Application of Information and Communication Technologies for Public Services Management in Smart Villages
Abstract
1. Introduction
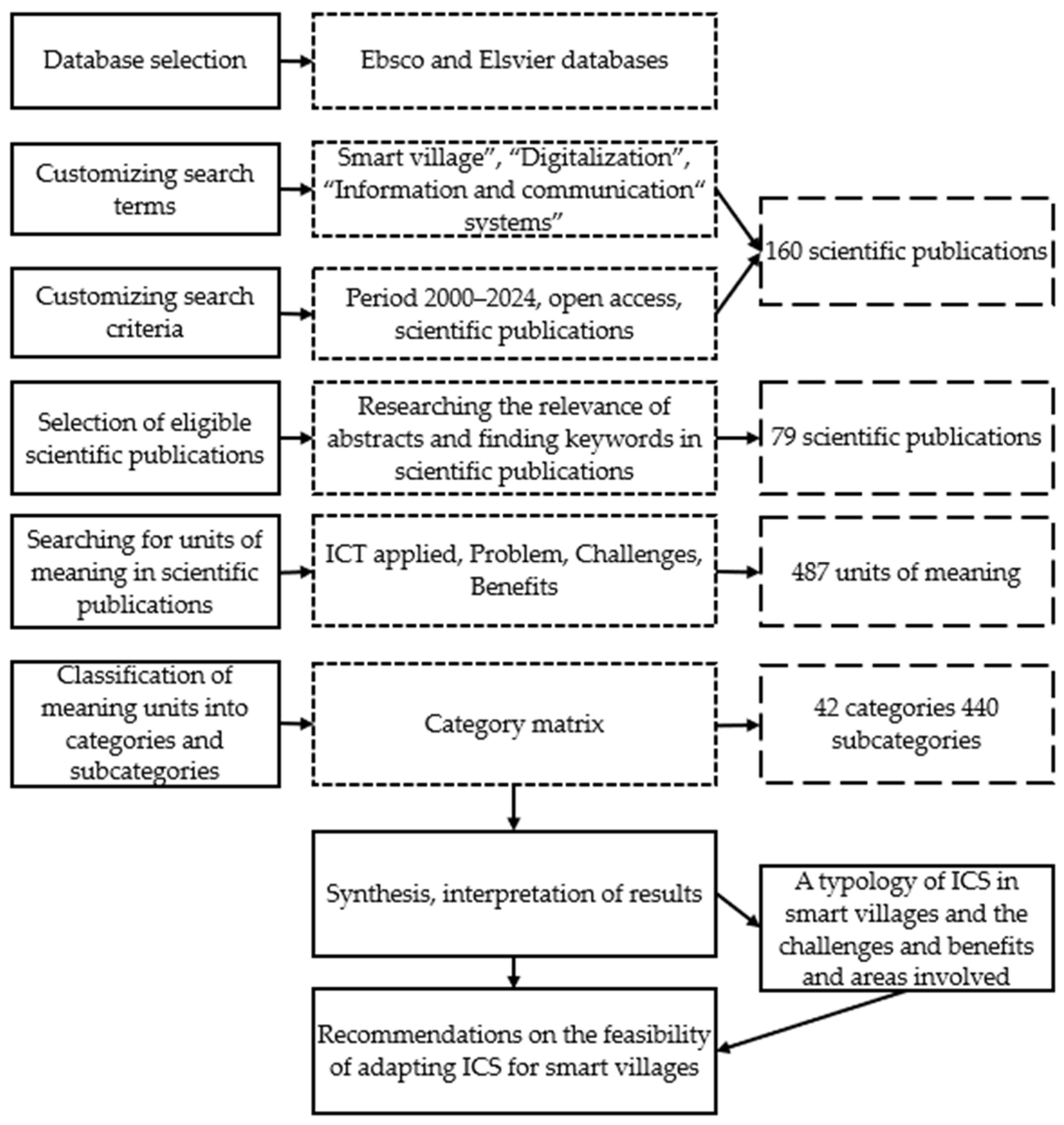
2. Materials and Methods
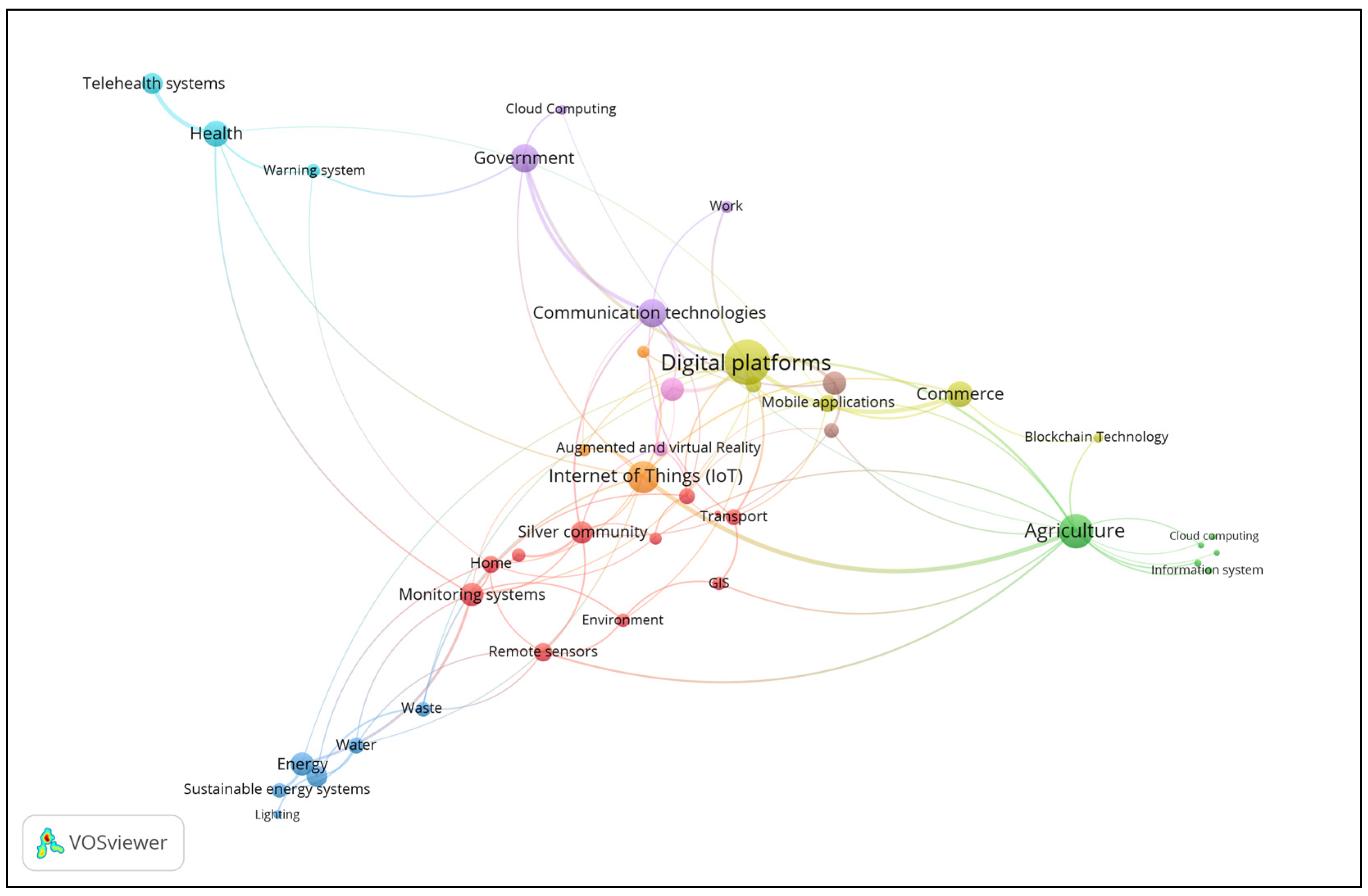
3. Results
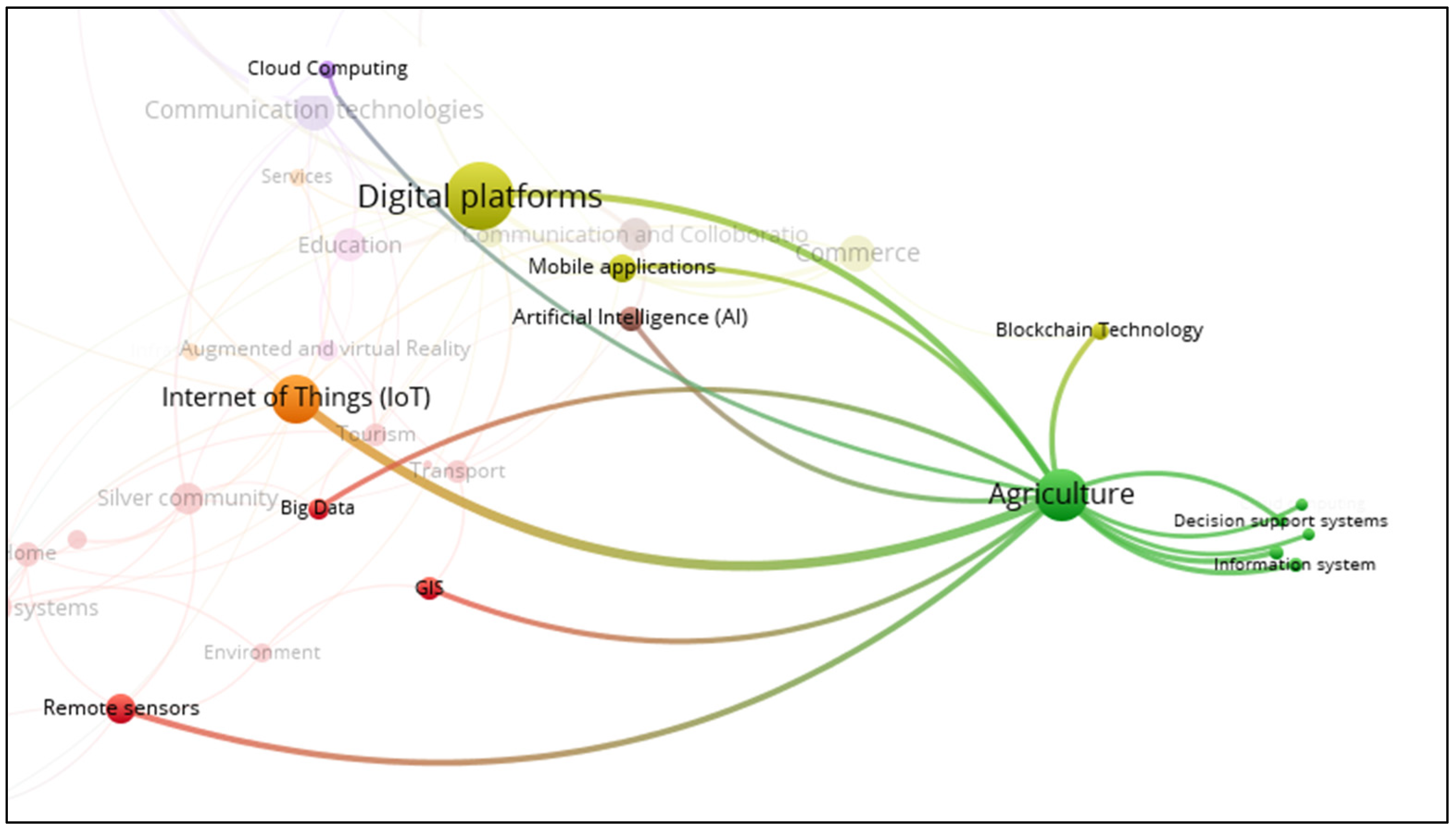
3.1. Smart Agriculture
3.2. Smart Communication and Collaboration
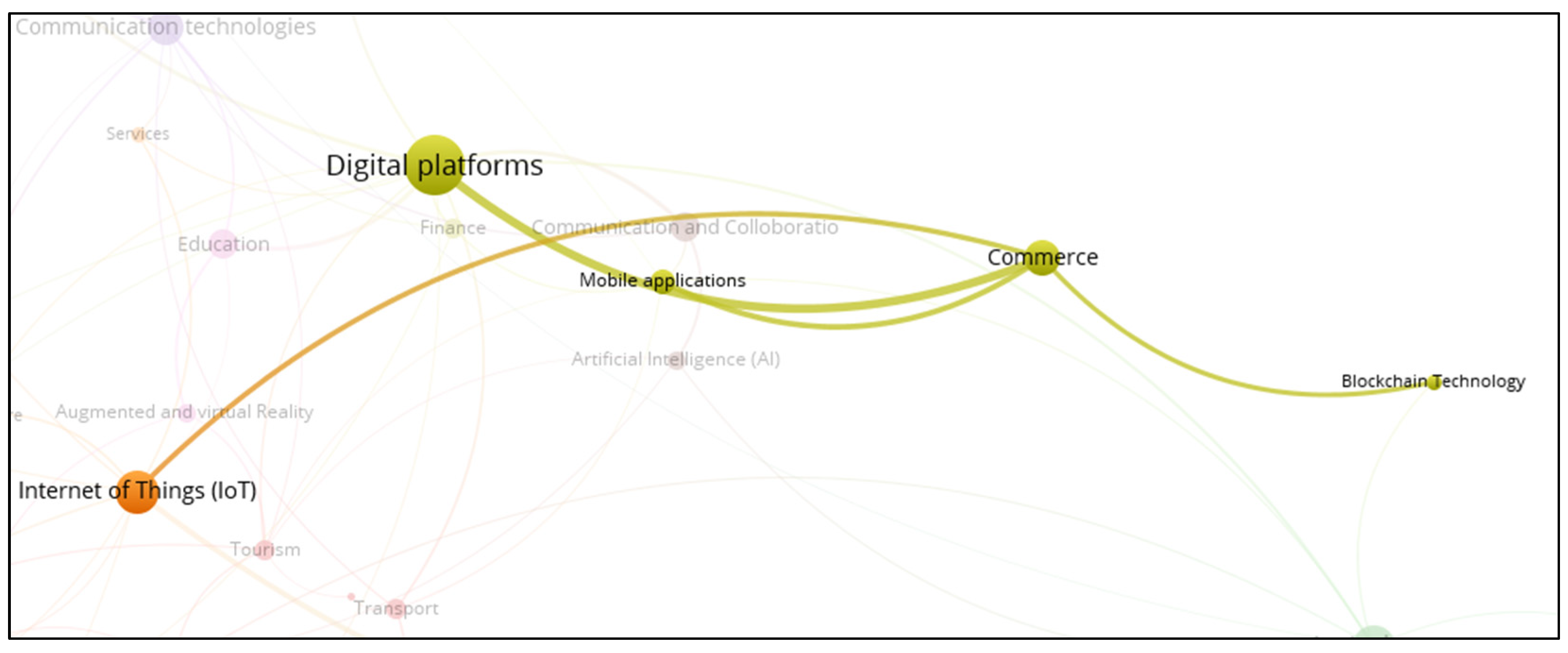
3.3. Smart Commerce
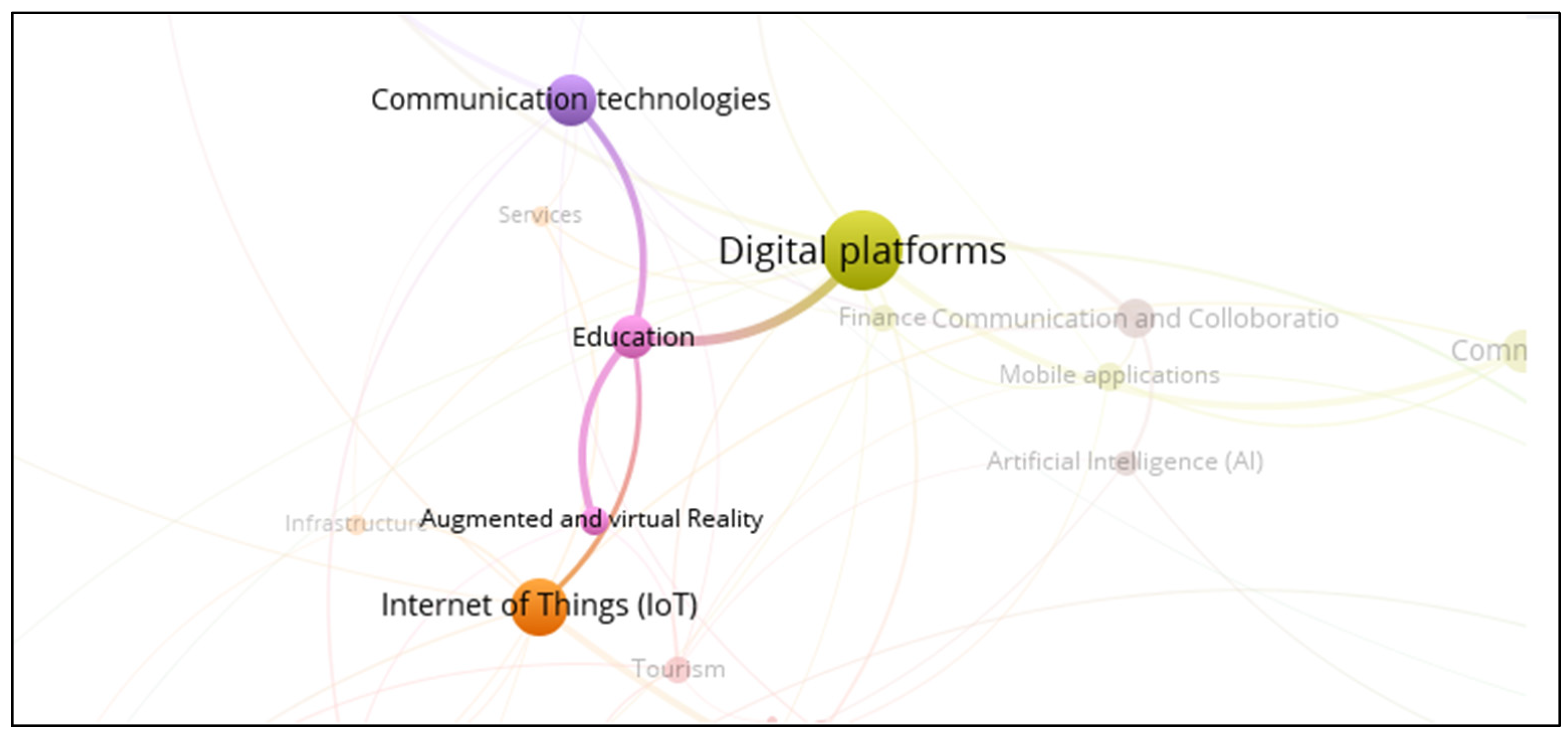
3.4. Smart Education
3.5. Smart Health
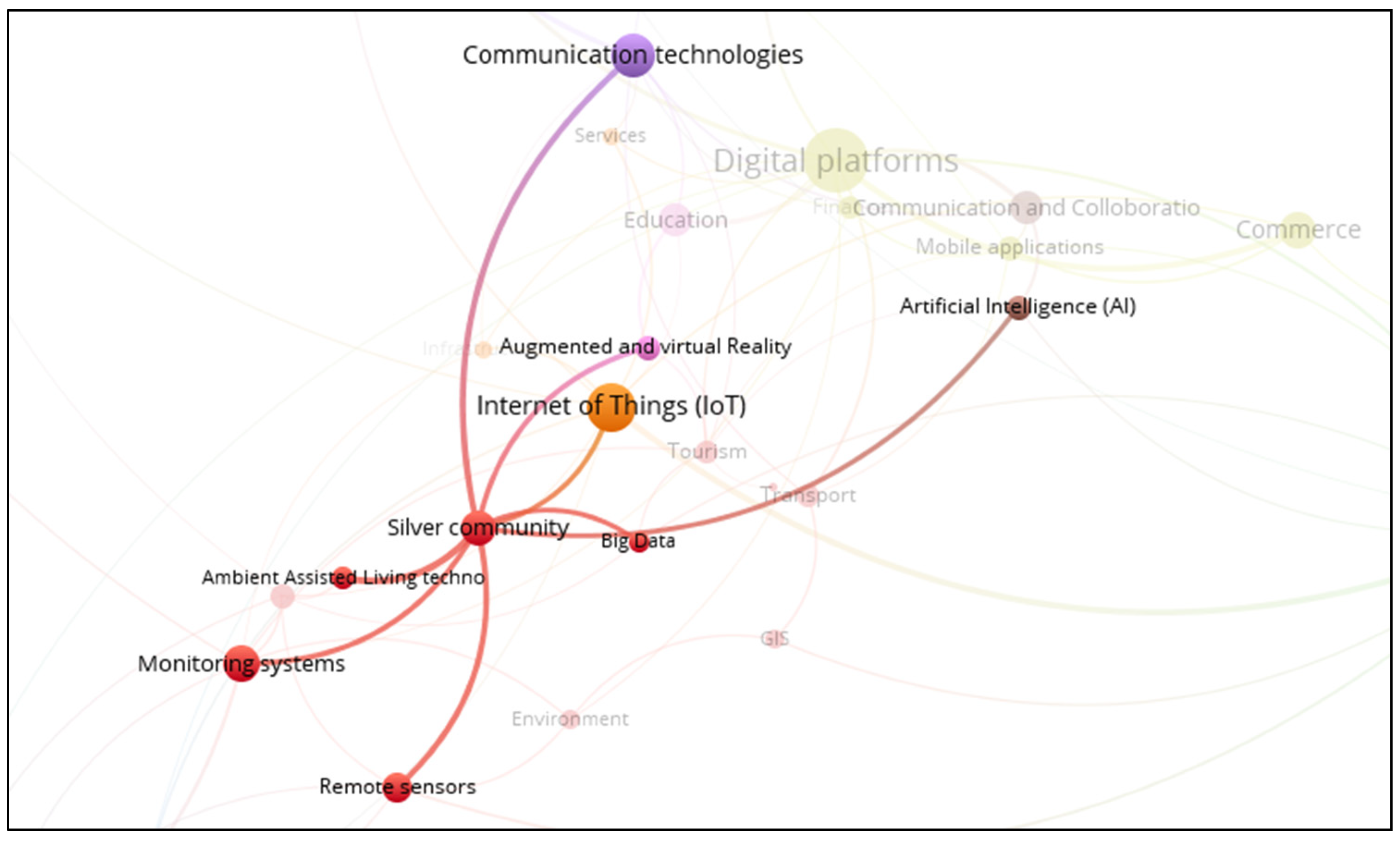
3.6. Smart Silver Community
3.7. Smart Home
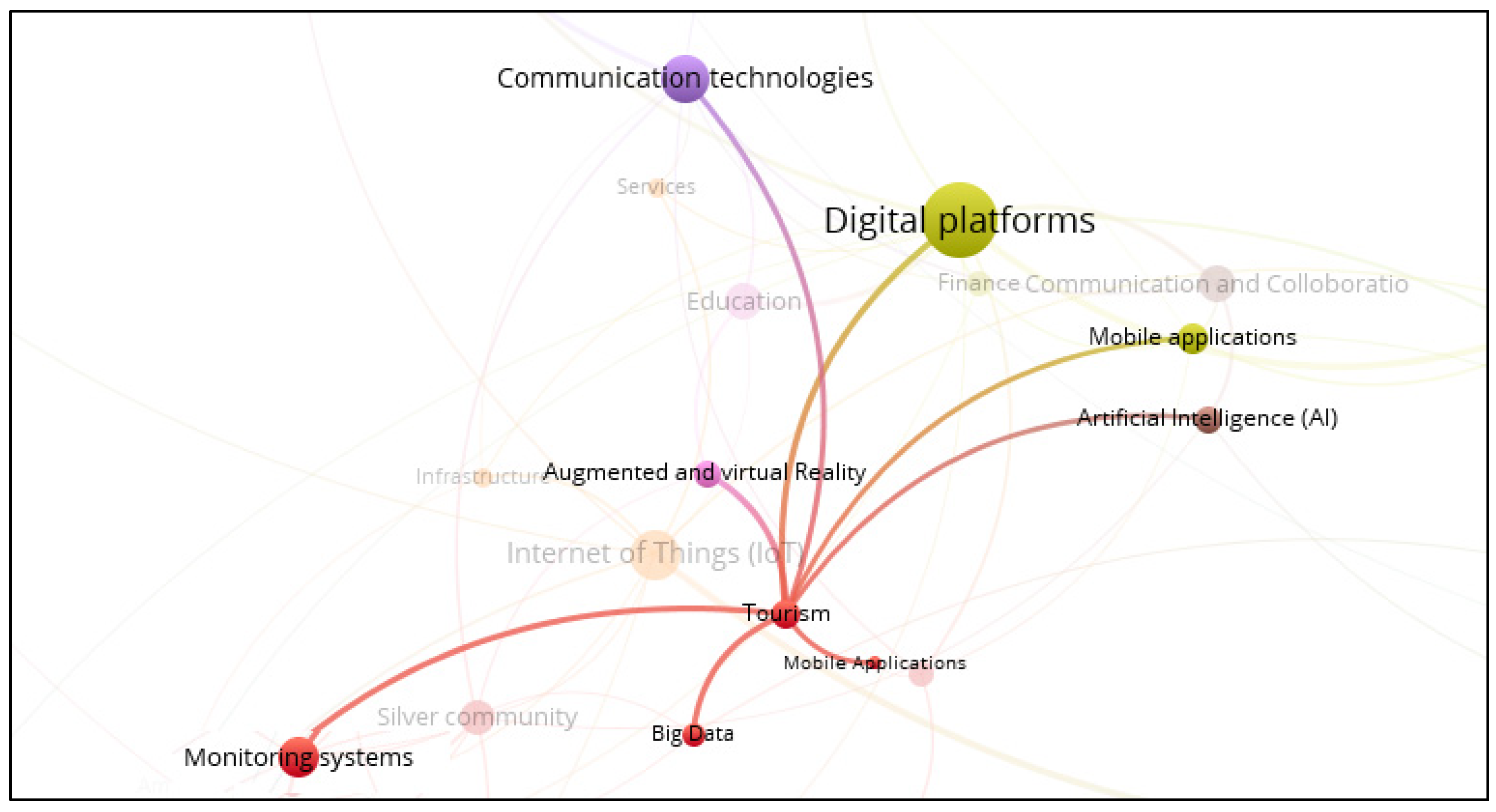
3.8. Smart Tourism
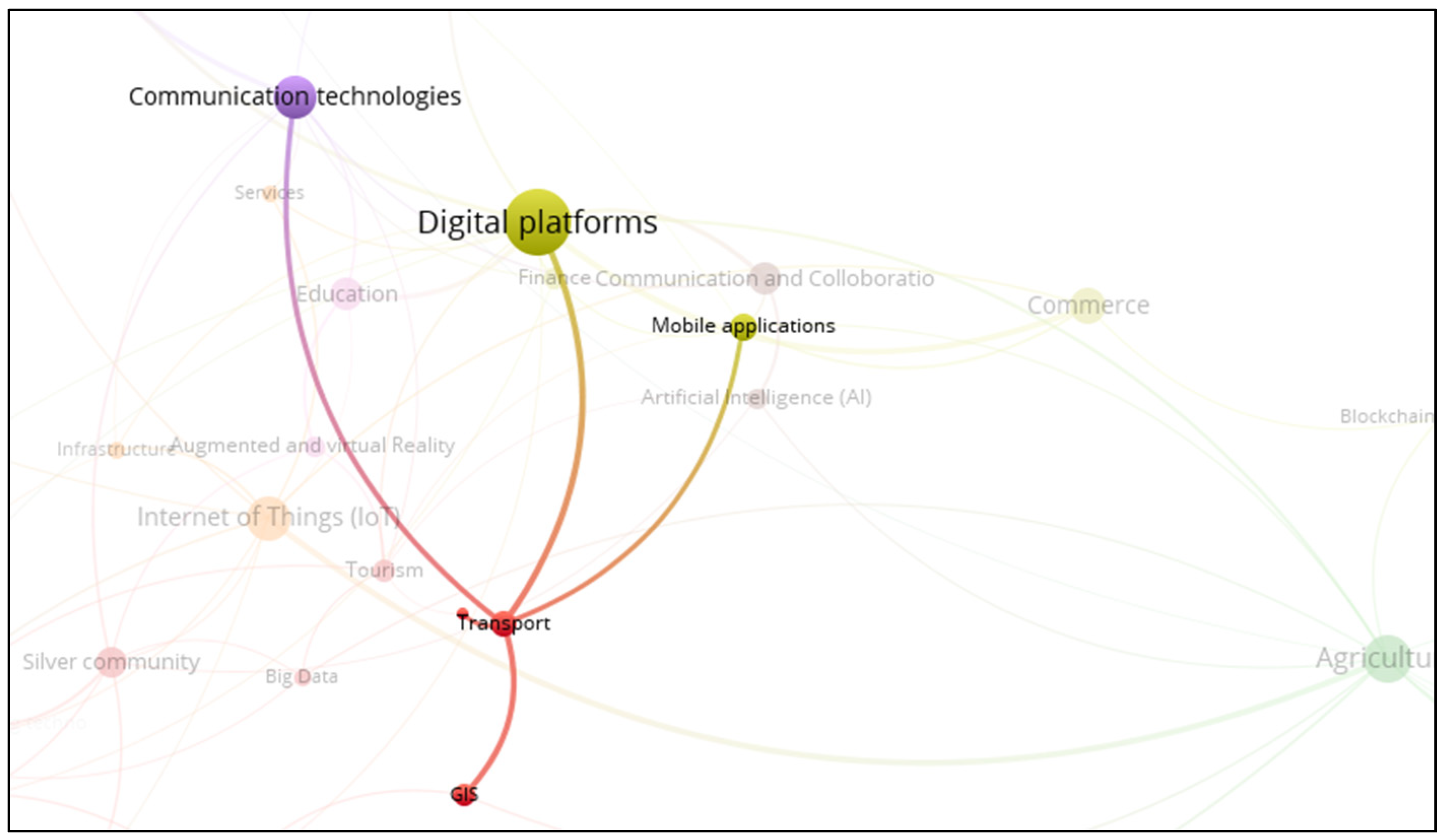
3.9. Smart Transport
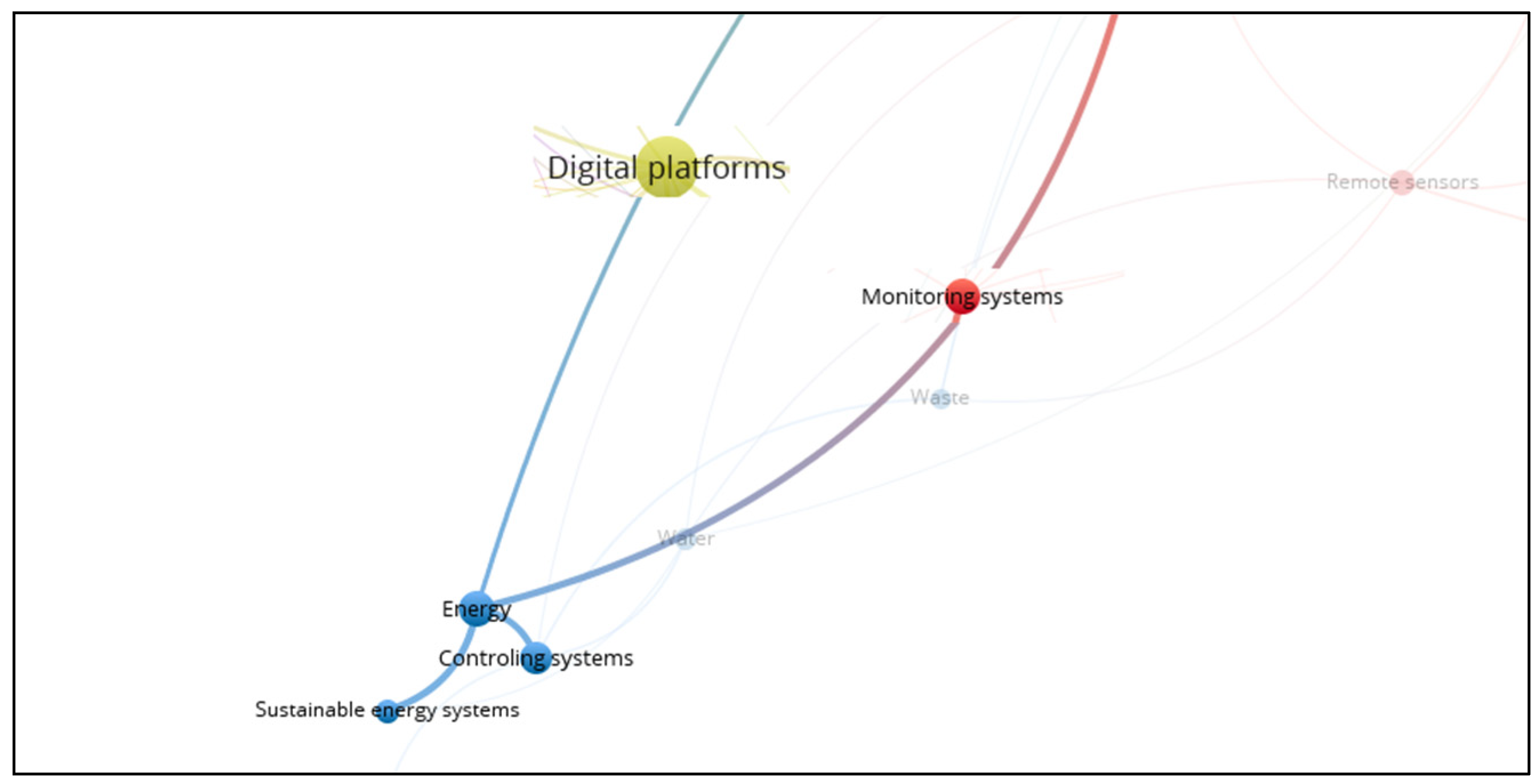
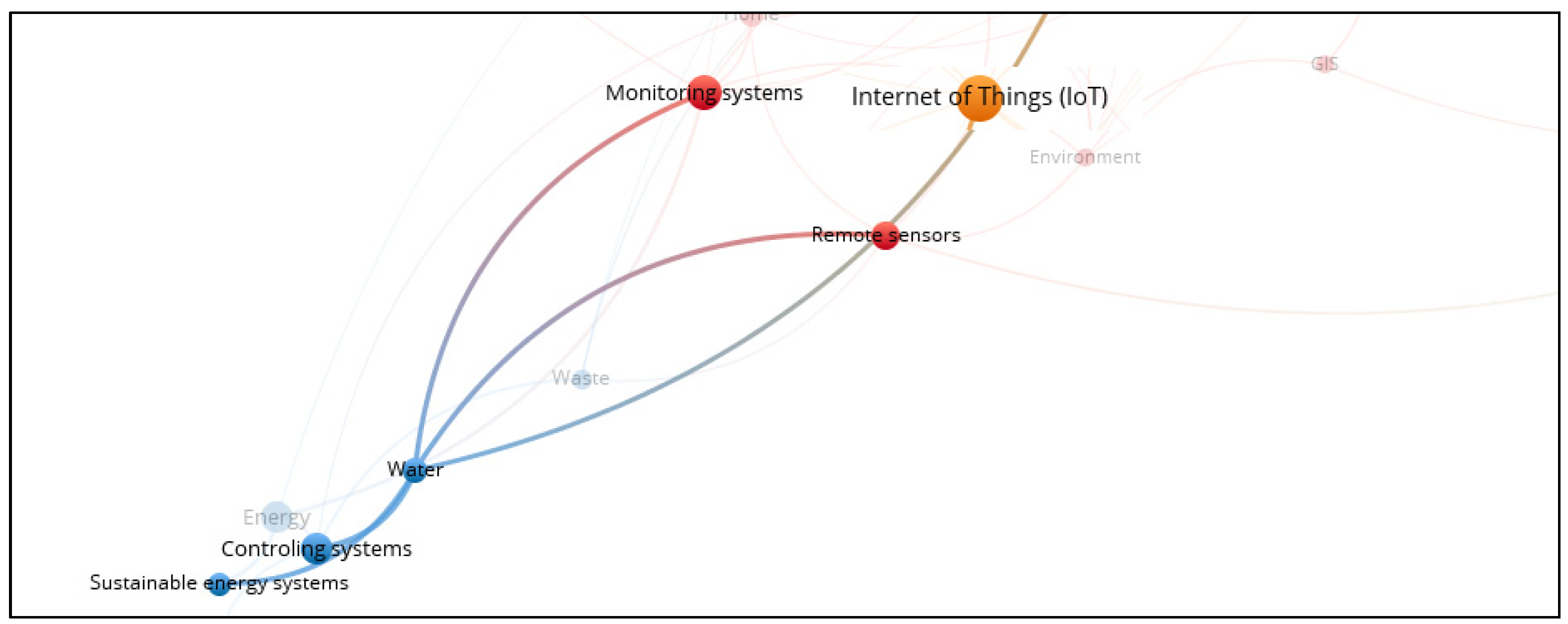
3.10. Smart Energy
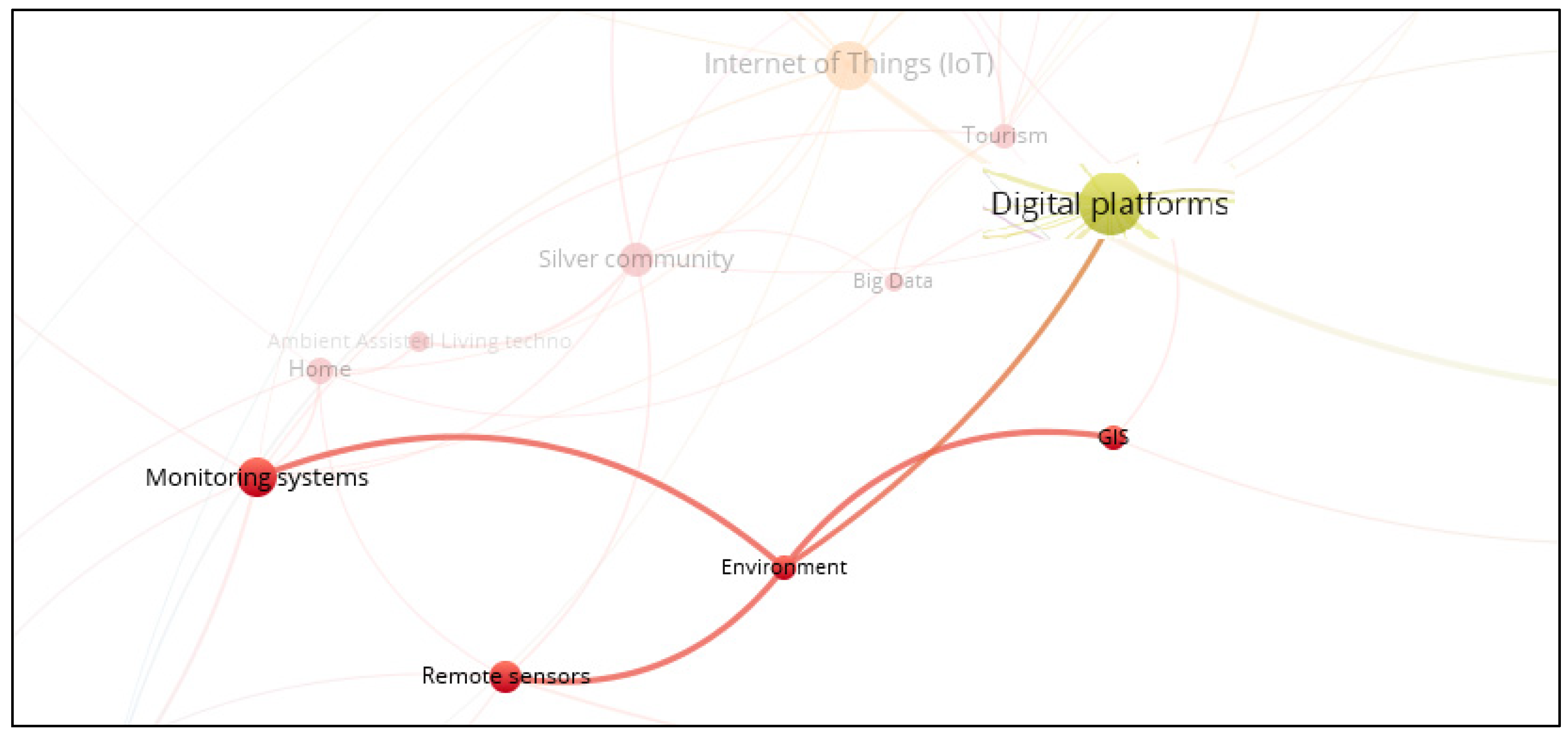
3.11. Smart Environment
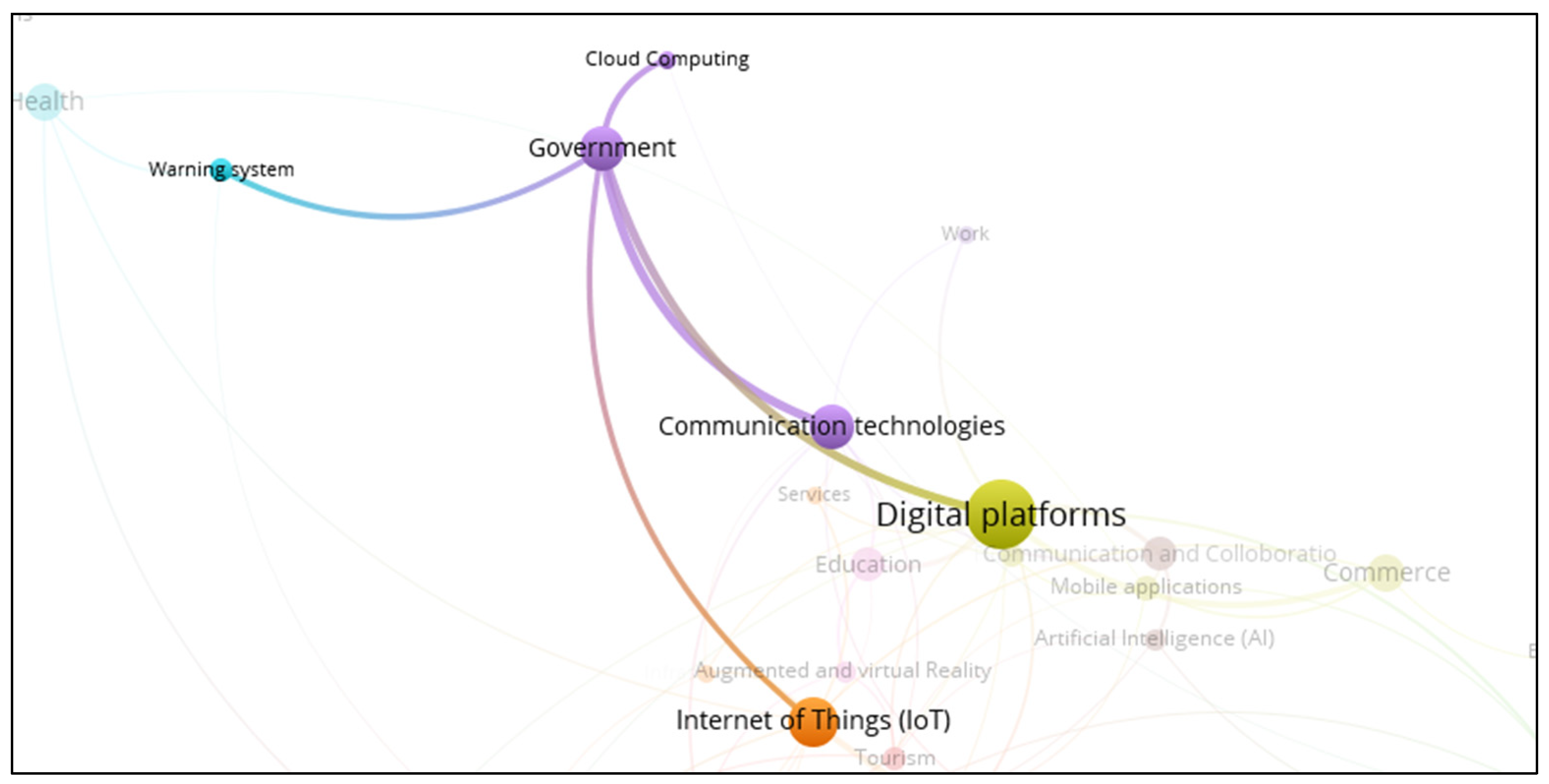
3.12. Smart Government
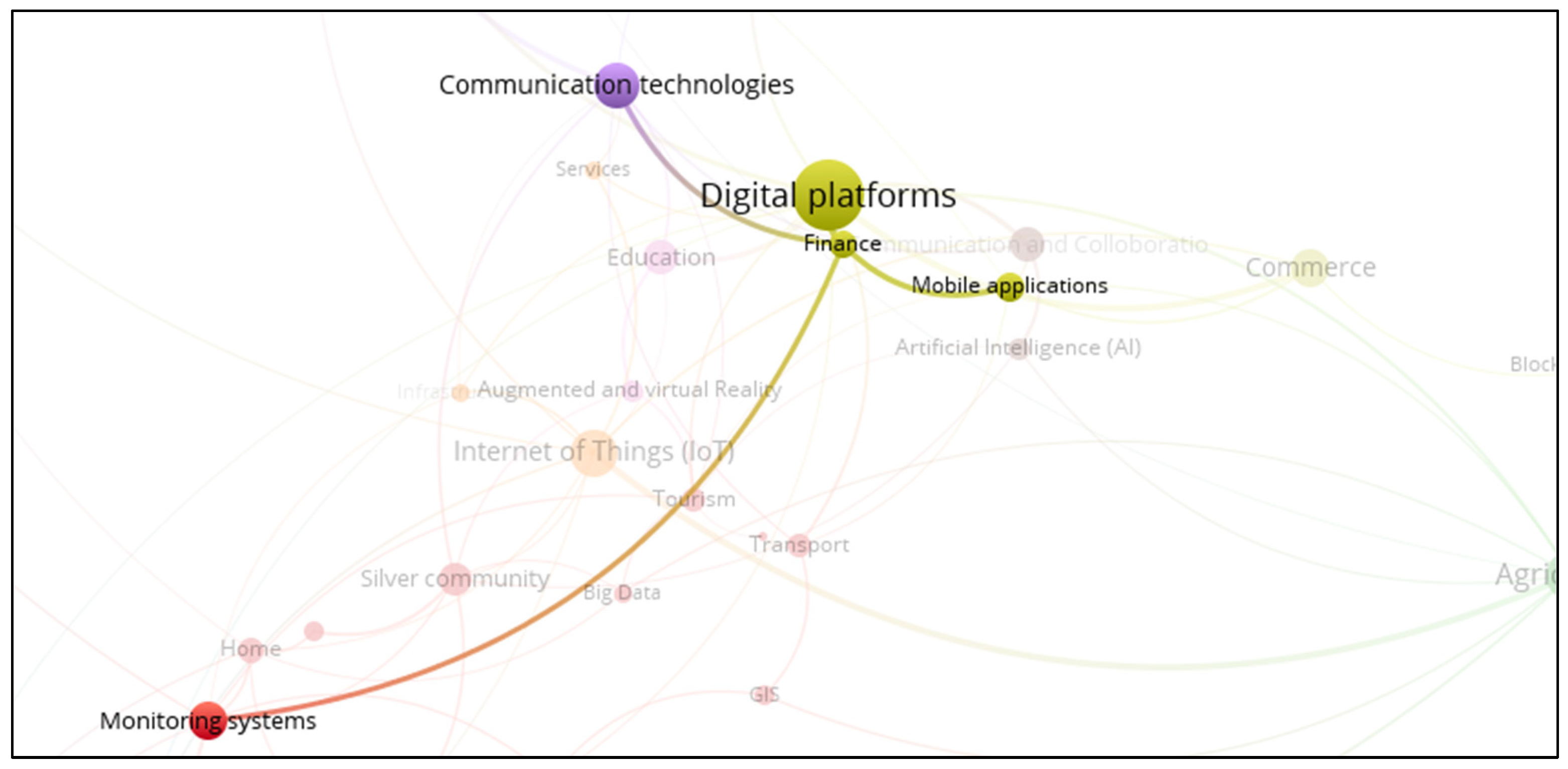
3.13. Smart Finance
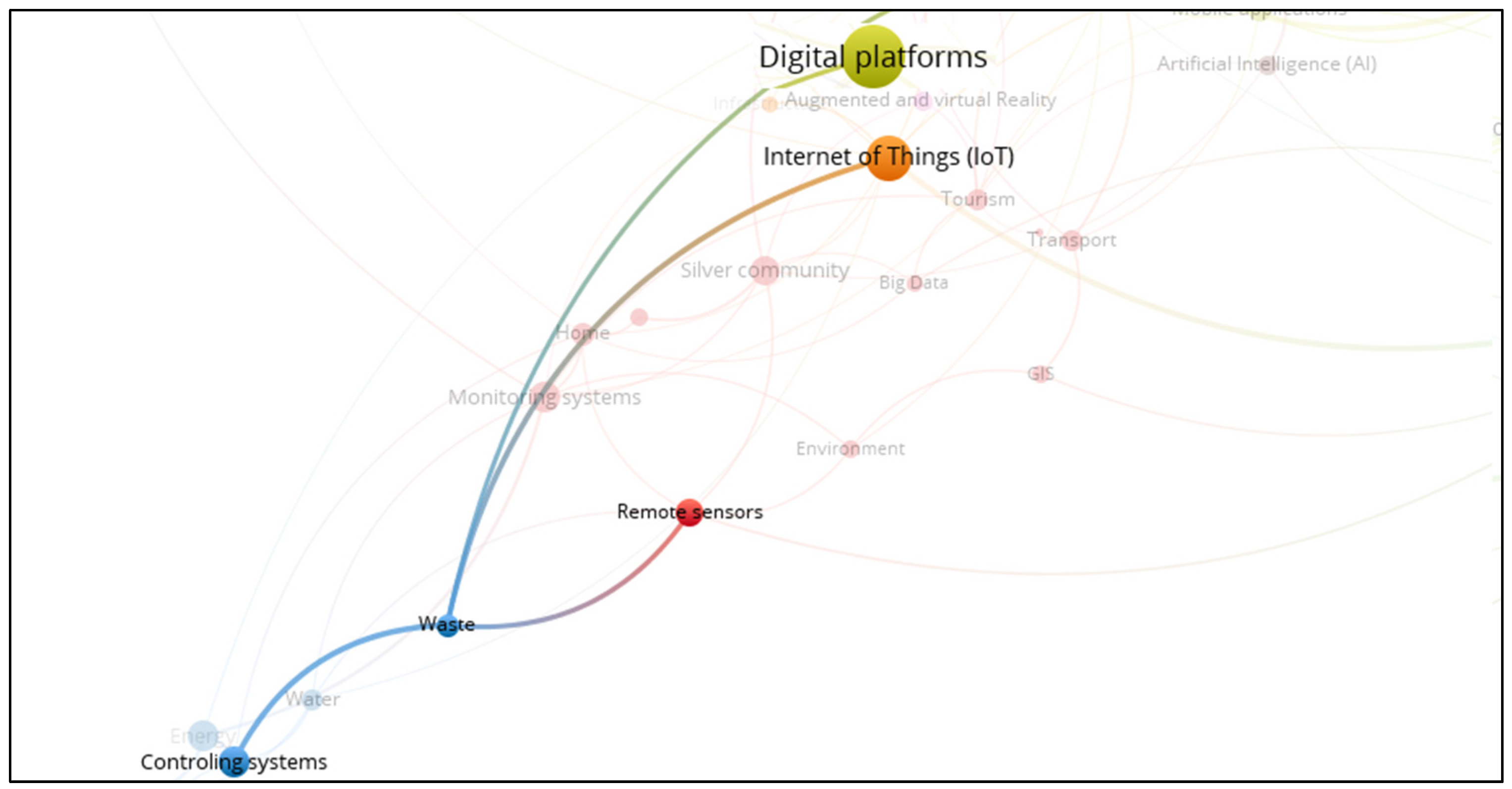
3.14. Smart Waste System
3.15. Smart Water System
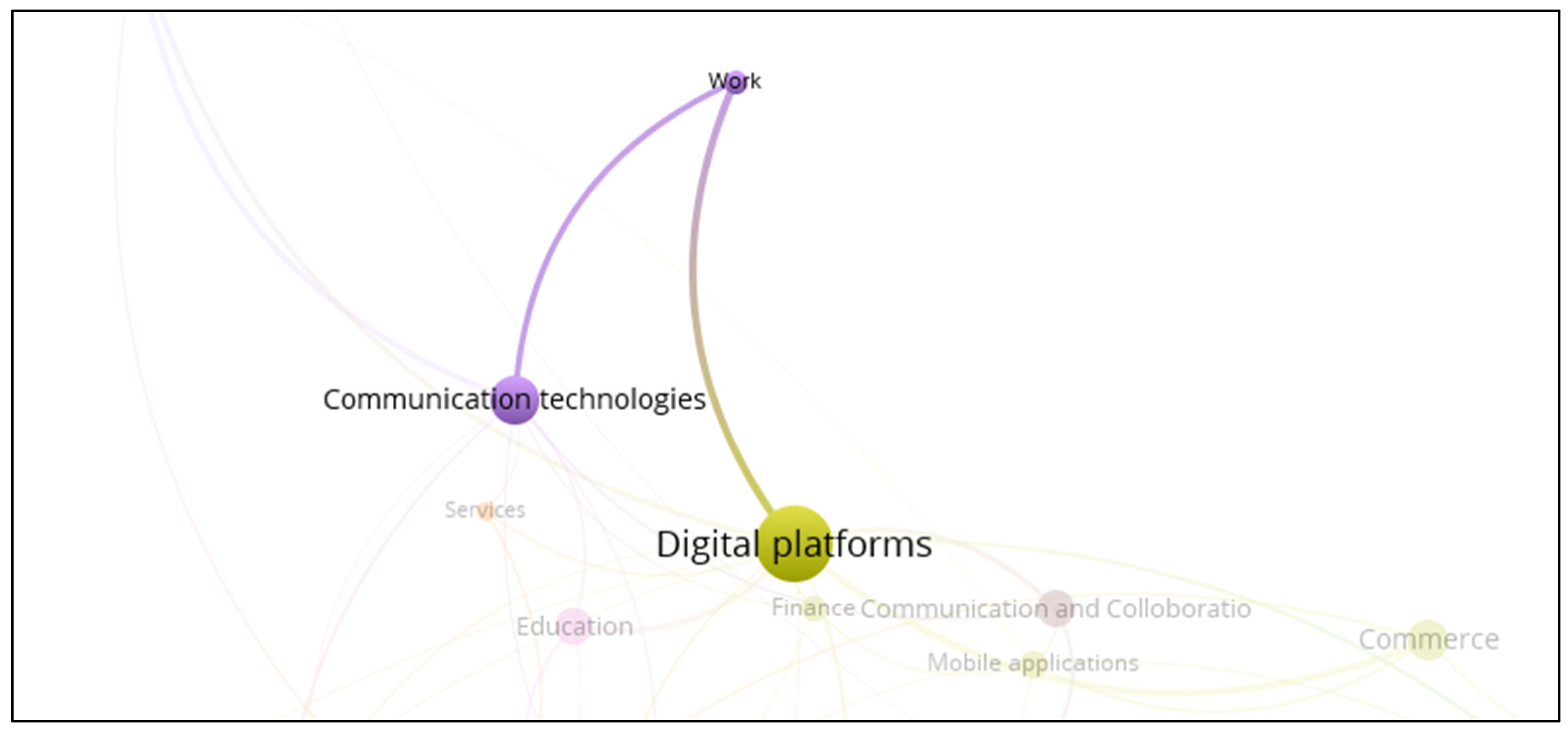
3.16. Smart Work System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Smart villages use a wide range of information and communication technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, blockchain, cloud computing, geographic information systems, mobile applications, and others. These technologies are being applied to a wide range of public services, from agriculture to healthcare, energy, tourism, finance, and waste management.
- ICTs address the fundamental problems of rural areas: limited access to services due to geographical distance, inefficient management of resources, demographic challenges (aging and depopulation), social exclusion and geographic isolation, and lack of economic opportunities. In each field, technologies are adapted to specific problems; for example, telemedicine systems address limited access to healthcare, while the Internet of Things in agriculture addresses resource inefficiency.
- The study confirmed the importance of urban–rural cooperation in the development of ICT-enabled solutions. Smart villages, faced with a lack of technological and infrastructural resources, can take advantage of the technological potential of cities, and cities can take advantage of rural resources and products. Such integration helps to reduce the digital divide and ensure more balanced technological development.
- The most successful implementation of ICTs has been achieved through a neo-endogenous model that emphasizes the role of local communities in planning processes. The study shows that technological solutions need to be tailored to the local context, taking into account the specific needs, capacities, and available resources of rural communities.
- The introduction of ICTs in the context of smart villages covers all of the dimensions of sustainable development: economic (increasing productivity, creating business opportunities models), social (improving access to services, promoting social inclusion), and environmental (more efficient use of resources, mitigating the effects of climate change). Technology acts as a lever to improve all of these dimensions in a balanced way.
- The study has shown that effective ICT deployment requires an integrated approach, encompassing not only technological solutions but also infrastructure development, digital skills training, appropriate cooperation models, and the adaptation of social practices. Technologies are not just neutral tools but factors that interact with social processes, community goals, and capabilities.
- Despite the clear potential benefits of ICTs, their deployment faces significant challenges: inadequate infrastructure (especially broadband internet), limited digital skills, high deployment and maintenance costs, the complexity of adapting technologies to specific local contexts, and data security and privacy issues.
- Successful deployment of ICT solutions requires collaboration between different stakeholders, from local communities and businesses to public sector institutions and technology developers. The role of local leaders is particularly important in promoting the adoption and adaptation of technologies to community needs.
- The study has shown that there is no one-size-fits-all ICT solution for all rural areas—technologies need to be adapted according to demographic, geographical, economic and socio-cultural factors. This is particularly important in addressing the digital divide between different age groups and across regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICTs | Information and communication technologies |
References
- Andrei, R., Ioana, C., Ionuț, G., Oana Maria, S., & Nicoleta, M. (2023). Smart villages: A global perspective on rural development. Agricultural Management/Lucrari Stiintifice Seria I, Management Agricol, 25(3), 417. [Google Scholar]
- Atkočiuniene, V., & Vaznoniene, G. (2019). Smart village development principles and driving forces: The case of Lithuania. European Countryside, 11(4), 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayu Purnamawati, I. G., Yuniarta, G. A., & Jie, F. (2023). Strengthening the role of corporate social responsibility in the dimensions of sustainable village economic development. Heliyon, 9(4), e15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balco, P., Košecká, D., & Bajzík, P. (2021). Analysis of the needs of small towns and municipalities in the field of SMART services. Procedia Computer Science, 184, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielska, A., Stańczuk-Gałwiaczek, M., Sobolewska-Mikulska, K., & Mroczkowski, R. (2021). Implementation of the smart village concept based on selected spatial patterns—A case study of Mazowieckie Voivodeship in Poland. Land Use Policy, 104, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogataj, D., Bolarin, F. C., Kavšek, M., & Rogelj, V. (2020). Smart silver villages as part of social infrastructure for older adults in rural areas. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53(2), 16914–16919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogataj, D., Emerlahu, V., & Rogelj, V. (2022). Capacity planning for social infrastructure of smart retirement villages. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 55(39), 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokun, K., & Nazarko, J. (2023). Smart villages concept—A bibliometric analysis and state-of-the-art literature review. Progress in Planning, 175, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J. Y., & Park, S. K. (2023). Key factors for sustainable operation of smart rural communities in aging societies: Voices of Korean community leaders. Technology in Society, 74, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, P., Townsend, L., & Salemink, K. (2020). Smart rural futures: Will rural areas be left behind in the 4th industrial revolution? Journal of Rural Studies, 79, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvar, N., Trilar, J., Kos, A., Volk, M., & Duh, E. S. (2020). The use of iot technology in smart cities and smart villages: Similarities, differences, and future prospects. Sensors, 20(14), 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotović, A., Joksimović, M., & Jovanović, M. (2020). Demographic revitalization of montenegrin rural areas through the smart village concept. Agriculture and Forestry, 66(4), 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokl, D., Rogelj, V., & Bogataj, D. (2022). Smart age-friendly villages: Literature review and research agenda. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 55(10), 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobež, E., Rogelj, V., Bogataj, D., & Bogataj, M. (2021). Planning digital transformation of care in rural areas. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 54(13), 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerllahu, V., & Bogataj, D. (2024). Smart Villages as infrastructure of rural areas: Literature review and research agenda. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 58(3), 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M., Arlikatti, S., & Ramesh, M. V. (2024). A qualitative analysis of rural fishermen: Potential for blockchain-enabled framework for livelihood sustainability. Heliyon, 10(2), e24358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, S., Kaur, P., Jhunjhunwala, A., Narayanan, D., Loyola, C., Bedi, J., & Singh, Y. (2018). Examining linkages between smart villages and smart cities: Learning from rural youth accessing the internet in India. Telecommunications Policy, 42(10), 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A., Bacco, M., Gaber, K., Jedlitschka, A., Hess, S., Kaipainen, J., Koltsida, P., Toli, E., & Brunori, G. (2022). Drivers, barriers and impacts of digitalisation in rural areas from the viewpoint of experts. Information and Software Technology, 145, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Crespo, P., Bermudez-Edo, M., & Garrido, J. L. (2022). Smart tourism in villages: Challenges and the Alpujarra case study. Procedia Computer Science, 204, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A. (2022). ‘You can’t eat data’?: Moving beyond the misconfigured innovations of smart farming. Journal of Rural Studies, 91, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, S., Yang, C., Xue, Y.-J., & Geng, L. (n.d.). Information and communication technology (ICT) adoption and its impact on entrepreneurial outcome in rural China. Srusti Management Review, XVI, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Głębocki, K. (2023). Smart village concept: What are the crucial categories of elements? In European conference on knowledge management. Academic Conferences International Limited. [Google Scholar]
- González, A., Arranz-Piera, P., Olives, B., Ivancic, A., Pagà, C., & Cortina, M. (2023). Thermal energy community-based multi-dimensional business model framework and critical success factors investigation in the mediterranean region of the EU. Technology in Society, 75, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelova, I., Bellini, F., & D’Ascenzo, F. (2024). Understanding smart territories: A conceptual framework. Cities, 152, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Carmona, O., Buján-Carballal, D., Casado-Mansilla, D., López-de-Ipiña, D., Cano-Benito, J., Cimmino, A., Poveda-Villalón, M., García-Castro, R., Almela-Miralles, J., Apostolidis, D., Drosou, A., Tzovaras, D., Wagner, M., Guadalupe-Rodriguez, M., Salinas, D., Esteller, D., Riera-Rovira, M., González, A., Clavijo-Ágreda, J., … Bujalkova, N. (2023). Mind the gap: The AURORAL ecosystem for the digital transformation of smart communities and rural areas. Technology in Society, 74, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváček, P., Kopáček, M., Kopáčková, L., & Hruška, V. (2023). Barriers for and standpoints of key actors in the implementation of smart village projects as a tool for the development of rural areas. Journal of Rural Studies, 103, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Souki, S., Wojtech, A., Schäfer, M., & Conrad, A. (2024). Analysing micrologistics initiatives in rural areas—Approaches to typologise and assess complex logistics solutions in regional supply networks. Journal of Rural Studies, 110, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. (2024). Smart home system using blockchain technology in green lighting environment in rural areas. Heliyon, 10(4), e26620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, N., Opera, I.-A., Turcea, V.-C., & Parnus, A. (2022). New dimensions of rural communities’ development in romania-smart village concept. Scientific Papers Series Management, Economic Engineering in Agriculture and Rural Development, 22(2), 425–436. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen, K., Mikalsen, M., & Lilleng, G. (2023). A literature review of smart technology domains with implications for research on smart rural communities. Technology in Society, 75, 102397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janota, L., Vávrová, K., & Bízková, R. (2023). Methodology for strengthening energy resilience with SMART solution approach of rural areas: Local production of alternative biomass fuel within renewable energy community. Energy Reports, 10, 1211–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaidi, A., Othman, M. S. B., Mohd Hashim, S. Z., Mohamad, M. M., Danial Kesa, D., & Nurfikri, A. (2025). Smart villages: A systematic review of trends, models, and metrics. Cogent Social Sciences, 11(1), 2492833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinka, M., Geipele, S., Pudzis, E., Lazdins, A., Krutova, U., & Holms, J. (2020). Indicators for the smart development of villages and neighbourhoods in baltic sea coastal areas. Sustainability, 12(13), 5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M., Li, W., Gao, Z., & Xing, Z. (2024). Evaluation, mechanism and policy implications of the symbiotic relationship among rural digitization, agricultural development and farmer enrichment: Evidence from digital village pilots in China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 12, 1361633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Xi, S., Wei, J., & Li, X. (2024). Exploring interventions for improving rural digital governance performance: A simulation study of the data-driven institutional pressure transmission mechanism. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 208, 123695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L., Saeli, M., & Campisi, T. (2023). Smart technological tools for rising damp on monumental buildings for cultural heritage conservation. A proposal for smart villages implementation in the Madonie montains (Sicily). Sustainable Futures, 6, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lučan, J., Pokmajević, M., & Kunčič, U. (2024). Impact of technology on the quality of life of elderly people in smart villages: Literature review. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 58(3), 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P. K., Singh, R., Gehlot, A., Akram, S. V., & Kumar Das, P. (2022). Village 4.0: Digitalization of village with smart internet of things technologies. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 165, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manapa Sampetoding, E. A., & Er, M. (2024). Digital transformation of smart village: A systematic literature review. Procedia Computer Science, 239, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mańkowska, D., Szałata, Ł., & Derlukiewicz, N. (2023). Managing rural development towards smart village. Przegląd Organizacji, 3, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioara, I., & Armanca, L. (2020). Sustainable development initiatives and practices for smart villages. Agricultural Management/Lucrari Stiintifice Seria I, Management Agricol, 21(3), 412. [Google Scholar]
- Metta, M., Dessein, J., & Brunori, G. (2024). Between on-site and the clouds: Socio-cyber-physical assemblages in on-farm diversification. Journal of Rural Studies, 105, 103193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navío-Marco, J., Rodrigo-Moya, B., & Gerli, P. (2020). The rising importance of the “Smart territory” concept: Definition and implications. Land Use Policy, 99, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljko, M., Bogataj, D., Perovic, B. T., & Kaucic, B. M. (2023). Smart and age-friendly Communities: A review of research, policy and literature. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 56(2), 9546–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OCED. (2010). Strategies to improve rural service delivery. Organization for Economic Cooperation & Development Ebrary, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill Somers, S., & Stapleton, L. (2020). A human-centred systems theory of e-agriculture automation and control systems adoption: An empirical study of the social effects of digital control and automation systems in agricultural communities. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53(2), 17433–17438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma Pinar, G., & Mecha López, R. (2022). Hacia un nuevo desarrollo rural en Europa: Análisis de la Iniciativa Smart Rural 21 e Interreg en España y Portugal [Towards a new rural development in Europe: Analysis of the smart rural 21 initiative and interreg in Spain and Portugal]. TERRA: Revista de Desarrollo Local, 11, 113–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórniak-Krzykacz, A., Przywojska, J., & Wiktorowicz, J. (2020). Smart and age-friendly communities in Poland. An analysis of institutional and individual conditions for a new concept of smart development of ageing communities. Energies, 13(9), 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontones-Rosa, C., Pérez-Morote, R., & Santos-Peñalver, J. F. (2021). ICT-based public policies and depopulation in hollowed-out Spain: A survey analysis on the digital divide and citizen satisfaction. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 169, 120811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinsloo, G., Mammoli, A., & Dobson, R. (2016). Discrete cogeneration optimization with storage capacity decision support for dynamic hybrid solar combined heat and power systems in isolated rural villages. Energy, 116, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaju, T., Kurniawan, B., Noer Falaq, M., Fadiyah Hidayat, M., & Bagus Badi, M. (2023). Learning in smart village concept case study Tanggungan village Baureno district Bojonegoro Regency. Technium Social Sciences Journal, 50, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajer, C., & Bogataj, D. (2022). Digital transformation of home care: Literature review and research agenda. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 55(39), 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasu, L., Parnus, A., & Marcuta, L. (2024). Funding opportunities for smart village projects through the leader intervention. Scientific Papers Series Management, Economic Engineering in Agriculture and Rural Development, 24, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Senkayas, H., & Aysun, S. (2019). Digital farming and productivity effect: “The smart village” in Turkey. Annals of the University of Oradea, Economic Science Series, 28, 371. [Google Scholar]
- Sept, A. (2020). Thinking together digitalization and social innovation in rural areas: An exploration of rural digitalization projects in Germany. European Countryside, 12(2), 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N., Kumar, A., & Dey, K. (2023). Unlocking the potential of knowledge economy for rural resilience: The role of digital platforms. Journal of Rural Studies, 104, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soluk, J., Kammerlander, N., & Darwin, S. (2021). Digital entrepreneurship in developing countries: The role of institutional voids. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 170, 120876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasekhar, G., Srujanraju, K., Huchaiah, M. D., & Bhaskar, N. (2022). Artificial intelligence: A new hope in agriculture. In Artificial intelligence for smart cities and villages (Vol. 2022). Bentham Science Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, V., Pentzold, C., Peter, S., & Sterly, S. (2022). Digitalization and civic participation in rural areas. A systematic review of scientific journals, 2010–2020. Raumforschung Und Raumordnung, 80(3), 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez Roldan, C., Méndez Giraldo, G. A., & López Santana, E. (2023). Sustainable development in rural territories within the last decade: A review of the state of the art. Heliyon, 9(7), e17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, Á., Varró, K., & Fabula, S. (2021). Towards a multiscalar perspective on the prospects of ‘the actually existing smart village’—A view from Hungary. Hungarian Geographical Bulletin, 70(2), 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B. C., Lau, T. C., Khan, N., Tan, W. H., & Ooi, C. P. (2021). Elderly customers’ open innovation on smart retirement village: What they want and what drive their intention to relocate? Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(4), 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh Quarshie, P., Abdulai, A. R., Duncan, E., Bahadur KC, K., Roth, R., Sneyd, A., & D.G Fraser, E. (2023). Myth or reality? The Digitalization of Climate-Smart Agriculture (DCSA) practices in smallholding agriculture in the Bono East Region of Ghana. Climate Risk Management, 42, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackara, J. (2019). Bioregioning: Pathways to urban-rural reconnection. She Ji, 5(1), 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P., & Thapa, D. (2022). What is ‘smart’ about smart village? Emerging discourses and future research directions. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, 657, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwasing, P., Clark, B., & Gkartzios, M. (2022). How can rural businesses thrive in the digital economy? A UK perspective. Heliyon, 8(10), e10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi, Z. A., Rezvani, M. R., Hall, C. M., & Allam, Z. (2023). On the post-pandemic travel boom: How capacity building and smart tourism technologies in rural areas can help—Evidence from Iran. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 193, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishar, A., & Št’astná, M. (2019). Smart village and sustainability. Southern Moravia case study. European Countryside, 11(4), 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, P. (2016). Exploring other concepts of smart-cities within the urbanising Indian context. Procedia Technology, 24, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Veeranna, D. G., Boraiah, S. S., Muniyappa, R., Boraiah, M. K. S., Narayanappa, D. S., Bhushan, M., Iyer, S., Kumar, A., Choudhury, T., & Negi, A. (2022). IoT enabled smart village for sustainable development. In Artificial intelligence for smart cities and villages (Vol. 2022). Bentham Science Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Veselinović, P., Ristić, L., & Despotović, D. (2021). Digitalization of rural areas and precision agriculture. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.5555/20210292701 (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Vidmar, B., Bogataj, D., & Rogelj, V. (2022). The framework for research of smart silver villages. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 55(39), 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q., Webster, N. A., Han, S., & Ayele, W. Y. (2023). Contextualizing the rural in digital studies: A computational literature review of rural-digital relations. Technology in Society, 75, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydziunaite, V., & Sabaliauskas, S. (2017). Qualitative research: Principles and methods. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315834139 (accessed on 13 May 2025).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazlauskienė, I.; Atkočiūnienė, V. Application of Information and Communication Technologies for Public Services Management in Smart Villages. Businesses 2025, 5, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5030031
Kazlauskienė I, Atkočiūnienė V. Application of Information and Communication Technologies for Public Services Management in Smart Villages. Businesses. 2025; 5(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazlauskienė, Ingrida, and Vilma Atkočiūnienė. 2025. "Application of Information and Communication Technologies for Public Services Management in Smart Villages" Businesses 5, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5030031
APA StyleKazlauskienė, I., & Atkočiūnienė, V. (2025). Application of Information and Communication Technologies for Public Services Management in Smart Villages. Businesses, 5(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses5030031






