Operational Impacts of On-Demand Ride-Pooling Service Options in Birmingham, AL
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Simulation Model Selection
3.3. Simulation Study Experimental Design
3.4. Birmingham MATSim Simulation Model
4. Results
4.1. Status of Ride-Pooling Vehicles
4.2. Vehicle Occupancy Profiles
4.3. Impact of Ride-Pooling Service Availability on Modal Choice
| TNC Fleet Size (Vehicles) | Scenario | Transit Trips (Total Ridership) | Walk Trips | Private Auto Trips | Ride-Pooling Trips | Vehicle Trips (Private Auto + Ride-Pooling) | Change in Vehicle Trips Due to Ride-Pooling (Baseline—Number of Vehicle Trips) | % Change in Vehicle Trips Due to Ride-Pooling Compared to Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 TNCs | Baseline | 2648 | 5172 | 144,014 | 0 | 144,014 | 0 | 0% |
| 200 TNCs | d2d | 4590 | 8115 | 135,156 | 1386 | 136,542 | −7472 | −5.19% |
| sB | 3649 | 7987 | 136,167 | 2909 | 139,076 | −4938 | −3.43% | |
| 400 TNCs | d2d | 4359 | 7693 | 133,445 | 2718 | 136,163 | −7851 | −5.45% |
| sB | 3423 | 7840 | 135,914 | 3853 | 139,767 | −4247 | −2.95% | |
| 800 TNCs | d2d | 3919 | 7093 | 131,333 | 5420 | 136,753 | −7261 | −5.04% |
| sB | 3272 | 7851 | 135,828 | 4146 | 139,974 | −4040 | −2.81% |
4.4. Impact of Ride-Pooling Service Availability on Network-Wide Operations
4.4.1. Total Daily Network VKT
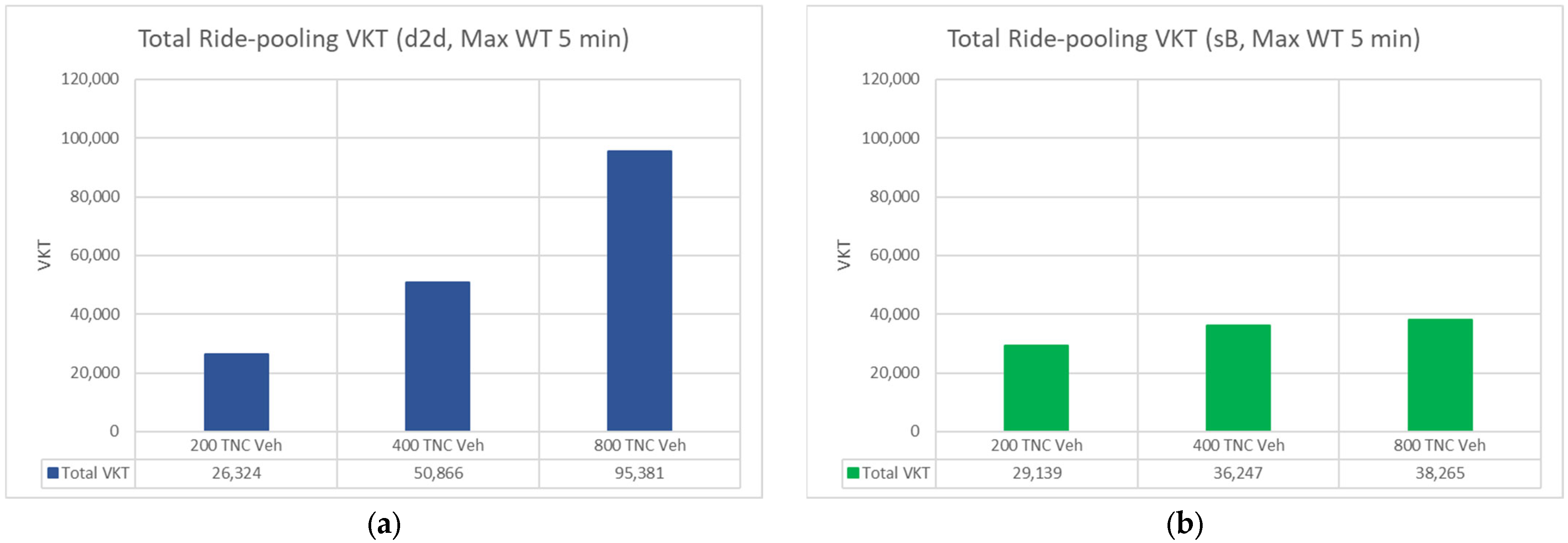
4.4.2. Ride-Pooling Daily VKT

4.4.3. Ride-Pooling Vehicle Distance Travelled
4.4.4. Customer Service Time and Ride Request Rejection Rate
5. Summary and Conclusions
6. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ke, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, H.; Ye, J. Data-Driven Analysis on Matching Probability, Routing Distance and Detour Distance in Ride-Pooling Services. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 124, 102922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.; Sener, I.N. Strangers On This Road We Are On: A Literature Review of Pooling in On-Demand Mobility Services. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2677, 03611981221123801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.; Morseman, S. The Perfect uberPOOL: A Case Study on Trade-Offs. In Proceedings of the Ethnographic Praxis in Industry Conference Proceedings, Honolulu, HI, USA, 10–12 October 2018; pp. 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Uber. Your Guide to Driving with UberPool. Available online: https://www.uber.com/us/en/drive/services/shared-rides/ (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Li, S.; Fei, F.; Ruihan, D.; Yu, S.; Dou, W. A Dynamic Pricing Method for Carpooling Service Based on Coalitional Game Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on High-Performance Computing and Communications, IEEE 14th International Conference on Smart City, and IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Sydney, Australia, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, J.; Yan, D.; Yuan, L.; Jafarzadehfadaki, M.; Adhikari, S.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Jiang, Z. Realistic Urban Traffic Simulation with Ride-Hailing Services: A Revisit to Network Kernel Density Estimation (Systems Paper). In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 1–4 November 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, F.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Khalil, J.; Jafarzadehfadaki, M.; Yan, D. Quantifying the Impact of Transportation Network Companies on Urban Congestion at a Medium Sized City. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2023, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisiopiku, V.; Salman, F. Simulation Options for Modeling Shared Mobility. In Proceedings of the 2019 AlaSim International Conference and Exhibition, Huntsville, AL, USA, 24 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, T.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Khalil, J.; Yan, D. Potential Benefits of Increased Public Transit Ridership in Medium Sized Cities: A Case Study. J. Transp. Technol. 2021, 12, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viergutz, K.; Schmidt, C. Demand Responsive-vs. Conventional Public Transportation: A MATSim Study about the Rural Town of Colditz, Germany. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 151, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwick, F.; Kuehnel, N.; Moeckel, R.; Axhausen, K.W. Agent-Based Simulation of City-Wide Autonomous Ride-Pooling and the Impact on Traffic Noise. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 90, 102673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Maciejewski, M.; Wu, H.; Nagel, K. Demand-Responsive Transport for Students in Rural Areas: A Case Study in Vulkaneifel, Germany. 2022. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4181254 (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Chen, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Exploring Impacts of On-Demand Ridesplitting on Mobility via Real-World Ridesourcing Data and Questionnaires. Transportation 2021, 48, 1541–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Mo, H. The Potential of Ride-Pooling in VKT Reduction and its Environmental Implications. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 103, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.; Maciejewski, M.; Nagel, K. City-Wide Shared Taxis: A Simulation Study in Berlin. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 October 2017; pp. 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tirachini, A.; Gomez-Lobo, A. Does Ride-Hailing Increase or Decrease Vehicle Kilometers Traveled (VKT)? A Simulation Approach for Santiago de Chile. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2020, 14, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagho, G.O.; Hensle, D.; Balac, M.; Freedman, J.; Twumasi-Boakye, R.; Broaddus, A.; Fishelson, J.; Axhausen, K.W. Demand Responsive Transit Simulation of Wayne County, Michigan. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizi, A.; Twumasi-Boakye, R.; Djavadian, S.; Fishelson, J. Agent-Based Simulation Approach to Determine Safety Impacts of Demand-Responsive Transport (DRT) in Wayne County, Michigan. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2676, 03611981221089542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; MacKenzie, D. Assessing the VMT Effect of Ridesourcing Services in the US. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 94, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.D. Transportation Network Companies and the Ridesourcing Industry: A Review of Impacts and Emerging Regulatory Frameworks for Uber. In Report Prepared for the City of Vancouver; University of British Columbia Library: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rayle, L.; Dai, D.; Chan, N.; Cervero, R.; Shaheen, S. Just a Better Taxi? A Survey-Based Comparison of Taxis, Transit, and Ridesourcing Services in San Francisco. Transp. Policy 2016, 45, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clewlow, R.R.; Mishra, G.S. Disruptive Transportation: The Adoption, Utilization, and Impacts of Ride-Hailing in the United States; UC Davis Institute of Transportation Studies: Davis, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelela, M.; Tirachini, A.; Chaniotakis, E.; Antoniou, C. Characterizing the Adoption and Frequency of Use of a Pooled Rides Service. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 138, 103632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ban, X.J. Characterization of Ridesplitting Based on Observed Data: A Case Study of Chengdu, China. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 100, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, S.C.-K.; Shen, S.; Zhou, Y. Decentralized Ride-Sharing and Vehicle-Pooling Based on Fair Cost-Sharing Mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 23, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielbaum, A.; Alonso-Mora, J. Unreliability in Ridesharing Systems: Measuring Changes in Users’ Times Due to New Requests. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 121, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieterman, J.; Smith, C.S. Sharing the Ride: A Paired-Trip Analysis of UberPool and Chicago Transit Authority Services in Chicago, Illinois. Res. Transp. Econ. 2018, 71, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leich, G.; Bischoff, J. Should Autonomous Shared Taxis Replace Buses? A Simulation Study. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 41, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demographics Alabama. Available online: https://www.alabama-demographics.com/counties_by_population (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Macrotrends. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Reporter Census. Available online: https://censusreporter.org/profiles/05000US26163-wayne-county-mi/ (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Jefferson County, Alabama History. Available online: https://www.ereferencedesk.com/resources/counties/alabama/jefferson.html (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Countywide Overview. Available online: https://www.shelbyal.com/DocumentCenter/View/61/part-one?bidId= (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Jefferson County, Alabama (AL). Available online: https://www.city-data.com/county/Jefferson_County-AL.html (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Shelby County, Alabama (AL). Available online: https://www.city-data.com/county/Shelby_County-AL.html (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Getting from Here to There: Transportation and Mobility. Available online: https://www.birminghamal.gov/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/CH12_Transportation-Mobility.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Sisiopiku, V.P.; Thompson, R.C.; Ramadan, O.E. UAB Commuter Survey; The University of Alabama at Birmingham: Birmingham, AL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sisiopiku, V.P.; Hadi, M.; McDonald, N.; Steiner, R.; Ramadan, O.E. Technology Influence on Travel Demand and Behaviors; Final Report to the Southeastern Transportation Research, Innovation; Development and Education Center (STRIDE): Birmingham, AL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Horni, A.; Nagel, K.; Axhausen, K.W. The Multi-Agent Transport Simulation MATSim; Ubiquity Press London: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- MATSim. Available online: https://matsim.org/ (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Kuehnel, N.; Zwick, F.; Hörl, S. Shifts in Perspective: Operational Aspects in (non-) Autonomous Ride-Pooling Simulations. In Arbeitsberichte Verkehrs-und Raumplanung; IVT ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1627. [Google Scholar]
- Zwick, F.; Axhausen, K.W. Impact of Service Design on Urban Ridepooling Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rhodes, Greece, 20–23 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, J.; Führer, K.; Maciejewski, M. Impact Assessment of Autonomous DRT Systems. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 41, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.; Márquez-Fernández, F.J.; Domingues-Olavarría, G.; Maciejewski, M.; Nagel, K. Impacts of Vehicle Fleet Electrification in Sweden—A Simulation-Based Assessment of Long-Distance Trips. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Kraków, Poland, 5–7 June 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zwick, F.; Axhausen, K.W. Analysis of Ridepooling Strategies with MATSim. In Proceedings of the 20th Swiss Transport Research Conference (STRC 2020), Virtual, 13–14 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Grahn, R.; Qian, S.; Matthews, H.S.; Hendrickson, C. Are travelers substituting between transportation network companies (TNC) and public buses? A case study in Pittsburgh. Transportation 2021, 48, 977–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.; Castiglione, J.; Mislove, A.; Wilson, C. Profiling transport network company activity using big data. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TNC Fleet Size (Vehicles) | Scenario | Total Daily VKT | Change in Total Daily VKT (Baseline—Ride-Pooling Scenario) | VKT % Diff. to Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 TNCs | Baseline | 2,265,716 | ||
| 200 TNCs | d2d | 2,134,646 | −131,070 | −5.78% |
| sB | 2,204,292 | −61,424 | −2.71% | |
| 400 TNCs | d2d | 2,157,837 | −107,879 | −4.76% |
| sB | 2,209,273 | −56,443 | −2.49% | |
| 800 TNCs | d2d | 2,193,750 | −71,966 | −3.18% |
| sB | 2,212,335 | −53,381 | −2.36% |
| TNC Fleet Size (Vehicles) | Scenario | Total Daily Distance Traveled (km) | Daily Distance Traveled While Empty (km) | Empty Ratio (%) | Total Detour Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 TNC Veh | d2d | 26,324 | 2145 | 8.15% | 1395 |
| sB | 29,139 | 3248 | 11.15% | 2974 | |
| 400 TNC Veh | d2d | 50,866 | 4132 | 8.12% | 2743 |
| sB | 36,247 | 3518 | 9.71% | 3948 | |
| 800 TNC Veh | d2d | 95,381 | 7354 | 7.71% | 5492 |
| sB | 38,265 | 3455 | 9.03% | 4250 |
| TNC Fleet Size (Vehicles) | Scenario | Mean Passenger Wait Time (s) | Mean In-Vehicle Travel Time (IVTT) (s) | Mean Passenger Service Time (s) | Mean Travel Distance (m) | Ride Request Rejection Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 TNC Veh | d2d | 219 | 1153 | 1372 | 17,486 | 55% |
| sB | 182 | 703 | 885 | 9415 | 18% | |
| 400 TNC Veh | d2d | 220 | 1195 | 1415 | 17,271 | 47% |
| sB | 164 | 669 | 833 | 9050 | 10% | |
| 800 TNC Veh | d2d | 214 | 1132 | 1346 | 16,485 | 33% |
| sB | 163 | 676 | 839 | 9011 | 8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salman, F.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Khalil, J.; Yang, W.; Yan, D. Operational Impacts of On-Demand Ride-Pooling Service Options in Birmingham, AL. Future Transp. 2023, 3, 519-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3020030
Salman F, Sisiopiku VP, Khalil J, Yang W, Yan D. Operational Impacts of On-Demand Ride-Pooling Service Options in Birmingham, AL. Future Transportation. 2023; 3(2):519-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalman, Furat, Virginia P. Sisiopiku, Jalal Khalil, Wencui Yang, and Da Yan. 2023. "Operational Impacts of On-Demand Ride-Pooling Service Options in Birmingham, AL" Future Transportation 3, no. 2: 519-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3020030
APA StyleSalman, F., Sisiopiku, V. P., Khalil, J., Yang, W., & Yan, D. (2023). Operational Impacts of On-Demand Ride-Pooling Service Options in Birmingham, AL. Future Transportation, 3(2), 519-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3020030







