Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Experimental Conditions
2.2. Phenotypic Data Collection and Phenotypic Correlation Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.4. Genetic Linkage Map Construction and QTL Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Variation/Evaluation
3.2. Trait Correlation and Linkage Map
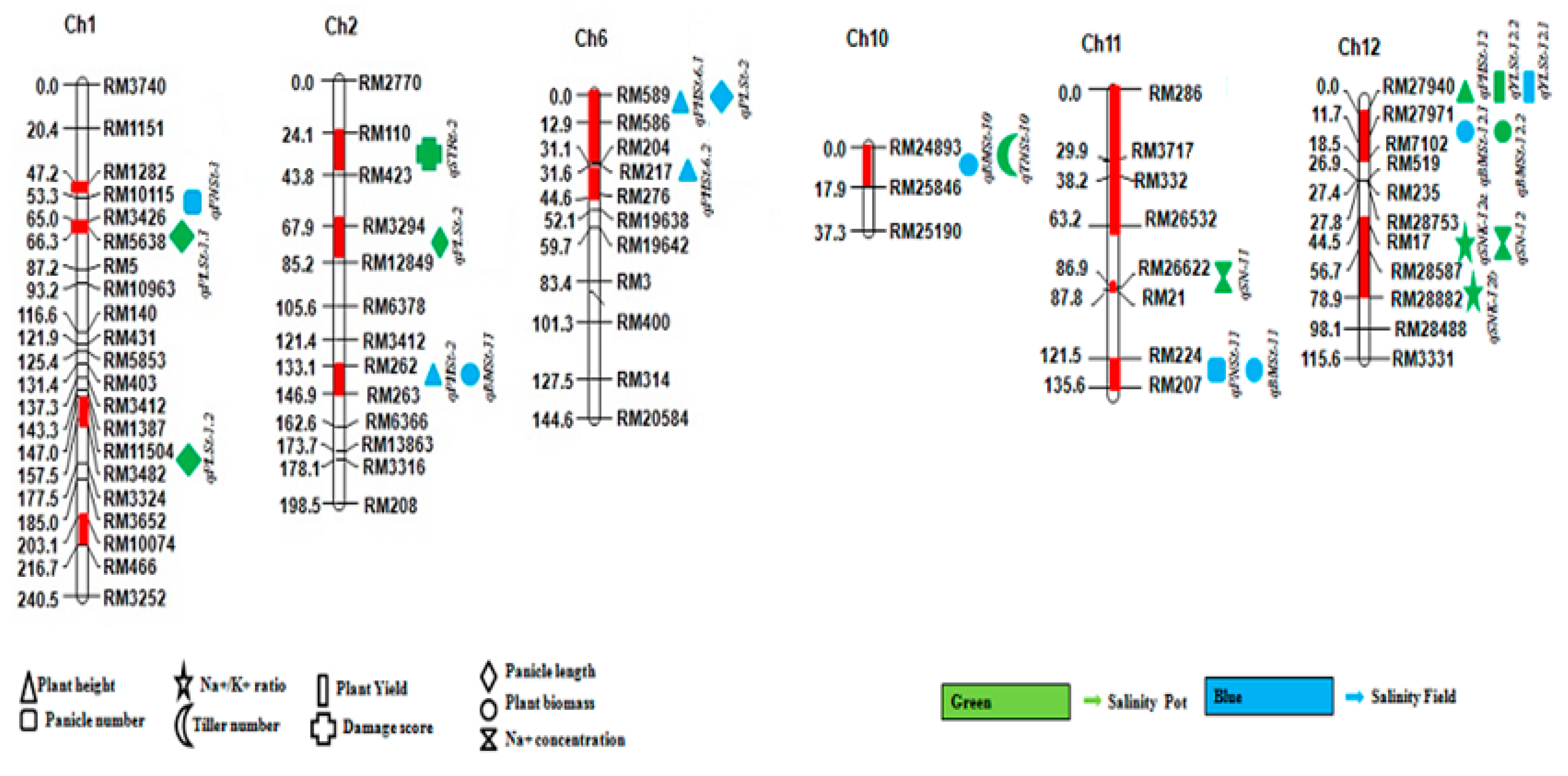
3.3. QTL Mapping of Salt Tolerance-Related Traits (Plant Height, Panicle Number, Panicle Length, Biomass, and Yield)
3.4. QTL Mapping of Salt Tolerance-Related Biochemical Traits (Na+ Concentration, Na+/K+ Ratio, and Salinity Tolerance)
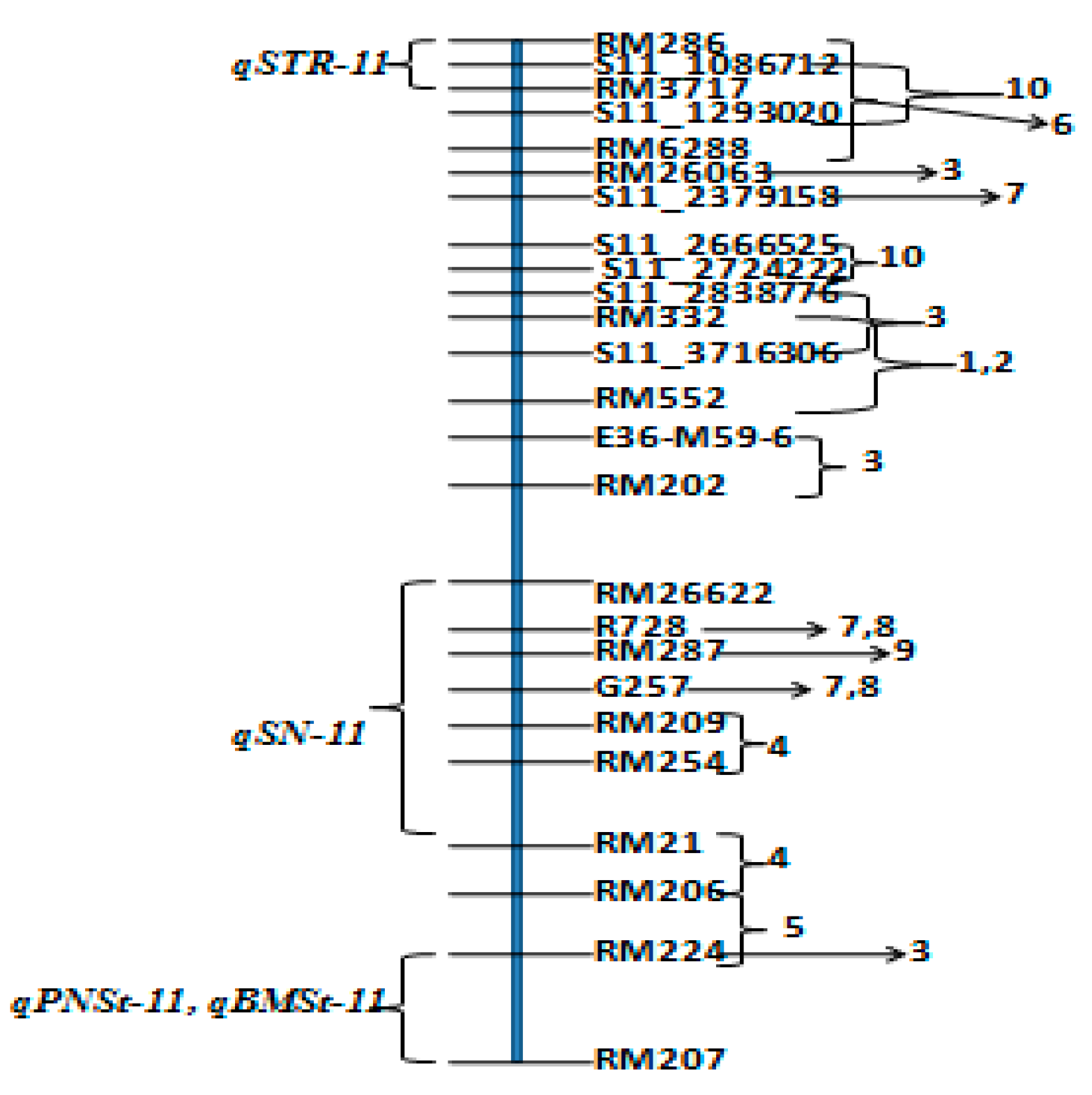
3.5. QTL Clusters
4. Discussion
4.1. QTLs Associated with Salinity Tolerance in Rice
4.2. QTLs for Component Traits of Salinity Tolerance on Chromosome 2
4.3. QTLs for Component Traits of Salinity Tolerance on Chromosome 11
4.4. QTLs for Component Traits of Salinity Tolerance on Chromosome 12
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO Global Map of Salt Affected Soils Version 1.0. 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data hub/soil-maps-and-databases/global-map-of-salt-affected-soils/en/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirjani, M.R. Effect of NaCl on some physiological parameters of rice. Eur. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 3, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The threat of soil salinity: A European scale review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.; Drechsel, P.; Noble, A. Economics of salt-induced land degradation and restoration. Nat. Res. Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, K.; Mondal, S.; Gorai, S.; Singh, A.P.; Kumari, A.; Ghosh, T.; Roy, A.; Hembram, S.; Gaikwad, D.J.; Mondal, S.; et al. Impacts of salinity stress on crop plants: Improving salt tolerance through genetic and molecular dissection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1241736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, L.; Aycan, M.; Lopes Hornai, E.M.; Baslam, M.; Mitsui, T. Tolerance with high yield potential is provided by lower Na+ ion accumulation and higher photosynthetic activity in tolerant YNU31-2-4 rice genotype under salinity and multiple heat and salinity stress. Plants 2023, 12, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.M.L.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, T.K.T.; Williams, B.; Wurm, P.; Bellairs, S.; Mundree, S. Improvement of salinity stress tolerance in rice: Challenges and opportunities. Agronomy 2016, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, D.; Dhital, M.; Chaudhary, B.; Pandey, R.; Bastakoti, B.; Shrestha, S. Effect of different nitrogen levels on yield and yield attributes of different rice varieties in DDSR condition at Kanchanpur, Nepal. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2022, 7, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.; Ali, M.M.; Mahadi, M.R.; Abdullah, A.F.; Wayayok, A.; Kassim, M.S.M.; Jamaluddin, A. Smart farming for sustainable rice production: An insight into application, challenge, and future prospect. Rice Sci. 2024, 31, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Luo, J.; Park, E.; Barcaccia, G.; Masin, R. Soil salinization in agriculture: Mitigation and adaptation strategies combining nature-based solutions and bioengineering. iScience 2024, 26, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, R. Advances and challenges in the breeding of salt-tolerant rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Rafii, M.Y.; Yusoff, M.M.; Ali, N.S.; Yusuff, O.; Datta, D.R.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Ikbal, M.F. Advanced breeding strategies and future perspectives of salinity tolerance in rice. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, P.; Kiran, B.; Punita, D.L.; Kavi Kishor, P.B. Overexpression of SbAP37 in rice alleviates concurrent imposition of combination stresses and modulates different sets of leaf protein profiles. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 773–786. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasheker, G.; Anil Kumar, S.; Surender Reddy, P.; Sujatha, E.; Divya, K.; Reddy, P.S.; Jalaja, N.; Jawahar, G.; Insaf, Q.M.; Nagaraju, M.; et al. Overexpression of RNA-binding bacterial chaperones in rice lead to stay-green phenotype, improved yield and tolerance to salt and drought stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 1351–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Ortuño, M.F.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J.; Hernandez, J.A. Plant responses to salt stress: Adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Heuer, S.; Thomson, M.J.; Wissuwa, M. Genetic and genomic approaches to develop rice germplasm for problem soils. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 547–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Huang, B. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 701596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Khare, T.; Guddimalli, R.; Parveda, M.; Solymosi, K.; Suprasanna, P.; Kavi Kishor, P.B. Engineering salinity tolerance in plants: Progress and prospects. Planta 2020, 251, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karumanchi, A.R.; Sudhakar, P.; Krishna Satya, A.; Meghana, K.; Tejaswini, N.; Geethika Gayatri, P.; Kavi Kishor, P.B. Discerning the dynamics of sodium transport in plants crucial for developing crops resilient to salt stress. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2023, 17, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Tester, M.; Roy, S.J. Quantifying the three main components of salinity tolerance in cereals. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Khan, N.U.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Tang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, Z. Genetic basis and identification of candidate genes for salt tolerance in rice by GWAS. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerelli, K.; Balakrishnan, D.; Addanki, K.R.; Surapaneni, M.; Rao, V.Y.; Neelamraju, S. Mapping of QTLs for yield traits using F2:3:4 populations derived from two alien introgression lines reveals qTGW8.1 as a consistent QTL for grain weight from Oryza nivara. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 790221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.R.; Balachandran, S.M.; Ulaganathan, K. Molecular mapping of QTLs for yield related traits in recombinant inbred line (RIL) population derived from the popular rice hybrid KRH-2 and their validation through SNP genotyping. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Kota, S.; Flowers, T.J. Salt tolerance in rice: Seedling and reproductive stage QTL mapping come of age. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3495–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M.J.; de Ocampo, M.; Egdane, J.; Rahman, M.K.; Sajise, A.G.; Adorada, D.L.; Tuminbang-Raiz, E.; Blumwald, E.; Seraj, Z.I.; Singh, R.K.; et al. Characterizing the Saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice 2010, 3, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, K.; Huang, Y.; Shi, C.; Hu, W.S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.J.; Xia, E.H.; Hutang, G.R.; Zhu, X.G.; et al. SMRT sequencing of the Oryza rufipogon genome reveals the genomic basis of rice adaptation. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Tiwari, S.; Kumar, N.; Sinha, S.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Singh, R.; Kalia, S.; Singh, N.K.; Rai, V. QTLs and genes for salt stress tolerance: A journey from seed to seed continued. Plants 2024, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hazarika, M. Application of correlation analysis in conventional plant breeding and genome wide association mapping. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 3372–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghai-Maroof, M.A.; Soliman, K.M.; Jorgesen, R.A.; Allard, R.W. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 8014–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Temnykh, S.; Xu, Y. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 95, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooijen, J.W. JoinMap 5: Software for the Calculation of Genetic Linkage Maps in Experimental Populations; Kyazma, B.V., Ed.; Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kosambi, D.D. The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann. Eugen. 1944, 12, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Basten, C.J.; Zeng, Z.B. Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. In User Manual; Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2007; pp. 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, B.; Jini, D.; Sujatha, S. Biological and physiological perspectives of specificity in abiotic salt stress response from various rice plants. Asian J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 2, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Rajat, P.; Rao, P.V.R.; John, O.; Prasanta, S.K. Genetics of yield component traits under salt stress at flowering stage and selection of salt tolerant pre-breeding lines for rice improvement. Genetica 2022, 150, 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Messmer, R.; Fracheboud, Y.; Banziger, M.; Vargas, M.; Stamp, P.; Ribaut, J.M. Drought stress and tropical maize: QTL-by-environment interactions and stability of QTLs across environments for yield components and secondary traits. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Khanna, R.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, K.; Kaur, R.; Sharma, N.; Mangat, G.S. Performance under multi-environment trial for quantitative traits of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes in North-West India (Punjab). Ecolog. Genet. Genom. 2023, 28, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.S.L.K.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B.; Rao, A.; Mithra, S.V.A. Mapping QTLs for salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by bulked sergeant analysis of recombinant inbred lines using 50K SNP chip. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Liang, X.; Li, H.; Xie, C.; He, W.; Qin, Y. Identification and characterization of wheat germplasm for salt tolerance. Plants 2021, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Sethi, G.S.; Plaha, P. Some useful characters implicated in tolerance to low phosphorus and water stresses in hexaploid triticale × bread wheat derivatives. Cereal Res. Commun. 2000, 28, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porch, T.G. Application of stress indices for heat tolerance screening of common bean. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2006, 192, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Gautam, R.K.; Mahajan, R.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, R.K.; Ismail, A.M. Stress indices and selectable traits in SALTOL QTL introgressed rice genotypes for reproductive stage tolerance to sodicity and salinity stresses. Field Crops Res. 2013, 154, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabesan, T.; Suresh, R.; Saravanan, K. Genetic variability and correlation for yield and grain quality characters of rice grown in coastal saline low land of Tamil Nadu. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2009, 1, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Das, P.K.; Guha, B.; Kalyan, K.S.; Barman, B. Quantitative genetic analysis for yield and yield components in boro rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2010, 2, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Jeung, J.U.; Kang, K.H.; Shim, K.S.; Jung, K.W.; You, M.K.; Ok, S.H.; Chung, Y.S.; Hwang, H.G.; Choi, H.C.; et al. Identification of genes induced in wound-treated wild rice (Oryza minuta). Mol. Cells 2004, 17, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.G.; Thiruvengadam, V.; Vinod, K.K. Genetic diversity among cultivars, landraces and wild relatives of rice as revealed by microsatellite markers. J. Appl. Genet. 2007, 48, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, C.A.; Yong, M.T.; Vinarao, R.; Jena, K.; Holford, P.; Shabala, L.; Zhou, M.; Shabala, S.; Chen, Z.H. Back to the wild: On a quest for donors toward salinity tolerant rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, A.L.; Aparajita, D.C.; Lily, G.; Susmita, M.; Sudipta, R. Introgression of a novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka (PcINO1) confers salt tolerance to evolutionary diverse organisms. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 3980–3988. [Google Scholar]
- Takehisa, H.; Shimodate, T.; Fukuta, Y.; Ueda, T.; Yano, M.; Yamaya, T.; Kameya, T.; Sato, T. Identification of quantitative trait loci for plant growth of rice in paddy field flooded with salt water. Field Crop Res. 2004, 89, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Cha, Y.S.; Yun, D.W.; Lee, M.C.; Ko, J.C.; Lee, K.S.; Eun, M.Y. Mapping related to salinity tolerance of rice at the young seedling stage. Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Gao, J.P.; Li, L.G.; Cai, X.L.; Huang, W.; Chao, D.Y.; Zhu, M.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Luan, S.; Lin, H.X. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimpong, I.K.; Manneh, B.; Diop, B.; Ghislain, K.; Sow, A.; Amoah, N.K.A.; Gregorio, G.; Singh, R.K.; Ortiz, R.; Wopereis, M. New quantitative trait loci for enhancing adaptation to salinity in rice from Hasawi, a Saudi landrace into three African cultivars at the reproductive stage. Euphytica 2014, 200, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, N.K.A.; Akromah, R.; Kena, A.W.; Manneh, B.; Dieng, I.; Bimpong, I.K. Mapping QTLs for tolerance to salt stress at the early seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a newly identified donor “Madina Koyo”. Euphytica 2020, 216, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.H.M.; Pandit, A.; Singh, R.K.; Sameena, S.; Chauhan, M.S.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, P.C.; Gaikwad, K.; Sharma, T.R.; Mohapatra, T.; et al. Mapping of QTLs controlling Na+, K+ and CI− ion concentrations in salt tolerant Indica rice variety CSR27. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, H.; Rahman, M.A.; Alam, M.S.; Singh, R.K. Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with reproductive-stage salt tolerance in rice. J. Agron Crop Sci. 2015, 201, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Singh, R.K.; Thomson, M.J. Mapping QTLs for reproductive stage salinity tolerance in rice using a cross between Hasawi and BRRI dhan28. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhla, W.R.; Sun, W.; Fan, K.; Yang, K.; Zhang, C.; Yu, S. Identification of QTLs for salt tolerance at the germination and seedling stages in rice. Plants 2021, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.B.; Senadhira, D.; Mendoza, R.D. Screening rice for salinity tolerance. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines. In IRRI Discussion Paper Series Number 22; IRRI: Los Baños, Philippines, 1997; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sabouri, H.; Rezai, A.M.; Moumeni, A.; Kavousi, A.; Katouzi, M.; Sabouri, A. QTLs mapping of physiological traits related to salt tolerance in young rice seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, T.B.; Linscombe, S.; Subudhi, P.K. Molecular dissection of seedling salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a high- density GBS-Based SNP linkage map. Rice 2016, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Coca, L.I.; García González, M.T.; Gil Unday, Z.; Jiménez Hernández, J.; Rodríguez Jáuregui, M.M.; Fernández Cancio, Y. Effects of Sodium Salinity on Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivation: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimpong, I.K.; Manneh, B.; El-Namaky, R.; Diaw, F.; Amoah, N.K.A.; Sanneh, B.; Ghislain, K.; Sow, A.; Singh, R.K.; Gregorio, G.; et al. Mapping QTLs related to salt tolerance in rice at the young seedling stage using 384-plex single nucleotide polymorphism SNP, marker sets. Euphytica 2013, 200, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, K.; Rabiei, B.; Sabcuri, H.; Sabouri, A. Mapping QTLs for traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage of rice (Oryza sativa L.). OMICS J. Inte. Biol. 2013, 17, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, I.; Neang, S.; Kuroki, R.; Reyes, V.P.; Doi, K.; Skoulding, N.S.; Taniguchi, M.; Yamauchi, A.; Mitsuya, S. QTL analysis for sodium removal ability in rice leaf sheaths under salinity using an IR-44595/318 F2 population. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1002605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Jian, Z.; Xiao-biao, P.; Zang, F.; Tian-qing, Z.; Xiu-qing, Z.; Wang, W.; Ali, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Z. Advanced backcross QTL analysis for the whole plant growth duration salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.R.; Seo, J.; Park, S.; Jin, M.; Jeong, O.Y.; Park, H.S. Identification of potential QTLs related to grain size in rice. Plants 2023, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Identification of QTLs with main, epistatic and QTL × environment interaction effects for salt tolerance in rice seedlings under different salinity conditions. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Seiji, Y.; Zabta, K.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Anwar, R. Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for salt tolerance in rice (Oryza Sativa) using RFLPs. Pak. J. Bot. 2004, 36, 825–834. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.M. Identification of candidate genes for salt tolerance at the seedling stage using integrated genome-wide association study and transcriptome analysis in rice. Plants 2023, 12, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, M.A.; Huyop, F.Z.; Wagiran, A.; Salleh, F.M. Identification of QTLs for morph-physiological traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage in indica rice. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satasiya, P.; Patel, S.; Patel, R.; Raigar, O.P.; Modha, K.; Parekh, V.; Joshi, H.; Patel, V.; Chaudhary, A.; Sharma, D.; et al. Meta-analysis of identified genomic regions and candidate genes underlying salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5730. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zou, D. QTL analysis of Na+ and K+ concentrations in shoots and roots under NaCl stress based on linkage and association analysis in japonica rice. Euphytica 2015, 201, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, R.; Rahman, M.S.; Seraj, Z.I.; Thomson, M.J.; Ismail, A.M.; Tumimbang-Raiz, E.; Gregorio, G.B. Investigation of seedling-stage salinity tolerance QTLs using backcross lines derived from Oryza sativa L. Pokkali. Plant Breed. 2011, 130, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.X.; Zhu, M.Z.; Yano, M.; Gao, J.P.; Liang, Z.W.; Su, W.A.; Hu, X.H.; Ren, Z.H.; Chao, D.Y. QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Haq, T.; John, G.B.; Javaid, A.C.; Nasim, A.D.; Katherine, A.; Steele, B.E. Dynamic quantitative trait loci for salt stress components on chromosome 1 of rice. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Hu, X.; Cui, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ali, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Z. Identification of salt-tolerant QTLs with strong genetic background effect using two sets of reciprocal introgression lines in rice. Genome 2011, 55, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, P.; Dvorak, J.; Mackill, D.; Deal, K.; Gregorio, G. RFLP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philipp. J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 85, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Nath, D.; Mohanta, R.L.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Marndi, B.C.; Nayak, A.K. Diversity and validation of microsatellite markers in ‘Saltol’ QTL region in contrasting rice genotypes for salt tolerance at the early vegetative stage. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2014, 8, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Niones, J.M. Fine Mapping of the Salinity Tolerance Gene on Chromosome 1 of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using Near-Isogenic Lines. Master’s Thesis, University of the Philippines, Los Banos, Philippines, 2004; 78p. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Abdullah, Z. Salinity-sodicity induced changes in reproductive physiology of rice (Oryza sativa) under dense soil conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2003, 49, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
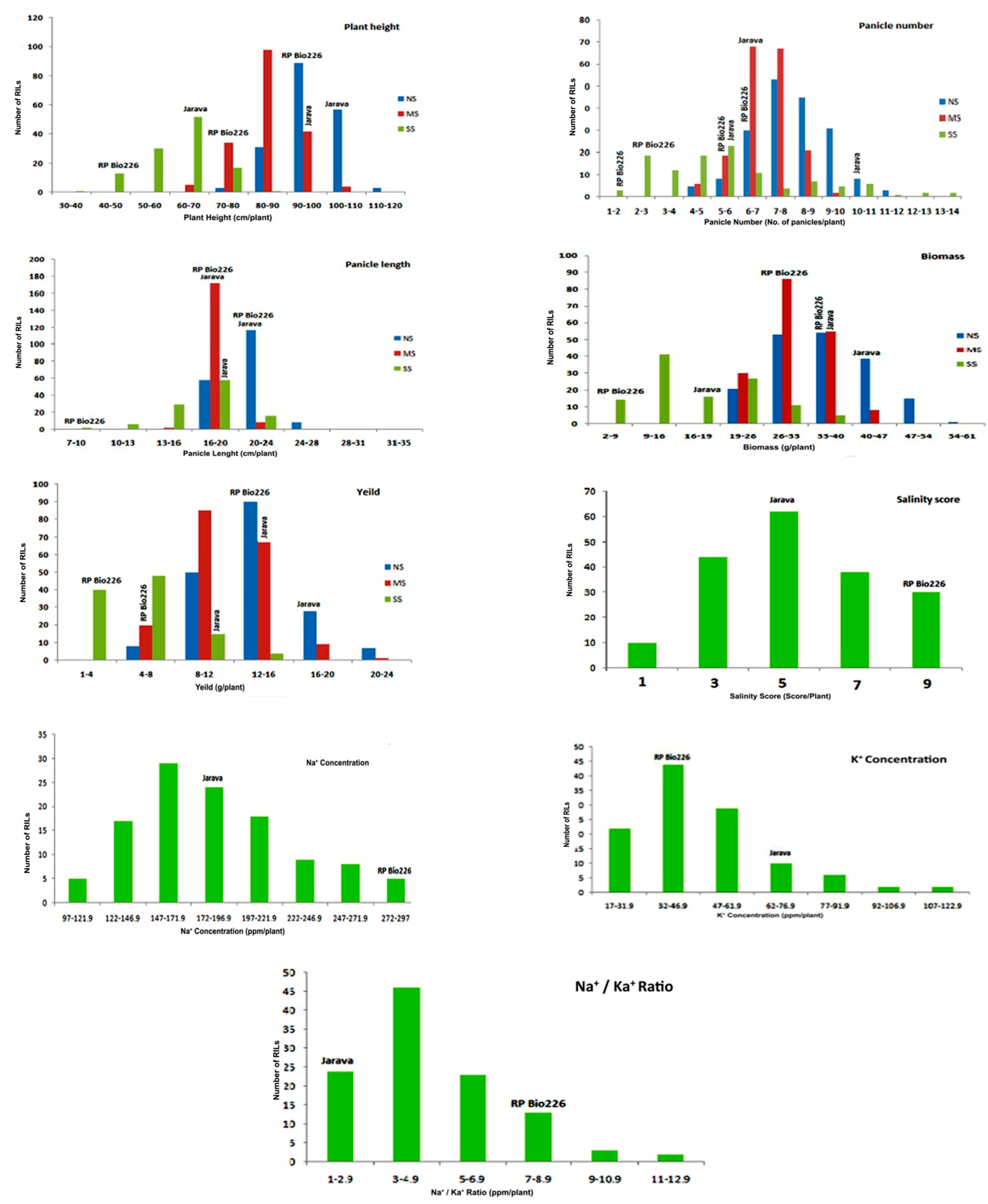

| Parental Lines | Recombinant Inbred Lines | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jarava | RPBio226 | Mean | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | |||||||||||||
| C | FS | PS | C | FS | PS | C | FS | PS | C | FS | PS | C | FS | PS | C | FS | PS | |
| PH | 109 | 98.5 | 68.37 | 95.8 | 78.6 | 40 | 96.47 ± 6.95 | 72.7 ± 7.61 | 61.16 ± 8.59 | 76.6–121 | 65.2–104.4 | 37.5–80.5 | −0.34 | −0.01 | −0.32 | 0.19 | 0.31 | −0.01 |
| PN | 10.2 | 6.8 | 5.62 | 6.7 | 5.6 | 1 | 7.89 ± 1.39 | 2.79 ± 1.27 | 5.37 ± 2.79 | 4.1–11.8 | 4.2–9.6 | 1–14 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.27 | −0.6 | 0.64 |
| PL | 22.4 | 20 | 19.34 | 21.1 | 16.5 | 9 | 20.79 ± 1.74 | 14.37 ± 3.65 | 17.06 ± 3.41 | 16.5–25.3 | 15.8–22.4 | 8–31.75 | 0.04 | −0.16 | 0.27 | −0.09 | 1.47 | 2.45 |
| BM | 42.2 | 33.5 | 18 | 35 | 26.3 | 5 | 35.74 ± 7.64 | 18.83 ± 7.21 | 17.10 ± 7.40 | 19.7–57 | 19.5–46.9 | 2–37.5 | 0.23 | 0.66 | 0.62 | −0.49 | 0.51 | 0.06 |
| YL | 19.2 | 13.1 | 8.18 | 15.1 | 7.4 | 1.5 | 13.33 ± 3.4 | 11.44 ± 2.79 | 5.32 ± 3.14 | 7.9–22.5 | 4.3–20.3 | 1–16 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 1.02 | −0.15 | 0.29 | 1 |
| Na+ | 183.5 | 286.6 | 185.17 ± 43.28 | 97.4–296.9 | 0.53 | −0.21 | ||||||||||||
| K+ | 64.5 | 37.03 | 47.81 ± 19.34 | 17.1–119 | 1.24 | 2.01 | ||||||||||||
| Na+/K+ | 2.89 | 7.81 | 4.74 ± 2.33 | 1.1–12.9 | 0.99 | 1.27 | ||||||||||||
| Score | 4.5 | 8.25 | 5.37 ± 2.27 | 1–9 | 0.08 | −0.81 | ||||||||||||
| Traits | Parental Lines | Recombinant Inbred Lines | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jarava | RPBio226 | Mean | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
| SSI Plant height | 0.1 | 0.18 | 0.99 ± 0.58 | −0.57–2.25 | −0.26 | −0.19 |
| SSI Tiller number | 0.33 | 0.16 | 0.83 ± 1.37 | −5.90–4.06 | −0.94 | 3.03 |
| SSI Panicle number | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.83 ± 1.38 | −6.33–4.05 | −1.02 | 3.71 |
| SSI Panicle length | −0.03 | 0.08 | 0.96 ± 0.58 | −0.79–2.53 | −0.18 | −0.02 |
| SSI Biomass | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.75 ± 1.64 | −5.50–4.75 | −0.5 | 1.14 |
| SSI Yield | 0.24 | 0.55 | 0.73 ± 1.85 | −5.33–4.61 | −0.81 | 0.16 |
| Trait | Stress | PH | TN | PN | PL | BM | YL | Na+ Conc | K+ Conc | Na+/K+ Conc | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | Control | ||||||||||
| FS | −0.03 | ||||||||||
| PS | 0.28 ** | ||||||||||
| PN | Control | 0.05 | |||||||||
| FS | −0.03 | 0.99 | |||||||||
| PS | 0.26 ** | 0.68 ** | |||||||||
| PL | Control | 0.35 ** | 0.1 ** | ||||||||
| FS | 0.68 ** | −0.12 | −0.11 | ||||||||
| PS | 0.45 ** | 0.00 | 0.15 | ||||||||
| BM | Control | 0.4 ** | 0.5 ** | 0.21 ** | |||||||
| FS | 0.2 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.12 | |||||||
| PS | 0.2 * | 0.32 ** | 0.16 | 0.26 ** | |||||||
| YL | Control | 0.29 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.14 | 0.74 ** | ||||||
| FS | 0.2 ** | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.67 ** | ||||||
| PS | 0.2 * | 0.36 ** | 0.24 * | 0.30 ** | 0.87 ** | ||||||
| Na+ conc | PS | −0.16 | −0.19 * | −0.09 | 0.05 | −0.35 ** | −0.38 ** | ||||
| K+ conc | PS | 0.05 | 0.31 ** | 0.21 * | −0.01 | 0.35 ** | 0.41 ** | −0.34 | |||
| Na++/K+ conc | PS | −0.09 | −0.33 ** | −0.33 | −0.02 | −0.50 ** | −0.57 ** | 0.54 | −0.67 | ||
| Score | PS | −0.13 | −0.27 ** | 0.19 * | −0.23 * | −0.61 ** | −0.71 ** | 0.36 | −0.44 ** | 0.68 ** | 1 |
| Trait | QTL | Chr | LOD Score | Marker Interval | Additive Effect | PVE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | qPHSt-2 | 2 | 5.2 | RM262-RM263 | 42.45 | 28.12 |
| qPHSt-6.1 | 6 | 2.62 | RM589-RM586 | −2.64 | 5.93 | |
| qPHSt-6.2 | 6 | 3.41 | RM204-RM276 | −2.64 | 10.32 | |
| PN | qPNSt-1 | 1 | 2.66 | RM10115-RM3426 | 0.31 | 7.56 |
| qPNSt-11 | 11 | 2.71 | RM224-RM207 | −0.53 | 10.44 | |
| PL | qPLSt-6 | 6 | 3.16 | RM589-RM586 | −0.49 | 6.89 |
| BM | qBMSt-2 | 2 | 2.69 | RM262-RM263 | 1.81 | 9.03 |
| qBMSt-10 | 10 | 3.93 | RM24893-RM25846 | −4.49 | 10.78 | |
| qBMSt-11 | 11 | 2.94 | RM224-RM207 | −1.76 | 9.33 | |
| qBMSt-12 | 12 | 3.02 | RM27971-RM7102 | −1.99 | 9.97 | |
| SPYL | qYLSt-12 | 12 | 2.81 | RM27940-RM27971 | −0.78 | 6.41% |
| Trait | QTL | Chr | LOD Score | Marker Interval | Additive Effect | PVE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | qPHSt-12.2 | 12 | 2.5 | RM27940-RM27971 | −9.07 | 8.07 |
| PN | qTNSt-10 | 10 | 2.73 | RM24893-RM25846 | −0.5 | 6.1 |
| PL | qPLSt-1.1 | 1 | 3.93 | RM3426-RM5638 | −1.05 | 13.25 |
| qPLSt-1.2 | 1 | 2.97 | RM11504-RM3482 | −0.86 | 10.9 | |
| qPLSt-2 | 2 | 2.5 | RM3294-RM12849 | −0.77 | 6.97 | |
| ST | qSTR-2 | 2 | 2.6 | RM110-RM423 | 0.6 | 8.9 |
| qSTR-11 | 11 | 2.23 | RM3717-RM286 | 0.69 | 8.9 | |
| NC | qSN-11 | 11 | 2.92 | RM26622-RM21 | 24.77 | 6.49 |
| qSN-12 | 12 | 2.8 | RM17-RM28587 | 26.86 | 7.51 | |
| NK | qSNK-12.1 | 12 | 3.53 | RM17-RM28587 | 1.27 | 15.65 |
| qSNK-12.2 | 12 | 2.77 | RM28587-RM28882 | 1.06 | 11.19 | |
| qYLSt-2 | 2 | 2.05 | RM13863-RM3316 | 0.72 | 5.8 |
| RILs | Score | Yield (g) | Na+ Conc. | K+ Conc. | Na+/K+ | QTL | % Inc. Over SP | % Inc. Over RP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP 5899-RIL-52 | 1 | 11.5 | 164.6 | 84.7 | 1.94 | qSN-12 + qSNK-12.1 + qYLSt-12 | 86.96 | 28.87 |
| RP 5899-RIL-57 | 1 | 11 | 154.3 | 46.7 | 3.30 | qSN-11 | 86.36 | 25.64 |
| RP 5899-RIL-60 | 1 | 15 | 148.2 | 48.3 | 3.07 | qSTR-2 + qSN-12 + qSNK-12.1 + qSNK-12.2 + qYLSt-12 | 90.00 | 45.47 |
| RP 5899-RIL-114 | 1 | 5.5 | 131.7 | 33.2 | 3.97 | qSN-12 + qSNK-12.1 + qSNK-12.2 | 72.73 | −48.73 |
| RP 5899-RIL-141 | 1 | 9 | 168 | 88.1 | 1.91 | qSN-11 + qSN-12 + qSNK-12.1 | 83.33 | 9.11 |
| RP 5899-RIL-142 | 1 | 11 | 132.7 | 119 | 1.12 | qSTR-2 + qSN-12 + qSNK-12.1 | 86.36 | 25.64 |
| Jarava | 4.5 | 8.18 | 183.5 | 64.5 | 2.89 | |||
| RP Bio226 | 8.25 | 1.5 | 286.6 | 37.03 | 7.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugasi, Y.D.; Srivastava, A.; Badri, J.; Pandey, M.; Parmar, B.; Singh, A.K.; Kishor, P.B.K.; Tilatoo, R. Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice. Crops 2024, 4, 684-700. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040047
Sugasi YD, Srivastava A, Badri J, Pandey M, Parmar B, Singh AK, Kishor PBK, Tilatoo R. Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice. Crops. 2024; 4(4):684-700. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugasi, Yamini Deepthi, Akanksha Srivastava, Jyothi Badri, Manish Pandey, Brajendra Parmar, Arun Kumar Singh, Polavarapu Bilhan Kavi Kishor, and Ram Tilatoo. 2024. "Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice" Crops 4, no. 4: 684-700. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040047
APA StyleSugasi, Y. D., Srivastava, A., Badri, J., Pandey, M., Parmar, B., Singh, A. K., Kishor, P. B. K., & Tilatoo, R. (2024). Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) for Reproductive Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice. Crops, 4(4), 684-700. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040047







