Multimodal Feature Inputs Enable Improved Automated Textile Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
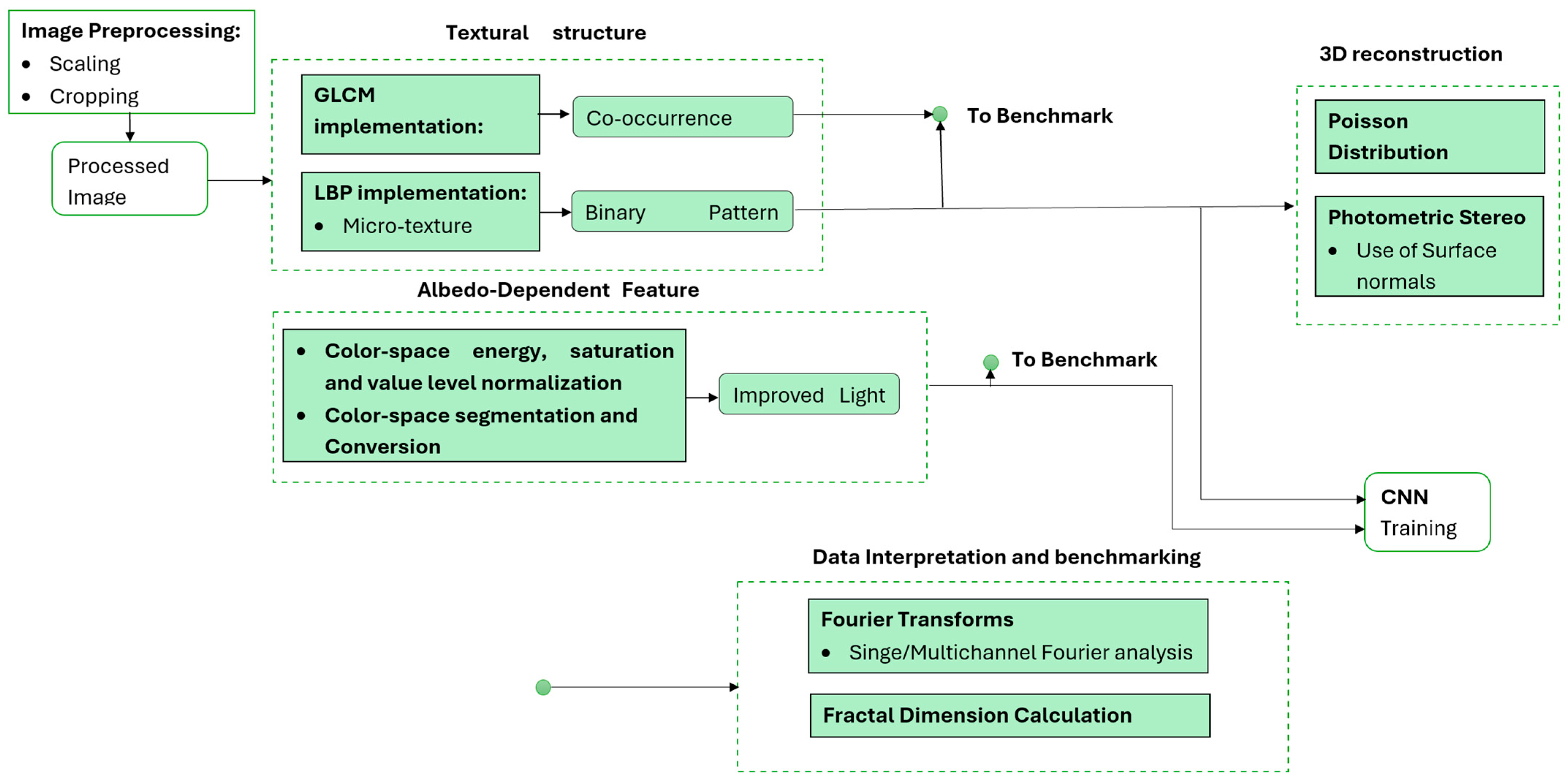
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset and Preprocessing Pipeline
2.2. Traditional Image Processing Methods
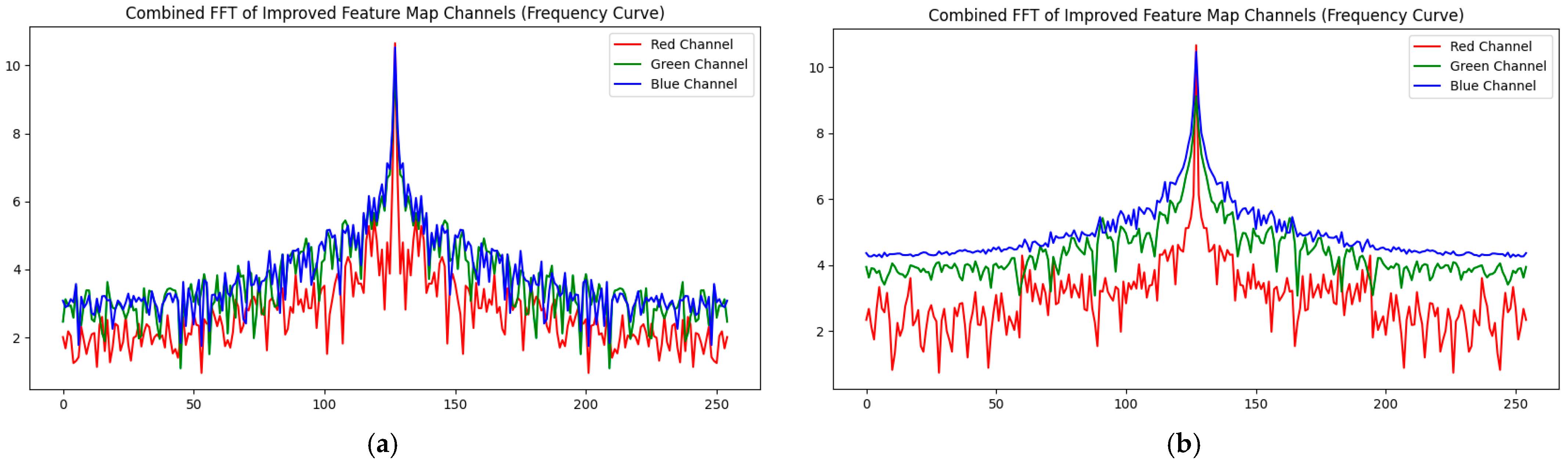
- Hue Channel: Peaks may correspond to color patterns.
- Saturation Channel: Peaks reveal color intensity variations.
- Value Channel: Peaks reflect texture variations.
2.3. Deep-Learning-Based Texture Classification
3. Results and Discussion
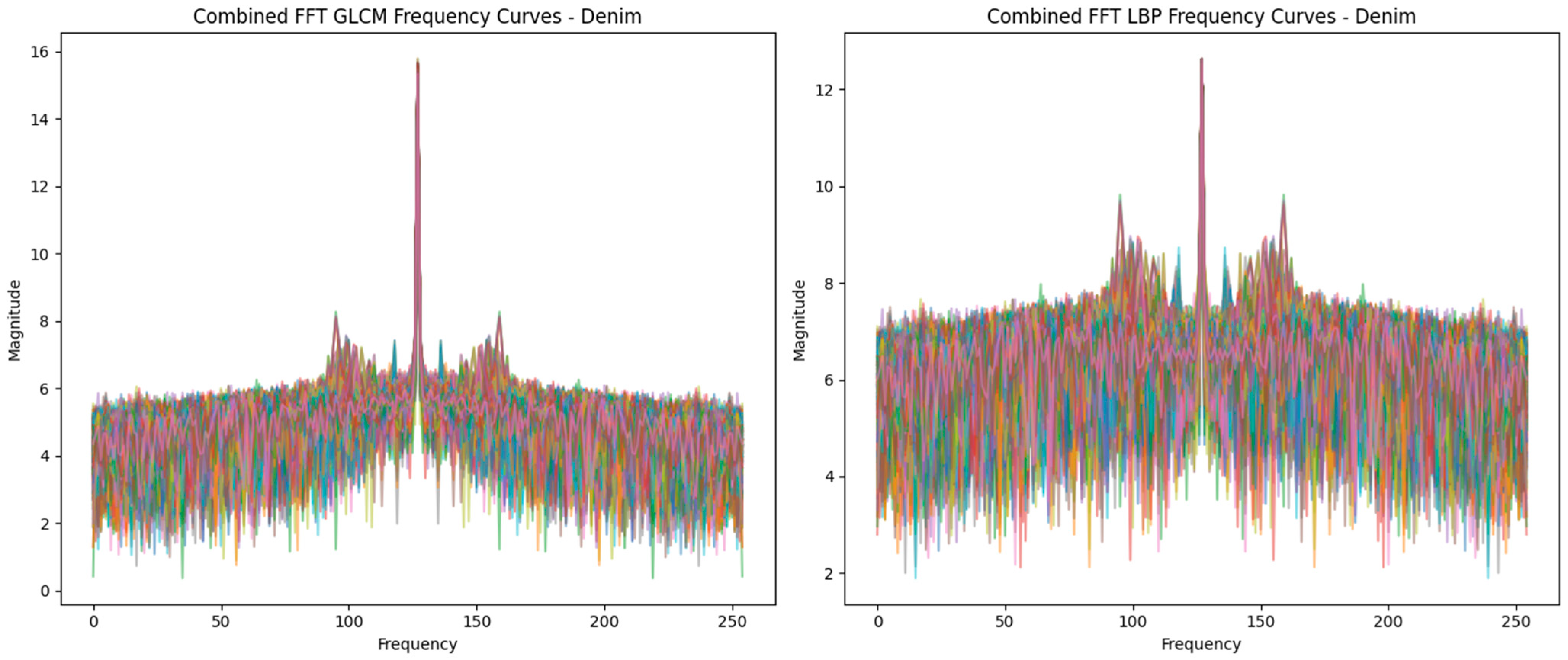
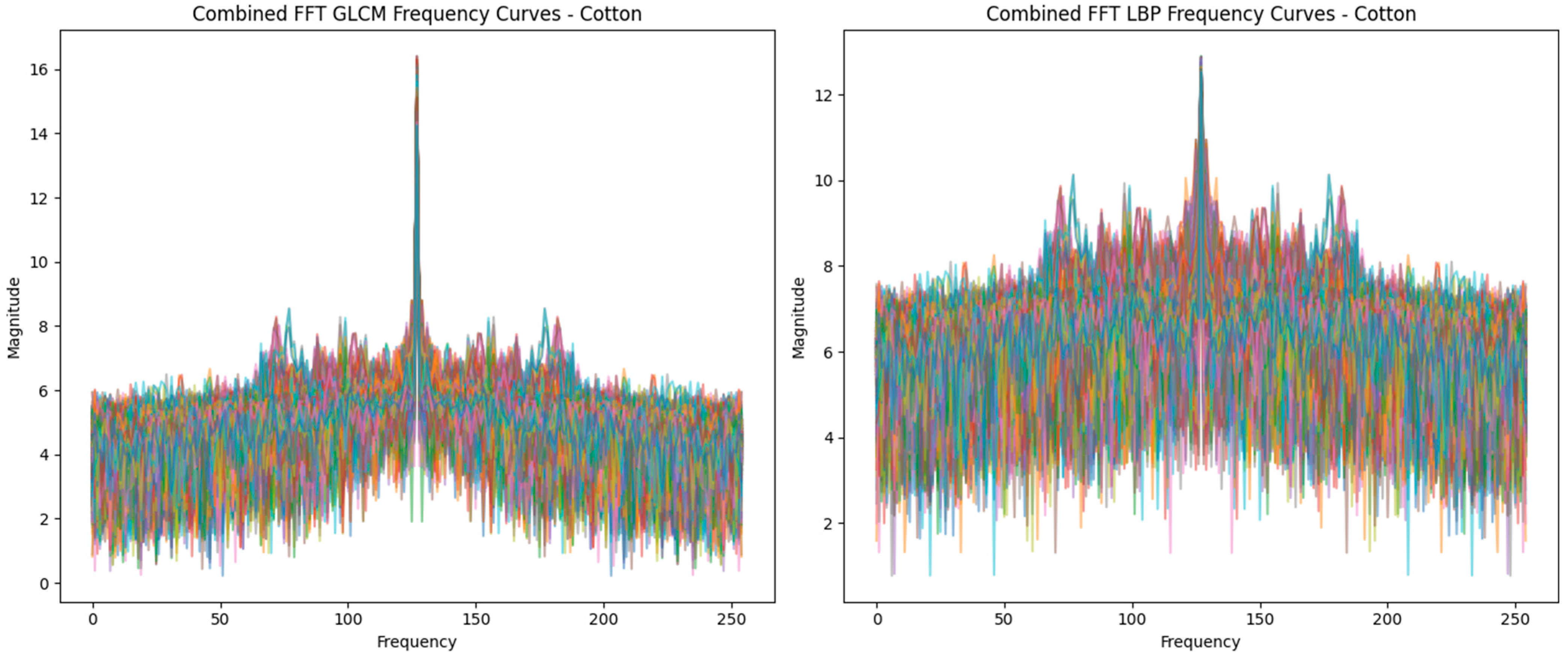
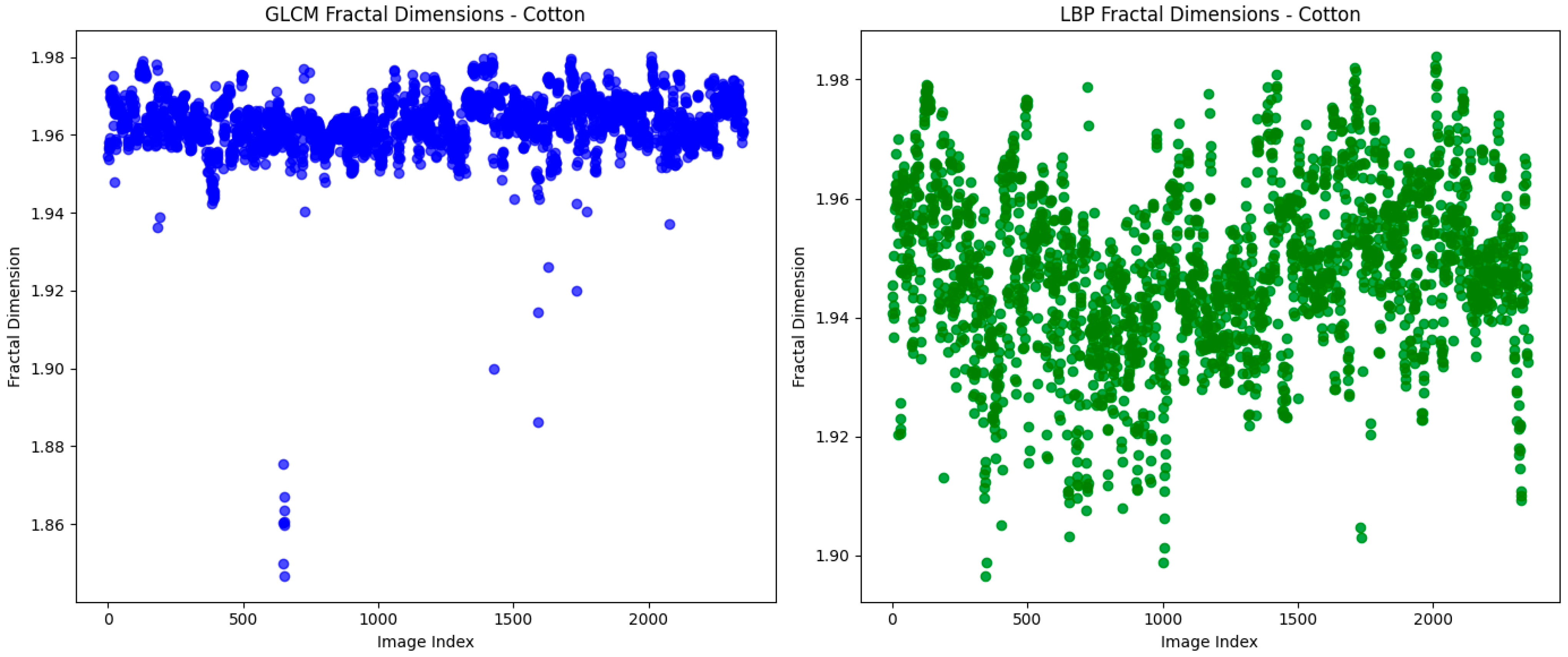
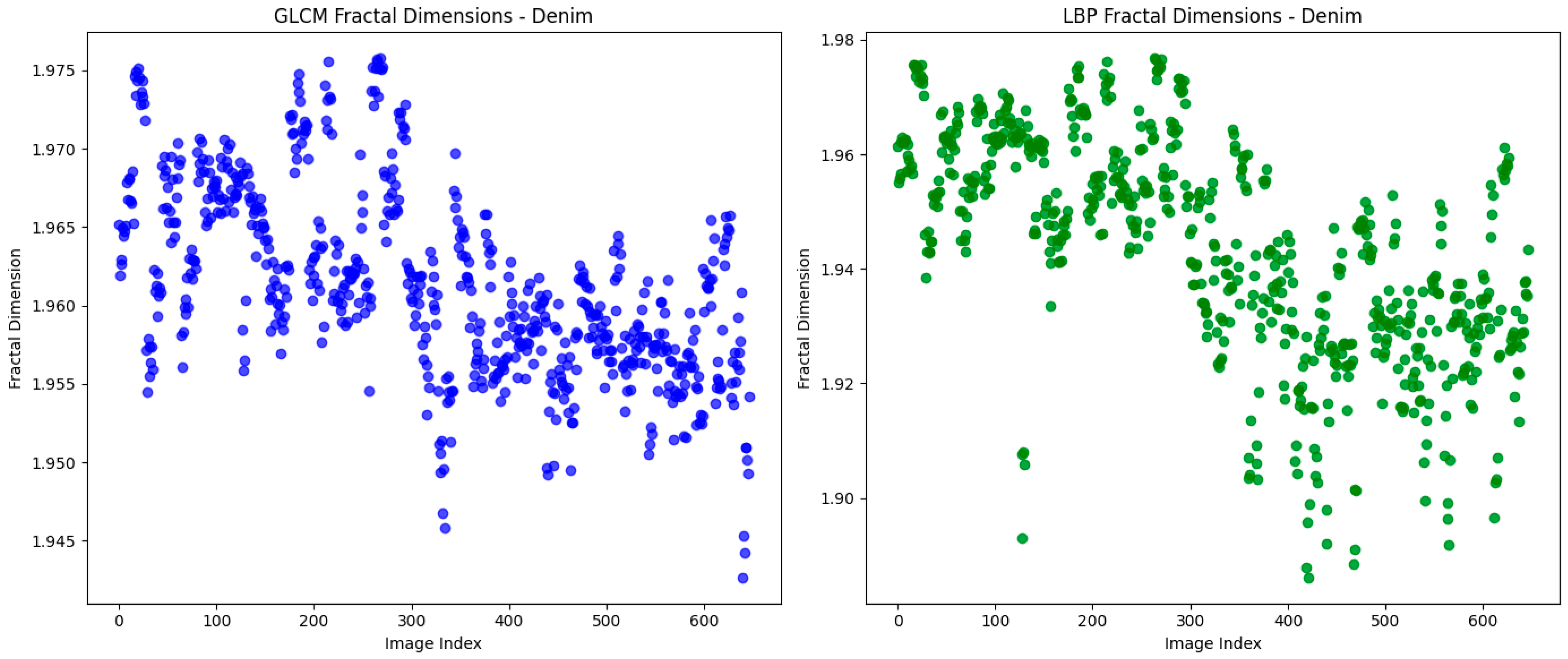
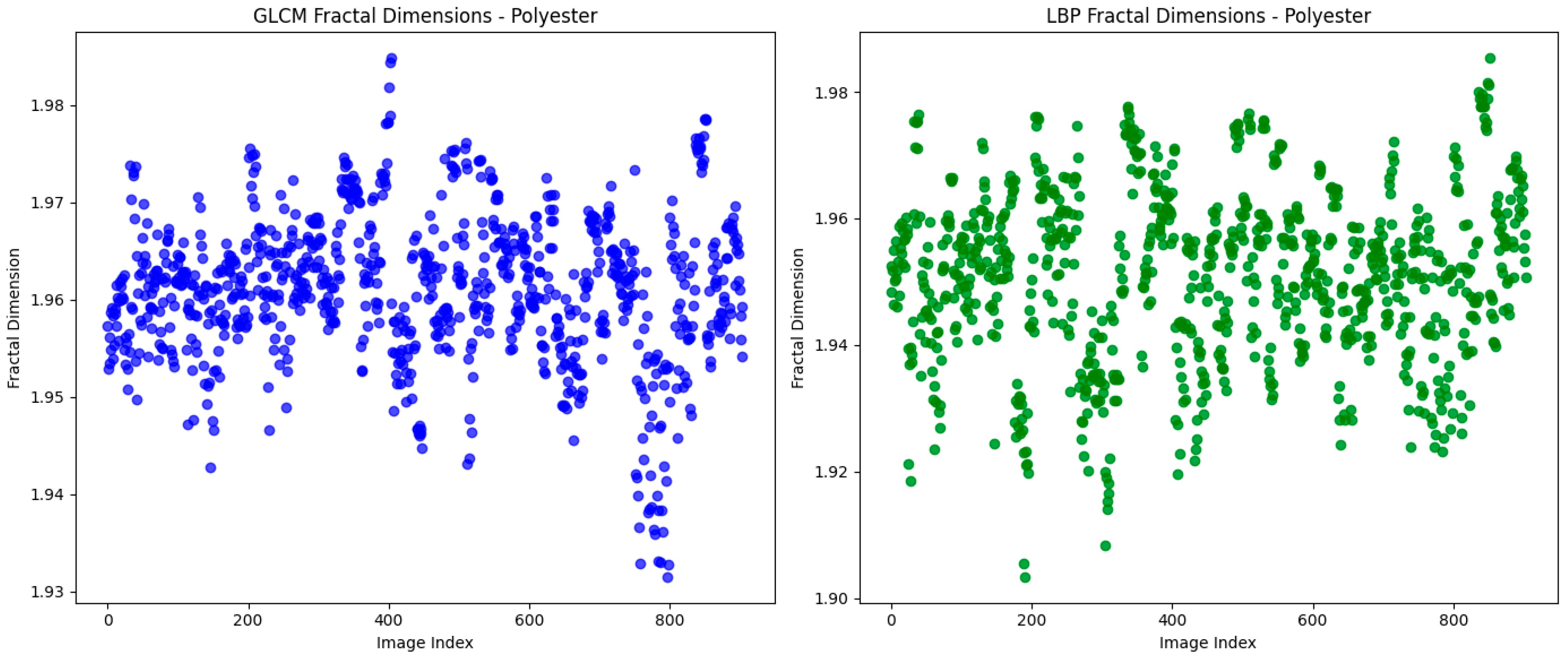
3.1. Macro- and Micro-Texture Analysis
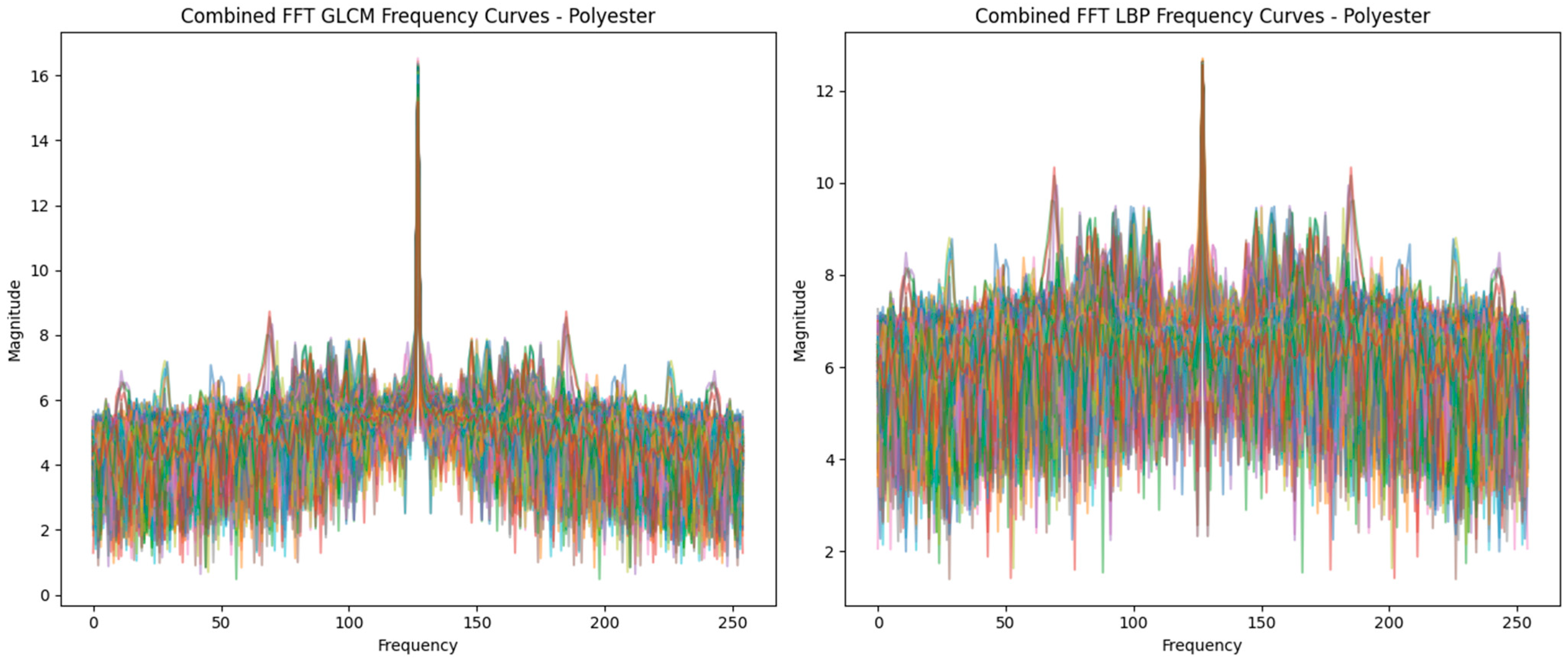
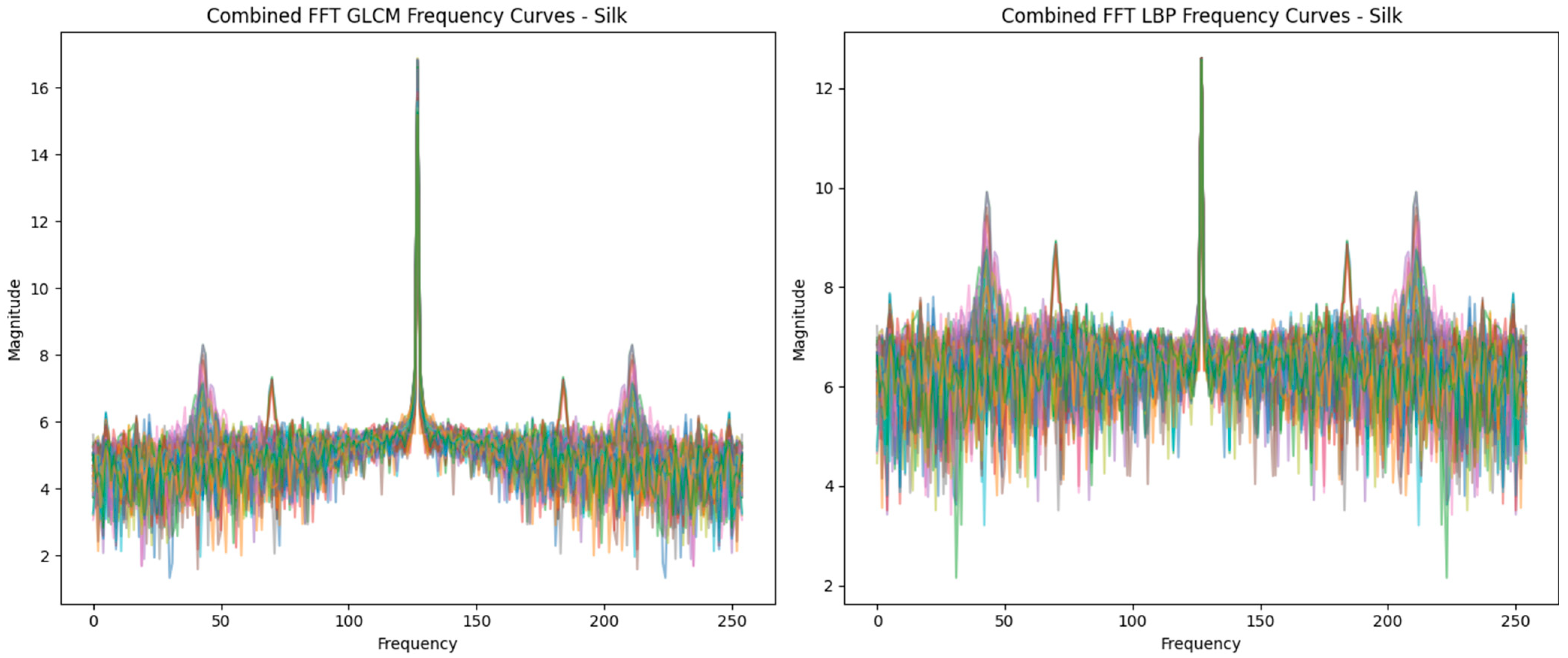
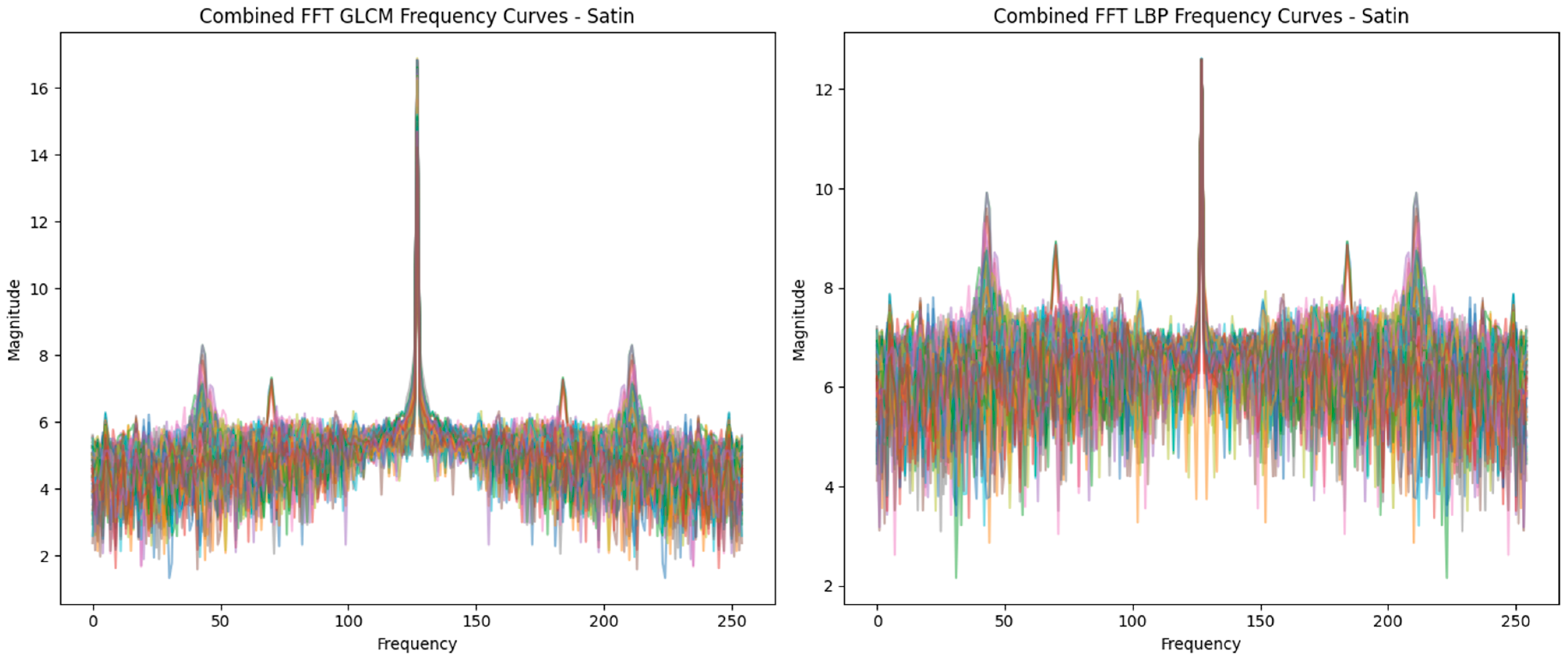
3.2. Frequency Domain Analysis via FFT
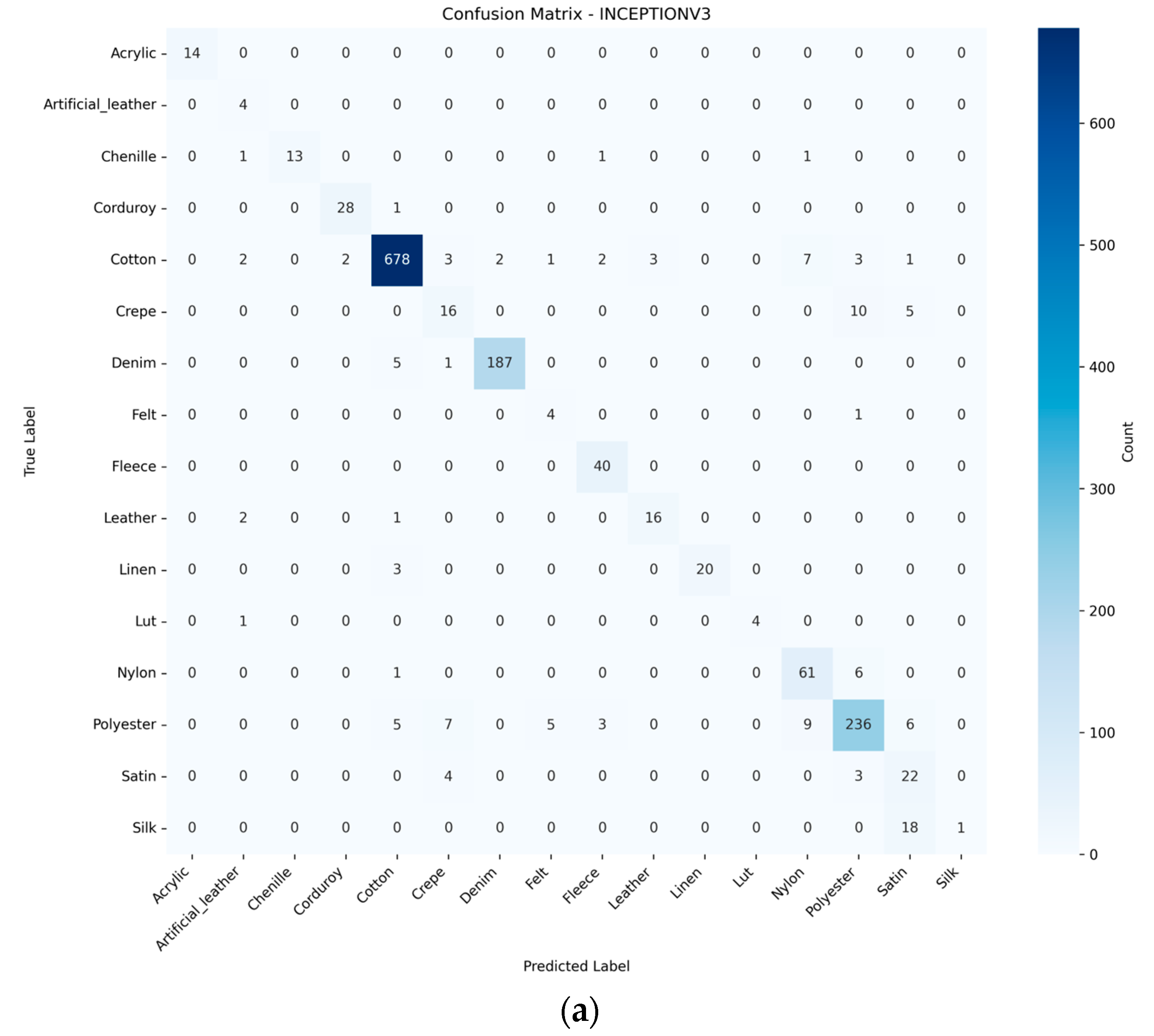
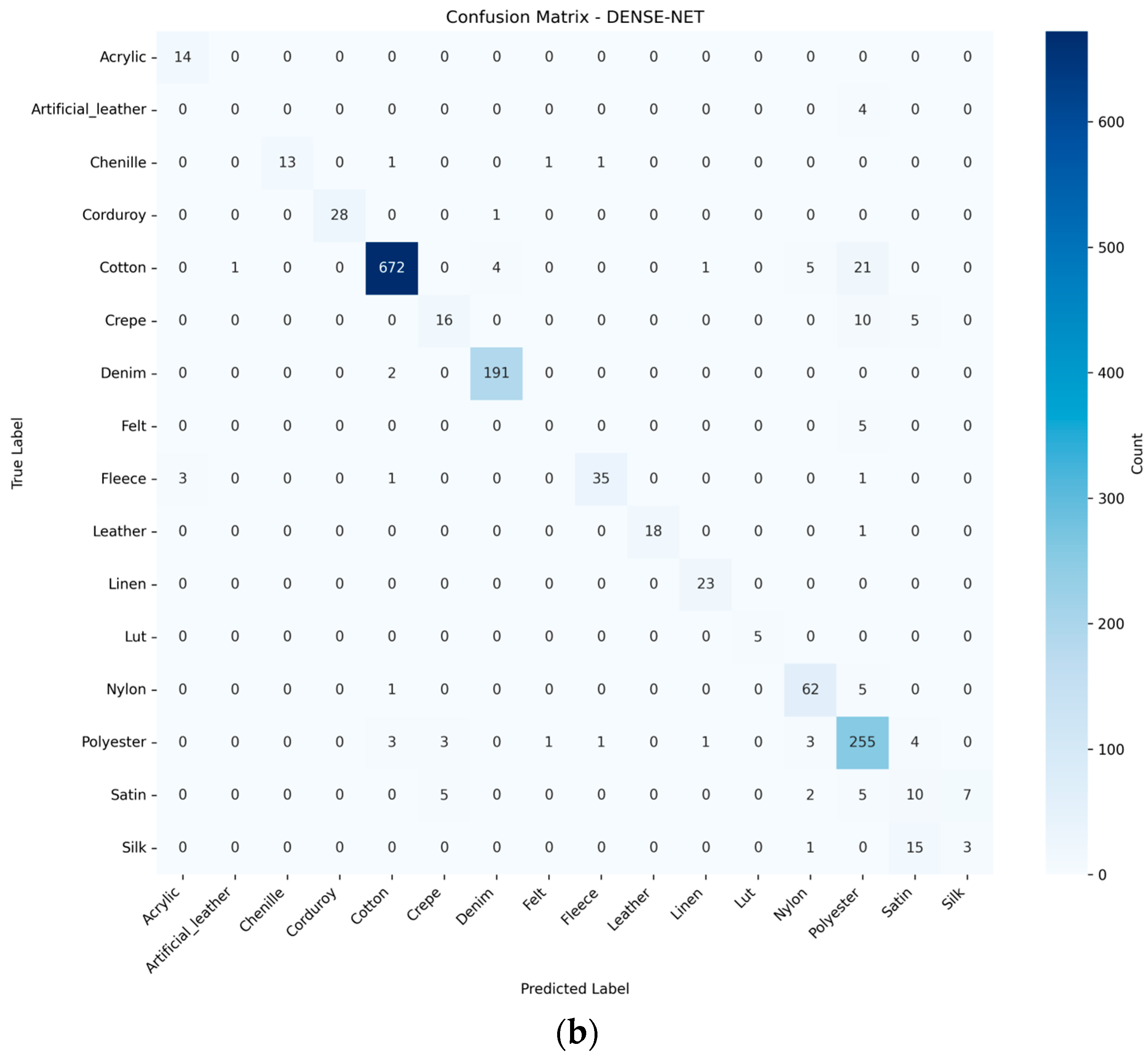
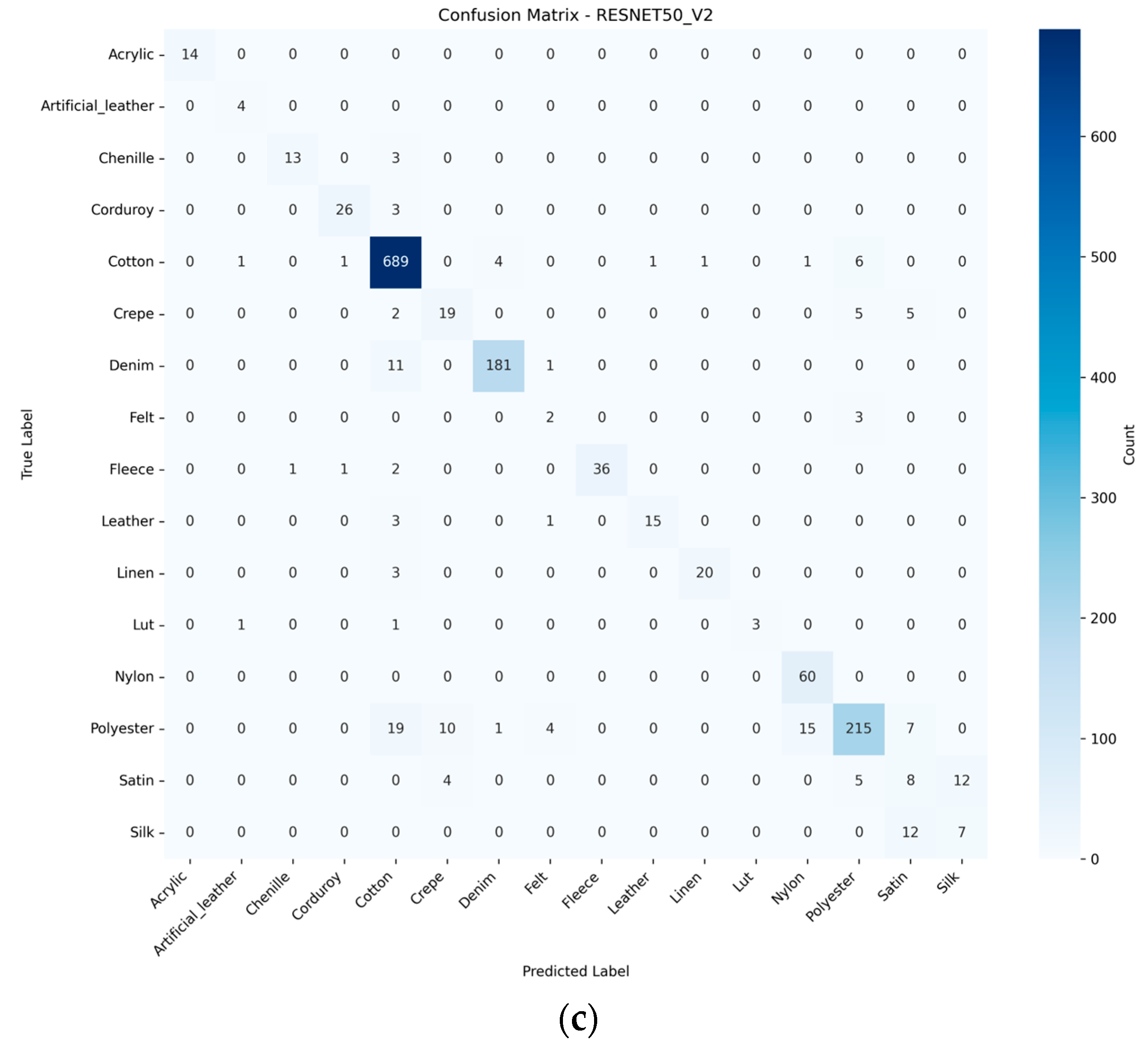
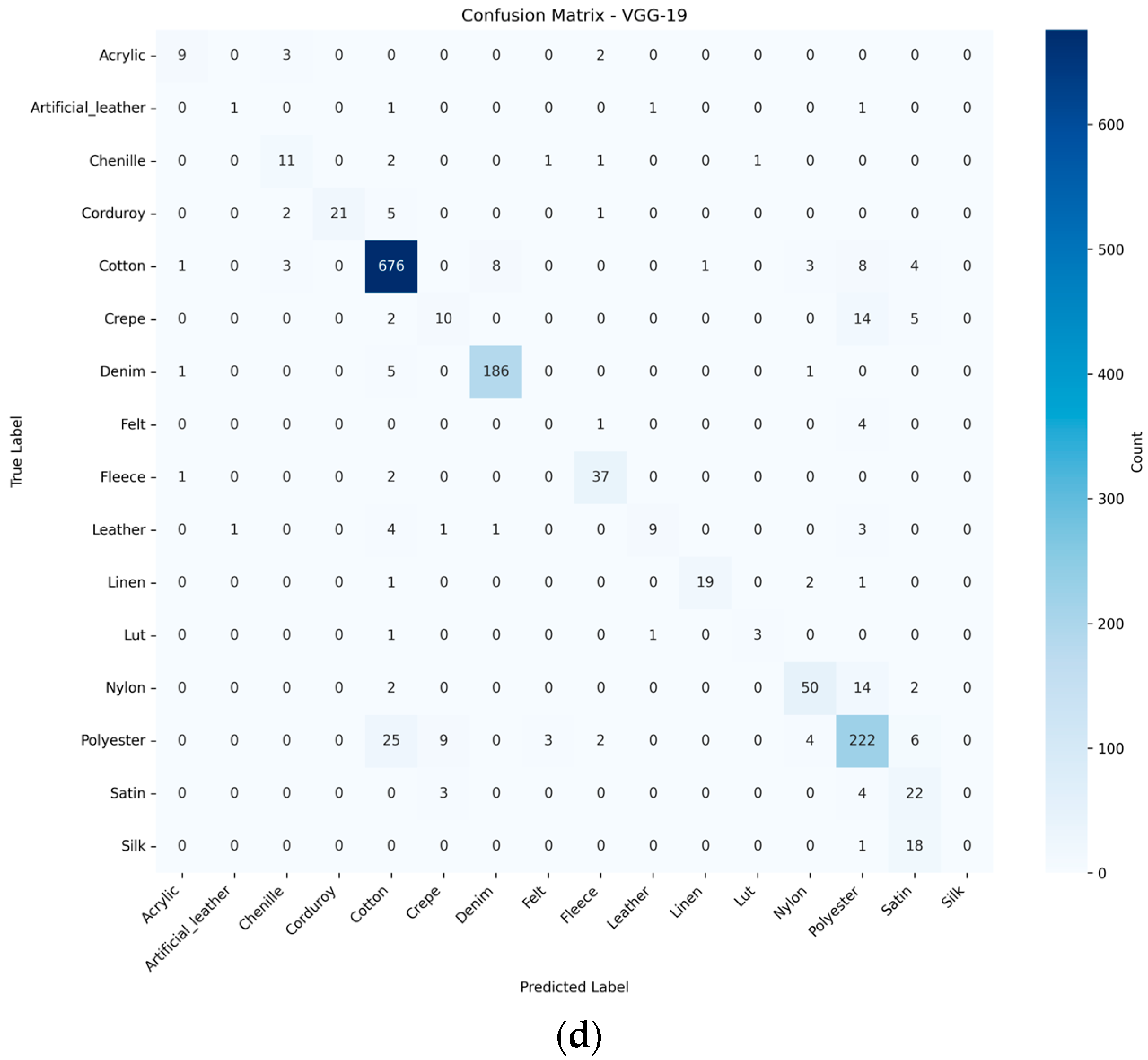
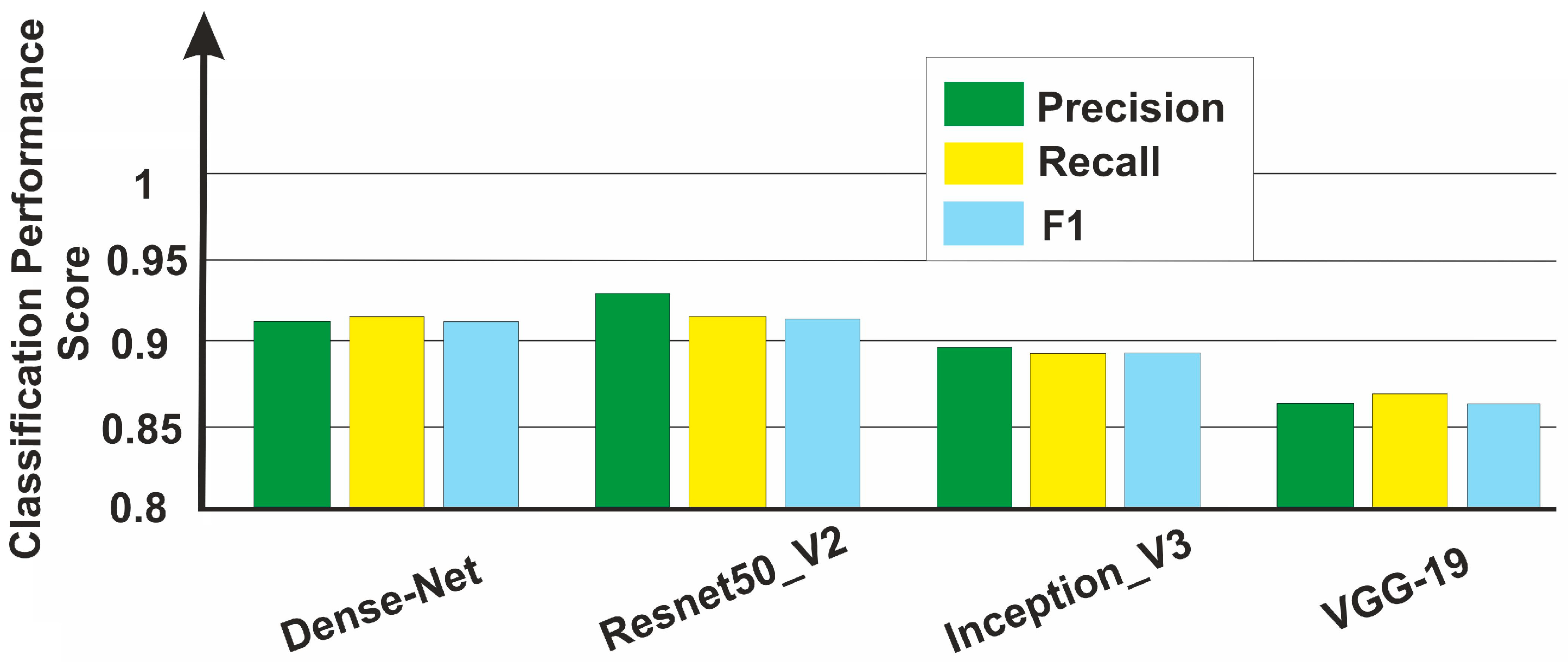
3.3. CNN-Based Fabric Classification
Comparative Analysis of CNN Model Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| ProGAN | Progressive Growing of GANs |
References
- Tian, Y.; Zhu, F. Application of computer vision algorithm in ceramic surface texture analysis and prediction. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2025, 25, 200482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.T.; São Mamede, H.; Duarte dos Santos, V. Industrial anomaly detection on textures: Multilabel classification using MCUs. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 239, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, B.; Zhan, H.; Xie, Z.; Tian, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yue, H.; Yang, F. A soft robotic system imitating the multimodal sensory mechanism of human fingers for intelligent grasping and recognition. Nano Energy 2024, 130, 110120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, K.M.C.; Kumar, S.S.; Prasad, G. Defective texture classification using optimized neural network structure. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 135, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Ji, L.; Zhu, J. Multi-scale LBP fusion with the contours from deep CellNNs for texture classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.; Saradha, S. Efficient prediction and classification for cirrhosis disease using LBP, GLCM and SVM from MRI images. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 81, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Huang, L.; Ning, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y. Enhanced detection of measurement anomalies in cartridge cases using 3D gray-level co-occurrence matrix. Forensic Sci. Int. 2025, 367, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataky, S.T.M.; Saqui, D.; de Matos, J.; de Souza, A.B.J.; Koerich, A.L. Multiscale analysis for improving texture classification. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, C.E.; Plotnick, R. Image analysis techniques and gray-level co-occurrence matrices (GLCM) for calculating bioturbation indices and characterizing biogenic sedimentary structures. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhong, Y. Fabric Identification Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence on Fashion and Textiles (AIFT) Conference 2018, Hong Kong, 3–6 July 2018; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Wong, W., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 849. [Google Scholar]
- Nisa, H.; Van Amber, R.; English, J.; Alavi, A. A systematic review of reimagining fashion and textiles sustainability with AI: A circular economy approach. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.; Beliatis, M.J.; Radziwon, A.; Menciassi, A.; Oddo, C.M. Textile fabric defect detection using enhanced deep convolutional neural network with safe human–robot collaborative interaction. Electronics 2024, 13, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampouris, C.; Zafeiriou, S.; Ghosh, A.; Malassiotis, S. Fine-Grained Material Classification Using Micro-Geometry and Reflectance. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanaiah, P.; Sathyanarayana, P.; GuruKumar, L. Image Texture Feature Extraction Using GLCM Approach. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, B. Symmetry-constrained linear sliding co-occurrence LBP for fine-grained leaf image retrieval. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaguchi, T.; Kawasaki, H. Surface Normal estimation from optimized and distributed light sources using DNN-based photometric stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2023, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Feng, Y.; Shang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, C.; Zong, Z.; Shao, T.; Wu, H.; Zhou, K.; Jiang, C.; et al. Gaussian Splashing: Unified Particles for Versatile Motion Synthesis and Rendering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z. Self-supervised reconstruction of re-renderable facial textures from single image. Comput. Graph. 2024, 124, 104096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, M.H.; Liu, J.J.; MacGregor, J.F. Image texture analysis: Methods and comparisons. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2004, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, P.; Reddy, K.R.; Srilakshmi, G. Medical Image Retrieval based on LBP Histogram Fourier features and KNN classifier. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Engineering & Technology Research, Unnao, India, 1–2 August 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ahonen, T.; Matas, J.; He, C.; Pietikäinen, M. Rotation Invariant Image Description with Local Binary Pattern Histogram Fourier Features. In Image Analysis; SCIA 2009; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Salberg, A.B., Hardeberg, J.Y., Jenssen, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5575. [Google Scholar]
- Navas, W.; Vásquez Espinosa, R. Analysis of Texture Using the Fractal Model; NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS): Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.R.; Qadri, S.; Bibi, H.; Shah, S.M.W.; Sharif, M.I.; Marinello, F. Comparing Inception V3, VGG 16, VGG 19, CNN, and ResNet 50: A Case Study on Early Detection of a Rice Disease. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Fu, Q.; Li, J. An Improved Neural Network Model Based on DenseNet for Fabric Texture Recognition. Sensors 2024, 24, 7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, M.; Al-Wajih, A.; Shaiea, M.; Rageh, M.; Alqasemi, F.A. Clothing image classification using VGG-19 deep learning model for e-commerce web application. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Emerging Smart Technologies and Applications (eSmarTA)(IEEE), Sana’a, Yemen, 6–7 August 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
| Fabric Type | Training Set (Images, %) | Test Set (Images, %) | Unseen Set (Images, %) | Total Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | 1478 (62.97%) | 634 (27.02%) | 235 (10.02%) | 2347 |
| Polyester | 569 (62.94%) | 244 (27.00%) | 91 (10.07%) | 904 |
| Denim | 404 (62.85%) | 174 (27.06%) | 65 (10.11%) | 643 |
| Nylon | 143 (62.72%) | 62 (27.19%) | 23 (10.09%) | 228 |
| Fleece | 82 (62.12%) | 36 (27.27%) | 14 (10.61%) | 132 |
| Crepe | 65 (62.50%) | 28 (26.92%) | 11 (10.58%) | 104 |
| Corduroy | 60 (62.50%) | 26 (27.08%) | 10 (10.42%) | 96 |
| Satin | 60 (62.50%) | 26 (27.08%) | 10 (10.42%) | 96 |
| Linen | 47 (61.84%) | 21 (27.63%) | 8 (10.53%) | 76 |
| Leather | 39 (60.94%) | 18 (28.12%) | 7 (10.94%) | 64 |
| Silk | 39 (61.90%) | 17 (26.98%) | 7 (11.11%) | 63 |
| Acrylic | 30 (62.50%) | 13 (27.08%) | 5 (10.42%) | 48 |
| Chenille | 32 (61.54%) | 14 (26.92%) | 6 (11.54%) | 52 |
| Fabric Type | Weave Type | Dominant Weave | Fiber Compositions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | plain, twill, satin | plain (51.13%) | Cotton (92–100% or blends with elastane ≤ 7%, polyester ≤ 6%) |
| Polyester | plain, twill, satin | plain (49.78%) | Polyester (100% or blends + elastane/viscose ≤ 8%) |
| Denim | plain, twill, satin | twill (90.41%) | Cotton (100% or blends with polyester ≤ 34%, viscose ≤ 13%, elastane ≤ 2%) |
| Nylon | plain, twill, satin | plain (52.63%) | Polyamide (nylon) (100% or blends with elastane ≤ 7%) |
| Fleece | plain, twill, satin | plain (71.97%) | 100% Polyester |
| Crepe | plain, twill, satin | plain (43.27%) | Polyester (65–100% or blends with viscose ≤ 30%, elastane ≤ 6%) |
| Corduroy | plain, twill, satin | twill (78.13%) | Cotton (84–100% or blends with polyester ≤ 15%, elastane ≤ 2%) |
| Satin | plain, twill, satin | satin (79.17%) | 100% silk, 100% polyester |
| Linen | plain, twill, satin | plain (65.79%) | 100% linen |
| Leather | plain, twill, satin | plain (70.31%) | 100% leather |
| Silk | plain, twill, satin | twill (41.67%) | 100% silk |
| Acrylic | plain, twill, satin | plain (62.5%) | 100% acrylic, 98% acrylic 2% elastane |
| Chenille | plain, twill, satin | plain (67.31%) | 100% cotton |
| Models | Learning | Batch Size | Epochs | Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 1 × 10−4 | 32 | 50 | CPU |
| Method | Denim | Acrylic | Nylon | Cotton |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original image |  |  |  |  |
| GLCM feature map |  |  | 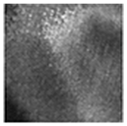 |  |
| LBP (underlying textures) | 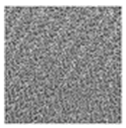 | 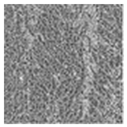 | 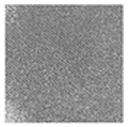 | 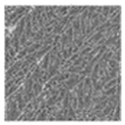 |
| Albedo-dependent map | 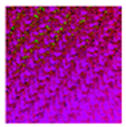 | 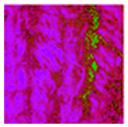 | 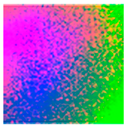 | 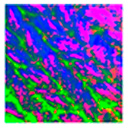 |
| Relative 3D height map constructed from GLCM | 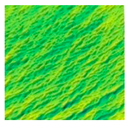 | 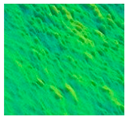 | 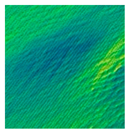 | 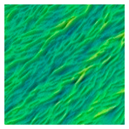 |
| Relative 3D height map constructed from LBP |  |  |  |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enow Gnoupa, M.G.; Augousti, A.T.; Duran, O.; Lanets, O.; Liaskovska, S. Multimodal Feature Inputs Enable Improved Automated Textile Identification. Textiles 2025, 5, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5030031
Enow Gnoupa MG, Augousti AT, Duran O, Lanets O, Liaskovska S. Multimodal Feature Inputs Enable Improved Automated Textile Identification. Textiles. 2025; 5(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnow Gnoupa, Magken George, Andy T. Augousti, Olga Duran, Olena Lanets, and Solomiia Liaskovska. 2025. "Multimodal Feature Inputs Enable Improved Automated Textile Identification" Textiles 5, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5030031
APA StyleEnow Gnoupa, M. G., Augousti, A. T., Duran, O., Lanets, O., & Liaskovska, S. (2025). Multimodal Feature Inputs Enable Improved Automated Textile Identification. Textiles, 5(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5030031









