Onset and Progression of Infection Based on Viral Loads in Rhesus Macaques Exposed to Zika Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Animal sex;
- Animal age;
- Study: Animals were grouped at the study level as both control article and actual exposure dose had a 1:1 relationship with study and so were completely confounded.
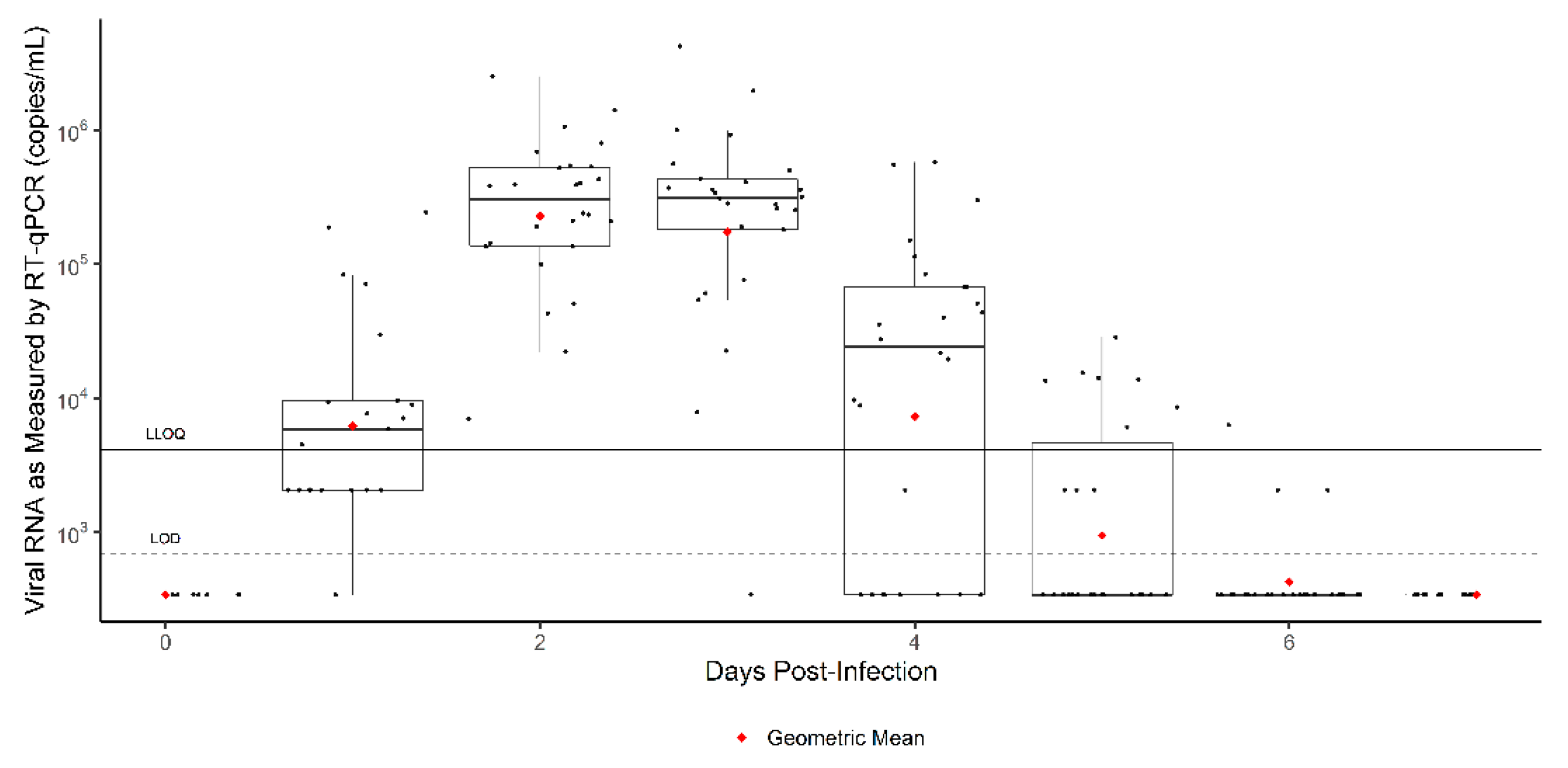
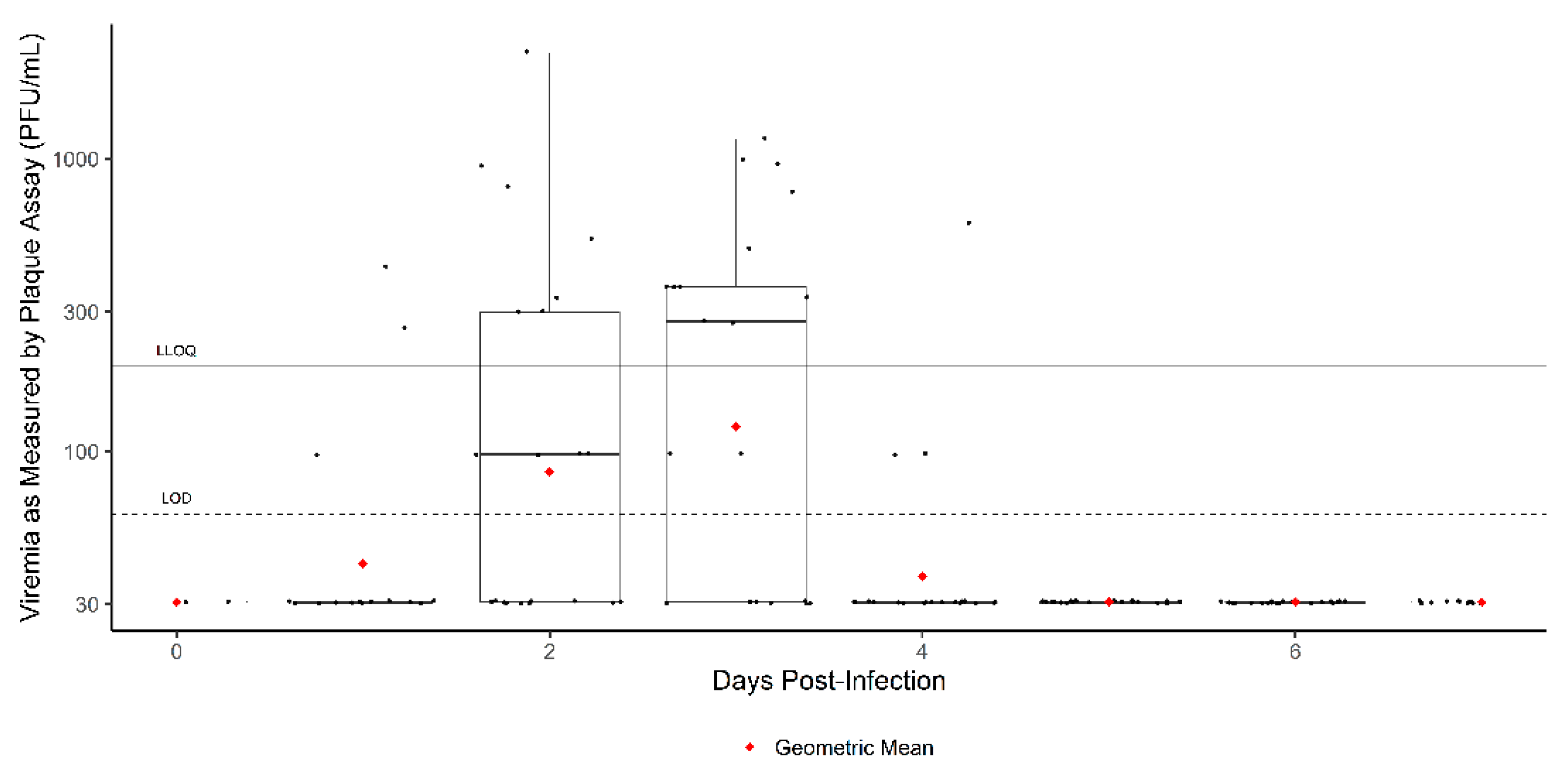
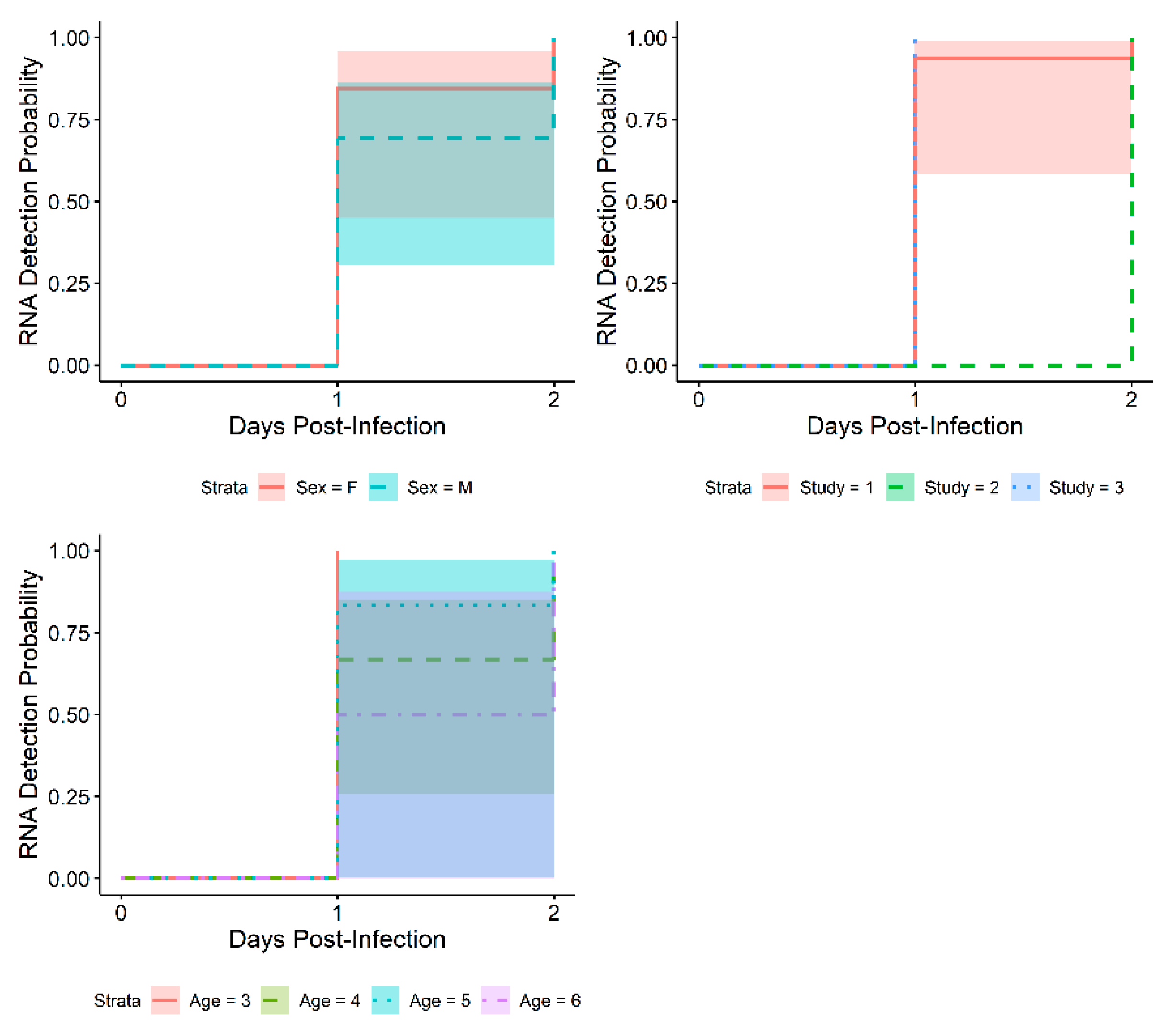
3. Results
3.1. Time to Onset
3.2. Exploratory Analysis: Results by Weight
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dick, G.W.A.; Kitchen, S.F.; Haddow, A.J. Zika virus (I). Isolations and serological specificity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnamara, F.N. Zika Virus: A Report on Three Cases of Human Infection During an Epidemic of Jaundice in Nigeria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1954, 48, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.R.; Chen, T.; Hancock, W.T.; Powers, A.M.; Kool, J.L.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Pretrick, M.; Marfel, M.; Holzbauer, S.; Dubray, C.; et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2536–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Johnson, A.J.; Stanfield, S.M.; Duffy, R.M. Genetic and serologic properties of Zika virus associated with an epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, M.; Lastere, S.; Teissier, A.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Musso, D. Evidence of perinatal transmission of Zika virus, French Polynesia, December 2013 and February 2014. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, D.; Nhan, T.; Robin, E.; Roche, C.; Bierlaire, D.; Zisou, K.; Yan, A.S.; Cao-Lormeau, V.; Broult, J. Potential for Zika virus transmission through blood transfusion demonstrated during an outbreak in French Polynesia, November 2013 to February 2014. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler-Faccini, L.; Ribeiro, E.M.; Feitosa, I.M.; Horovitz, D.D.; Cavalcanti, D.P.; Pessoa, A.; Doriqui, M.J.; Neri, J.I.; Neto, J.M.; Wanderley, H.Y.; et al. Possible association between Zika virus infection and microcephaly–Brazil, 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakar, J.; Korva, M.; Tul, N.; Popovic, M.; Poljsak-Prijatelj, M.; Mraz, J.; Kolenc, M.; Resman, K.; Vipotnik, T.V.; Vodusek, V.F.; et al. Zika virus associated with microcephaly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. WHO Ends Zika as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. 2016. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/who-ends-zika-public-health-emergency-international-concern (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Gruber, M.F.; Krause, P.R. Regulating vaccines at the FDA: Development and licensure of Zika vaccines. Vaccines 2017, 16, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marston, H.D.; Lurie, N.; Borio, L.L.; Fauci, A.S. Considerations for developing a Zika virus vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.K.; Kimmelman, J.; Drapkin Lyerly, A.; Fernandez Lynch, H.; McCutchan, F.; Miller, F.G.; Palacios, R.; Pardo-Villamizar, C.; Zorrilla, C. Ethical Considerations for Zika Virus Human Challenge Trials: Report and Recommendations. Available online: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/sites/default/files/EthicsZikaHumanChallengeStudiesReport2017.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER); Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Product Development under the Animal Rule: Guidance for Industry. October 2015. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/product-development-under-animal-rule (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Vang, L.; Morello, C.S.; Mendy, J.; Thompson, D.; Manayani, D.; Guenther, B.; Julander, J.; Sanford, D.; Jain, A.; Patel, A.; et al. Zika virus-like particle vaccine protects AG129 mice and rhesus macaques against Zika virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.R. Regression Models and Life Tables (with Discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1972, 34, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.R.; Oakes, D. Analysis of Survival Data; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bradburn, M.J.; Clark, T.G.; Love, S.B.; Altman, D.G. Survival Analysis Part II: Multivariate data analysis–an introduction to concepts and methods. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D. Applied Survival Analysis Using R, 1st ed.; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Musso, D.; Gubler, D.J. Zika Virus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 487–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, D.; Rouault, E.; Teissier, A.; Lanteri, M.C.; Zisou, K.; Broult, J.; Grange, E.; Nhan, T.-X.; Aubry, M. Molecular detection of Zika virus in blood and RNA load determination during the French Polynesian outbreak. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuna, C.E.; Whitney, J.B. Nonhuman Primate Models of Zika Virus Infection, Immunity, and Therapeutic Development. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216 (Suppl. S10), S928–S934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorshkov, K.; Shiryaev, S.A.; Fertel, S.; Lin, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-T.; Pinto, A.; Farhy, C.; Strongin, A.Y.; Zheng, W.; Terskikh, A.V. Zika Virus: Origins, Pathological Action, and Treatment Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzon, L.; Trevisan, M.; Sinigaglia, A.; Lavezzo, E.; Palù, G. Zika virus: From pathogenesis to disease control. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, J.M.; Mengelle, C.; Pasquier, C.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Delobel, P.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Izopet, J. Zika Virus Infection and Prolonged Viremia in Whole-Blood Specimens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.; Friedrich, T.C.; O’Connor, D.H. Macaque monkeys in Zika virus research: 1947-present. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, Y.; Mendelson, E.; Paran, N.; Melamed, S.; Schwartz, E. Detection of Zika virus RNA in whole blood of imported Zika virus disease cases up to 2 months after symptom onset, Israel, December 2015 to April 2016. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, D.M.; Aliota, M.T.; Mohr, E.L.; Weiler, A.M.; Lehrer-Brey, G.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Mohns, M.S.; Breitbach, M.E.; Rasheed, M.N.; Newman, C.M.; et al. A rhesus macaque model of Asian-lineage Zika virus infection. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, J.D.; Wong, S.W.; Brenchley, J.M. Nonhuman primate models of human viral infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuna, C.E.; Lim, S.Y.; Deleage, C.; Griffin, B.D.; Stein, D.; Schroeder, L.T.; Omange, R.; Best, K.; Luo, M.; Hraber, P.T.; et al. Zika viral dynamics and shedding in rhesus and cynomolgus macaques. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driggers, R.W.; Ho, C.-Y.; Korhonen, E.M.; Kuivanen, S.; Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Smura, T.; Rosenberg, A.; Hill, D.A.; DeBiasi, R.L.; Vezina, G.; et al. Zika Virus Infection with Prolonged Maternal Viremia and Fetal Brain Abnormalities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study 1 | Study 2 | Study 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | ||
| Age (Years) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Effect. | Baseline Category | Detection of Viral RNA | Positive Viremia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval for Hazard Ratio | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval for Hazard Ratio | ||
| Sex | F | 0.7059 | (0.3174, 1.5697) | 0.5503 | (0.1904, 1.5909) |
| Age | - | 0.6834 | (0.4198, 1.1126) | 1.1898 | (0.6280, 2.2542) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Triplett, C.; Dufek, S.; Niemuth, N.; Kobs, D.; Cirimotich, C.; Mack, K.; Sanford, D. Onset and Progression of Infection Based on Viral Loads in Rhesus Macaques Exposed to Zika Virus. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 544-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030042
Triplett C, Dufek S, Niemuth N, Kobs D, Cirimotich C, Mack K, Sanford D. Onset and Progression of Infection Based on Viral Loads in Rhesus Macaques Exposed to Zika Virus. Applied Microbiology. 2022; 2(3):544-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleTriplett, Cheryl, Sally Dufek, Nancy Niemuth, Dean Kobs, Christopher Cirimotich, Karla Mack, and Daniel Sanford. 2022. "Onset and Progression of Infection Based on Viral Loads in Rhesus Macaques Exposed to Zika Virus" Applied Microbiology 2, no. 3: 544-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030042
APA StyleTriplett, C., Dufek, S., Niemuth, N., Kobs, D., Cirimotich, C., Mack, K., & Sanford, D. (2022). Onset and Progression of Infection Based on Viral Loads in Rhesus Macaques Exposed to Zika Virus. Applied Microbiology, 2(3), 544-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030042






