New Geometrical Modelling for 2D Fabric and 2.5D Interlock Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Objective
1.2. State of the Art
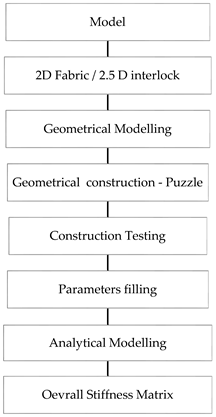
2. Geometrical Modelling
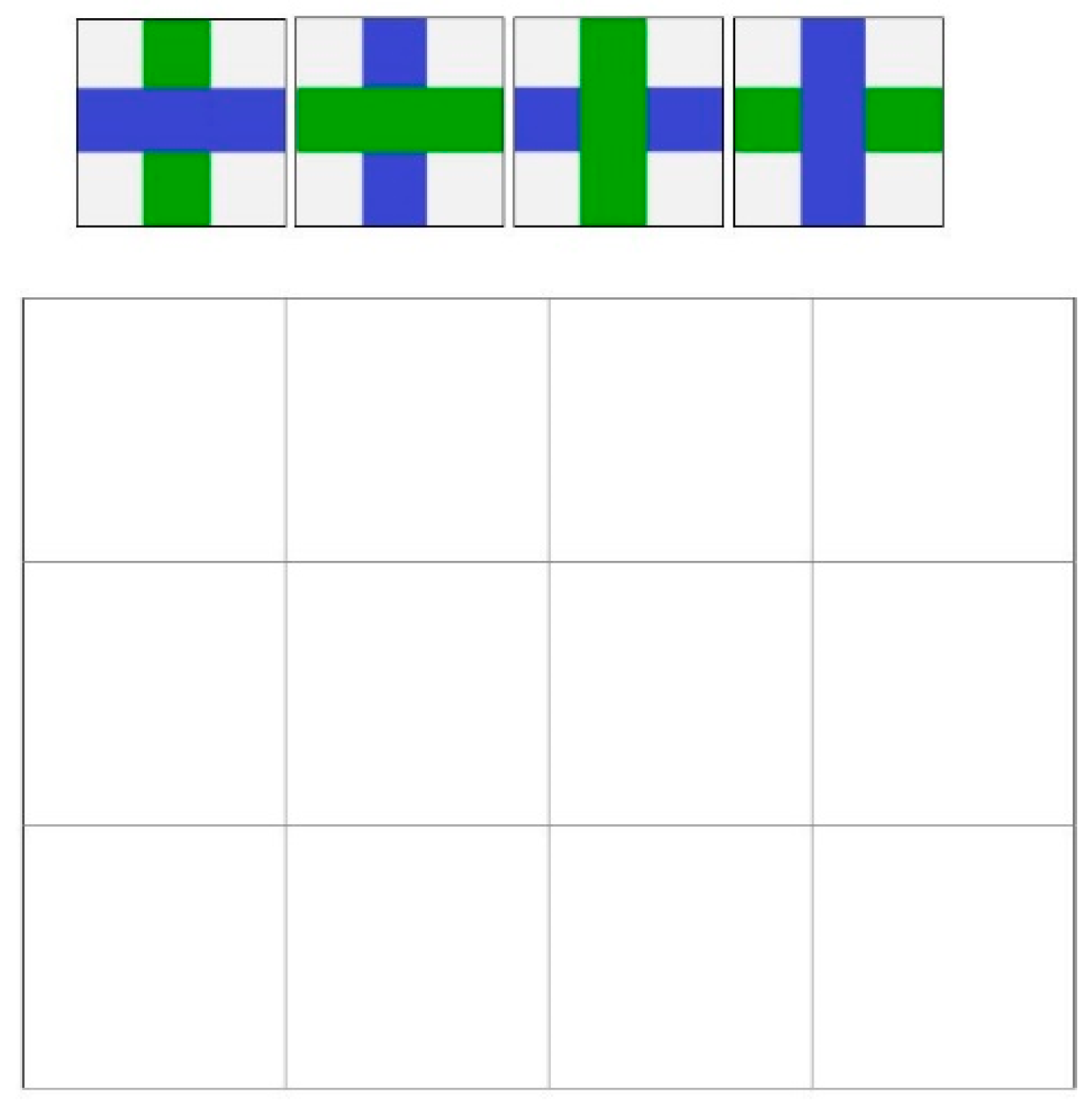
2.1. 2D Fabric
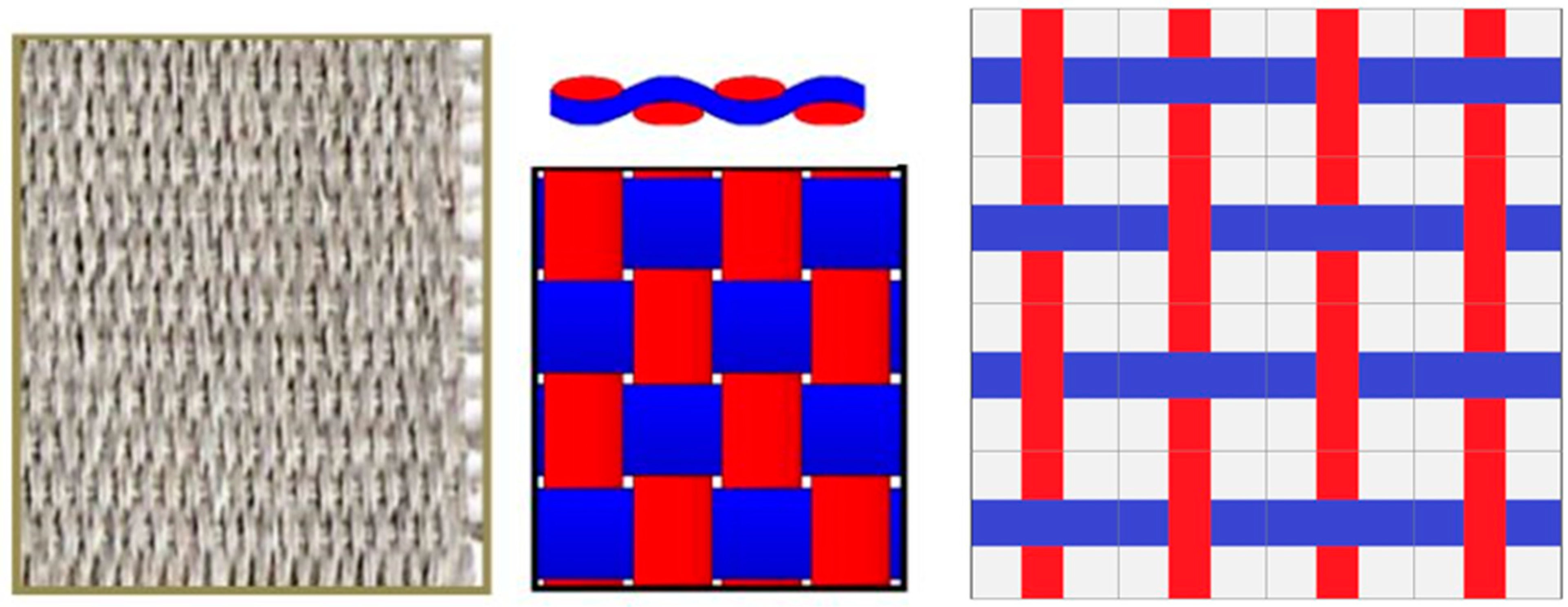
2.1.1. Plain Weave Fabric [1/1]
2.1.2. Twill [2/1, 3/1]
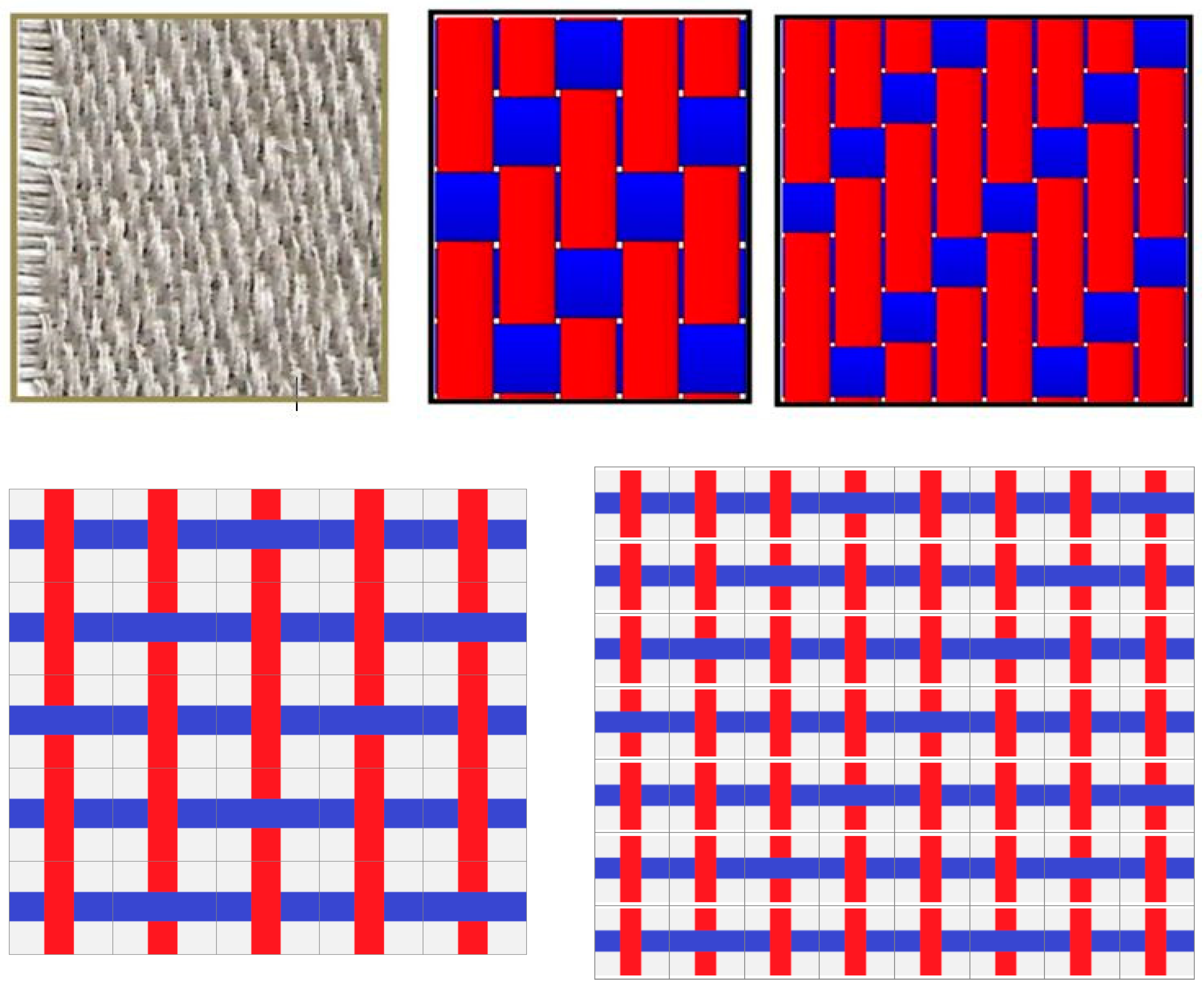
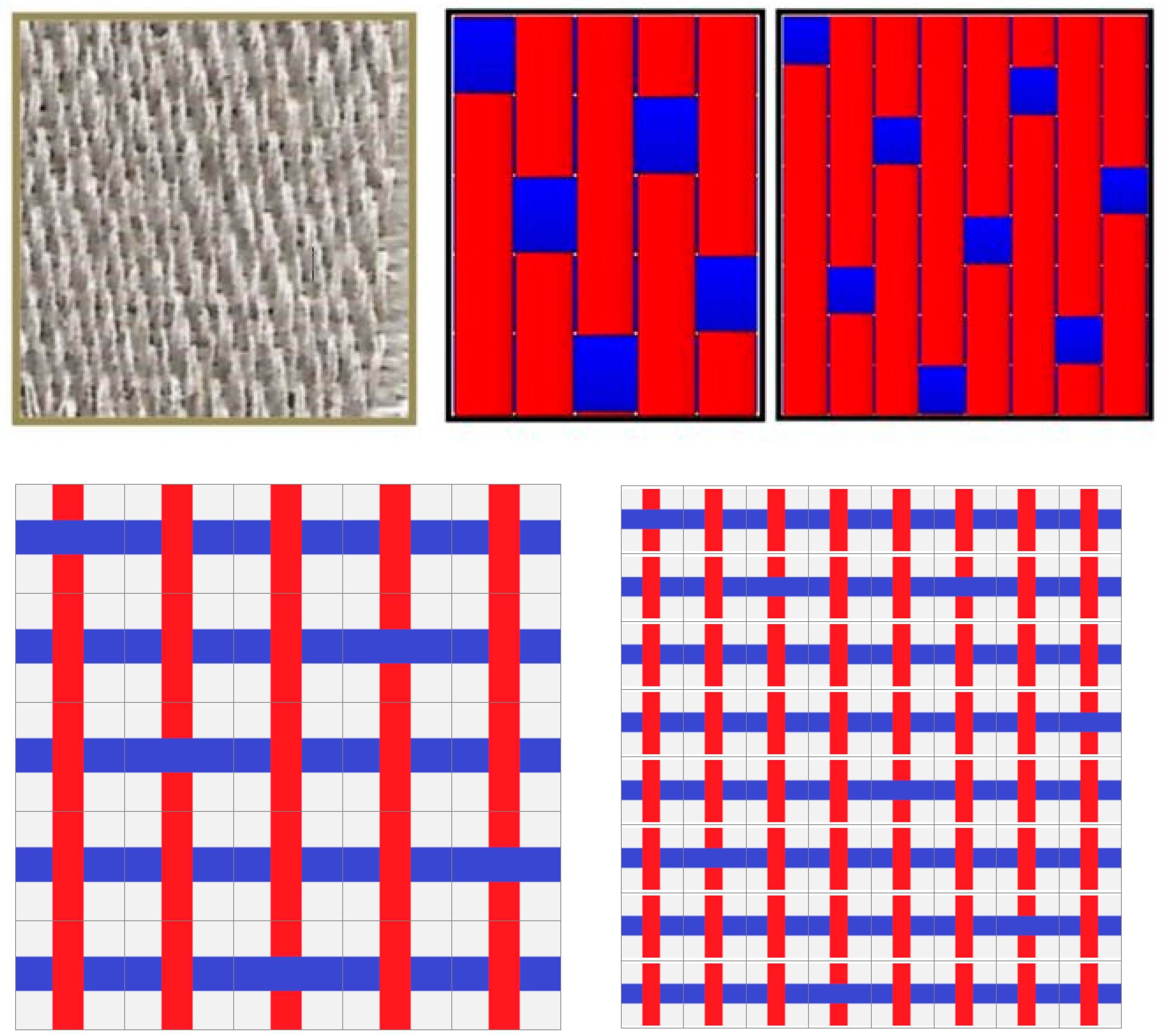
2.1.3. Sateen/Satin [5-end, 8-end]
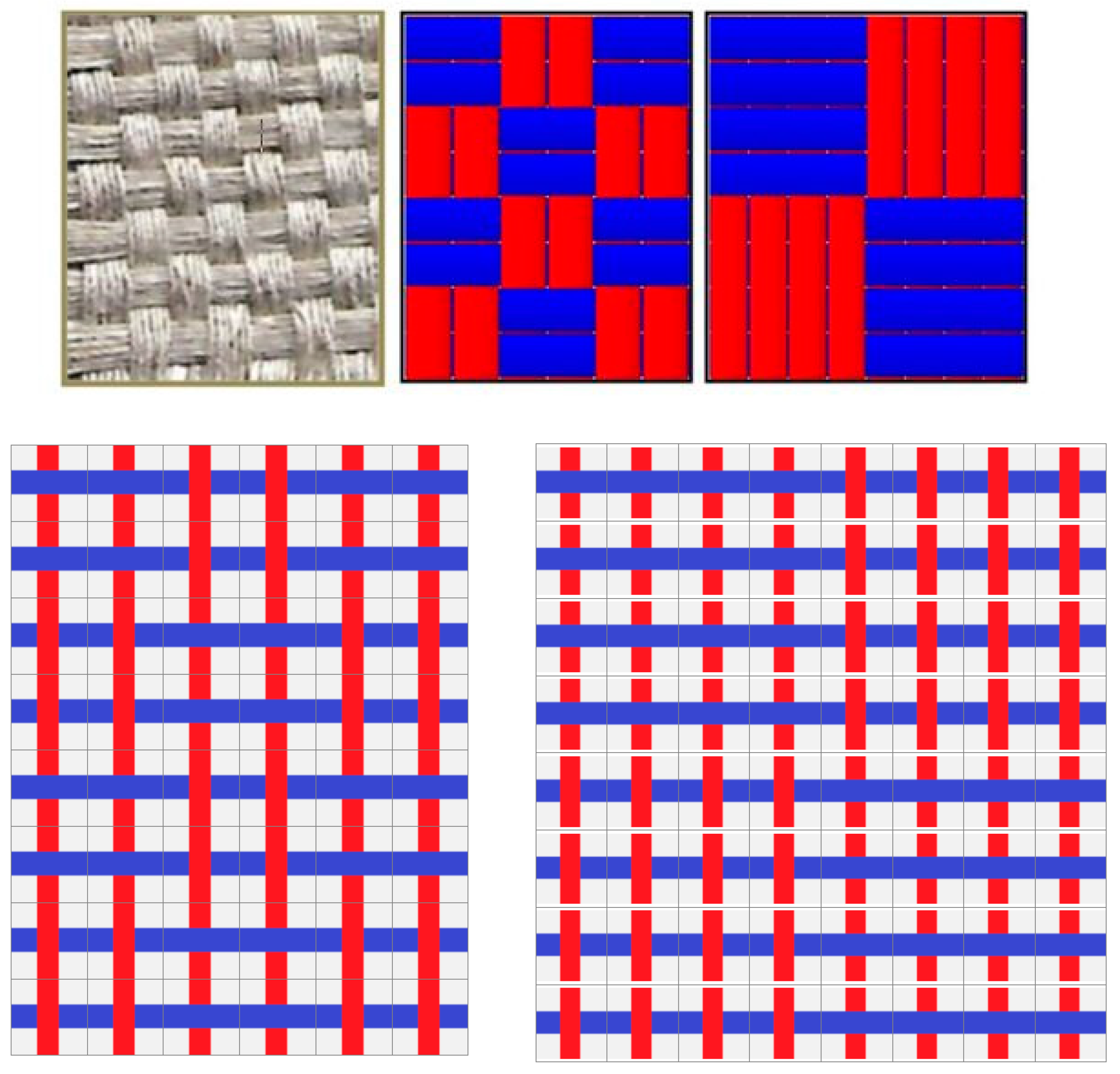
2.1.4. Basket Weave [2/2, 4/4]
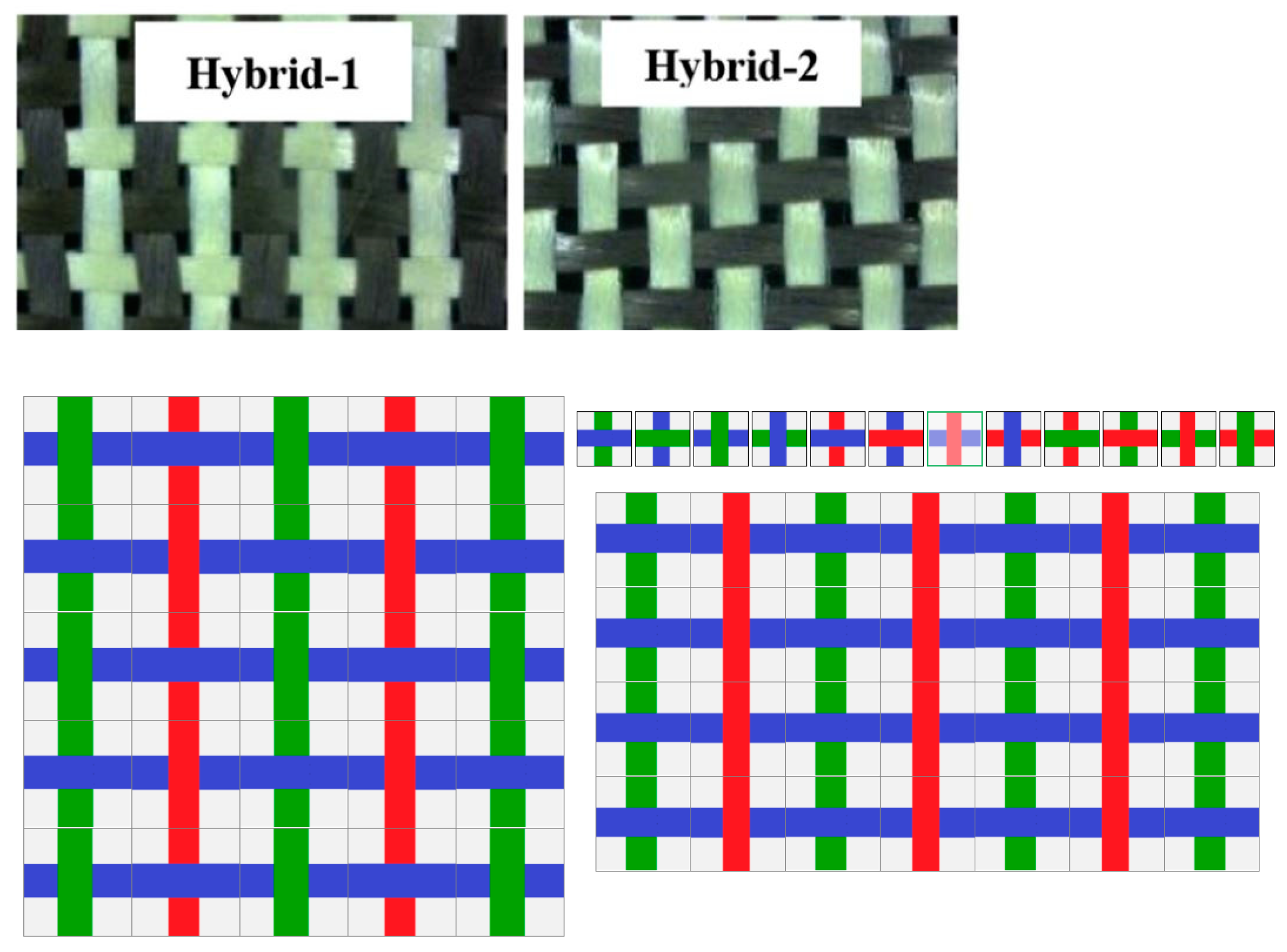
2.1.5. 2D Fabric Hybrid Composites
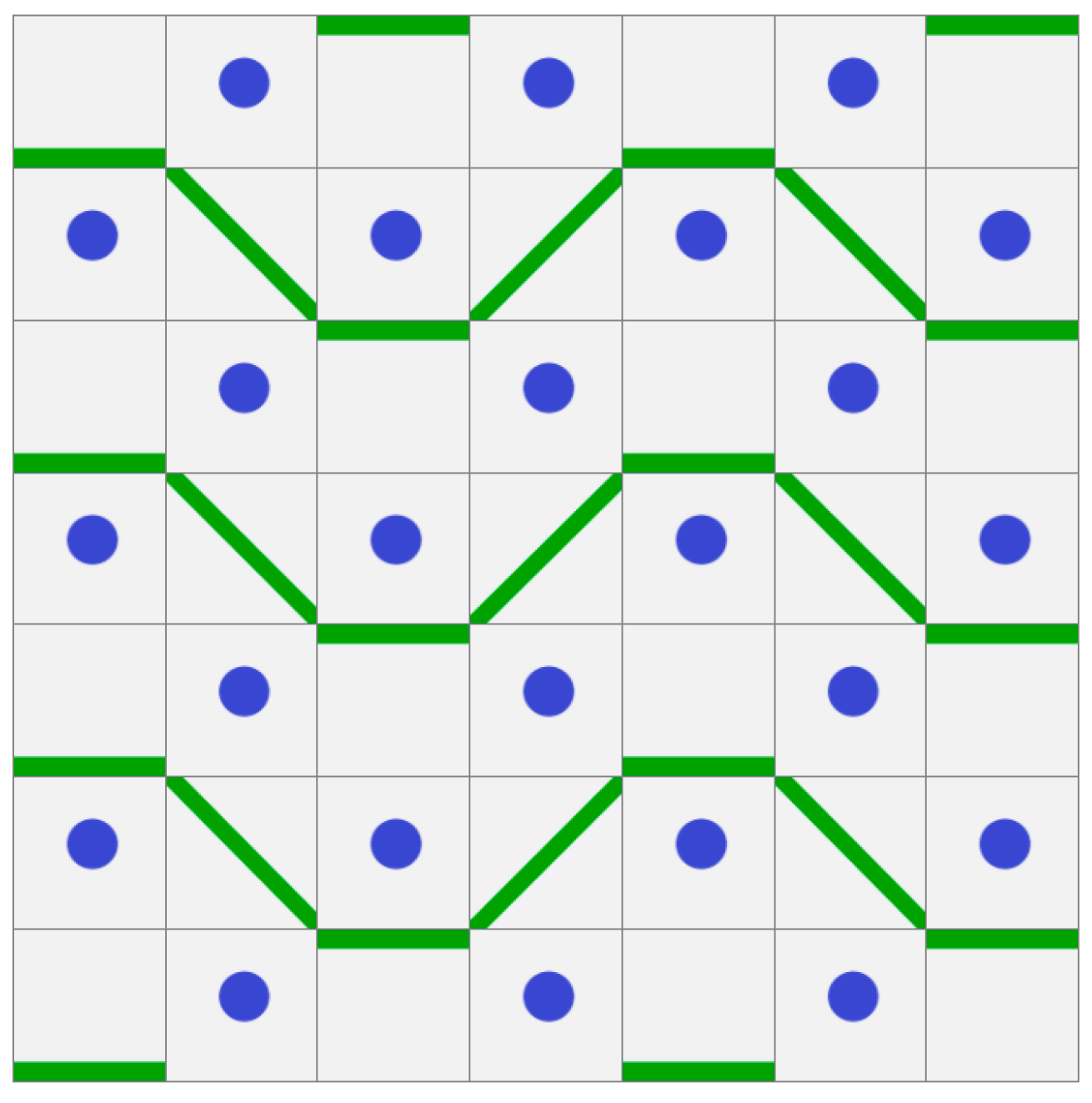
2.2. Interlock Composite 2.5D
- 1
- Layer to Layer Angle Interlock
- 2
- Through the Thickness Angle Interlock
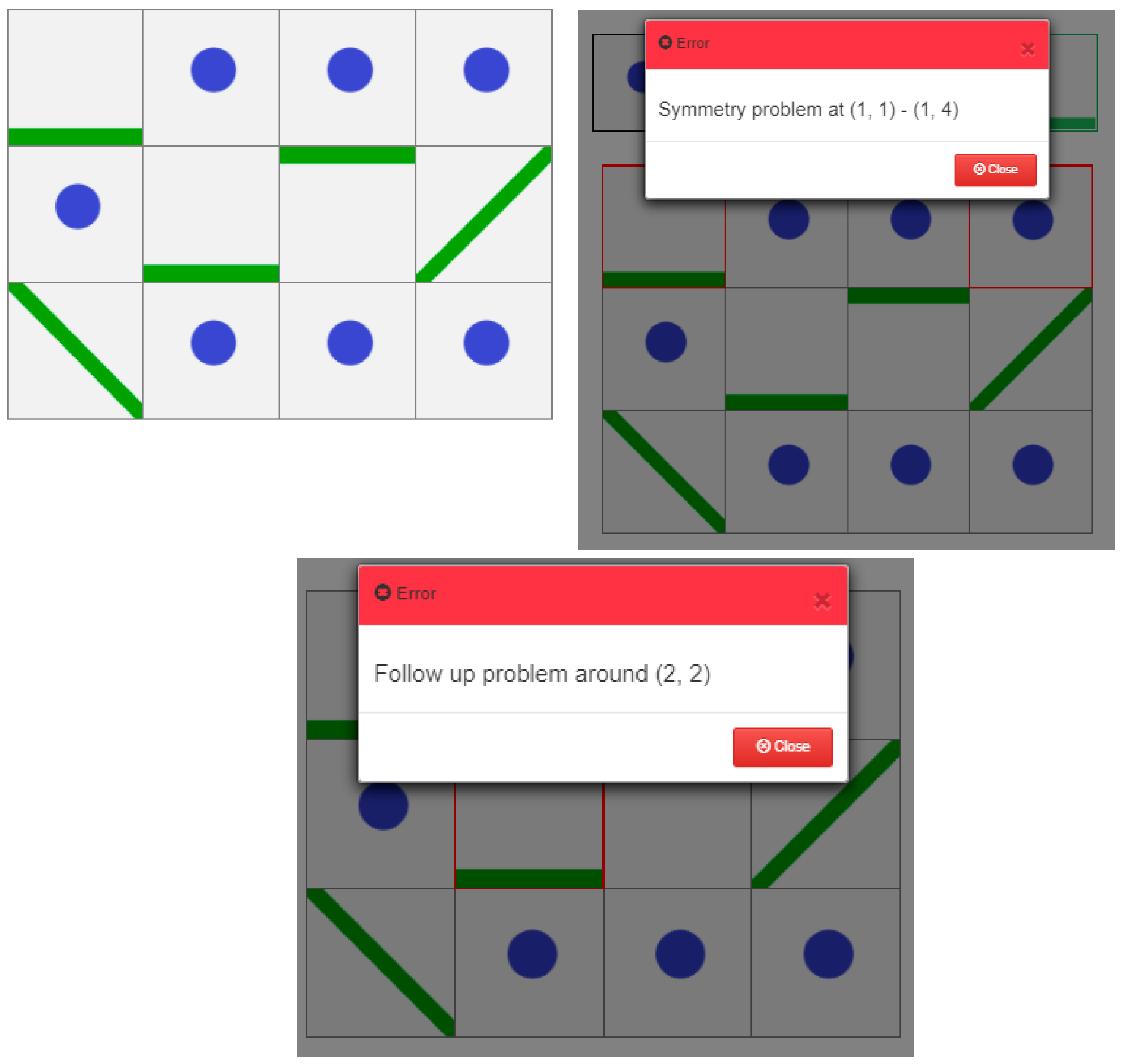
2.3. Construction Testing
- -
- Follow up test.
- -
- Pattern test.
- -
- Symmetry test (not obligatory).
2.4. Analytical Modelling
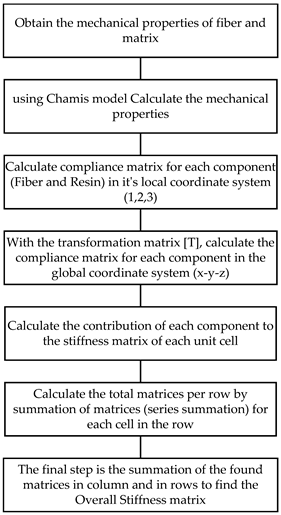
3. Materials
3.1. 2D Fabric
- E-glass/epoxy—I;
- E-glass/epoxy—II;
- T300/epoxy;
- EW220/5284.
3.2. 2.5D Interlock
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. 2D Fabric
4.2. 5D Interlock
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghlaim, D.K. Woven factor for the mechancial properties of woven composite materials. J. Eng. 2010, 16, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T.; Matsushima, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Chou, T.W. Experimental confirmation of the theory of elastic moduli of fabric composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1985, 19, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Tong, L.Y.; Steven, G.P.; Ishikawa, T. Behavior of 3D orthogonal woven CFRP composites. Part I. Experi-mental investi-gation. Composites A 2000, 31, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Figiel, L.; Rezende, M.C.; Lauke, B. Mechanical behavior of carbon fiber reinforced polyamide compo-sites. Com-pos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, D.M. Effect of Fabric Structures on the Mechanical Properties of 3-D Textile Composites. J. Ind. Text. 2006, 35, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greena, S.D.; Matveevb, M.Y. Mechanical modelling of 3D woven composites considering realistic unit cell ge-ometry. Compos. Struct. 2014, 118, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wvan, A.; Vuure, J.; Ivens, A.; Verpoest, I. Mechanical properties of composite panels based on woven sand-wich-fabric preforms. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Wen, D.W. Fatigue life prediction model of 2.5D woven composites at various temperatures. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovich, A.E.; Pastore, C.M. Mechanics of Textile and Laminated Composites, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb, J.; Noh, J.; Chapman, C. Evaluation of Various Approximate Analyses for Plain Weave Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1999, 33, 1958–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluri, P.; Thammandra, V.S. Influence of uniaxial and biaxial tension on meso-scale geometry and strain fields in a woven composite. Compos. Struct. 2007, 77, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Chou, T.-W. Elastic Behavior of Woven Hybrid Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1982, 16, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Chou, T.W. Stiffness and strength behavior of woven fabric composite. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Chou, T.W. One-dimensional micro-mechanical analysis of woven fabric composites. AIAA J. 1983, 21, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.K.; Shembekar, P.S. Elastic Behavior of Woven Fabric Composites: I—Lamina Analysis. J. Compos. Mater. 1992, 26, 2196–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.K.; Tiwari, S.I.; Kumar, R.S. An analytical model for compressive strength of plain weave fabric composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, K.; Harding, J. A simple laminate theory approach to the prediction of the tensile impact strength of woven hybrid composites. Composites 1990, 21, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.; Munro, M.; Fahim, A. Longitudinal Elastic Modulus Prediction of a 2-D Braided Fiber Composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2003, 22, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.Y.; Tan, P.; Steven, G.P. Effect of yarn waviness on strength of 3D orthogonal woven CFRP composite ma-terials. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2002, 21, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollegal, M.G.; Sridharan, S. A Simplified Model for Plain Woven Fabrics. J. Compos. Mater. 2000, 34, 1756–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.Z.; Hoa, V.S. Three-dimensional micro-mechanical modeling of woven fabric composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2003, 37, 763–789. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Harding, J. A numerical micromechanics analysis of the mechanical properties of a plain weave composite. Comput. Struct. 1990, 36, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, H. Finite Element Modeling of Plain Weave Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1999, 33, 1491–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039M-2000 (R06); Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000.
- ASTM D695-02a; Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid Plastics. ASTM: WEST Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Sherburn, M. Geometric and Mechanical Modelling of Textiles; University of Nottingham: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Long, A.C.; Brown, L.P. Modelling the geometry of textile reinforcements for composites: TexGen. In Composite Reinforcements for Optimum Performance; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 239–264. [Google Scholar]
- Verpoest, I.; Lomov, S.V. Virtual textile composites software WiseTex: Integration with micro-mechanical, permeability and structural analysis. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomov, S.V.; Ivanov, D.S.; Verpoest, I.; Zako, M.; Kurashiki, T.; Nakai, H.; Hirosawa, S. Meso-FE modelling of textile composites: Road map, data flow and algorithms. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1870–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Han, L.; Zhang, C. Predicting the tensile and compressive failure behavior of angleply spread tow woven composites. Compos. Struct. 2019, 234, 111701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Binienda, W.K. A meso-scale finite element model for simulating free-edge effect in carbon/epoxy textile composite. Mech. Mater. 2014, 76, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.S.; Long, A.C.; Gommer, F.; Endruweit, A.; Clifford, M. Modelling compaction effect on permeability of 3D carbon reinforcements. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Composites Materials, Jeju Island, Korea, 21–26 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf, Z.; Potluri, P.; Withers, P.J. Influence of Tow Architecture on Compaction and Nesting in Textile Preforms. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Sun, L.; Ge, J.; Wu, W.; Liang, J.; Fang, D. Damage characterization and numerical simulation of shear experiment of plain woven glass-fiber reinforced composites based on 3D geometric reconstruction. Compos. Struct. 2019, 233, 111746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X. Digital-element simulation of textile processes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Multi-chain digital element analysis in textile mechanics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durville, D. Simulation of the mechanical behaviour of woven fabrics at the scale of fibers. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2010, 3, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durville, D.; Baydoun, I.; Moustacas, H.; Périé, G.; Wielhorski, Y. Determining the initial configuration and characterizing the mechanical properties of 3D angle-interlock fabrics using finite element simulation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 154, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahadik, Y.; Hallett, S.R. Finite element modelling of tow geometry in 3D woven fabrics. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, S.D.; Long, A.C.; El Said, B.S.F.F.; Hallett, S.R. Numerical modelling of 3D woven preform deformations. Compos. Struct. 2014, 108, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Vidal-Sallé, E.; Boisse, P.; Park, C.H.; Saouab, A.; Bréard, J.; Hivet, G. Mesoscopic scale analyses of textile composite reinforcement compaction. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 44, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivet, G.; Boisse, P. Consistent 3D geometrical model of fabric elementary cell. Application to a meshing preprocessor for 3D finite element analysis. Finite Elements Anal. Des. 2005, 42, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goda, I.; Assidi, M.; Ganghoffer, J.-F. Equivalent mechanical properties of textile monolayers from discrete asymptotic homogenization. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2013, 61, 2537–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahali, Y.; Assidi, M.; Goda, I.; Zghal, A.; Ganghoffer, J.F. Computation of the effective mechanical properties including nonclassical moduli of 2.5D and 3D interlocks by micromechanical approaches. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 98, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Meso-scale finite element analyses of three-dimensional five-directional braided composites subjected to uniaxial and biaxial loading. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 1989–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplentere, F.; Lomov, S.V.; Woerdeman, D.L.; Verpoest, I.; Wevers, M.; Bogdanovich, A. Micro-CT characterization of variability in 3D textile architecture. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.S.U.; Renggli, M.; van Lenthe, G.H.; Müller, R.; Ermanni, P. Micro-computed tomography determination of glass fibre re-inforced polymer meso-structure. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.S.U.; Deleglise, M.; Binetruy, C.; Krawczak, P.; Ermanni, P. Numerical prediction and experimental characterisation of meso-scale-voids in liquid composite moulding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazmino, J.; Carvelli, V.; Lomov, S.V. Micro-CT analysis of the internal deformed geometry of a non-crimp 3D or-thogonal weave E-glass composite reinforcement. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 65, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naouar, N.; Vidal-Sallé, E.; Schneider, J.; Maire, E.; Boisse, P. Meso-scale FE analyses of textile composite reinforcement deformation based on X-ray computed tomography. Compos. Struct. 2014, 116, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naouar, N.; Vidal-Salle, E.; Schneider, J.; Maire, E.; Boisse, P. 3D composite reinforcement meso F.E. analyses based on X-ray computed tomography. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Naouar, N.; Vidal-Salle, E.; Boisse, P. Longitudinal compression and Poisson ratio of fiber yarns in meso-scale finite element modeling of composite reinforcements. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 141, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badel, P.; Vidal-Sallé, E.; Maire, E.; Boisse, P. Simulation and tomography analysis of textile composite reinforcement deformation at the mesoscopic scale. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, A.; Schneider, J.; Parra, E.; Obert, E.; Roux, S. Differentiating 3D textile composites: A novel field of application for Digital Volume Correlation. Compos. Struct. 2019, 208, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, A.; Schneider, J.; Parra, E.; Roux, S. Measuring yarn deformations induced by the manufacturing process of woven composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 120, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parvanesh, V.; Shariati, M.; Nezakati, A. Statistical analysis of the parameters influencing the mechanical properties of layered MWCNTs/PVA nano composites. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2015, 6, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.J.; Shenoi, R.A.; Cheng, X. A modified micromechanical curved beam analytical model to predict the tension modulus of 2D plain weave fabric composites. Compos. Part B 2009, 40, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallal, A.; Younes, R.; Fardoun, F.; Nehme, S. Improved analytical model to predict the effective elastic properties of 2.5D interlock woven fabrics composite. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3009–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Geometry Parameters | E-Glass/Epoxy—I | E-Glass/Epoxy—II | T300/Epoxy | EW220/5284 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vf | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.44 | 0.55 |
| E1 (GPa) | 51.5 | 51.1 | 148.8 | 65.1 |
| E2 (GPa) | 17.5 | 16 | 12.2 | 22.9 |
| G12 (GPa) | 5.8 | 5.77 | 4.81 | 8.4 |
| ν12 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| Em (GPa) | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.2 |
| Gm (GPa) | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| νm (GPa) | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.42 |
| Carbon Fibers | Ef11 (GPa) | Ef22 (GPa) | Gf12 (GPa) | vf12 | vf23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T300-J | 230 | 15 | 50 | 0.278 | 0.3 |
| Resin RTM6 | Em (GPa) | — | — | vm | — |
| — | 2.89 | — | — | 0.35 | — |
| E1 (GPa) [57] | E1 (GPa)—Author | Percentage of Error (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-glass/epoxy—I | 14.5 | 14.38 | 0.82 |
| E-glass/epoxy—II | 60.3 | 60.57 | 0.44 |
| T300/epoxy | 58.91 | 59.39 | 0.814 |
| EW220/5284 | 19.3 | 19.67 | 1.91 |
| Effective Elastic Properties | Ex (GPa) | Ey (GPa) | Gxy (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Results by 3SHM | 25.93 | 54.82 | 3.22 |
| Results by Author | 28.8 | 55.3 | 2.86 |
| Percentage of error (%) | 10 | 1 | 1.125 |
| Effective Elastic Properties | Ex (GPa) | Ey (GPa) | Gxy (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Results by 3SHM | 40.7 | 31.21 | 3.14 |
| Results by Author | 40.95 | 32.5 | 3.102 |
| Percentage of error (%) | 0.614 | 4.13 | 1.21 |
| Effective Elastic Properties | Ex (GPa) | Ey (GPa) | Gxy (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Results by 3SHM | 28.98 | 37.23 | 3.41 |
| Results by Author | 28.69 | 39.12 | 3.365 |
| Percentage of error (%) | 1 | 5.07 | 1.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaddaha, M.A.; Younes, R.; Lafon, P. New Geometrical Modelling for 2D Fabric and 2.5D Interlock Composites. Textiles 2022, 2, 142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010008
Kaddaha MA, Younes R, Lafon P. New Geometrical Modelling for 2D Fabric and 2.5D Interlock Composites. Textiles. 2022; 2(1):142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaddaha, Mohamad Abbas, Rafic Younes, and Pascal Lafon. 2022. "New Geometrical Modelling for 2D Fabric and 2.5D Interlock Composites" Textiles 2, no. 1: 142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010008
APA StyleKaddaha, M. A., Younes, R., & Lafon, P. (2022). New Geometrical Modelling for 2D Fabric and 2.5D Interlock Composites. Textiles, 2(1), 142-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010008






