Longitudinal Sequencing and Variant Detection of SARS-CoV-2 across Southern California Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Handling
2.2. Wastewater Sample RNA Extraction
2.3. Sequencing Library Preparation
2.4. Bioinformatics and Sequence Data Processing
2.5. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Library Statistics, Sample Composition, and SARS-CoV-2 Genome Coverage
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 Read Classification
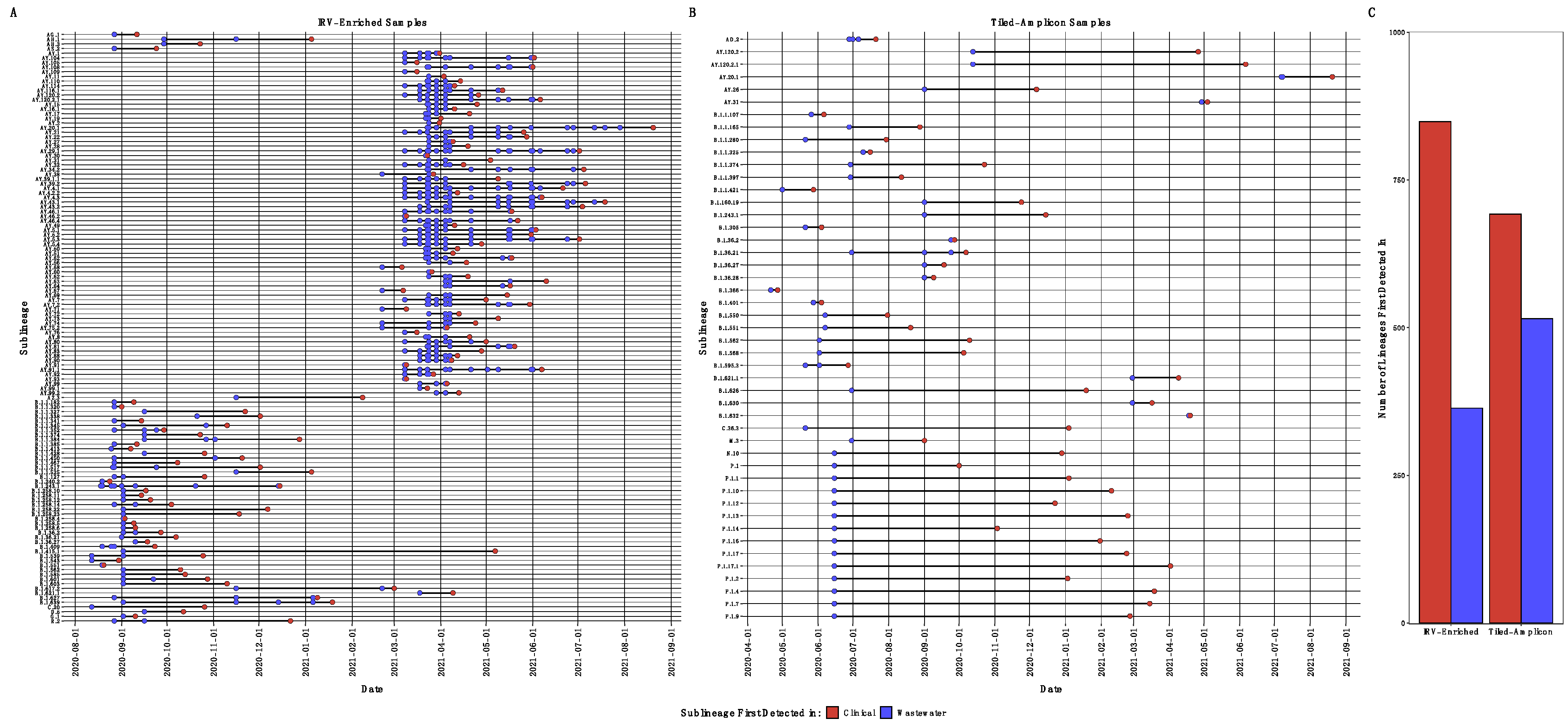
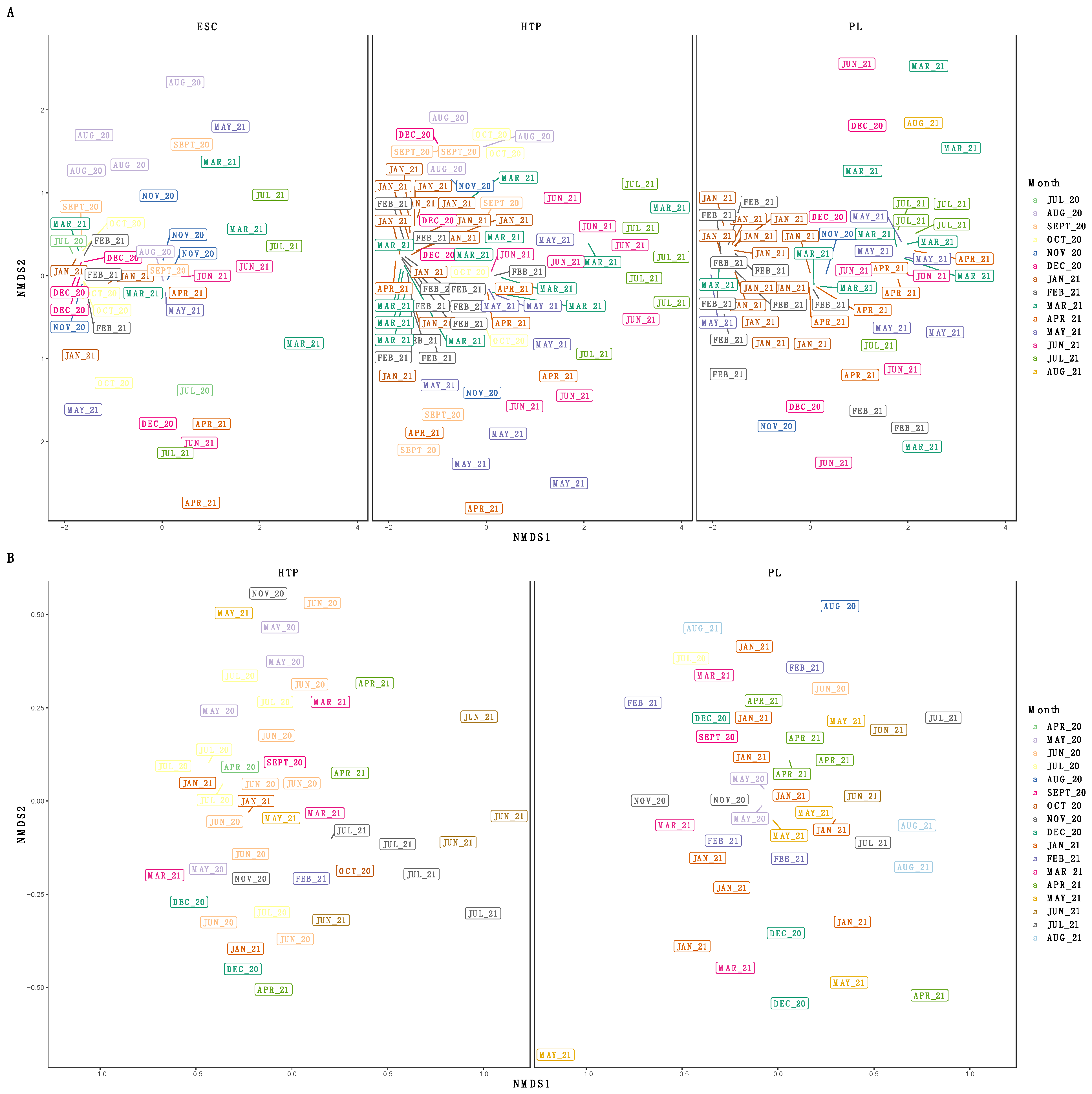
3.3. Diversity of SARS-CoV-2 Subclades
3.4. SARS-CoV-2 Single Nucleotide Variants
4. Discussion
4.1. Classifying SARS-CoV-2 Reads and Comparing Wastewater to Clinical Sequencing
4.2. Identifying SARS-CoV-2 Single Nucleotide Variants
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An Interactive Web-Based Dashboard to Track COVID-19 in Real Time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.-W.; Kok, K.-H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.-W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genomic Characterization of the 2019 Novel Human-Pathogenic Coronavirus Isolated from a Patient with Atypical Pneumonia after Visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, R.C.; Barber, R.M.; Collins, J.K.; Zheng, P.; Adolph, C.; Albright, J.; Antony, C.M.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Bachmeier, S.D.; Bang-Jensen, B.; et al. Modeling COVID-19 Scenarios for the United States. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Lee, W.L.; Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Chandra, F.; Armas, F.; Xiao, A.; Leifels, M.; Rhode, S.F.; Wuertz, S.; et al. Making Waves: Wastewater Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in an Endemic Future. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, H.; Lindsay, C.; Kumar, M. COVID-19 Outbreak: Implications on Healthcare Operations. TQM J. 2020, 39, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharara, N.; Endo, N.; Duvallet, C.; Ghaeli, N.; Matus, M.; Heussner, J.; Olesen, S.W.; Alm, E.J.; Chai, P.R.; Erickson, T.B. Wastewater Network Infrastructure in Public Health: Applications and Learnings from the COVID-19 Pandemic. PLOS Glob. Public Health 2021, 1, e0000061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Ronquillo, N.; Belda-Ferre, P.; Alvarado, D.; Javidi, T.; Longhurst, C.A.; Knight, R. High-Throughput Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 Detection Enables Forecasting of Community Infection Dynamics in San Diego County. mSystems 2021, 6, e00045-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.C.; Thompson, J.R.; Filho, C.R.M.; Street, R.; Li, X.; Castiglioni, S.; Thomas, K.V. A World of Wastewater-Based Epidemiology. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, C.C.; Roman, F.A., Jr.; Alvarado, A.G.F.; Tariqi, A.Q.; Deeming, M.A.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; Rose, J.B.; Medema, G.; Ahmed, W.; et al. Show Us the Data: Global COVID-19 Wastewater Monitoring Efforts, Equity, and Gaps. FEMS Microbes 2023, 4, xtad003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccia, J.; Zulli, A.; Brackney, D.E.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Kaplan, E.H.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Ko, A.I.; Malik, A.A.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; et al. Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater Tracks Community Infection Dynamics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivins, A.; North, D.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmed, W.; Alm, E.; Been, F.; Bhattacharya, P.; Bijlsma, L.; Boehm, A.B.; Brown, J.; et al. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology: Global Collaborative to Maximize Contributions in the Fight against COVID-19. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7754–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrom, D.; Elston, L.; Washington, J.; Prettyjohns, M.; Cann, K.; Myles, S.; Groves, P. Effectiveness of Tests to Detect the Presence of SARS-CoV-2 Virus, and Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, to Inform COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Rapid Systematic Review. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2022, 27, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Whitaker, B.; Murray, J.; Kamili, S.; Lynch, B.; Malapati, L.; Burke, S.A.; Harcourt, J.; et al. US CDC Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Panel for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, C.; Walker, P.G.T.; Alhaffar, M.; Hamlet, A.; Djaafara, B.A.; Ghani, A.; Ferguson, N.; Dahab, M.; Checchi, F.; Watson, O.J. Under-Reporting of Deaths Limits Our Understanding of True Burden of COVID-19. BMJ 2021, 375, n2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasmieh, S.A.; Robertson, M.M.; Teasdale, C.A.; Kulkarni, S.G.; McNairy, M.; Borrell, L.N.; Nash, D. The Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Uptake of COVID-19 Antiviral Treatments during the BA.2/BA.2.12.1 Surge, New York City, April-May 2022. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitsma, M.B.; Claypool, A.L.; Vargo, J.; Shete, P.B.; McCorvie, R.; Wheeler, W.H.; Rocha, D.A.; Myers, J.F.; Murray, E.L.; Bregman, B.; et al. Racial/Ethnic Disparities In COVID-19 Exposure Risk, Testing, And Cases At The Subcounty Level In California. Health Aff. 2021, 40, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Xiao, A.; Zhang, J.; Moniz, K.; Endo, N.; Armas, F.; Bonneau, R.; Brown, M.A.; Bushman, M.; Chai, P.R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RNA Concentrations in Wastewater Foreshadow Dynamics and Clinical Presentation of New COVID-19 Cases. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, J.A.; Loveless, T.B.; Kapcia, J., 3rd; Adams, E.D.; Steele, J.A.; Zimmer-Faust, A.G.; Langlois, K.; Wanless, D.; Griffith, M.; Mao, L.; et al. RNA Viromics of Southern California Wastewater and Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Single-Nucleotide Variants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0144821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Gupta, R.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Fera, D.; Shafer, R.W. The Biological and Clinical Significance of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badua, C.L.D.C.; Baldo, K.A.T.; Medina, P.M.B. Genomic and Proteomic Mutation Landscapes of SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1702–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, Á.; Scher, E.; Underwood, A.; Jackson, B.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Colquhoun, R.; Ruis, C.; Abu-Dahab, K.; Taylor, B.; et al. Assignment of Epidemiological Lineages in an Emerging Pandemic Using the Pangolin Tool. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; O’Toole, Á.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Ruis, C.; du Plessis, L.; Pybus, O.G. A Dynamic Nomenclature Proposal for SARS-CoV-2 Lineages to Assist Genomic Epidemiology. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Alm, E.; Broberg, E.K.; Connor, T.; Hodcroft, E.B.; Komissarov, A.B.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Melidou, A.; Neher, R.A.; O’Toole, Á.; Pereyaslov, D.; et al. Geographical and Temporal Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 Clades in the WHO European Region, January to June 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Kmiec, D.; Koepke, L.; Zech, F.; Jacob, T.; Sparrer, K.M.J.; Kirchhoff, F. Omicron: What Makes the Latest SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern So Concerning? J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0207721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crits-Christoph, A.; Kantor, R.S.; Olm, M.R.; Whitney, O.N.; Al-Shayeb, B.; Lou, Y.C.; Flamholz, A.; Kennedy, L.C.; Greenwald, H.; Hinkle, A.; et al. Genome Sequencing of Sewage Detects Regionally Prevalent SARS-CoV-2 Variants. mBio 2021, 12, 1110–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenele, R.S.; Kraberger, S.; Hadfield, J.; Driver, E.M.; Bowes, D.; Holland, L.A.; Faleye, T.O.C.; Adhikari, S.; Kumar, R.; Inchausti, R.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Provides Insights into Circulating Variants. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Gao, K.; Hozumi, Y.; Yin, C.; Wei, G.-W. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Mutations in the United States Suggests Presence of Four Substrains and Novel Variants. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Rouchka, E.C.; Chariker, J.H.; Chung, D. Variant Analysis of 1040 SARS-CoV-2 Genomes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Levy, J.I.; De Hoff, P.; Humphrey, G.; Birmingham, A.; Jepsen, K.; Farmer, S.; Tubb, H.M.; Valles, T.; Tribelhorn, C.E.; et al. Wastewater Sequencing Reveals Early Cryptic SARS-CoV-2 Variant Transmission. Nature 2022, 609, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, D.S.; Trujillo, M.; Gregory, D.A.; Cheung, K.; Gao, A.; Graham, M.; Guan, Y.; Guldenpfennig, C.; Hoxie, I.; Kannoly, S.; et al. Tracking Cryptic SARS-CoV-2 Lineages Detected in NYC Wastewater. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.; Tillett, R.L.; Papp, K.; Shen, S.; Gu, R.; Gorzalski, A.; Siao, D.; Markland, R.; Chang, C.-L.; Baker, H.; et al. Use of Wastewater Surveillance for Early Detection of Alpha and Epsilon SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Estimation of Overall COVID-19 Infection Burden. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, K.M.; Allen, D.J.; Fine, P.; Asghar, H. The Challenges of Informative Wastewater Sampling for SARS-CoV-2 Must Be Met: Lessons from Polio Eradication. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e189–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilder, M.L.; Middleton, F.; Larsen, D.A.; Du, Q.; Fenty, A.; Zeng, T.; Insaf, T.; Kilaru, P.; Collins, M.; Kmush, B.; et al. Co-Quantification of CrAssphage Increases Confidence in Wastewater-Based Epidemiology for SARS-CoV-2 in Low Prevalence Areas. Water Res. X 2021, 11, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J.A.; Zimmer-Faust, A.G.; Griffith, J.F.; Weisberg, S.B. Sources of Variability in Methods for Processing, Storing, and Concentrating SARS-CoV-2 in Influent from Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.J.; McClary, J.S. The Flux and Impact of Wastewater Infrastructure Microorganisms on Human and Ecosystem Health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achak, M.; Alaoui Bakri, S.; Chhiti, Y.; M’hamdi Alaoui, F.E.; Barka, N.; Boumya, W. SARS-CoV-2 in Hospital Wastewater during Outbreak of COVID-19: A Review on Detection, Survival and Disinfection Technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaijens, J.A.; Zulli, A.; Ott, I.M.; Petrone, M.E.; Alpert, T.; Fauver, J.R.; Kalinich, C.C.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Breban, M.I.; Duvallet, C.; et al. Variant Abundance Estimation for SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Using RNA-Seq Quantification. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amman, F.; Markt, R.; Endler, L.; Hupfauf, S.; Agerer, B.; Schedl, A.; Richter, L.; Zechmeister, M.; Bicher, M.; Heiler, G.; et al. National-Scale Surveillance of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Wastewater. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivins, A.; Greaves, J.; Fischer, R.; Yinda, K.C.; Ahmed, W.; Kitajima, M.; Munster, V.J.; Bibby, K. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in Water and Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Simpson, S.L.; Bertsch, P.M.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; Blackall, L.L.; Bofill-Mas, S.; Bosch, A.; Brandão, J.; Choi, P.M.; et al. Minimizing Errors in RT-PCR Detection and Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA for Wastewater Surveillance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 149877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philo, S.E.; Keim, E.K.; Swanstrom, R.; Ong, A.Q.W.; Burnor, E.A.; Kossik, A.L.; Harrison, J.C.; Demeke, B.A.; Zhou, N.A.; Beck, N.K.; et al. A Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater Concentration Methods for Environmental Surveillance. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, J.A.; Saghir, A.; Chung, S.-A.; Boyajian, N.; Dinh, T.; Kim, J.; Oval, J.; Sharavanan, V.; York, C.; Zimmer-Faust, A.G.; et al. Longitudinal Metatranscriptomic Sequencing of Southern California Wastewater Representing 16 Million People from August 2020-21 Reveals Widespread Transcription of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Water Res. 2022, 229, 119421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, B. BBTools Software Package, 2014. Available online: https://sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Picard Toolkit; Broad Institute: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019.
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Thielen, P.; Salzberg, S.L. Bracken: Estimating Species Abundance in Metagenomics Data. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2017, 2017, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Quick, J.; Matteson, N.L.; De Jesus, J.G.; Main, B.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Brackney, D.E.; Grewal, S.; et al. An Amplicon-Based Sequencing Framework for Accurately Measuring Intrahost Virus Diversity Using PrimalSeq and IVar. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turakhia, Y.; Thornlow, B.; Hinrichs, A.S.; De Maio, N.; Gozashti, L.; Lanfear, R.; Haussler, D.; Corbett-Detig, R. Ultrafast Sample Placement on Existing TRees (UShER) Enables Real-Time Phylogenetics for the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, Disease and Diplomacy: GISAID’s Innovative Contribution to Global Health. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Health and Human Services Agency. COVID-19 Variant Data—California Health and Human Services Open Data Portal; California Health and Human Services Agency: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2023.
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable Association Discovery in Population-Scale Meta-Omics Studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. {lmerTest} Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowikowski, K. Ggrepel: Automatically Position Non-Overlapping Text Labels with “Ggplot2”, R package version 0. 8. 0. 2018. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/ggrepel/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Nowosad, J. Rcartocolor:’CARTOColors’ Palettes, 2018. Available online: https://jakubnowosad.com/rcartocolor/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Pedersen, T.L. Patchwork: The Composer of Plots, R Package Version 1.2.0.9000. 2020. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/ggrepel/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Schumann, V.-F.; de Castro Cuadrat, R.R.; Wyler, E.; Wurmus, R.; Deter, A.; Quedenau, C.; Dohmen, J.; Faxel, M.; Borodina, T.; Blume, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Dynamics Revealed by Wastewater Sequencing Analysis and Deconvolution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, F.S.; Brown, M.R.; Bassano, I.; Denise, H.; Khalifa, M.S.; Wade, M.J.; van Aerle, R.; Kevill, J.L.; Jones, D.L.; Farkas, K.; et al. City-Wide Wastewater Genomic Surveillance through the Successive Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Delta Variants. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Li, K.; Shen, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.-D.; Wan, J. GESS: A Database of Global Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2/HCoV-19 Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D706–D714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.T.; Altschuler, K.; Zhan, S.H.; Chan, Y.A.; Deverman, B.E. COVID-19 CG Enables SARS-CoV-2 Mutation and Lineage Tracking by Locations and Dates of Interest. eLife 2021, 10, e63409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, G.; Lacoux, C.; Leclercq, V.; Diamant, A.; Lebrigand, K.; Lazuka, A.; Soyeux, E.; Lacroix, S.; Fassy, J.; Couesnon, A.; et al. Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 Variants Alterations in Nice Neighborhoods by Wastewater Nanopore Sequencing. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 10, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemudryi, A.; Nemudraia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Surya, K.; Buyukyoruk, M.; Cicha, C.; Vanderwood, K.K.; Wilkinson, R.; Wiedenheft, B. Temporal Detection and Phylogenetic Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Wastewater. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskela von Sydow, A.; Lindqvist, C.M.; Asghar, N.; Johansson, M.; Sundqvist, M.; Mölling, P.; Stenmark, B. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing Using Tiled Amplicon Enrichment and Bait Hybridization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaerschot, M.; Mann, S.A.; Webber, J.T.; Kamm, J.; Bell, S.M.; Bell, J.; Hong, S.N.; Nguyen, M.P.; Chan, L.Y.; Bhatt, K.D.; et al. Identification of a Polymorphism in the N Gene of SARS-CoV-2 That Adversely Impacts Detection by Reverse Transcription-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 59, e02369-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, A.; Gu, X.; Lee, W.L.; Armas, F.; Kauffman, K.; Hanage, W.; Matus, M.; Ghaeli, N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Titers in Wastewater Are Higher than Expected from Clinically Confirmed Cases. mSystems 2020, 5, e00614-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, J.A.; Loveless, T.B.; Griffith, M.L.; Steele, J.A.; Griffith, J.F.; Whiteson, K.L. Metagenomics of Wastewater Influent from Southern California Wastewater Treatment Facilities in the Era of COVID-19. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Wastewater Treatment Plant | Library Preparation Method | Number of Samples | Date Span | Approximate Inflow (Million Gallons/Day) | Approximate Population Served |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escondido Hale Avenue Resource Recovery Facility (ESC) | IRV | 47 | 20 July 2020–19 July 2021 | 14 | 190,000 |
| Hyperion Water Reclamation Plant (HTP) | IRV | 89 | 11 August 2020–29 July 2021 | 275 | 4,000,000 |
| Tiled amplicon | 47 | 21 April 2020–25 July 2021 | |||
| Joint Water Pollution Control Plant (JWPCP) | IRV | 15 | 11 August 2020–17 November 2020 | 400 | 4,800,000 |
| North City Water Reclamation Plant (NC) | IRV | 5 | 14 August 2020–23 October 2020 | 30 | 1,400,000 |
| Orange County Reclamation Plant #1 (OC) | IRV | 14 | 12 August 2020–21 December 2020 | 140 | 2,600,000 |
| Point Loma Water Treatment Plant (PL) | IRV | 77 | 13 August 2020–3 August 2021 | 175 | 2,200,000 |
| Tiled amplicon | 48 | 30 April 2020–18 August 2021 | |||
| San Jose Creek Water Reclamation Plant (SJ) | IRV | 15 | 12 August 2020–18 November 2020 | 100 | 1,000,000 |
| South Bay Water Reclamation Plant (SB) | IRV | 7 | 13 August 2020–5 November 2020 | 15 | 107,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rothman, J.A.; Saghir, A.; Zimmer-Faust, A.G.; Langlois, K.; Raygoza, K.; Steele, J.A.; Griffith, J.F.; Whiteson, K.L. Longitudinal Sequencing and Variant Detection of SARS-CoV-2 across Southern California Wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 635-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020044
Rothman JA, Saghir A, Zimmer-Faust AG, Langlois K, Raygoza K, Steele JA, Griffith JF, Whiteson KL. Longitudinal Sequencing and Variant Detection of SARS-CoV-2 across Southern California Wastewater. Applied Microbiology. 2024; 4(2):635-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleRothman, Jason A., Andrew Saghir, Amity G. Zimmer-Faust, Kylie Langlois, Kayla Raygoza, Joshua A. Steele, John F. Griffith, and Katrine L. Whiteson. 2024. "Longitudinal Sequencing and Variant Detection of SARS-CoV-2 across Southern California Wastewater" Applied Microbiology 4, no. 2: 635-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020044
APA StyleRothman, J. A., Saghir, A., Zimmer-Faust, A. G., Langlois, K., Raygoza, K., Steele, J. A., Griffith, J. F., & Whiteson, K. L. (2024). Longitudinal Sequencing and Variant Detection of SARS-CoV-2 across Southern California Wastewater. Applied Microbiology, 4(2), 635-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020044







