Encapsulated Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Reduces Enteric Bacterial Pathogens on Melon Surfaces during Differing Contamination and Sanitization Treatment Scenarios
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Melon Preparation for Microbial Inoculation and Testing
2.2. Microorganisms for Sample Inoculation and Sample Inoculation Processes
2.3. Sample Inoculation and Treatment Scenarios
2.4. Sanitizing Treatment Preparation and Application to Sample Surfaces
2.5. Microbiological Analysis of Samples
2.6. Experimental Design and Data Analysis
3. Results
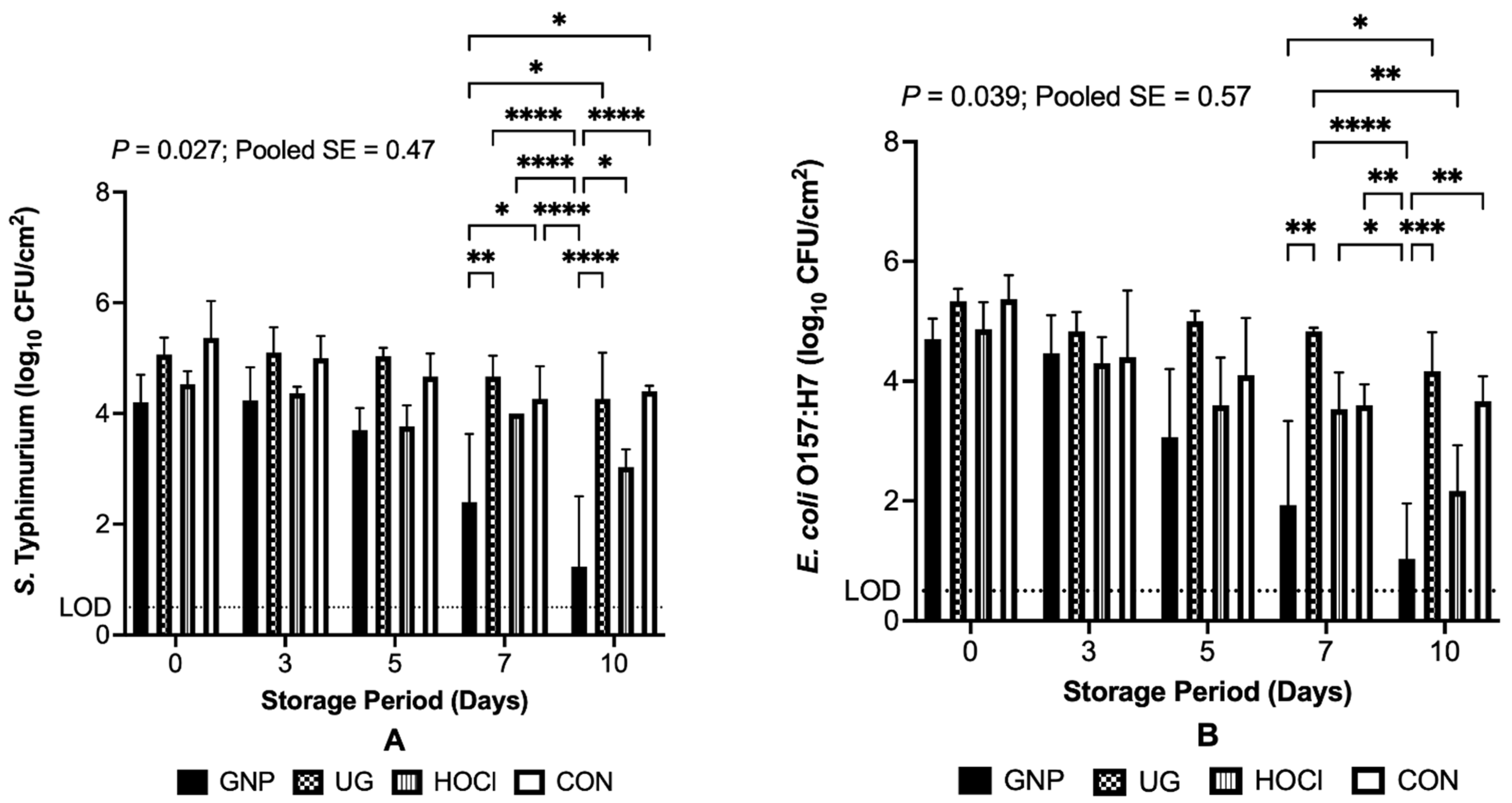
3.1. Scenario 1: Sanitizing Treatments to Reduce Pathogens Contaminating Melons Pre-Treatment
3.2. Scenario 2: Efficacy of Sanitizing Treatments Applied to Reduce Pathogens Contaminating Melons Prior to and Following Treatment
3.3. Scenario 3: Efficacy of Sanitizing Treatments to Reduce Pathogens Contaminating Melons Post-Treatment
3.4. The Interaction of Sanitizing Treatment x Treatment Scenario
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Department of Agriculture; U.S. Department of Healtha and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, 9th ed. Available online: www.dietaryguidelines.gov (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- World Health Organization. Healthy Diet. Available online: https://www.who.int/initiatives/behealthy/healthy-diet (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for Foodborne Disease Outbreaks, United States. Annual Report. 2017. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fdoss/pdf/2017_FoodBorneOutbreaks_508.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Multi-Country Outbreak of Salmonella Braenderup ST22, Presumed to Be Linked to Imported Melons. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/en-6807 (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. List of Selected Multistate Foodborne Outbreak Investigations. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/outbreaks/multistate-outbreaks/outbreaks-list.html (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Batz, M.B.; Hoffmann, S.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Ranking the disease burden of 14 pathogens in food sources in the United States using attribution data from outbreak investigations and expert elicitation. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USDA-ERS. Cost Estimates of Foodborne Illnesses. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/cost-estimates-of-foodborne-illnesses/ (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- FDA. Title 21, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, §112: Standards for the Growing, Harvesting, Packing, and Holding of Produce for Human Consumption. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=6065be805bbe8488f8cf57bf0299dfd9&mc=true&node=pt21.2.112&rgn=div5 (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Ramos, B.; Miller, F.A.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Teixeira, P.; Silva, C.L.M. Fresh fruits and vegetables-an overview on applied methodologies to improve its quality and safety. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Guevara, J.J.; Arenas-Hernandez, M.M.P.; Martinez de la Peña, C.; Silva, J.L.; Luna-Guevara, M.L. The role of pathogenic E. coli in fresh vegetables: Behavior, contamination factors, and preventive measures. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 2894328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowotarska, S.W.; Nowotarski, K.J.; Friedman, M.; Situ, C. Effect of structure on the interactions between five natural antimicrobial compounds and phospholipids of bacterial cell membrane on model monolayers. Molecules 2014, 19, 7497–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Lu, J.; Zhong, S.; Schwarz, P.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Influence of nonionic and ionic surfactants on the antifungal and mycotoxin inhibitory efficacy of cinnamon oil nanoemulsions. Foods Funct. 2019, 10, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.-Z.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Pan, Z.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Xu, J.; Zielinska, M.; Xiao, H.-W. Emerging chemical and physical disinfection technologies of fruit and vegetables: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2481–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Corato, U. Improving the shelf-life and quality of fresh and minimally-processed fruits and vegetables for a modern food industry: A comprehensive critical review from the traditional technologies into the most promising advancements. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 940–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruengvisesh, S.; Kerth, C.R.; Taylor, T.M. Inhibition of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica isolates on spinach leaf surfaces using eugenol-loaded surfactant micelles. Foods 2019, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Lewis, K.L.; Yegin, Y.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Castillo, A.; Kerth, C.R.; Akbulut, M.; Taylor, T.M. Geraniol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles inhibit enteric pathogens on spinach during posttreatment refrigerated and temperature abuse storage. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruengvisesh, S.; Oh, J.K.; Kerth, C.R.; Akbulut, M.; Taylor, T.M. Inhibition of bacterial human pathogens on tomato skin surfaces using eugenol-loaded surfactant micelles during refrigerated and abuse storage. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegin, Y.; Perez-Lewis, K.L.; Zhang, M.; Akbulut, M.; Taylor, T.M. Development and characterization of geraniol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity against foodborne bacterial pathogens. J. Food Eng. 2016, 170, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammari, N.; Louaer, O.; Meniai, A.H.; Elaissari, A. Encapsulation of essential oils via nanoprecipitation process: Overview, progress, challenges and prospects. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegin, Y.; Perez-Lewis, K.L.; Liu, S.; Kerth, C.R.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Castillo, A.; Akbulut, M.; Taylor, T.M. Antimicrobial-loaded polymeric micelles inhibit enteric bacterial pathogens on spinach leaf surfaces during multiple simulated pathogen contamination events. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 646980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.J.; Farber, J.N.; Beuchat, L.R.; Parish, M.E.; Suslow, T.V.; Garrett, E.H.; Busta, F.F. Outbreaks associated with fresh produce: Incidence, growth, and survival of pathogens in fresh and fresh-cut produce. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2003, 2, 78–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, A.; Lucia, L.M.; Goodson, K.J.; Savell, J.W.; Acuff, G.R. Use of hot water for beef carcass decontamination. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Critzer, F.; Davidson, P.M.; Zhong, Q. Organic thyme oil emulsion as an alternative washing solution to enhance the microbial safety of organic cantaloupes. Food Control 2016, 67, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annous, B.A.; Solomon, E.B.; Cooke, P.H.; Burke, A. Biofilm formation by Salmonella spp. on cantaloupe melons. J. Food Saf. 2005, 25, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, M.; Moreira, R.G.; Omac, B.; Castell-Perez, E. Quantifying the effectiveness of washing treatments on the microbial quality of fresh-cut romaine lettuce and cantaloupe. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 86, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Yegin, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Verkhoturov, S.V.; Schweikert, E.A.; Perez-Lewis, K.; Scholar, E.A.; et al. The influence of surface chemistry on the kinetics and thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFlorio, W.; Liu, S.; White, A.R.; Taylor, T.M.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Min, Y.; Scholar, E.M.A. Recent developments in antimicrobial and antifouling coatings to reduce or prevent contamination and cross-contamination of food contact surfaces by bacteria. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3093–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Oh, J.K.; Huang, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-R.; Liu, Y.; Mannan, M.S.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Akbulut, M. Priming with nano-aerosolized water and sequential dip-washing with hydrogen peroxide: An efficient sanitization method to inactivate Salmonella Typhimurium LT2 on spinach. J. Food Eng. 2015, 161, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, A. Produce surface characteristics affect product quality and safety. Acta Hort. 2007, 746, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gálvez, F.; Allende, A.; Selma, M.V.; Gil, M.I. Prevention of Escherichia coli cross-contamination by different commercial sanitizers during washing of fresh-cut lettuce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.; Aldossari, H.; Wu, F.; Warriner, K. Dynamic changes in free-chlorine levels within a commercial post-harvest wash and prevention of cross-contamination between shredded lettuce batches. Food Control 2018, 85, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
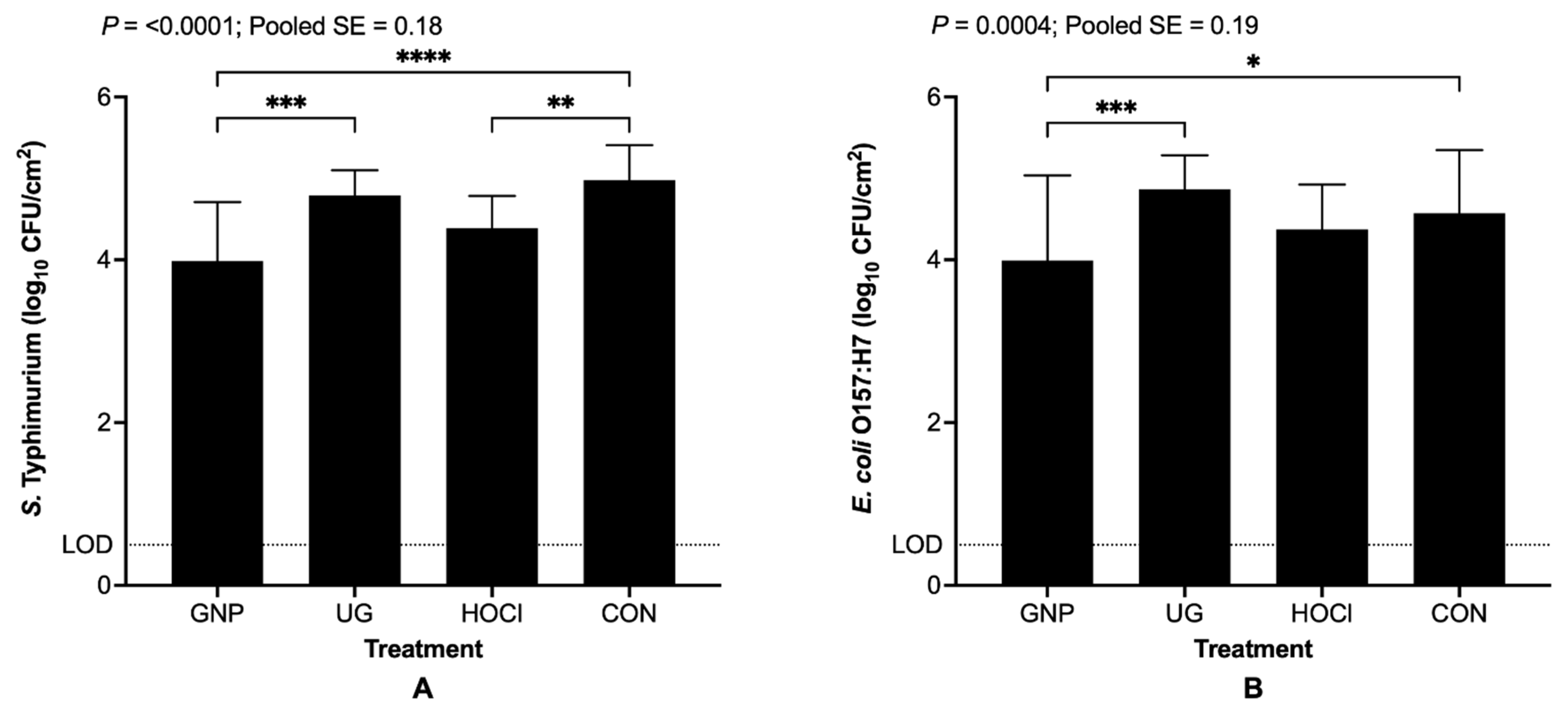

| Sanitizing Treatment 1 | Scenario 1 2 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GNP | 3.15 E 3 | 3.99 BC | 3.17 E |
| UG | 4.85 A | 4.79 A | 3.45 CDE |
| HOCl | 3.94 BCD | 4.39 AB | 3.52 CDE |
| CON | 4.74 A | 4.98 A | 3.36 DE |
| Sanitizing Treatment 1 | Scenario 1 2 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GNP | 3.04 E 3 | 3.99 BCD | 3.01 E |
| UG | 4.77 A | 4.87 A | 3.49 DE |
| HOCl | 3.69 CDE | 4.37 ABC | 3.45 DE |
| CON | 4.23 ABC | 4.57 AB | 3.17 E |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez-Lewis, K.L.; Yegin, Y.; Oh, J.K.; Castillo, A.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Kerth, C.R.; Scholar, E.; Taylor, T.M. Encapsulated Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Reduces Enteric Bacterial Pathogens on Melon Surfaces during Differing Contamination and Sanitization Treatment Scenarios. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 1, 460-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol1030030
Perez-Lewis KL, Yegin Y, Oh JK, Castillo A, Cisneros-Zevallos L, Kerth CR, Scholar E, Taylor TM. Encapsulated Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Reduces Enteric Bacterial Pathogens on Melon Surfaces during Differing Contamination and Sanitization Treatment Scenarios. Applied Microbiology. 2021; 1(3):460-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol1030030
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez-Lewis, Keila L., Yagmur Yegin, Jun Kyun Oh, Alejandro Castillo, Luis Cisneros-Zevallos, Chris R. Kerth, Ethan Scholar, and Thomas M. Taylor. 2021. "Encapsulated Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Reduces Enteric Bacterial Pathogens on Melon Surfaces during Differing Contamination and Sanitization Treatment Scenarios" Applied Microbiology 1, no. 3: 460-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol1030030
APA StylePerez-Lewis, K. L., Yegin, Y., Oh, J. K., Castillo, A., Cisneros-Zevallos, L., Kerth, C. R., Scholar, E., & Taylor, T. M. (2021). Encapsulated Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Reduces Enteric Bacterial Pathogens on Melon Surfaces during Differing Contamination and Sanitization Treatment Scenarios. Applied Microbiology, 1(3), 460-470. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol1030030








