Adsorptive Removal of Bisphenol A by Polyethylene Meshes Grafted with an Amino Group-Containing Monomer, 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Photografting
2.3. Determination of BPA Concentration
2.4. Adsorption of BPA
2.5. Kinetic Analysis
2.6. Isotherm Analysis
2.7. Desorption and Regeneration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PE-g-PDMAEMA Meshes
3.2. BPA Adsorption Performance
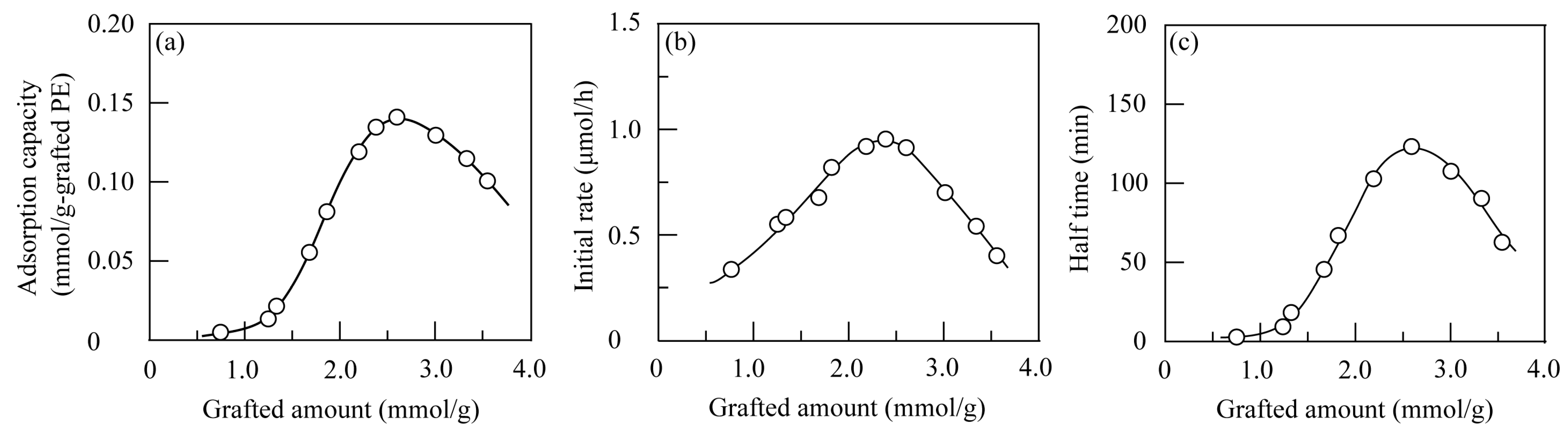
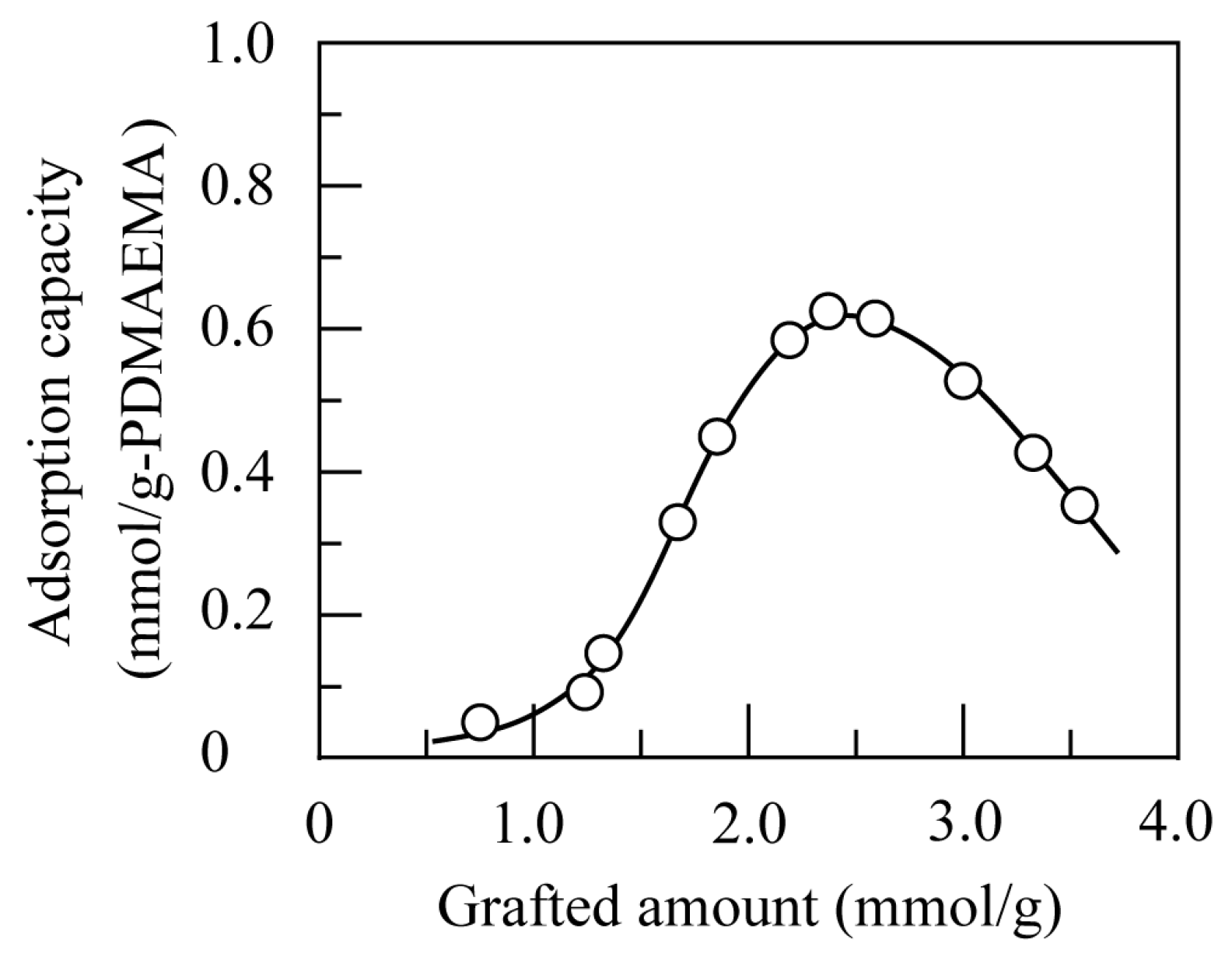
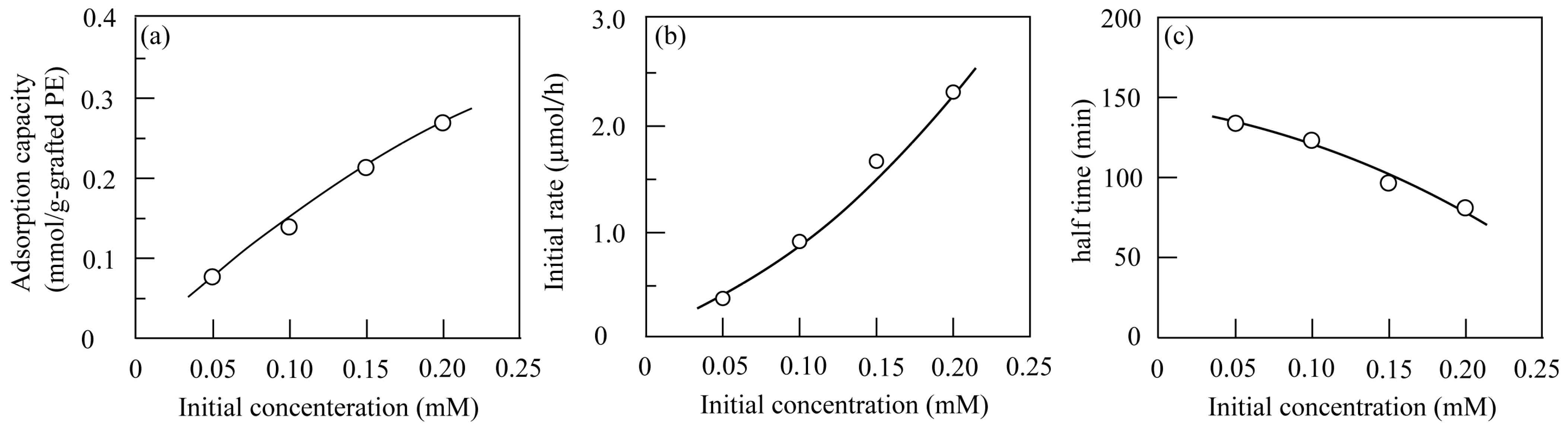
3.2.1. Effect of Grafted Amount
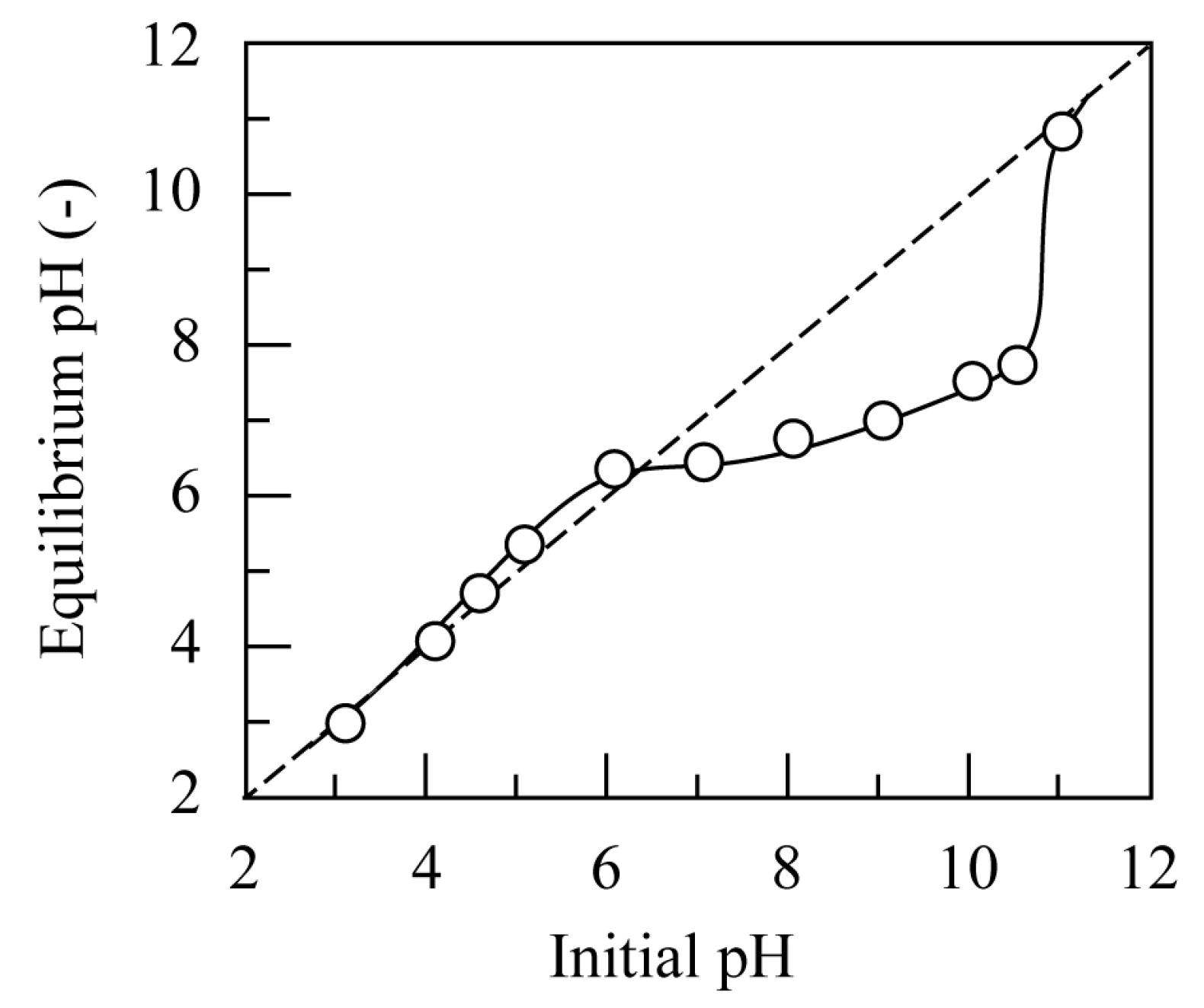
3.2.2. Effect of pH Value
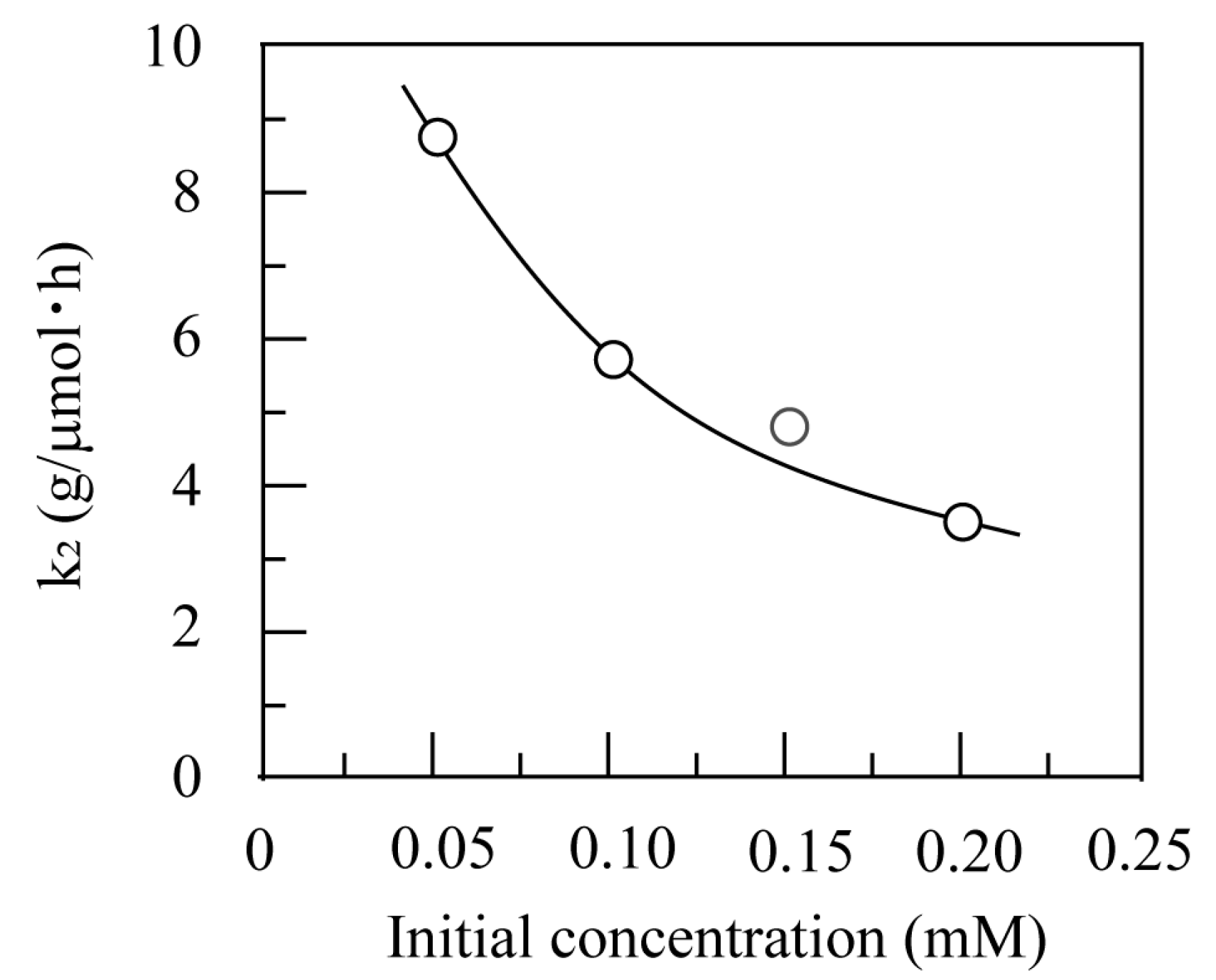
3.2.3. Analysis by Kinetic Equations
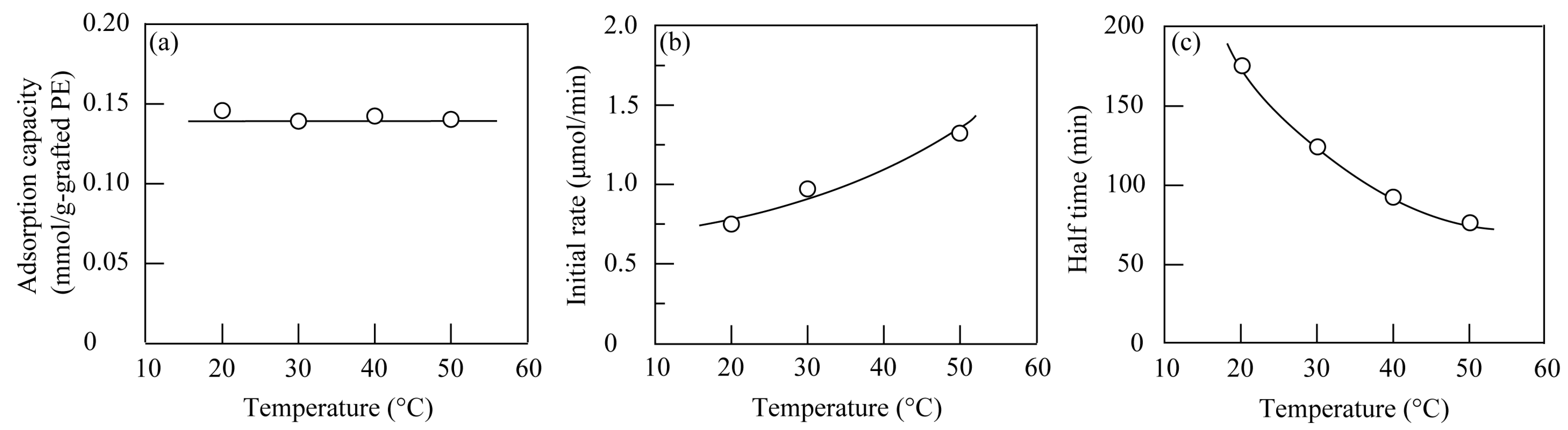
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature
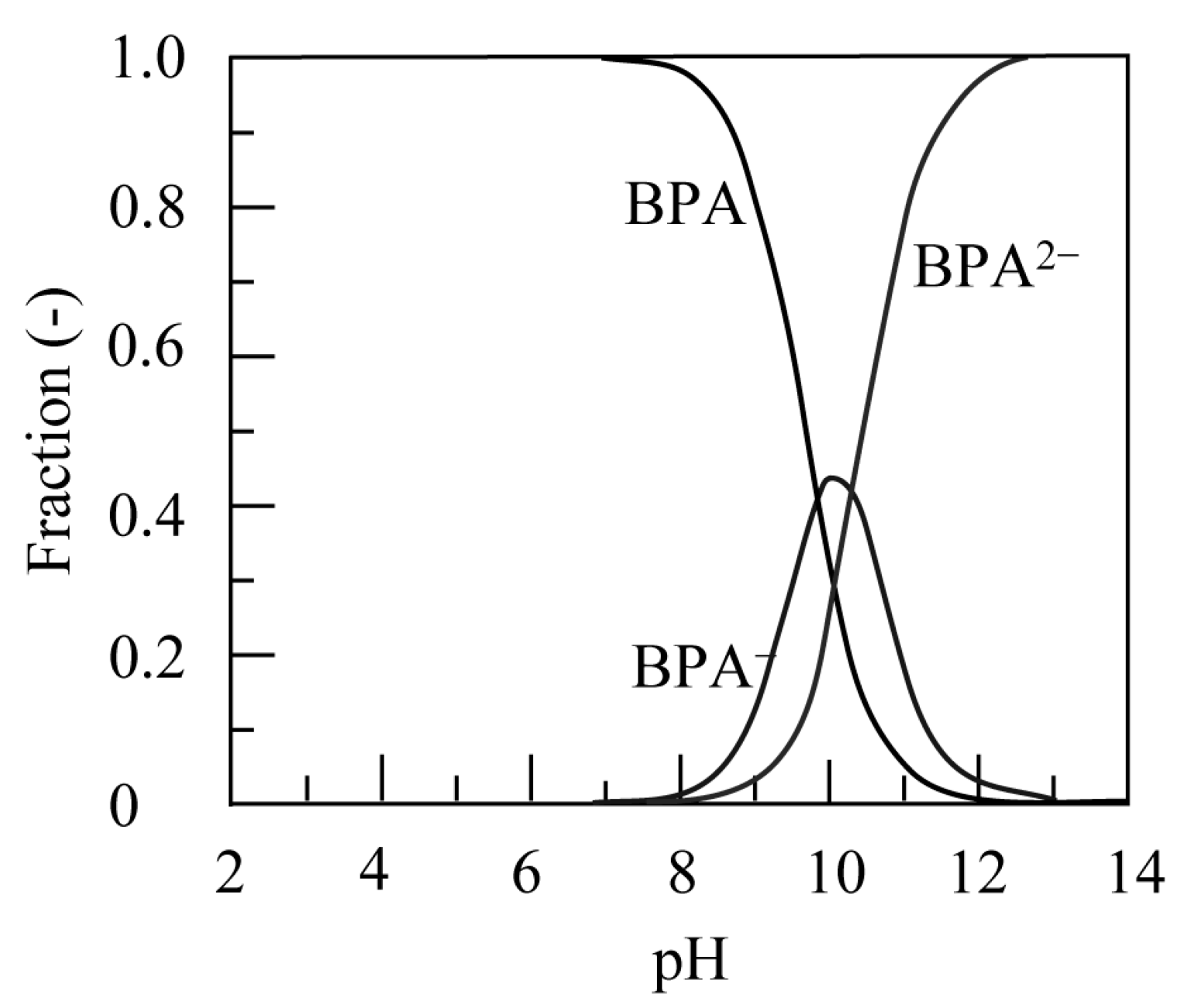
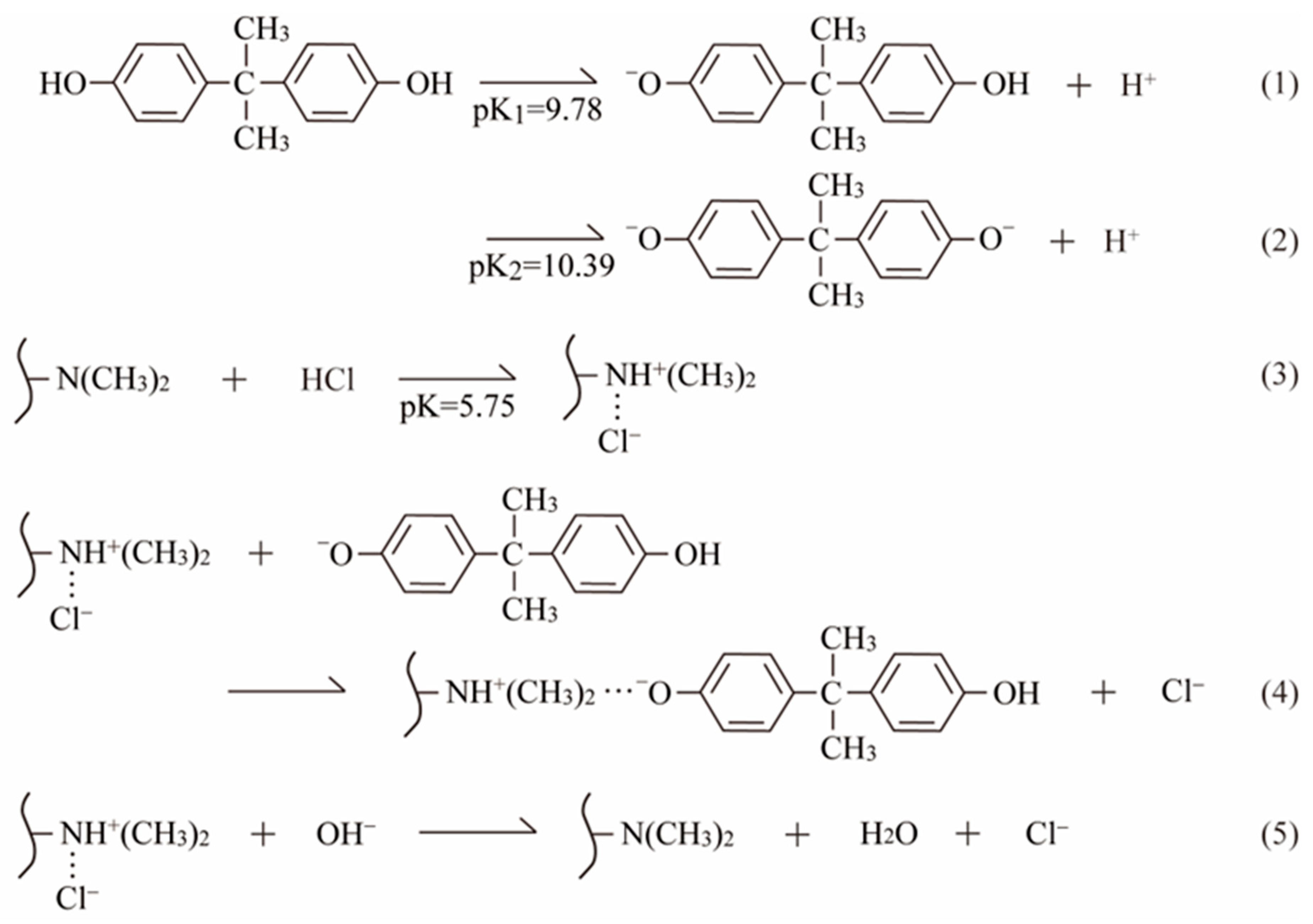
3.2.5. Adsorption Mechanism
3.3. Comparison with Other Adsorbents
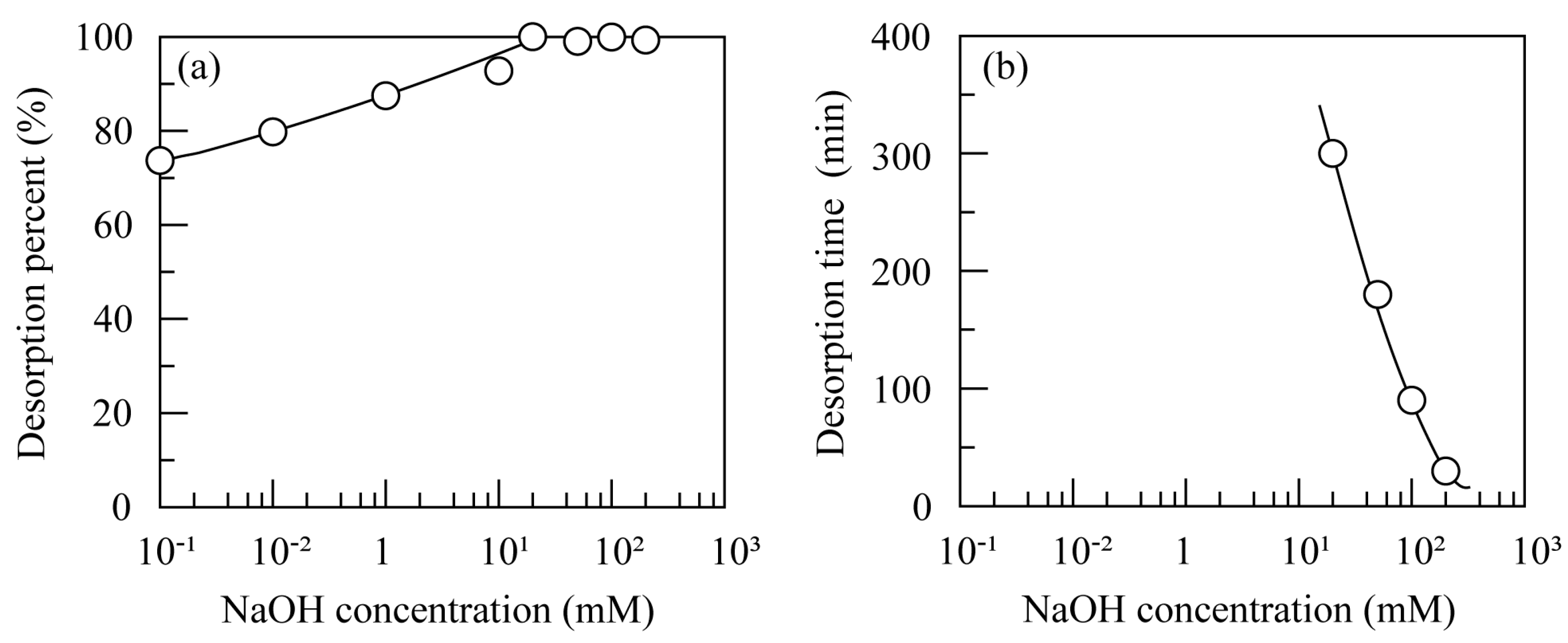
3.4. Desorption of BPA and Repetitive Use
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | frequency factor |
| C0 | initial concentration of BPA (mM) |
| Ceq | BPA concentration at equilibrium (mM) |
| Ct | concentration of BPA at time t (mM) |
| E | activation energy (J/mol) |
| KL | Langmuir constant (1/h) |
| KF | Freundlich constant ((L/μmol)1/n) |
| k1 | pseudo first-order rate constant (1/h) |
| k2 | pseudo second-order rate constant (g/μmol·h) |
| MDMAEMA | molar mass of DMAEMA (157.21 g/mol) |
| n | empirical parameter (-) |
| Qeq | adsorption amount at equilibrium = adsorption capacity (mmol/g) |
| Qmax | maximum adsorption capacity (mmol/g) |
| Qt | adsorption amount at time t (mmol/g) |
| R | gas constant (8.314 J/K·mol) |
| V | volume of aqueous BPA solution (0.050 L) |
| weight of cut PE-g-PDMAEMA mesh (mg) | |
| Wg | weight of a PE-g-PDMAEMA mesh |
| W0 | weight of an ungrafted PE mesh |
References
- Ramírez-Melgarejo, M.; Stringer, T. Wastewater treatment, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions: An operational approach to comparing Barcelona and Mexico City. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.R.; van Vliet, T.H.; Qadir, M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Country-level and gridded estimates of wastewater production, collection, treatment and reuse. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, W.T.; de Farias, M.B.; Spaolonzi, M.P.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Removal of endocrine disruptors in waters by adsorption, membrane filtration and biodegradation. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1113–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petratcam, M.H.; Perez, M.A.F.; Amelia, S.; Tfouni, V. Bisphenol A and its structural analogues in infant formulas available in the Brazilian market: Optimisation of a UPLC-MS/MS method, occurrence, and dietary exposure assessment. Food. Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrabad, E.K.; Hashmi, S.A.; Nadjarzadeh, A.; Askari, E.; Mohajeri, F.A.; Ramroudi, F. Bisphenol A release from food and beverage containers—A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 3718–3728. [Google Scholar]
- Gomi, M.; Mizukawa, K.; Takada, H. Monitoring of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals by direct acetylation method: Pollution status in Tokyo rivers in 2016–2019 and estimation of their sources. Environ. Monit. Contam. Res. 2022, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Wu, S.; Han, Z.; Guo, R.; Chen, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Bisphenol Analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: Occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Česen, M.; Lenarčič, K.; Mislej, V.; Levstek, M.; Kovačič, A.; Cimrmančič, B.; Uranjek, N.; Kosjek, T.; Heath, D.; Dolenc, M.S.; et al. The occurrence and source identification of bisphenol compounds in wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Santana-Mayor, A.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Delgado, A. Recent advances in the analysis of plastic migrants in food. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, F.; Sendón, R.; van der Kellen, A.; Vaz, M.F.; Sanches Silva, A. Bisphenol A in food as a result of its migration from food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/213 of 12 February 2018 on the use of Bisphenol A in Varnishes And Coatings Intended To Come Into Contact With Food And Amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as regards the use of that substance in plastic food contact materials. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, L41, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, A.; Biswas, S.; Pal, A. A comprehensive review on BPA degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 714–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, D.A.; Abu Hasan, H.; Muhamad, M.H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Abu Baker, S.N.H.; Buhari, J. Physica-chemical and biologica techniques of Bisphenol A removal in an aqueous solution. J. Ecolog. Eng. 2021, 22, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, Q.; Qayyum, S. Biological and enzymatic treatment of Bisphenol A and other endocrine disrupting compounds: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 33, 260–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Park, B.J. Removal of Bisphenol A from wastewater by physical, chemical and biological remediation techniques. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1801–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of Bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, M.C.; Tarley, C.R.T. Bisphenol A adsorption in aqueous medium by investigating organic and inorganic components of hybrid polymer (polyvinylpyridine/SiO2/APTMS). Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 367, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlDhawi, Z.A.; BinSharfan, I.I.; Abdulhamid, M.A. Carboxyl-functionalized polyimides for efficient Bisphenol A removal: Influence of wettability and porosity on adsorption capacity. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Guo, X.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lang, W. Design of functionalized polypropylene non-woven fabric with high β-CD grafting degree for Bisphenol A removal: Adsorption performance and resistance. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 287, 119744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, S.; Rene, E.R.; Dong, S.; Ma, W. Green synthesis of magnetic azo-linked porous organic polymers with recyclable properties for enhanced Bisphenol-A adsorption from aqueous solutions. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Musashi, E.; Kobiyama, Y.; Kashiwada, A.; Matsuda, K.; Yamada, K. Use of chitosan for removal of Bisphenol A and bisphenol derivatives through tyrosinase-catalyzed quinone oxidation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, C.; Kashiwada, A.; Matsuda, K.; Yamada, K. Soybean peroxidase-catalyzed treatment and removal of BPA and bisphenol derivatives from aqueous solutions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2011, 30, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takano, Y.; Kashiwada, A.; Matsuda, K.; Hirata, M. Determination of optimum process parameters for peroxidase-catalysed treatment of Bisphenol A and application to the removal of bisphenol derivatives. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamoto, H.; Kimura, Y.; Ishiguro, Y.; Minamiswa, H.; Yamada, K. Use of polyethylene films photografted with 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate as a potential adsorbent for removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous medium. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Kitao, Y.; Asamoto, H.; Minamisawa, H. Development of recoverable adsorbents for Cr (VI) ions by grafting of a dimethylamino group-containing monomer on polyethylene substrate and subsequent quaternization. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 2025–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. New insights into pseudo-second-order kinetic equation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 320, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tseng, R.; Huang, S.; Juang, R. Characteristics of pseudo-second-order kinetic model for liquid-phase adsorption: A mini-review. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Kim, W.; Park, J.; Cho, J.; Jeong, T.; Park, P. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms to predict absorbate removal efficiency or required amount of adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, R.L.; Csontos, M.; Gyöngyösi, S.; Elek, J.; Parditka, B.; Deák, G.; Kuki, Á.; Kéki, S.; Erdélyi, Z. Surface characterization of plasma-modified low density polyethyelene by attenuated total reflectance fourier-transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Polym. Test. 2021, 96, 107080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Hua, J.; Li, R.; Xing, Z.; Pang, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, L.; Wu, G. Radiation-induced graft polymerization for the preparation of a highly efficient UHMWPE fibrous adsorbent for Cr (VI) removal. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2017, 130, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoğlu, G.; Arica, M.Y. Synthesis of Cr (VI)-imprinted poly(4-vinyl pyridine-co-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) particles: Its adsorption propensity to Cr (VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Wu, G. An efficient and reusable quaternary ammonium fabric adsorbent prepared by radiation grafting for removal of Cr (VI) from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11045–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, J.F.; Barsbay, M.; Abed, L.; Güven, O. Grafting of N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate from PE/PP nonwoven fabric via radiation-induced RAFT polymerization and quaternization of the grafts. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 124, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavakli, C.; Kavakli, P.A.; Turan, B.D.; Hamurcu, A.; Güven, O. Quaternized dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate strong base anion exchange fibers for As (V) adsorption. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 102, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysostomou, V.; Pispas, S. Stimuli-responsive amphiphilic PDMAEMA-b-PLMA copolymers and their cationic and zwitterionic analogs. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2018, 56, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Mochizuki, K.; Yamada, K. Adhesion of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene plates photografted with hydrophilic monomers and evaluation of failure location by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Sato, K.; Hirata, M. Uphill transport of organic electrolytes using polyethylene films photografted with 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, J.; Breidbach, A.; Wenzl, T. Derivatization of Bisphenol A and its analogues with pyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride+: Multivariate optimization and fragmentation patterns by liquid chromatography/Orbitrap mass spectroscopy. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Mo, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Lv, W. Efficient removal of bisphenol pollutants on imine-based covalent organic frameworks: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18308–18320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zuo, L.; Wei, C.; Fu, H.; Qu, H.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, D. Enhanced adsorption of Bisphenol A, tylosin, and tetracycline from aqueous solution to nitrogen-doped multiwall carbon nanotubes via cation-π and π-π electron-donor-acceptor (EDA) interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrakchi, F.; Zafar, F.F.; Wei, M.; Yuan, C.; Cao, B.; Wang, S. N-poded mesoporous H3PO4-pyrocarbon from seaweed and melamine for batch adsorption of the endocrine disruptor Bisphenol A. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Comparative sorption kinetic studies of dye and aromatic compounds onto fly ash. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 1999, 34, 1179–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Yu, D.; Hong, S.; Xing, B. Mechanism and performance for adsorption of 2-chlorophenol onto zeolite with surfactant by one-step process from aqueous phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anari-Anaraki, M.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A. Modification of an Iranian clinoptilolite nano-particles by hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium cationic surfactant and dithizone for removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 440, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Haseeb, S. Adsorption of Pb (II) on Mentha piperita carbon (MTC) in single and quaternary systems. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S412–S421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onursal, N.; Altunkaynak, Y.; Baran, A.; Dal, M.C. Adsoeption of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solutions using Malatya clay: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, e14150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Lukic, J.; Kolarski, D.; Veljović, D.; Radovanović, Ž.; Dimitrijević, S. Isotherm, thermodynamic and kinetic studies of elemental sulfur removal from mineral insulating oils using highly selective adsorbent. Materials 2023, 16, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Ganji, F.; Wang, C.; Balarak, D. Preparation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes coated with CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and their adsorption performance for Bisphenol A compound. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Kilic, M.; Arica, M.Y. Tramates trogii biomass in carboxymethyl-cellulose-lignin composite beads for adsorption and biodegradation of Bisphenol A. Biodegradation 2023, 34, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Kong, L.; Shen, R.; Hu, J.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Lang, W. Construction of stable beta-cyclodextrin grafted polypropylene nonwoven fabrics for the adsorption of Bisphenol A. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 198, 110223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias, M.B.; Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of Bisphenol A from aqueous solution onto organoclay: Experimental design, kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heoa, J.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, G.; Kim, Y.; Han, J.; Park, C.M. Enhanced adsorption of Bisphenol A and sulfamethoxazole by a novel magnetic CuZnFe2O4-biochar composite. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwak, S. Rapid adsorption of Bisphenol A from wastewater by β-cyclodextrin functionalized mesoporous magnetic cluster. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, L.; Sun, D.; Dong, Z. Fabrication of novel Fe/Mn/N co-doped biochar and its enhanced adsorption for Bisphenol A based on π–π electron. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 128018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wu, Z.; Manzoli, M.; Wu, Z.; Cravotto, G. Feasibility and the mechanism of desorption of phenolic compounds from activated carbons. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 12223–12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S. Effective adsorption of Bisphenol A from aqueous solution over a novel mesoporous carbonized material based on spent bleaching earth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40035–40048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, H.H.C.; Llop, M.E.G.; Maniezzo, R.D.; Moisés, M.P.; Janeiro, V.; Arroyo, P.A.; Guiherme, M.R.; Rinaldi, A.W. Enhanced removal of Bisphenol A using pine-fruit shell-derived hydrochars: Adsorption mechanisms and reusability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Adsorbent | pH (-) | Temp. (°C) | Dose (g/L) | BPA conc. (mg/L) | Qexp (mg/g) | Qmax (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE-g-PDMAEMA mesh | 8 | 30 | 0.135 | 22.83 | 31.43 | 94.75 | this study |
| 0.145 | 45.66 | 61.73 | |||||
| polyvinylpyridine/SiO2/APTMS particles | 9.0 | unclear | 1.25 | 10 | 19.97 | [17] | |
| 700 | 160 | 184.4 | |||||
| 6FDA-based polyimides | unclear | 22 | 1.0 | 20 | 17.6 | 67 | [18] |
| PP-g-MAH-β-CD nonwoven fabric | 7.1 | 25 | 2 | 50 | 16.02 | [19] | |
| imine(TAPB)-based covalent organic frameworks | 4–7 | 30 | 0.2 | 50 | 145 | 149.25 | [45] |
| N-doped mesoporous activated pyrocarbons | 5–9 | 30 | 1 | 50 | 51.038 | [46] | |
| 400 | 285.5 | 270.6 | |||||
| multi-walled carbon nanotubes coated with CoFe2O4 | 3.0 | 25 | 0.8 | 25 | 30.84 | 294.1 | [54] |
| 100 | 121.7 | ||||||
| carboxymethyl cellulose-lignin composite beads | 6 | 25 | 1 | 25 | 14.6 | [55] | |
| 400 | 95.6 | 98.9 | |||||
| PP-g-PGMA-βCD nonwoven fabric | 7.0 | 25 | 2 | 75 | 27.72 | 123.79 | [56] |
| 300 | 65.59 | ||||||
| bentonite functionalized with dialkyl | 7.0 | 25 | 1.28 | 14.6 | 10.27 | 64.606 | [57] |
| -dimethylammonium | 168 | 42.69 | |||||
| CuZnFe2O4-supported biochar composite | 7.0 | 25 | 0.2 | 20 | 101.5 | 263.2 | [58] |
| β-CD functionalized mesoporous magnetic clusters | 6.5–7.0 | 30 | 1.0 | 130 | 49.1 | 52.7 | [59] |
| Fe/Mn/N co-doped biochar | 6.9 | 25 | 0.2 | 20 | 48.64 | [60] | |
| 200 | 78.51 | 80.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, K.; Terada, S.; Yamamoto, R.; Anh, D.C.; Naitou, T.; Yamamoto, S. Adsorptive Removal of Bisphenol A by Polyethylene Meshes Grafted with an Amino Group-Containing Monomer, 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate. Physchem 2024, 4, 431-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4040030
Yamada K, Terada S, Yamamoto R, Anh DC, Naitou T, Yamamoto S. Adsorptive Removal of Bisphenol A by Polyethylene Meshes Grafted with an Amino Group-Containing Monomer, 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate. Physchem. 2024; 4(4):431-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Kazunori, Saori Terada, Rena Yamamoto, Dương Cẩm Anh, Takaya Naitou, and Sakura Yamamoto. 2024. "Adsorptive Removal of Bisphenol A by Polyethylene Meshes Grafted with an Amino Group-Containing Monomer, 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate" Physchem 4, no. 4: 431-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4040030
APA StyleYamada, K., Terada, S., Yamamoto, R., Anh, D. C., Naitou, T., & Yamamoto, S. (2024). Adsorptive Removal of Bisphenol A by Polyethylene Meshes Grafted with an Amino Group-Containing Monomer, 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl Methacrylate. Physchem, 4(4), 431-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4040030








