Factors Affecting Acoustic Properties of Natural-Fiber-Based Materials and Composites: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Acoustic Properties of Fibrous Materials and Composites
2.1. Classification of Sound in Terms of SAC
2.2. Sound-Absorbing Materials
2.3. Factors Affecting Acoustic Properties of Fibrous Sound-Absorbing Materials and Composites
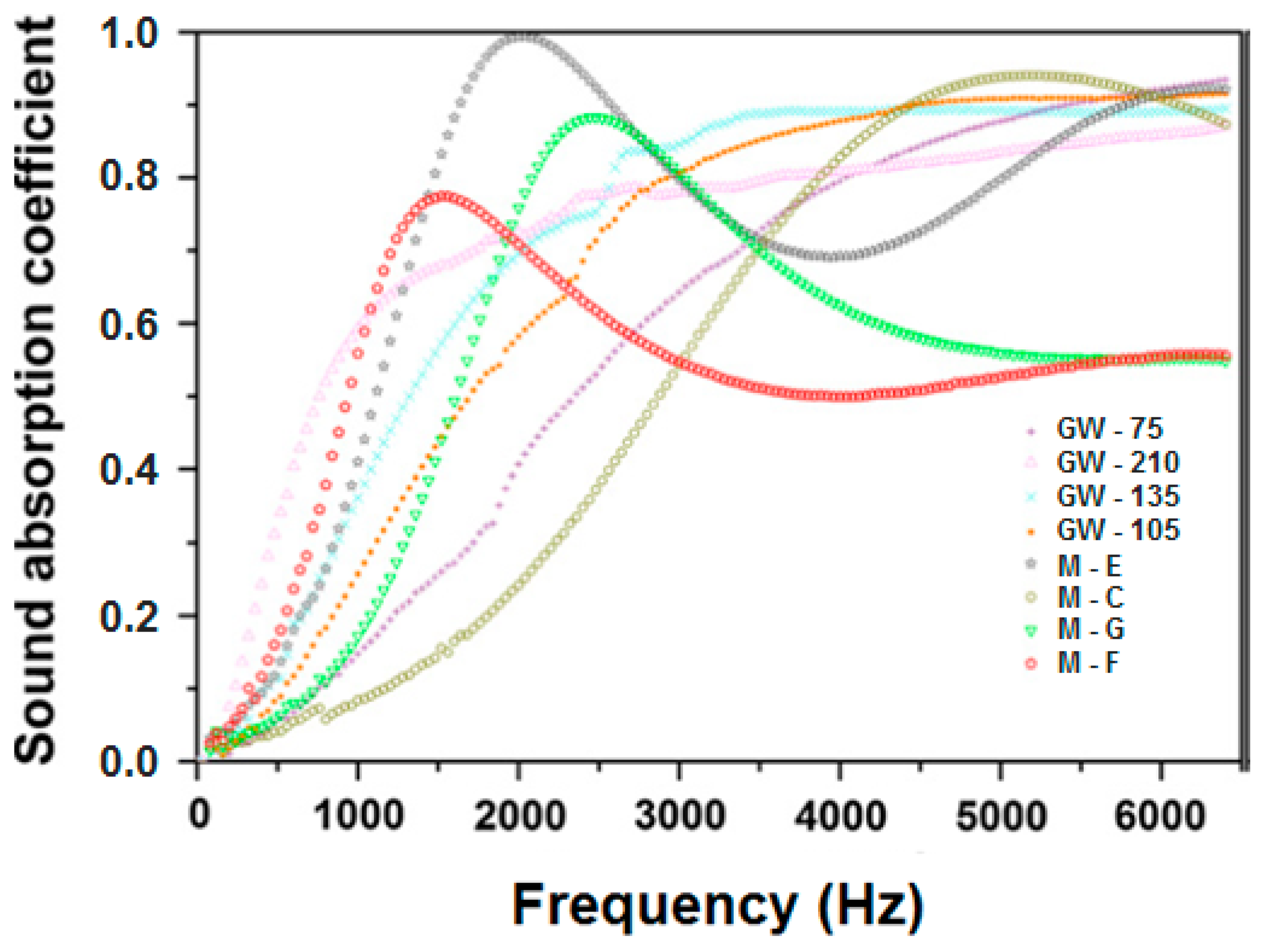
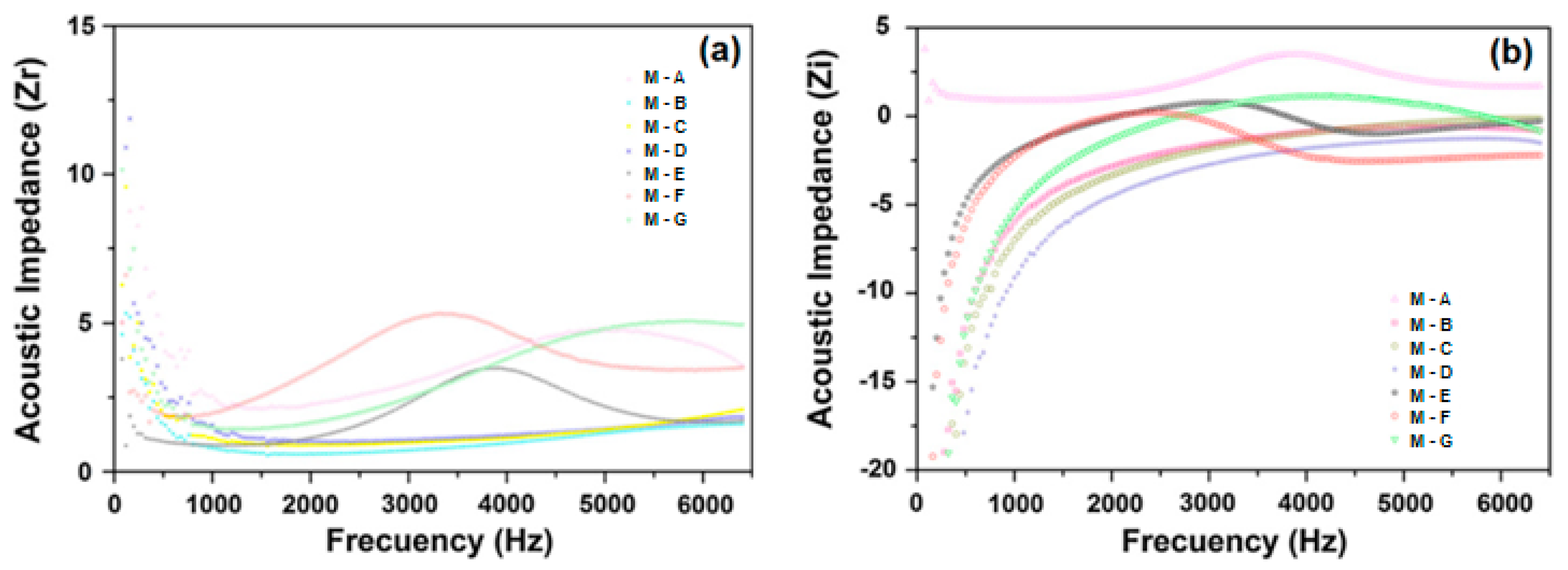
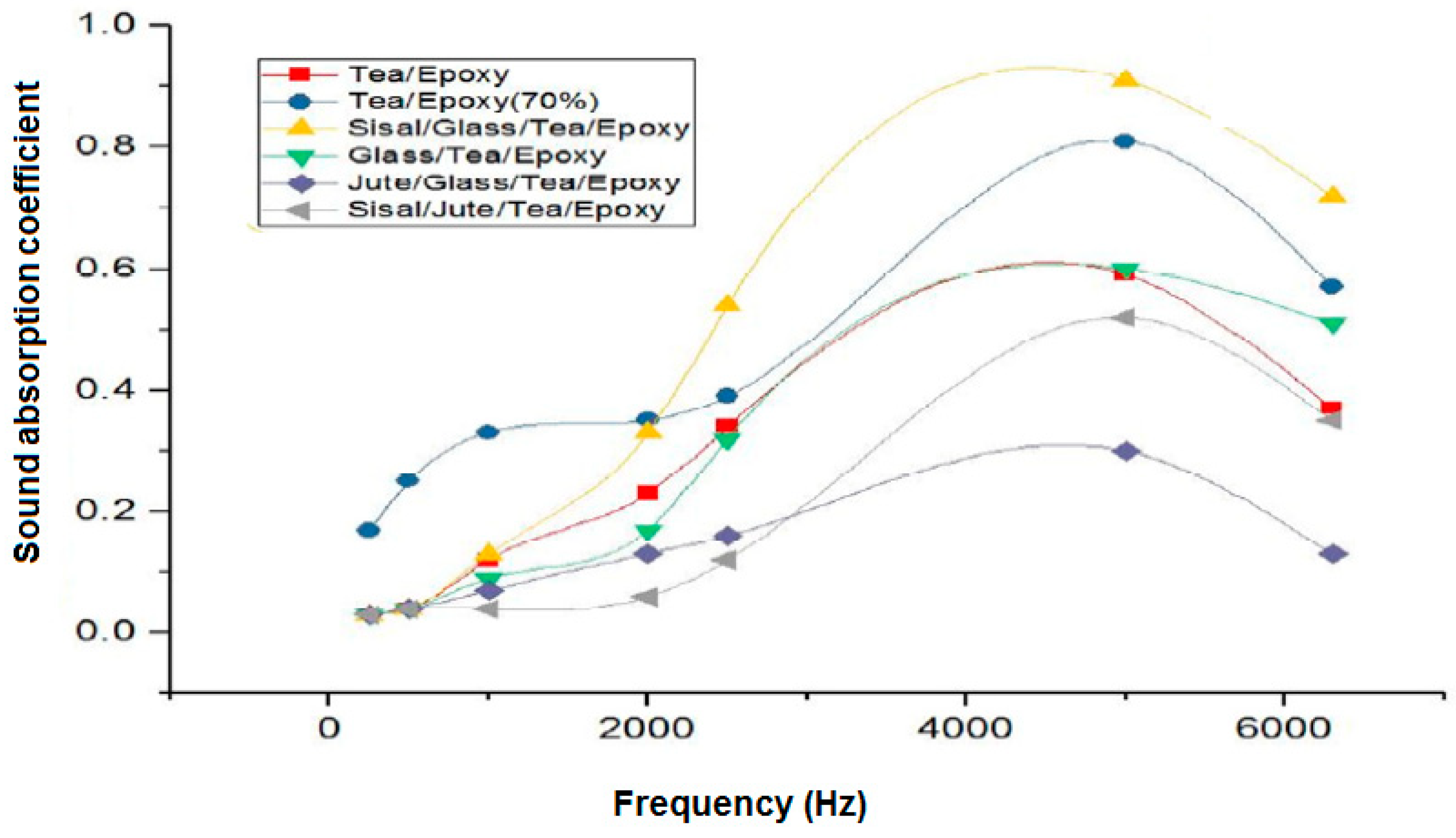
2.3.1. Effect of Different Fiber Types
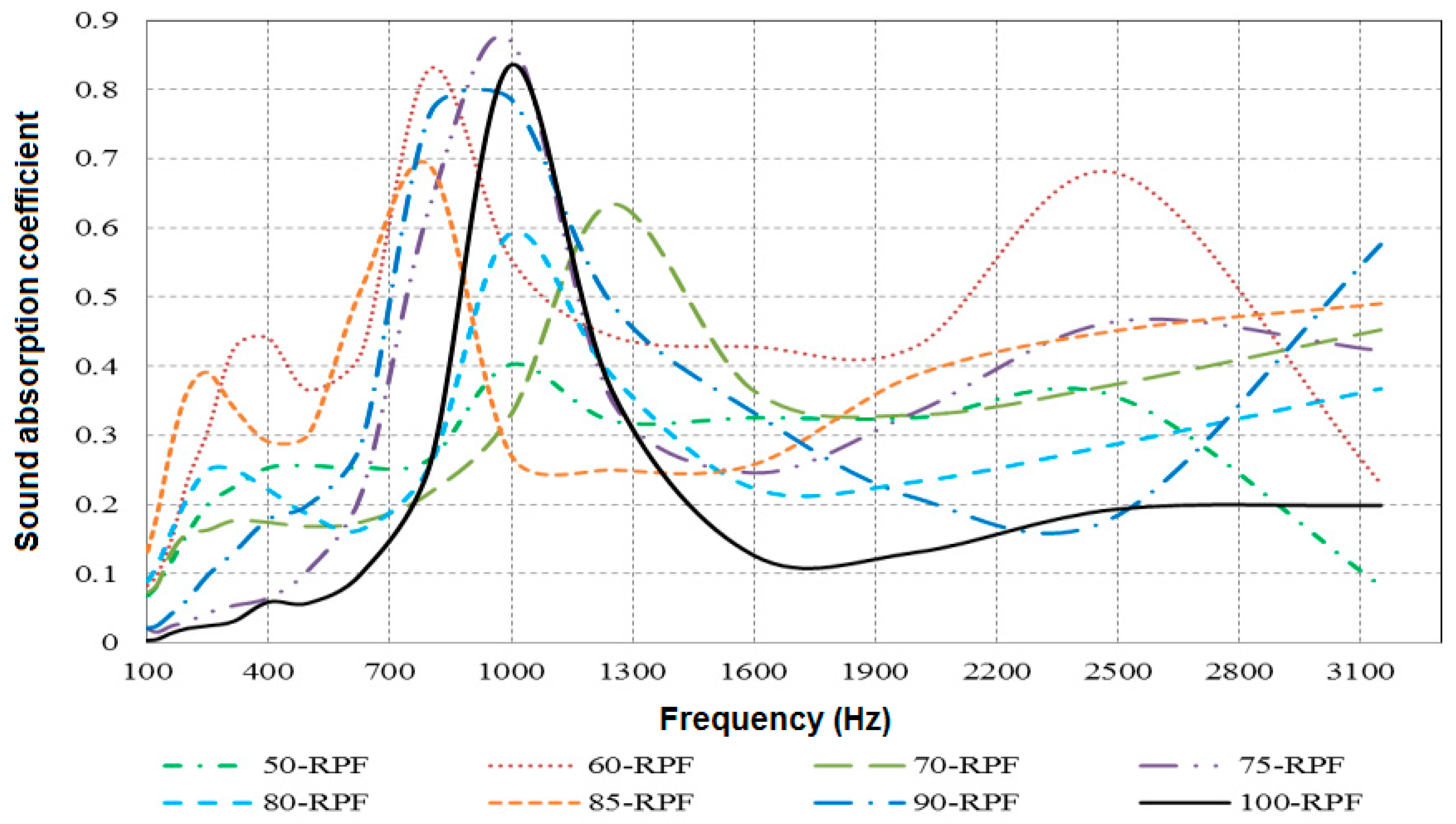
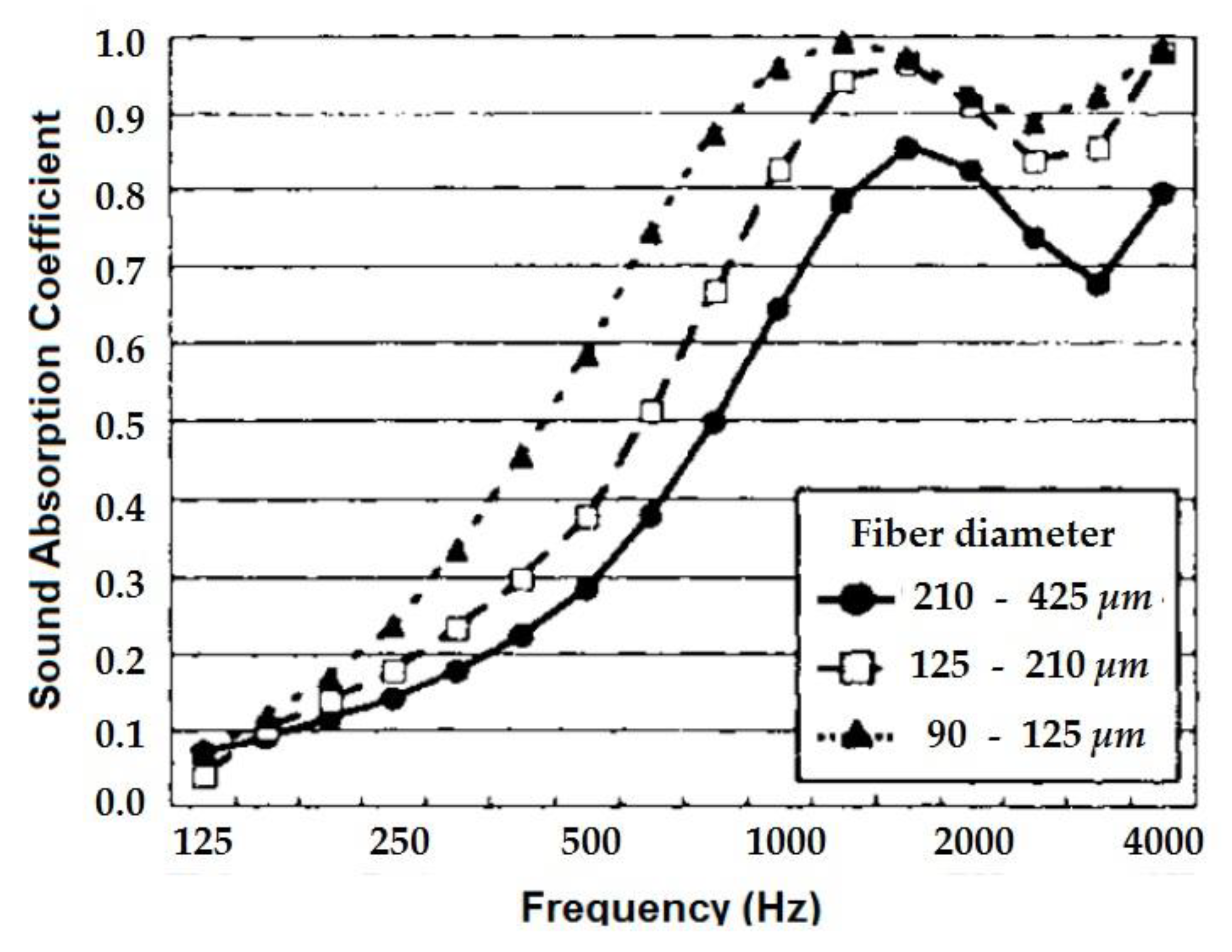
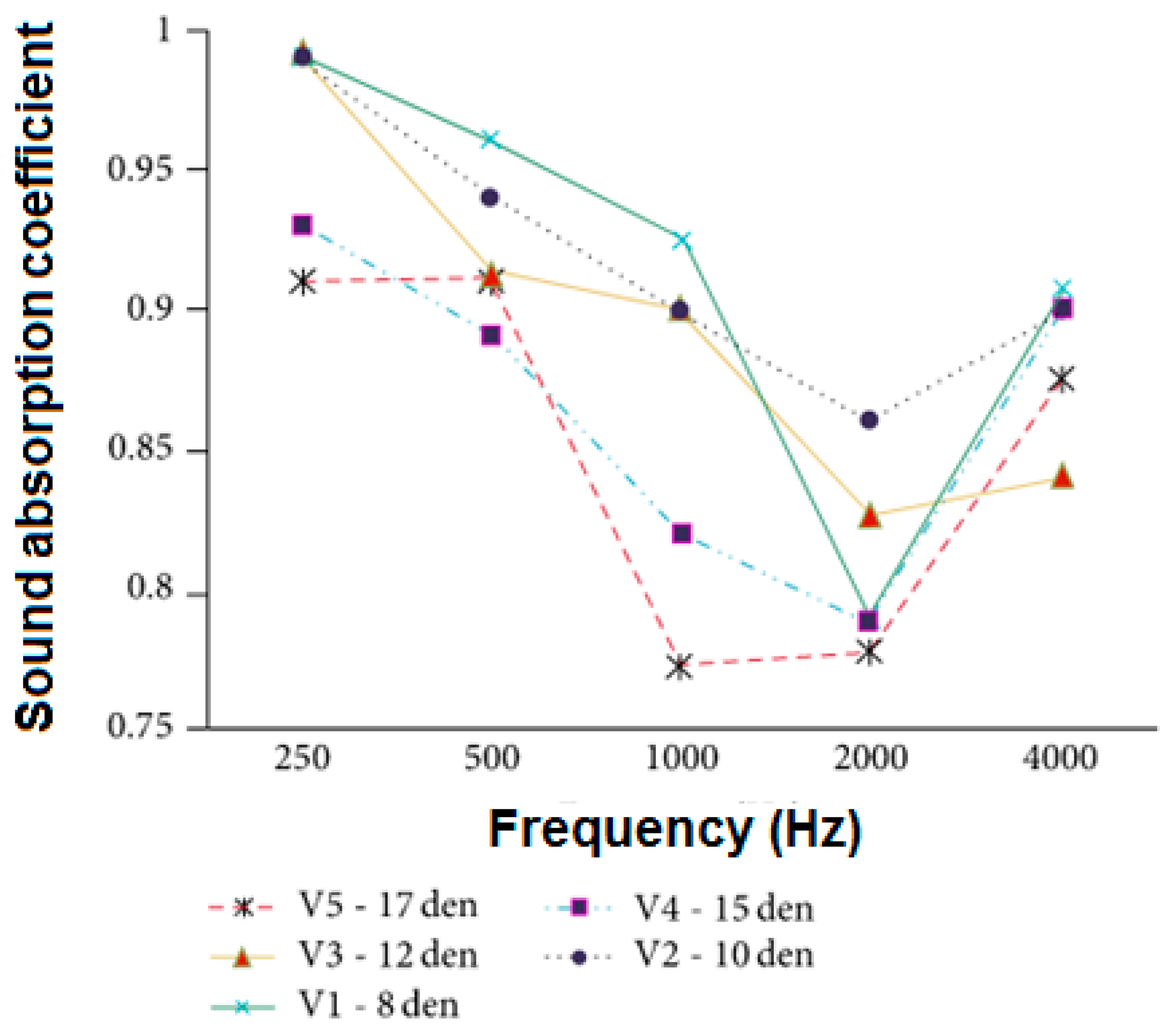
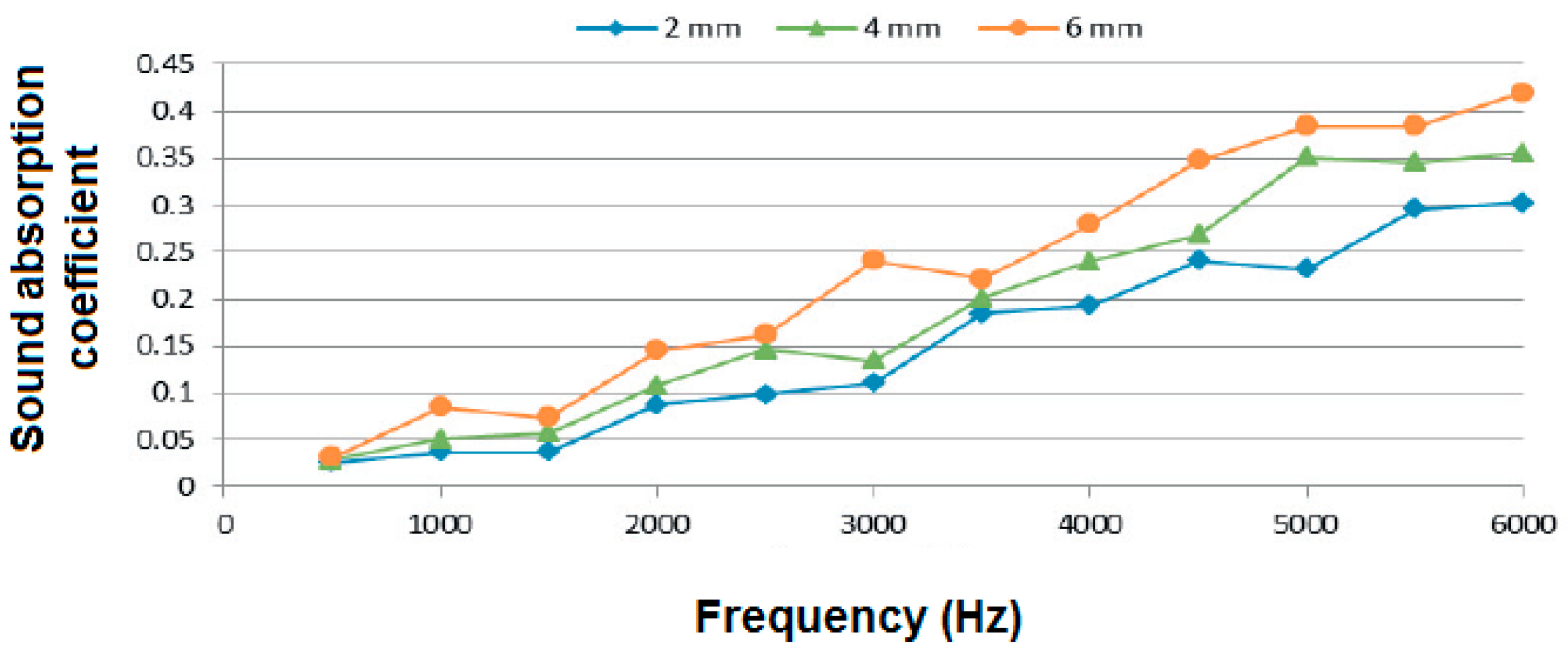
2.3.2. Effect of Fiber Size
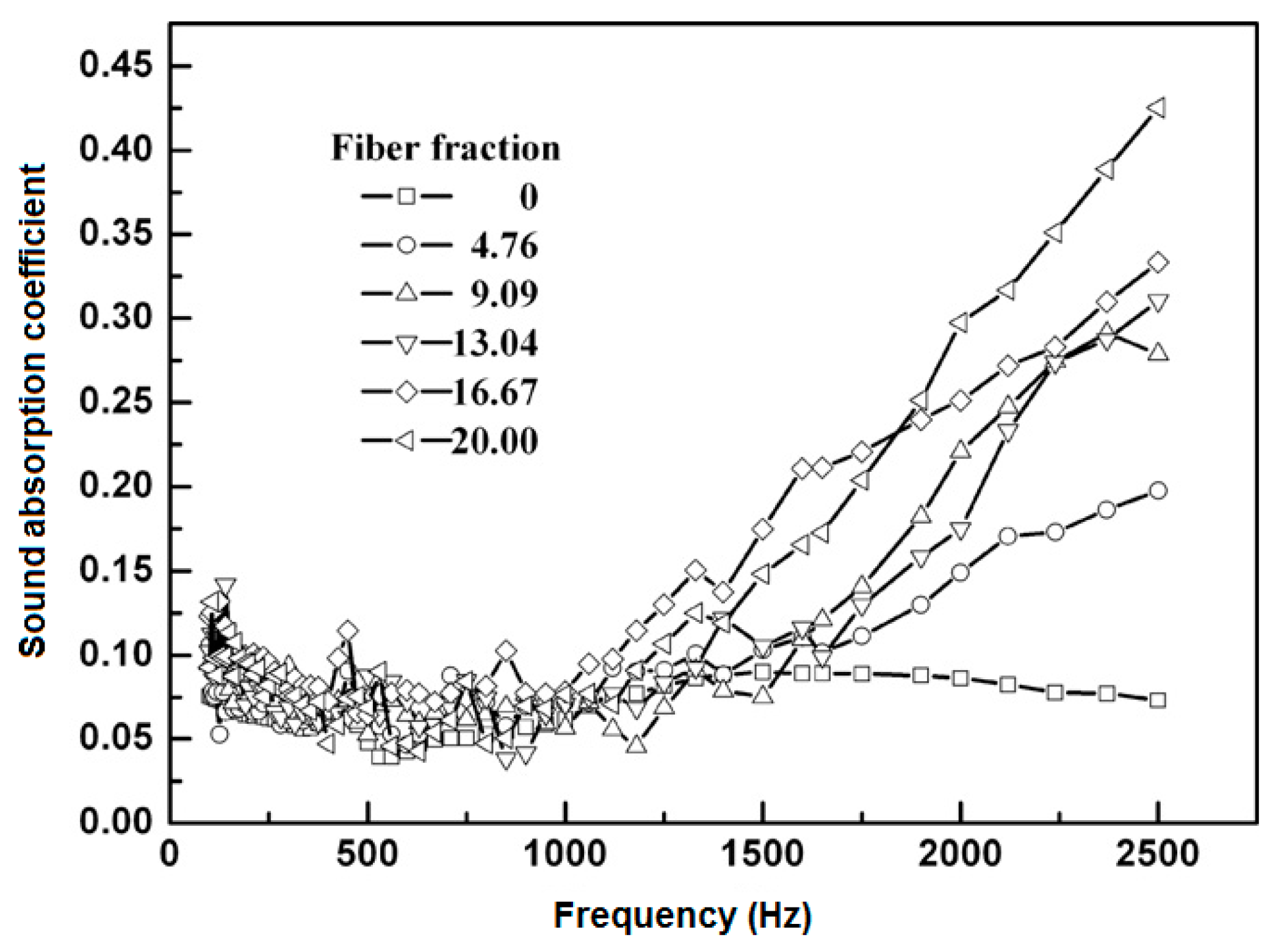
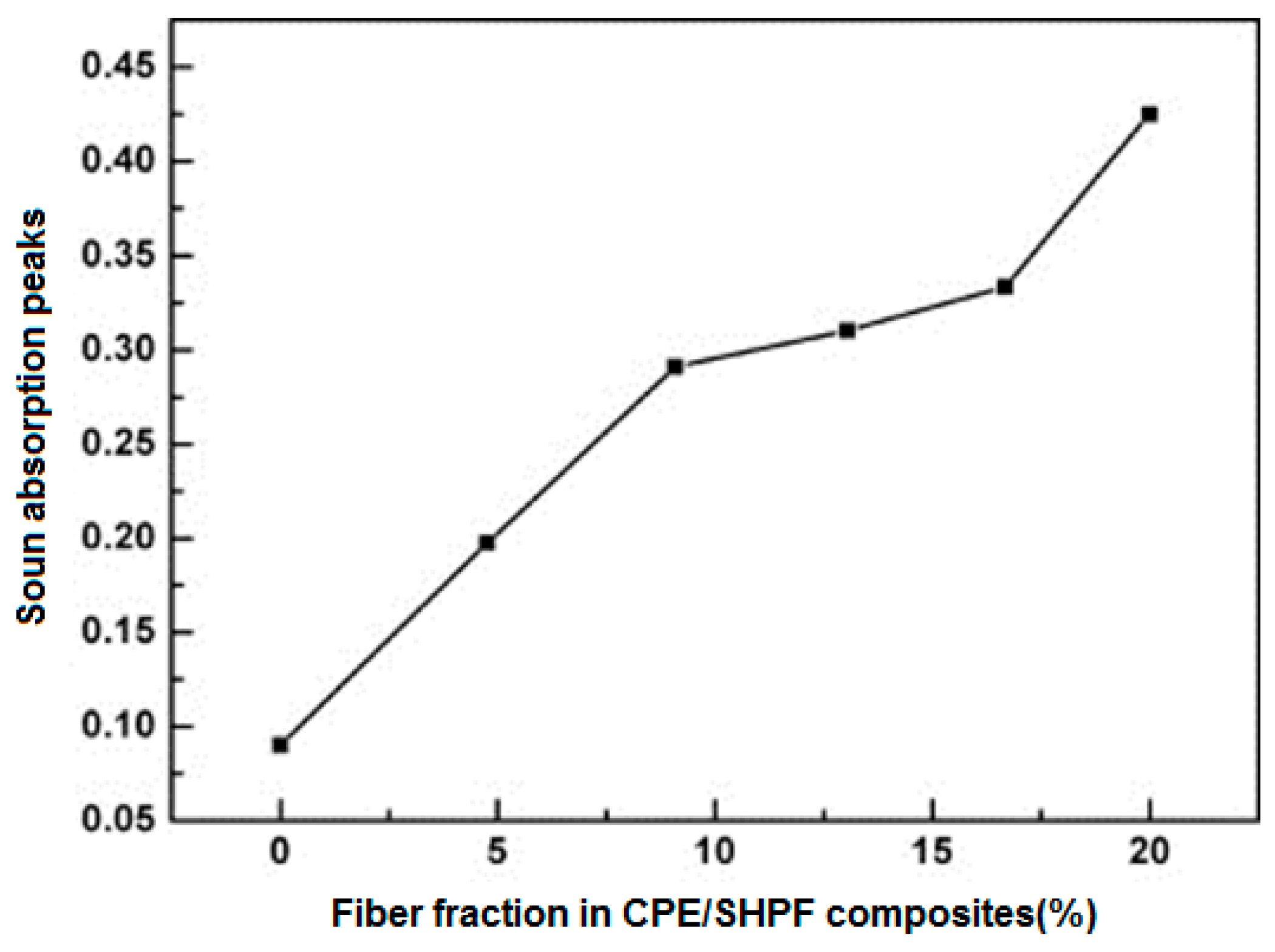
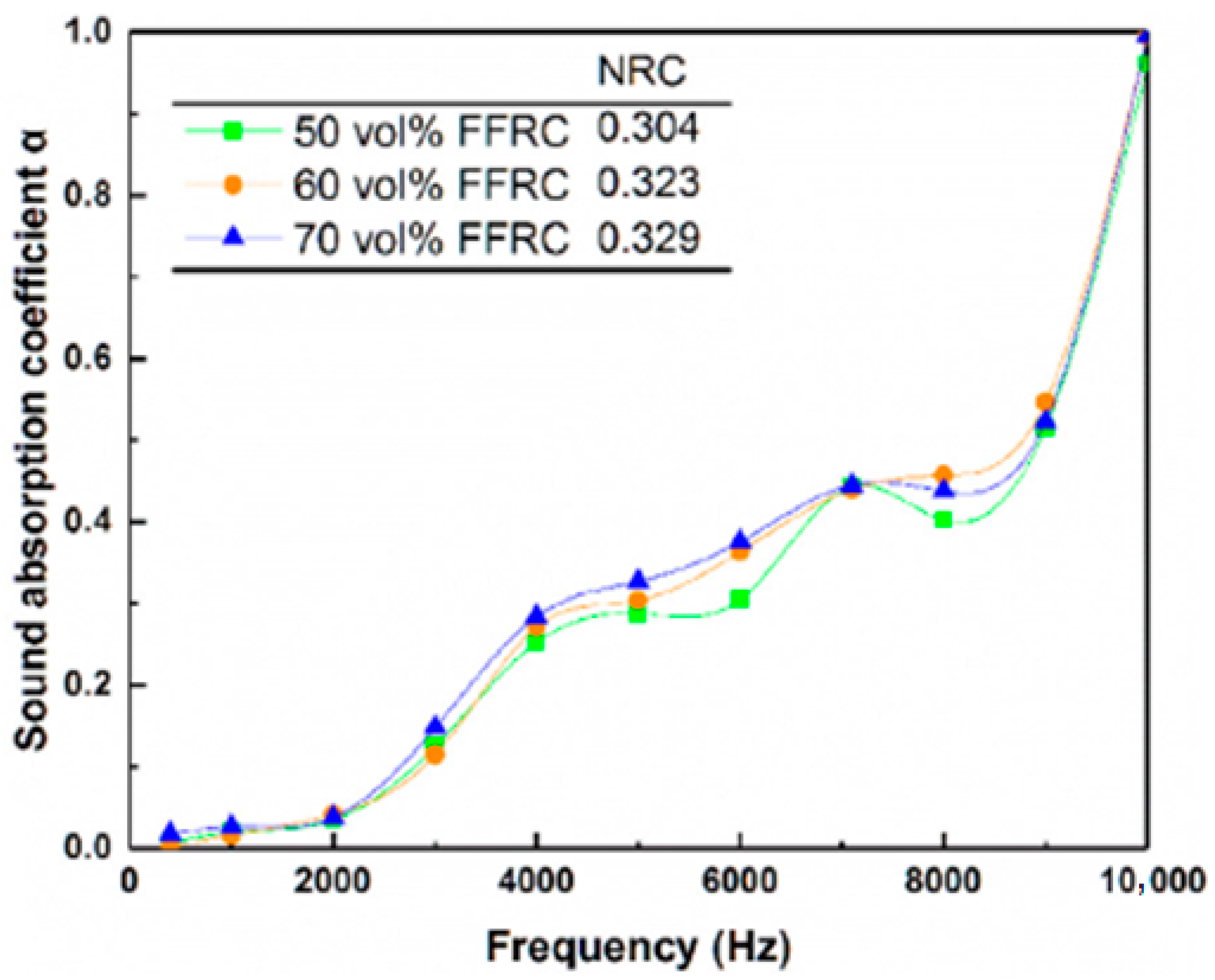
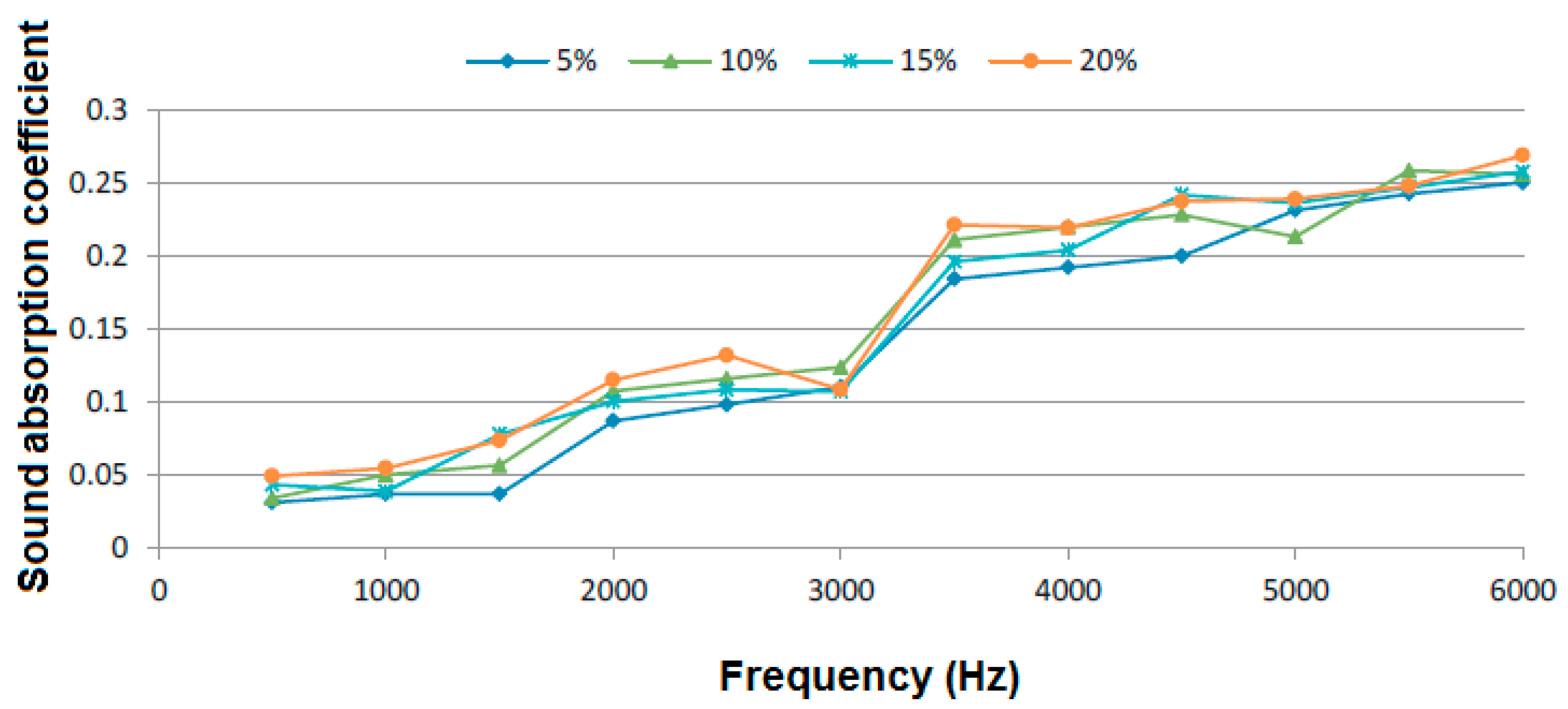
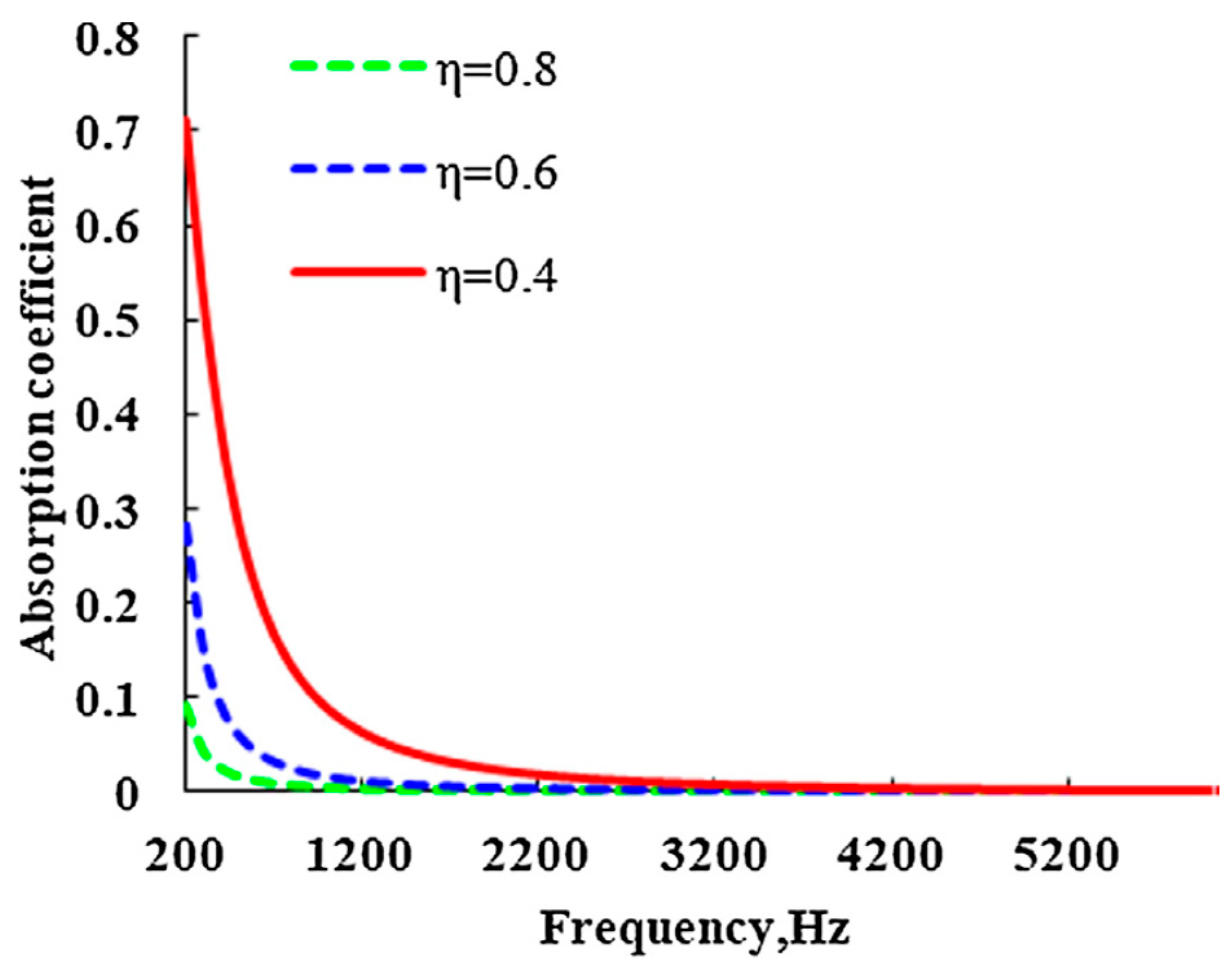
2.3.3. Effect of Fiber Fraction
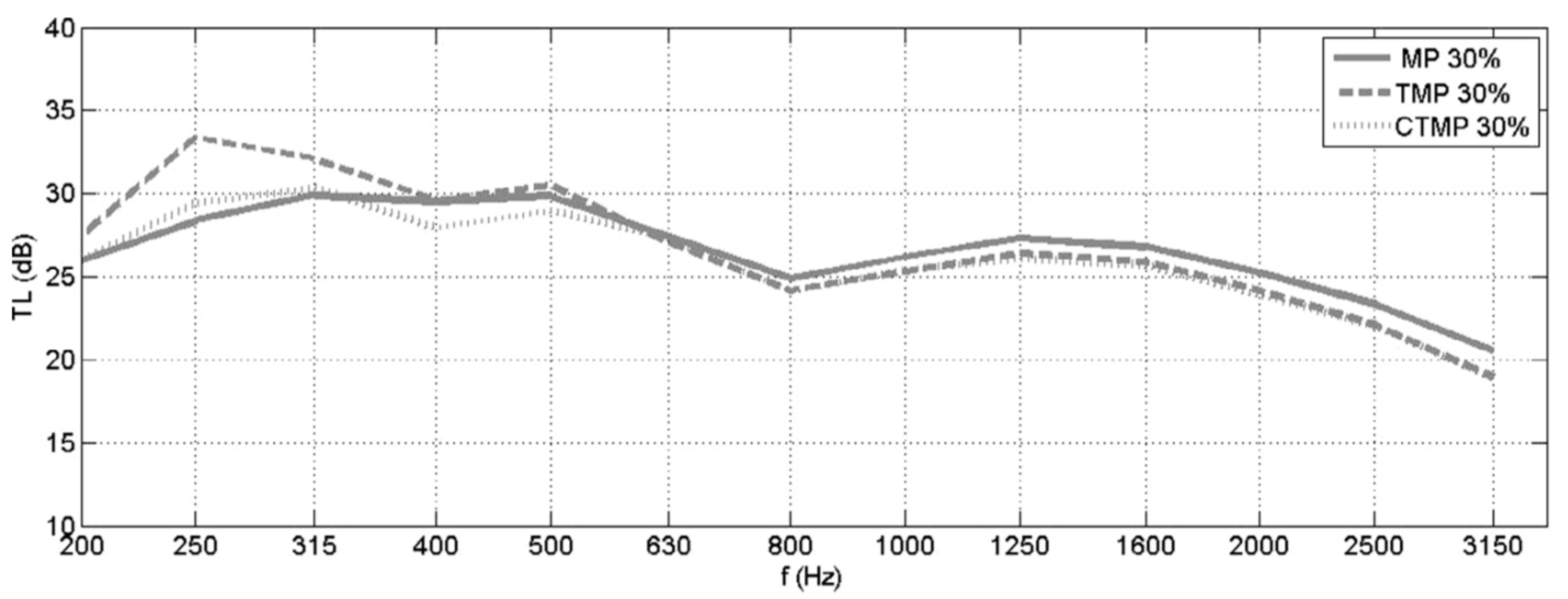
2.3.4. Effect of Fiber Treatment
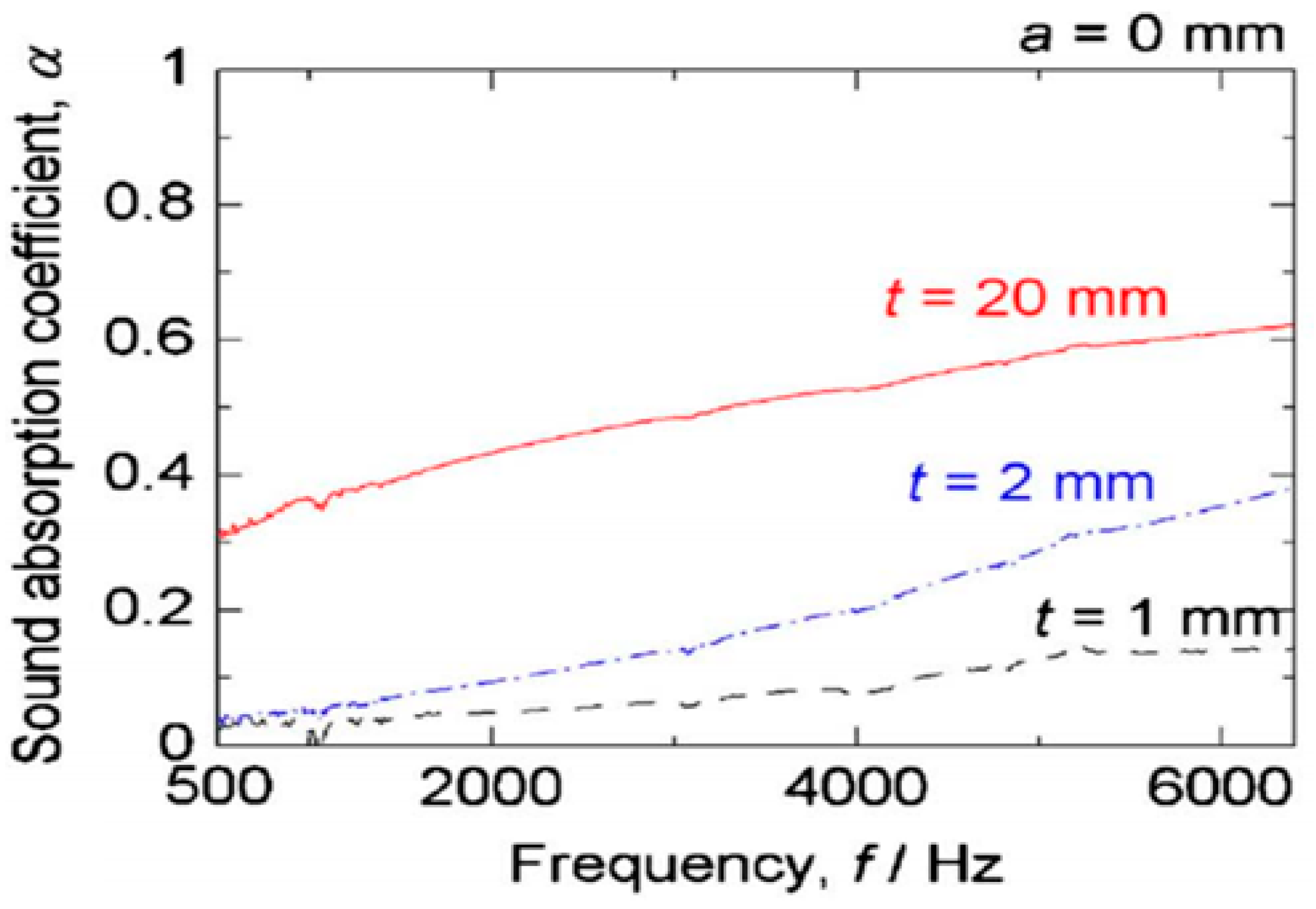
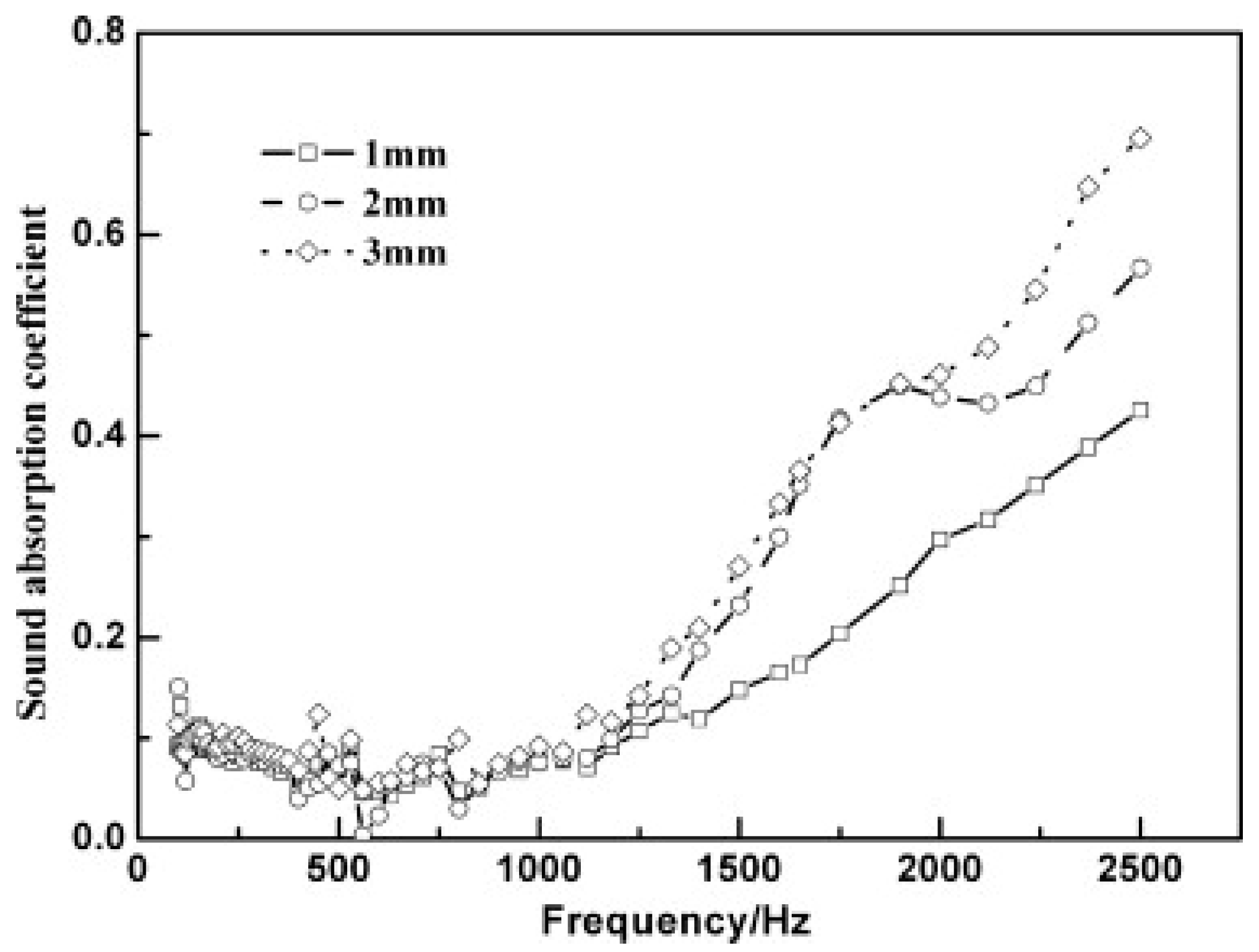
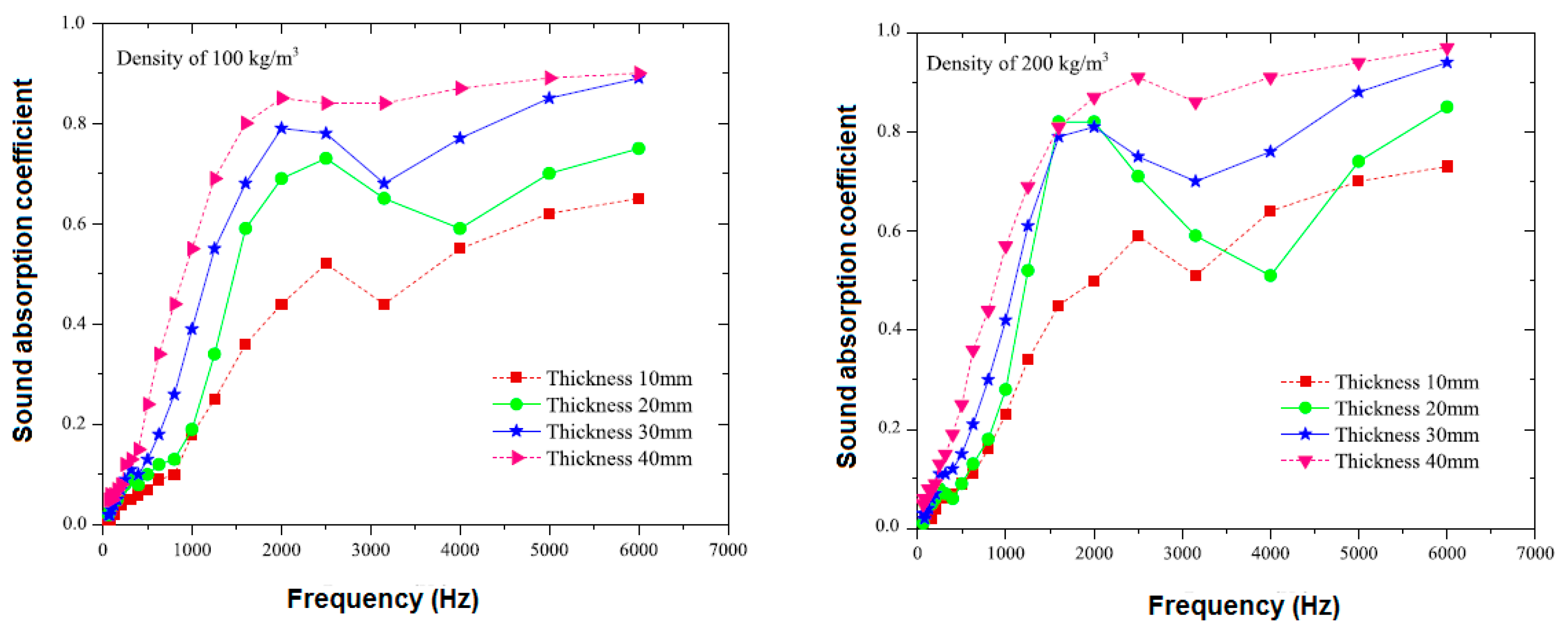
2.3.5. Effect of Sample Thickness
2.3.6. Effect of Gluing and Multiple Layering of Composites
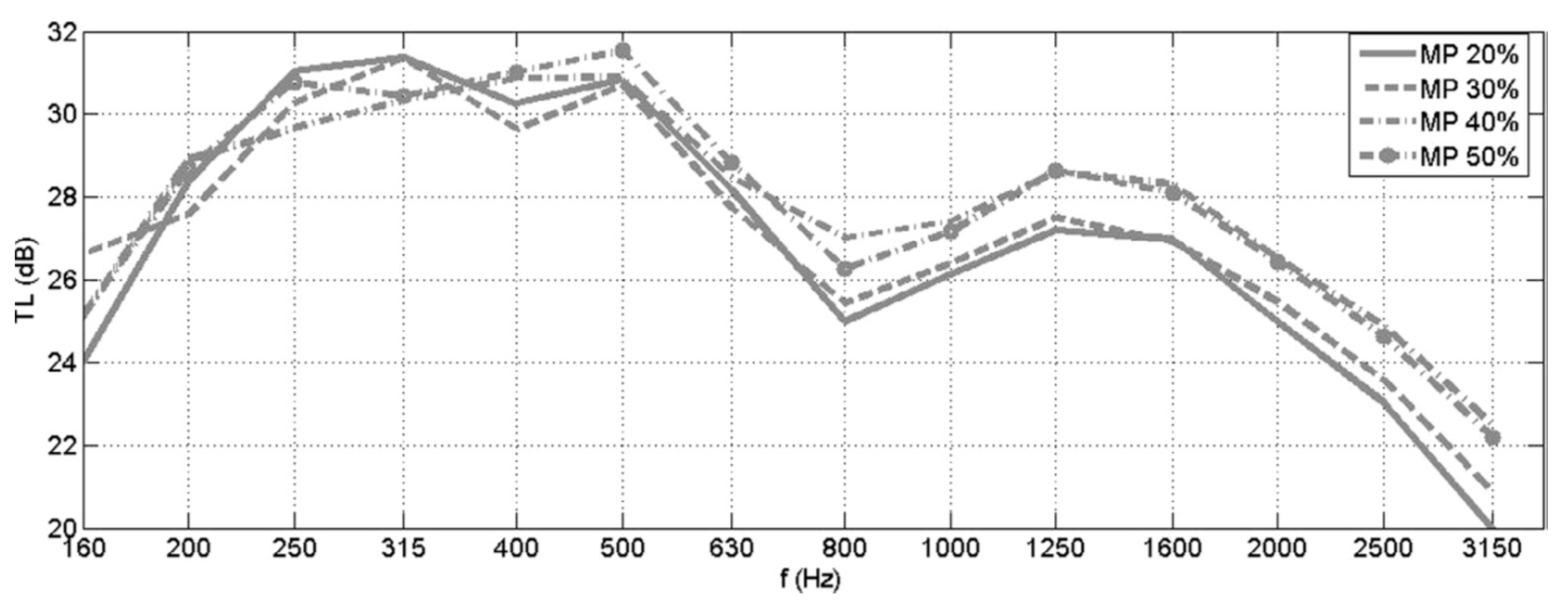
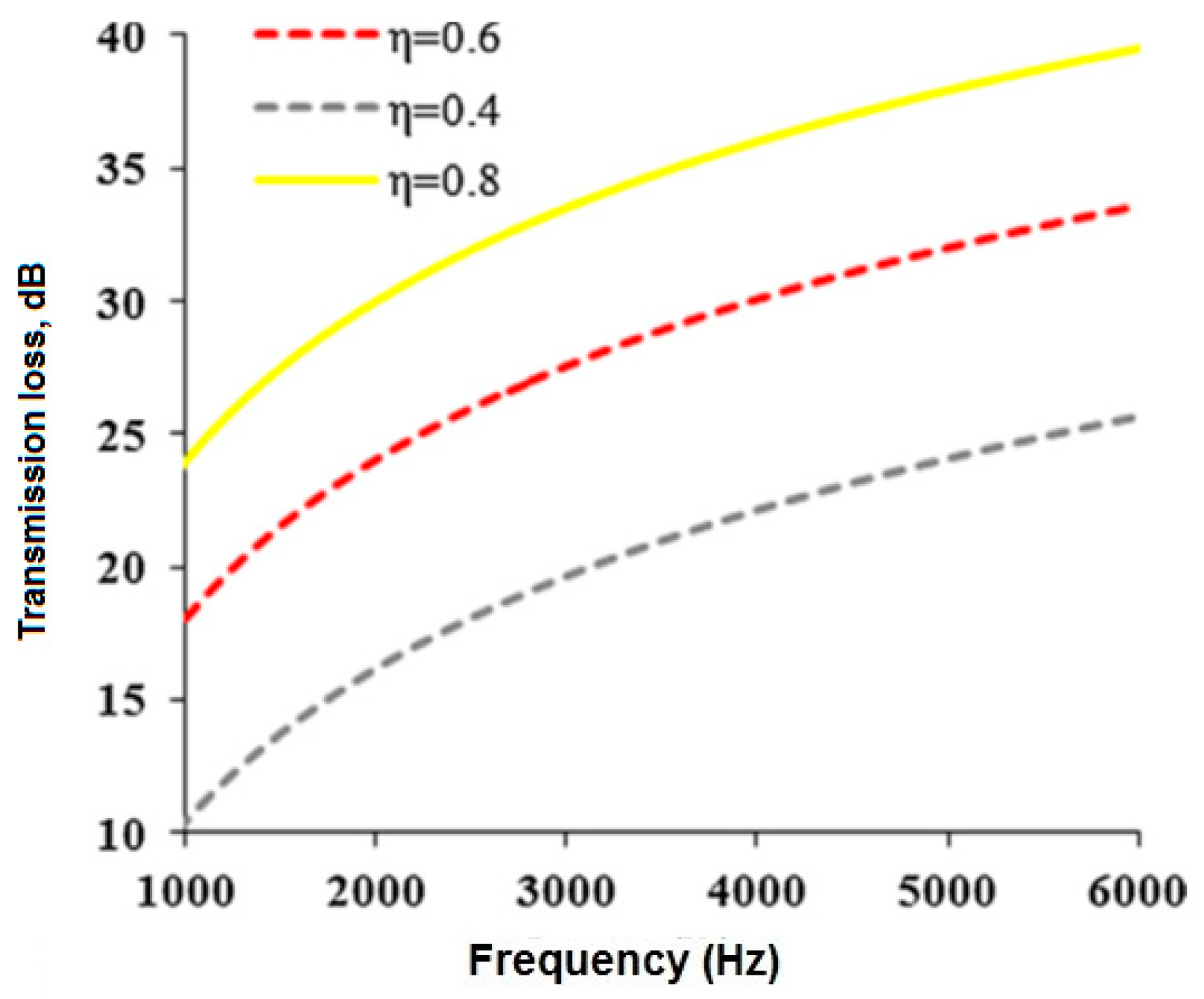
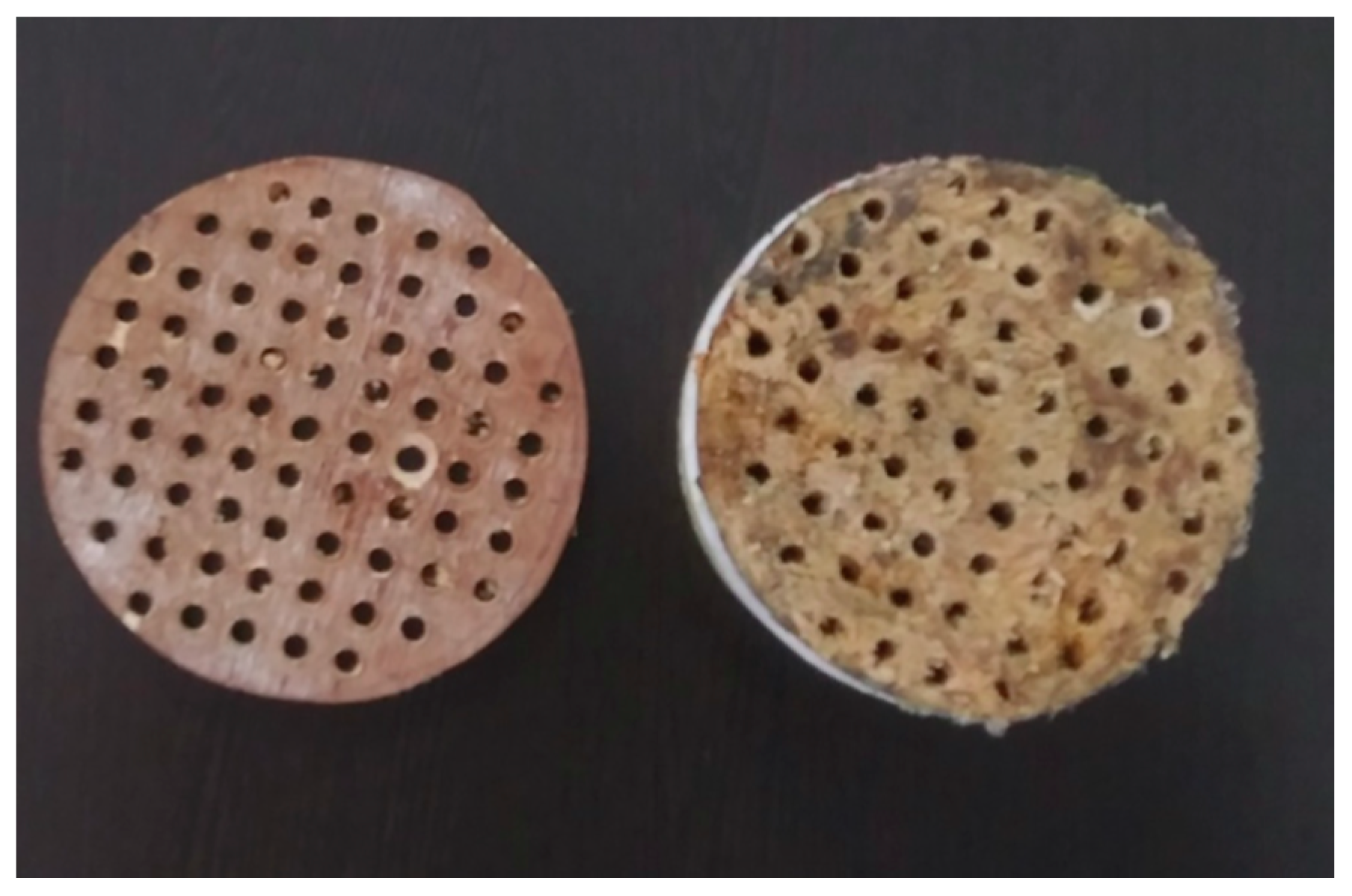
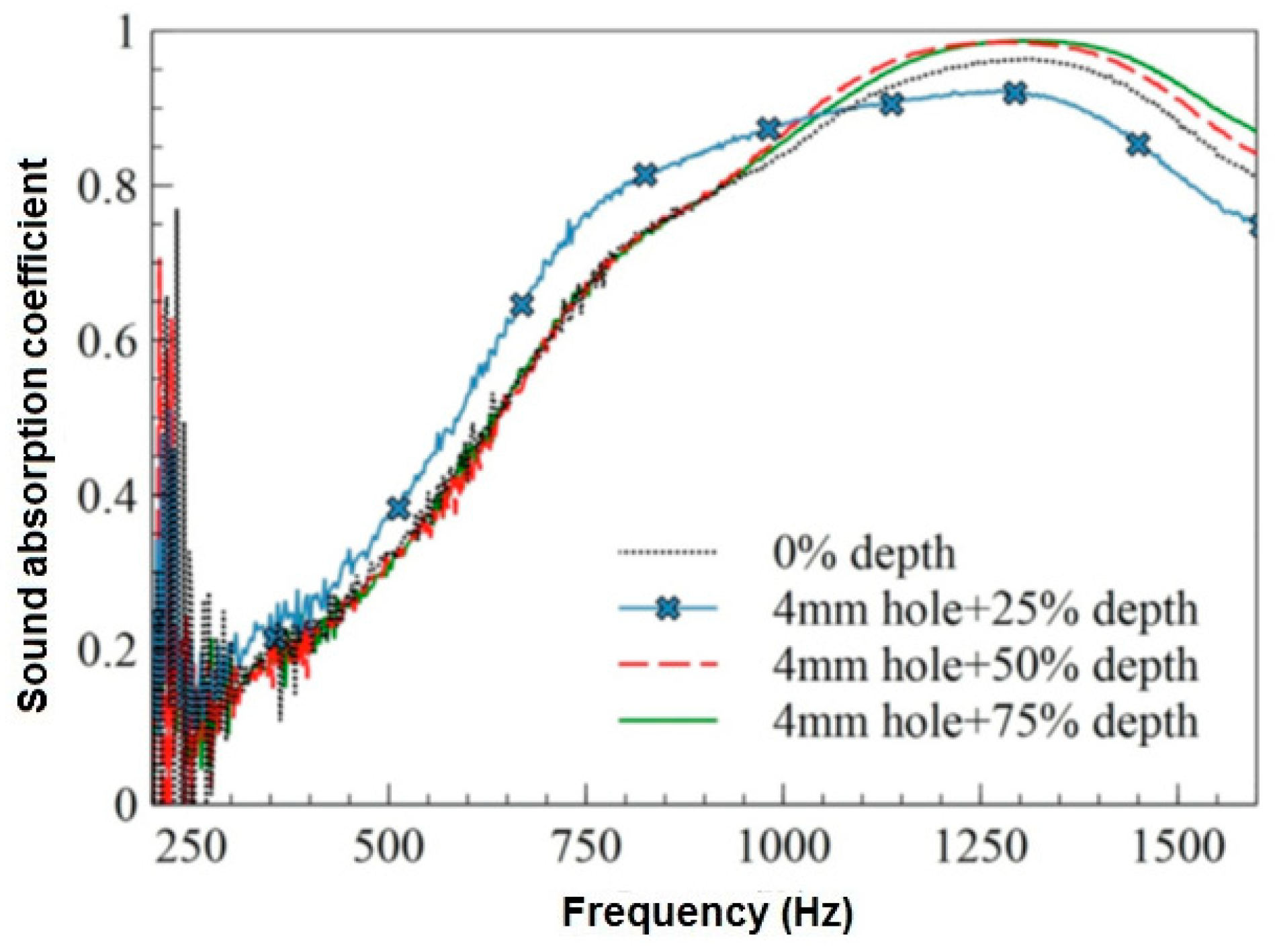
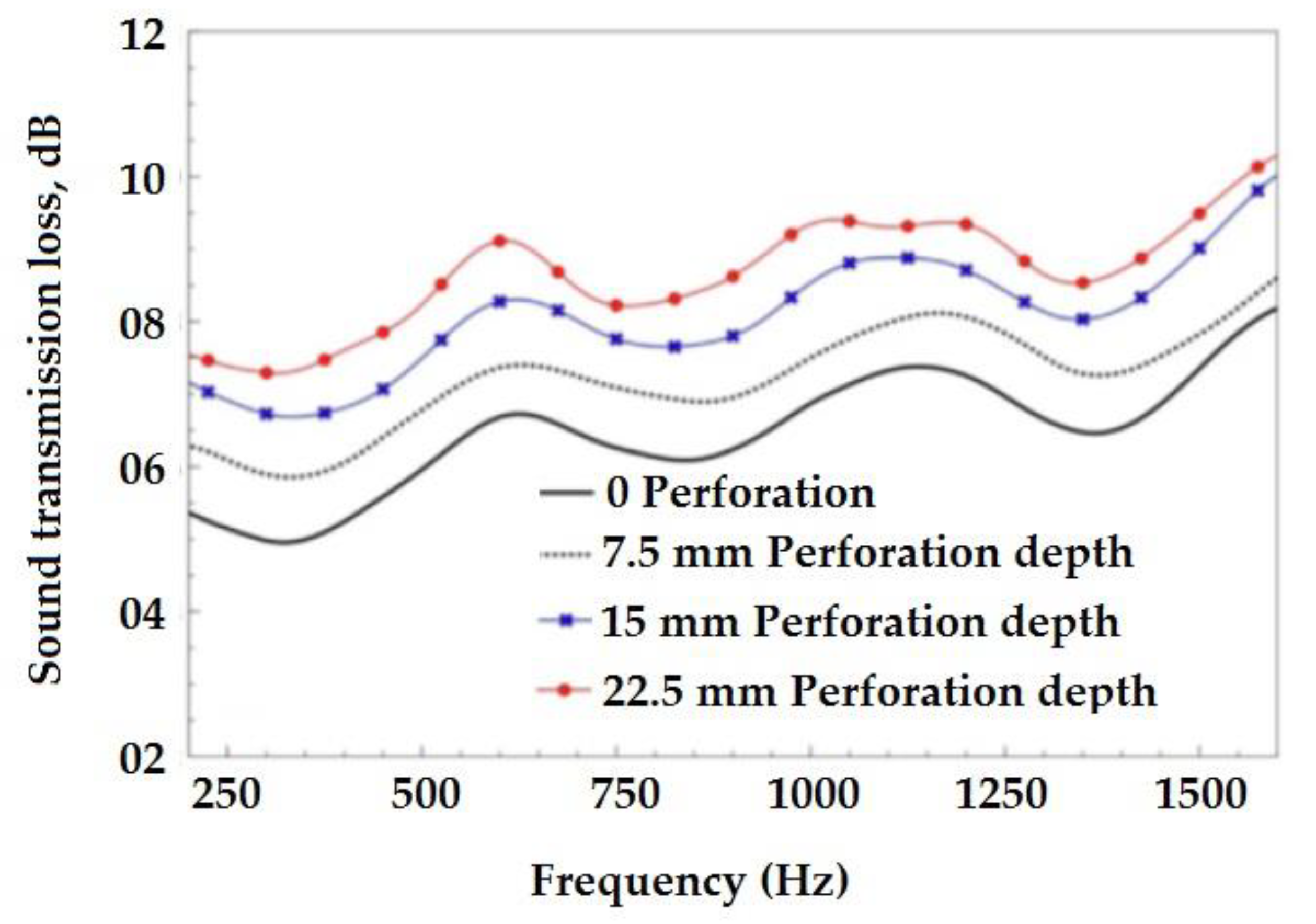
2.3.7. Effect of Perforation
2.3.8. Effect of Adding Plasticizer and Flame Retardants
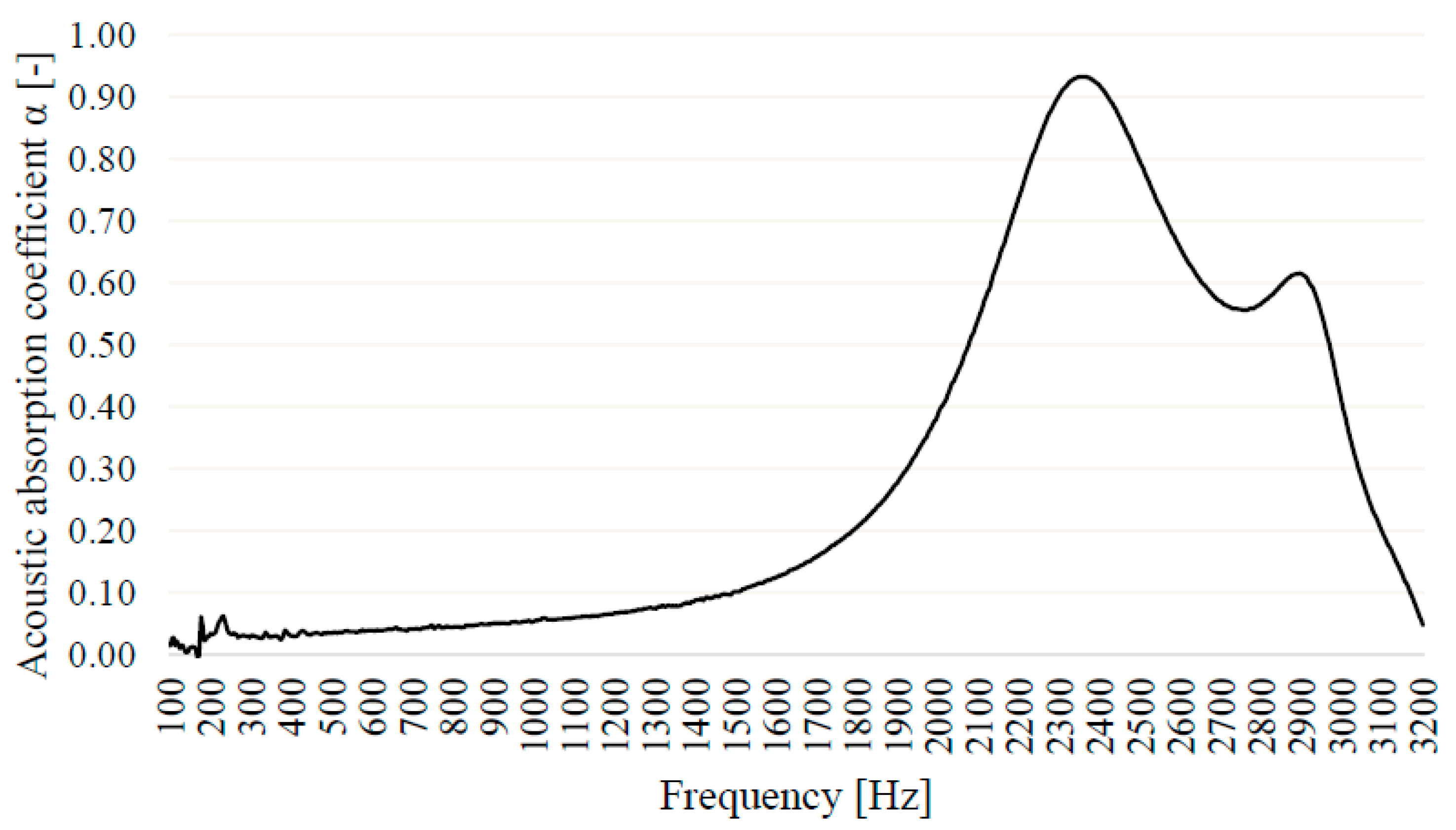
2.3.9. Effect of Frequency
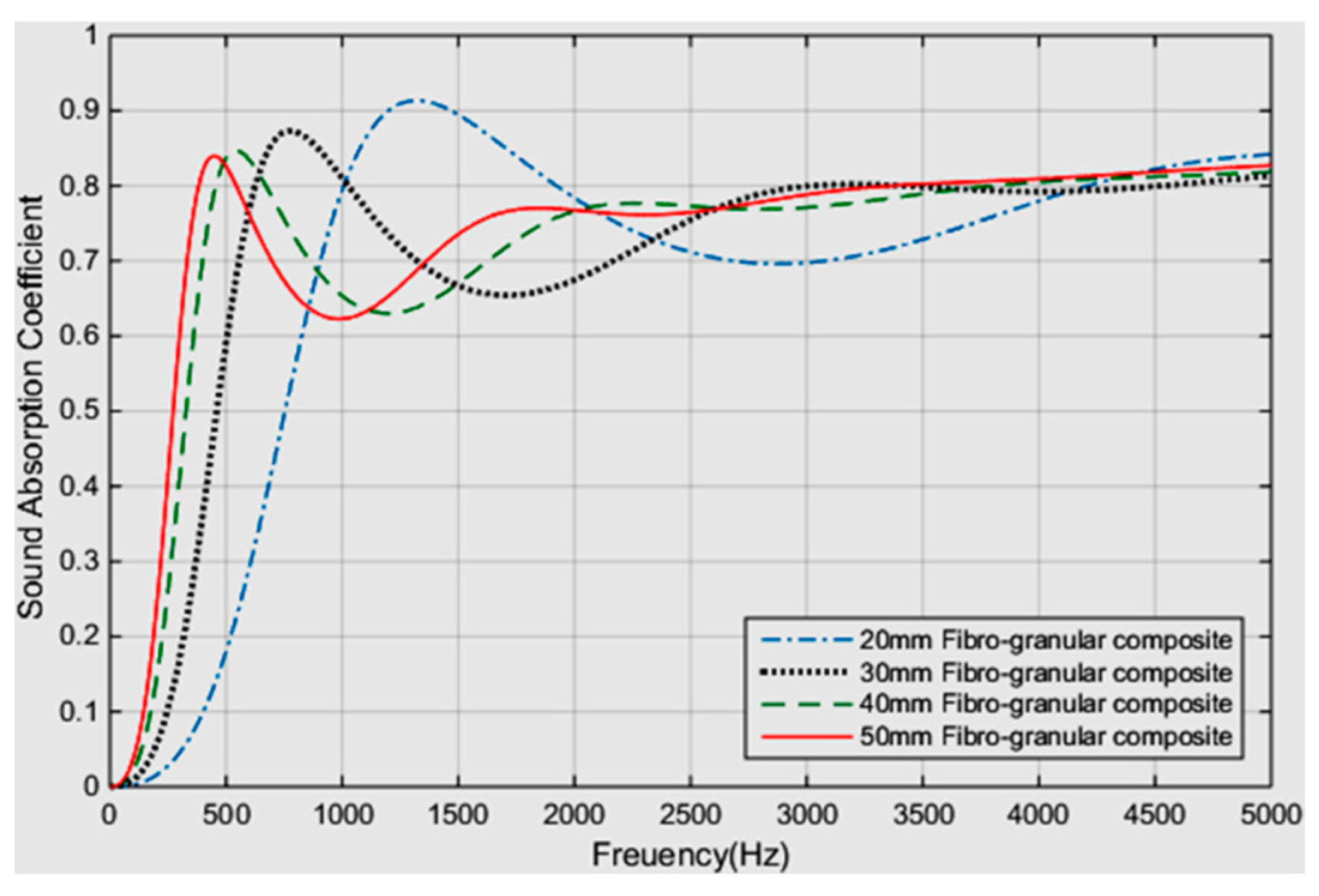
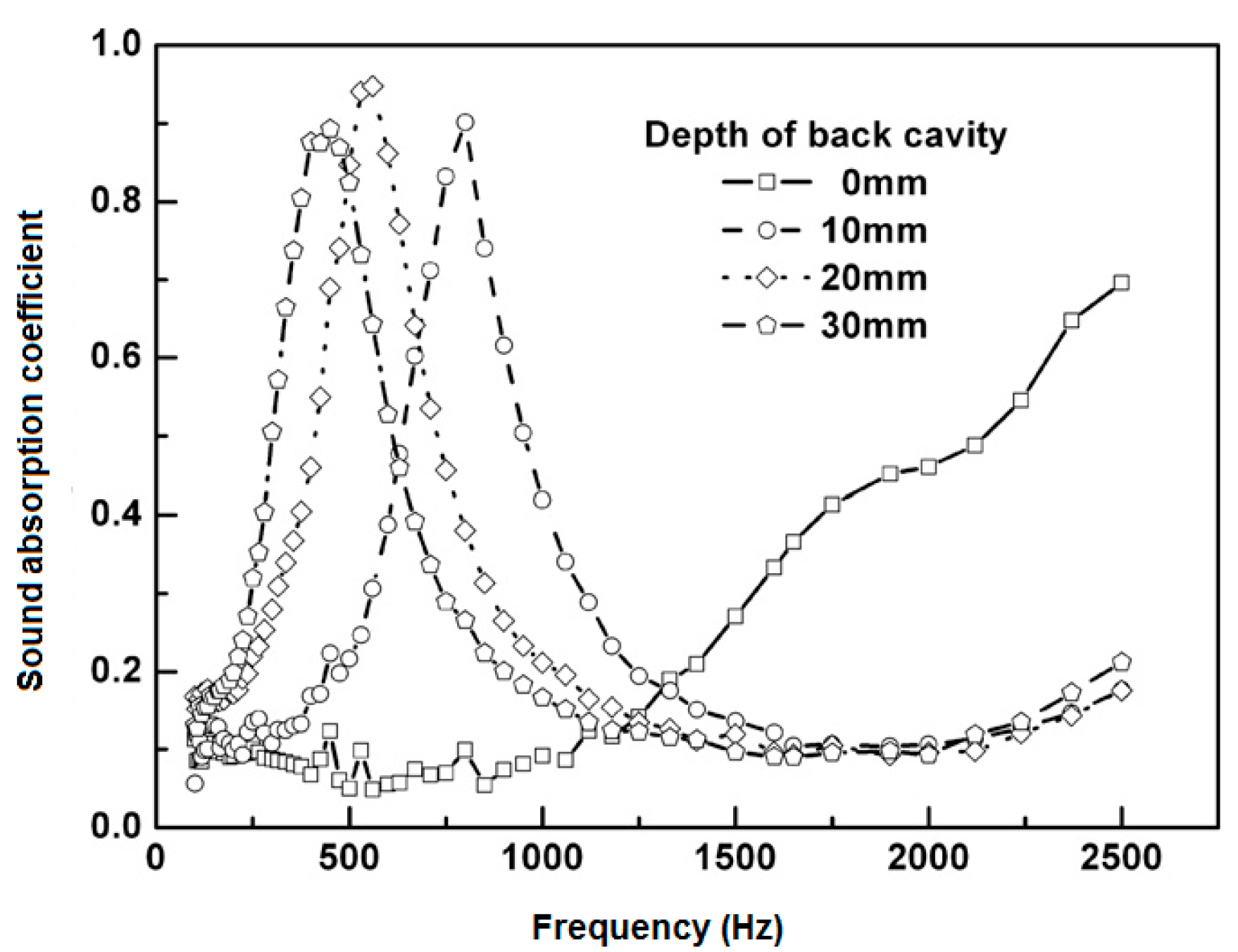
2.3.10. Effect of Back Cavity Depth
2.3.11. Effect of Temperature
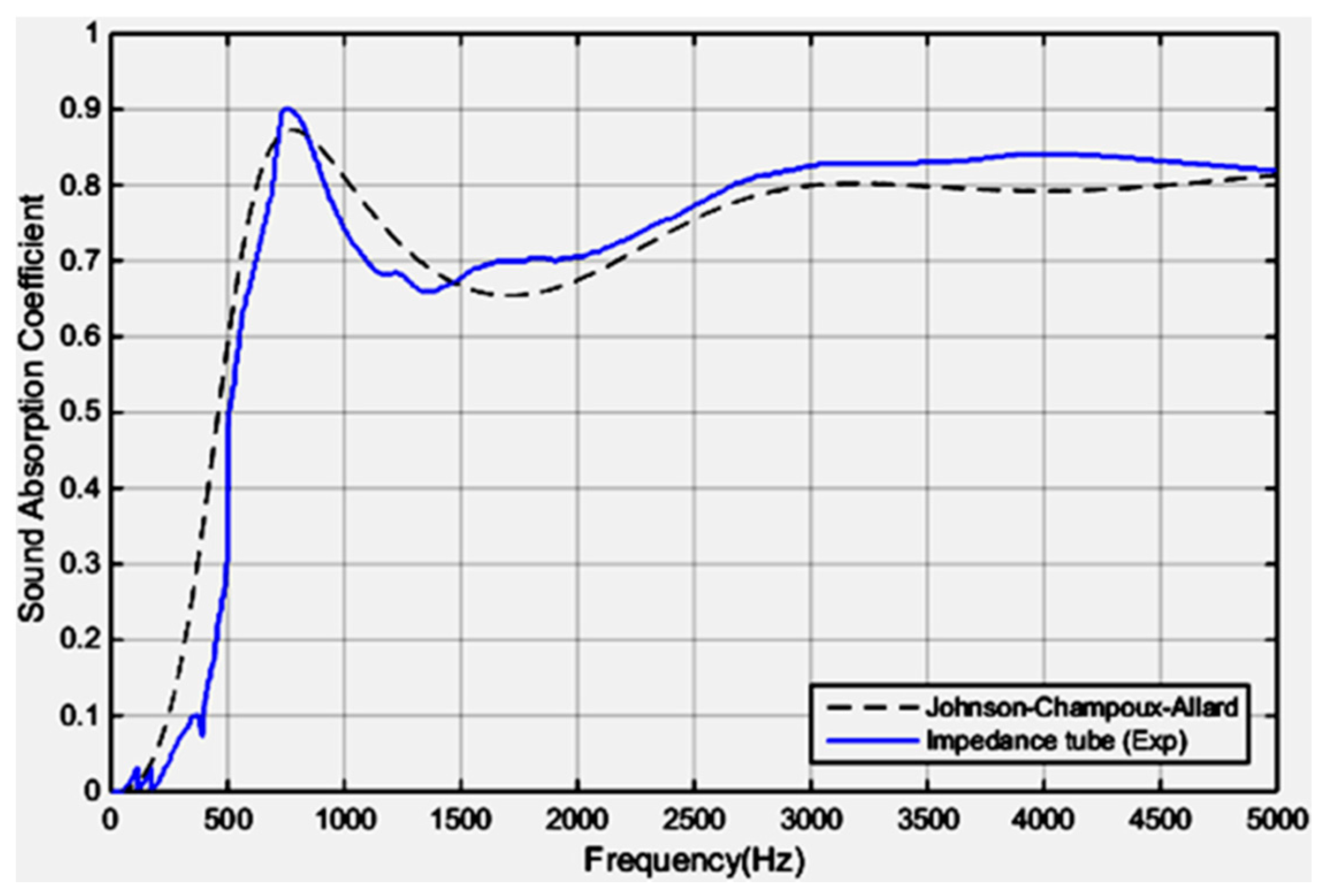
2.3.12. Effect of Porosity and Tortuosity
2.3.13. Effect of Flow Resistivity
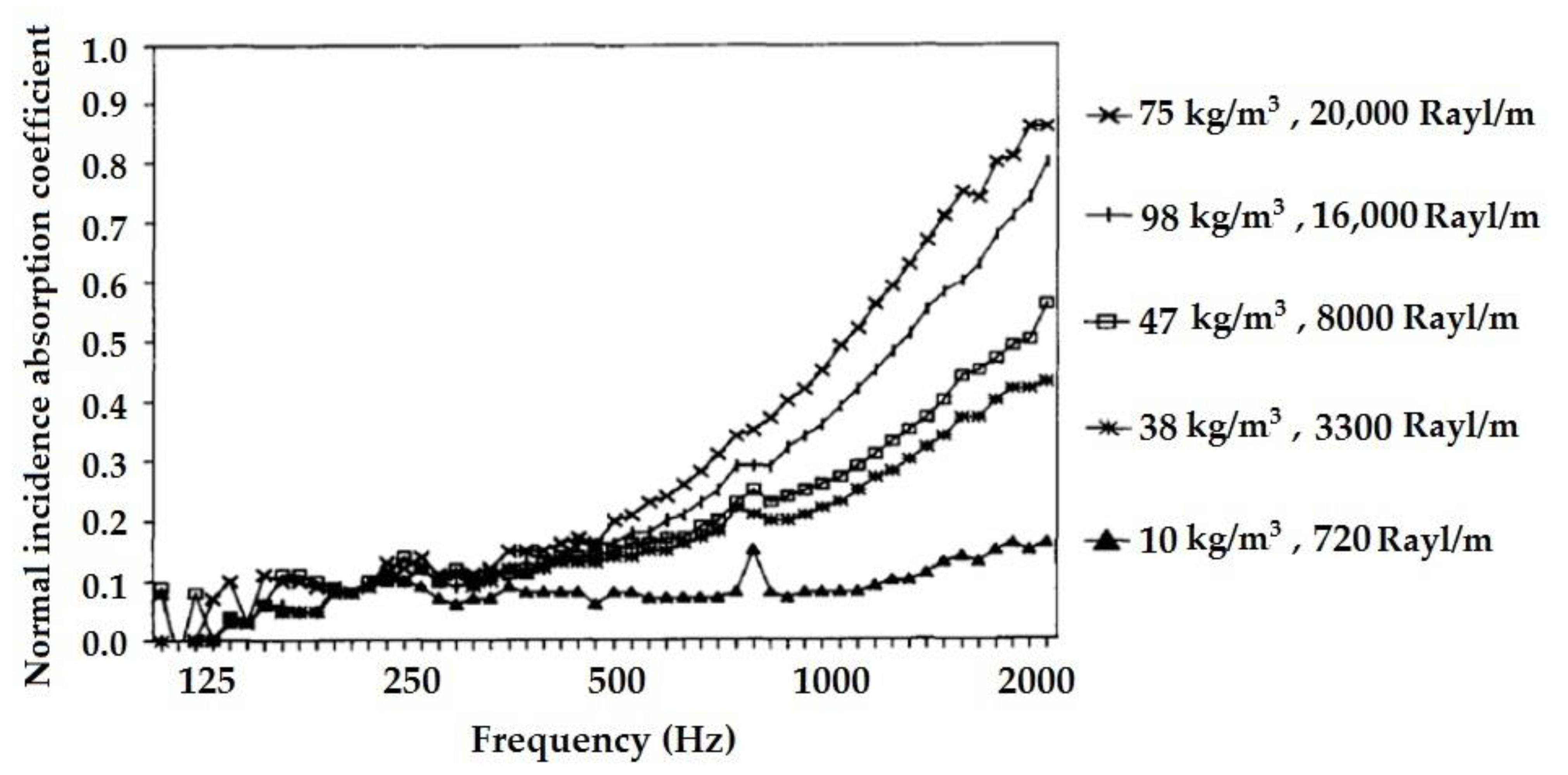
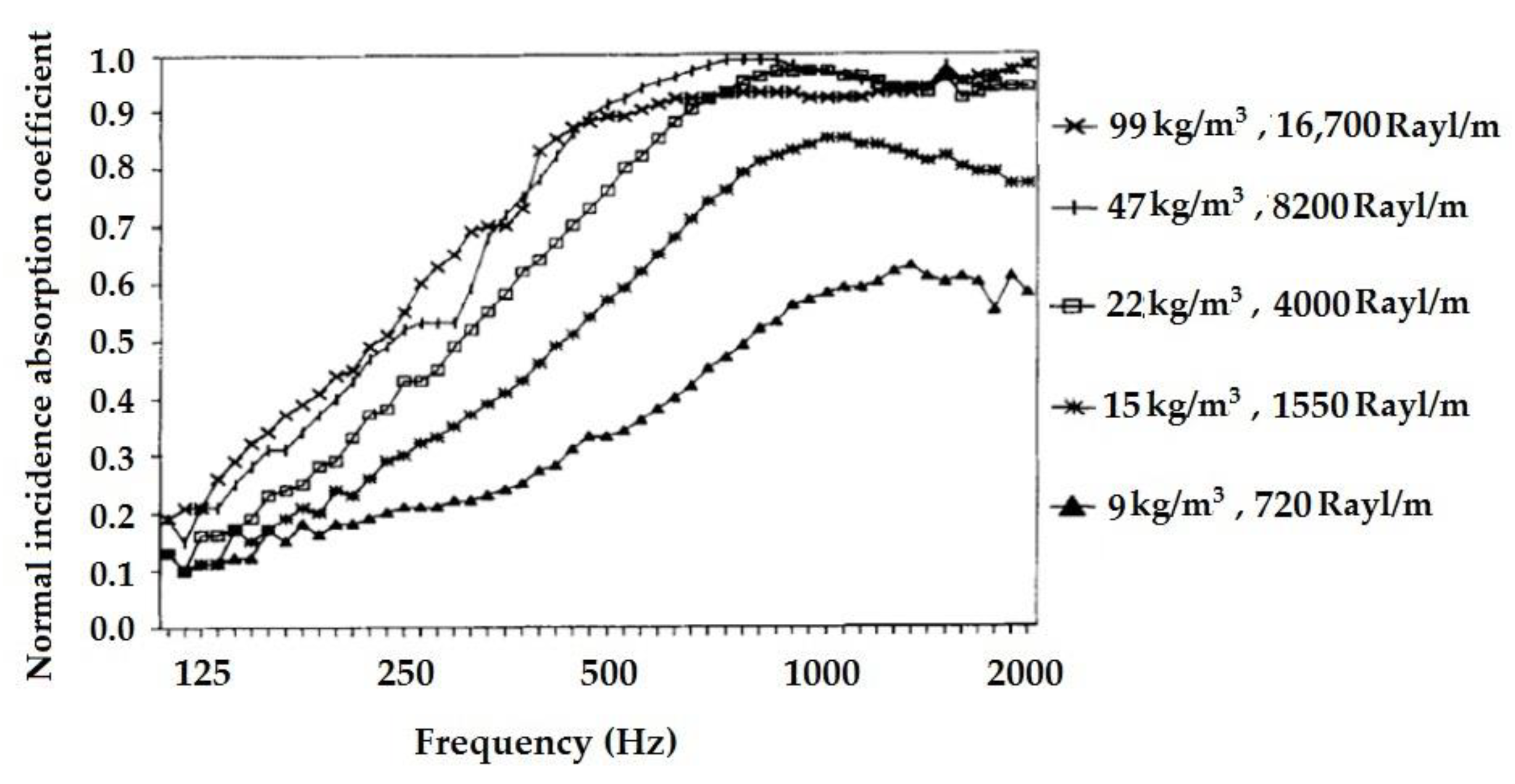
2.3.14. Effect of Density
2.3.15. Effect of Compression
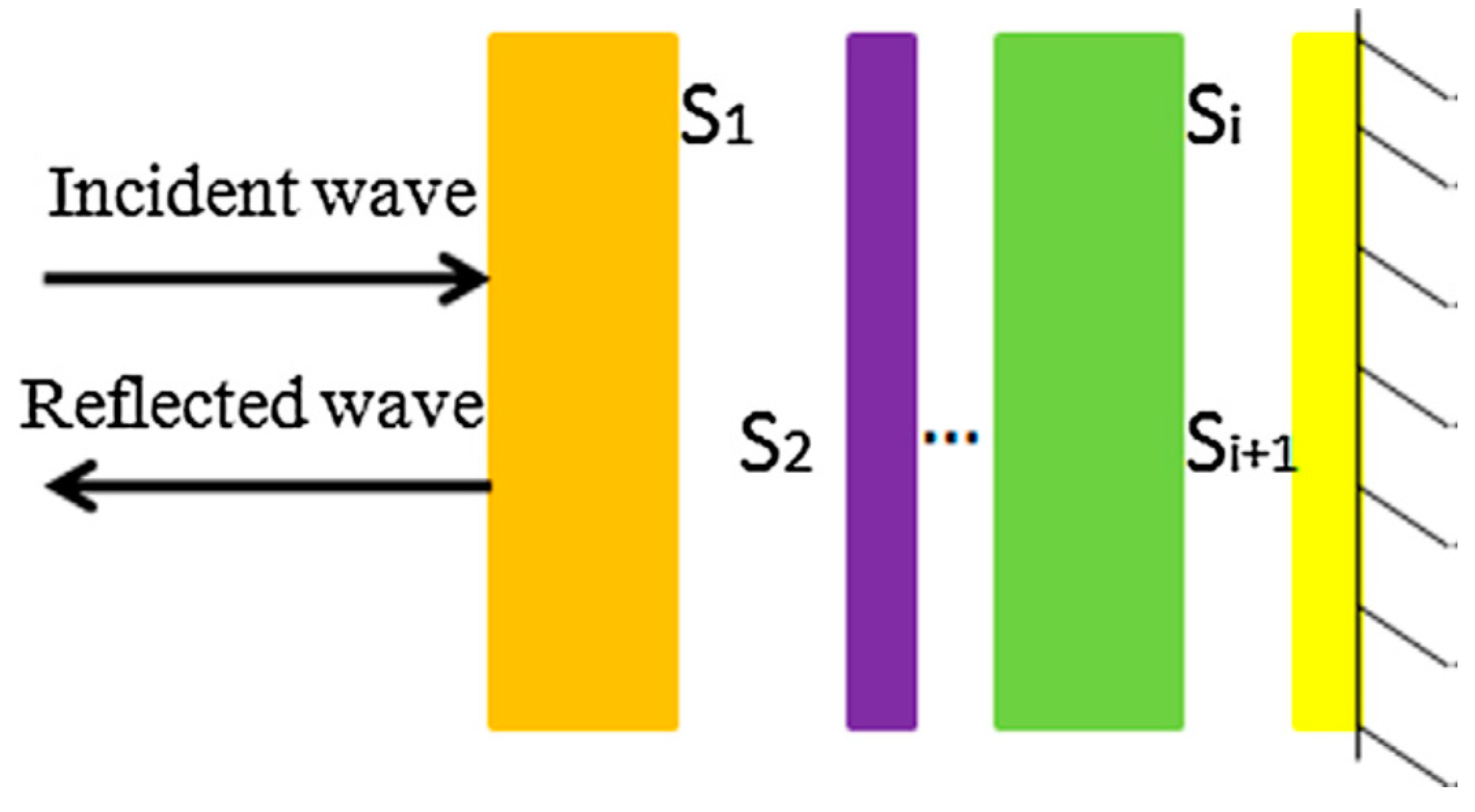
2.3.16. Effect of Location of Sound Absorbers
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erden, S.; Kingsley, H. Fiber reinforced composites. In Fiber Technology for Fiber-Reinforced Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 51–79. [Google Scholar]
- Vallittu, P.; Akikazu, S. Structural Properties of Dental FRC Structures. A Clinical Guide to Fiber Reinforced Composites (FRCs) in Dentistry; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, K.L.; Efendy, M.G.A.; Le, T.M. A review of recent developments in natural fiber composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y. Evaluation of statistical strength of bamboo fiber and mechanical properties of fiber reinforced green composites. J. Central South Univ. Technol. 2008, 15, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. C. United States Department of Health and Human Services. Report on Carcinogens, 12th ed.; National Toxicology Program: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kogel, J.E.; Trivedi, N.C.; Barker, J.M.; Krukowski, S.T. Industrial Minerals & Rocks: Commodities, Markets, and Uses, 7th ed.; SME: Englewood, CO, USA, 2006; Available online: www.smenet.org (accessed on 29 May 2021).
- Hubaux, R.; Becker-Santos, D.D.; Enfield, K.S.S.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L.; Martinez, V.D. Arsenic, asbestos and radon: Emerging players in lung tumorigenesis. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouette, H.K.; Schwager, B. Encyclopedia of Textile Finishing, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.C.; Cheng, Y.S. Deposition of man-made fibers in human respiratory airway casts. J. Aeros. Sci. 2009, 40, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragomeni, S.; Venkatesan, S. Incorporating Sustainable Practice in Mechanics and Structures of Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mamtaz, H.; Fouladi, M.; Al-Atabi, H.M.; Namasivayam, S.N. Acoustic absorption of natural fiber composites. J. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5836107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadam, V.V.; Nayak, R. Basics of Acoustic Science; Springer Science & Business Media: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. ASTM C423—17. Standard Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Absorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method; 1850 M Street, NW, Suite 1030; ASTM: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Song, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. Study on sound insulation performance of double-layer perforated panelunder normal incidence waves. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 174, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiyao, L.; Wana, B.; Chuanren, D.; Sakanishi, A. The non-linear model of sound wave diffusion in Chrysanthemum callus. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2002, 24, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowoswiat, A.; Bochen, J.; Dulak, L.; Zuchowski, R. Investigation studies involving sound absorbing parameters of roadsidescreen panels subjected to aging in simulated conditions. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Abdelhady, A.; Yang, J. Effect of different factors on sound absorption property of porous concrete. Transp. Res. Part D Trans. Environ. 2020, 87, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, R.D.; Alba, J.; Arenas, J.P.; Sanchis, V.J. An empirical modelling of porous sound absorbing materials made of recycled foam. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.J.; Antonio, P.D. Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Application, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bratu, M.; Vasile, O.; Dumitrescu, O. Sound-absorbing properties of composite materials reinforced with various wastes. Environ. Eng. Manag. 2011, 10, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y. Sound absorption performance of natural fibers and their composites. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 2278–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamani, E.; Hamdan, S.; Rahman, M.R.; Bakri, M.K.B.; Kakar, A. An investigation of sound absorption coefficient on sisal fiber poly lactic acid bio-composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, Y. Sound absorption characterization of natural materials and sandwich structure composites. Aerospace 2018, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Z. Effect of physiochemical structure on energy absorption properties of plant fibers reinforced composites: Dielectric, thermal insulation, and sound absorption properties. Comp. Comm. 2018, 10, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, H.J. Rice straw–wood particle composite for sound absorbing wooden construction materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; Nadal-Gisbert, A.; Crespo-Amoros, J.; Parres-García, F. A novel sound absorber with recycled fibers coming from end of life tires (ELTs). Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; Morillas, J.; Martin-Castizo, M.; Escobar, V.G.; Gozalo, G.R. Acoustical performance of porous absorber made from recycled rubber and polyurethane resin. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 10, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, L.; Krishnaraj, V.; Gokulkumar, S.; Sathish, S.; Ramesh, M. Mechanical, chemical and acoustical behavior of sisal—Tea waste—Glass fiber reinforced epoxy reinforced hybrid polymer composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 16, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiuc, A.E.; Vermesan, H.; Gabor, T.; Vasile, O. Improved sound absorption properties of polyurethane foam mixed with textile waste. Energy Proc. 2016, 85, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Li, J.; Ren, J. Study on sound absorption property of ramie fiber reinforced poly (L-lactic acid) composites: Morphology and properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Joo, C. Sound absorption properties of recycled polyester fibrous assembly absorbers. Autex Res. J. 2003, 3, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, T.; Tsujiuchi, N.; Adachi, A. The development of sound absorbing materials using natural bamboo fibers. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2002, 59, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.H.; Sun, X.N.; Song, H. Study on the sound absorption properties of several kinds of fibers. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 332, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakri, M.K.B.; Jayamani, E.; Heng, S.K.; Hamdan, S.; Kakar, A. An experimental and simulation studies on sound absorption coefficients of banana fibers and their reinforced composites. Nano Hyb. Compos. 2017, 12, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamtaz, H.; Hosseini, M.; Zaki, M.; Narayana, S.; Ghassem, M.; Al-atabi, M. Acoustic absorption of fibro-granular composite with cylindrical grains. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 126, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.T.; Panneton, R. Effective fiber diameter for modeling the acoustic properties of polydisperse fiber networks. J. Acoustl. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, EL96–EL101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, H.; Wang, D.; Liua, H.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Investigation on sound absorption properties of kapok fibers. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 31, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, V.; Kumar, B.; Santulli, C. Effect of fiber orientation in unidirectional glass epoxy laminate using acoustic emission monitoring. Acta Metall. Sin. 2011, 24, 351–364. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; White, C.B.; Yan, X. Seven-hole hollow polyester fibers as reinforcement in sound absorption chlorinated polyethylene composites. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.H.; Azharia, A.; Salleh, F.M. Sound absorption cofficient of natural fibers hybrid reinforced polyester composites. J. Teknol. 2015, 76, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jayamani, E.; Hamdan, S.; Heng, S.K.; Rahman, R. Sound absorption property of agricultural lignocellulsic residue fiber reinforced polymer matrix composites. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 663, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Dhabal, R.L.; Suman, B.M.; Saini, A.; Panchal, P. An estimation of correlation on thermo-acoustic properties of mineral wool. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2006, 65, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Reixach, R.; Rey, R.D.; Alba, J.; Arbat, G.; Espinach, F.; Mutjé, P. Acoustic properties of agroforestry waste orange pruning fibers reinforced polypropylene composites as an alternative to laminated gypsum boards. Const. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayamani, E.; Heng, S.K.; Bakri, M.K.; Hamdan, S. Comparative study of sound absorption coefficients of coir/kenaf/sugarcane bagasse fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 730, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M. Absorption of sound in air versus humidity and temperature. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1966, 40, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, V.O. The absorption of sound in air, in oxygen, and in nitrogen—Effects of humidity and temperature. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1933, 5, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapen, E.; Lanoye, R.; Vermeir, G.; Lauriks, W.; Gemert, D.V. Acoustic properties of sound absorbing, polymer-modified porous cement mortars. In Proceedings of the 6th Internatioanl conference on Material Science and Restoration, MSR VI, Karlsruhe, Germany, 16–18 September 2003; Aedificatio Publishers: Freiburg, Germany, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Sakagami, K.; Kiyama, M.; Morimoto, M.; Takahashi, D. Sound absorption of a cavity-backed membrane: A step towards design method for membrane-type absorbers. Appl. Acoust. 1996, 49, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, T.; Leclaire, P.; Sicot, O.; Gong, X.L.; Panneton, R. Acoustic properties of air-saturated porous materials containing dead-end porosity. J. Appl. Phy. 2011, 110, 094903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bies, D.H.; Hansen, C.H. Engineering Noise Control, 1st ed.; Spon Press, Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Crocker, M.J. Handbook of Noise and Vibration Control, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X. Acoustic testing and evaluation of textiles for buildings and office environments. In Performance Testing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 103–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ballagh, K.O. Acoustical properties of wool. Appl. Acoust. 1996, 48, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, M.; Kierzkowski, M. Thermoformable Acoustic Sheet. Acoust. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 122, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Mohanty, A.R. Acoustical and fire-retardant properties of jute composite materials. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, T.; McCaa, D.; Rebandt, R.; Rusch, P.; Saha, P. Application of noise control and heat insulation materials and devices in the automotive industry. SAE Tech. Paper 1995. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Melik, R.W. Physical parameters affecting acoustic absorption characteristics of fibrous materials. Proc. Math. Phys. Soc. Egypt 1978, 46, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hakamada, M.; Kuromura, T.; Chen, Y.; Kusuda, H.; Mabuchi, M. High sound absorption of porous aluminum fabricated by spacer method. Appl. Phy. Lett. 2006, 88, 106–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Tu, S.T. Flexural behavior and damage evolution of pultruded fibre-reinforced composite by acoustic emission test and a new progressive damage model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 188, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, E.; Khavanin, A.; Ohadi, A.; Putra, A.; Jafari, A.J.; Faridan, M.; Soleimanian, A. Study on the acoustic characteristics of natural date palm fibers: Experimental and theoretical approaches. Build. Environ. 2019, 161, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiney, A.; Premlet, B. Acoustic properties of composite coir mats. IOSR J. Appl. Phy. 2014, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Zheng, L.; Deng, Z. Study on acoustic properties at normal incidence of three-multilayer composite made of glass wool, glue and polyurethane foam. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 156, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, L.; Jeyanthi, S.; Yogananda, A. An acoustical investigation of partial perforation in jute fiber composite panel. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Krishnaraj, V.; Senthilkumar, M.; Zitoune, R. Sound and vibration damping properties of flax fiber reinforced composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayamani, E.; Hamdan, S.; Rahman, R.; Bin Bakri, M.K. Investigation of fiber surface treatment on mechanical, acoustical and thermal properties of betelnut fiber polyester composites. Proceedia Eng. 2014, 97, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, G.; Hu, Y.; Jia, H.; Liu, P.; Du, P.; Xu, D. Acoustic and dielectric properties of epoxy resin/hollow glass microspherecomposite acoustic materials. J. Phy. Chem. Solid 2019, 135, 109105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Wu, D. Acoustic emission study of effect of fiber weaving on properties of fiber-resin composite materials. Compos. Struct. 2020, 237, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ren, F.; Liu, B.; Zhou, S. Acoustic fatigue properties investigation of plain weave C/SiC composite plate. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamani, E.; Hamdan, S.; Bakri, M.K.; Heng, S.K.; Rahman, M.R.; Kakar, A. Analysis of natural fiber polymer composites: Effects of alkaline treatment on sound absorption. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, V.; Brown, L.; Chronopoulos, D. Multi-scale wave propagation modelling for two-dimensional periodic textile composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 150, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamas-Gavrea, D.R.; Denes, T.O. Mechanical, thermal and acoustical properties of an innovative lime-wool composite. Proceedia Manuf. 2019, 46, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiénzar-Navarro, R.; Bonet-Aracil, M.; Gisbert-Payá, J.; Rey, R.D.; Picó, R. Sound absorption of textile fabrics doped with microcapsules. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 164, 107285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcay, H.; Kocak, E.D. Rice plant waste reinforced polyurethane composites for use as the acoustic absorption material. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Qin, R.; Han, K.; Wei, Z.; Ma, L.H. Progressive damage visualization and tensile failure analysis of three-dimensional braided composites by acoustic emission and micro-CT. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelis, D.G.; El Kadi, M.; Tysmans, T.; Blom, J. Effect of propagation distance on acoustic emission fracture mode classification in textile reinforced cement. Const. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruk, H.; Gen, G. Investigationoftheacousticpropertiesofbioluffa fiber andcomposite materials. Mater. Lett. 2015, 157, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witczak, E.; Jasinska, I.; Lao, M.; Krawczynska, I.; Kaminska, I. The influence of structural parameters of acoustic panels textile fronts on their sound absorption properties. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 178, 107964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangouri, E.; Michels, L.; El Kadi, M.; Tysmans, T.; Aggelis, D.G. A fundamental investigation of textile reinforced cementitious composites tensile response by acoustic eEmission. Cement Conc. Res. 2019, 123, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Bhat, G. Environmentally-friendly thermal and acoustic insulation materials from recycled textiles. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, Z.; Behera, B.K. Sustainable hybrid composites reinforced with textile waste for construction and building applications. Const. Build. Mater. 2021, 284, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, C.A.; Handoko, W.; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. Cascading use of textile waste for the advancement of fibre reinforced composites for building applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Fan, X.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Investigation of effective factors of woven structure fabrics for acoustic absorption. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 161, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggui, M.; Mahi, A.E.; Jendli, Z.; Akrout, A.; Haddar, M. Static and fatigue characterization of flax fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites by acoustic emission. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 147, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariprasad, K.; Ravichandran, K.; Jayaseelan, V.; Muthuramalingam, T. Acoustic and mechanical characterisation of polypropylene composites reinforced by natural fibres for automotive applications. J. Mater. Res.Technol. 2020, 9, 14029–14035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czigany, T. Special manufacturing and characteristics of basalt fiber reinforced hybrid polypropylene composites: Mechanical properties and acoustic emission study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 3210–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherradi, Y.; Rosca, I.C.; Cerbu, C.; Kebir, H.; Guendouz, A.; Benyoucef, M. Acoustic properties for composite materials reinforced on alfa and wood fibers. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 174, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnede, B.; Aknine, A.; Brouard, B.; Tarnow, V. Effects of compression on the sound absorption of fibrous materials. Appl. Acoust. 2000, 61, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.N.; Kuo, Y.M.; Chen, S.K. Effects of compression on the sound absorption of porous materials with an elastic frame. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, M.; Ayub, M.; Zulkifli, R.; Amin, N.; Fouladi, M.H. Effect of compression on the acoustic absorption of coir fiber. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keshavarz, R.; Ohadi, A. Effects of compression on sound absorption of transversely isotropic fibrous materials at oblique incidence. Appl. Acoustics 2013, 74, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everest, F.A. Master Handbook of Acoustics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aso, S.; Kinoshita, R. Maximum sound absorption coefficient of a fiber assembly. J. Text. Mach. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 11, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.J.; Chen, F.; He, D. Sound absorption of cellular metals with semiopen cells. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

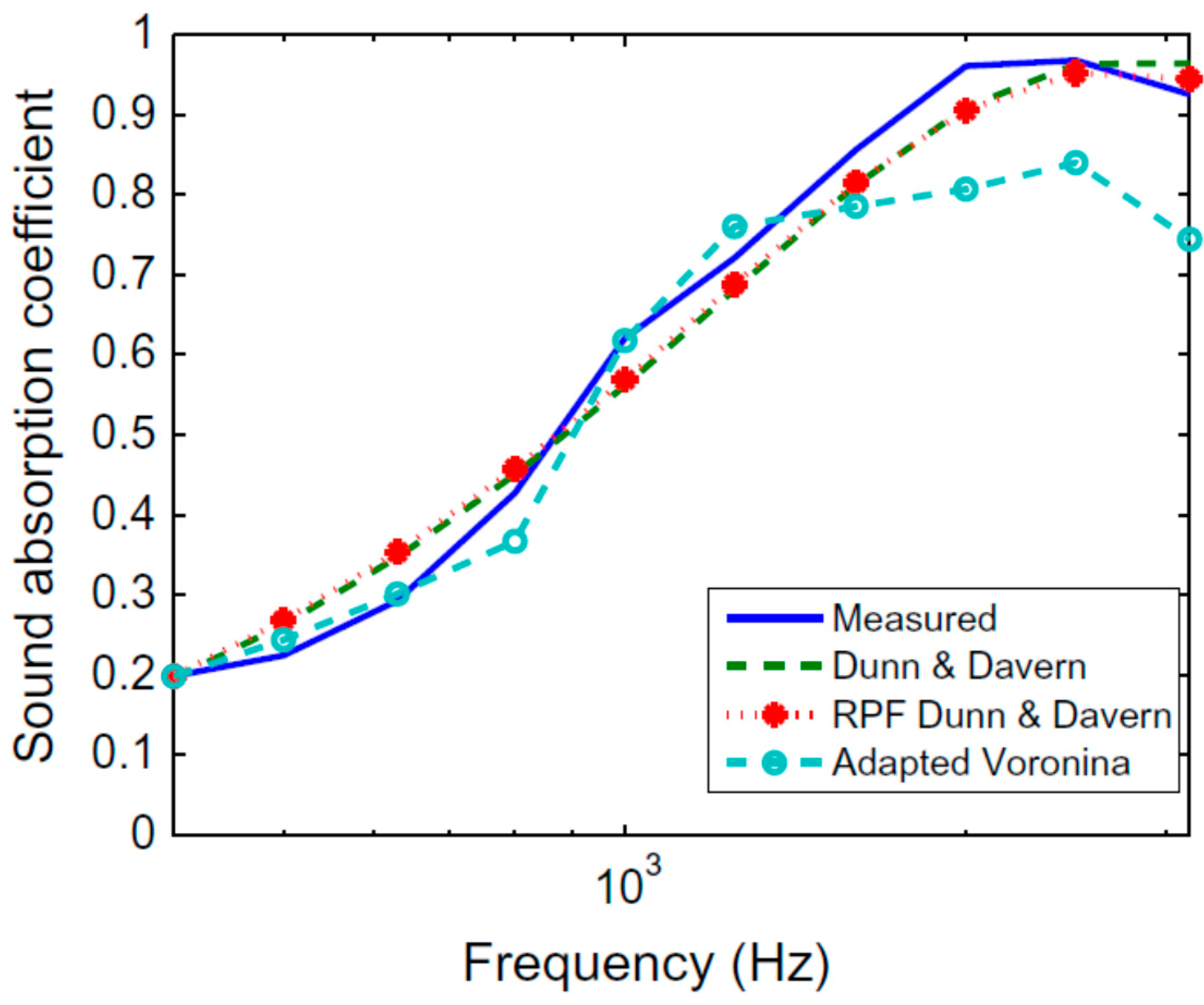
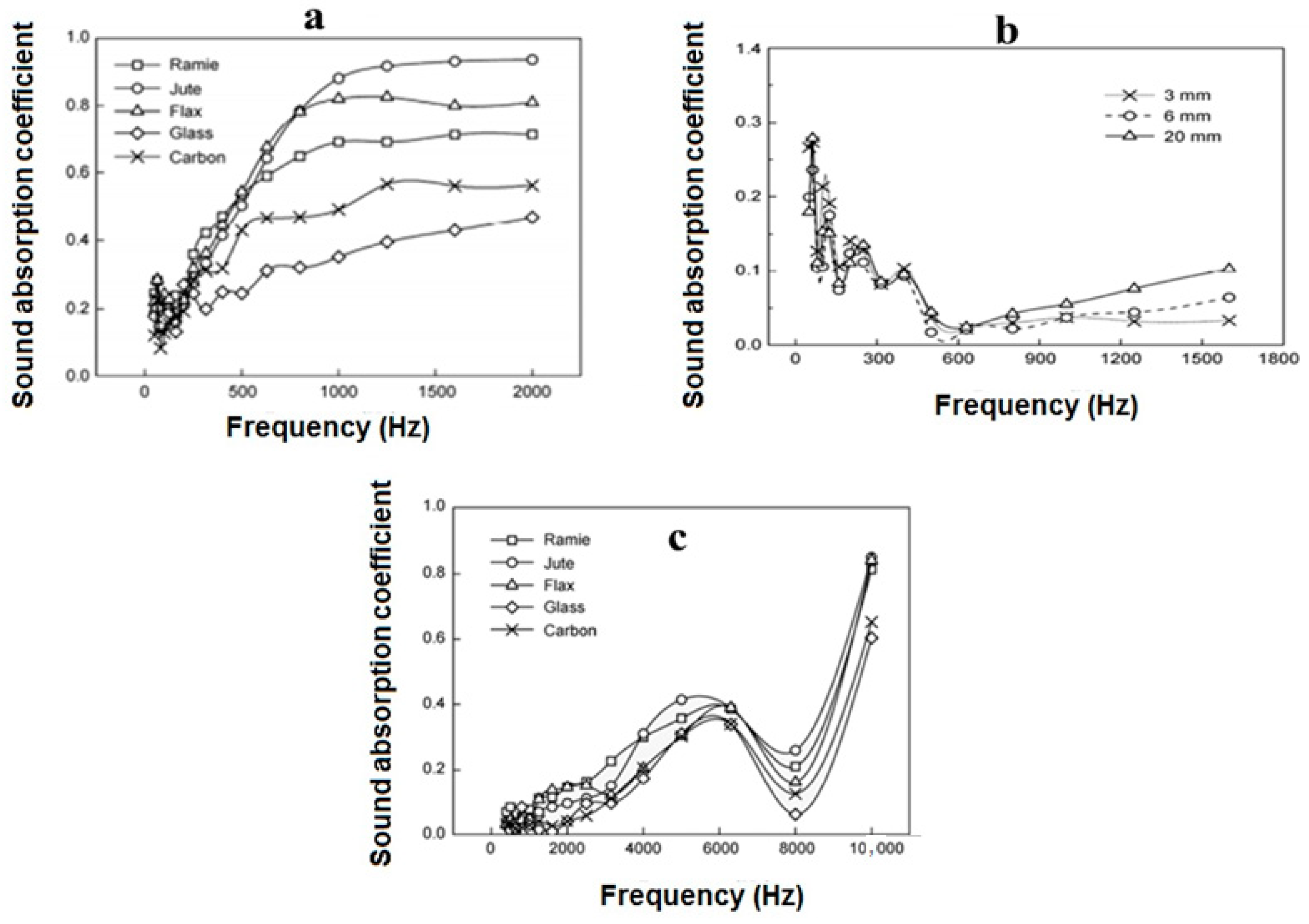
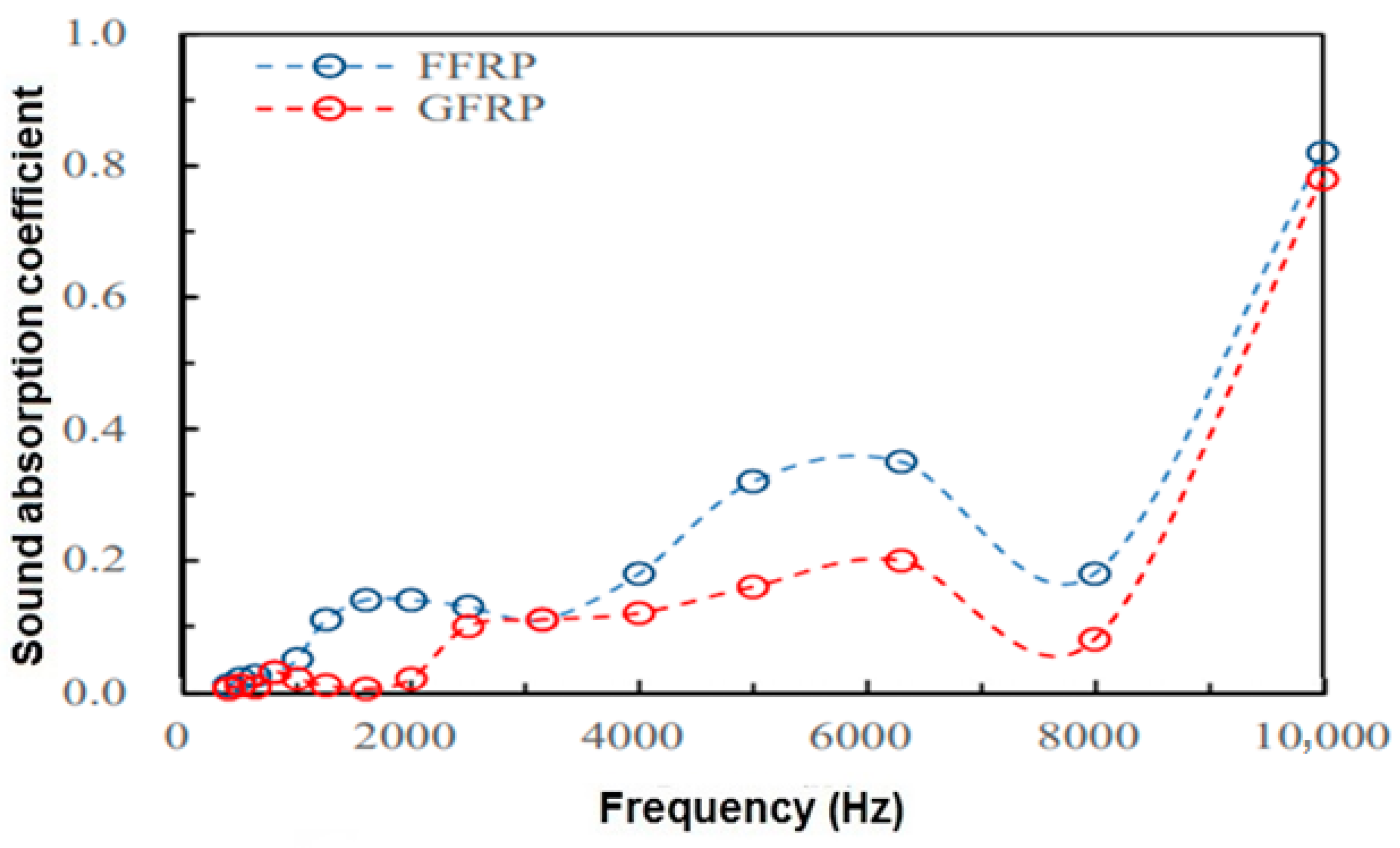
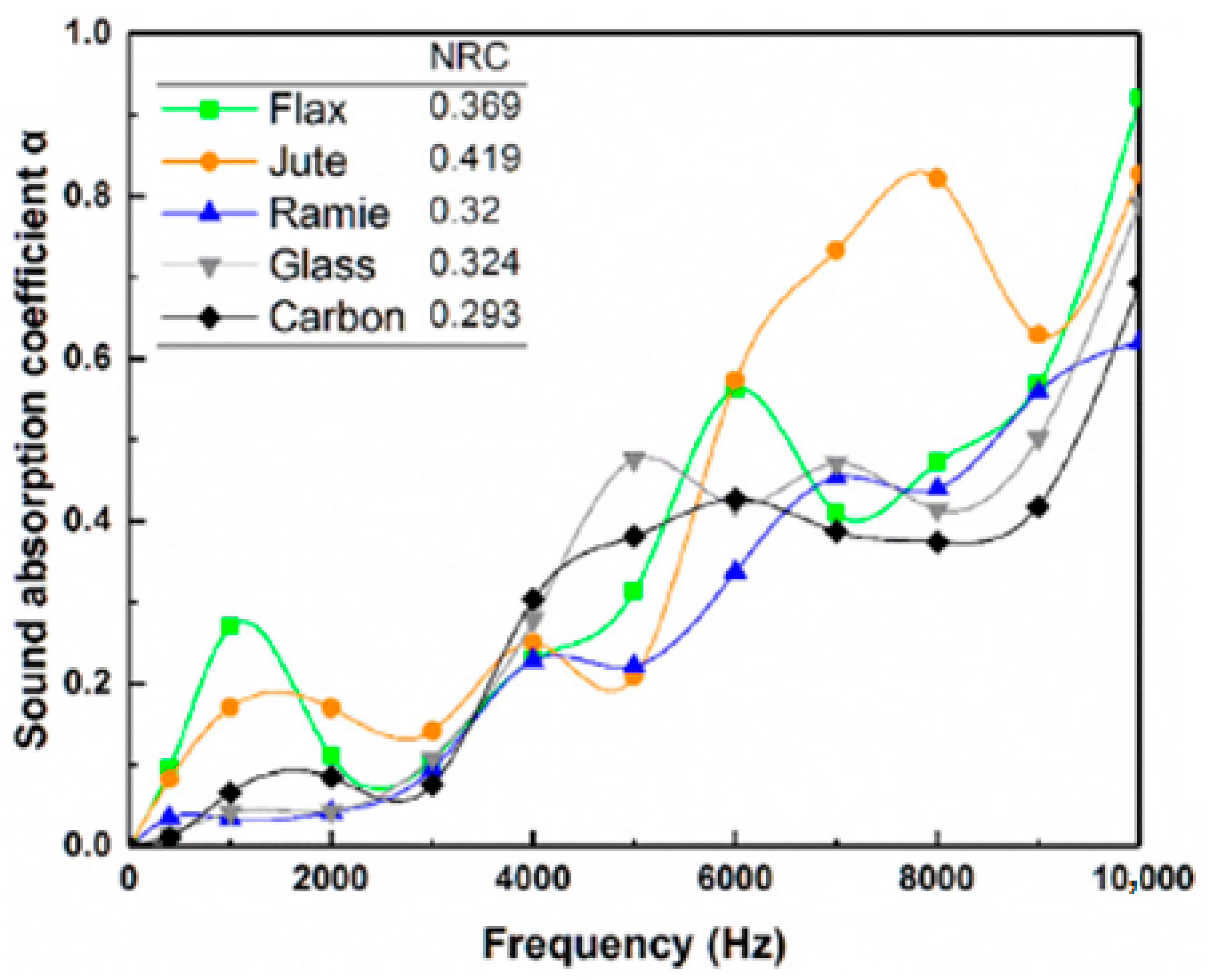

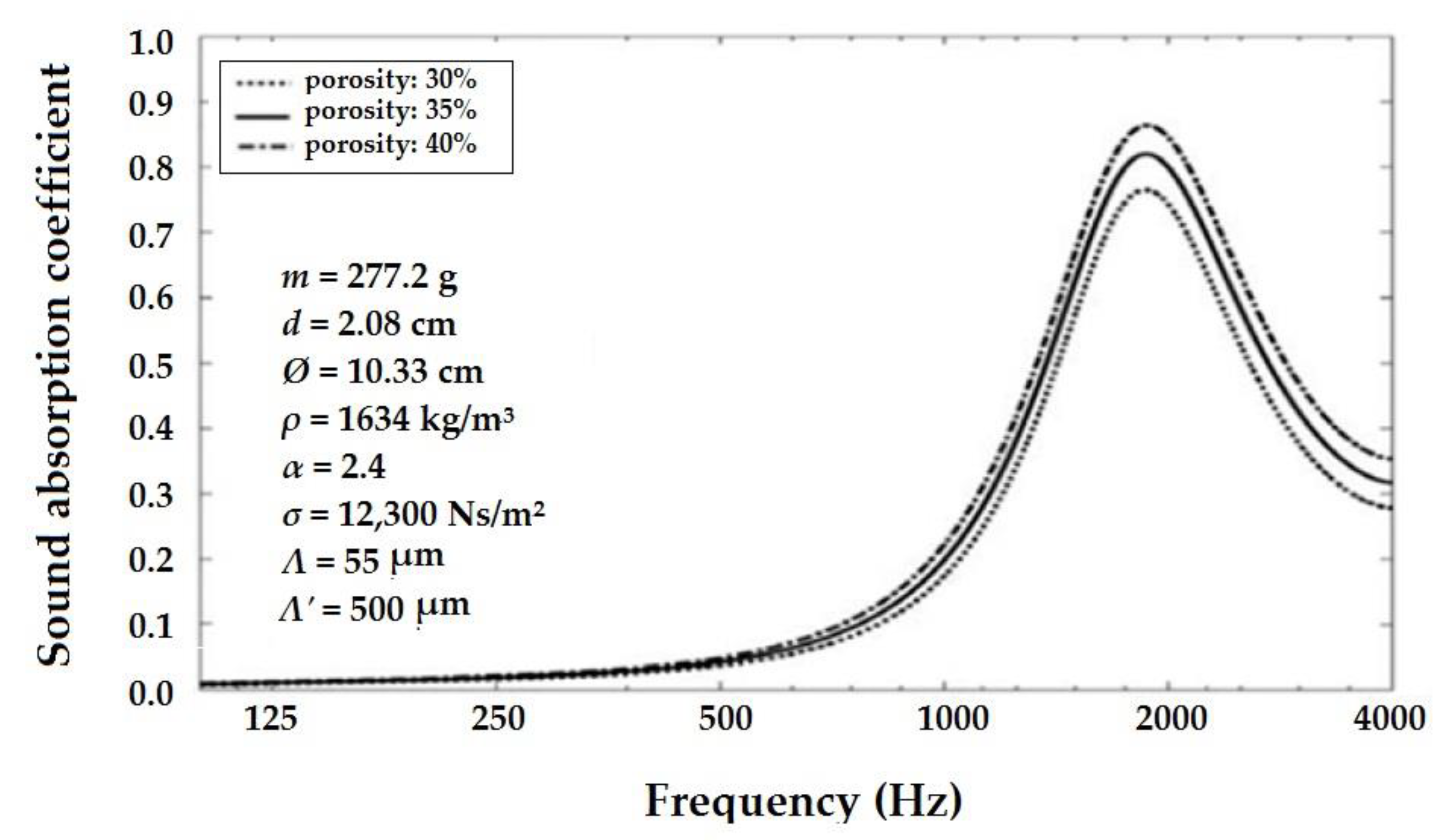
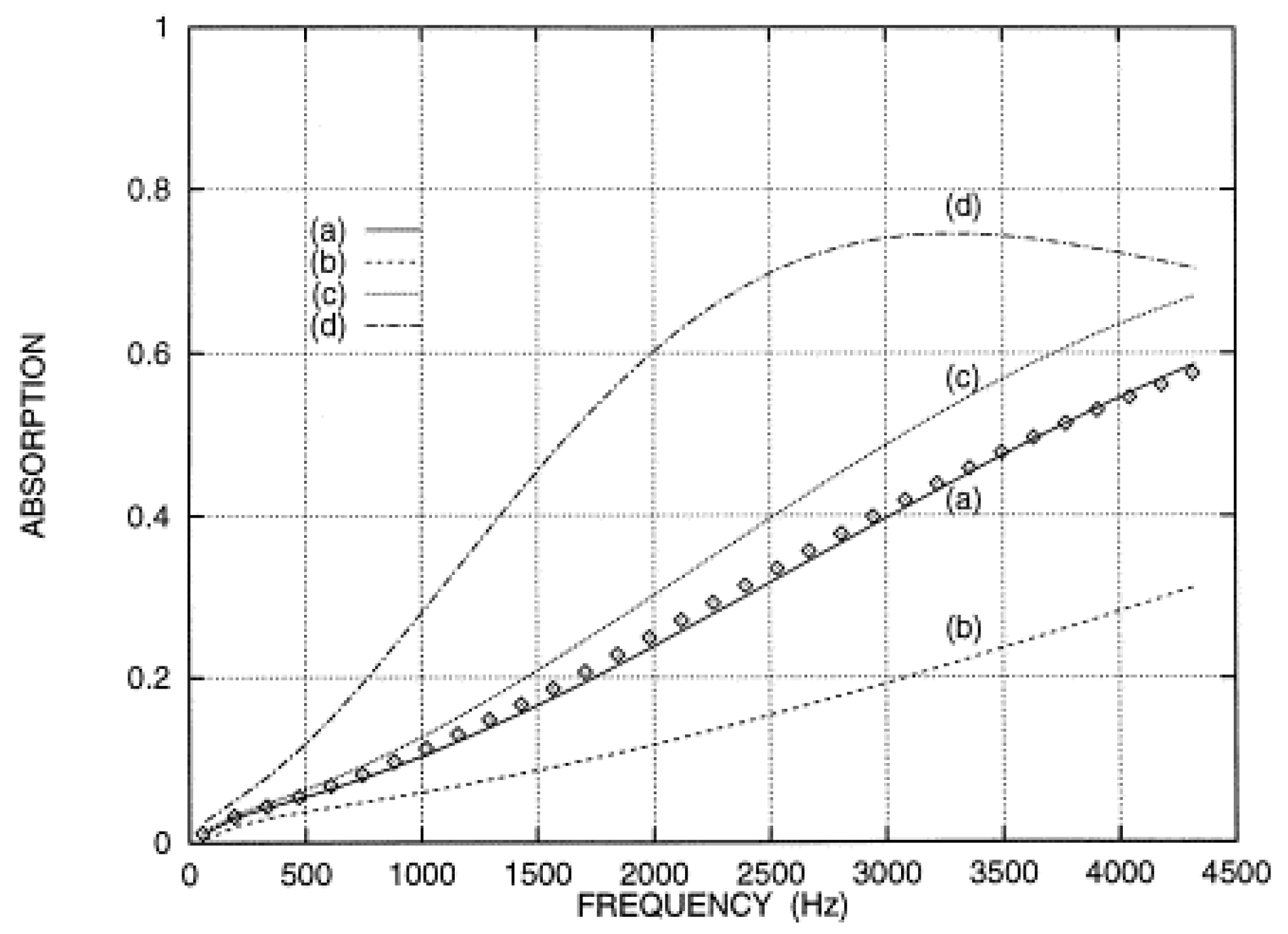
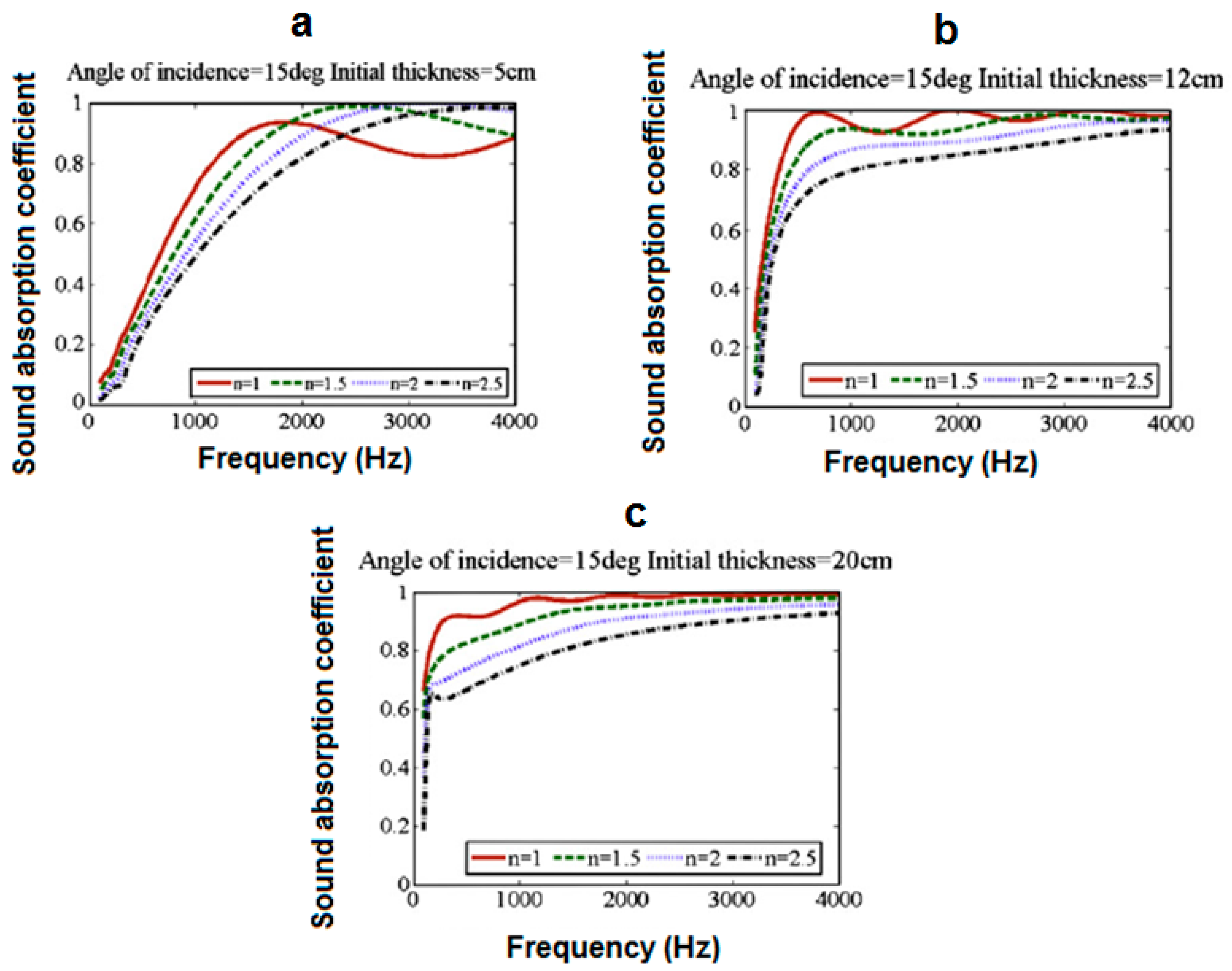
| Range | SAC Class |
|---|---|
| 0.90, 0.95, 1.00 | A |
| 0.80, 0.85 | B |
| 0.60, 0.65, 0.70, 0.75 | C |
| 0.30, 0.35, 0.40, 0.50, 0.55 | D |
| 0.15, 0.20, 0.25 | E |
| 0.00, 0.05, 0.10 | F |
| No. | Reinforcement | Matrix | Sample Parameters | Fabrication Method | Results/SAC | Ref# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Banana Fiber | Epoxy | Fiber loading 20 % wt.%, Thickness 20 mm | Hot Compression (1000 psi 24 °C) | 0.11 (6000 Hz) | [48] |
| 2 | Ramie Fiber | Poly L Lactic Acid (PLLA) | Thickness 3 mm, Fiber Loading 30% wt.% | Hot Pressing (Pressure 20 MPa, Temperature 170 °C, Time 4 min | 0.12 (1600 Hz) | [49] |
| 3 | Oil Seed Waste | Formaldehyde Resin | - | - | 0.8 (3200 Hz) | [50] |
| Fiber Glass waste | 0.9 (3200 Hz) | |||||
| Wood Waste | 0.9 (3200 Hz) | |||||
| Steel Slag | 0.65 (3200 Hz) | |||||
| 4 | Rice Straw | Urea Formaldehyde | Thickness 10 mm , fiber loading of 0–30 wt.%, | Hot compression (500 psi 140 °C) | 0.05–0.5 (8000 Hz) | [51] |
| 5 | Ramie Fiber | Epoxy | Thickness 3 mm | Hot Press Compression Machine | 0.6 (2000 Hz) | [52] |
| Flax | 0.65 (2000 Hz) | |||||
| Jute | 0.65 (2000 Hz) | |||||
| 6 | Sugarcane Bagasse | Polyester Resin | Fiber Loading 30% | - | 0.63 (4000 Hz) | [53] |
| Banana Fiber | 0.68 (4000 Hz) | |||||
| 7 | Hybrid Composite | 0.73 (4000 Hz) | ||||
| 8 | Hemp | Recycled latex | Thickness 300 mm | - | 0.50 (2000 Hz) | [54] |
| Thickness 40 mm | 0.50 (3000 Hz) | |||||
| 9 | Rice straw | Polypropylene | Fiber Loading 10% wt.% | Hot Pressing Machine, Pressure 1000 psi, Temperature 190 °C, Time 30 min | 0.08 (2000 Hz) | [55] |
| Kenaf | Urea-formaldehyde | 0.065 (2000 Hz) | ||||
| 10 | Sisal Fibers | Poly Lactic Acid | Fiber Loading 30%, Thickness 8 mm | Hot Press Machine | 0.085 (2000 Hz) | [56] |
| 11 | Coconut/Coir | Epoxy | Fiber Loading 20%, Thickness 10 mm | Compression Molding Machine, Pressure 7 MPa, Time 24 h, Temperature 24 °C. | 0.086 (6000 Hz) | [57] |
| Kenaf | 0.085 (6000 Hz) | |||||
| Sugarcane | 0.083 (6000 Hz) | |||||
| Ramie | Poly-(I-Lactic acid) | 0.089 (1600 Hz) | ||||
| Wheat straw | Polypropylene | 0.03 (1800 Hz) | ||||
| Jute | Zein | 0.06 (5000 Hz) | ||||
| 12 | Seven-hole hollow polyester fibers (SHPF) | Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) | Thickness 1 mm, Fiber Loading 20%) | - | 0.42 (2500 Hz) | [58] |
| 3 mm (Fiber Loading 20%) | 0.695 (2500 Hz) | |||||
| 13 | Wheat straw | Polypropylene | Thickness of 3.2 mm, fiber loading of 40–80 wt.% | Hot compression | 0.03–0.23 (3000 Hz) | [59] |
| 14 | Flax | Bisphenol-A base Epoxy | Fiber Loading 60%, | Hot-pressing method, Pressure 2.5 MPa, Temperature 120 °C | 0.369 (10 kHz) | [60] |
| Carbon | 0.293 (10 kHz) | |||||
| Glass | 0.324 (10 kHz) | |||||
| Ramie | 0.32 (10 kHz) | |||||
| Jute | 0.419 (10 kHz) | |||||
| 15 | Flax | Epoxy resin | Fiber loading 50%, Thickness 4 mm | Hot press machine under pressure of 1 MPa and temperature of 120 °C for 2 h for complete curing | 0.96 (3200 Hz) | [61,62] |
| Balsa Wood | 0.58 (3200 Hz) | |||||
| 16 | Lufa | Epoxy | Fiber Loading 25%, Thickness 5 mm | Hot and cold compression hydraulic press machine | 0.095 (500–6000 Hz) | [63] |
| Betel Nut | Unsaturated Polyester (MEKP) | 0.085 (500–6000 Hz) | ||||
| Sisal | Poly-lactic Acid | 0.10 (500–6000 Hz) | ||||
| Rice Straw | Polypropylene | 0.12 (500–6000 Hz) | ||||
| Oil palm | Zein | 0.095 (500–6000 Hz) | ||||
| 17 | Banana Fiber | Epoxy Resins | Fiber Loading 20% | Hydraulic hot/cold press machine, Pressure 10 MPa | 0.1 (500–6000 Hz) | [64] |
| 18 | Flax | Epoxy | Thickness of 3 mm | Compression (laminated) | 0.11 (2000 Hz) | [65] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, T.; Jamshaid, H.; Mishra, R.; Khan, M.Q.; Petru, M.; Tichy, M.; Muller, M. Factors Affecting Acoustic Properties of Natural-Fiber-Based Materials and Composites: A Review. Textiles 2021, 1, 55-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1010005
Hassan T, Jamshaid H, Mishra R, Khan MQ, Petru M, Tichy M, Muller M. Factors Affecting Acoustic Properties of Natural-Fiber-Based Materials and Composites: A Review. Textiles. 2021; 1(1):55-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Tufail, Hafsa Jamshaid, Rajesh Mishra, Muhammad Qamar Khan, Michal Petru, Martin Tichy, and Miroslav Muller. 2021. "Factors Affecting Acoustic Properties of Natural-Fiber-Based Materials and Composites: A Review" Textiles 1, no. 1: 55-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1010005
APA StyleHassan, T., Jamshaid, H., Mishra, R., Khan, M. Q., Petru, M., Tichy, M., & Muller, M. (2021). Factors Affecting Acoustic Properties of Natural-Fiber-Based Materials and Composites: A Review. Textiles, 1(1), 55-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1010005










