Monitoring Landform Changes in a Mining Area in Mexico Using Geomatic Techniques
Highlights
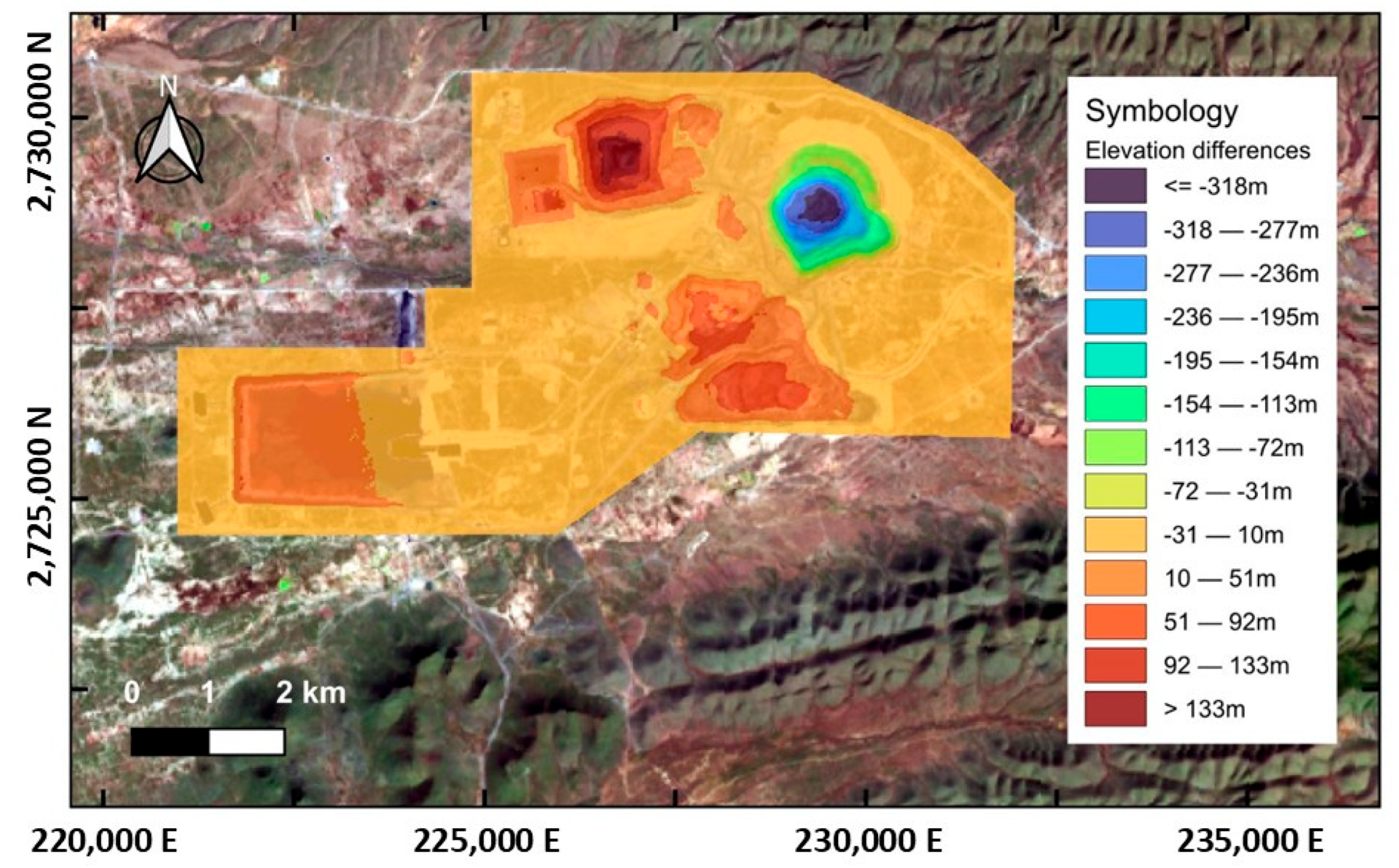
- This study reveals that mining activities in Mazapil, Zacatecas, Mexico, have caused significant changes in the terrain, with ground depressions greater than −333 m and waste accumulations greater than +152 m.
- Remote sensing (RS) techniques were used, with multi-temporal Landsat 5 and 8 images, as well as Digital Elevation Models (DEM) from 1998 and 2014.
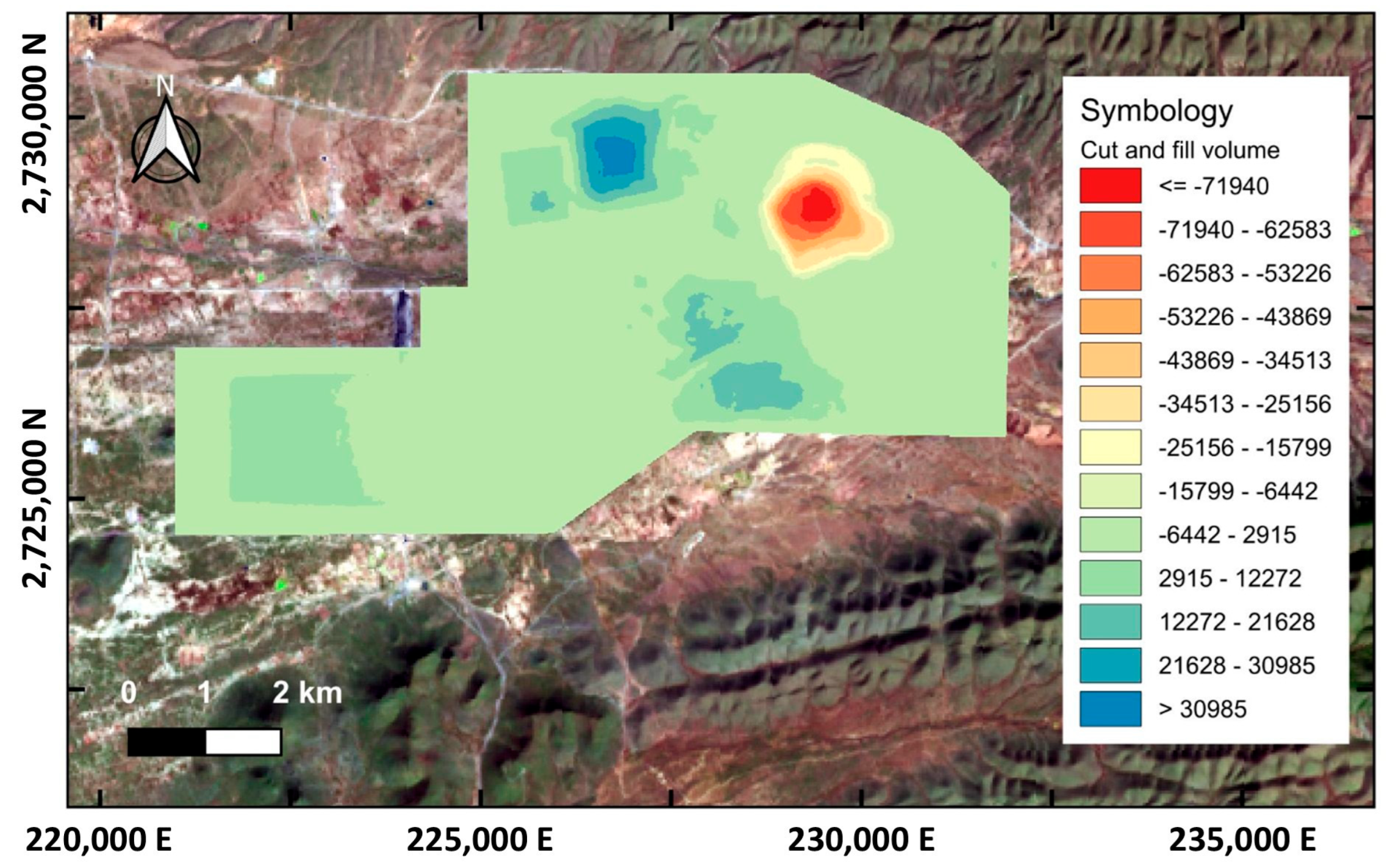
- The analysis quantified a total excavation volume of 413,524,124 m3 and an embankment volume of 431,194,785 m3.
- Despite limitations related to DEM resolution and data availability, the method used proved to be effective for remote quantification of large-scale topographic alterations.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
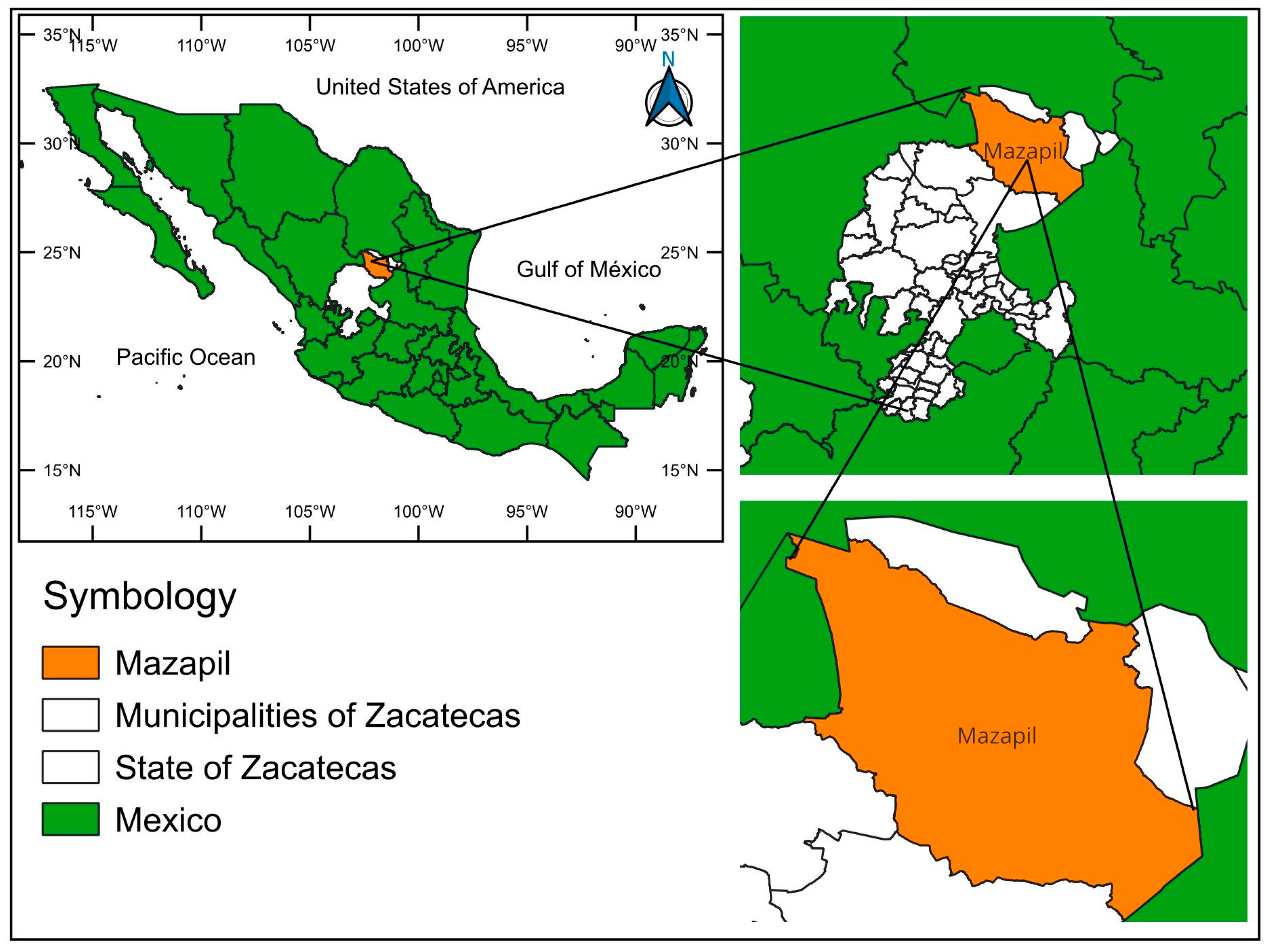
2.1. Study Area
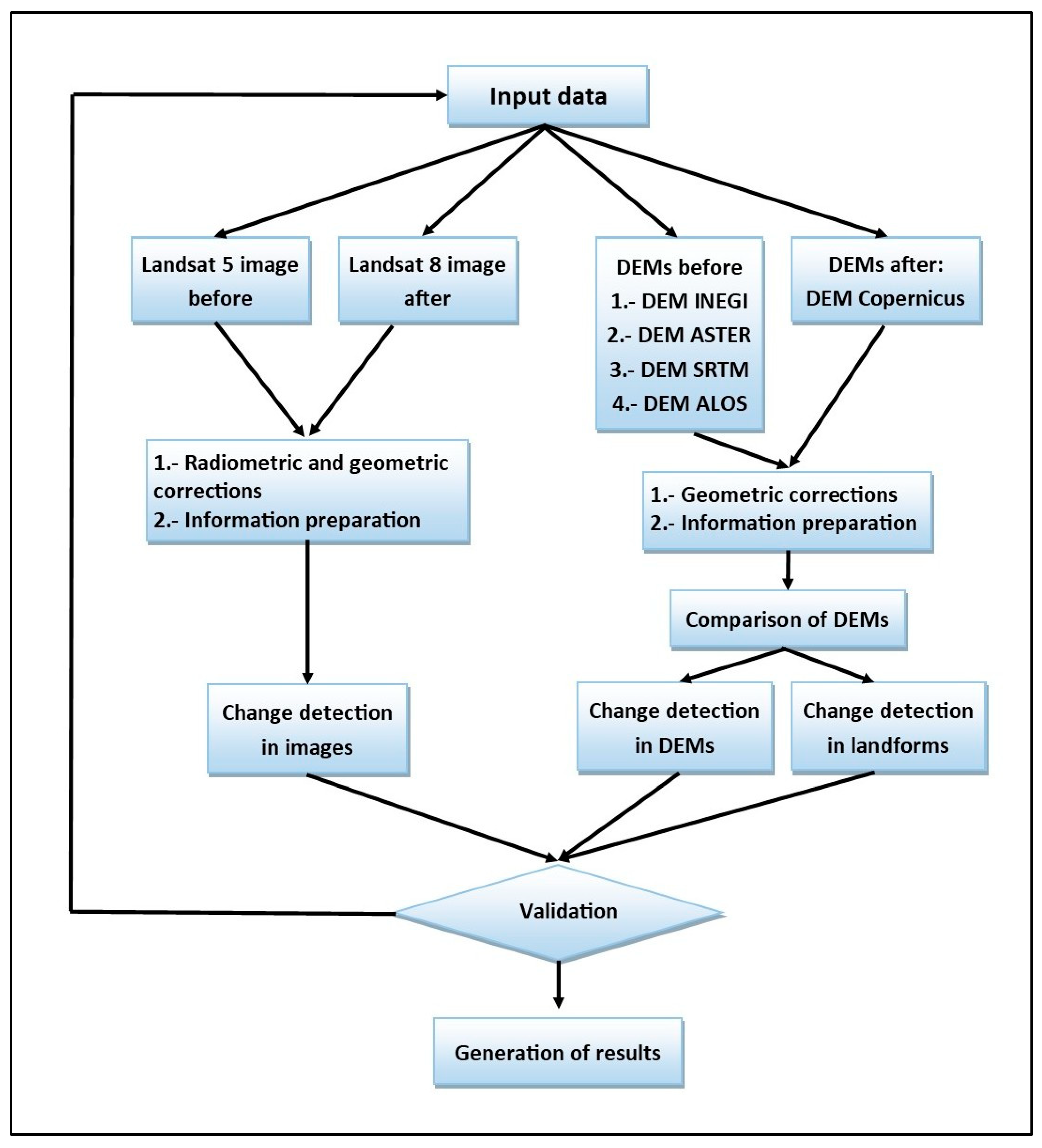
2.2. Methodology
- Acquisition of input data (satellite and DEM images, before and after mining activity).
- Radiometric and geometric corrections and information preparation.
- Change detection and analysis.
- Evaluation of the reliability of the obtained data.
- Generation of results.
2.2.1. Acquisition of Satellite Images and DEMs Before and After Mining Activity
2.2.2. Radiometric and Geometric Corrections and Preparation of Satellite Images and DEM
2.2.3. Detection of Changes in Satellite Images and DEMs
2.2.4. Evaluation of Data Reliability
2.2.5. Generation of Final Maps of Terrain Alterations
3. Results
3.1. Vertical Error, Standard Deviation, and Mean Square Error for the Different DEMs
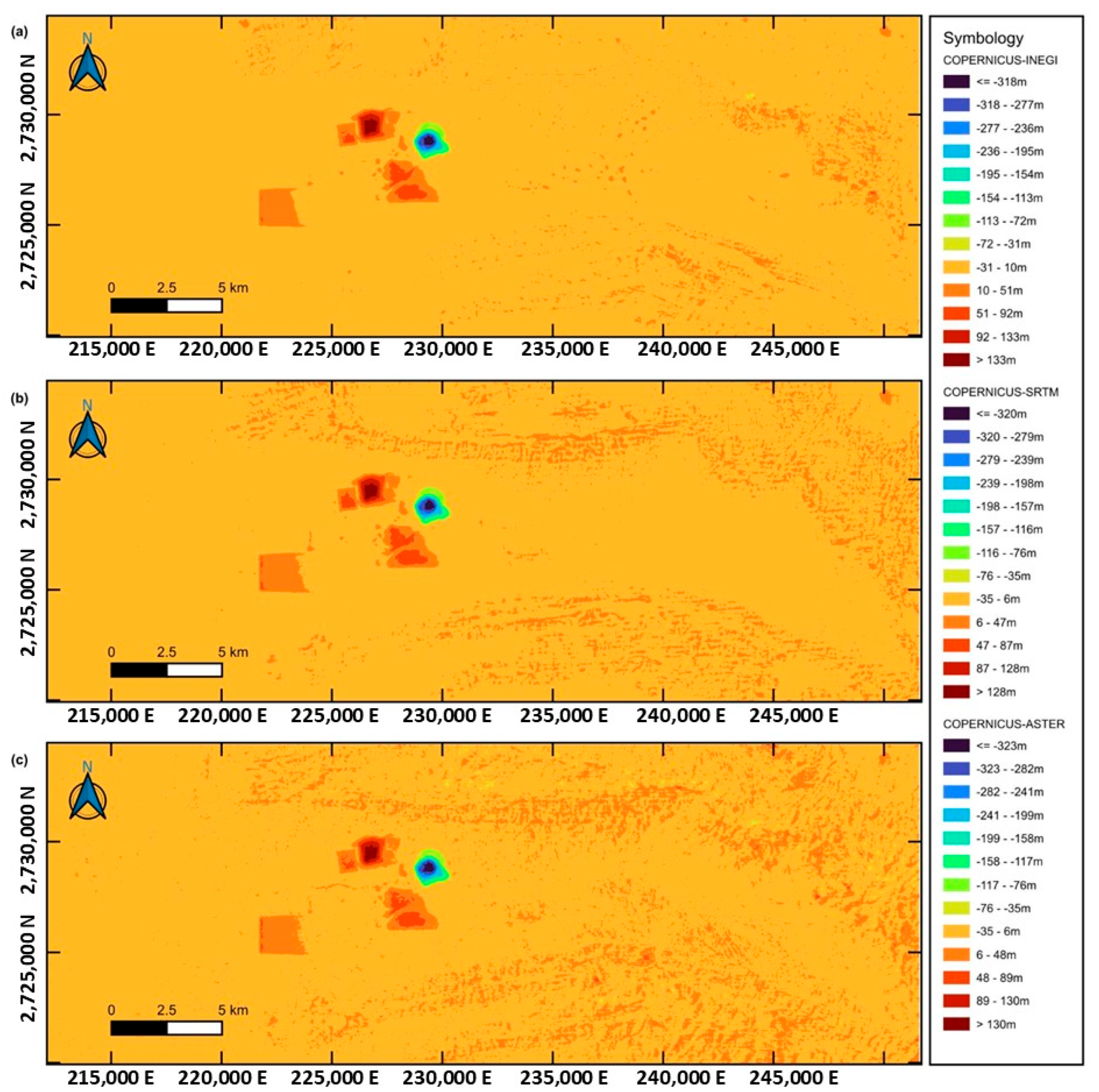
3.2. Detection of Physical Changes in the Mining Area Using Satellite Images and DEMs
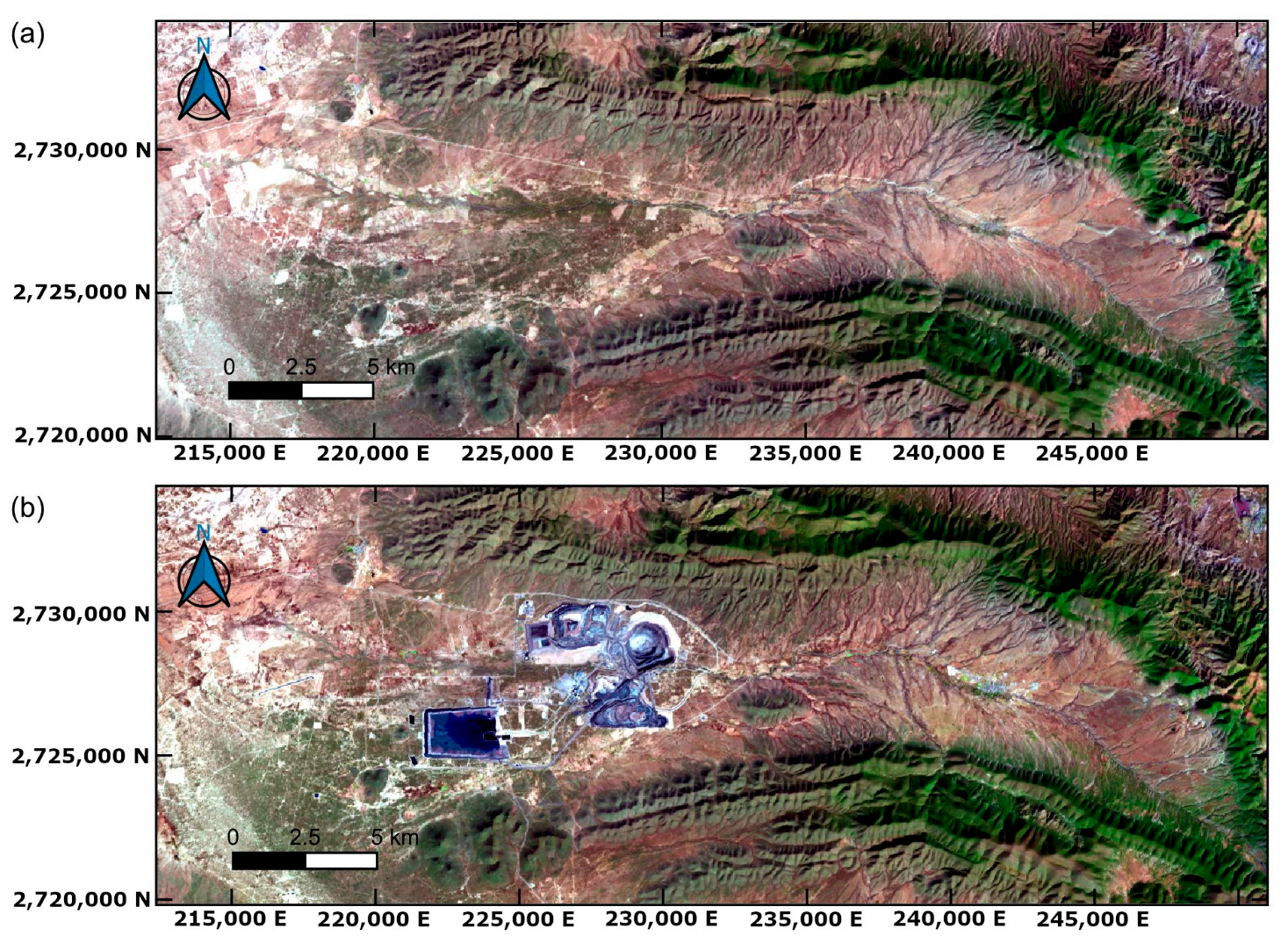
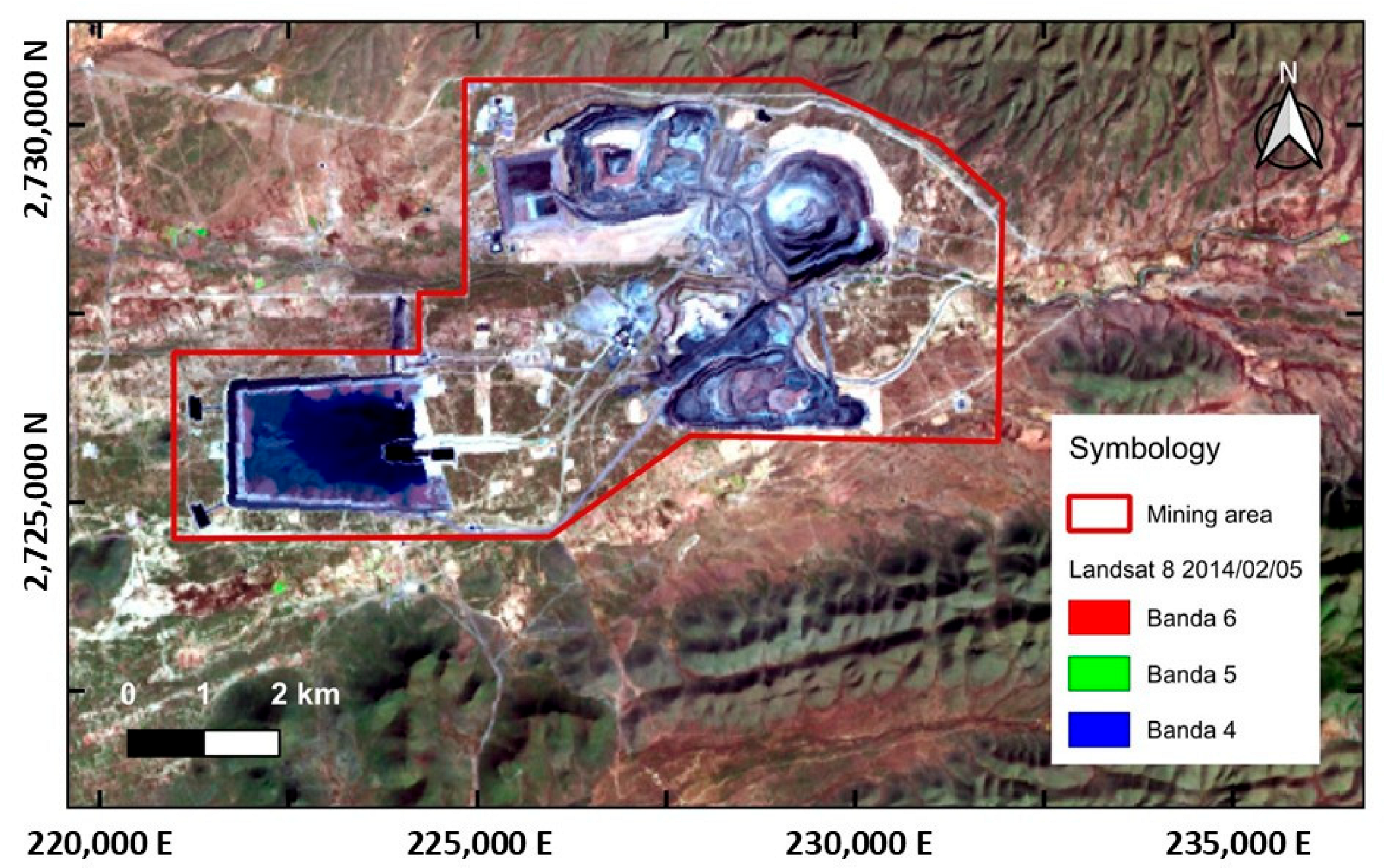
3.2.1. Detection of Changes in Satellite Images
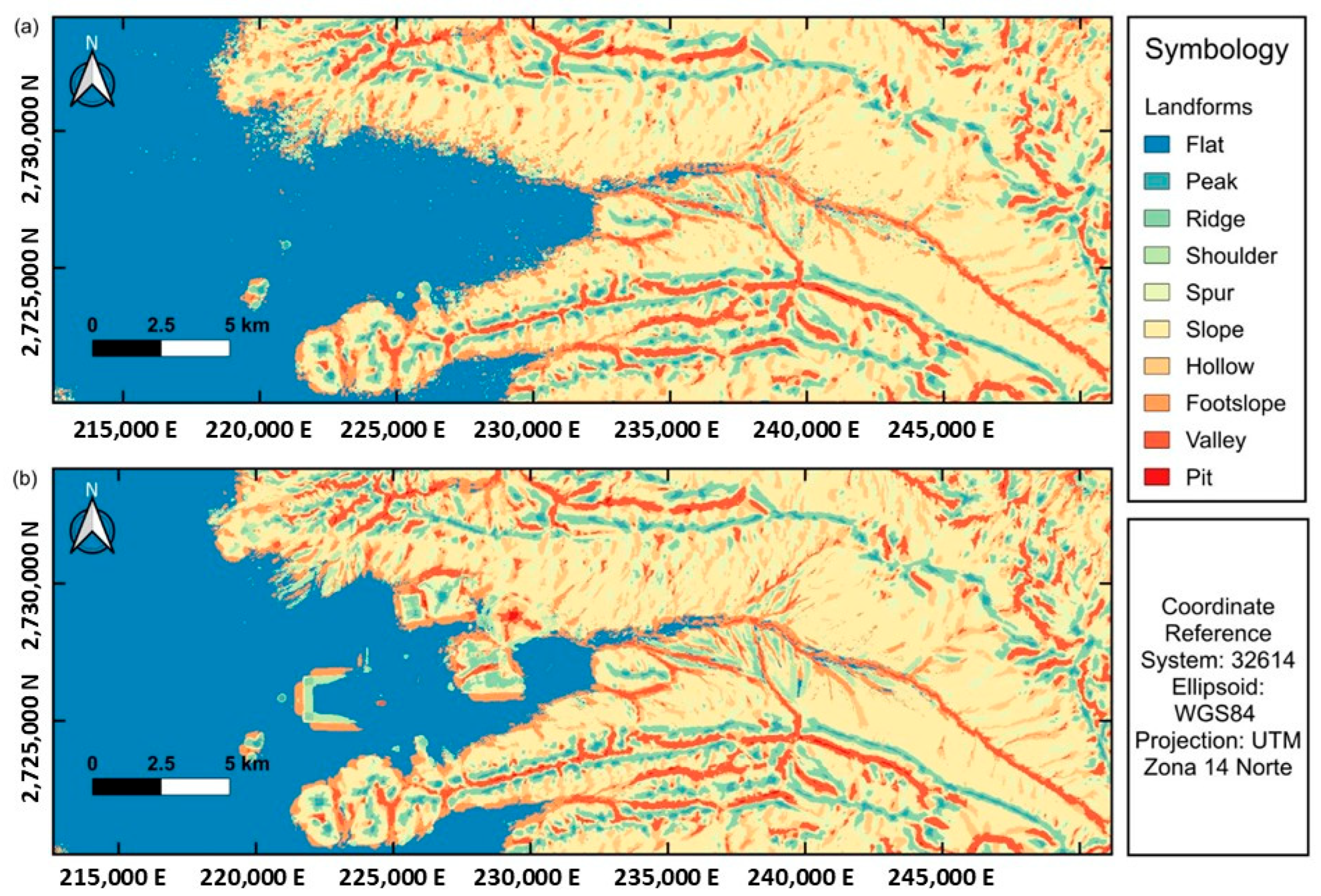
3.2.2. Detection of Relief Changes Using Multitemporal DEM
3.2.3. Detection of Elevation Changes Using Multitemporal DEMs
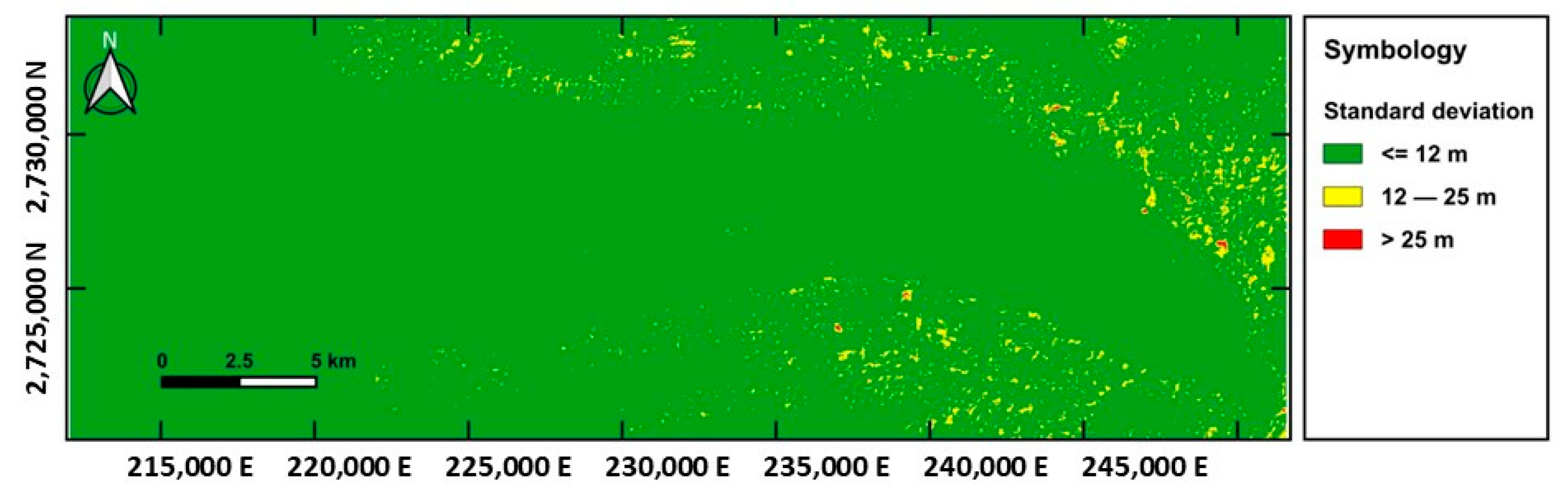
3.3. Evaluation of the Reliability of Elevation Differences Through Standard Deviation Analysis
3.4. Generation of the Final Maps
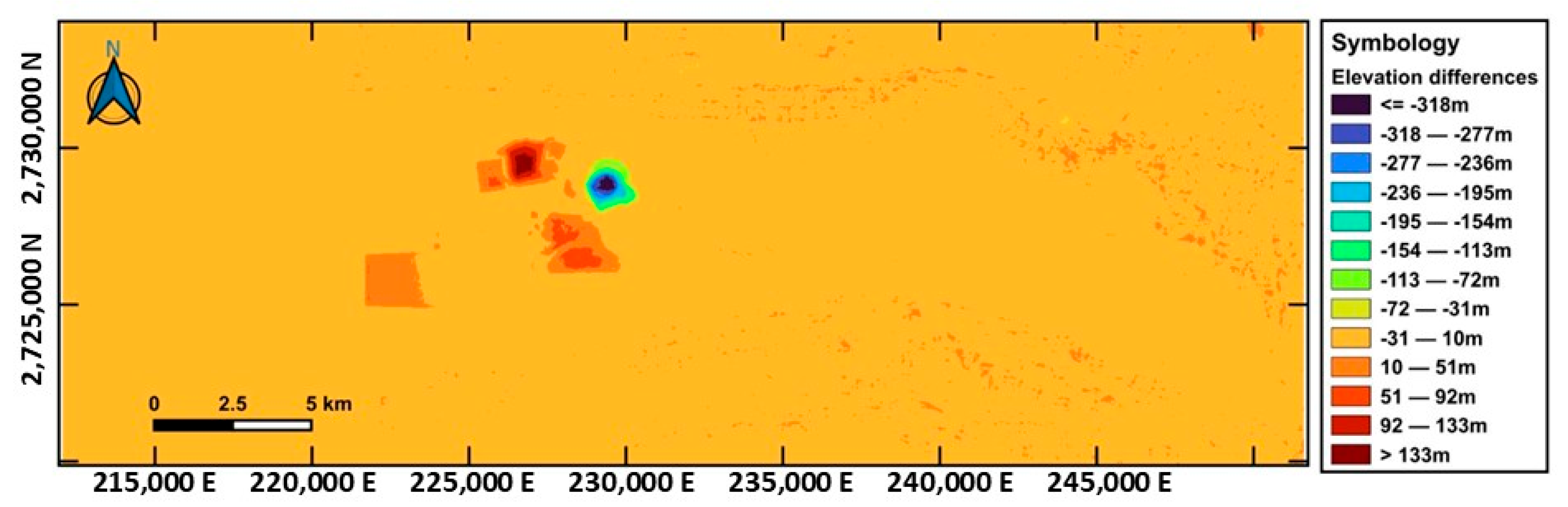
3.4.1. Average Map of Topographic Alterations in the Mining Area
3.4.2. Delimitation of the Active Mining Area
3.4.3. Elevation Changes Within the Mining Footprint
3.4.4. Calculation of Excavation and Filling Volumes Within the Mining Area
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| SPOT | Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre |
| ASTER | Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| INEGI | National Institute of Statistics and Geography |
| ALOS | Advanced Land Observing Satellite |
| USGS | United States Geological Survey |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
References
- Werner, T.T.; Bebbington, A.; Gregory, G. Assessing Impacts of Mining: Recent Contributions from GIS and Remote Sensing. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2019, 6, 993–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seloa, P.; Ngole-Jeme, V. Community Perceptions on Environmental and Social Impacts of Mining in Limpopo South Africa and the Implications on Corporate Social Responsibility. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2022, 19, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, M. Environmental Impacts of Mining: Monitoring, Restoration, and Control, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-003-16401-2. [Google Scholar]
- Laker, M.C. Environmental Impacts of Gold Mining—With Special Reference to South Africa. Mining 2023, 3, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Huante, P.; Rincón, E. Restauración de Minas Superficiales En México; SEMARNAT: Zapopan, Mexico, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Khobragade, K. Impact of Mining Activity on Environment: An Overview. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2020, 10, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiwumi, F.A.; Butler, D.R. Mining and Environmental Change in Sierra Leone, West Africa: A Remote Sensing and Hydrogeomorphological Study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 142, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charou, E.; Stefouli, M.; Dimitrakopoulos, D.; Vasiliou, E.; Mavrantza, O.D. Using Remote Sensing to Assess Impact of Mining Activities on Land and Water Resources. Mine Water Environ. 2010, 29, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeć, A.; Trybała, P.; Głąbicki, D.; Buczyńska, A.; Owczarz, K.; Bugajska, N.; Kozińska, P.; Chojwa, M.; Gattner, A. Application of Remote Sensing, GIS and Machine Learning with Geographically Weighted Regression in Assessing the Impact of Hard Coal Mining on the Natural Environment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, K.; Ke, L. Integration of TanDEM-X and SRTM DEMs and Spectral Imagery to Improve the Large-Scale Detection of Opencast Mining Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.W. Use of Remote Sensing and GIS in a Risk Assessment of Gold and Uranium Mine Residue Deposits and Identification of Vulnerable Land Use. PhD Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Emel, J.; Plisinski, J.; Rogan, J. Monitoring Geomorphic and Hydrologic Change at Mine Sites Using Satellite Imagery: The Geita Gold Mine in Tanzania. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 54, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, D.S.; Yucel, M.A.; Baba, A. Change Detection and Visualization of Acid Mine Lakes Using Time Series Satellite Image Data in Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Can (Canakkale) County, NW Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4311–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cássia Leopoldino, J.; dos Anjos, C.S.; Simões, D.P.; Fernandes, L.F.R. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of the Collapse of the Tailings Dam in Brumadinho, Brazil. Rev. Agrogeoambiental 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, L.; Zhao, L.; Niu, R. Automatic Identification and Dynamic Monitoring of Open-Pit Mines Based on Improved Mask R-CNN and Transfer Learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Sedighi, A.; Firozjaei, H.K.; Kiavarz, M.; Homaee, M.; Arsanjani, J.J.; Makki, M.; Naimi, B.; Alavipanah, S.K. A Historical and Future Impact Assessment of Mining Activities on Surface Biophysical Characteristics Change: A Remote Sensing-Based Approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza Ramos, I.A.; Pech Canché, J.M.; Escobar León, M.C. Externalidades Ambientales Generadas Por La Unidad Minera Peñasquito, Mazapil, Zacatecas, México. 2021. Available online: https://cdigital.uv.mx/server/api/core/bitstreams/3da78d55-fb1a-40d1-a612-05a5d911b417/content (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Mulková, M.; Popelková, R. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Development of Mining Landforms Using Aerial Photographs: Case Study from the Ostrava–Karviná Mining District. Morav. Geogr. Rep. 2024, 32, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimbye, Z.E.; Loggenberg, K. A Scoping Review of Landform Classification Using Geospatial Methods. Geomatics 2023, 3, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, W.; Breach, M. Engineering Surveying, 6th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh, B.F.; Slattery, D. Surveying with Construction Applications; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ghilani, C.D.; Wolf, P.R. Elementary Surveying. An Introduction to Geomatics, 13th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Facciolo, G.; De Franchis, C.; Meinhardt-Llopis, E. Automatic 3D Reconstruction from Multi-Date Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1542–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.-J.; Tseng, C.-W.; Tseng, C.-M.; Liao, T.-C.; Yang, C.-J. Application of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Acquired Topography for Quantifying Typhoon-Driven Landslide Volume and Its Potential Topographic Impact on Rivers in Mountainous Catchments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, I. Corrected Precision of Topographic Measurements by Radar Interferometry. TechRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI. Compendio de Información Geográfica Municipal 2010; INEGI: Mazapil, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Marco Geoestadístico Integrado, Diciembre 2021; INEGI: Mazapil, Mexico, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo Neri, R.A. El Impacto Social de La Megaminería En Mazapil, Zacatecas. Context. Latinoam. 2022, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Fernández, L.Á. Métodos de Detección de Cambios En Teledetección 2017. Available online: https://riunet.upv.es/entities/publication/adfaa657-89f5-4300-ba18-9111e3b7011a (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Angeles, G.R.; Geraldi, A.M.; Marini, M.F. Procesamiento Digital de Imágenes Satelitales. Metodologías y Técnicas; Bahia Blanca, Argentina, 2020; ISBN 978-987-86-4773-9. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352544576_PROCESAMIENTO_DIGITAL_DE_IMAGENES_SATELITALES_METODOLOGIAS_Y_TECNICAS_2020 (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Earth Resources Observation and Science Center. Landsat 4-5 Thematic Mapper Level-1, Collection 2; Earth Resources Observation and Science Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Earth Resources Observation and Science Center. Landsat 8-9 Operational Land Imager/Thermal Infrared Sensor Level-1, Collection 2; Earth Resources Observation and Science Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Continuo de Elevaciones Mexicano y Modelos Digitales de Elevación; INEGI: Mazapil, Mexico, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ASA/METI/AIST/Japan Spacesystems and U.S. Team ASTER DEM Product 1999. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/documents/434/ASTGTM_User_Guide_V3.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Earth Resources Observation and Science Center. Digital Elevation-Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global; Earth Resources Observation and Science Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Earth Observation Research and Application Center. ALOS Data Users Handbook; Revision, C., Ed.; Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA): Tokyo, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus. ESA Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem (CDSE) 2023. Available online: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- USGS Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook 2019. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-8-data-users-handbook (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Blanchard, S.D.; Rogan, J.; Woodcock, D.W. Geomorphic Change Analysis Using ASTER and SRTM Digital Elevation Models in Central Massachusetts, USA. GIScience Remote Sens. 2010, 47, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. What Are the Band Designations for the Landsat Satellites? 2025. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-are-band-designations-landsat-satellites (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Jasiewicz, J.; Stepinski, T.F. Geomorphons—a Pattern Recognition Approach to Classification and Mapping of Landforms. Geomorphology 2013, 182, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.; Dan, W. Study on Calculation of Earthwork Filling and Excavation Based on ModelBuilder. Sci. J. Intell. Syst. Res. Vol. 2021, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, M.; Tariq, A.; Anwar, M.M.; Khan, A.M.; Arshad, F.; Mumtaz, F.; Farhan, M.; Zhang, L.; Zafar, A.; Aziz, M.; et al. Monitoring of Land Use–Land Cover Change and Potential Causal Factors of Climate Change in Jhelum District, Punjab, Pakistan, through GIS and Multi-Temporal Satellite Data. Land 2021, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashala, M.J.; Dube, T.; Mudereri, B.T.; Ayisi, K.K.; Ramudzuli, M.R. A Systematic Review on Advancements in Remote Sensing for Assessing and Monitoring Land Use and Land Cover Changes Impacts on Surface Water Resources in Semi-Arid Tropical Environments. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, B.E.; Kafy, A.-A.; Samuel, A.A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Ayowole, O.E.; Shahrier, M.; Duti, B.M.; Rahman, M.T.; Peter, O.T.; Abosede, O.O. Monitoring and Predicting the Influences of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Cropland Characteristics and Drought Severity Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh, Y.G.; Tracz, W.; Matthews, H.D.; Turner, S.E. Application of Machine Learning Approaches for Land Cover Monitoring in Northern Cameroon. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 74, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggel, C.; Schneider, D.; Miranda, P.J.; Granados, H.D.; Kääb, A. Evaluation of ASTER and SRTM DEM Data for Lahar Modeling: A Case Study on Lahars from Popocatépetl Volcano, Mexico. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 170, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, A.; Welch, R.; Lanh, H. Mapping from ASTER Stereo Image Data:DEM Validation and Accuracy. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 5, 256–370. [Google Scholar]
- Uuemaa, E.; Ahi, S.; Montibeller, B.; Muru, M.; Kmoch, A. Vertical Accuracy of Freely Available Global Digital Elevation Models (ASTER, AW3D30, MERIT, TanDEM-X, SRTM, and NASADEM). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allobunga, S.; Putri, R.; Siamashari, M.; Julita, I.; Fathoni, A.; Dwiriawan, H. The Mined Volume Calculation in the Traditional Mining Area by Using the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Approach in the Observation Area of CV. Sinergi Karya Solutif, Patikraja District, Banyumas Regency, East Java Province, Indonesia. J. Earth Mar. Technol. JEMT 2022, 2, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Input Data | Year | Number of Bands | Pixel Resolution | Sources of Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 images | 1998 | 7 | 30m | [31] |
| Landsat 8 images | 2014 | 11 | 30m | [32] |
| INEGI DEM | 1998 | 1 | 15m | [33] |
| ASTER DEM | 1999 | 1 | 30m | [34] |
| SRTM DEM | 2000 | 1 | 30m | [35] |
| ALOS PALSAR DEM | 2006 | 1 | 30m | [36] |
| Copernicus DEM | 2014 | 1 | 17m | [37] |
| Differences | ME (m) | SD (m) | RMSE (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALOS-INEGI | −14.420 | 5.685 | 15.501 |
| ASTER-INEGI | 1.259 | 8.560 | 8.652 |
| SRTM-INEGI | 1.272 | 6.372 | 6.498 |
| Elevation Range (m) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Dominant Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| <−19 | 2.587 | 5.82% | Deep excavation |
| −19 to +10 | 29.281 | 65.8% | Areas of moderate and no alteration |
| >+10 | 12.632 | 28.38% | Waste or tailings deposit |
| Parameter | Volume |
|---|---|
| Excavation volume | 413,524,124 m3 |
| Fill volume | 431,194,785 m3 |
| Std. deviation per pixel | ±810 m3 |
| Max. excavation volume per pixel | −71,940 m3 |
| Max. fill volume per pixel | +30,985 m3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dávila-Cisneros, S.; Castañeda-Miranda, A.G.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.F.; Mattos-Villarroel, E.D.; Rodríguez-Abdalá, V.I.; Robles Rovelo, C.O.; Pinedo-Torres, L.A.; Rodríguez-Trejo, A.; Ibarra-Delgado, S. Monitoring Landform Changes in a Mining Area in Mexico Using Geomatic Techniques. Geomatics 2025, 5, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040063
Dávila-Cisneros S, Castañeda-Miranda AG, Bautista-Capetillo CF, Mattos-Villarroel ED, Rodríguez-Abdalá VI, Robles Rovelo CO, Pinedo-Torres LA, Rodríguez-Trejo A, Ibarra-Delgado S. Monitoring Landform Changes in a Mining Area in Mexico Using Geomatic Techniques. Geomatics. 2025; 5(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleDávila-Cisneros, Saúl, Ana G. Castañeda-Miranda, Carlos Francisco Bautista-Capetillo, Erick Dante Mattos-Villarroel, Víktor Iván Rodríguez-Abdalá, Cruz Octavio Robles Rovelo, Laura Alejandra Pinedo-Torres, Alejandro Rodríguez-Trejo, and Salvador Ibarra-Delgado. 2025. "Monitoring Landform Changes in a Mining Area in Mexico Using Geomatic Techniques" Geomatics 5, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040063
APA StyleDávila-Cisneros, S., Castañeda-Miranda, A. G., Bautista-Capetillo, C. F., Mattos-Villarroel, E. D., Rodríguez-Abdalá, V. I., Robles Rovelo, C. O., Pinedo-Torres, L. A., Rodríguez-Trejo, A., & Ibarra-Delgado, S. (2025). Monitoring Landform Changes in a Mining Area in Mexico Using Geomatic Techniques. Geomatics, 5(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics5040063










