Abstract
For animals that typically live in groups or family units, being isolated from their conspecifics can be stressful. Horned passalus beetles (genus Odontotaenius), inhabit decaying logs in forests in the eastern United States. While not a truly social insect, they do coinhabit logs and maintain family units, and they are known to communicate with each other using stridulations that produce varying types of “chirps”. This project investigated if the auditory environment within these logs affects the beetles, specifically by exposing larval or adult beetles in a lab to sounds of (1) other beetles chirping, (2) no sound, or (3) the sounds of crickets, for varying time periods. Beetles were weighed before and after the exposures to determine changes in body mass. Beetle larvae experienced the slowest growth rates when listening to crickets or no sound, and the highest growth rates when hearing adult chirps. Adult beetles experienced mass losses in the treatments without beetle sounds, and this finding was replicated in three different experiments. The mass loss was greatest in the experiment that had the longest duration. The fact that the mass losses were observed in both the silent treatment, plus the treatment of cricket sounds, indicates that the lack of conspecific sounds (of other passalus beetles) was driving the effect. Surprisingly, there was no added effect of nematode parasitism on adult weight loss. Also, there was no evidence that the beetles were foraging less in the treatments without beetle sound, which suggest those beetles were experiencing elevated metabolism. The reduced growth rates and lost mass are signs that the beetles experienced chronic stress when deprived of the sounds of their kin. Combined, these experiments demonstrate how the acoustic environment, and especially the sounds of other beetles, is important to the lives of these insects, perhaps owing to the fact that they live in dark tunnels.
1. Introduction
Animals can become stressed when faced with unfamiliar conditions, especially those that involve anthropogenic, and therefore unnatural stimuli. For example, birds can become stressed when they nest in close proximity to loud traffic noise [1]. Similarly, monarch butterfly caterpillars experience an increase in heart rate when exposed to road noise [2]. Marine animals also experience stress after exposure to boat noises [3]. While these examples highlight how excess noise can be stressful to organisms, rarely does the opposite happen, when the absence of certain noises can lead to stress. For example, social or group-living animals live their entire lives in close proximity to other individuals, either with family members or unrelated conspecifics, often with near-constant communication occurring. Such close interactions require routine communication for the group to function, such as by visual cues [4], chemical messengers [5], vibrations [6], or by acoustic means [7,8]. Individuals who are deprived of this close contact due to physical isolation typically exhibit signs of chronic stress [9].
This project examines how the presence or absence of auditory stimuli affects the fitness of a sub-social insect that communicates with conspecifics using auditory signals. Horned passalus beetles are saproxylic insects endemic to the eastern United States and which build networks of tunnels in decaying hardwood logs in forests (Figure 1). Recent evidence shows that in the United States, there are four cryptic species within the genus Odontotaenius, with different species even inhabiting the same log [10]. Within the state of Georgia, where this project took place, there are two species that are identical in appearance: O. disjunctus, and O. cryptodisjunctus [10]. For all passalus beetles, the majority of their 1–2 year lives are spent in log tunnels, where adults care for their grubs in the summer by providing them with triturated wood [11,12]. Adults communicate with a series of chirping sounds produced by stridulating a section of their abdomen against the elytron. Larvae also have a mechanism for producing sound using their metathoracic leg, which is scraped against the mesothoracic coxa [13]. The adult chirps can vary in complexity, so that the beetles actually have a rich repertoire of communication signals, which they use to participate in their log-living societies [14,15]. In fact, horned passalus have 14 different types of chirps for different situations, which they use to indicate alarm, aggregation, aggression, courtship, copulatory behavior, postcopulatory behavior, etc. [14]. Logs can have many families of beetles living in them, often with tunnels that connect, or at least are nearby (Davis, pers. obs.). Given this close proximity and social lifestyle, the beetles likely spend the majority of their lives listening to the everyday sounds of neighboring beetles, or members of their family.
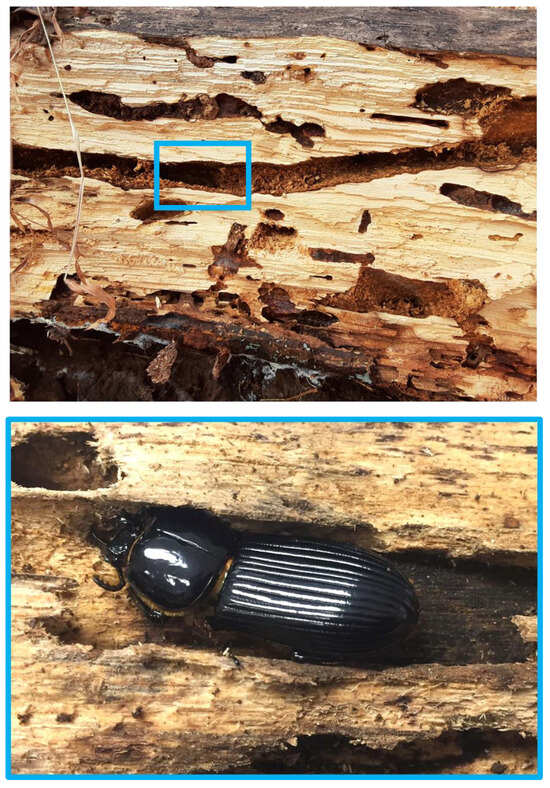

Figure 1.
Photo of the inside of a decaying hardwood log with tunnels of horned passalus beetles (genus Odontotaenius, top) and a closeup of one adult beetle (bottom). Photographs taken by A. Davis.
The rationale for this project stems from a prior laboratory study of these beetles in the author’s lab; specifically, observations of how adult beetles appear to lose body mass when collected in the wild and brought indoors [16]. Mass loss can be a sign of stress [17], and at the time, it was thought that the beetles simply perceived the act of collection (i.e., removal from their log homes) as a stressor. However, another possible explanation is that the lab environment does not match their natural state, because in most projects in this lab, the beetles are typically housed individually in containers filled with decaying wood [16,18,19,20], which allows for individual monitoring and study. In this type of housing (i.e., individually), the beetles could perceive the lack of social stimuli to be stressful. Here, a series of laboratory experiments are described that attempt to assess this idea more rigorously, whereby larval and adult passalus beetles were housed and exposed to different acoustic stimuli, while changes in their body mass were tracked. These experiments reveal how the absence of such stimuli appears to (1) disrupt the growth of beetle larvae and (2) result in weight loss in adult beetles. To the author’s knowledge, this represents the first demonstration of how individuals of this species can become stressed if they perceive themselves as alone.
2. Results
2.1. Larvae Experiment
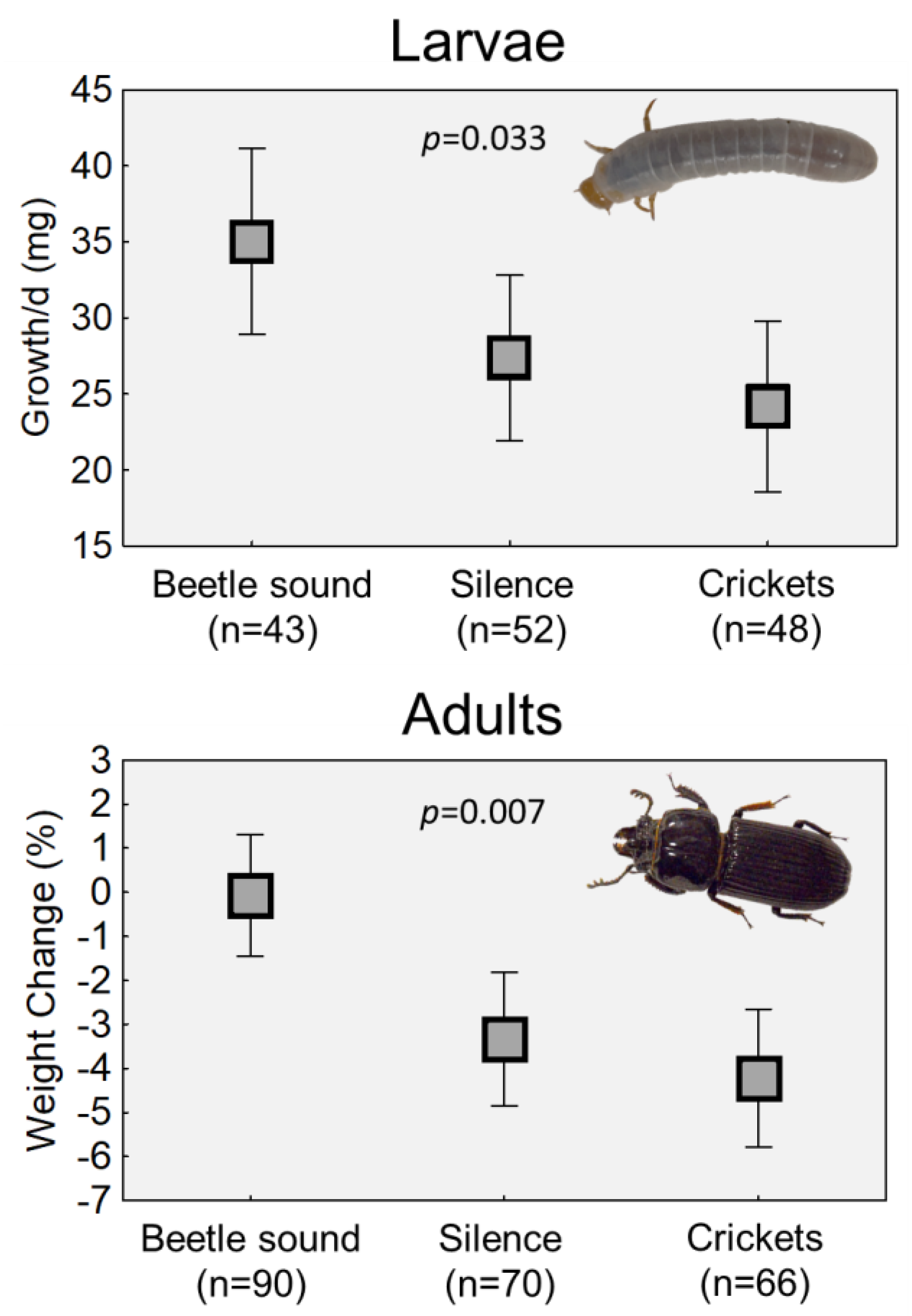
The average growth rates of beetle grubs were significantly different across the sound treatments (p = 0.033; see Table 1A). Grubs that were exposed to sounds of adult beetles had the highest mean daily growth (Figure 2). The growth rate of grubs that were not exposed to sound was 22% lower than that of those exposed to the beetle sound treatment, and the growth rate of grubs in the cricket sound group was 31% lower.

Table 1.
Summary of ANOVA model results, testing the effects of sound stimuli (treatment) on larval beetle growth (A) and adult beetle body mass maintenance. Two models were tested for the adult beetle data, one using all available data from three replicate experiments (only including predictors with data across all experiments, B) and one using all data from two replicates where beetle sex and nematode parasitism was available (C). Replicate was included as a random factor in the adult models.
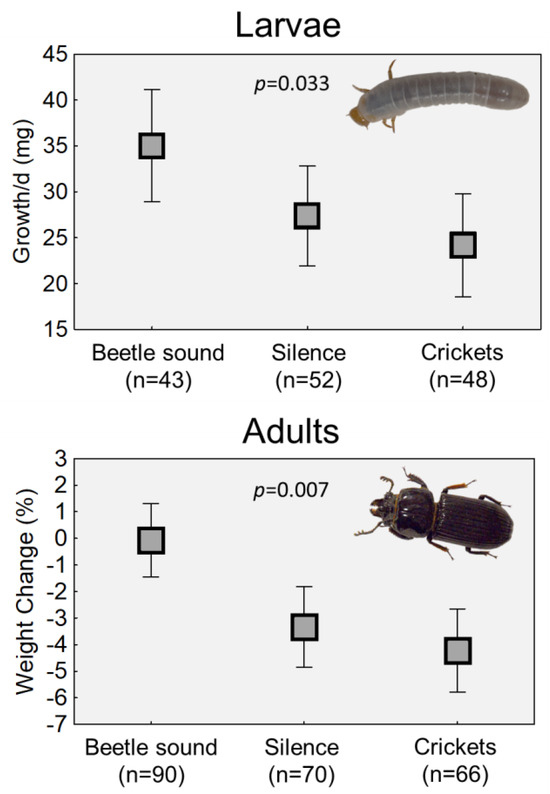
Figure 2.
Effects of the presence or absence of conspecific beetle sounds on growth rates of larvae (top) and weight maintenance of adults (below). Each graph shows the means of treatment groups plus 95% confidence intervals. The adult graph shows combined data from three different replicated trials. Beetles were exposed to sounds of adult “chirping” (beetle sound), no sounds (silence) or to the sound of crickets. The duration of the sound treatment varied with each trial, but the pattern remained the same. p values denote the significance of the treatment effect in analyses (see Table 1).
2.2. Adult Experiments
Because the three replicate experiments differed in terms of the variables collected, two modeling approaches were used, but in both cases, regardless of which variables were included, there was significant variation in the sound treatment-related mass changes in adults (p = 0.0002, or p = 0.0073; Table 1B,C). The beetles exposed to sounds of other beetles tended to remain the same mass at the end of the exposure period (Figure 2). Meanwhile, beetles that were exposed to no sounds or to the sounds of crickets lost about 3–5% of their initial mass.
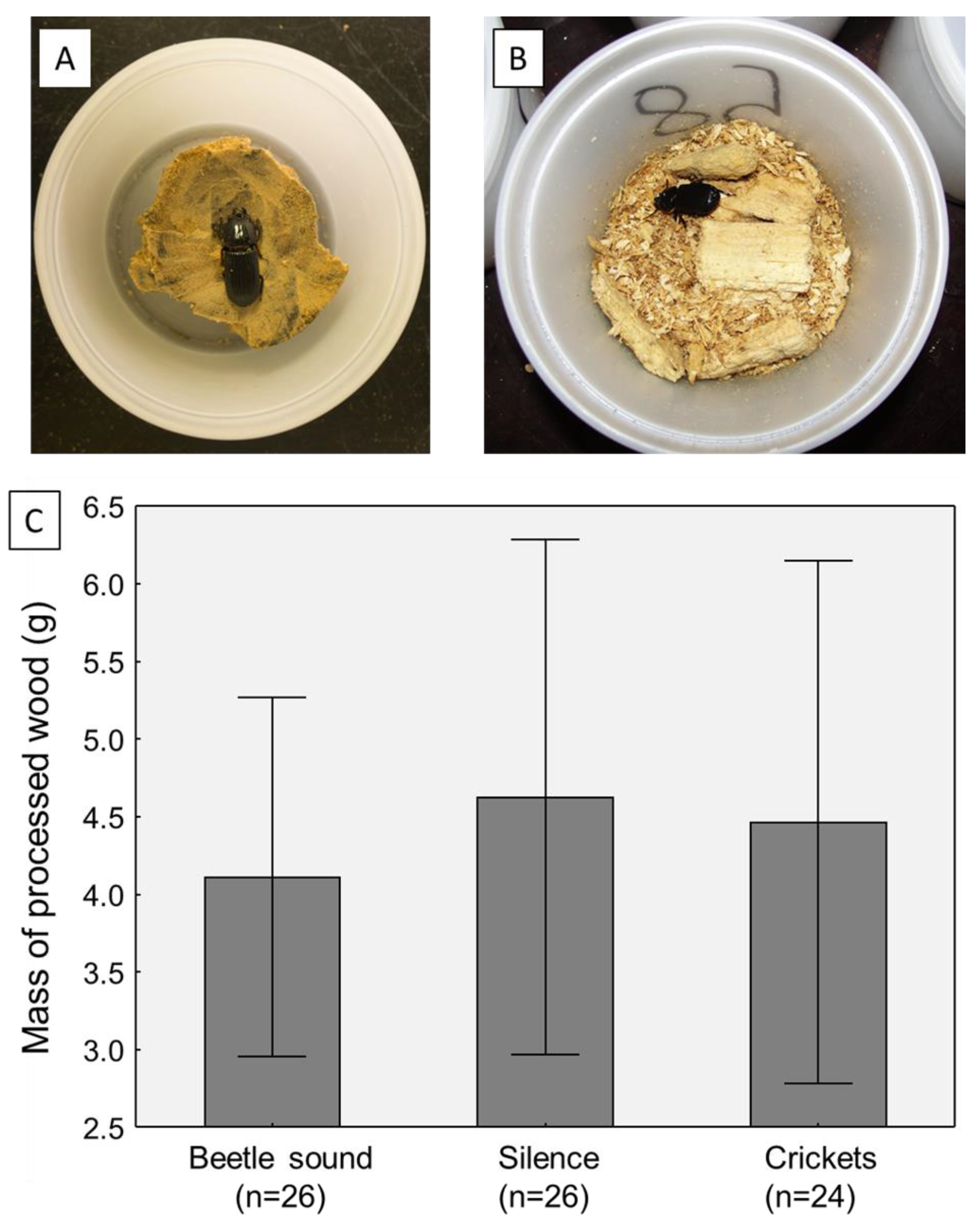
In the final experiment, the mass of each beetle’s processed wood was measured to determine if the beetles were lowering their foraging activity in the treatments, perhaps explaining the body mass losses. This was not the case; there was no significant effect of sound treatment on the final mass of processed wood in the beetle containers (one-way ANOVA, F2,71 = 0.177, p = 0.8380; Figure 3).
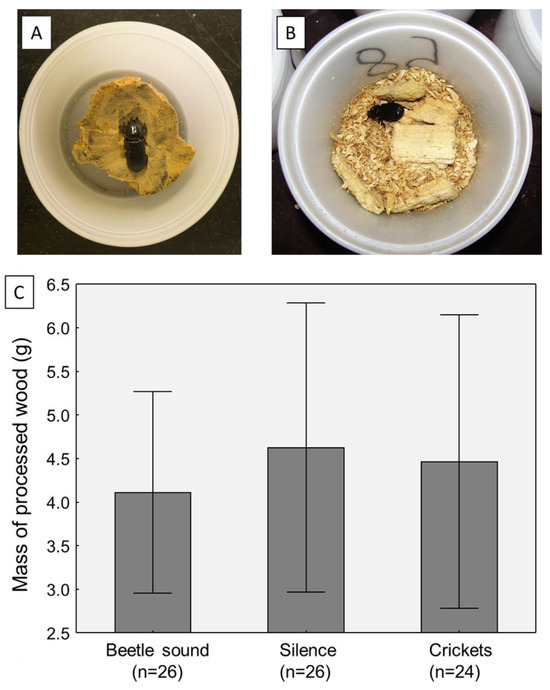
Figure 3.
Comparison of foraging/food consumption activity of adult beetles across sound treatments in the third experiment (where this was tracked). All beetles started with a uniform block of decayed hardwood (A), and at the end of the trials, the wood debris and frass (B) were weighed. (C) Plot of the average masses of processed wood from the duration of the sound exposure trials (7 days). Graph shows means plus 95% confidence intervals.
Finally, both models showed significant differences in mass loss across replicates, likely because of the different exposure periods in each case. In fact, comparisons across experiments revealed that the largest difference between sound treatments was observed in the 7-day exposure experiment (Figure S1).
3. Discussion
This project sought to ascertain how the acoustic environment affects the lives of horned passalus beetles, which live in family groups within decaying logs. Living in groups or families necessitates a degree of routine communication between individuals. By exposing beetles to the presence or absence of conspecific sounds for multiple days, this study showed that (1) beetle grubs show reduced growth rates when deprived of adult sounds, and (2) adult beetles lose mass when not exposed to other beetle sounds (Figure 2). Since the mass losses were seen when beetles were kept in silence, plus when they were exposed to only the sound of crickets, it is reasonable to conclude that it was the absence of sounds from other passalus beetles that drove the mass losses, and not necessarily the absence of sound. In other words, the beetles lost mass when they perceived themselves to be isolated from their conspecifics.
While this experiment focused only on the acoustic environment of these beetles, the treatments with no beetle sounds were not that different from the well-studied phenomenon of “social isolation” in social insects or other group-living animals (since the lack of other beetle sounds would simulate isolation). From this body of work, it is clear that when individuals from a colony are physically isolated from the rest of the colony, they typically undergo behavioral and physiological changes consistent with stress, including increases in stress hormones in small mammals [9], reduced lifespan in ants [21], reduced growth in developing mites [22] and heightened aggression in crickets [23]. Given these findings, the results of the current investigation appear consistent with the notion that passalus beetles also experience the negative impacts of “social isolation”. By inference, this suggests that these beetles will function most adequately (i.e., as in their ecological niche as wood processors) when surrounded by conspecifics.
As part of the final experiment, the wood consumption of the adult beetles was measured, similar to the experiment conducted by Davis and Prouty [24], to ascertain if the weight loss observed in the quiet or cricket sound treatments was because of a reduction in foraging level and/or food consumption. Surprisingly, the answer was no, as there was no difference in wood breakdown rates between the three sound treatments (Figure 3). This argues that beetles were not reducing their foraging levels in the treatments without beetle sounds. Given this scenario, a possible mechanism for the weight loss is an elevation in body metabolism, which would be consistent with elevated stress levels [17].
Interestingly, the results from this project differ from a prior study on this species in which young adult beetles had been isolated from their family units for 6–8 weeks in a lab setting, in conditions that were not that different from those of the current project [25]. In that project, the beetles were simply held in plastic containers with wood debris (no external sound was supplied), and beetle mass was tracked weekly. Yet, that experiment saw no overall loss of body mass in the isolated beetles, and in fact they gained mass, as did those that were housed with family members. Since that project’s time course was much longer than the current one, this could mean that the mass loss resulting from isolation can eventually be compensated for. Or perhaps the difference was due to the beetles in that study being very young (freshly eclosed), compared to the generally older beetles used here (all adult beetles were collected during the months after the typical eclosion period). Given that three separate replicate experiments were conducted in the current study, with qualitatively similar outcomes (see Figure S1), the result found here seems robust.
It is worth noting here that the magnitude of the sound treatments differed across the three replicate experiments on the adult beetles, as noted in Table 1B,C. This is due to the difference in exposure times across the replicates, which were 3 days in 2021, 4 days in 2022 and 7 days in the 2023 experiment. These differences are highlighted in Figure S1, which compares the three experiments. In short, increasing the exposure time resulted in the sounds (or absence of sounds) having greater effects. This finding makes it difficult to interpret the lack of an effect of social isolation found in the prior Dillard and Maigret [25] study, which lasted over 6 weeks.
Interestingly, the presence of the nematode parasite, C. passali, had no discernable effect on adult beetle mass change in the experiments where this was tracked (Table 1C). Prior research on this parasite has revealed how it can diminish aspects of the host’s acute stress response [26,27], as well as reduce behaviors and bodily functions that require bouts of energy [16,20]. Thus, the parasites appear to exact the heaviest toll on the host during times of acute energetic need. Meanwhile, beetles show minimal negative effects during everyday routine activities. In fact, in some wild-caught collections of beetles, individuals with parasites tend to be larger [28]. An important piece of evidence though, is that parasitized adults tend to consume more wood [24], perhaps as a compensatory mechanism for the energetic drain of the parasites. This may be the reason why we saw no effect of the C. passali nematodes on host weight changes.
This study also documented differences in the magnitude of the mass loss between male and female beetles (Table 1C). A comparison of the means shows that females tended to lose more mass than males. Possibly, this is simply because females tend to be larger than males to begin with [28], so that their relative losses seem larger. Alternatively, recent evidence from other work in this lab shows how female passalus beetles tend to be more active than males [29]. This argues that their energy demand is inherently greater than that of males. Consistent with this, other work has demonstrated how female passalus beetles have greater metabolic rates than males when dealing with an energetic demand [20]. It would be logical then, if females also experience a greater mass drain as a result of being stressed.
The discovery that passalus beetles lose weight because of social isolation helps to clarify the findings from a prior project in this lab, which involved the same species. Specifically, it was found that when wild-collected adults were brought into the lab and housed in individual plastic containers, they tended to lose weight [16]. After 1 week in this captive setting, the beetles had lost between 10 and 14% of their mass compared to the day of collection from the field. Given that the captive setting in that case essentially mimicked the “quiet” treatment used here (i.e., beetle containers were housed in a quiet lab), it makes sense (now) that those beetles were also experiencing the effects of social isolation after removal from their log habitats in the wild. In the prior study, the beetles slowly began to regain mass after three weeks in captivity, but never reached their initial mass [16]. This discovery illuminates the possible downside of conducting lab-based studies of this species, and maybe argues that the beetles should be housed in groups. In fact, in an older study of this species, Gray [30] noted that when grubs are housed in the lab, the “single isolated larvae do not seem to thrive as do those in colonies of several”. This early observation also can be explained by the negative effects of social isolation.
This project engenders a number of questions that could be addressed in future experiments, now that it is clear that socially isolated passalus beetles experience stress. For example, are there other behavioral or physiological alterations in the isolated beetles? Prior work with this species showed how their heart rates become elevated when they are stressed [19], and there are coinciding changes to immune cell abundance within the hemolymph [26]. Additionally, chronically stressed beetles tend to “squeak” more when disturbed [27]. Other avenues to explore could include how isolation affects the beetles’ thanatosis response to threats [31]. Such experiments would not only add to the body of work related to social isolation in animals (e.g., [9,21,22,23]), but would also help to clarify the nature of the insect stress response mechanism [32].
4. Methods
4.1. Larvae Experiment
In June 2021, immature passalus beetles (hereafter called grubs) were collected from decaying hardwood logs in Clarke County, GA, USA. This region of the state of Georgia corresponds with the range of O. cryptodisjunctus, as outlined in Fontanella et al. [10]. The grubs (n = 143) were transported to a nearby lab and housed individually in 1 L plastic containers filled with moistened wood debris produced by captive adult beetles (which were held in separate containers). Each container held one grub and it contained enough debris for both refugia and for food. While this method does allow grubs to be raised to adulthood in captivity [33], it likely does not fully replicate the development conditions and parental care provided in the wild. Nevertheless, in this experiment, this housing scenario was consistent across all sound treatments. Since the grubs came from natural burrow in the wild, they represented varying developmental stages and sizes at the start of the experiment, though this did not matter, as the mass change per day thereafter was the variable of interest.
The grubs were randomly divided into three groups (see Table 2 for sample sizes), which each contained a mix of developmental stages. Each grub was weighed when the experiment began using an electronic balance (Ohaus Scout, with 0.01 g sensitivity). The experiment involved exposing each group to different noise treatments (though not at the same time). Each group of containers was placed in a sound-proof room (on a bench). Next to the containers were two speakers connected to a portable audio-player, which played the sound of interest on a loop. The grub containers were arranged so that all containers were the same distance from the speakers (30 cm). For the experiment, the grubs were exposed to one of the following treatments: the sound of a horned passalus beetle chirping (for 1 min every 10 min), the sound of a cricket chirping (1 min every 10 min), or no sound. Sound files are provided in the Supplemental Materials. The recording of adult beetle chirping was obtained from a prior experiment whereby beetles were held upside down and gently prodded with a blunt probe, while recording their stridulations [26]. Based on comparisons between these chirps, and descriptions given in Schuster [14], these sounds would be classified as “aggression” signals for this species. For both the beetle sound, and the cricket sound treatments, the speaker volume was set to 60 decibels. The grubs, and the setup, were left untouched thereafter for 72 h. Then, each grub was weighed again. The difference in weight from the initial weight was calculated to compute the growth rate (in mg) per day, which was used for analyses (below).

Table 2.
Summary of sample sizes across sound treatments for each experiment/replicate of this project. Grubs or adults were only used in one experiment each.
4.2. Adult Experiments
Similar noise exposure trials were conducted using wild-collected adult passalus beetles, exposing them to the same three sound treatments (beetle sound, cricket sound, or no sound), using the same audio setup. There were three separate iterations of the adult experiment, conducted over different time periods (June 2021, February 2022 and March 2023, sample sizes shown in Table 2). Each iteration involved exposing three different groups of beetles to the sound treatments. For each iteration, adult beetles were collected from decaying logs in nearby forests (Clarke County, GA, USA), and housed in the lab individually in plastic containers filled with decaying hardwood, where they remained until the experiment began (1 week). Again, given the location of collections, these beetles likely were of the species O. cryptodisjunctus, as outlined in Fontanella et al. [10].
At the start of the experiment, the adults were weighed with an electronic balance. For the first two iterations of the experiment, adults were simply provided enough decaying wood pieces to last for the duration of experiment, though in the last trial, a secondary goal was to evaluate their wood processing and eating activity level [24]. Specifically, each beetle was initially provided with a uniform block of decaying hardwood, and after the sound trials were complete, the processed wood debris in the container (i.e., what the beetle had chewed and processed from the initial block) was weighed as an index of feeding activity. The sound exposures varied in duration across the three iterations: from 3 days in 2021 to 4 days in 2022 and 7 days in 2023. At the end of each sound exposure treatment, each beetle was re-weighed. The percentage change in weight (compared to the start of the experiment) was calculated for use in analyses.
In the 2021 and 2023 experiments, once the sound exposure trials were complete, the adult beetles were killed in ethanol and dissected to determine their gender, based on the presence or absence of the male aedeagus; they were also checked for the presence of the nematode parasite, Chondronema passali. While horned passalus beetles can harbor a variety of parasites [34], this nematode can be exceptionally abundant within hosts, and it has been shown to (positively) affect wood processing/feeding activity in their host [24]. Dissections were not performed for the 2022 experiment, as the beetles were used for unrelated experiments afterward.
4.3. Data Analyses
For the experiment with grubs, the growth rate per day was the response variable of interest. For the adult experiments, the percentage change in mass was the response variable. These data, for both the grubs and adults, were normally distributed based on visual inspection of histograms. A one-way ANOVA was used to determine if sound treatment (beetle sound, cricket sound or no sound) affected growth rates in beetle grubs. Similarly, an ANOVA was used to examine effects of sound treatment on adult mass change, though because one of the three replicates lacked data on beetle sex and parasitism, the model was run in two ways. In one model, a “replicate” was included as a random factor, and sound treatment was used as a categorical predictor. This model used data from all three iterations of the experiment (2021, 2022 and 2023). The second model used a replicate of the sound treatment, but also included beetle sex and nematode parasitism (yes or no) as categorical predictors. This model used data from the 2021 and 2023 experiments only. Lastly, an ANOVA model was used to determine if feeding activity (mass of chewed wood debris) differed across sound treatments in the 2023 experiment. Statistical analyses were conducted using the Statistica 13.5 software package (TIBCO Software, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/stresses5010011/s1, Figure S1: Comparison of sound treatment effects across experimental replicates; Audio file S1: clip of beetle chirping sound; Audio file S2: clip of cricket chirping sound.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data from this project can be made available from the author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The author is indebted to Anna Shattuck, Amitesh Anerao, and Farran Smith for assistance with the beetle experiments. The manuscript was improved after receiving helpful comments from three anonymous reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Ware, H.E.; McClure, C.J.W.; Carlisle, J.D.; Barber, J.R. A phantom road experiment reveals traffic noise is an invisible source of habitat degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12105–12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.K.; Schroeder, H.; Yeager, I.; Pearce, J. Effects of simulated highway noise on heart rates of larval monarch butterflies, Danaus plexippus: Implications for roadside habitat suitability. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, 20180018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbe, C.; Marley, S.A.; Schoeman, R.P.; Smith, J.N.; Trigg, L.E.; Embling, C.B. The Effects of Ship Noise on Marine Mammals—A Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R.; Greggers, U.; Smith, A.D.; Reynolds, D.R.; Menzel, R. The flight paths of honeybees recruited by the waggle dance. Nature 2005, 435, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, F.J.; Hunt, J.H. Intracolony chemical communication in social insects. Insectes Sociaux 2013, 60, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.H.; Richard, F.J. Intracolony vibroacoustic communication in social insects. Insectes Sociaux 2013, 60, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manser, M.B.; Jansen, D.; Graw, B.; Hollén, L.I.; Bousquet, C.A.H.; Furrer, R.D.; le Roux, A. Vocal Complexity in Meerkats and Other Mongoose Species. In Advances in the Study of Behavior; Naguib, M., Barrett, L., Brockmann, H.J., Healy, S., Mitani, J.C., Roper, T.J., Simmons, L.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 46, pp. 281–310. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.; Zapetis, M.; Samuelson, M.M.; Ridgway, S. Sounds produced by bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops): A review of the defining characteristics and acoustic criteria of the dolphin vocal repertoire. Bioacoustics 2020, 29, 399–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Khan, M.I.; Zubair, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Neurobiology and consequences of social isolation stress in animal model-A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanella, F.M.; Whitaker, M.; Smallwood, J.; Enderle, K.; Shinall-Graham, A.; Adams, J. Disentangling disjunctus: An integrated analysis of the patent leather beetle, Odontotaenius disjunctus complex (Passalidae: Coleoptera) with the description of two new species. Syst. Biodivers. 2024, 22, 2413503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, A.S.; Patterson, M.; Rankin, J.S.; Wharton, G.W. The ecology of Passalus cornutus Fabricius, a beetle which lives in rotting logs. Ecol. Monogr. 1936, 6, 456–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, J.R. High rates of extra-pair paternity in a socially monogamous beetle with biparental care. Ecol. Entomol. 2017, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Castillo, P.; Jarman, M. Some notes on larval stridulation in neotropical Passalidae (Coleoptera: Lamellicornia). Coleopt. Bull. 1980, 34, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, J.C. Acoustical signals of passalid beetles: Complex repertoires. Fla. Entomol. 1983, 66, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.C.; Schuster, L.B. Social behavior in passalid beetles (Coleoptera, Passalidae): Cooperative brood care. Fla. Entomol. 1985, 68, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFeuvre, J.; Davis, A.K. Effects of a naturally-occurring nematode parasite on lifting strength and captivity-related body mass patterns in horned passalus beetles, Odontotaenius disjunctus. Coleopt. Bull. 2015, 69, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuti, D.; Winkler, Z.; Horváth, K.; Juhász, B.; Szilvásy-Szabó, A.; Fekete, C.; Ferenczi, S.; Kovács, K.J. The metabolic stress response: Adaptation to acute- repeated- and chronic challenges in mice. iScience 2022, 25, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez, D., Jr.; Willoughby, A.; Davis, A.K. Fighting while parasitized: Can nematode infections affect the outcome of staged combat in beetles? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Coogler, B.; Johnson, I. The heartrate reaction to acute stress in horned passalus beetles (Odontotaenius disjunctus) is negatively affected by a naturally-occurring nematode parasite. Insects 2017, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Calderon, L.; Lefeuvre, J.; Sims, S.; Pearce, J.; Prouty, C. Healing while parasitized: Impact of a naturally-occurring nematode during energy-intensive wound-healing in a beetle. Physiol. Entomol. 2020, 45, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koto, A.; Mersch, D.; Hollis, B.; Keller, L. Social isolation causes mortality by disrupting energy homeostasis in ants. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2015, 69, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schausberger, P.; Gratzer, M.; Strodl, M.A. Early social isolation impairs development, mate choice and grouping behaviour of predatory mites. Anim. Behav. 2017, 127, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.A.; Rillich, J. Isolation Associated Aggression—A Consequence of Recovery from Defeat in a Territorial Animal. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.K.; Prouty, C. The sicker the better: Nematode-infected passalus beetles provide enhanced ecosystem services. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillard, J.R.; Maigret, T.A. Delayed dispersal and prolonged brood care in a family-living beetle. J. Evol. Biol. 2017, 30, 2230–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.K.; Vasquez, D.; LeFeuvre, J.; Sims, S.; Craft, M.; Vizurraga, A. Parasite manipulation of its host’s physiological reaction to acute stress: Experimental results from a natural beetle-nematode system. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2017, 90, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebot-Ojong, F.; Jurado, E.; Davis, A.K. Direct measurement of fight or flight behavior in a beetle reveals individual variation and the influence of parasitism. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.; Davis, A.K. Effect of a parasitic nematode, Chondronema passali Leidy (Incertae sedis), on the size and strength of the horned passalus, Odontotaenius disjunctus Illiger (Coleoptera: Passalidae). Coleopt. Bull. 2013, 67, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Hurd, C.; Brandon, C.; Vasquez, D. Walking while parasitized: Effects of a naturally-occurring nematode on locomotor activity of horned passalus beetles. J. Insect Behav. 2021, 34, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, I.E. Observations on the life history of the horned passalus. Am. Midl. Nat. 1946, 35, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Ladd, R.R.E.; Smith, F.; Shattuck, A. Sex-specific effects of a parasite on stress-induced freezing behavior in a natural beetle-nematode system. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, S.A.; Baker, J.L. Conserved features of chronic stress across phyla: The effects of long-term stress on behavior and the concentration of the neurohormone octopamine in the cricket, Gryllus texensis. Horm. Behav. 2011, 60, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, L.; Davis, A.K. Observations of Steinernema nematode and Tachinid fly parasites in horned passalus beetles, Odontotaenius disjunctus, from Georgia, U.S.A. Comp. Parasitol. 2016, 83, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, J.A. Parasites associated with Popilius disjunctus in South Carolina (Coleoptera: Passalidae). Fla. Entomol. 1973, 56, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).