Abstract
The Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 clone, identified in the mid-1990s, has emerged as a global antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) high-risk clone, significantly contributing to the global health challenge also posed by other AMR K. pneumoniae lineages. The acquisition of a blaCTX-M-15-carrying plasmid has facilitated its widespread dissemination. At Europe’s major transport hub for the movement of live animals, Frankfurt Airport, a shipment of 20 live leopard tortoises was sampled during German border control in 2014. Phylogenetic analysis (MLST) identified a K. pneumoniae ST307 strain, prompting further investigation. Our analysis revealed the presence of a ~193 kb plasmid carrying a broad range of AMR genes, including blaCTX-M-15, blaTEM-1B, blaOXA-1, aac(3)-IIa, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, and qnrB1. Additionally, mutations in the quinolone resistance-determining region in gyrA (S83I) and parC (S80I) were detected. Phenotypic testing demonstrated resistance of the isolate to the most common antimicrobials used in both human and veterinary medicine; exceptions included carbapenems and newer β-lactamase inhibitor combinations. Because the role of imported exotic animals in the dissemination of AMR genes is largely deficient, the present study fills yet missing mosaic pieces in the complete picture of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacterales.
Keywords:
Klebsiella pneumoniae; ST307; CTX-M-15; plasmid; tortoise; antimicrobial resistance; virulence 1. Introduction
Klebsiella (K.) pneumoniae is a Gram-negative opportunistic pathogen of the Enterobacterales order that is frequently associated with antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) nosocomial infections worldwide. K. pneumoniae sequence type ST307 is an emerging AMR high-risk clone that was described in Europe in 2008 for the first time [1,2]. Since then, it has spread globally among humans and animals, causing severe hospital- and community-acquired infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract and bloodstream infections. Moreover, K. pneumoniae ST307 has become a threat to public health as it frequently produces extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) and carbapenemases, both of which are β-lactamases inactivating their corresponding antibiotic by cleaving the β-lactam ring. Therefore, both enzyme groups contribute to an AMR phenotype by hydrolyzing penicillins and cephalosporins, and in the case of carbapenemases, carbapenem antibiotics [2,3,4,5]. Among ESBLs, cefotaximase-Munich (CTX-M)-type ESBLs have become dominant in clinical Enterobacterales isolates [6]. CTX-M-15 ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae was first isolated from human urine and pulmonary specimens collected from hospitalized patients in India in 1999 [7]. Today, CTX-M-15 frequently emerges in K. pneumoniae with a multidrug-resistant (MDR) phenotype and is often associated with the presence of multiple ESBL genes, thereby accounting for limitations in antimicrobial treatment [2,6,8]. CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 has often been isolated from humans worldwide and is increasingly found in various animal species as well [5,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. In Europe, it was first isolated from an African spurred tortoise (Centrochelys sulcata) in the UK in 2019, followed by several reports on the isolation in other species, such as cats, dogs, horses, cattle, and birds [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Because the importation of live exotic companion animals is still at a high level, fundamental research on the potential risk posed by the dissemination of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria seems to be justified [25]. Therefore, it is imperative to screen for antimicrobial resistance and AMR genes of bacteria present in these imported animals. In the context of another research project analyzing the prevalence and AMR genes of Enterobacterales (unpublished data) and Acinetobacter spp. in imported pet reptiles, a K. pneumoniae ST307 strain was isolated and subsequently further analyzed [26,27]. As a result, we report here the isolation of an MDR CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 from leopard tortoises (Stigmochelys pardalis) imported to Germany from Ecuador.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Bacterial Species Identification
The acquisition and cultivation of samples were performed as previously described [26]. In brief, a pooled fecal sample was collected in 2014 at Frankfurt Airport, Germany, from a shipment of 20 farm-bred leopard tortoises from Ecuador, as declared in the relevant travel documents, in cooperation with authorized veterinarians from the Border Control Post of Frankfurt Airport. The sample was stored in a sterile, fecal sample tube at 4–7 °C and transported to the Institute of Hygiene and Infectious Diseases of Animals in less than 48 h. For cultivation, the sample was streaked onto 5% sheep blood agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), water-blue-metachrome-yellow-lactose-agar (Gassner agar; Oxoid, Wesel, Germany), and MacConkey agar (Oxoid) containing 1 mg/L cefotaxime (Sigma-Aldrich/Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) directly after arrival of the sample in the laboratory. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h in ambient air. Species identification was accomplished by MALDI-TOF MS (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany; DB 9045). All obtained isolates were stored in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth (Oxoid) containing 30% glycerol at −70 °C until further use.
2.2. Genomic Analysis
The K. pneumoniae isolate IHIT34097 was subjected to whole-genome sequencing using the Nextera XT Library Preparation Kit (Illumina GmbH, Munich, Germany), which was sequenced on a MiSeq sequencer (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) in 250 bp paired-end mode with a minimum coverage of 100-fold. Genomes were de novo assembled using SPAdes v.3.15.1. and annotated using RAST v.2.0 [28,29]. To verify the plasmid sequence, the DNA was additionally sequenced on an Oxford Nanopore GridION GI1-5 (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK) using FLO-MIN114 (R10.4.1) flow cells. Sample preparation was accomplished according to the manufacturer’s protocol without any optional steps or size selection using the Rapid Barcoding Kit SQK-RBK114-24, running on ONT’s MinKNOW control software Version 4.5.0.
The Bacterial Isolate Genome Sequence Database (BIGSdb) Version 1.42.3 was used for the detection of virulence genes, sero(geno)typing, and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) [30]. Capsule biosynthesis (K) and lipopolysaccharide antigen (O) loci were typed using Kaptive [31]. Additionally, BacWGSTdb was utilized to determine isolates with close synteny based on a core genome multilocus sequence typing (cgMLST)-based comparison [32]. All isolates with a maximum difference of 50 alleles were extracted from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database, and cgMLST allelic distances were used for the calculation of a minimum spanning tree as implemented in Ridom Seqsphere+ v9.0 [33,34]. Additionally, isolate BL714 (SRA ERS9590854), a CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 strain that was isolated in 2019 from a tortoise in the UK, was included in the minimum spanning tree (Supplementary Table S1) [24]. For the determination of plasmids and AMR genes, PlasmidFinder 2.1 and ResFinder 4.4.2 were employed [35,36]. Based on the results of PlasmidFinder, highly related plasmids were searched with the NCBI microbial nucleotide basic local alignment search tool (BLAST). They were aligned using Geneious 8.1.9 (Biomatters, Auckland, New Zealand) in order to display the complete plasmid of IHIT34097. Alignment was verified using bridging polymerase chain reactions (PCR) (Supplementary Table S2). Closely related plasmids according to single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based analysis of BacWGSTdb containing a blaCTX-M-15 gene were extracted from the NCBI database, and BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG) was used to display circular comparisons [32,33]. Plasmid pIHIT34097 was used as a reference with an upper identity threshold of 90% and a lower identity threshold of 70%, and nucleotide sequence search was performed with BLASTn (Supplementary Table S1).
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed by broth microdilution using the Merlin Micronaut-S software Version 6.00 with the companion animal layout E1-319-100 (Merlin Diagnostika GmbH, Bornheim-Hersel, Germany), which includes antimicrobial substances typically used in veterinary medicine. For antimicrobial substances utilized in human medicine, the VITEK®2 compact 15 with the VITEK®2 system (v9.03.3, bioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany) was employed (AST-N430, AST-XN24, bioMérieux).
For the detection of a hypermucoviscous phenotype, a string test was performed as previously described by Fang et al. (2004) [37]. Therefore, a fresh single colony cultivated on a 5% sheep blood agar plate (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was touched with a sterile inoculation loop. The test was considered positive if a viscous filament of >5 mm was formed.
Siderophore production was determined qualitatively by using the chrome azurol S (CAS) plate assay. Plates were prepared based on Schwyn and Neilands (1987) and 5 µL of an overnight culture of the isolate in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium [containing NaCl and yeast extract (both Merck), bacto-tryptone (Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany) and agar-agar (Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe, Germany)], adapted to an optical density (OD) at 600 nm of 0.1, were deposited on the CAS agar plate and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h [38,39]. Then, the color change in the CAS agar from blue to orange was documented and measured.
To evaluate survival in human blood, a modified version of the serum resistance assay by Taylor and Kroll (1983) was performed [40]. Bacterial cultures were set to 0.5 McFarland standard turbidity in 0.9% NaCl solution (Merck). An amount of 1 mL of the bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 7500× g for 5 min at room temperature and resuspended in 1 mL of 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Next, 100 µL of the suspension was mixed with 100 µL of human serum (Pan Biotech, Aidenbach, Germany) in 1.5 mL tubes. Subsequently, 10 µL of the mixture was serially diluted, and 50 µL of each serial dilution was plated onto LB agar plates (Merck, 0 h count plates). The tubes were incubated at 37 °C for 4 h in ambient air. A second serial dilution was then performed and plated onto LB agar plates (Merck, 4 h count plates). All plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h in ambient air. After incubation, colony-forming units (CFU) were counted. Serum-sensitive strain W3110 served as a negative and serum-resistant strain PBIO1289 as a positive control [41]. To validate the bactericidal effect of the serum, serum-sensitive W3110 mixed with heat-inactivated serum was also included as a control. The assay was performed in duplicates with one biological control.
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Chromosomal Mutations
The K. pneumoniae strain IHIT34097 isolated from a pooled fecal sample of leopard tortoises was identified as ST307, displaying the KL102 capsular type, associated with the wzi allele 173 and O2V2 serotype. Antimicrobial resistance genes included blaCTX-M-15 for ESBL production, blaTEM-1B, blaSHV-28 and blaOXA-1 for broad and narrow β-lactam resistance, respectively, and aac(3)-IIa, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, aph(3″)-Ib, and aph(6)-Id for aminoglycoside resistance. The genes qnrB1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, and oqxB-like conferring quinolone resistance were detected; additionally, mutations in the quinolone resistance determining region (QRDR) were detected in gyrA (S83I) and parC (S80I). Also, dfrA14 and sul2 for folate pathway antagonist resistance, fosA for fosfomycin resistance, and tet(A) for tetracycline resistance were found.
3.2. Virulence-Associated Genes
Strain IHIT34097 harbored the type 3 fimbrial gene cluster mrkABCDFHIJ, type 1 fimbrial gene cluster fimABCDEFGHIK, and regulatory genes rcsAB, which confer the up-regulation of cps gene expression. For siderophore production, the gene cluster for enterobactin (entABCEF, fepABCDG, fes, and ybdA) and iutA coding for the aerobactin receptor were found. Genes encoding other proteins involved in iron acquisition, such as yersiniabactin, aerobactin synthesis, and salmochelin, were not identified. The isolate was also negative for the genotoxin colibactin encoding chromosomal island gene pks and the gene cluster for the bacteriocin microcin E492. Moreover, peg344 (unspecific metabolite transporter) and rmpA/rmpA2 (synthesis of capsular polysaccharide), both attributed to a hypervirulent phenotype, were not present.
3.3. Genomic Analysis
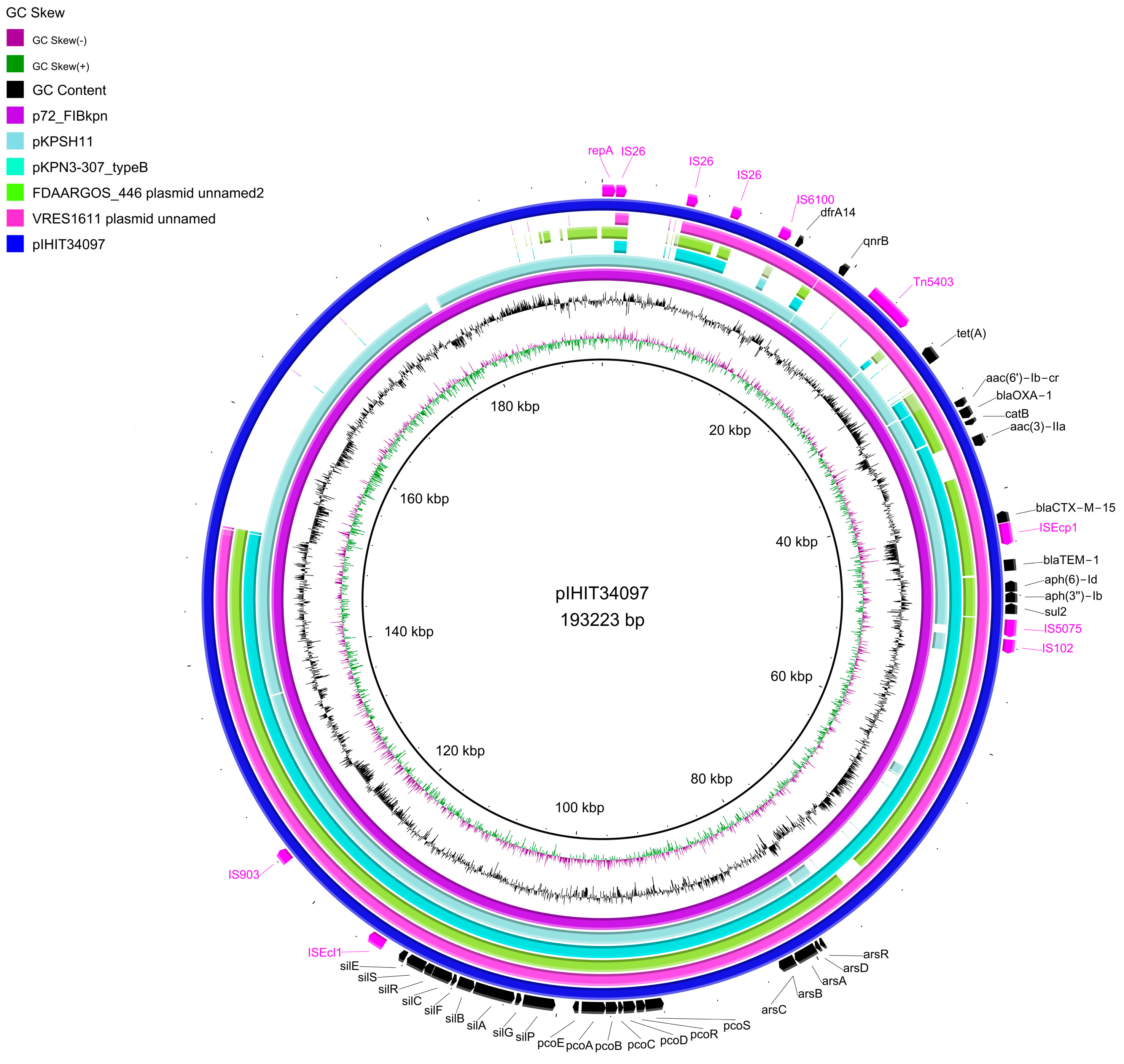
The full assembly of strain IHIT34097 resulted in the 5,493,197 bp chromosome and a 193,223 bp IncFIBK:IncFIIK plasmid termed pIHIT34097 (Bioproject ID: PRJNA1095285). Based on a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) comparison, the most closely related plasmid was p72_FIBkpn (Acc. No. NZ_CP034282.1), isolated from a human patient of an intensive care unit in a public hospital in South Africa in 2014 [42]. All detected AMR genes could be demonstrated on the plasmid pIHIT34097, except for blaSHV-28, fosA, and oqxAB, which were encoded on the chromosome. The genomic comparison showed a high similarity to other global plasmids including a conserved multi-drug resistance region of ~40 kb. This MDR region contains the genes blaCTX-M-15, blaTEM-1, blaOXA-1, aac(3)-IIa, aac(6′)Ib-cr, aph(6)-Id, aph(3″)-Ib, sul2, catB, and partially qnrB1 and dfrA14, as well as an arsenic, copper and silver resistance gene cluster (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Circular visualization of K. pneumoniae plasmids as compared to pIHIT34097 using BRIG [43]. Details of the origin and genes harbored by the plasmids are presented in Supplementary Table S1.
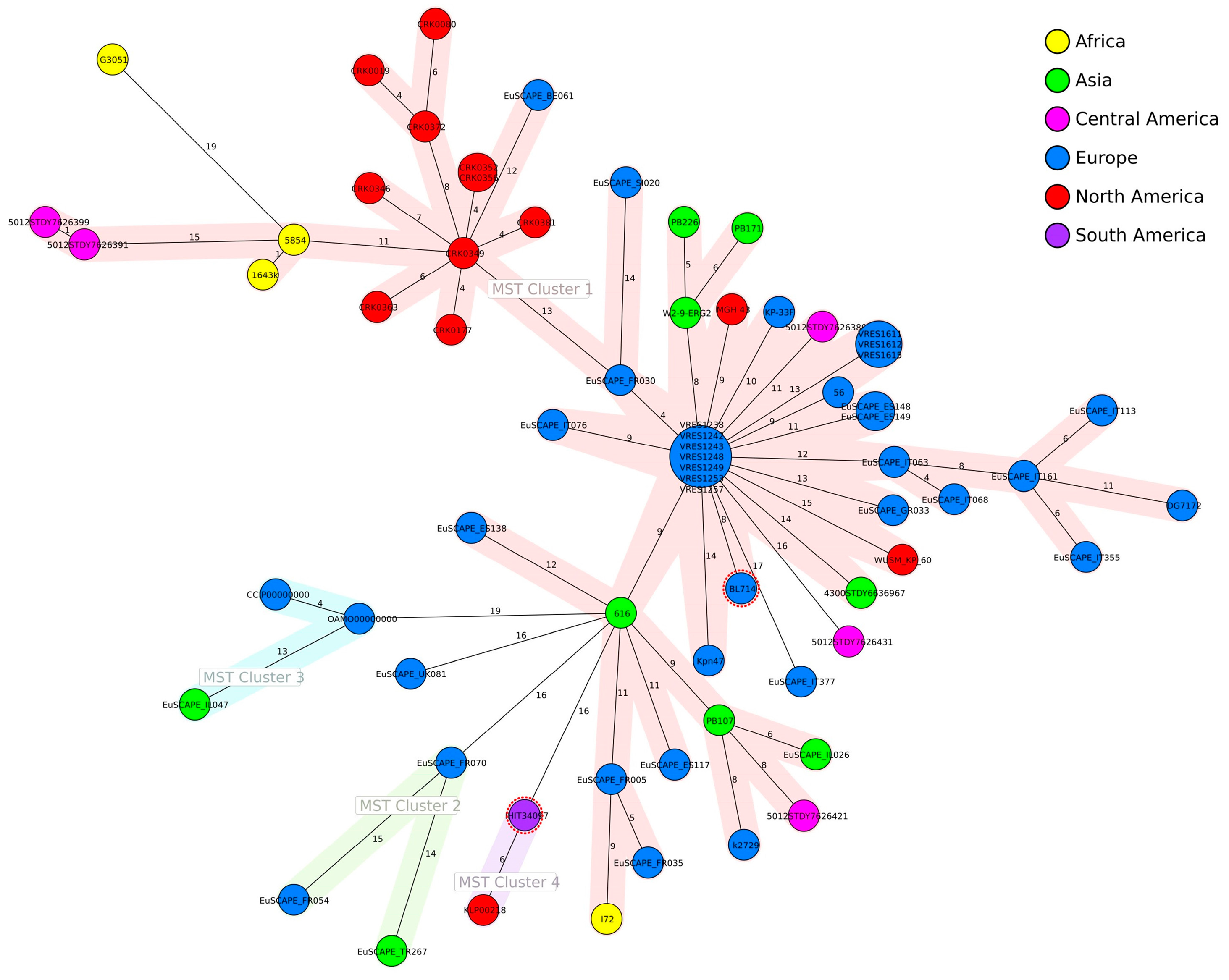
All of the 68 closely related K. pneumoniae isolates were of human origin (n = 60) or were retrieved from the environment (n = 8). Only IHIT34097 and BL714 (SRA ERS9590854) were of animal origin, both isolated from tortoises. Core genome MLST-based distance calculations revealed no clustering of isolates according to their geographical origin (Figure 2).
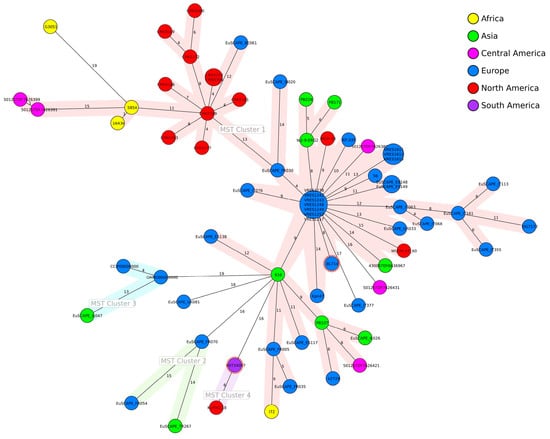
Figure 2.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on allelic distances of 70 K. pneumoniae genomes (60 × human, 8 × environment, 2 × tortoise) determined by cgMLST analysis. The nodes are colored according to the geographical origin of the strains. The size of the nodes is proportional to the number of isolates. Numbers on branches indicate allele differences between core genomes. The nodes representing IHIT34097 and BL714, both isolated from tortoises, are marked with a dotted margin. Strains are assigned to MST clusters 1 to 4 with a threshold of 15 allele differences. Details of the origin and genes harbored by the strains are presented in Supplementary Table S1.
3.4. Phenotypic Analysis
3.4.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of strain IHIT34097 revealed an MDR pattern, defined as non-susceptibility to at least one agent in three or more antimicrobial categories, according to Magiorakos et al. (2012) [44]. VITEK®2 testing confirmed an ESBL phenotype (Table 1).

Table 1.
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae strain IHIT34097, cultured from the feces of leopard tortoises.
3.4.2. Mucoid Phenotype, Siderophore Production and Serum Resistance
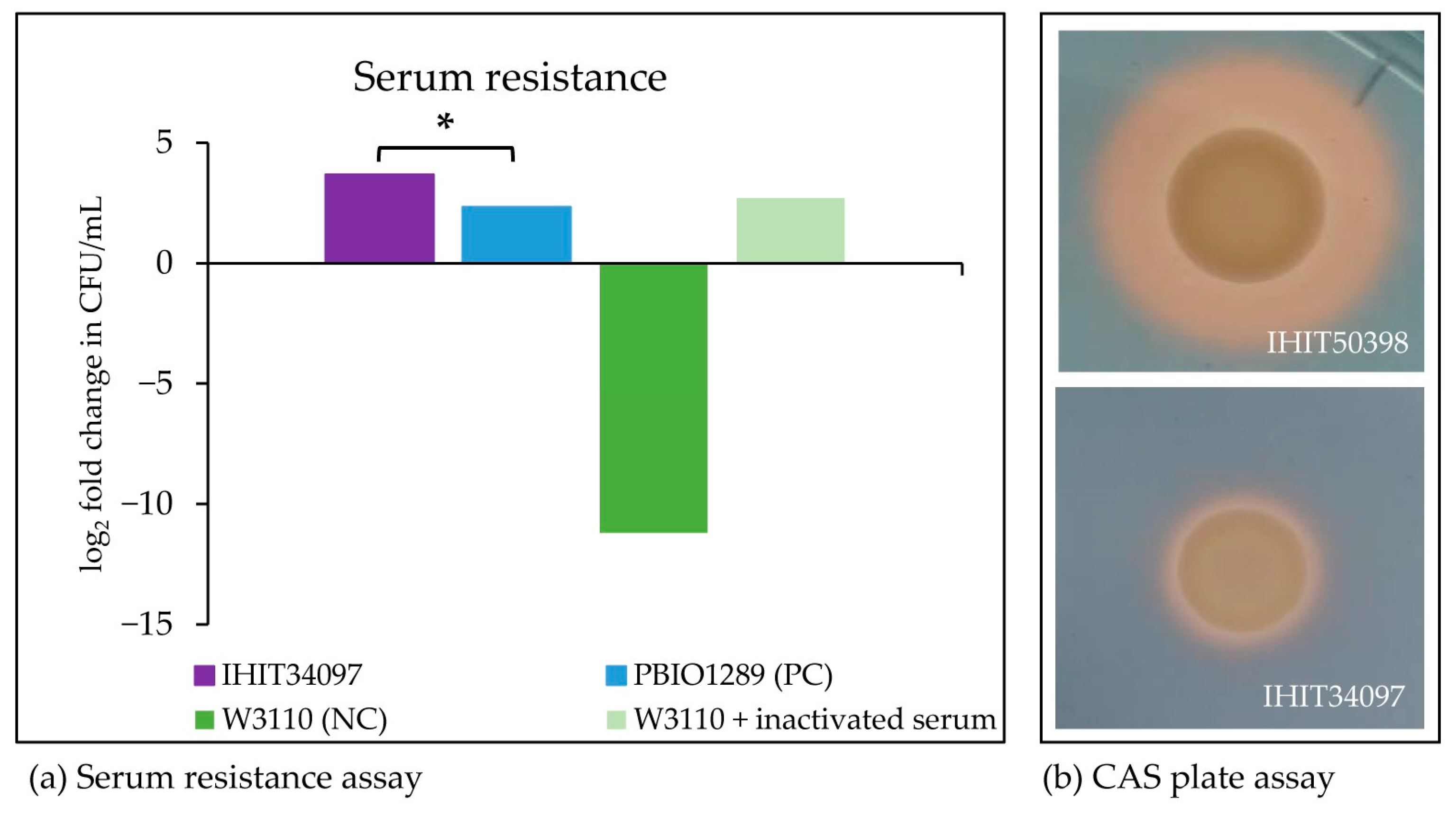
The isolate did not demonstrate a hypermucoviscous phenotype, as confirmed by the negative string test. However, it did exhibit a serum-resistant phenotype (Figure 3a). Siderophore production was detected by the qualitative CAS plate assay based on the formation of a halo. For better comparability, the halo formation of IHIT34097 is shown in Figure 3b together with the internal iucABCD positive K. pneumoniae control strain IHIT50398 (liver, pig, Germany, 2022), which displayed a very broad halo. Both isolates additionally harbored the siderophore production genes entABCEF, fepABCDG, fes, ybdA, and iutA. IHIT34097 revealed a small halo of 9.5 mm surrounding a 7.5 mm wide colony, indicating comparatively low siderophore production, possibly due to the absence of iucABCD genes, which encode for aerobactin synthesis [1,45].
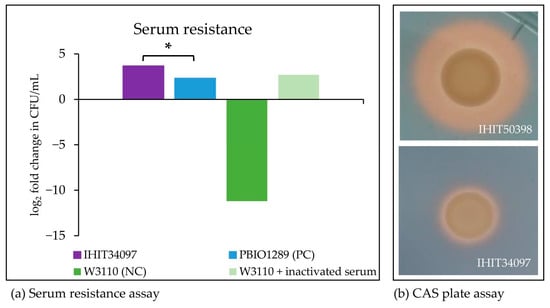
Figure 3.
Results of phenotypic virulence-associated assays. (a) Survival in 50% human serum after 0 and 4 h of incubation compared to serum-resistant strain PBIO1289 and serum-sensitive strain W3110 revealed a serum-resistant phenotype of IHIT34097. The serum-sensitive strain W3110 mixed with heat-inactivated serum was added to validate the bactericidal effect of the serum. Results are given as a log2 fold change in CFU/mL. IHIT34097 showed a significantly greater increase in growth after 4 h of incubation compared to the positive control PBIO1289 (Fisher exact * p < 0.00001; the result is significant at p < 0.05). (b) Qualitative siderophore production of IHIT34097 revealed a small halo of 9.5 mm and therefore positive siderophore production (entABCEF, fepABCDG, fes, ybdA, and iutA). For better comparability, iucABCD positive strain IHIT50398 is also shown, indicating an increased siderophore production as defined by halo comparison (16.5 mm halo, 8.5 mm colony).
4. Discussion
Initial isolation of CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 strains from mammals in Europe was documented in cats, dogs, and horses between 2012 and 2014 [18,19,21]. The first occurrence of ST307 K. pneumoniae from a reptile in Europe, namely the UK, was reported by Foster et al. (2020). In 2019, K. pneumoniae strain BL714 was isolated from the lung tissue of an African spurred tortoise (Centrochelys sulcata) deceased due to pneumonia [24]. The isolation of the CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 from leopard tortoises imported from Ecuador to Germany presented in this study dates back to 2014. This proves an earlier introduction of this strain to reptiles in Europe than previously assumed.
The isolation of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae from turtles has been reported previously from several sources. In free-living turtles, there are reports on the isolation of a temoneira (TEM)-236 and sulfhydryl variable (SHV)-12 ESBL-producing strain of Citrobacter (C.) freundii isolated from an injured loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) in Italy between 2016 and 2019 [46]. Also, Goldberg et al. (2019) reported CTX-M-15-producing strains of C. freundii and Enterobacter hormaechei isolated from the infected wrists of a captured green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas) in Brazil in 2016 [47]. In 2012, Cortés-Cortés et al. (2016) analyzed cloacal swabs from 71 adult turtles sheltered in a herpetarium in Puebla, Mexico, previously kept as pets (n = 67) or collected from household environments (n = 4). In 5.6% of the turtles CTX-M-producing E. coli were detected [48]. In addition, Hossain et al. (2020) analyzed fecal swabs from 49 turtles randomly collected from pet shops in Seoul, South Korea. Klebsiella sp. was present in 32.7% of the samples, of which 18.8% were CTX-M-positive [49]. Morrison et al. (2020) detected CTX-M-producing strains of mainly E. coli, but also Citrobacter and Enterobacter in turtle meat (frozen soft-shell turtles and a dried carapace) imported into Canada from China and Thailand in 2015 [50].
As imported reptile products are usually niche market foods, they are often not routinely targeted by national surveillance programs [50]. In 2007, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) analyzed the public health risks associated with the consumption of reptile meat, including turtle meat. The assessment highlighted the lack of data regarding the presence of bacterial species and drug residues of veterinary medicines in farmed reptiles and reptile meat, apart from the well-documented high contamination rates of Salmonella [51,52]. Although imports of reptile meat into the European Union increased by more than 50% between 2007 and 2017, data on biological hazards are still limited [53]. Turtle farming for meat production focuses mainly on freshwater turtle species, particularly the Chinese softshell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) in Asia and the diamondback terrapin (Malaclemys terrapin) in the USA [52]. As the leopard tortoise is a protected terrestrial species that is not typically farmed for meat production, it is likely that the leopard tortoises from which IHIT34097 was isolated were imported for the pet market [54]. With respect to Ecuador as the country of origin, it cannot be ruled out that the information in the shipping documents was incorrect. Although breeding facilities for the restoration of giant tortoises on the Galapagos Islands have been reported in Ecuador, to the authors’ knowledge, there are no sources to support the existence of breeding facilities for leopard tortoises native to Africa in South America [55].
With proper hygiene measures (e.g., hand washing after reptile contact), there is, like in the well-documented cases of pet turtle-associated human salmonellosis, a negligible zoonotic risk. The same holds true also for the aforementioned findings of CTX-M-producing Enterobacteriaceae in pet turtles. Among the plethora of sources for AMR bacteria, it is not surprising that imported reptiles also represent potential reservoirs for ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae [49,56,57]. While reptiles are still popular pets, the isolation of MDR isolates like IHIT34097 represents yet missing mosaic pieces in the complete picture of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae in reptiles in general and CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 in particular.
In Europe, some of the most commonly used antimicrobials in reptile medicine appear to be fluoroquinolones and third-generation cephalosporins [58]. Additionally, the use of doxycycline, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and amikacin is recommended. In Ecuador, there are no official reports of the use of antimicrobial substances in most species, but the majority of the antibiotics can be acquired without prescription [59]. According to Nieto-Claudin et al. (2021), antimicrobials often used for farm animals and small animals are penicillin, oxytetracycline, gentamicin, erythromycin, and streptomycin [59]. To address this data gap, a five-year plan to establish a national surveillance system for AMR in humans, animals and the environment was implemented by the government in 2019. Also, the use of products containing colistin in animals was prohibited [60]. As our sample originates from farm-bred animals, the tortoises may have been treated with antimicrobials by the breeder. Unfortunately, no data was available to the authors. Another possibility for obtaining antimicrobial resistance is contact with AMR bacteria from the environment. In recent years, the contamination of the environment with AMR genes caused by agricultural production, solid waste disposal, and wastewater management has attracted increasing attention [61]. Wild animals or farm animals can then serve as reservoirs, and AMR bacteria can be reintroduced to humans [62]. Exposure to urban-impacted coastal waters is suggested as the reason for the isolation of human-associated bacteria in wild sea turtles, serving as bioindicators for human pollution in marine habitats [46,47]. Several studies have highlighted the burden of AMR genes in giant tortoises (Chelonoidis spp.) on the Galapagos archipel. They found between 34.0% and 35.7% of MDR isolates in the microbiome of these turtles, as well as high rates of tetracycline resistance [59,63,64].
Fortunately, IHIT34097 demonstrated susceptibility or intermediate susceptibility to all antimicrobial agents in the reserve group according to the World Health Organization (WHO) AWaRe (access, watch, reserve) classification of 2023.
In 2019, an outbreak of an extensively drug-resistant K. pneumoniae ST307 lineage associated with hypervirulence was recorded in four medical facilities in north-eastern Germany, adding to the growing number of global reports of known K. pneumoniae high-risk clones (e.g., ST11, ST147, and ST307) developing an MDR and hypervirulent phenotype [1,65]. While convergent MDR and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae (hvKp) have been documented in animals, to the authors’ knowledge, the documentation of MDR hvKp ST307 is limited to human isolation [19]. In order to monitor the further spread of the hvKp pathotype, we conducted phenotypic and genotypic tests specific to hvKp. Screening for the genotoxin colibactin encoding gene island pks was also conducted. It is closely related to the hvKp pathotype, as most pks positive isolates belong to the main hypervirulent sequence type ST23 and serotype K1 [66]. Furthermore, the acquisition of colibactin is assumed to be a critical event in the increase in hvKp within the CG23-I sublineage, contributing to its subsequent global spread. In hvKp, pks is often found on the mobile genetic element ICEKp10 alongside genes for microcin E492, the combination of which is thought to confer a strong colonization advantage over other Enterobacteriaceae in the presence of salmochelin, enabling cellular uptake of microcin E492 [67]. However, our isolate did not harbor pks or the genes for microcin E492 or salmochelin. Furthermore, IHIT34097 did not exhibit phenotypic characteristics of a hypervirulent pathotype, such as hypermucovisity or indication of extensive production of siderophores, nor did it possess genotypic markers like peg344, iucA, rmpA, and rmpA2.
The blaCTX-M-15 gene was located in close proximity to ISEcp1, both harbored by the IncF plasmid. ISEcp1 is recognized for its efficient mobilization of blaCTX-M genes within the Enterobacteriaceae family [3,68]. Furthermore, the isolate harbors mutations in gyrA (S83L) and parC (S80I) within the quinolone resistance region, placing it within a lineage of widespread global distribution [2,18,19,69]. In support of this finding, core genome MLST-based distance calculations with closely related K. pneumoniae ST307 strains revealed no clustering according to geographic origin, while the closest related plasmids detected by single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based analysis originated from South Africa, the UK, Israel, and Canada. Previous isolates with similar plasmids have also been recovered from South America; however, there are no reports of isolates originating from Ecuador. Additionally, the IncF plasmid is associated with the AMR genes blaTEM-1, blaOXA-1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, qnrB1, oqxAB, sul2, dfrA14, catB3, and fosA [2,42,70].
This study highlights the role of imported reptiles as a possible source of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae, including CTX-M-15-producing K. pneumoniae ST307, posing a potential threat to human and animal health. Since 2017, the WHO Global Priority Pathogens List has classified ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae as a critical public health threat as it compromises the treatment of infectious diseases [71]. Given the putative transmission of K. pneumoniae to humans, inadequate hygiene measures when handling reptiles can lead to a risk of human infection [49].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020054/s1. Table S1: Plasmids and K. pneumoniae genomes with high similarity to pIHIT34097 and to IHIT34097; Table S2: Bridging PCRs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.E., T.J.S. and S.A.; methodology, T.J.S. and S.A.; software, S.A.; validation, C.E., T.J.S. and S.A.; formal analysis, T.J.S. and S.A.; investigation, T.J.S., S.A., F.U. and T.E.; resources, C.E.; data curation, T.J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, T.J.S. and S.A.; writing—review and editing, C.E.; visualization, T.J.S. and S.A.; supervision, C.E.; project administration, C.E.; funding acquisition, C.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The basic study was co-funded by the Ingo and Waltraud Pauler-Fonds of the German Herpetological Society (DGHT), and F.U. was awarded a scholarship from the Justus Liebig University Giessen, Germany.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in this study is openly available under NCBI BioProject PRJNA1095285, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/1095285, accessed on 15 April 2024.
Acknowledgments
We thank Katharina Schaufler and Elias Eger from the Helmholtz Institute for One Health in Greifswald, Germany, for their help in establishing the methods for phenotypic testing of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae. We also thank Torsten Semmler, Silver Wolf and Lakshmipriya Thrukonda of the Genome Competence Centre of the Robert Koch Institute in Berlin, Germany, for their support regarding whole-genome sequencing and for processing raw sequence data. Additionally, we thank Ursula Leidner for her excellent technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Heiden, S.E.; Hübner, N.-O.; Bohnert, J.A.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Kramer, A.; Balau, V.; Gierer, W.; Schaefer, S.; Eckmanns, T.; Gatermann, S.; et al. A Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 outbreak clone from Germany demonstrates features of extensive drug resistance, hypermucoviscosity, and enhanced iron acquisition. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirano, G.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Pitout, J.D.D. Emerging antimicrobial-resistant high-risk Klebsiella pneumoniae clones ST307 and ST147. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01148-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, R. Growing group of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: The CTX-M enzymes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Oh, J.Y.; Sum, S.; Park, H.M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella species isolated from clinically ill companion animals. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 22, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbolu, D.O.; Alli, O.A.T.; Webber, M.A.; Oluremi, A.S.; Oloyede, O.M. CTX-M-15 is established in most multidrug-resistant uropathogenic Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonaceae from hospitals in Nigeria. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. (Bp) 2018, 8, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Poirel, L.; Nagarajan, S.; Nordmann, P. Plasmid-mediated extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (CTX-M-3 like) from India and gene association with insertion sequence ISEcp1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 201, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Lokate, M.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Arends, J.; Lo-Ten Foe, J.; Grundmann, H.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Friedrich, A.W. Characterization of a CTX-M-15 producing Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak strain assigned to a novel sequence type (1427). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufler, K.; Nowak, K.; Düx, A.; Semmler, T.; Villa, L.; Kourouma, L.; Bangoura, K.; Wieler, L.H.; Leendertz, F.H.; Guenther, S. Clinically relevant ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae ST307 and E. coli ST38 in an urban West African rat population. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, Y.M.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Dropa, M.; Lincopan, N.; Gomes, V.T.M.; Moreno, L.Z.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Moreno, A.M.; Knöbl, T. Pandemic clones of CTX-M-15 producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15, ST147, and ST307 in companion parrots. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, L.; Sellera, F.P.; Moura, Q.; Cardoso, B.; Cerdeira, L.; Lincopan, N. Multidrug-resistant CTX-M-15-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 causing urinary tract infection in a dog in Brazil. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 19, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sghaier, S.; Abbassi, M.S.; Pascual, A.; Serrano, L.; Díaz-De-Alba, P.; Said, M.B.; Hassen, B.; Ibrahim, C.; Hassen, A.; López-Cerero, L. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from animal origin and wastewater in Tunisia: First detection of O25b-B23-CTX-M-27-ST131 Escherichia coli and CTX-M-15/OXA-204-producing Citrobacter freundii from wastewater. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, S.A.; Mediannikov, O.; Abdallah, R.; Kuete Yimagou, E.; Medkour, H.; Dubourg, G.; Elamire, Y.; Afouda, P.; Ngom, I.I.; Angelakis, E.; et al. Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clones from wild chimpanzees and termites in Senegal. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0255720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerji, S.; Sahibzada, S.; Abraham, R.; Stegger, M.; Jordan, D.; Hampson, D.J.; O’Dea, M.; Lee, T.; Abraham, S. Proximity to human settlement is directly related to carriage of critically important antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in silver gulls. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 280, 109702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Castillo, D.; Shiva, C.; Lincopan, N.; Sano, E.; Fontana, H.; Streicker, D.G.; Mahamat, O.O.; Falcon, N.; Godreuil, S.; Benavides, J.A. Global high-risk clone of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 emerging in livestock in Peru. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Shimizu, T.; Mukai, Y.; Kuwajima, K.; Sato, T.; Usui, M.; Tamura, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Tsuyuki, Y.; et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella spp. isolates from companion animals in Japan: Clonal dissemination of multidrug-resistant extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Alonso, C.A.; Silva, V.; Pimenta, P.; Cunha, R.; Martins, C.; Igrejas, G.; Torres, C.; Poeta, P. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from healthy and sick dogs in Portugal. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Cabal Rosel, A.; Szostak, M.P.; Licka, T.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W.; Spergser, J. Broad-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Klebsiella spp. isolated from diseased horses in Austria. Animals 2020, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Fierro, R.; Drapeau, A.; Dazas, M.; Saras, E.; Rodrigues, C.; Brisse, S.; Madec, J.-Y.; Haenni, M. Comparative phylogenomics of ESBL-, AmpC- and carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae originating from companion animals and humans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Cabassi, C.S.; Fiaccadori, E.; Cavirani, S.; Parisi, A.; Bacci, C.; Lamperti, L.; Rega, M.; Conter, M.; Marra, F.; et al. Detection of carbapenemase- and ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from bovine bulk milk and comparison with clinical human isolates in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 387, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin-Puget, L.; El Garch, F.; Bertrand, X.; Valot, B.; Hocquet, D. Genome analysis of Enterobacteriaceae with non-wild type susceptibility to third-generation cephalosporins recovered from diseased dogs and cats in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 242, 108601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Salinas, F.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.; García-Meniño, I.; Lumbreras, P.; López-Beceiro, A.M.; Fidalgo, L.E.; Rodicio, M.R.; Mora, A.; Fernández, J. High prevalence and diversity of cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae including extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli CC648 lineage in rural and urban dogs in Northwest Spain. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brilhante, M.; Gobeli Brawand, S.; Endimiani, A.; Rohrbach, H.; Kittl, S.; Willi, B.; Schuller, S.; Perreten, V. Two high-risk clones of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae that cause infections in pets and are present in the environment of a veterinary referral hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; AbuOun, M.; Pizzi, R.; Tennant, B.; McCall, M.; Anjum, M.F. Isolation of the human-associated blaCTX-M-15-harbouring Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 from a tortoise in the UK. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2, acmi000172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CITES Secretariat. World Wildlife Trade Report 2022 (a Pilot Edition for CoP19). Available online: https://bvearmb.do/handle/123456789/3779 (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Unger, F.; Eisenberg, T.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Leidner, U.; Semmler, T.; Ewers, C. Imported pet reptiles and their “blind passengers”-in-depth characterization of 80 Acinetobacter species isolates. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, F.; Eisenberg, T.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Leidner, U.; Ludwig, M.-L.; Rothe, M.; Semmler, T.; Ewers, C. Imported reptiles as a risk factor for the global distribution of Escherichia coli harbouring the colistin resistance gene mcr-1. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPAdes v.3.15.1. Available online: http://cab.spbu.ru/software/spades/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- RAST v.2.0. Available online: http://rast.nmpdr.org/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Bacterial Isolate Genome Sequence Database (BIGSdb) Version 1.42.3. Available online: https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Kaptive. Available online: https://kaptive-web.erc.monash.edu/ (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- BacWGSTdb. Available online: http://bacdb.cn/BacWGSTdb/ (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- NCBI Database. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/ (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Jünemann, S.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Prior, K.; Albersmeier, A.; John, U.; Kalinowski, J.; Mellmann, A.; Goesmann, A.; von Haeseler, A.; Stoye, J.; et al. Updating benchtop sequencing performance comparison. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PlasmidFinder 2.1. Available online: https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/PlasmidFinder/ (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- ResFinder 4.4.2. Available online: http://genepi.food.dtu.dk/resfinder (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Fang, C.-T.; Chuang, Y.-P.; Shun, C.-T.; Chang, S.-C.; Wang, J.-T. A novel virulence gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing primary liver abscess and septic metastatic complications. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J.B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himpsl, S.D.; Mobley, H.L.T. Siderophore detection using chrome azurol S and cross-feeding assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2021, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.W.; Kroll, H.P. Killing of an encapsulated strain of Escherichia coli by human serum. Infect. Immun. 1983, 39, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, E.; Heiden, S.E.; Becker, K.; Rau, A.; Geisenhainer, K.; Idelevich, E.A.; Schaufler, K. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 420 with a chromosomally inserted virulence plasmid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.; Kock, M.M.; Coetzee, J.; Hoosien, E.; Peirano, G.; Strydom, K.-A.; Ehlers, M.M.; Mbelle, N.M.; Shashkina, E.; Haslam, D.B.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 with blaOXA-181, South Africa, 2014-2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.-T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; La Hoz, R.M.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of biomarkers for differentiation of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from classical K. pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, A.; Cirilli, M.; Marinaro, M.; Bosak, S.; Diakoudi, G.; Ciccarelli, S.; Paci, S.; Buonavoglia, D.; Corrente, M. Detection of multi-drug resistance and AmpC β-lactamase/extended-spectrum β-lactamase genes in bacterial isolates of loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta) from the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.W.; Fernandes, M.R.; Sellera, F.P.; Costa, D.G.C.; Loureiro Bracarense, A.P.; Lincopan, N. Genetic background of CTX-M-15-producing Enterobacter hormaechei ST114 and Citrobacter freundii ST265 co-infecting a free-living green turtle (Chelonia mydas). Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés-Cortés, G.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Torres, C.; Castañeda, M.; Sánchez, G.M.; Alonso, C.A.; López-Pliego, L.; Mayen, M.G.G.; Martínez-Laguna, Y.; Del Rocha-Gracia, R.C. Detection and molecular characterization of Escherichia coli strains producers of extended-spectrum and CMY-2 type beta-lactamases, isolated from turtles in Mexico. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; de Silva, B.C.J.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Heo, G.-J. Phylogenetic relationships, virulence and antimicrobial resistance properties of Klebsiella sp. isolated from pet turtles in Korea. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, B.J.; Rubin, J.E. Detection of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria from imported reptile and amphibian meats. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colon, V.A.; Lugsomya, K.; Lam, H.K.; Wahl, L.C.; Parkes, R.S.V.; Cormack, C.A.; Horlbog, J.A.; Stevens, M.; Stephan, R.; Magouras, I. Serotype diversity and antimicrobial resistance profile of Salmonella enterica isolates from freshwater turtles sold for human consumption in wet markets in Hong Kong. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 912693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion of the panel on biological hazards on a request from the European Commission on public health risks involved in the human consumption of reptile meat. EFSA J. 2007, 578, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU Considers Limit for Salmonella Levels in Reptile Meat. Available online: https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2019/01/eu-considers-limit-for-salmonella-levels-in-reptile-meat/ (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- CITES Appendices I, II and III. Available online: https://cites.org/eng/app/appendices.php (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Cayot, L.J. The restoration of giant tortoise and land iguana populations in Galapagos. Galapagos Res. 2008, 65, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pees, M.; Brockmann, M.; Steiner, N.; Marschang, R.E. Salmonella in reptiles: A review of occurrence, interactions, shedding and risk factors for human infections. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1251036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zając, M.; Skarżyńska, M.; Lalak, A.; Kwit, R.; Śmiałowska-Węglińska, A.; Pasim, P.; Szulowski, K.; Wasyl, D. Salmonella in captive reptiles and their environment-can we tame the dragon? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Whitehead, M.L.; Munns, C.; Pellett, S.; Abou-Zahr, T.; Calvo Carrasco, D.; Wissink-Argilaga, N. Antibiotic stewardship for reptiles. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Claudin, A.; Deem, S.L.; Rodríguez, C.; Cano, S.; Moity, N.; Cabrera, F.; Esperón, F. Antimicrobial resistance in Galapagos tortoises as an indicator of the growing human footprint. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancha, G.; Celis, Y.; Irazabal, J.; Falconi, M.; Villacis, K.; Thekkur, P.; Nair, D.; Perez, F.; Verdonck, K. High levels of antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella from poultry in Ecuador. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2023, 47, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, A.M.; Ahlstrom, C.A. Antibiotic resistant bacteria in wildlife: Perspectives on trends, acquisition and dissemination, data gaps, and future directions. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.; Wang, J.; Fanning, S.; McMahon, B.J. Antimicrobial resistance in wildlife: Implications for public health. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Claudin, A.; Esperón, F.; Blake, S.; Deem, S.L. Antimicrobial resistance genes present in the faecal microbiota of free-living Galapagos tortoises (Chelonoidis porteri). Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, E.; Hong, P.-Y.; Bedon, L.C.; Mackie, R.I. Carriage of antibiotic-resistant enteric bacteria varies among sites in Galapagos reptiles. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: An update on epidemiology, detection and antibiotic resistance. Acta Microbiol. Et Immunol. Hung. 2023, 70, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Jian, Z.; Yan, Q.; Tang, B.; Yang, A.; Liu, W. Genomic and clinical characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae carrying the pks island. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1189120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, A.J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D. The role of epidemic resistance plasmids and international high-risk clones in the spread of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 565–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Hawkey, J.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Fostervold, A.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Hamidian, M.; Howden, B.P.; Löhr, I.H.; Holt, K.E. Emergence and rapid global dissemination of CTX-M-15-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ST307. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance plasmid families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-needed/en/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).