Tuning Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Properties of PLA Films Through Surface Fluorination and Drying
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PLA Films
2.2. Surface Fluorination of PLA
2.3. Drying of Fluorinated PET
2.4. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
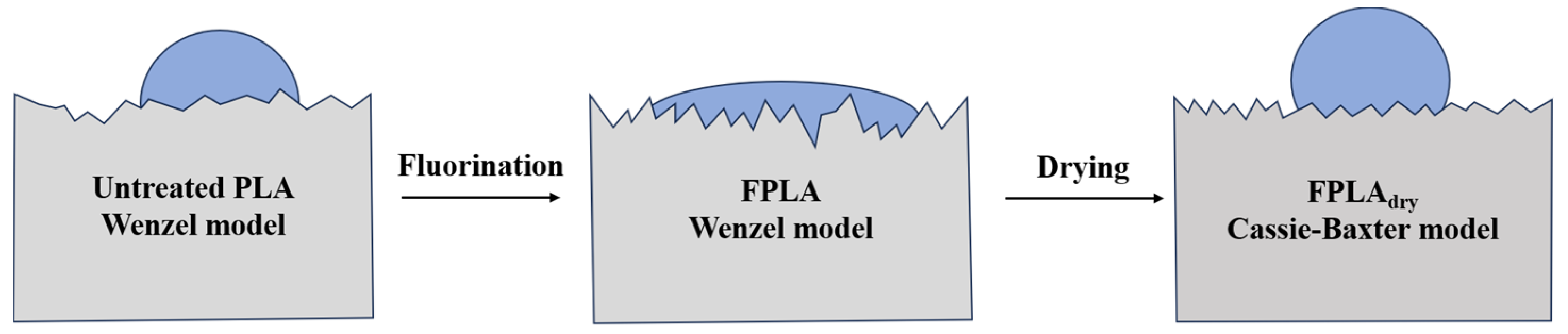
3.1. Effects of Fluorination and Drying on the Surface Composition and Structure
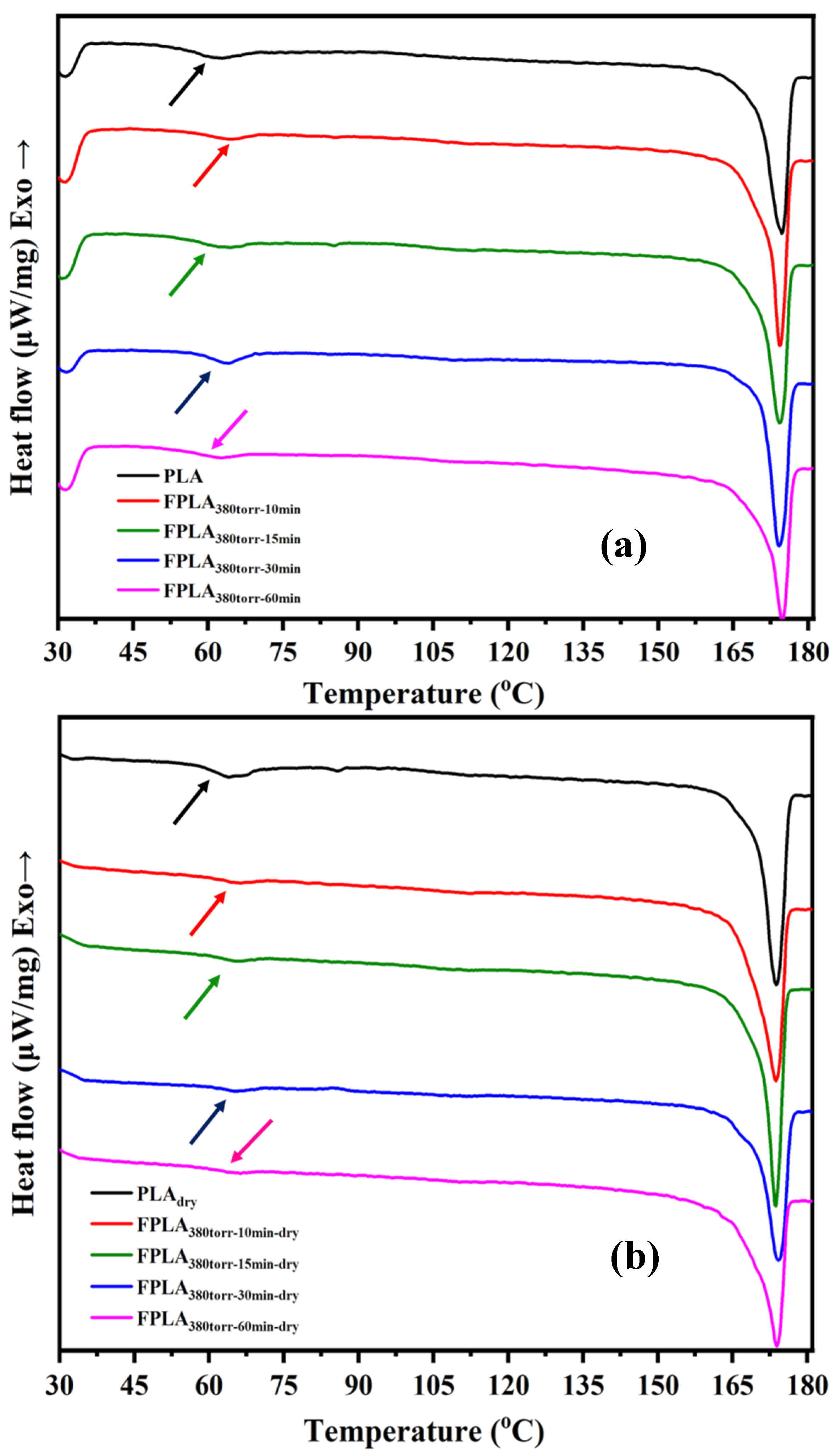
3.2. Effects of Fluorination and Drying on Thermodynamic Properties
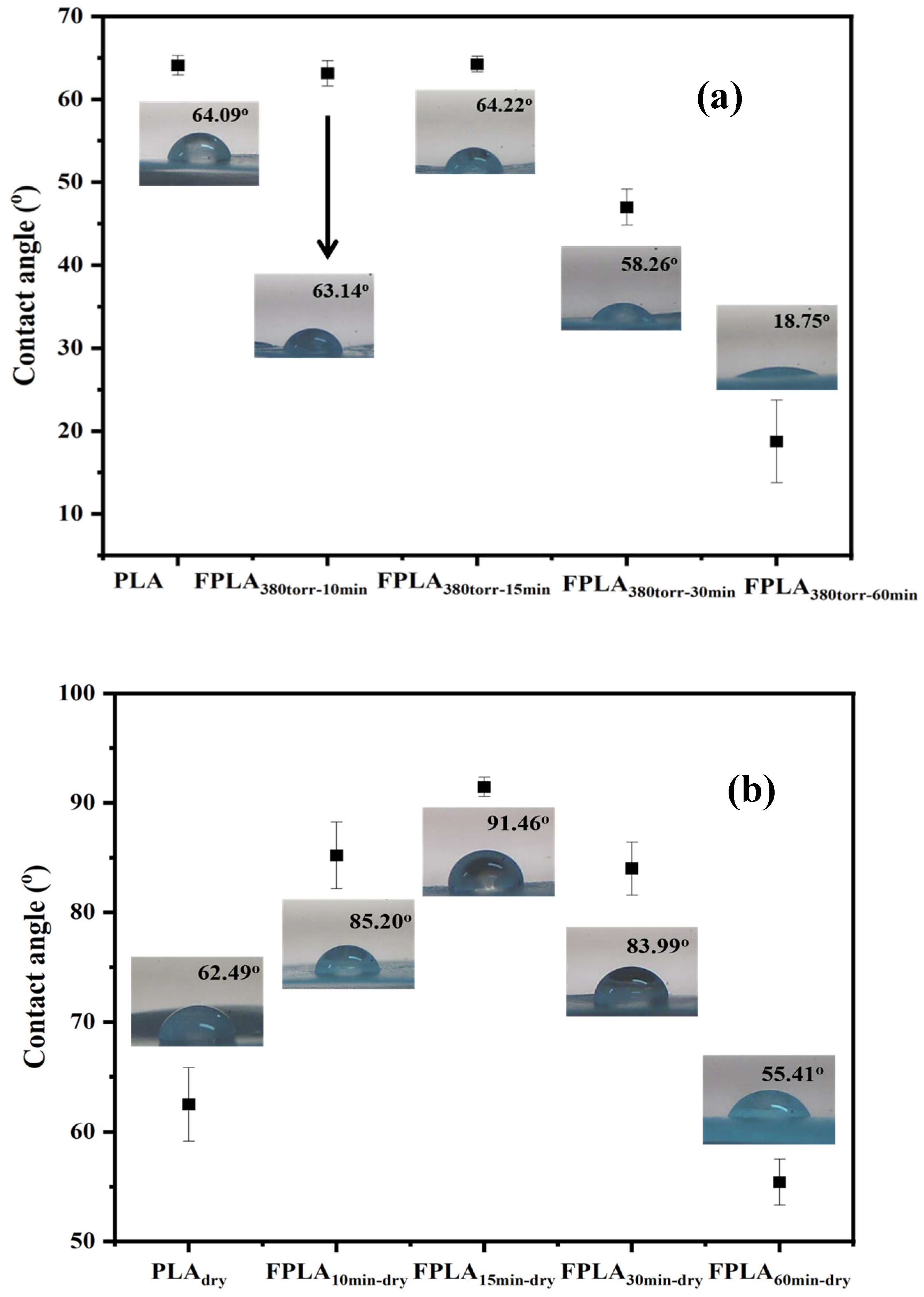
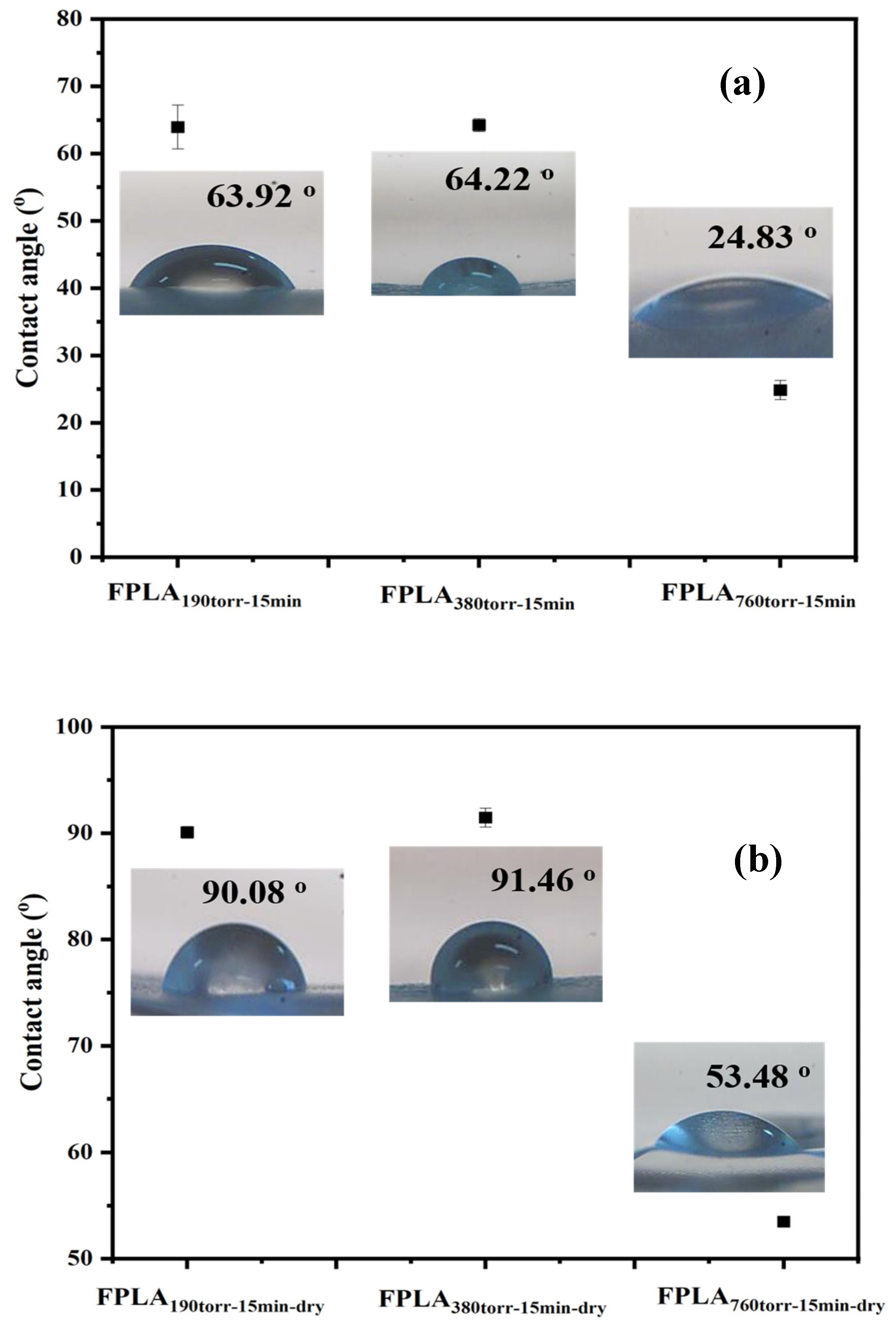
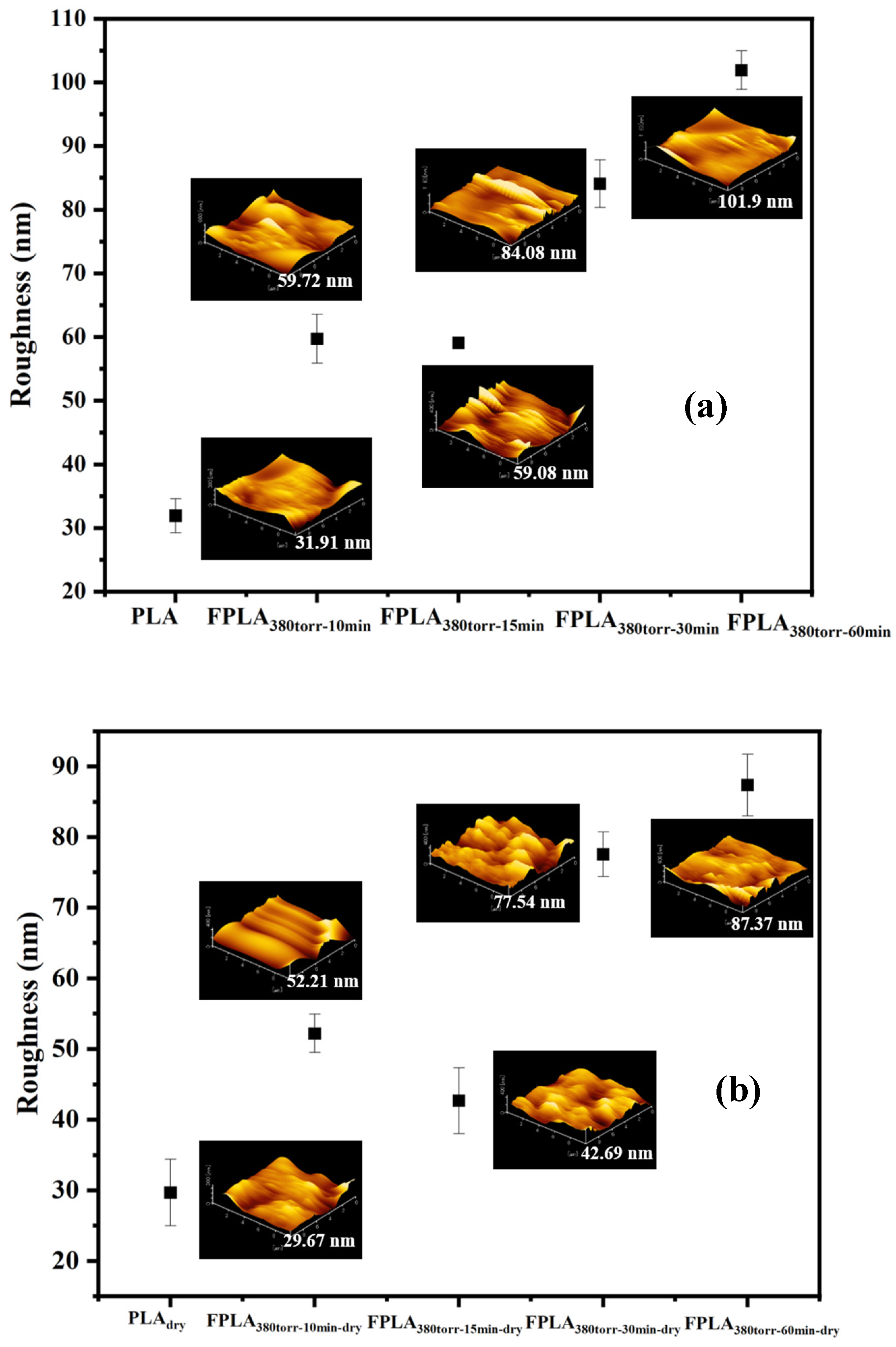
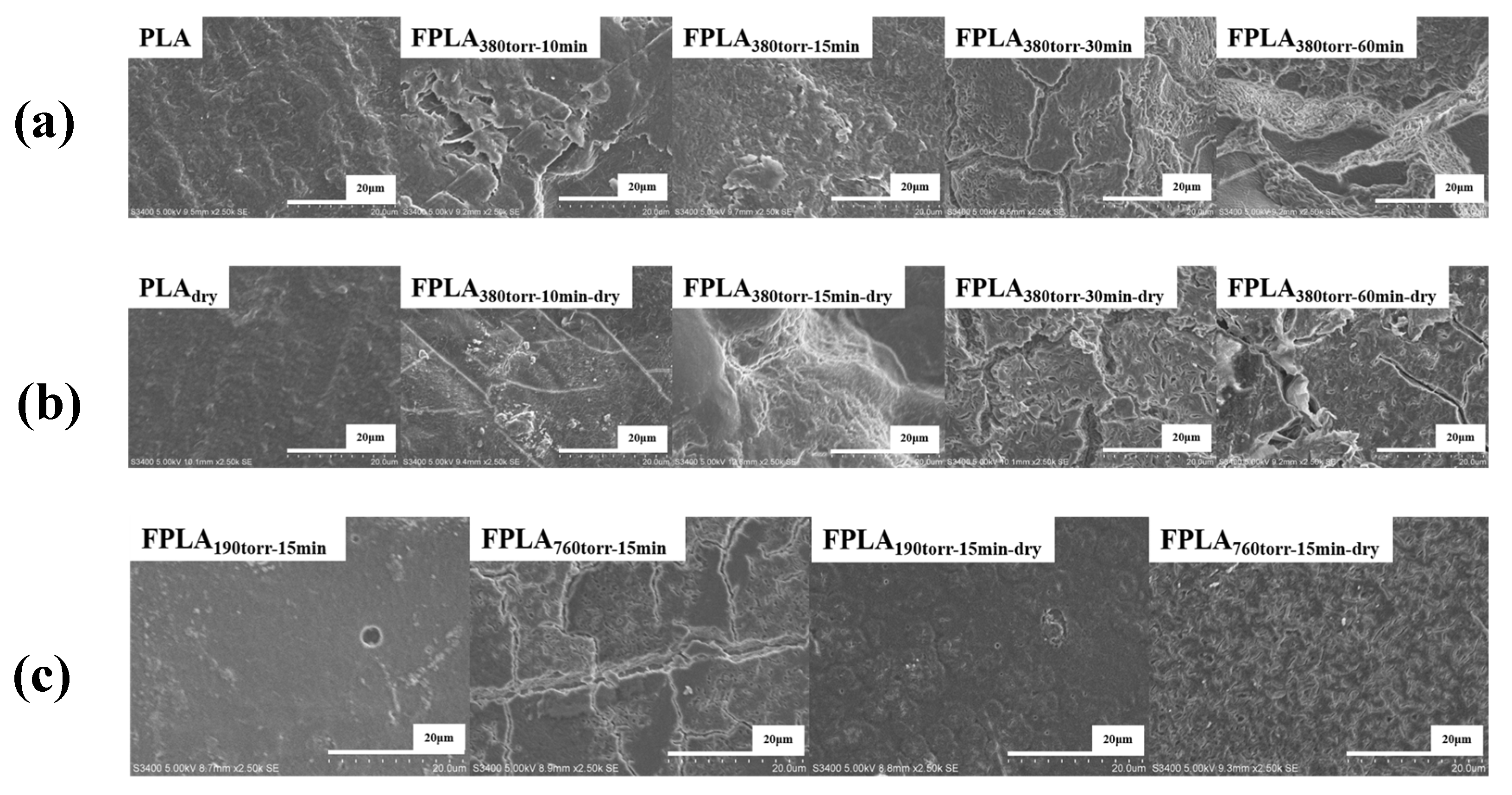
3.3. Effects of Fluorination and Drying on the Surface Properties and Morphology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Polylactic acid (PLA): Research, development and industrialization. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, K.; Kaseem, M.; Yang, H.W.; Deri, F.; Ko, Y.G. Properties and medical applications of polylactic acid: A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Polylactic acid (PLA) synthesis and modifications: A review. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneillie, S.; Smet, M. PLA architectures: The role of branching. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Varshney, S.K. Polylactides—Chemistry, Properties and Green Packaging Technology: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Ramezani Dana, H. Poly lactic acid (PLA) polymers: From properties to biomedical applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 71, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrom, J.S.; Hayman, D. An Overview of Mechanical Properties and Material Modeling of Polylactide (PLA) for Medical Applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, T.H.; Park, Y.; Hwang, Y. Facile Surface Treatment of 3D-Printed PLA Filter for Enhanced Graphene Oxide Doping and Effective Removal of Cationic Dyes. Polymers 2023, 15, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthumana, M.; Santhana Gopala Krishnan, P.; Nayak, S.K. Chemical modifications of PLA through copolymerization. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2020, 25, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standau, T.; Zhao, C.; Murillo Castellon, S.; Bonten, C.; Altstadt, V. Chemical Modification and Foam Processing of Polylactide (PLA). Polymers 2019, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordá-Vilaplana, A.; Fombuena, V.; García-García, D.; Samper, M.D.; Sánchez-Nácher, L. Surface modification of polylactic acid (PLA) by air atmospheric plasma treatment. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 58, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Favi, P.; Cheng, X.; Golshan, N.H.; Ziemer, K.S.; Keidar, M.; Webster, T.J. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) surface nanomodified 3D printed polylactic acid (PLA) scaffolds for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016, 46, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Desmet, T.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C. Plasma Surface Modification of Biodegradable Polymers: A Review. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Villarreal, M.H.; Ulloa-Hinojosa, M.G.; Gaona-Lozano, J.G. Surface functionalization of poly(lactic acid) film by UV-photografting of N-vinylpyrrolidone. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.Y.; Jang, J.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lyoo, W.S.; Min, B.G. Superhydrophobic PLA fabrics prepared by UV photo-grafting of hydrophobic silica particles possessing vinyl groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandanamsamy, L.; Harun, W.S.W.; Ishak, I.; Romlay, F.R.M.; Kadirgama, K.; Ramasamy, D.; Idris, S.R.A.; Tsumori, F. A comprehensive review on fused deposition modelling of polylactic acid. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 8, 775–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, E.H.; Erbil, H.Y. Surface Modification of 3D Printed PLA Objects by Fused Deposition Modeling: A Review. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, M.N. Biodegradation of poly(l-lactide) (PLA) exposed to UV irradiation by a mesophilic bacterium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Naskar, A.K.; Haynes, D.; Drews, M.J.; Smith, D.W. Synthesis, characterization and surface properties of poly(lactic acid)–perfluoropolyether block copolymers. Polym. Int. 2010, 60, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifehzadeh, R.; Ratner, B.D. Trifluoromethyl-functionalized poly(lactic acid): A fluoropolyester designed for blood contact applications. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3764–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenn, N.; Follain, N.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Poncin-Epaillard, F.; Labrugère, C.; Marais, S. Impact of hydrophobic plasma treatments on the barrier properties of poly(lactic acid) films. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5626–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwong, C.; Rachtanapun, P.; Wongchaiya, P.; Auras, R.; Boonyawan, D. Effect of plasma treatment on hydrophobicity and barrier property of polylactic acid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2933–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroepfer, M.; Junghans, F.; Voigt, D.; Meyer, M.; Breier, A.; Schulze-Tanzil, G.; Prade, I. Gas-Phase Fluorination on PLA Improves Cell Adhesion and Spreading. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5498–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Mishina, T.; Namie, M.; Nishimura, F.; Yonezawa, S. Effects of surface fluorination on the dyeing of polycarbonate (PC) resin. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 19, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, A.P.; Simbirtseva, G.V.; Tressaud, A.; Durand, E.; Labrugère, C.; Dubois, M. Comparison of the surface modifications of polymers induced by direct fluorination and rf-plasma using fluorinated gases. J. Fluor. Chem. 2014, 165, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prorokova, N.P.; Istratkin, V.A.; Kumeeva, T.Y.; Vavilova, S.Y.; Kharitonov, A.P.; Bouznik, V.M. Improvement of polypropylene nonwoven fabric antibacterial properties by the direct fluorination. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44545–44549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriprom, W.; Sangwaranatee, N.; Herman; Chantarasunthon, K.; Teanchai, K.; Chamchoi, N. Characterization and analyzation of the poly (L-lactic acid) (PLA) films. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 14803–14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragkumar, N.T.; Edith, D.; Six, J.-L. Surface characteristics of PLA and PLGA films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2758–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, A.P. Direct fluorination of polymers—From fundamental research to industrial applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 61, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Nishimura, F.; Kim, J.H.; Yonezawa, S. Dyeable Hydrophilic Surface Modification for PTFE Substrates by Surface Fluorination. Membranes 2023, 13, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, E.; Bertoti, I.; Vargha-Butler, E.I. XPS and wettability characterization of modified poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactic/glycolic acid) films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 245, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namie, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Yonezawa, S. Improving the Dyeing of Polypropylene by Surface Fluorination. Colorants 2022, 1, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mróz, P.; Białas, S.; Mucha, M.; Kaczmarek, H. Thermogravimetric and DSC testing of poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 573, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.; Botelho, G.; Oliveira, M.; Machado, A.V. Influence of clay organic modifier on the thermal-stability of PLA based nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 88–89, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.S.; Borhan, A. A Volume-Corrected Wenzel Model. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8875–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
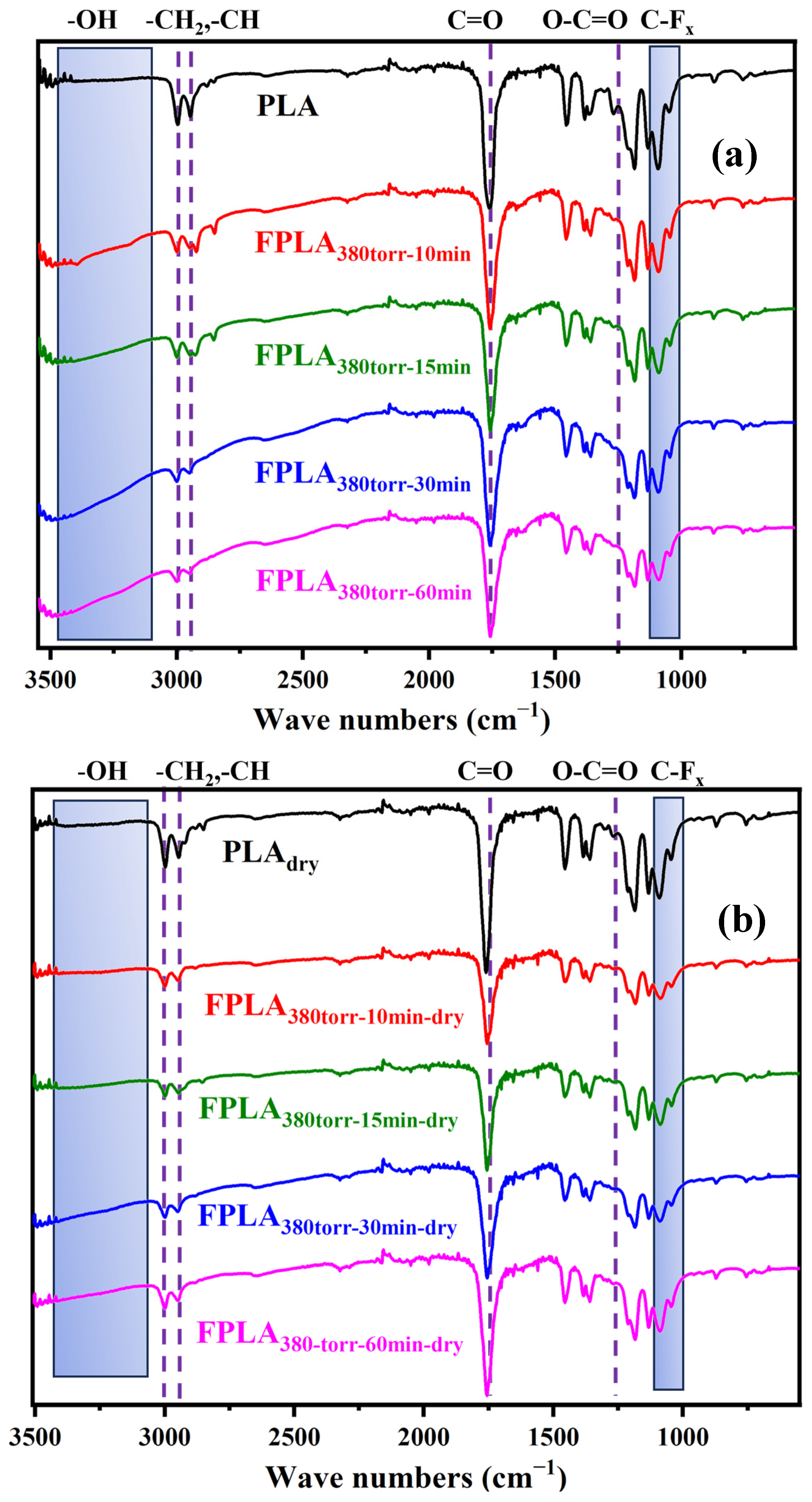
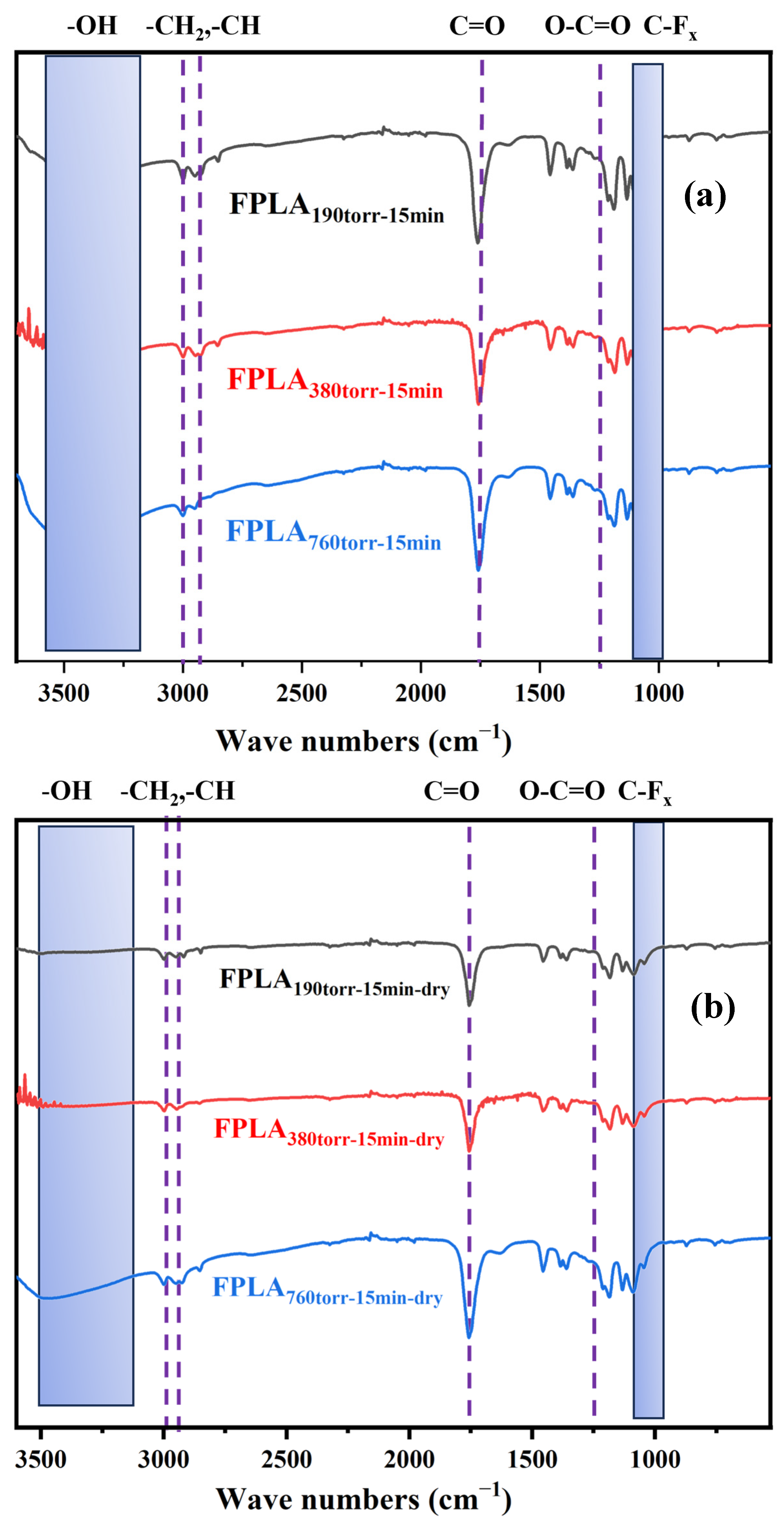


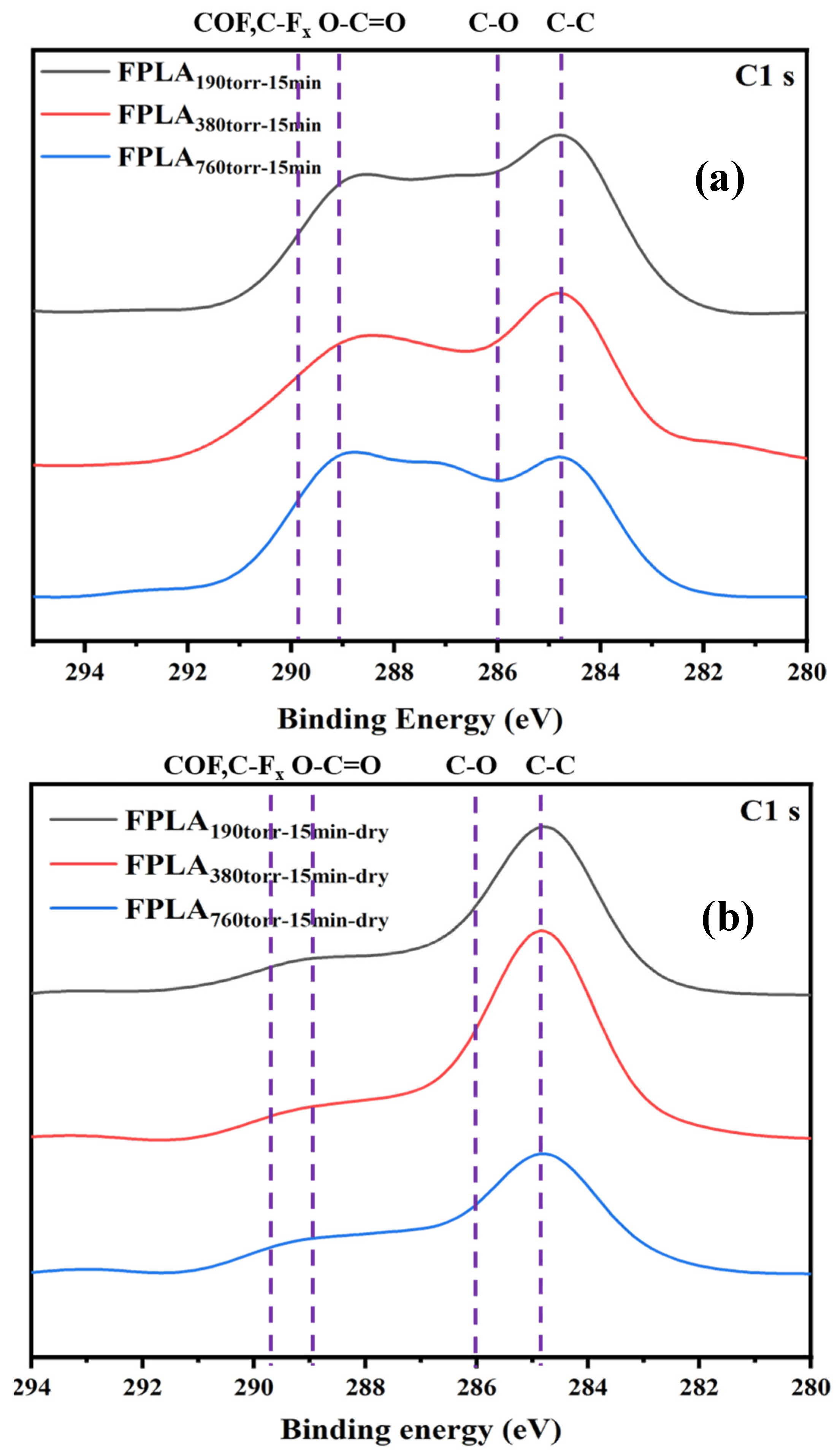
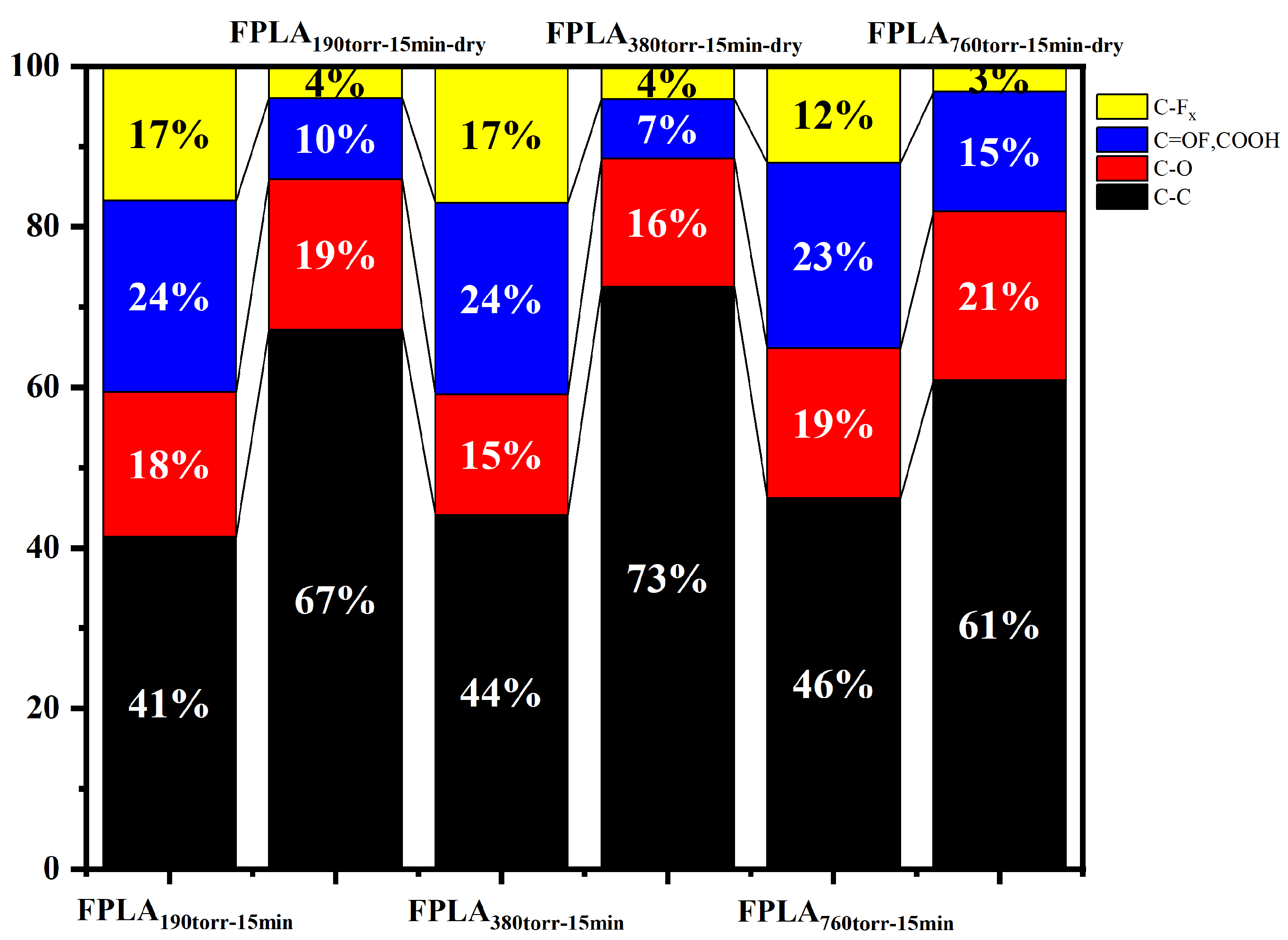





| PLA | FPLA380torr-10min | FPLA380torr-15min | FPLA380torr-30min | FPLA380torr-60min | |
| Tg | 57.30 °C | 58.78 °C | 60.52 °C | 60.71 °C | 57.51 °C |
| PLA | FPLA380torr-10min-dry | FPLA380torr-15min-dry | FPLA380torr-30min-dry | FPLA380torr-60min-dry | |
| Tg | 61.12 °C | 62.05 °C | 63.12 °C | 63.26 °C | 61.33 °C |
| FPLA190torr-15min | FPLA380torr-15min | FPLA760torr-15min | |
| Tg | 60.27 °C | 60.52 °C | 59.27 °C |
| FPLA190torr-15min-dry | FPLA380torr-15min-dry | FPLA760torr-15min-dry | |
| Drying | 61.60 °C | 63.12 °C | 60.19 °C |
| PLA | FPLA380torr-10min | FPLA380torr-15min | FPLA380torr-30min | FPLA380torr-60min | |
| CA | 64.09° ± 1.17 | 63.14° ± 1.53 | 64.22° ± 0.95 | 58.26° ± 3.82 | 18.75° ± 4.99 |
| PLA | FPLA380torr-10min-dry | FPLA380torr-15min-dry | FPLA380torr-30min-dry | FPLA380torr-60min-dry | |
| CA | 62.49° ± 3.33 | 85.20° ± 3.05 | 91.46° ± 0.90 | 83.99° ± 2.41 | 55.41° ± 2.08 |
| FPLA190torr-15min | FPLA380torr-15min | FPLA760torr-15min | |
| CA | 63.92° ± 3.26 | 64.22° ± 0.95 | 24.83° ± 1.43 |
| FPLA190torr-15min-dry | FPLA380torr-15min-dry | FPLA760torr-15min-dry | |
| CA | 90.08° ± 0.55 | 91.46° ± 0.90 | 53.48° ± 0.11 |
| PLA | FPLA380torr-10min | FPLA380torr-15min | FPLA380torr-30min | FPLA380torr-60min | |
| Ra | 31.91 nm ± 2.69 | 59.72 nm ± 3.84 | 59.08 nm ± 0.89 | 84.08 nm ± 3.76 | 101.9 nm ± 3.04 |
| PLA | FPLA380torr-10min-dry | FPLA380torr-15min-dry | FPLA380torr-30min-dry | FPLA380torr-60min-dry | |
| Ra | 29.67 nm ± 4.70 | 52.21 nm ± 2.69 | 42.69 nm ± 4.66 | 77.54 nm ± 3.17 | 87.37 nm ± 4.37 |
| FPLA190torr-15min | FPLA380torr-15min | FPLA760torr-15min | |
| Ra | 55.43 nm ± 1.65 | 59.08 nm ± 0.89 | 81.18 nm ± 3.39 |
| FPLA190torr-15min-dry | FPLA380torr-15min-dry | FPLA760torr-15min-dry | |
| Ra | 44.45 nm ± 3.01 | 42.69 nm ± 4.66 | 78.54 nm ± 2.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Kim, J.-H.; Yonezawa, S. Tuning Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Properties of PLA Films Through Surface Fluorination and Drying. Physchem 2026, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem6010002
He Z, Kim J-H, Yonezawa S. Tuning Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Properties of PLA Films Through Surface Fluorination and Drying. Physchem. 2026; 6(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem6010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhipeng, Jae-Ho Kim, and Susumu Yonezawa. 2026. "Tuning Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Properties of PLA Films Through Surface Fluorination and Drying" Physchem 6, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem6010002
APA StyleHe, Z., Kim, J.-H., & Yonezawa, S. (2026). Tuning Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Properties of PLA Films Through Surface Fluorination and Drying. Physchem, 6(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem6010002









