Abstract
Comparative metatranscriptomics of the bacterial and yeast communities of two milk kefir beverages (MKAA1 and MKAA2) was carried out. They were obtained by fermentation with two different frozen stocks of the kefir grain CIDCA AGK1, differing in rheological features and production of organic acids. We hypothesised that the differences in their physicochemical and rheological properties might be due to the microbial activity in each product. The dominance of lactic acid bacteria, yeast, and a marginal amount of acetic acid bacteria characterised the microbiome. The bacterial families Lactobacillaceae and Streptococcaceae accounted for almost all of the bacterial gene transcripts, with Lactobacillus helveticus, L. kefiranofaciens, L. gallinarum, and Lactococcus lactis being most frequent in the microbiome of the MKAA1 beverage and L. kefiranofaciens, Lc. Lactis, and Leuconostoc mesenteroides being the most prevalent in MKAA2. Dipodascaceae and Saccharomycetaceae were the leading yeast families, represented by Yarrowia lipolytica, Saccharomyces unisporus, and Kluyveromyces marxianus. MKAA1 and MKAA2 shared >75% KEGG Ortologs (KOs) in their bacteria and yeast libraries. The considerable decreases in total expressed genes (KEGG Ortologs) assigned to Lactobacillus helveticus and L. gallinarum might be related to the variations in the rheological features of the beverages, probably by compromising the interrelations with L. kefiranofaciens, which might explain the variations in the rheological features of the beverages.
1. Introduction
Kefir is a homemade viscous fermented beverage obtained by incubating milk with kefir grains, a stable community of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), acetic acid bacteria (AAB), and yeasts included in a protein–polysaccharide (kefiran) matrix [1,2,3,4,5].
Kefir grains are small, irregularly shaped discrete structures with a cauliflower-like appearance. During fermentation, microorganisms multiply in the grain and produce the matrix components, augmenting grain biomass by increasing in size during fermentation from several millimetres to 2–3 cm in diameter or producing new grains [6,7,8,9]. Grain formation is still a matter of research. It was proposed that the mechanism of grain formation is due the arrangement of microbiota on or in a polysaccharide–protein matrix [8]. Grain growth is affected by multiple factors, such as the type of milk, which defines the essential nutrients in the growth medium; the time of fermentation; the cultivation temperature; and grain washing, among other factors that affect active microbiota [5,6]. Furthermore, a dynamic partitioning of microorganisms between the grain and milk happens, where free/planktonic microorganisms reproduce, each with their own kinetics, and metabolic cooperation between community members is produced [5,6,7,10].
Many health and nutritional benefits are attributed to kefir [11]. The health-promoting properties can be ascribed to potential probiotic microorganisms or to metabolites produced by them, such as organic acid, antimicrobial compounds, and heteropolysaccharides with biological activity, among others [5,12,13]. Kefir microorganisms also hydrolyse milk proteins, releasing bioactive peptides with several biological activities (e.g., with antihypertensive, antioxidative, antiallergenic, antitumor, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-lowering activities) [14]. The biological activity of kefir can also be ascribed to microbiota modulation [12] or to an enhancement in the host’s immune response through the production of organic acids, exopolysaccharides, polypeptides or surface proteins, and other metabolites [15]. All of these properties depend on the activity of the microorganisms present in kefir.
High-throughput sequencing investigations of kefir grains and their corresponding fermented milk demonstrated an uneven distribution of microorganisms between the grain and fermented product, showing a more diverse microbial community in the fermented product [7,16,17]. While Lactobacillaceae is the most prominent family present in the grain, represented by the microorganisms formerly included in the Lactobacillus genus, with L. kefiranofaciens as the most abundant species, in the fermented product, Lactococcus predominates, accompanied by Acetobacter, Lactobacillus, and Leuconostoc. The most common fungal genera across both kefir and kefir grains are Kazachstania, Kluyveromyces, Naumovozyma, and Saccharomyces. Regarding the yeast community, the main difference between grains and kefir is the higher proportion of Dekkera in the fermented product [7,16,18,19,20].
A kefir grain’s microbial composition depends on the grain’s origin and affects the fermented product’s microbiota. Other variables, such as the type of milk, and the temperature and time of fermentation, also affect the microbial composition of kefir [13,21]. Studies of commercial Turkish kefir´s microbiota demonstrated that Lactococcus is the most abundant genus present, followed by Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, and Leuconostoc [22].
Walsh et al. (2023) used 64 kefir grains from different countries to prepare kefir, and a deep study of the microorganisms present in the fermented product was performed using a metagenomics-based approach. This study allowed for the definition of a pattern of domination, including the species Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactobacillus helveticus, and Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens. Only a few samples are dominated by Acetobacter orientalis or Leuconostoc mesenteroides [23]. This pangenome study determined a core microbiome in kefir represented by Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, or Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, which could be defined as the minimal bacterial composition for a fermented milk to be considered as kefir.
Milk fermentation by kefir grains produces different metabolites, including lactic acid, acetic acid, CO2, acetaldehyde, acetoin, and diacetyl, which provide the unique organoleptic properties of this beverage. Moreover, the exopolysaccharide kefiran, produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens subsp. kefiranofaciens during fermentation [24,25], is necessary for grain growth and contributes to the rheological properties of the fermented product [26,27]. The organoleptic qualities of kefir are subjected to variations due to factors such as the origin of the kefir grain, the type of milk, the grain-to-milk proportion, and the culture conditions [18,21,28]. Both the physicochemical properties and the metabolites of kefir may depend on microbial activity during fermentation, which could significantly affect the health-promoting properties of this fermented beverage [29].
Regarding this, the analysis of the physiologically active microbial cells of kefir is relevant to understand the relation between the microbial active profile and the physicochemical properties of the fermented product obtained. The physiologically active microbial cells can be analysed in a specific time or place by sequencing the complete set of protein-coding RNA transcripts using a high-throughput NGS technology called RNA-Seq [30]. The metatranscriptome analysis of a complex community of microorganisms, such as that present in kefir, elucidates the expression and regulation of the complete transcripts from those active populations [31]. Additionally, a more accurate composition of bacteria and yeast of the kefir community could be achieved by seeking transcripts of housekeeping and ribosomal protein genes, generating a transcriptionally active microbiome (TAM) [32,33].
The present study aimed to compare the functionally active microbiota present in two kefirs differing in their rheological features using a metatranscriptomic approach to understand the relation between differences in physicochemical and rheological properties of kefir and the microbial active profile associated with each product.
This research will contribute to deepening the knowledge of the functional profiles of the kefir microbial communities responsible for the physicochemical parameters of the fermented milk and its health-promoting properties, significantly contributing to a better understanding of the kefir ecosystem.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Kefir Grains and Fermented Milk (kefir) Preparation
Two different frozen stocks of CIDCA AGK1 kefir grain from the CIDCA collection (CIDCA-CONICET-UNLP, La Plata, Buenos Aires, Argentina) were used to obtain the corresponding fermented products: kefir MKAA1 and kefir MKAA2. Grains were inoculated into an appropriate volume of commercial UHT skim milk (Percentual composition (w/w): 3.1% protein, 4.8% lactose, 1.5% lipid and 0.67% of ashes; La Serenisima, General Rodríguez, Buenos Aires, Argentina) to maintain 10% (w/v) of inoculum and cultured by successive passages at 25 °C for 24 h, as described by Garrote et al. [28]. Several subcultures (backslopping) were performed to maintain the grains in an active form and grain weight augment was determined. For microbiological and physicochemical analyses, kefir was prepared by inoculating 3 g of kefir grain in 100 mL of UHT skim milk and then incubated for 24 h at 25 °C followed by 24 h incubation at 4 °C.
2.2. Physicochemical and Microbiological Characterisation of Fermented Milk
The concentration of viable microorganisms in kefir was determined by diluting the fermented product in tryptone 0.1% w/v. Then, 0.1 mL of the appropriate dilutions was spread plated in triplicate on MRS agar (Biokar Diagnostic, Oise, France) for LAB and YGC agar (Biokar Diagnostic) for yeasts. The Petri dishes were then incubated at 30 °C for 48 h in aerobiosis, except those from MRS, which were incubated in anaerobiosis. The results were expressed as colony-forming units (CFU) per ml of fermented product. Enumeration of viable microorganisms was performed in two independent samples.
Organic acid quantification was performed by high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) employing an ion exchange column. Briefly, 25 mL of 45 mM H2SO4 was added to 5 mL of the kefir and homogenised for 1 h in a rotary shaker (430 Incubator; Nova Ética, São Paulo, Brazil) at 250 rpm. The supernatant fluid was then separated by centrifugation at 6000× g (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and filtered through a 0.45 μm filter (Millipore Corp., Burlington, MA, USA). The samples were injected (50 µL) in triplicate into an HPLC system (Shimadzu Corp., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an HPX-87H Aminex fermentation monitoring column (150 × 7.8 mm id) and protected by a cation H+ Micro protection cartridge (30 × 4.6 mm id; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) maintained at 65 °C. Organic acids (lactic, acetic, citric, succinic, formic, butyric, and propionic acids) were quantified using a model SPD-M20A diode array detector (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) at the absorbance of 210 nm. Under these chromatographic conditions, the chromatogram of the standard mixture of organic acids investigated in this study was obtained. The mobile phase (isocratic flow rate at 0.7 mL/min) was 3 mM H2SO4. HPLC chromatograms and quantification of compounds were obtained using LC Solution software (Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan). Standard curves based on peak area were calculated for individual organic acids, covering a wide range of concentrations. Standards (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) were prepared in deionised water filtered through 0.45 µm filters (Millipore Corp., Burlington, MA, USA) [34].
The pH was measured using an HI1131B microelectrode coupled to a pH meter pH 211 (Hanna Instrument, Woonsocket, RI, USA). The apparent viscosity of the fermented milks was estimated at 25 °C in a Haake ReoStress 600 rheometer with a plate–plate sensor system PP35 and a gap of 1 mm (Thermo Haake, Karlsruhe, Germany) according to Hamet et al. [35]. Shear stress was plotted as a function of shear rate and apparent viscosities (mPa.s) were calculated at 300 s−1. Experiments were performed at least in duplicate and each determination was conducted in at least three independent samples.
The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). GraphPad Prism version 5.01 software for Windows (GraphPad®, Boston, MA, USA) was used. Quantitative data were analysed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s tests. A p-value < 0.05 indicates significant differences.
2.3. Identification of the Transcriptionally Active Microorganisms in Kefir by RNA-seq Analysis
One millilitre of kefir was centrifuged (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) for 10 min at 10,000× g. The resulting cell pellet was suspended in 0.5 mL of TE buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA) with RNasin® Ribonuclease inhibitor (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and was transferred to a microtube with 0.3 g of zirconium beads, which was then ruptured in the FastPrep-24 equipment (MP Biomedicals, San Diego, CA, USA). Total RNA was extracted using the RNAeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Sao Paulo, Brazil), according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The samples were divided into two parts, one for analysing the bacteria and the other for studying yeasts. The bacterial sample was treated with the Ribo-Zero rRNA removal kit, and the yeast sample was enriched with the capture of mRNAs by the poly-A tail. All the procedures were performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Illumina, Albany, NY, USA). The extracted RNA was reversed-transcripted to cDNA by the reverse transcriptase using either random primers (bacterial RNA) or oligo(dT) primers (yeast mRNA) to build libraries for NGS sequencing.
The cDNA libraries were elaborated according to the RNA Sample sequencing protocol from Illumina, which consisted of the following steps: purification and fragmentation of mRNA; synthesis of the first cDNA chain; synthesis of the second cDNA chain; repair of extremities; adenylation, adapter binding, amplification, library validation, standardisation, and pooling of libraries. The sequencing was carried out by using bridging PCR in a MiSeq sequencer. All these procedures were performed as stated by the manufacturer (Illumina). MiSeq reagent kit v3 (600-cycle) enabled the highest output of sequenced information (15 Gb, 2 × 300 bp, up to 25 million reads).
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
The bioinformatics analysis was carried out in the servers Sagarana and Truta, located at the Laboratories of Informatics of the ICB/UFMG and Fiocruz/MG, using a GNU Linux/Debian operating system. Some computational algorithms were developed and made in Python throughout the project. Multithreading was used to increase performance and reduce the processing time associated with the programs. Rios et al. described the in-house metatranscriptome pipeline for analysing large RNA-seq datasets in Docker containers for supercomputing cluster environment pipeline in detail [32]. It creates a manifest.tsv file describing the application settings, location of databases, and fastq files. Briefly, the pipeline performs the first step of processing raw DNA paired-end reads forming consensus sequences, which are aligned using the HS-BLASTN accelerating Megablast search tool [36] against the NCBI RefSeq database; the taxonomic identification uses algorithms similar to MEGAN [37], and the functional annotation is also performed using the generated RefSeq.json file, along with another pre-processed file that cross-references between NCBI protein accession numbers and KO, already in the KEGG hierarchy (acc2KO.json).
In the second step, the reads are mounted in contigs by Trinity software [38] and are analysed, and predicted protein-coding regions are extracted by the TransDecoder tool [39]. The unannotated contigs are then taxonomically and functionally annotated by the AC-DIAMOND v1 tool [40]. The transcoder identifies which contigs are mRNA and what possible ORFs are. The AC-DIAMOND aligns the annotated contigs as mRNA by BLASTx against the NCBI NR database (non-redundant protein sequences) and UEKO-UniRef Enriched KEGG Orthology [41]. Lastly, the STAR tool [42] aligns the reads against mRNA-annotated contigs to quantify the gene expression.
In the third step, due to the absence of biological replicates in our experimental design, we compared paired kefir samples through a fast Bayesian statistic method called CORNAS—coverage-dependent RNA-Seq [43]. The sequencing coverage and size values of contigs aligned with AC-DIAMOND were used in the analysis. A sequencing coverage parameter determined from the concentration of the RNA sample was used to estimate the posterior distribution of true gene counts to support calling differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Genes were considered differentially expressed if the 0.5th percentile of the count probability distribution for one sample was at least two-fold higher than the 99.5th percentile of the other sample.
The comparison of datasets through Venn diagrams used the InteractiVenn web-based tool [44]. Other scientific analyses and graphing were carried out in GraphPad Prism 6 (Dotmatics, Boston, MA, USA). The pipeline generates smear MA plots, PCC plots, and Heatmap graphics as a final output. MA plots were generated to visualise the variances between differentially expressed genes in the RNA-seq libraries. Points are annotated genes, the x-axis indicates the log10 normalised mean average, and the y-axis shows the log2 fold change. The KEGG mapping occurred between the kefir libraries, and colours stated the most significant differentially expressed genes. The native R function cor (x, y, method) in version 4.3.1 measured Pearson’s correlation coefficient values between KO pathway genes to build PCC plots. Heatmap graphics were created in RStudio, using dplyr, glue, fs, stringr, ggplot2, treeio, ggtree, and ggnewscale software tools. All libraries were normalised to 300 million reads, and values were converted to log10. The heatmaps from the bacteria and yeast libraries had a limit of 25 and 15 species, most expressed in absolute normalised reads, respectively (Supplementary Information File).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Kefir Biomass Growth during Successive Subcultures and Physicochemical and Microbiological Characterisation of Kefir
Two stocks of frozen kefir CIDCA AGK1 grains (MKAA1 and MKAA2) inoculated into skim milk and incubated for 24 h increased their weight differently. The analysis of grain growth as a function of the number of subcultures (Figure 1A) showed that stock MKAA1 increased its biomass, reaching a 5-fold increment after 20 subcultures, while stock MKAA2 doubled its weight. The difference in grain growth behaviour was not reflected in the total number of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts observed in each grain, with 3.5 × 108 CFU/g LAB and 3 × 107 CFU/g yeasts evidenced in MKAA1 and 1.25 × 108 CFU/mL LAB and 6.5 × 107 CFU/mL yeasts in MKAA2.
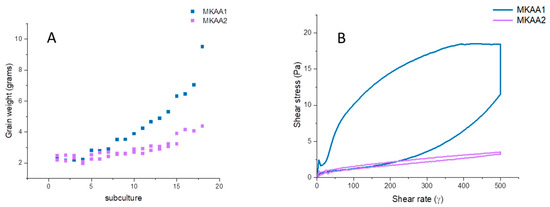
Figure 1.
(A) Increase in grain weight during successive 24 h subcultures at 20 °C. (B) Flow curves of the fermented products (kefir) obtained with each frozen stock of kefir grains AGK1.
In the fermented milks, the numbers of viable lactic acid bacteria and yeasts were not significantly different between kefir MKAA1 and MKAA2, reaching values of 2 × 109 CFU/mL for LAB and 3 × 106 CFU/mL for yeasts (Table 1). However, they had different pH values after 48 h fermentation. The pH of kefir MKAA1 was 4.28, while kefir MKAA2 showed a significantly lower value (pH 4.07). A decrease in pH is associated with the production of organic acids during fermentation, which represents an essential feature because they are linked to the organoleptic characteristics as well as the antimicrobial properties of the final product [5]. The organic acid profiles of both kefirs revealed that lactic acid and acetic acid were the main organic acids produced (Table 1), with kefir MKAA2 showing higher levels of acetic acids. These results are in agreement with the lower pH observed for kefir MKAA2.

Table 1.
Physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of kefir prepared with CIDCA AGK1 kefir grain from two frozen stocks (MKAA1 and MKAA2).
Flow curves of both kefirs displayed a pseudoplastic behaviour, with kefir MKAA1 showing a higher hysteresis loop (Figure 1B). Furthermore, the apparent viscosity of kefir MKAA1 at 300 s−1 was higher than that observed for kefir MKAA2. This difference could be associated with changes in the kefir grain and/or the fermented milk active microbiota that influences the production of kefiran, an exopolysaccharide that plays a crucial role in improving the rheological properties of kefir [45]. Kefiran is also relevant because of its biological activities since several health-promoting properties of kefir are ascribed to this biopolymer, so understanding kefiran production during fermentation is an essential aspect in kefir research [25,46].
3.2. Sequencing Overview
Normalised mRNA read counts were used for taxonomic and functional profile analysis of both kefir beverages’ microbial communities. High-quality sequencing data were generated for all samples (yeast and bacteria libraries of milk kefir MKAA1 and MKAA2). After merging the corresponding paired-end reads, quality control assessment, and trimming sequencing artefacts and duplicates, a total of 9 million reads resulted for all further downstream analyses (a mean of 2.25 million sequences per sample), 6.6 million and 2.4 million reads mapped to bacteria and yeasts, respectively. Unclassified reads were observed, approximately 4.74% of the kefir transcripts (Table 2).

Table 2.
Number of reads obtained by sequencing the transcriptome and annotating by pipeline.
Read counts in the four sequencing libraries ranged from 1,046,458 in MKAA2 (yeast) to 4,113,272 in MKAA1 (bacteria). In these, the reads identified taxonomically by HS-BLASTN ranged from 76.5% in MKAA2 (yeast) to 97.9% in MKAA1 (bacteria). The reads identified as part of an mRNA by TransDecoder ranged from 57.3% in MKAA1 (yeast) to 74.4% in MKAA1 (bacteria). Reads annotated with KEGG Orthology Entries (KO) ranged from 42.2% in MKAA1 (yeast) to 64.4% in MKAA1 (bacteria). Combining all the strategies employed to attempt the taxonomic and functional affiliation of the reads, the percentage of reads annotated by the pipeline ranged from 90.8% in MKAA2 (yeast) to 98.59% in MKAA1 (bacteria) (Table 2).
Trinity-generated contigs varied from 41,450 in MKAA1 (bacteria) to 63,859 in MKAA2 (yeast); they were TransDecoder-identified as mRNA ranging from 40.5% in MKAA2 (bacteria) to 47.2% in MKAA2 (yeast) and then annotated by KEGG Orthology (KO), ranging from 29.5% in MKAA1 (yeast) to 34.8% in MKAA2 (yeast) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Detailing the number of contigs mounted on transcriptome sequencing and annotated by the KEGG Orthology (KO) tool.
3.3. The Transcriptionally Active Microbiome (TAM) of MKAA1 and MKAA2 Kefir
3.3.1. Bacteria Taxonomy in the Metatranscriptome of Kefir Beverages
The microbial communities of kefir MKAA1 and MKAA2 were analysed based on all mRNA reverse-transcribed bacteria and yeast typing genes. The nomenclature used in this analysis considered the reclassification of the genus Lactobacillus into 25 genera as well as the incorporation of all genera that formerly belonged to Leuconostocaceae in the Lactobacillaceae family [47,48].
In the bacterial transcriptionally active microbiome (bTAM) analysis, the Firmicutes and Proteobacteria phyla comprise almost all protein-related readouts. However, the importance of each phylum in the kefir samples is slightly different, with Firmicutes and Proteobacteria accounting for 99.8% and 0.2% in MKAA1 and 98.3% and 1.7% in MKAA2. The lactic acid bacteria families Lactobacillaceae and Streptococcaceae dominated the bTAM (MKAA1 78.3%, 21.5% and MKAA2 66.5%, 31.9%), while the acetic acid bacteria family Acetobacteraceae had only marginal counts ranging from 0.2% to 1.7%.
The predominant bacterial genera in kefir MKAA1 and MKAA2 belong to the genus formerly named Lactobacillus, accounting for 67.9% and 50.3%, followed by Lactococcus (21.1% and 31.3%) and Leuconostoc (8.40% and 14.2%) in MKAA1 and MKAA2, respectively (Figure 2A). Additionally, there are noticeable differences between both kefirs regarding the genus Acetobacter, with a higher proportion in MKAA2 (1.25%) than in MKAA1 (0.12%). At the species level, it was found that Lactobacillus helveticus (27.7%), Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens (19.2%), Lactobacillus gallinarum (12.2%), Lactococcus lactis (20.2%), and Leuconostoc mesenteroides (7.76%) were more conspicuous in kefir MKAA1. However, in the MKAA2 sample, the relative abundance of these species significantly differed, with L. helveticus and L. gallinarum having marginal roles (5.31% and 0.94%, respectively), whereas L. kefiranofaciens (37.3%), L. lactis (29.9%), and L. mesenteroides (13.4%) predominated (Figure 2B).
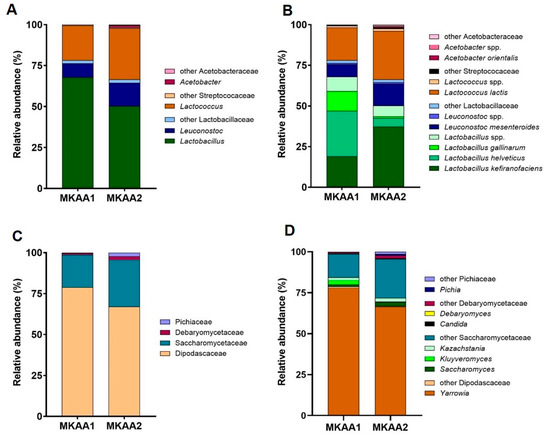
Figure 2.
Relative abundance of the dominant bacterial genera (A) and species (B) as well as fungal families (C) and genera (D) from communities in the metatranscriptome of MKAA1 and MKAA2 kefir.
These findings are in agreement with previously published data from similar fermentation stages, where L. kefiranofaciens, L. helveticus, Lactococcus lactis, and/or Leuconostoc mesenteroides were identified as the dominant microbiota depending on the grain and the fermentation time [7,23]. Metagenomic sequencing of kefir during fermentation revealed a shift from L. kefiranofaciens to Leuconostoc as the dominant species [23], highlighting the significant impact of fermentation time on microbial dominance.
In the present work, Lactobacillus gallinarum was found to be metabolically active in kefir MKAA1 despite not being described as dominant in previous metagenome analysis reporting. When comparing results from both kefir samples, it is worth noting that all the predominant active lactobacilli (L. helveticus, L. kefiranofaciens, and L. gallinarum) belong to the same clade, according to the new taxonomical classification that reflects the phylogenetic position of the microorganisms with shared ecological and metabolic properties [48]. On the contrary, microorganisms that were isolated from these kefir grains in previous studies, or have been described in the kefir grain microbiome, such as Lentilactobacillus kefiri, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, or Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, were not dominant in the fermented milk when analysing bTAM [17].
The comparison of the bTAM of MKAA1 and MKAA2 with two Brazilian milk kefirs [32] revealed remarkable differences in the relative abundances of genera. In Brazilian kefirs, the most prevalent bacterial genera were Leuconostoc (60%), Lactobacillus (25%), and Lactococcus (6%), while in Argentinian kefirs, Lactobacillus (59%), Lactococcus (26%), and Leuconostoc (11%) were predominant.
3.3.2. Yeast Taxonomy in the Metatranscriptome of Kefir Beverages
The phylum Ascomycota was dominant in yeast transcriptionally active microbiome (yTAM), with >99.9% of total protein-related reads. The families Dipodascaceae and Saccharomycetaceae were the most abundant in both samples (MKAA1, 78.8%, 19.9%; MKAA2, 67.0%, 28.6%, respectively), with a shallow occurrence of Debaryomycetaceae and Pichiaceae (Figure 2C). The main genus in the microbiome was Yarrowia (MKAA1, 78.0% and MKAA2, 66.5%), represented by the species Y. lipolytica, followed by other Saccharomycetaceae genera with low counts, including Kazachstania, Kluyveromyces, and Saccharomyces (around 2% each) (Figure 2D). These results agree with those described by Walsh et al. [23], who found that Saccharomyces eubayanus, Kluyveromyces marxianus, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae were detected at low relative abundance (<2%).
Comparing the yTAM of two Brazilian milk kefirs [32] with the Argentinian kefirs MKAA1 and MKAA2, remarkable differences are evidenced. In Brazilian kefirs, Pichiaceae was the dominant family accounting for 58.8% of the total compared to 1.23% in the Argentinian kefirs. Dipodascaceae showed a presence of 17.3% in the Brazilian kefirs against 72.9% in the Argentinian kefirs, while Saccharomycetaceae accounted for 11.8% in the Brazilian kefirs and 24.3% in the Argentinian kefirs. The most prevalent genera in Brazilian samples were Pichia and an unidentified genus of Pichiaceae at 18.3% and 40.5%, respectively, followed by Yarrowia at 17% and Saccharomyces at 4%. In contrast, in MKAA1 and MKAA2, Yarrowia accounted for 72.2%, Saccharomyces for 1.73%, and Pichia only for 0.46%.
3.4. The Functional Profile of the Kefir Microbial Community of MKAA1 and MKAA2 Beverages
Regarding KEGG PATHWAY mapping of the KO functional orthologs, there were 1622 and 1845 assigned KO entries in MKAA1 and MKAA2 bacteria libraries, respectively, out of a total of 1984 unique KO, and 2890 and 2938 assigned KO entries in yeast libraries, respectively, out of a total of 3186 unique KO. Both kefirs shared 74.7% of bacteria KO and 82.9% of yeast KO (Figure 3). KO found in only one kefir in the bacterial and fungal libraries were 7% and 7.8% in MKAA1 and 18.2% and 9.3% in MKAA2, respectively.
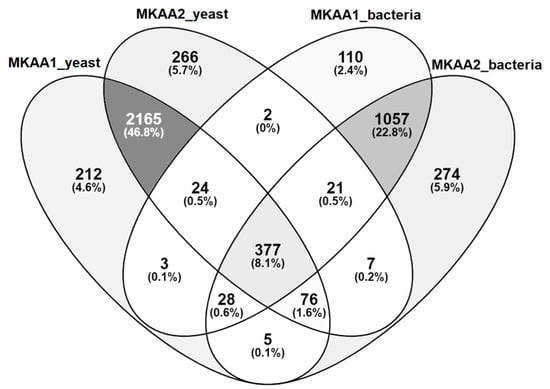
Figure 3.
Comparison of the KEGG ortholog (KO) gene entries of MKAA1 and MKAA2 bacteria and yeast libraries. Percentages are relative to the total unique KO.
Upon conducting a more in-depth analysis of the biological processes mapped in each kefir sample related to the five main LAB, we observed marked quantitative differences among lactobacilli, Lactococcus and Leuconostoc. Although both samples contained a similar number of KO (1454 KO in MKAA1 and 1428 KO in MKAA2, out of a total of 1555 unique KO), the roles of L. helveticus and L. gallinarum changed considerably. There was a notable decrease in the contribution of these two Lactobacillus species and a consequent increase in L. kefiranofaciens, Lactococcus lactis, and Leuconostoc mesenteroides in MKAA2 kefir (Table 4, Figure 4).

Table 4.
KEGG Orthologs (KOs) affiliated with the lactic acid bacteria species in the MKAA1 and MKAA2 beverages.
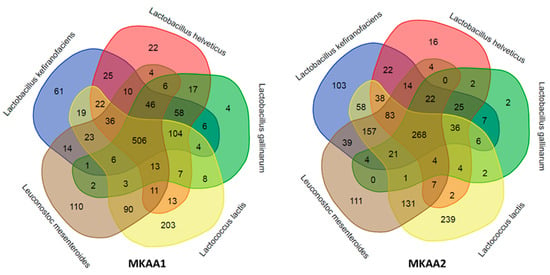
Figure 4.
Comparison of the KEGG ortholog (KO) gene entries of the five major lactic acid bacteria species in MKAA1 and MKAA2 bacterial libraries.
The species pair L. helveticus and L. gallinarum participated with 934 KO in MKAA1 and then dropped to 590 KO in MKAA2 (37% less), with a subsequent increase from 520 to 838 KO absent in both. Of these KO in MKAA1 and MKAA2, 757 and 361 were shared with at least one other lactic acid bacteria: 506 and 268 KO with the other three lactic acid bacteria, 104 and 36 with L. kefiranofaciens and Lc. lactis, 58 and 25 with L. kefiranofaciens only, 46 and 22 with L. kefiranofaciens and Leu. mesenteroides, 17 and 2 with each other, 13 and 4 with Lc. lactis and Leu. mesenteroides, 7 and 4 with Lc. lactis only, and 6 and 0 with Leu. mesenteroides only, respectively (Figure 4).
Concerning the top six categories for KEGG Pathway mapping (Figure 5A), the relative abundances of reads associated with “Metabolism” and “Genetic Information Processing” in bacteria and yeast are majorities, and others 23 to 29% were categorised as “Unclassified”. Only slight differences were observed in the total KO between bacteria and yeasts. Concerning the second-level categories under the top category “Metabolism” (Figure 5B), the relative abundance of transcripts associated with “Carbohydrate metabolism” was higher in bacteria than in yeasts (20% vs. 12%), also observed with “Nucleotide metabolism” (9% vs. 2%) and “Metabolism of other amino acids” (1.2% vs. 0.2%). Otherwise, yeasts showed a higher relative abundance of transcripts associated with “Energy metabolism” (5% vs. 2%), “Lipid metabolism” (4% vs. 0.8%), “Aminoacid metabolism” (4.5% vs. 3%), “Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins” (2% vs. 1%), and “Enzyme families” (6% vs. 2.5%).
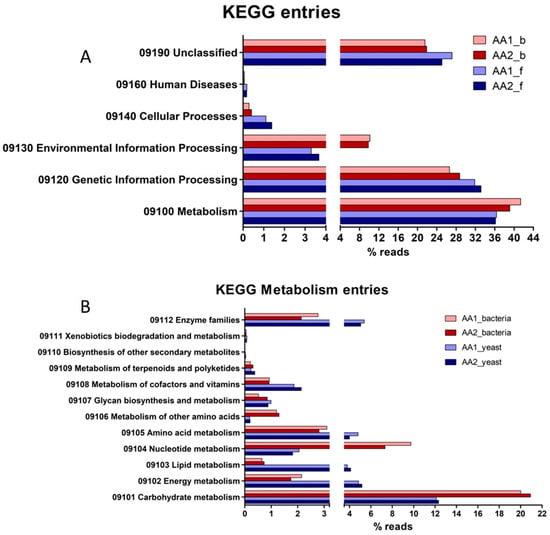
Figure 5.
KEGG ortholog gene categorisation (KO) of the main functional processes (A) and subprocesses (B) of MKAA1 and MKAA2 kefir bacterial and yeast libraries.
The differences observed between MKAA1 and MKAA2 include L. kefiranofaciens exclusive KO triplicated from MKAA1 to MKAA2, and the subsequent decreases in total KO assigned to L. helveticus and L. gallinarum. These changes might explain some of the differences in the physicochemical properties of both kefirs. Considering that L kefiranofaciens subsp. kefiranofaciens is described as a kefiran producer, there is no direct interpretation of the variations in rheological features of the beverages (Figure 1B), indicating a more complex relationship between kefir microorganims. L. helveticus strains are well known for their proteolytic ability [49], which may provide amino acids and short peptides. However, this is unrelated to the improvement of L. kefiranofaciens growth, since previous reports demonstrated that adding proteases to milk did not affect its growth. Moreover, L. kefiranofaciens positively affects the growth of Leuconostoc mesenteroides because of its proteolytic activity [7]. In this direction, the higher proportions of L. kefiranofaciens in MKAA2 could explain the increment in Leuconostoc observed compared to MKAA1.
bTAM analysis also demonstrated that Lactococcus and Acetobacter were in higher proportion in MKAA2, correlating with the higher lactic and acetic acid content of this fermented milk, in agreement with previous reports [18]. It was demonstrated that lactate and acetate, which are in higher proportion in MKAA2, may function as regulators of growth and metabolic activity of distinct species. Lactate stimulates the growth of L. kefiranofaciens [7] consistent with what is observed in MKAA2. Since higher kefiran production is achieved under pH-controlled culture [24,50], the differences in the final pH of MKAA2 and higher organic acid content may result in less viscosity. These findings are in agreement with previous reports. Kefir prepared with different kefir grain/milk ratios also presented differences in viscosity, as a lower kefir grain-to-milk ratio decreases the acidification rate, leading to higher viscosity. Additionally, differences in yeast active microbiome (Figure 2, lower panel) could also affect polysaccharide synthesis by L. kefiranofaciens.
The fact that kefir MKAA2 has a reduced growth in grain biomass indicates that fewer matrix components are being produced. Consequently, an increase in L. kefiranofaciens release from the grains is generated. However, the lower viscosity of the MKAA2 fermented product may indicate that the presence of L. kefiranofaciens is not enough for kefiran production, requiring other microorganisms that may produce unknown factors that could induce the production of this polysaccharide.
4. Conclusions
The present research contributes to understanding that physicochemical characteristics of kefir results from cooperative and competitive interaction within microorganisms of this natural complex ecosystem. The analysis of the meta-transcriptome of two kefir samples obtained from the same frozen grains but stored for different periods (MKAA1 and MKAA2), with different organic acid content as well as rheological parameters, revealed that they have similar microbial communities but with a notably different distribution of bacterial species. The main variations were observed in Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens, L. helveticus, L. gallinarum, and Lactococcus lactis. However, the main mapped functional processes were similar in both kefir samples. The kefir MKAA2 with low viscosity had lower counts of L. helveticus and L. gallinarum. However, no direct correlation was observed with the viscosity and L. kefiranofaciens relative abundance and activity, which is considered the main producer of kefiran. These findings indicate that in kefiran production during milk fermentation, not only is the activity of L. kefiranofaciens relevant, but also its relationship and interaction with other microorganisms forming the complex kefir community. Moreover, kefir grain biomass augmentation is affected by the change in the functional microbiome. Future investigations should be carried out to elucidate the implications of the ecological relationship between L. kefiranofaciens and other microorganisms present in kefir grains and their impact on the rheological parameters of kefir.
The results obtained in the present work suggest that changes in the dynamic balance of kefir´s active microbiota profile can lead to essential alterations in the physicochemical characteristics of the fermented product. However, as kefir is a complex microbial community, it is necessary to continue deepening the knowledge of the active microbiota relationship. Understanding its behaviours will contribute to future improvements in the development of kefir-like starter cultures or to defining fermentation conditions that lead to kefir with controlled physicochemical characteristics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/applmicrobiol4030078/s1. Figure S1: Relative expression levels of functional orthologs genes mapped by the KEGG database (KO) for bacteria (A) and yeasts (B) communities of milk kefir MKAA1 and MKAA2. The chart is a side-by-side comparison of the libraries, showing the path_a and path_b of the KO, a coloured cladogram for the family, and the heatmap of normalised expression in the log10 of absolute normalised reads. The bacterial and yeast heatmaps had the limit of 25 and 15 most expressed species, respectively; Figure S2: Pearson’s correlation coefficient (R) between the relative abundance of annotated reads by the KEGG database of MKAA1 vs MKAA2 bacteria and yeasts concerning A. Metabolism processing, B. Genetic Information Processing, C. Environmental Information Processing; Figure S3: MA plot between the relative abundance of MKAA1 vs MKAA2 bacteria and yeasts annotated reads by the KEGG database concerning A. Metabolism Processing, B. Genetic Information Processing, C. Environmental Information Processing; Table S1: List of KEGG ortholog entries in MKAA1 vs MKAA2 bacterial libraries; Table S2: List of KEGG ortholog entries KEGG orthologs in MKAA1 vs MKAA2 yeast libraries; Table S3: KEGG orthologs exclusive in MKAA1 or MKAA2 bacteria library; Table S4: KEGG orthologs exclusive in AA1 or AA2 Yeast libraries; Table S5: KEGG Orthologs (KO) of protein genes differentially expressed in MKAA1 and MKAA2 samples represented in Pearson´s correlation plots.
Author Contributions
D.L.R., P.C.L.d.S., C.S.S.M. and A.A.B. performed the kefir propagation, RNA extraction, library creation, metatranscriptomics sequencing, and subsequent bioinformatics analyses. E.N. and Á.C.N. designed and coordinated the metatranscriptomic study. J.R.N. and G.d.R.F. contributed experimental support in Brazil. A.A.B. performed experimental analysis in Argentina. E.N., Á.C.N., A.A.B., G.L.G. and A.G.A. contributed to the manuscript’s conceptualisation, writing, revision, and discussion. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the CAPES Foundation (project n. 84/2014—GPR/DRI/CAPES) in collaboration with the MINCyT, CONICET-University National of La Plata, Argentina cooperation project, and the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) (process 2070.01.0008851/2019-41; APQ 02928-16). In Argentina, experimental work was supported by CONICET (PIP2020-2786) and ANPCyT (PICT 2020-03239).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon request. The crude sequencing data were deposited at the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Centre for Biotechnological Information (NCBI), Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database, BioProject accession PRJNA1084273.
Acknowledgments
A.A.B., G.L.G. and A.G.A. are members of the Scientific Career of CONICET. We acknowledge the CEPAD-ICB-UFMG for providing the Sagarana HPC Cluster as a computational resource. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of CONICET, ANPCyT, MINCyT- CAPES, and FAPEMIG.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Leite, A.M.O.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, A.S.; Silva, J.T.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Microbiological, Technological and Therapeutic Properties of Kefir: A Natural Probiotic Beverage. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Aquilanti, L.; De Filippis, F.; Stellato, G.; Di Mauro, S.; Turchetti, B.; Buzzini, P.; Ercolini, D.; et al. Bacteria and Yeast Microbiota in Milk Kefir Grains from Different Italian Regions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorda, F.A.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Rakshit, S.K.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; Vandenberghe, L.P.D.S.; Soccol, C.R. Microbiological, Biochemical, and Functional Aspects of Sugary Kefir Fermentation—A Review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanirati, D.F.; Abatemarco, M.J.; de Cicco Sandes, S.H.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nunes, Á.C.; Neumann, E. Selection of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Brazilian Kefir Grains for Potential Use as Starter or Probiotic Cultures. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Iraporda, C.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Kefir Micro-Organisms: Their Role in Grain Assembly and Health Properties of Fermented Milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, P.; He, X.; Sadiq, F.A.; Li, J.; Sang, Y.; Gao, J. The Complex World of Kefir: Structural Insights and Symbiotic Relationships. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasche, S.; Kim, Y.; Mars, R.A.T.; Machado, D.; Maansson, M.; Kafkia, E.; Milanese, A.; Zeller, G.; Teusink, B.; Nielsen, J.; et al. Metabolic Cooperation and Spatiotemporal Niche Partitioning in a Kefir Microbial Community. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Liu, B.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. The Biofilm Hypothesis: The Formation Mechanism of Tibetan Kefir Grains. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, F.; Junne, S.; Neubauer, P. A Big World in Small Grain: A Review of Natural Milk Kefir Starters. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londero, A.; Hamet, M.F.; De Antoni, G.L.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Kefir Grains as a Starter for Whey Fermentation at Different Temperatures: Chemical and Microbiological Characterisation. J. Dairy Res. 2012, 79, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, N.F.; Kumar, M.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdullah, J.O.; Khalid, M.; Omar, A.R.; Osman, M.A.; Mortadza, S.A.S.; Alitheen, N.B. Kefir and Its Biological Activities. Foods 2021, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Jeong, D.; Kim, H.; Seo, K.H. Modern Perspectives on the Health Benefits of Kefir in next Generation Sequencing Era: Improvement of the Host Gut Microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1782–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’hir, S.; Ayed, L.; De Pasquale, I.; Fanizza, E.; Tlais, A.Z.A.; Comparelli, R.; Verni, M.; Latronico, R.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R.; et al. Comparison of Milk Kefirs Obtained from Cow’s, Ewe’s and Goat’s Milk: Antioxidant Role of Microbial-Derived Exopolysaccharides. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, F.G.; Coitinho, L.B.; Dias, A.T.; Friques, A.G.F.; Monteiro, B.L.; de Rezende, L.C.D.; Pereira, T.d.M.C.; Campagnaro, B.P.; De Pauw, E.; Vasquez, E.C.; et al. Identification of New Bioactive Peptides from Kefir Milk through Proteopeptidomics: Bioprospection of Antihypertensive Molecules. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Du, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, P.; Du, B.; Fang, X.; Liao, Z. Kefir Microbiota and Metabolites Stimulate Intestinal Mucosal Immunity and Its Early Development. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, A.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequencing-Based Analysis of the Bacterial and Fungal Composition of Kefir Grains and Milks from Multiple Sources. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Orozco, B.D.; García-Cano, I.; Escobar-Zepeda, A.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; Álvarez, V.B. Metagenomic Analysis and Antibacterial Activity of Kefir Microorganisms. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 2933–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Kilcawley, K.; O’Sullivan, O.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. Microbial Succession and Flavor Production in the Fermented Dairy Beverage Kefir. mSystems 2016, 1, e00052-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanoeva, C.; Rios, D.; Alvarenga, R.; Acurcio, L.; Sandes, S.; Nunes, A.; Nicoli, J.; Neumann, E. Functionally Active Microbiome and Physicochemical Properties of Milk and Sugary Water Kefir from Brazil. Austin Food Sci. 2021, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, C.J.; González-Orozco, B.D.; Jiménez-Flores, R. Evaluation of Kefir Grain Microbiota, Grain Viability, and Kefir Bioactivity from Fermenting Dairy Processing By-Products. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 4259–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satir, G.; Guzel-Seydim, Z.B. How Kefir Fermentation Can Affect Product Composition? Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegin, Z.; Yurt, M.N.Z.; Tasbasi, B.B.; Acar, E.E.; Altunbas, O.; Ucak, S.; Ozalp, V.C.; Sudagidan, M. Determination of Bacterial Community Structure of Turkish Kefir Beverages via Metagenomic Approach. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 129, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, L.H.; Coakley, M.; Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. Analysis of the Milk Kefir Pan-Metagenome Reveals Four Community Types, Core Species, and Associated Metabolic Pathways. iScience 2023, 26, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentry, B.; Cazón, P.; O’Brien, K. A Comprehensive Review of the Production, Beneficial Properties, and Applications of Kefiran, the Kefir Grain Exopolysaccharide. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 144, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, N.; Gagliarini, N.; Medrano, M.; Piermaria, J.; Abraham, A. Kefiran. In Polysaccharides of Microbial Origin; Oliveira, J., Radhouani, H., Reis, R., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–12. ISBN 9783662467640. [Google Scholar]
- Rimada, P.S.; Abraham, A.G. Polysaccharide Production by Kefir Grains during Whey Fermentation. J. Dairy Res. 2001, 68, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimada, P.S.; Abraham, A.G. Comparative Study of Different Methodologies to Determine the Exopolysaccharide Produced by Kefir Grains in Milk and Whey. Lait 2003, 83, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; De Antoni, G.L. Characteristics of Kefir Prepared with Different Grain:Milk Ratios. J. Dairy Res. 1998, 65, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrie, B.C.T.; Ju, T.; Fouhse, J.M.; Forgie, A.J.; Sergi, C.; Cotter, P.D.; Willing, B.P. Kefir Microbial Composition Is a Deciding Factor in the Physiological Impact of Kefir in a Mouse Model of Obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A Revolutionary Tool for Transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashiardes, S.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Elinav, E. Use of Metatranscriptomics in Microbiome Research. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2016, 10, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, D.L.; da Silva, P.C.L.; Moura, C.S.S.; Villanoeva, C.N.B.C.; da Rocha Fernandes, G.; Bengoa, A.A.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; Nicoli, J.R.; Neumann, E.; et al. Comparative Metatranscriptome Analysis of Brazilian Milk and Water Kefir Beverages. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 27, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasapolli, R.; Schütte, K.; Schulz, C.; Vital, M.; Schomburg, D.; Pieper, D.H.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Malfertheiner, P. Analysis of Transcriptionally Active Bacteria Throughout the Gastrointestinal Tract of Healthy Individuals. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1081–1092.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; De Antoni, G.L. Inhibitory Power of Kefir: The Role of Organic Acids. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamet, M.F.; Piermaria, J.A.; Abraham, A.G. Selection of EPS-Producing Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Kefir Grains and Rheological Characterization of the Fermented Milks. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. High Speed BLASTN: An Accelerated MegaBLAST Search Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7762–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Tappu, R.; Bazinet, A.L.; Xie, C.; Cummings, M.P.; Nieselt, K.; Williams, R. Fast and Simple Protein-Alignment-Guided Assembly of Orthologous Gene Families from Microbiome Sequencing Reads. Microbiome 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-Length Transcriptome Assembly from RNA-Seq Data without a Reference Genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Identification of Protein Coding Regions in RNA Transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Leung, H.C.-M.; Luo, R.; Wong, C.-K.; Ting, H.-F.; Lam, T.-W. AC-DIAMOND v1: Accelerating Large-Scale DNA-Protein Alignment. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3744–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.R.; Barbosa, D.V.C.; Prosdocimi, F.; Pena, I.A.; Santana-Santos, L.; Coelho Junior, O.; Barbosa-Silva, A.; Velloso, H.M.; Mudado, M.A.; Natale, D.A.; et al. A Procedure to Recruit Members to Enlarge Protein Family Databases--the Building of UECOG (UniRef-Enriched COG Database) as a Model. Genet. Mol. Res. 2008, 7, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.Z.B.; Khang, T.F.; Tammi, M.T. CORNAS: Coverage-Dependent RNA-Seq Analysis of Gene Expression Data without Biological Replicates. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A Web-Based Tool for the Analysis of Sets through Venn Diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimada, P.S.; Abraham, A.G. Kefiran Improves Rheological Properties of Glucono-δ-Lactone Induced Skim Milk Gels. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, S.É.D.L.; Rocha, C.D.S.; De Moura, M.S.B.; Barcelos, M.P.; Da Silva, C.H.T.D.P.; Hage-Melim, L.I.D.S. Potential Beneficial Effects of Kefir and Its Postbiotic, Kefiran, on Child Food Allergy. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3770–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetti, E.; O’Toole, P.W. The Genomic Basis of Lactobacilli as Health-Promoting Organisms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A Taxonomic Note on the Genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 Novel Genera, Emended Description of the Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and Union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasaki, K.; Staikou, A.; Theodorou, L.G.; Charamopoulou, V.; Zacharaki, P.; Papamichael, E.M. Purification and Kinetics of Two Novel Thermophilic Extracellular Proteases from Lactobacillus Helveticus, from Kefir with Possible Biotechnological Interest. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5804–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheirsilp, B.; Suksawang, S.; Yeesang, J.; Boonsawang, P. Co-Production of Functional Exopolysaccharides and Lactic Acid by Lactobacillus Kefiranofaciens Originated from Fermented Milk, Kefir. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).