Interactive Effects of Ionophore Antibiotic Monensin and Polystyrene Microplastics on the Growth and Physiology of Microcystis aeruginosa
Abstract
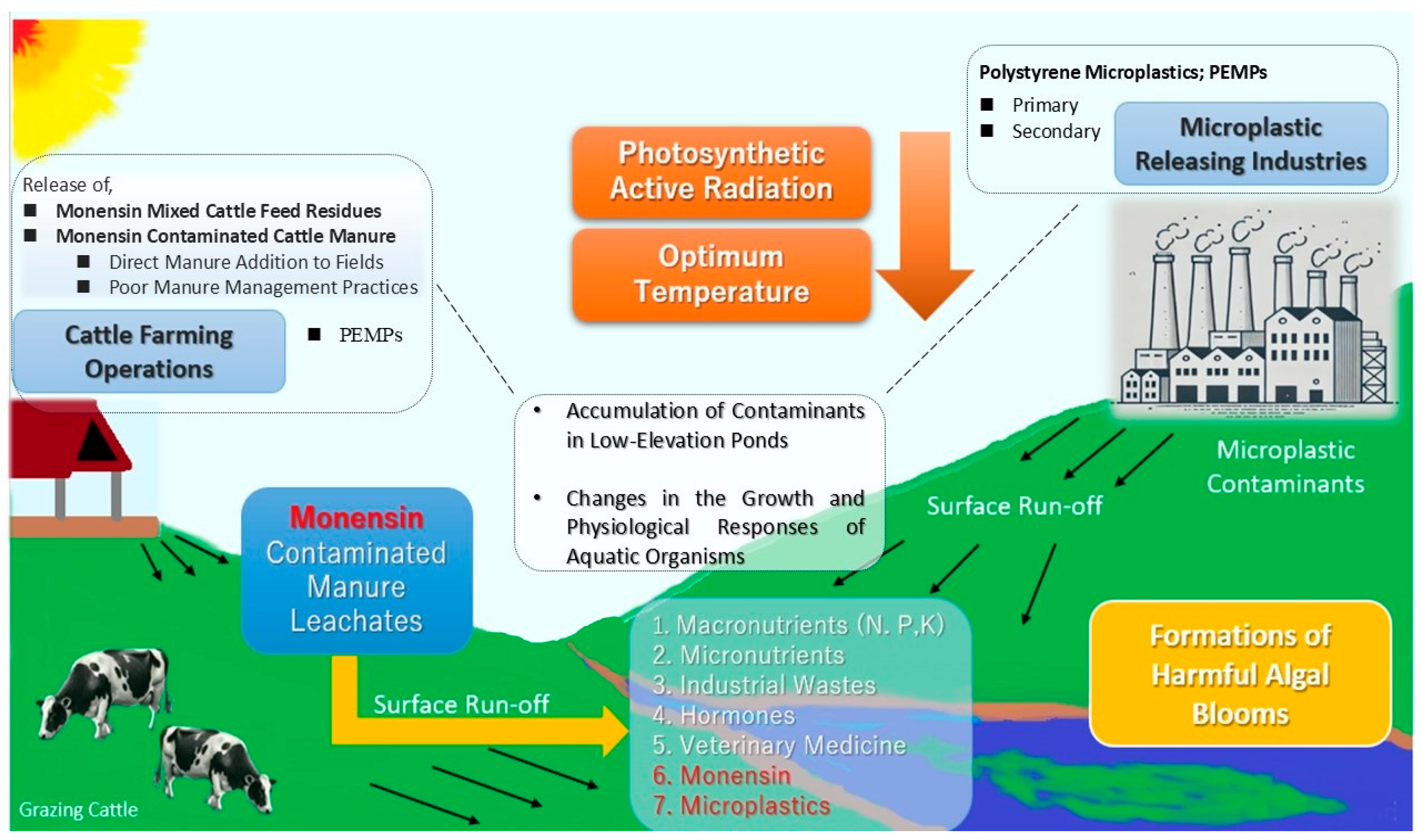
1. Introduction
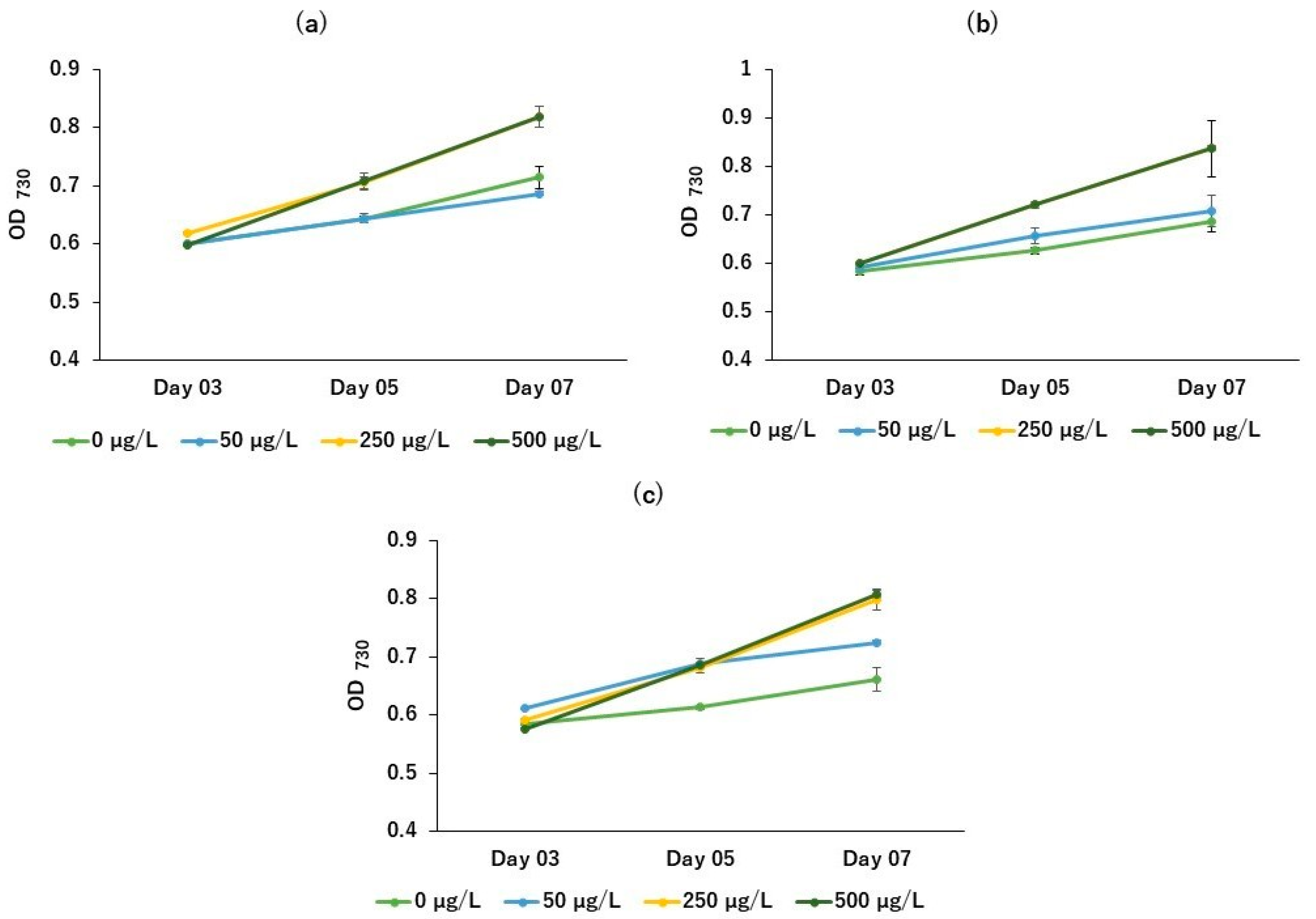
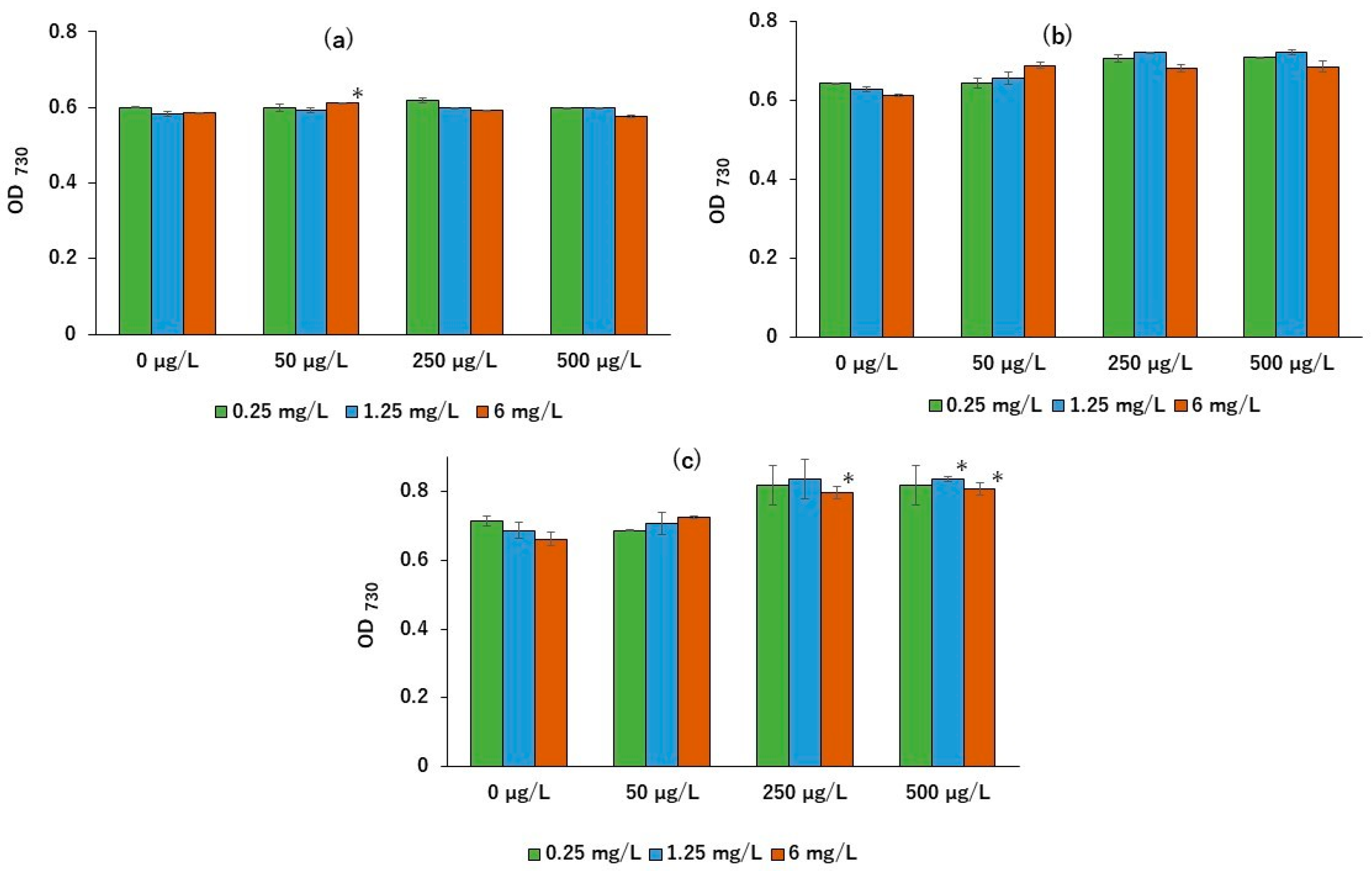
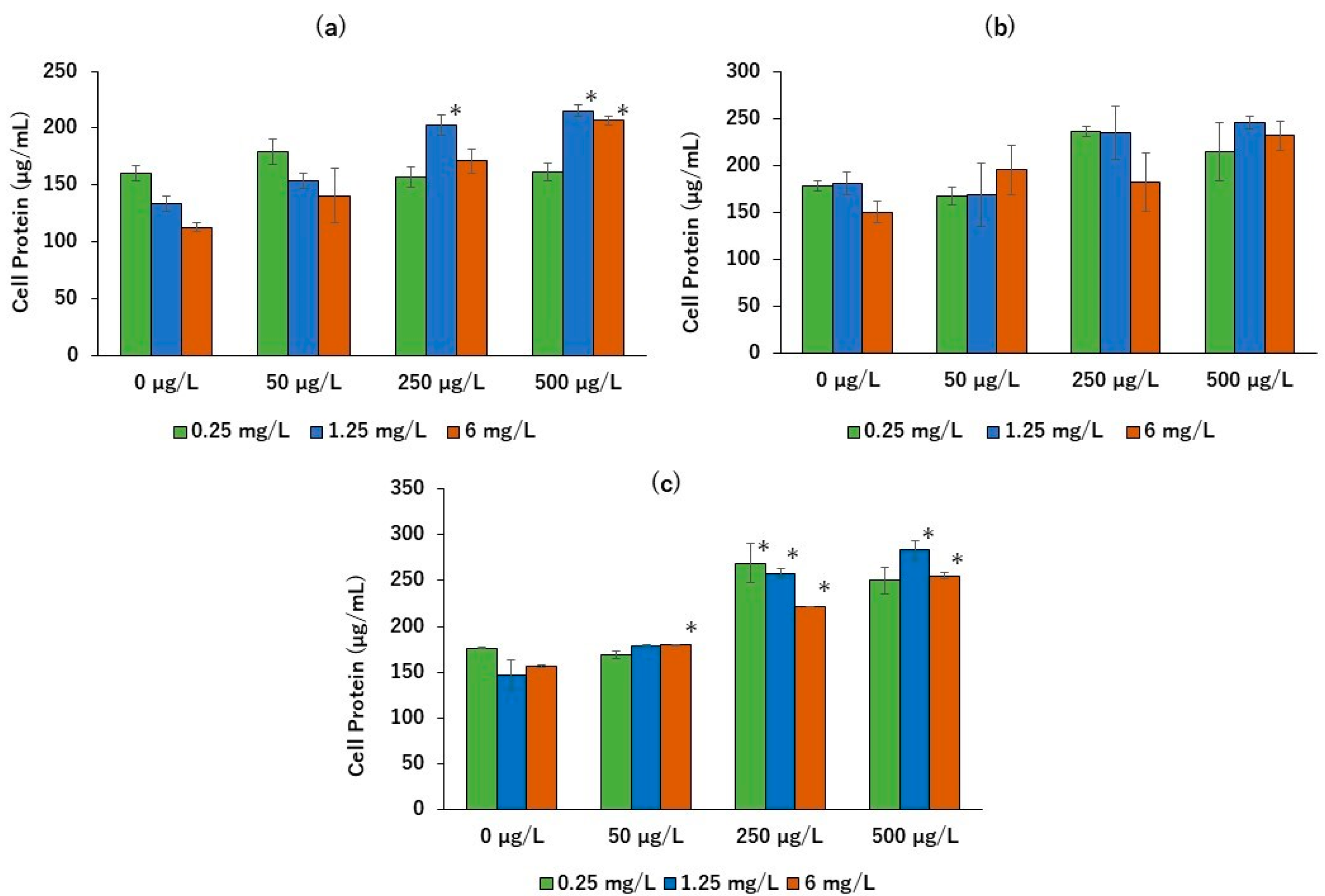
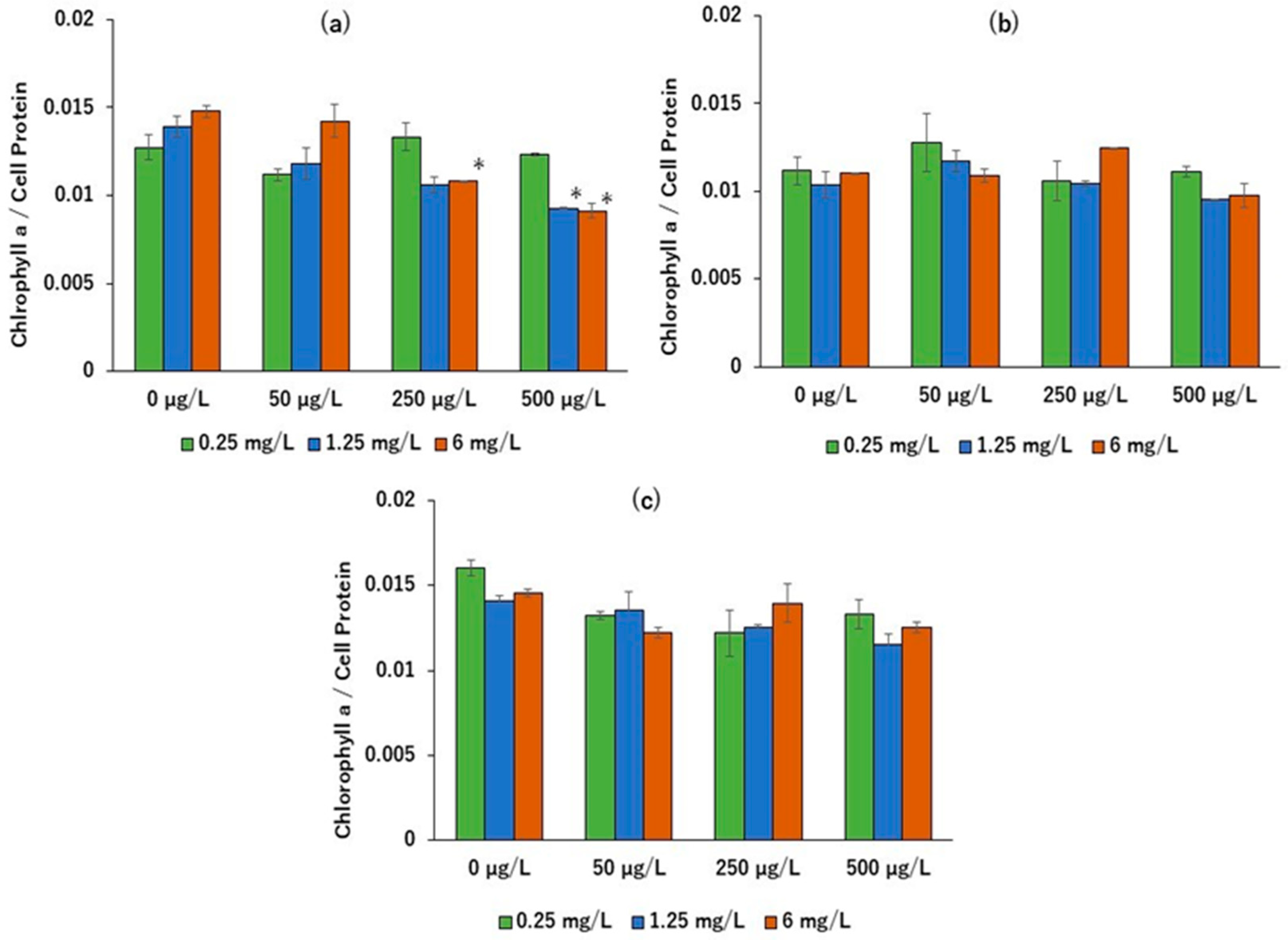
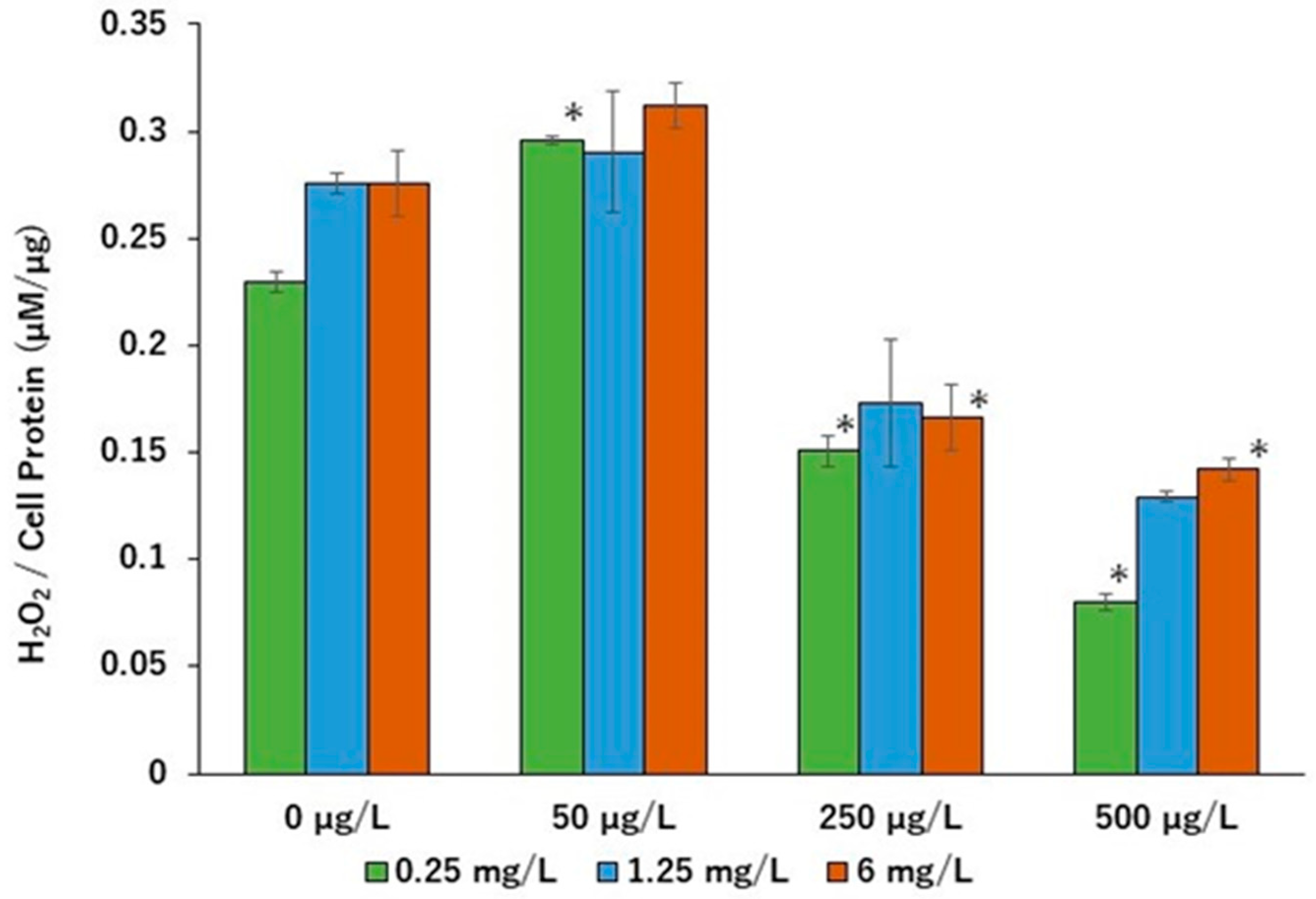
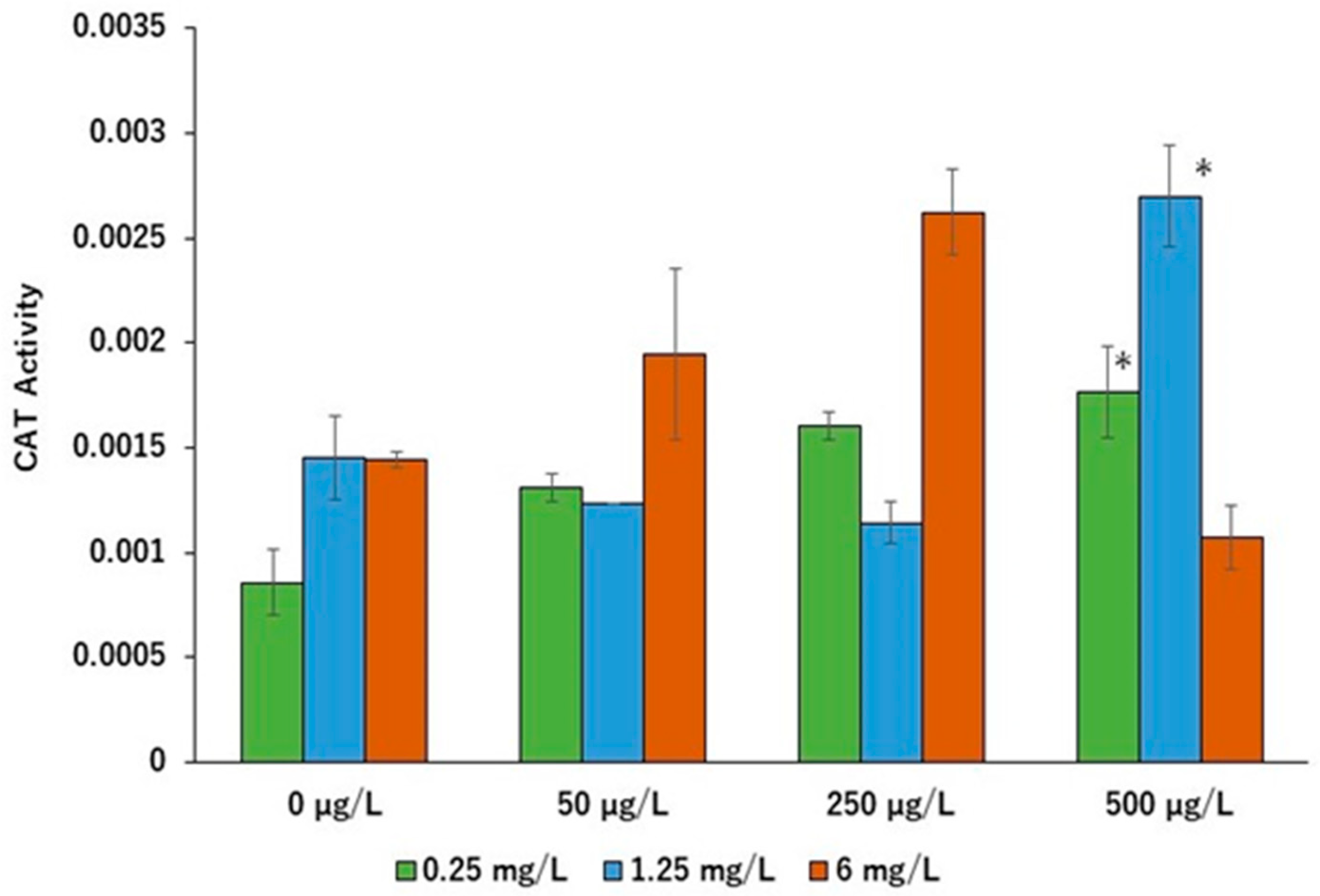
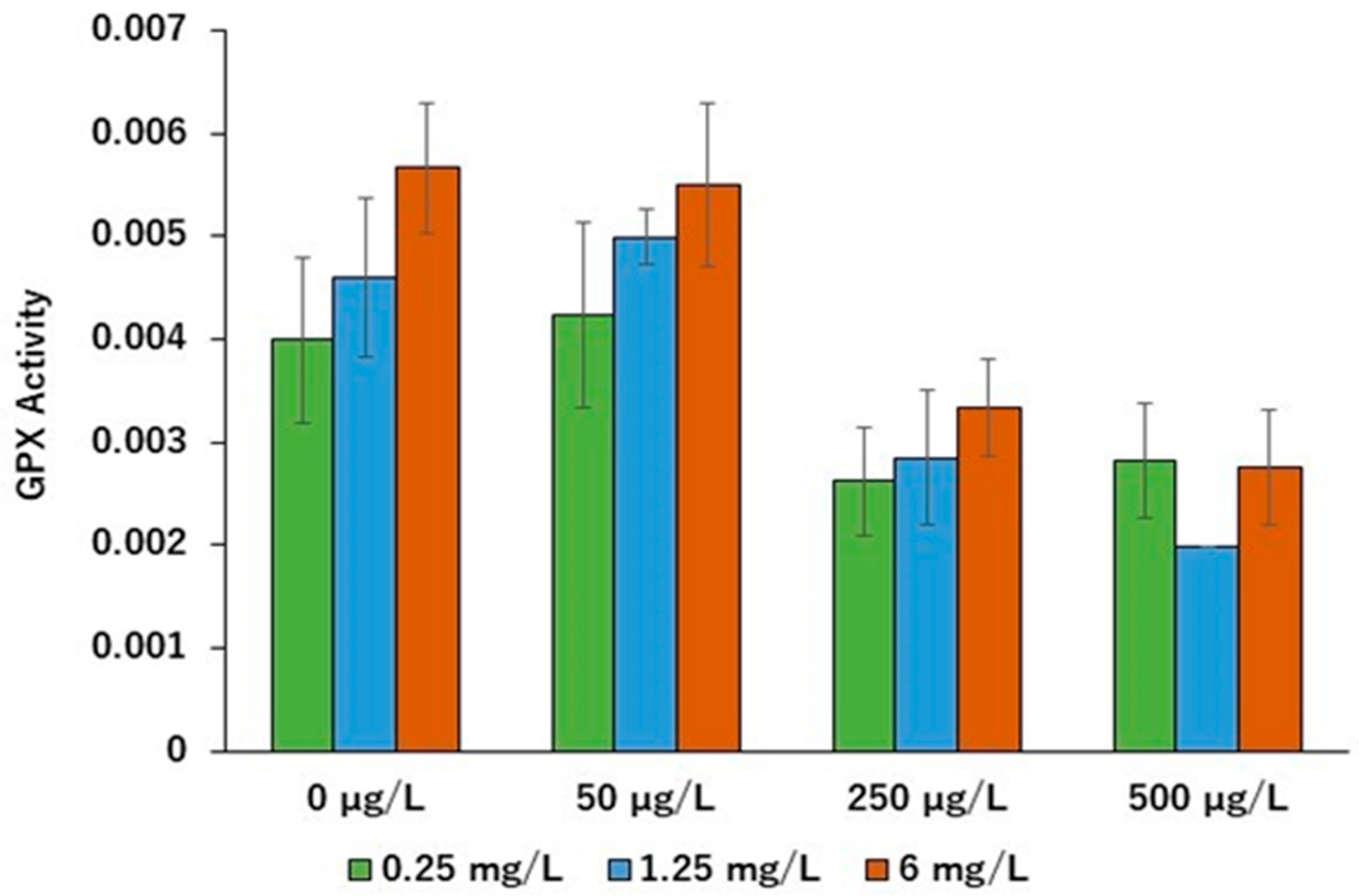
2. Results
3. Discussion
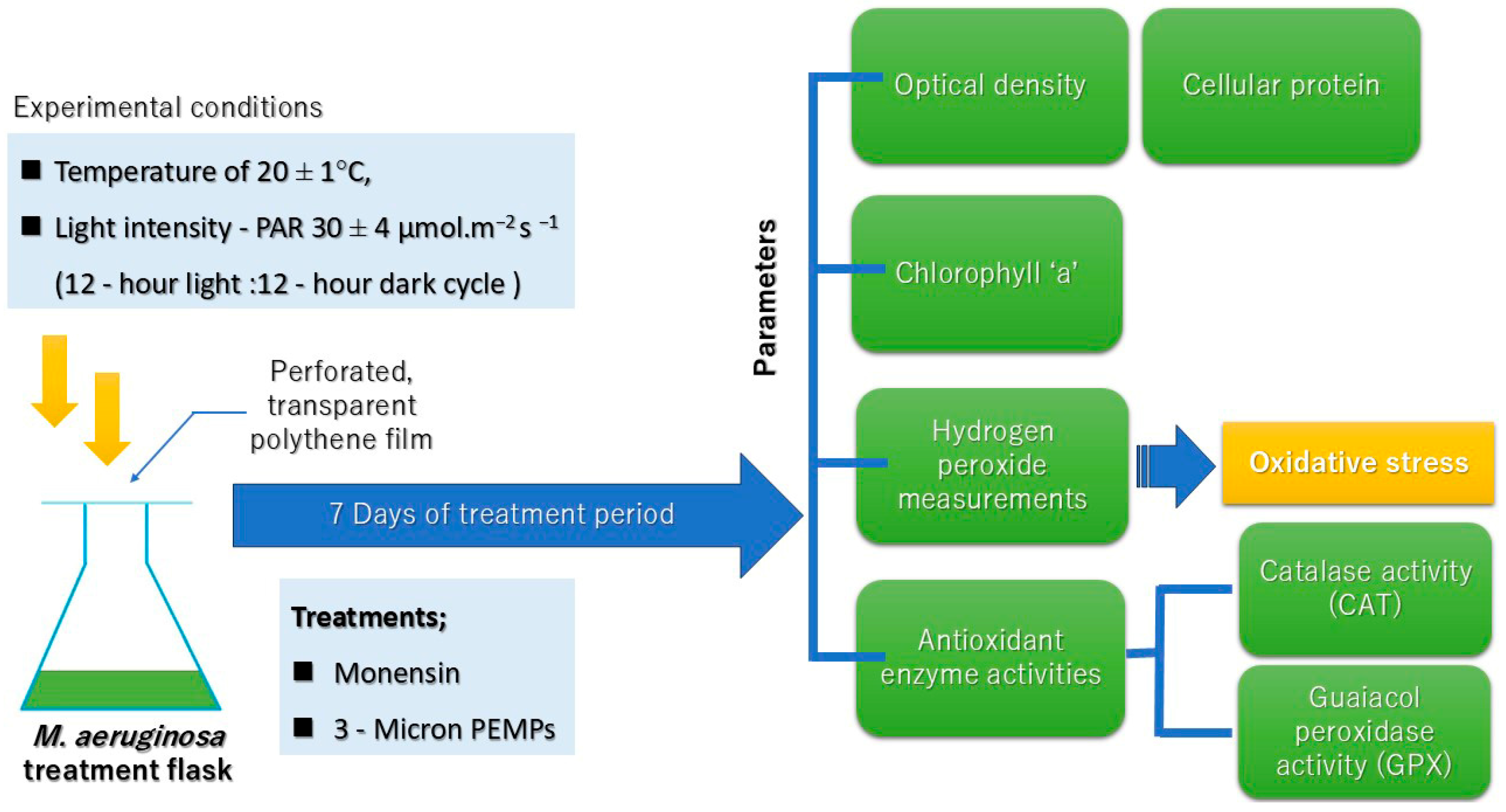
4. Materials and Methods
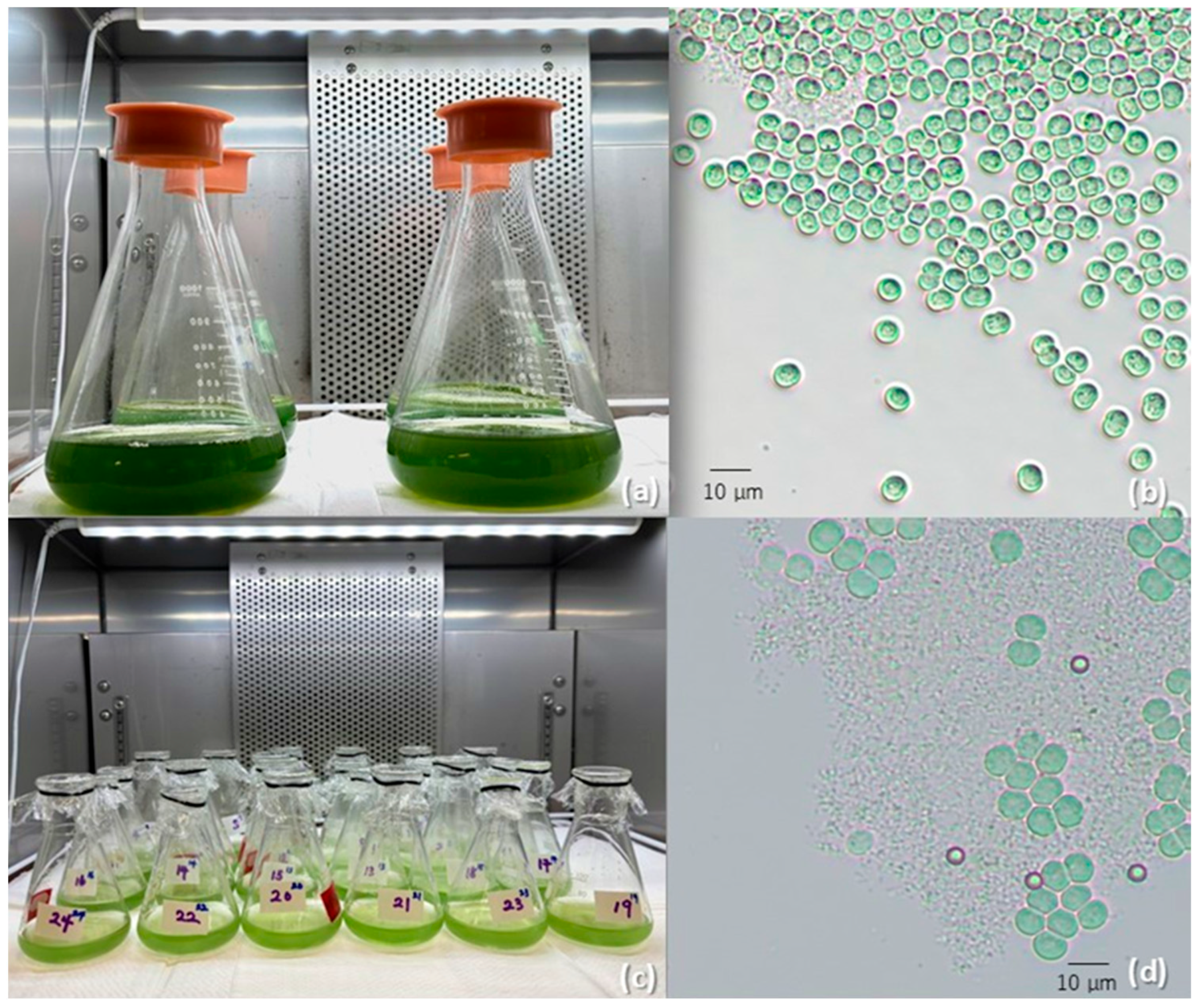
4.1. Cyanobacteria Culture Conditions
4.2. Preparation of the Treatments
4.3. Experimental Setup
4.4. Optical Density Measurements (OD730)
4.5. Chlorophyll ‘a’ Measurement
4.6. Cellular Protein Content
4.7. Hydrogen Peroxide Measurement
4.8. Antioxidant Activity Measurements
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAB | Harmful algal blooms |
| CAT | Catalase activity |
| GPX | Guaiacol peroxidase activity |
| MS | Monensin |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| MP | Microplastics |
| NP | Nano-plastics |
| PAR | Photosynthetically active radiation |
| OD730 | Optical density |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Zurawell, R.W.; Chen, H.; Burke, E.E.; Prepas, E.E. Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: A review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2005, 8 Pt B, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Kang, S.U.; Lim, A.S. The Harmful Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa Differently Affects the Growth Rate and Photosynthetic Efficiency of Several Species of Marine Phytoplankton. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2025, 17, e70091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juttner, F.; Watson, B. Biochemical and Ecological Control of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol in Source Waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, F.; Shi, X. Effects of filtered lake water on colony formation and growth rate in Microcystis aeruginosa of different physiological phases. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2005, 20, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Igarashi, Y.; Luo, F. Algicidal Effect of Tryptoline Against Microcystis aeruginosa: Excess Reactive Oxygen Species Production Mediated by Photosynthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806 Pt 4, 150719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, L.; Krock, B.; Minaglia, M.C.C.; Rosso, L.; Houghton, C.; Sedan, D.; Malanga, G.; Espinosa, M.; Andrinolo, D.; Hernando, M. Growth, Toxin production, Active Oxygen Species and Catalase Activity of Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanophyceae) Exposed to Temperature Stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 189, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Jiang, M. Physiological and Metabolic Responses of Microcystis aeruginosa to a Salinity Gradient. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 13226–13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B. Interactions Between Microcystis aeruginosa and Coexisting Amoxicillin Contaminant at Different Phosphorus Levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, S.; Horvat, A.J.M.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Kaštelan-Macan, M. Determination of pKa values of active pharmaceutical ingredients. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.G.; Lissemore, L.; Sibley, P.K.; Solomon, K.R. Effects of monensin on zooplankton communities in aquatic microcosms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6620–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odongo, N.E.; Bagg, R.; Vessie, G.; Dick, P.; Or-Rashid, M.M.; Hook, S.E.; Gray, J.T.; Kebreab, E.; France, J.; McBride, B.W. Long-Term Effects of Feeding Monensin on Methane Production in Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appuhamy, J.A.D.R.N.; Strathe, A.B.; Jayasundara, S.; Wanger-Riddle, C.; Dijkstra, J.; France, J.; Kebreab, E. Anti-methanogenic effects of monensin in dairy and beef cattle: A meta-analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5161–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Harter, T.H.; Bergamaschi, B.A. Environmental occurrence and shallow ground water detection of the antibiotic monensin from dairy farms. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37 (Suppl. S5), S-78–S-85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoz, M.A.; Wooten, K.J.; Clendening, S.L.; Hensley, L.L.; Smith, L.R.; Smith, P.N. Transport mechanisms for veterinary pharmaceuticals from beef cattle feedyards to wetlands: Is aerial deposition a contributing source. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassman, S.A.; Lee, L.S. Sorption and degradation in soils of veterinary ionophore antibiotics: Monensin and lasalocid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.L.; Demetrio, P.M.; Capparelli, A.L.; Marino, D.J.G. Behavior of ionophore antibiotics in aquatic environments in Argentina: The distribution on different scales in water courses and the role of wetlands in depuration. Environ. Int. 2019, 133 Pt A, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolliver, H.; Kumar, K.; Gupta, S.; Singh, A. Application of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Analysis for Determination of Monensin in Environmental Samples. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Chen, Y.; Ling, Z.; Xiang, P. Microplastics in the human body: A comprehensive review of exposure, distribution, migration mechanisms, and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, C.; Domenech, J.; Salazar, M.; Pastor, S.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Nano-plastics as a potential environmental health factor: Effects of polystyrene nanoparticles on human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Environ. Sci. 2020, 7, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandraiah, K.; Ameer, K.; Jiang, G.; Hong, G. Micro- and nano-plastic contamination in livestock production: Entry pathways, potential effects and analytical challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Jiao, J.; Yang, Z.; Lv, M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, C.; He, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Renewable sourced biodegradable mulches and their environment impact. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 268, 109375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanand, A.C.; Mohapatra, S.; Tyagi, V.K. Microplastics in aquatic environment: Challenges and perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, W.K.; Wipf, H.K.; Simon, W. Alkali cation specificity and carrier properties of the antibiotics nigericin and monensin. Helv. Chim. Acta 1970, 53, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeaux, R.; Sandeaux, J.; Gavach, C.; Brun, B. Transport of Na+ by monensin across bimolecular lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1982, 684, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B. A proposed mechanism of monensin action in inhibiting ruminal bacterial growth: Effects on ion flux and protonmotive force. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 64, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.S.; Singh, S.; Bahmid, N.A.; Shyu, D.J.H.; Dominguez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Camera, J.S. Polystyrene microplastic particles in the food chain: Characteristics and toxicity—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, T.; Budhiraja, V.; He, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Arora, A.; Koutsos, V.; Chatzisymeon, E. Antibiotic Adsorption by Microplastics: Effect of Weathering, Polymer Type, Size, and Shape. Environments 2025, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, R.; Xing, B. Interaction of Microplastics with Antibiotics in Aquatic Environment: Distribution, Adsorption, and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15579–15595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawadu, B.; Senavirathna, M.D.H.J.; Fujino, T. Individual and combined effects of ionophore antibiotics monensin and lasalocid on growth, oxidative stress and antioxidant responses of Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 90, 2585–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behara, S.; Das, S. Environmental impacts of microplastic and role of plastisphere microbes in the biodegradation and upcycling of microplastic. Chemosphere 2023, 334, 138928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Meredith, D.A.; Johnson, M.V.; Morton, S.L.; Perkins, D.A.K.; Reavie, E.D.; Scott, G.I.; Smith, S.A.; Steevens, J.A. Are Harmful Algal Blooms Becoming the Greatest Inland Water Quality Threat to Public Health and Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, D.J.; Okada, E.; Iturburu, F.G.; De Gerónimo, E.; Cantón, G.; Aparicio, V.C.; Costa, J.L.; Menone, M.L. Monensin occurrence in surface water and its impact on aquatic biota in a stream of the southeast Pampas, Argentina. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8530–8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yanyao, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z. Growth inhibition, toxin production and oxidative stress caused by three microplastics in Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Boiti, A.; Vallone, D.; Foulkes, N.S. Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling and Oxidative Stress: Transcriptional Regulation and Evolution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, N.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, N.; Guo, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, X.; et al. Higher toxicity induced by co-exposure of polystyrene microplastics and chloramphenicol to Microcystis aeruginosa: Experimental study and molecular dynamics simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Xing, Y.; Ya, H.; Lv, M.; Wang, X. Current status of microplastics pollution in the aquatic environment, interaction with other pollutants, and effects on aquatic organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16830–16859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Nałęcz-Jawecki, G.; Giebułtowicz, J.; Chojnacka, J.; Pajchel, Ł.; Drobniewska, A. The Sorption of Antidepressant Pharmaceuticals on Virgin and Aged Microplastics Is Lower than Bioconcentration in Protozoa. Water 2024, 16, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Ruiz, M.; Zhang, C. Oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 33, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, S.; Duan, X.; Zhang, N.; Ren, Y.; Liang, L.; Ye, X. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on growth, physiological traits of Microcystis aeruginosa and microcystin production and release. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, R.M.; Manoylov, K.M. The Effects of initial cell density on the growth and proliferation of the potentially toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 7, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keung Wong, Y. Algae; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oginni, G.F.; Dzakpasu, L.S.; Babu, W.A.; Ezekiel, A.O. Relative effects of varying light conditions on the growth of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Environ. Prot. 2021, 12, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, K.H. Chlorophyll and carotenoids; pigments of photosynthetic bio membranes. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; Volume 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10260; Water Quality—Measurement of Biochemical Parameters—Spectrometric Determination of the Chlorophyll-a Concentration. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992.
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.D.; Iviacrae, E.A.; Fergusont, A.B. Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium(W). Anal. Biochem. 1984, 139, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, J.F.; Janero, D.R. Microplate superoxide dismutase assay employing a nonenzymatic superoxide generator. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 232, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manawadu, B.; Senavirathna, M.D.H.J.; Fujino, T. Interactive Effects of Ionophore Antibiotic Monensin and Polystyrene Microplastics on the Growth and Physiology of Microcystis aeruginosa. Stresses 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030043
Manawadu B, Senavirathna MDHJ, Fujino T. Interactive Effects of Ionophore Antibiotic Monensin and Polystyrene Microplastics on the Growth and Physiology of Microcystis aeruginosa. Stresses. 2025; 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleManawadu, Behen, Mudalige Don Hiranya Jayasanka Senavirathna, and Takeshi Fujino. 2025. "Interactive Effects of Ionophore Antibiotic Monensin and Polystyrene Microplastics on the Growth and Physiology of Microcystis aeruginosa" Stresses 5, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030043
APA StyleManawadu, B., Senavirathna, M. D. H. J., & Fujino, T. (2025). Interactive Effects of Ionophore Antibiotic Monensin and Polystyrene Microplastics on the Growth and Physiology of Microcystis aeruginosa. Stresses, 5(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030043






