Shah, Z.; Dufossé, L.; Fouillaud, M.; Mukhtar, H.; ul Haq, I. An Overview on Industrial and Medical Applications of Bio-Pigments Synthesized by Marine Bacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.R.; Daud, N.S.; Tong, W.Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Tan, W.N.; Hamin, N.S.; Pa’ee, K.F. Gelatine Film Incorporated with Clitoria ternatea-Derived Anthocyanin Microcapsules, A Food Packaging Material Effective Against Foodborne Pathogens. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 59, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, L.F.A.; Mouro, C.; Riool, M.; Gouveia, I.C. Antimicrobial Food Packaging Based on Prodigiosin-Incorporated Double-Layered Bacterial Cellulose and Chitosan Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Dhumal, C.V.; Sengupta, P.; Kumar, A.; Pramanik, N.K.; Alam, T. Challenges and Possible Solutions to Mitigate the Problems of Single-Use Plastics Used for Packaging Food Items: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3251–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat, B.; Razzaghi, M.; Bolton, K.; Rousta, K. Design Affordance of Plastic Food Packaging for Consumer Sorting Behavior. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T. Divorcing from Plastics for a Sustainable Future Society. In Overcoming Environmental Risks to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals. Current Topics in Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine; Nakajima, T., Nakamura, K., Nohara, K., Kondoh, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, C.; Sandonnini, J.; Coppola, M.R.; Madonna, A.; Abdel-Gawad, F.K.; Sivieri, E.M.; Guerriero, G. Biocide vs. Eco-Friendly Antifoulants: Role of the Antioxidative Defence and Settlement in Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.; Vasconcelos, V. Natural antifouling compounds: Effectiveness in preventing invertebrate settlement and adhesion. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R. Microbial fuel cells: Novel microbial physiologies and engineering approaches. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, Y.; Miki, T.; Wang, X.-F.; Nagae, H. Dye-sensitized solar cells based on the principles and materials of photosynthesis: Mechanisms of suppression and enhancement of photocurrent and conversion efficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4575–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomat, E. Coordination Chemistry of Linear Tripyrroles: Promises and Perils. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2016, 36, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Zacarías, C.; Cantú-Cárdenas, M.E.; López-Chuken, U.J.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Garza-Gonzalez, M.T.; Rostro-Alanis, M.D.J.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F. Dissimilatory reduction of Fe(III) by a novel Serratia marcescens strain with special insight into the influence of prodigiosin. Int. Microbiol. 2019, 23, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagni, T.; Enciso, P.; Marizcurrena, J.J.; Castro-Sowinski, S.; Fontana, C.; Davyt, D.; Cerdá, M.F. Dye Sensitized Solar Cells Based on Antarctic Hymenobacter sp. UV11 Dyes. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 1, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, E.; Xu, R.; Soliveri, G.; Santato, C. Natural melanin pigments and their interfaces with metal ions and oxides: Emerging concepts and technologies. MRS Commun. 2017, 7, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusupova, D.V.; Gabdrakhmanova, L.A.; Kurkina, M.A.; Guryanov, I.D. Identification Method of Marked Oil. Products. Patent RU 2368645C2, 29 September 2009. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/RU2368645C2/en?q=(Gareishina)&oq=Gareishina#citedBy (accessed on 12 December 2024).







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guryanov, I.; Naumenko, E. Bacterial Pigment Prodigiosin as Multifaceted Compound for Medical and Industrial Application. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 1702-1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4040115
Guryanov I, Naumenko E. Bacterial Pigment Prodigiosin as Multifaceted Compound for Medical and Industrial Application. Applied Microbiology. 2024; 4(4):1702-1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4040115
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuryanov, Ivan, and Ekaterina Naumenko. 2024. "Bacterial Pigment Prodigiosin as Multifaceted Compound for Medical and Industrial Application" Applied Microbiology 4, no. 4: 1702-1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4040115
APA StyleGuryanov, I., & Naumenko, E. (2024). Bacterial Pigment Prodigiosin as Multifaceted Compound for Medical and Industrial Application. Applied Microbiology, 4(4), 1702-1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4040115





