Role of N1-Domain, Linker, N2-Domain, and Latch in the Binding Activity and Stability of the Collagen-Binding Domain for the Collagen-Binding Protein Cbm from Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression and Purification
2.2. Collagen-Binding Assay
2.3. Thermal Denaturation
3. Results and Discussion
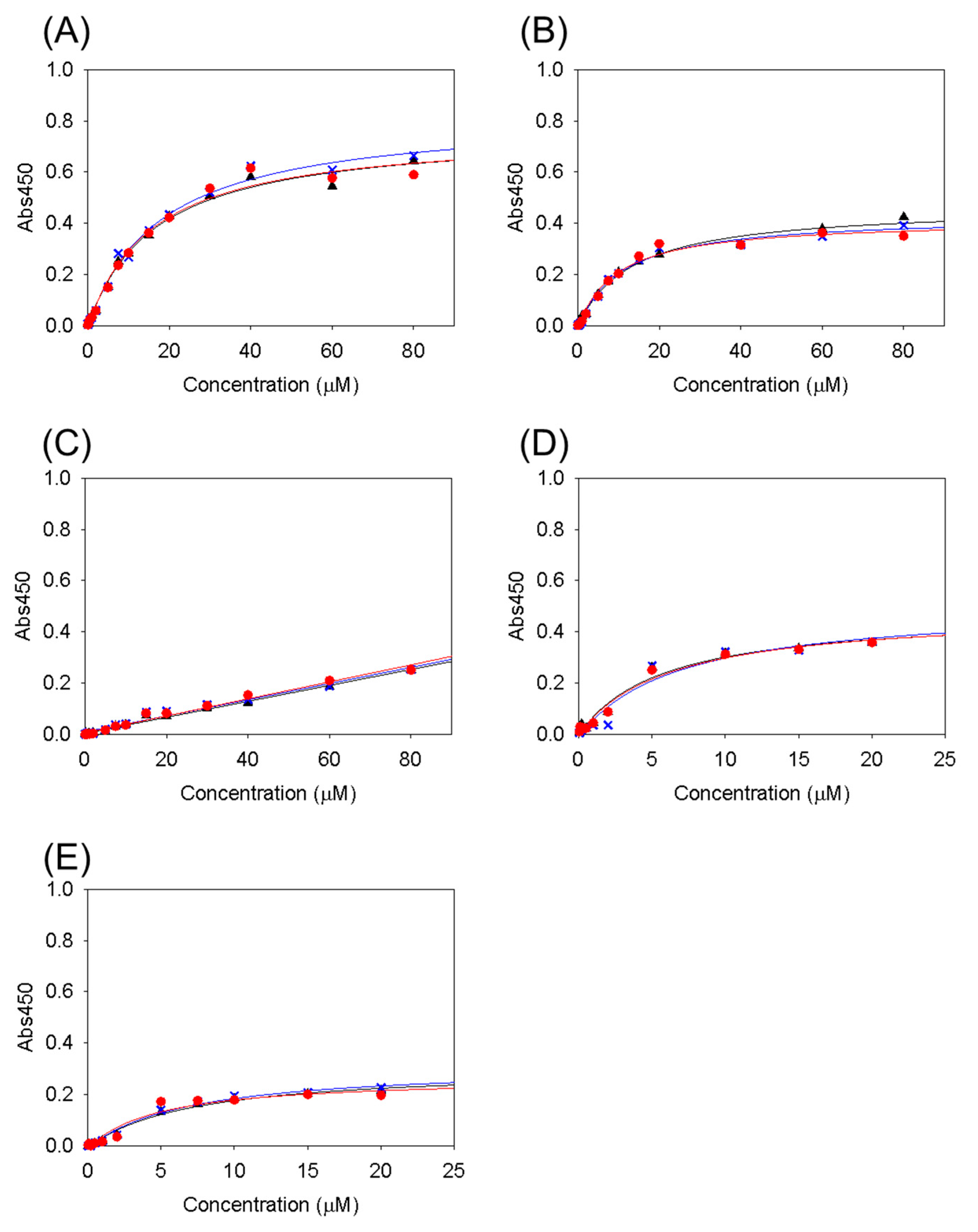
3.1. Collagen-Binding Activity of Cbm/CBD Domain/Region Exchange Variants
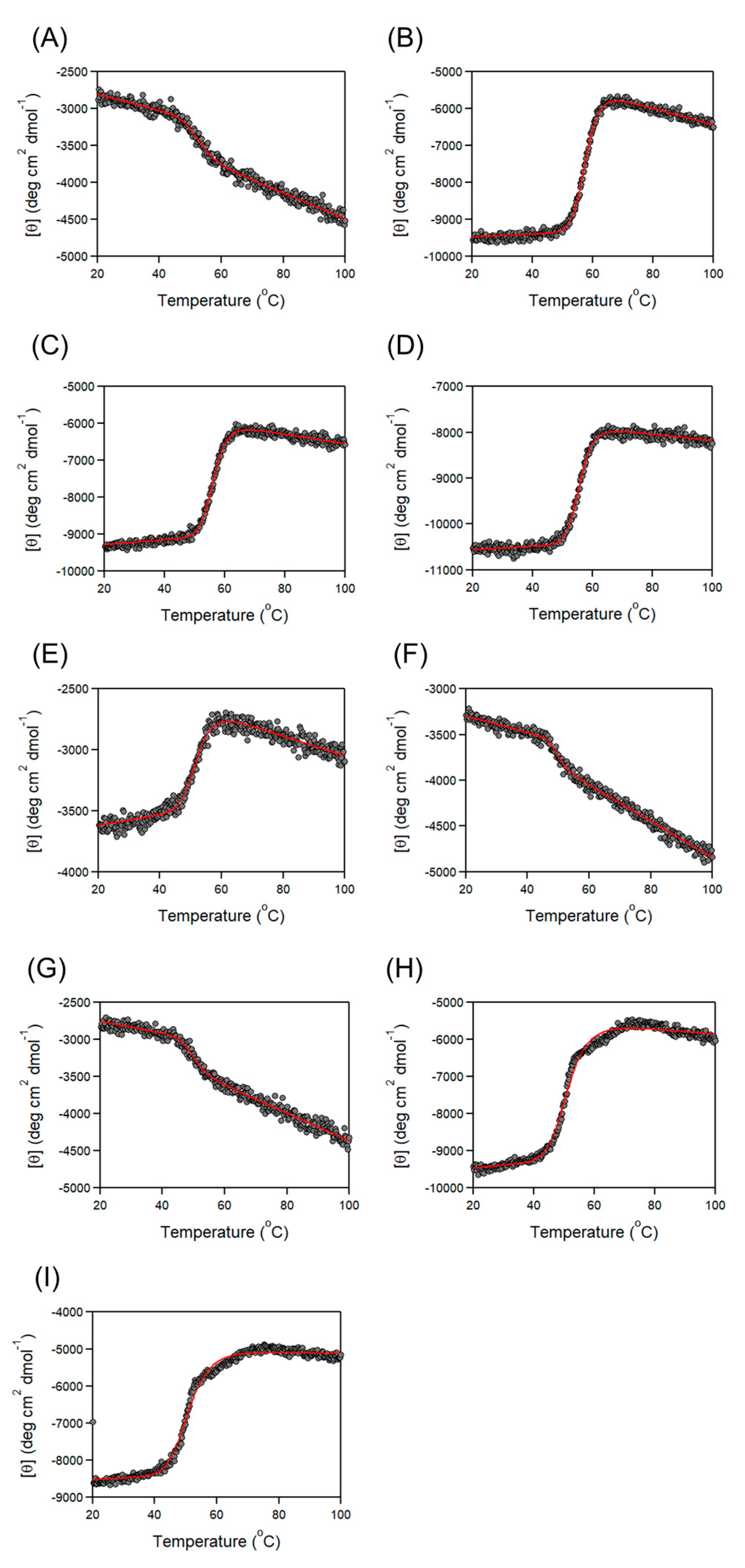
3.2. Thermal Stability of Cbm/CBD Domain/Region Exchange Variants
3.3. Characteristics of Cbm/CBD Domain/Region Exchange Variants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shklair, I.L.; Keene, H.J.; Simonson, L.G. Distribution and frequency of Streptococcus mutans in caries-active individuals. J. Dent. Res. 1972, 51, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Slade, H.D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Rev. 1980, 44, 331–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, J.A.; Palmer, S.R.; Zeng, L.; Wen, Z.T.; Kajfasz, J.K.; Freires, I.A.; Abranches, J.; Brady, L.J. The Biology of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10.1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, J.; Qi, F. The mutacins of Streptococcus mutans: Regulation and ecology. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2012, 27, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debelian, G.J.; Olsen, I.; Tronstad, L. Systemic diseases caused by oral microorganisms. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1994, 10, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.J.; Lucas, V.S.; Omar, J. Bacterial endocarditis and orthodontics. J. R. Coll. Surg. Edinb. 2000, 45, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Amano, A. Roles of oral bacteria in cardiovascular diseases—From molecular mechanisms to clinical cases: Implication of periodontal diseases in development of systemic diseases. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 113, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, R.A.; Lowry, R.; Whitworth, J.M.; Martin, M.V. Infective endocarditis, dentistry and antibiotic prophylaxis; time for a rethink? Br. Dent. J. 2000, 189, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T. Periodontal bacteremia and various vascular diseases. J. Periodontal. Res. 2009, 44, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfeld, J.; Kawai, T. Oral inflammation and bacteremia: Implications for chronic and acute systemic diseases involving major organs. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug. Targets 2015, 15, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parahitiyawa, N.B.; Jin, L.J.; Leung, W.K.; Yam, W.C.; Samaranayake, L.P. Microbiology of odontogenic bacteremia: Beyond endocarditis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, G.J.; Gardner, P.; Simmons, N.A. Optimum sampling time for detection of dental bacteraemia in children. Int. J. Cardiol. 1992, 35, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, M.H.; Durack, D.T. Clinical presentation of infective endocarditis. Cardiol. Clin. 2003, 21, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, A.S.; Bolger, A.F.; Taubert, K.A.; Wilson, W.; Steckelberg, J.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levison, M.; Chambers, H.F.; Dajani, A.S.; Gewitz, M.H.; et al. Diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis and its complications. Circulation 1998, 98, 2936–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiene, G.; Basso, C. Pathology and pathogenesis of infective endocarditis in native heart valves. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2006, 15, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, S.; Mitsutake, K.; Ohara, T.; Kokubo, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Hanai, S. CADRE Investigators: Recent picture of infective endocarditis in Japan-lessons from Cardiac Disease Registration (CADRE-IE). Circ. J. 2013, 77, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Nomura, R.; Ooshima, T. Streptococcus mutans and cardiovascular diseases. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2008, 44, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, K.W.; Hunter, N. The role of oral bacteria in the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis. Aust. Dent. J. 1991, 36, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhie, D.; Hutchison, J.G.; Nye, F.; Ball, A.P. Infective endocarditis caused by Streptococcus mutans. Br. Heart J. 1977, 39, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vose, J.M.; Smith, P.W.; Henry, M.; Colan, D. Recurrent Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Am. J. Med. 1987, 23, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, R.; Naka, S.; Nemoto, H.; Inagaki, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Ooshima, T.; Nakano, K. Potential involvement of collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans in infective endocarditis. Oral Dis. 2013, 19, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Hokamura, K.; Taniguchi, N.; Wada, K.; Kudo, C.; Nomura, R.; Kojima, A.; Naka, S.; Muranaka, Y.; Thura, M.; et al. The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonomura, S.; Ihara, M.; Kawano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Okuno, Y.; Saito, S.; Friedland, R.P.; Kuriyama, N.; Nomura, R.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage and deep microbleeds associated with cnm-positive Streptococcus mutans; a hospital cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 20074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, R.; Ogaya, Y.; Nakano, K. Contribution of the collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans to bacterial colonization of inflamed dental pulp. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Kagami, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Igarashi, T.; Kizaki, H. Streptococcus mutans strains harboring collagen-binding adhesin. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, R.; Nakano, K.; Naka, S.; Nemoto, H.; Masuda, K.; Lapirattanakul, J.; Alaluusua, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Kawabata, S.; Ooshima, T. Identification and characterization of a collagen-binding protein, Cbm, in Streptococcus mutans. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2012, 27, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Reyes, A.; Miller, J.H.; Lemos, J.A.; Abranches, J. Collagen-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans and related streptococci. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 32, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liang, X.; Keene, D.R.; Höök, A.; Gurusiddappa, S.; Höök, M.; Narayana, S.V. A ‘Collagen Hug’ model for Staphylococcus aureus CNA binding to collagen. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 4224–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ponnuraj, K.; Xu, Y.; Ganesh, V.K.; Sillanpää, J.; Murray, B.E.; Narayana, S.V.; Höök, M. The Enterococcus faecalis MSCRAMM ACE binds its ligand by the Collagen Hug model. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19629–19637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Bausier, P.; Valotteau, C.; Pietrocola, G.; Rindi, S.; Alsteens, D.; Foster, T.J.; Speziale, P.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Mechanical strength and inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus collagen-binding protein Cna. mBio 2016, 25, e01529-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotteau, C.; Prystopiuk, V.; Pietrocola, G.; Rindi, S.; Peterle, D.; De Filippis, V.; Foster, T.J.; Speziale, P.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Single-cell and single-molecule analysis unravels the multifunctionality of the Staphylococcus aureus collagen-binding protein Cna. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2160–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.V.; Nallapareddy, S.R.; Sillanpää, J.; Murray, B.E. Importance of the collagen adhesin ace in pathogenesis and protection against Enterococcus faecalis experimental endocarditis. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 8, e1000716. [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi, T.; Asaga, E.; Goto, N. The sortase of Streptococcus mutans mediates cell wall anchoring of a surface protein antigen. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 18, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekhorst, J.; de Been, M.W.; Kleerebezem, M.; Siezen, R.J. Genome-wide detection and analysis of cell wall-bound proteins with LPxTG-like sorting motifs. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4928–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, C.; Schwarzer, D. Engineered sortases in peptide and protein chemistry. Chembiochem 2021, 16, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Gordon, J.; Hook, M. Collagen binding proteins of gram-positive pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2021, 5, 628798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, A.; Matsui, H.; Hirata, A.; Mukaiyama, A.; Tanaka, S.-i.; Yoshizawa, T.; Matsumura, H.; Nomura, R.; Nakano, K.; Takano, K. Structure, stability and binding properties of collagen-binding domains from Streptococcus mutans. Chemistry 2023, 5, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, P.; Holm, L.; Sander, C. The immunoglobulin fold. Structural classification, sequence patterns and common core. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 242, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirny, L.A.; Shakhnovich, E.I. Universally conserved positions in protein folds: Reading evolutionary signals about stability, folding kinetics and function. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Garakani, K.; Mofrad, M.R.K. Molecular mechanics of Staphylococcus aureus adhesin, CNA, and the inhibition of bacterial adhesion by stretching collagen. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. The MSCRAMM family of cell-wall-anchored surface proteins of gram-positive cocci. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Fujita, K.; Ooshima, T. Comparison of glucan-binding proteins in cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 22, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, R.; Otsugu, M.; Naka, S.; Teramoto, N.; Kojima, A.; Muranaka, Y.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Ooshima, T.; Nakano, K. Contribution of the interaction of Streptococcus mutans serotype k strains with fibrinogen to the pathogenicity of infective endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 5223–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, B.; Ramshaw, J.A. The collagen triple-helix structure. Matrix Biol. 1997, 15, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Bansal, M. Collagen structure: The Madras triple helix and the current scenario. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirrah, I.N.; Lokanathan, Y.; Zulkiflee, I.; Wee, M.F.M.R.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B. A Comprehensive review on collagen type I development of biomaterials for tissue engineering: From biosynthesis to bioscaffold. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Sannino, A.; Salvatore, L. An overview of the use of equine collagen as emerging material for biomedical applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naomi, R.; Ridzuan, P.M.; Bahari, H. Current insights into collagen type I. Polymers 2021, 13, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, K.; Okamoto, T.; Okada, J.; Tanaka, S.; Angkawidjaja, C.; Koga, Y.; Kanaya, S. Stabilization by fusion to the C-terminus of hyperthermophile Sulfolobus tokodaii RNase HI: A possibility of protein stabilization tag. PLoS ONE 2011, 19, e16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Miyai, K.; Trakulnaleamsai, S.; Yomo, T.; Shima, Y.; Miki, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Urabe, I. Evolutionary molecular engineering by random elongation mutagenesis. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, Y.; Yao, H.; Wang, J. Importance of the C-terminal loop L137-S141 for the folding and folding stability of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4318–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variants | Residue Numbers |
|---|---|
| Cbm/CBD (N1–N2~) a | 31–330 |
| N1 a | 31–163 |
| N1– | 31–171 |
| N2 a | 172–320 |
| –N2~ | 164–330 |
| N2~ | 172–330 |
| –N2 | 164–320 |
| N1–N2 a | 31–320 |
| N2–N1~ a | 172–320/164–171/31–163/321–330 |
| N2–N1 | 172–320/164–171/31–163 |
| N1–N1~ | 31–171/31–163/321–330 |
| N1–N1 | 31–171/31–163 |
| N2–N2~ | 172–320/164–330 |
| N2–N2 | 172–320/164–320 |
| Variants | KD (μM) |
|---|---|
| Cbm/CBD (N1–N2~) a | 2.8 ± 0.2 a |
| N1–N2 | 28 ± 6.5 a |
| N2–N1~ | 27 ± 2.9 a |
| N2–N1 | 16 ± 1.1 |
| N1–N1~ | 11 ± 2.1 |
| N1–N1 | ND |
| N2–N2~ | 6.2 ± 0.6 |
| N2–N2 | 6.2 ± 1.3 |
| Variants | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|
| Cbm/CBD (N1–N2~) a | 57.6 ± 0.1 a |
| N1 | 50.7 ± 0.3 a |
| N1– | 52.4 ± 0.4 |
| N2 | 54.2 ± 0.1 a |
| –N2~ | 57.6 ± 0.1 |
| N2~ | 56.3 ± 0.1 |
| –N2 | 55.6 ± 0.1 |
| N1–N2 | 55.2 ± 0.1 a |
| N2–N1~ | 51.9 ± 0.1 a |
| N2–N1 | 52.1 ± 0.2 |
| N1–N1~ | 49.4 ± 0.3 |
| N1–N1 | 49.5 ± 0.4 |
| N2–N2~ | 51.2 ± 0.1 |
| N2–N2 | 50.8 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishi, A.; Hirata, A.; Mukaiyama, A.; Tanaka, S.-i.; Nomura, R.; Nakano, K.; Takano, K. Role of N1-Domain, Linker, N2-Domain, and Latch in the Binding Activity and Stability of the Collagen-Binding Domain for the Collagen-Binding Protein Cbm from Streptococcus mutans. Physchem 2024, 4, 120-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4020009
Nishi A, Hirata A, Mukaiyama A, Tanaka S-i, Nomura R, Nakano K, Takano K. Role of N1-Domain, Linker, N2-Domain, and Latch in the Binding Activity and Stability of the Collagen-Binding Domain for the Collagen-Binding Protein Cbm from Streptococcus mutans. Physchem. 2024; 4(2):120-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishi, Akari, Azumi Hirata, Atsushi Mukaiyama, Shun-ichi Tanaka, Ryota Nomura, Kazuhiko Nakano, and Kazufumi Takano. 2024. "Role of N1-Domain, Linker, N2-Domain, and Latch in the Binding Activity and Stability of the Collagen-Binding Domain for the Collagen-Binding Protein Cbm from Streptococcus mutans" Physchem 4, no. 2: 120-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4020009
APA StyleNishi, A., Hirata, A., Mukaiyama, A., Tanaka, S.-i., Nomura, R., Nakano, K., & Takano, K. (2024). Role of N1-Domain, Linker, N2-Domain, and Latch in the Binding Activity and Stability of the Collagen-Binding Domain for the Collagen-Binding Protein Cbm from Streptococcus mutans. Physchem, 4(2), 120-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem4020009






