Abstract
The increasing demand for sustainable construction materials has prompted the recycling of construction and demolition waste in concrete manufacturing. This study investigates the feasibility of utilizing porcelain and brick waste as partial substitutes for natural sand in concrete with the objective of improving sustainability and preserving mechanical and durability characteristics. The experimental program was conducted in three consecutive phases. During the initial phase, natural sand was partially substituted with porcelain waste powder (PWP) and brick waste powder (BWP) in proportions of 25%, 50%, and 75% of the weight of the fine aggregate. During the second phase, polypropylene fibers were mixed at a dosage of 0.5% by volume fraction to enhance tensile and flexural properties. During the third phase, zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) were utilized as a partial substitute for cement at concentrations of 0.5% and 1% to improve microstructure and strength progression. Concrete samples were tested at curing durations of 7, 28, and 91 days. The assessed qualities encompassed workability, density, water absorption, porosity, compressive strength, flexural strength, and splitting tensile strength. Microstructural characterization was conducted utilizing X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The findings indicated that porcelain waste powder markedly surpassed brick waste powder in all mechanical and durability-related characteristics, particularly at 25% and 50% sand replacement ratios. The integration of polypropylene fibers enhanced fracture resistance and ductility. Moreover, the incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles improved hydration, optimized the pore structure, and resulted in significant enhancements in compressive and tensile strength throughout prolonged curing durations. The best results were obtained with a mix of 50% porcelain sand aggregate, 1% zinc oxide nanoparticles as cement replacement, and 0.5% polypropylene fibers, for which the improvements in compressive strength, flexural strength, and splitting tensile strength were 39.5%, 46.2%, and 60%, respectively, at 28 days. The results confirm the feasibility of using porcelain and brick waste as sand replacements in concrete, as well as polypropylene fiber-reinforced concrete and polypropylene fiber-reinforced concrete mixed with zinc oxide nanoparticles as a sustainable option for construction purposes.
1. Introduction
The building industry has a dual challenge: the exhaustion of natural sand supplies and the accumulation of substantial amounts of construction and demolition waste (CDW) [1,2,3]. Sand is an essential element in concrete manufacturing, which is being depleted at an unsustainable rate, resulting in environmental deterioration and resource scarcity [4]. Ceramic and masonry waste, mainly from fractured tiles, porcelain, and bricks is concurrently being disposed of in landfills or illicit dumping sites, exacerbating ecological and urban management issues [5,6]. Recent research has investigated the utilization of recycled materials as partial substitutes for natural aggregates in concrete to reduce these difficulties [7,8]. Prominent candidates include porcelain waste and brick waste, which are numerous, inert, and exhibit physical characteristics that render them appropriate as alternatives for sand when adequately treated [9]. Porcelain waste derived from high-fired ceramic products demonstrates low water absorption, great hardness, and superior mechanical integrity. These attributes render it a significant competitor for augmenting the strength and durability of concrete [10]. Conversely, clay brick waste, despite being more porous and less strong than porcelain, is abundantly accessible and readily crushable, providing an economical option for resource recovery and landfill minimization [11,12]. Despite extensive research on the effects of recycled ceramics or masonry waste on concrete properties, there is a paucity of studies systematically comparing materials with distinct physical and mechanical characteristics such as porcelain and brick at various replacement levels [13,14]. There are many studies regarding the utilization of waste materials into concrete mix. Li et al., (2023) [15] examined the effects of porcelain waste as a replacement for coarse aggregate and fine aggregate in concrete subjected to various temperatures (25, 200, 400, 600, and 800 °C) at varying replacement levels (0 to 50%). The incorporation of porcelain waste enhanced the mechanical properties of modified samples under normal conditions. The changes in the properties with the addition of porcelain waste were analyzed using TGA-DSC, XRD, and SEM. The results indicated that increasing the temperatures of concrete samples modified with porcelain waste led to a greater loss of mass. The compressive strength of samples containing porcelain waste as a coarse aggregate diminished as temperature increased. Heating to 200 °C resulted in an (0.8%) increase in the CS of concrete containing porcelain waste as fine aggregate. A minor decrease in the splitting strength was observed when exposed to temperatures below 200 °C. The results revealed that concrete containing porcelain as a fine aggregate exhibited a superior resistance to increased temperatures compared to concrete containing porcelain as a coarse aggregate. Şenol and Karakurt, (2024) [16] studied the upgrading of high-strength compacted (concrete) samples incorporating fly ash (F.A) and recycled clay brick powder (R.CBP) as cement replacements at 10%, 15%, and 20% from construction demolition waste (C.D.W). The samples were tested for physical and mechanical characteristics as well as microstructural analysis after curing at 28, 56, and 90 days. The compressive strength of mixes with F.A and R.CBP was lower compared to that with R.CBP only, except for in the case of 10% R.CBP mixes. The compressive strength of 10% F.A, 10% R.CBP, and 15% R.CBP mixes was greater than the reference mix by 1.6%, 5.6%, and 1%, respectively, after 90 days. After 28 days of curing, SEM results indicated that the sample with 10% R.CBP cement replacement had a higher amount of hydration products found on the surface and fewer holes. Hosen and Bărbulescu (2025) [17] investigated the mechanical performance of concrete mixed with ceramic tile waste (C.T.W) as a substitute for brick aggregate and assessed its impact on strength and durability. Three sets of concrete samples were fabricated with 20%, 40%, and 70% of their brick aggregate substituted by C.T.W, in addition to a reference sample with standard coarse aggregate. A mix ratio of cement/sand/gravel (1:2:4) with a water-to-cement ratio of (0.5) was utilized. Mechanical and durability assessments were performed at 14 and 28 days. The findings demonstrated a notable enhancement in compressive strength by substituting brick chips with (C.T.W), with a minor increase in water absorption. Substituting brick aggregate with ceramic tile waste in concrete is a feasible approach to enhancing performance and providing significant environmental advantages.
A significant number of investigations have been done on the incorporation of various kinds of fibers into concrete including natural fibers (such as jute and cotton) and synthetic fibers including glass, steel, carbon, polypropylene and PVA [18]. Yuan and Jia (2021) [19] examined the influence of glass fibers (G.Fs) and polypropylene fibers (PP.Fs) on the microstructural and mechanical properties of concrete including the water-to-cement ratio and fiber quantity. Its utilized various proportions of w/b (0.30 and 0.35) with G.Fs or PP.Fs by volume fraction of (0.45, 0.90 and 1.35%) at (7 and 28 days) to fabricate the concrete samples. The compressive, flexural and split tensile strengths as well as water absorption of concrete samples were assessed. The findings indicated that the w/c ratio influenced the ideal proportion of fibers. At a w/b of 0.30, which is the water absorption of G.Fs and PP.Fs reinforced concrete remained constant during the tests. However, when the w/c ratio increased up to 0.35, water absorption increased in all samples particularly those with the highest fiber content. Chapoñan Inoñan et al. (2024) [20] evaluated the mechanical, physical and microstructural characteristics of PP.Fs-reinforced concrete. The PP.Fs with length (15–30) mm and diameter (0.05 mm) incorporated in volume fraction of (0.50%, 1.0%, 1.5% and 2.0%) and w/c of (0.705). The findings demonstrated that the best ratio of PP.Fs was 1.5% at which the workability and unit weight staying within acceptable limits, while the air volume decreased. Improvements were noted in compressive (CS), flexural, splitting strengths and elastic modulus with increases of 12.40%, 24.59%, 20.76% and 7.44%, respectively compared to the reference sample. Increasing the fiber content beyond 1.5% resulted in a decrease in strength compared to the reference sample. XRD of mixes with 1.5% PP.Fs indicated increased levels of silicates, Ca and SiO2 highlighting the substantial fibers influence on the concrete characteristics. SEM of mixes reinforced with 1.5% PP.Fs revealed a more homogeneous, denser and less porous structure in comparison to the reference sample. Tan et al. (2025) [21] studied the concrete modified by adding three types of polypropylene fibers: macro, Barchip and monofilament in amounts of 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.3% by volume fraction. Recycled granite powder was utilized as a partial substitute for fine aggregate to enhance matrix density and encourage sustainability. The findings indicated that increasing fiber amounts substantially enhanced mechanical characteristics. The hybrid of Macro-Barchip-Monofilament (MBM) polypropylene fiber mix demonstrated enhanced strength performance relative to the Barchip-Monofilament (BM) PP.Fs mix. These improvements were primarily attributed to the synergistic impact of the hybrid PP.Fs. Barchip PP.Fs effectively reduced fracture propagation, whereas macro PP.Fs provided fine reinforcement to restrict cracks. Simultaneously, the distribution of monofilament PP.Fs within the concrete matrix enhanced homogeneity. There are several studies involving the mixing of nanoparticles in concrete and cement mortar. Gopalakrishnan and Nithiyanantham (2020) [22] focused on evaluating the chemical, physical and mechanical properties of cement mortar modified by ZnO nanoparticles as cement replacement at percentages (1%, 2%, 3%, 4% and 5%). The mixtures were prepared with a w/c ratio of 0.4 and a cement to sand ratio of (1:3). The properties include setting time, compressive strength, bending strength, porosity, water absorption, sulfate resistance and electrical resistance were studied. The setting time of mixes incorporated with ZnO-NPs decreased dramatically with the increase in the CS. It’s indicated that the bending strength ZnO-NPs mixes exceeded that of the reference sample. The microstructure ZnO-NPs mixes showed that these nanoparticles largely filled the pores and decreased the dimensions of the large calcium hydroxide crystals to provide further hydration products. Patil and Dwivedi (2021) [23] studied the effects of ZnO nanoparticles on the compressive strength of the cemented mortar. Four mixes were produced by mixing of ZnO-NPs at (0.25, 0.50 and 0.75%) of the cement, respectively. Experimental results showed an increase in compressive strength up to (0.50%) and there after a gradual decreasing of compressive strength. The best performance for the mix with (0.50%) of ZnO-NPs. Garg and Garg (2021) [24] studied the incorporation of ZnO-NPs on the properties of silica fume-based cement composites. The effect of different quantities of silica fume (S.F) and of ZnO-NPs on the early and standard age compressive strength as well as the microstructure of composites was investigated. Compared with silica fume (S.F), ZnO-NPs had a more remarkable effect on the physical properties. The mechanical properties were related with microstructural characterization. The evaluation further demonstrated the advantageous effect of ZnO-NPs in enhancing the strength due to pore refinement compared to the reference sample.
Although several studies have investigated the feasibility of utilizing construction waste as a partial replacement for sand in concrete. Most studies have concentrated on only one waste type, without a systematic comparative analysis of different types of waste. Moreover, scientific examination of the synergistic impact of utilizing construction waste including porcelain and brick separately, along with the incorporation of polypropylene fibers and zinc oxide nanoparticles is limited in the current literature. Moreover, the influence of different combinations on the mechanical, physical and morphological characteristics of concrete has not been comprehensively investigated indicating a distinct research gap that this study aims to fill.
2. Experimental and Testing Program
2.1. Raw Materials
2.1.1. Cement
The study utilized Type I (42.5 R) ordinary Portland cement obtained from Iraq with the trade name “Al-Mass” at Al-Sulaymaniyah city. The chemical composition of the cement fulfilled the standards of Iraqi specification (No. (5)/1984) as well as the standard ASTM (C150) [25,26], as shown in Table 1. The physical characteristics of cement used illustrate in Table 2.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of cement used.

Table 2.
Physical characteristics of cement used.
2.1.2. Natural Aggregates
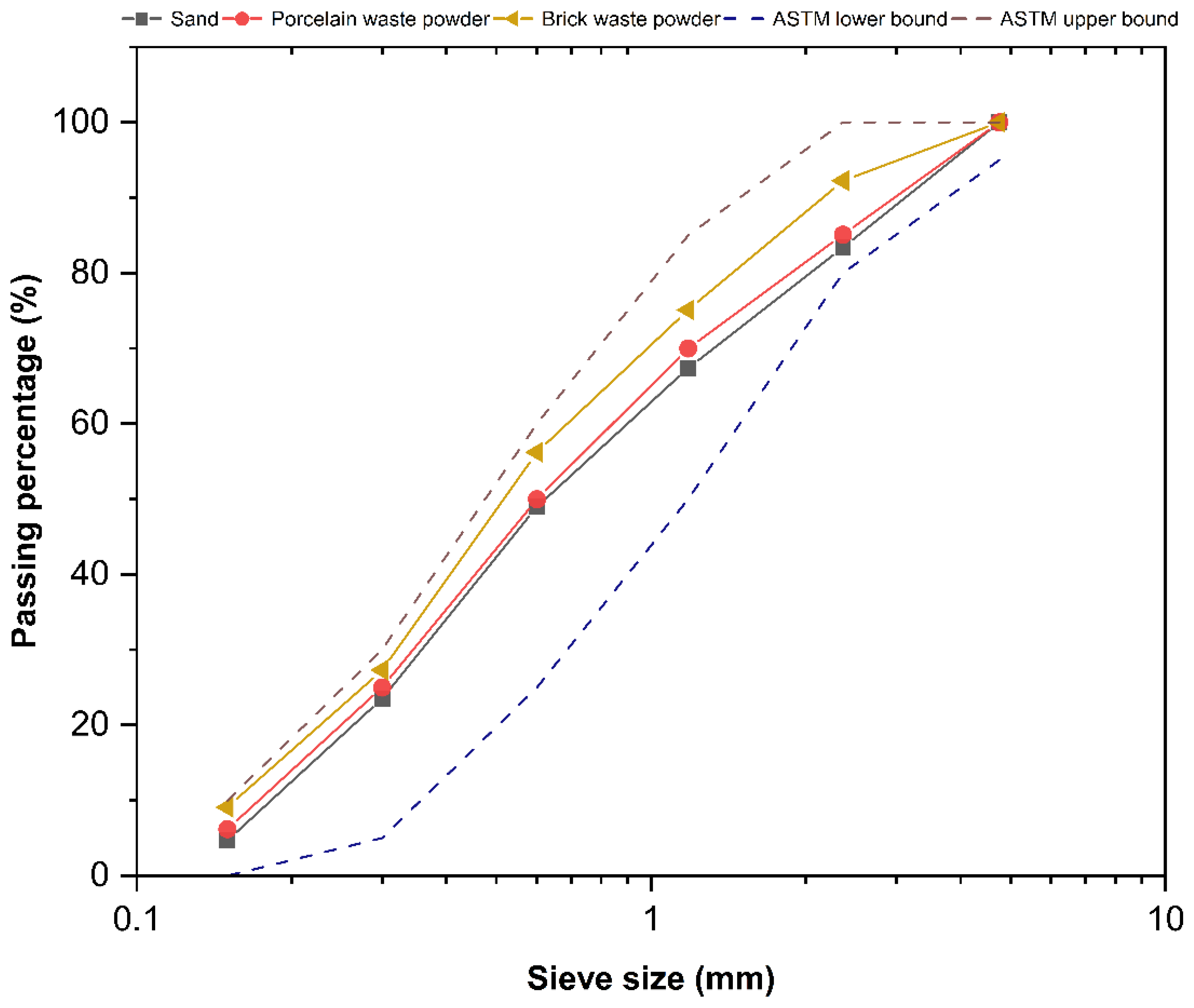
Crushed gravel having a specific gravity of 2.58 has been utilized as a coarse aggregate in all mixtures. The maximum size was less than 19 mm, and they were sourced from the Abu Sakhir site in the province of Al-Najaf, Iraq. The physical properties of the coarse gravel according to the Iraqi standard (IQS No. 45) and ASTM C33. The fine aggregates used in the study were sourced from the Al-Obaidy factory in the Al-Ekadir region in the province of Karbala, Iraq. The fine aggregates were passed through a No. 4 sieve, which is 4.75 mm in size. The material’s grading satisfies the requirements of the Iraqi specifications (IQS: 45/1984) and ASTM C33 [27,28], which are illustrated in Figure 1. The physical characteristics of the sand utilized are detailed in Table 3.
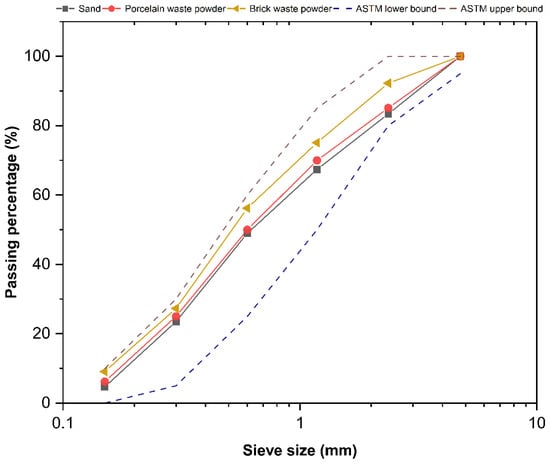
Figure 1.
Grading of sand, porcelain waste powder and brick waste powder.

Table 3.
Physical characteristics of sand.
2.1.3. Waste Powder Materials (WPMs)
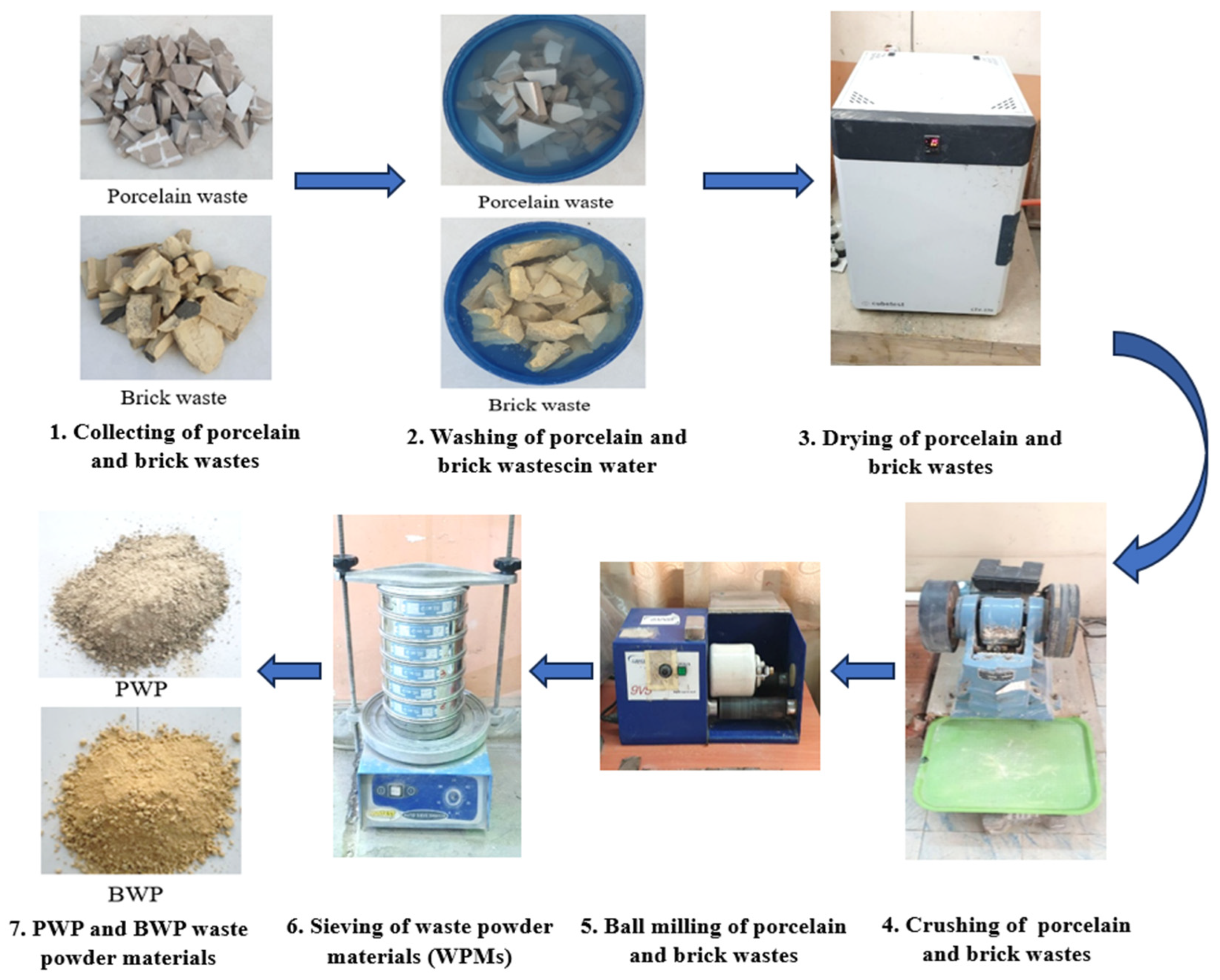
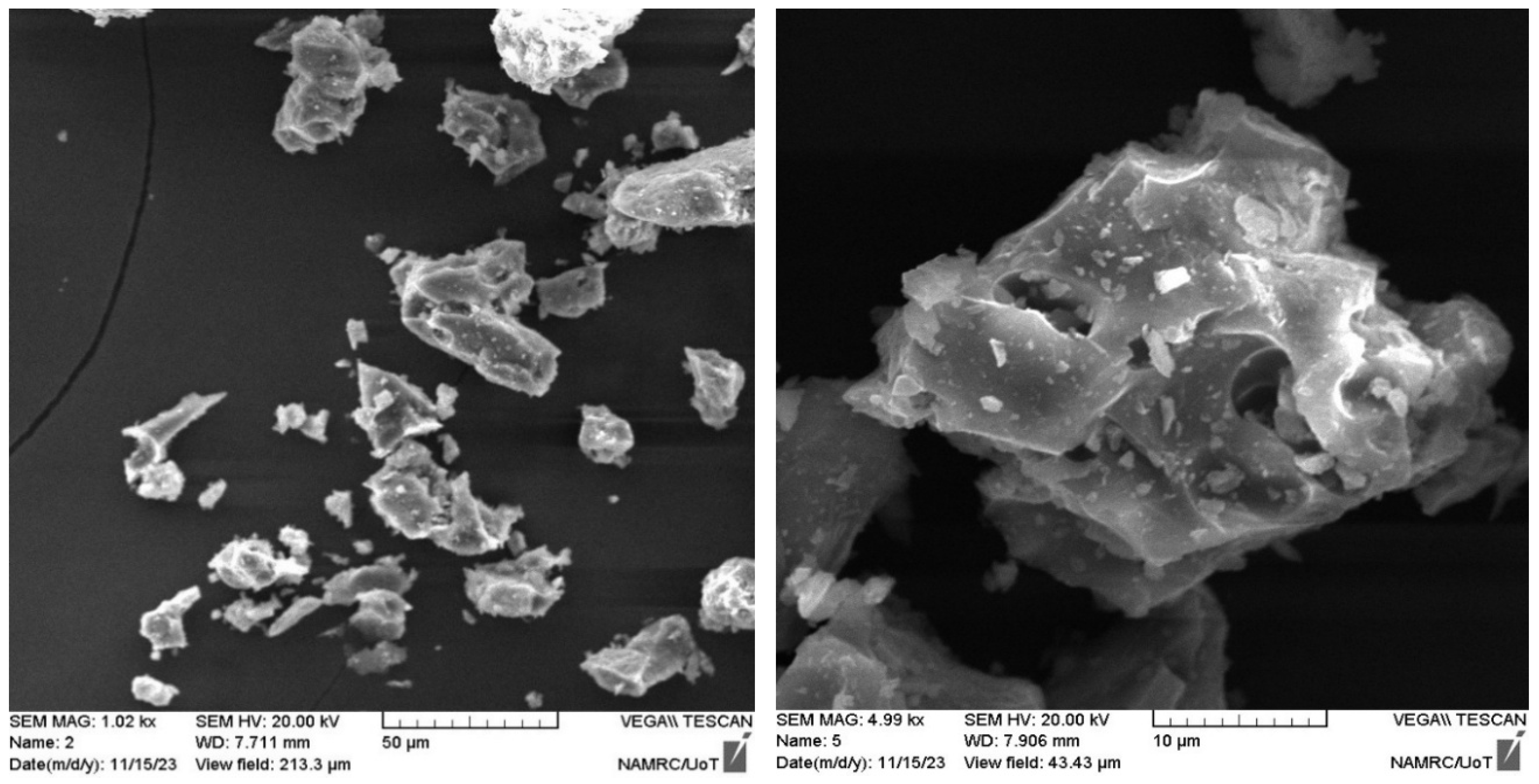
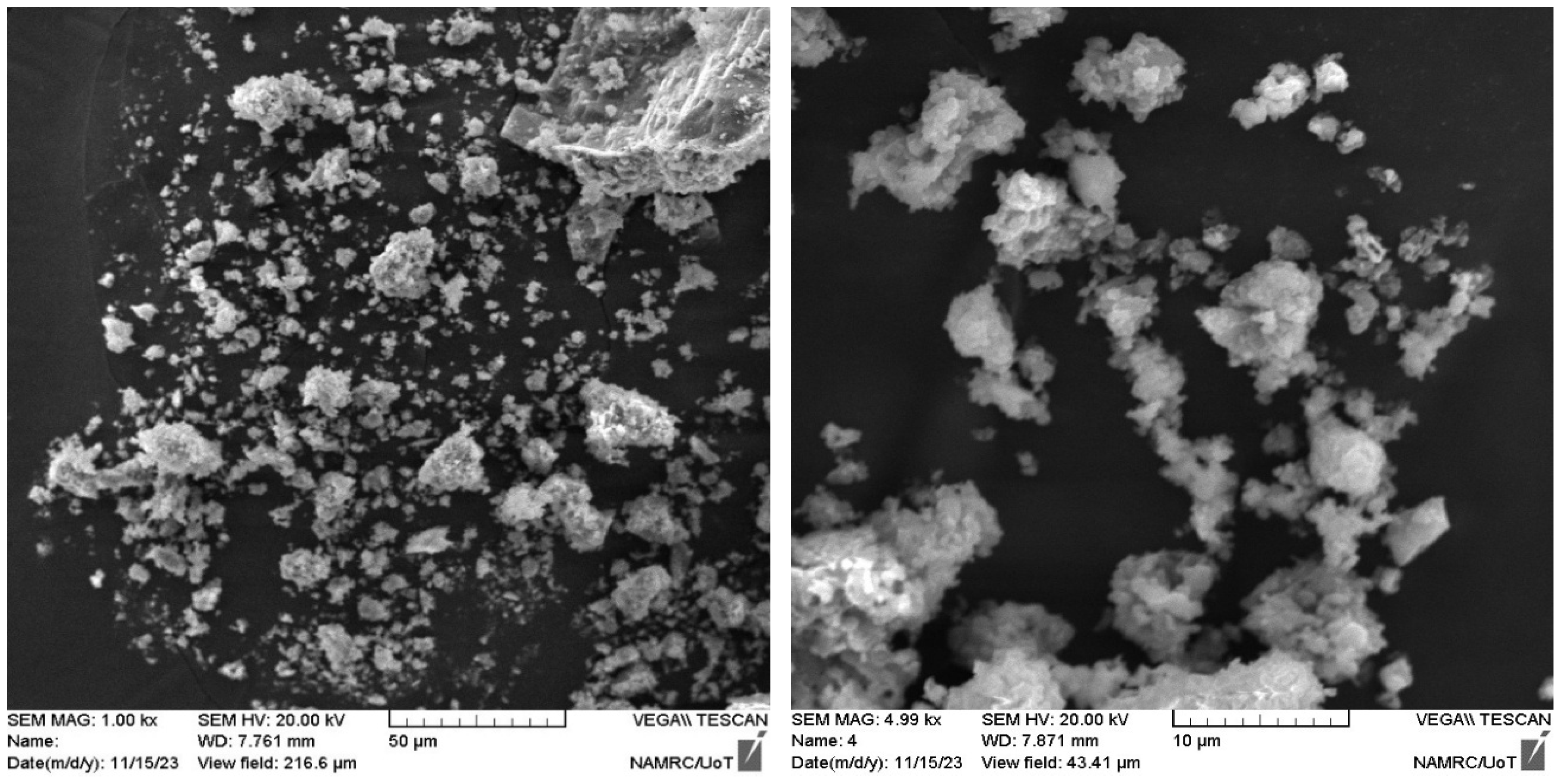
Powders were fabricated from construction waste to be utilized as replacements for fine aggregates in concrete mixtures in different proportions. Construction waste was collected from building demolition operations, cleaned, and separated for later treatment. The materials collected from demolition waste are porcelain and bricks. These wastes were crushed and ground to a granular gradation of sand with a size less than 4.75 mm in accordance with ASTM/C33. Figure 2 shows the processes for preparing waste powder. Table 4 depicts the main chemical composition of WPMs, including PWP and BWP. SEM micrographs of porcelain powder are illustrated in Figure 3. The images displayed a dense structure and irregular grains with sharp edges characterized by a broken surface with sharp angles. This data indicates the hardness of the original porcelain material and its considerable resistance to fine fracture [29]. Figure 4 presents the SEM micrographs of clay brick powder. It exhibits an elongated shape, rough surface texture, microcracks and a porous internal structure. This results from the porosity caused by brick production at comparatively low temperatures (700–900 °C) utilizing clay that contains organic material or burnt contaminants. The porosity, along with the brittle composition causes the brick particles to break down readily during grinding. This yields somewhat finer particles in comparison to materials of greater hardness [30].
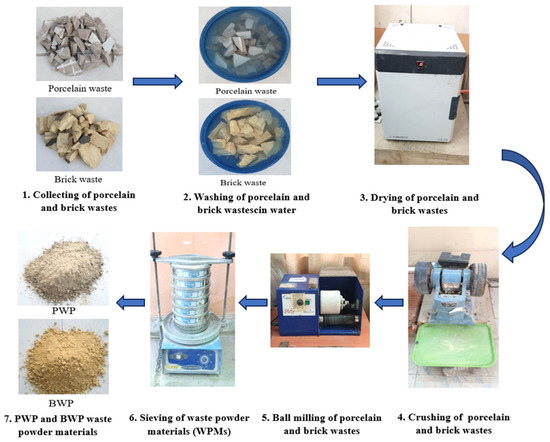

Figure 2.
Stages for production of Porcelain/brick waste powder materials (WPMs) from waste building materials.

Table 4.
Main chemical composition of PWP and BWP.

Figure 3.
SEM micrographs of porcelain waste powder (PWP).
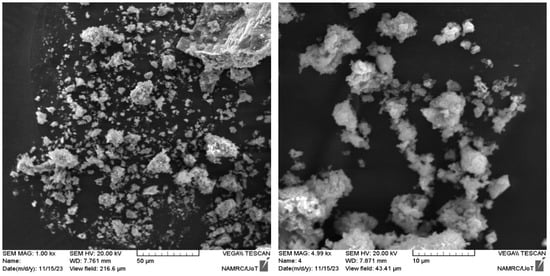
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs of brick waste powder (PWP).
2.1.4. Polypropylene Fibers (PP.Fs)
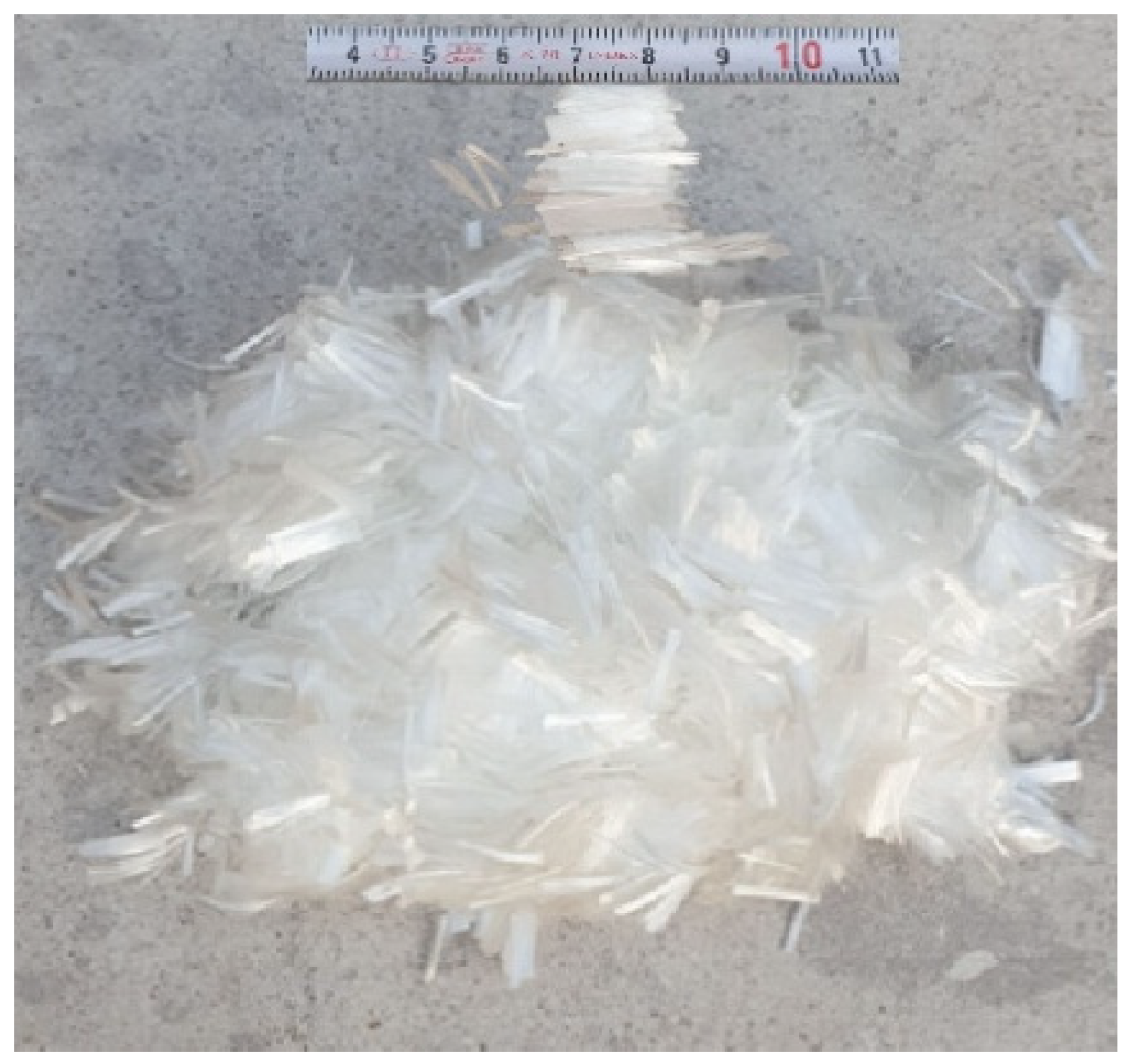
Polypropylene fiber is a long-chain polymer that is made up of only propylene units in weight. It comes in different sizes and is already packed and ready to use. Polypropylene fibers have a low elastic modulus, greater elongation, and high tensile strength, which means they meet the following standards: ASTM C1116 [31]. Polypropylene fibers with l = 12 mm and d = 0.032 mm were chosen for their small diameter and moderate length, facilitating uniform dispersion inside the concrete without clumping, so successfully reducing the microcracks and improving ductility as well as flexural performance. Polypropylene fibers were provided from the Sika branch for building chemicals in Baghdad/Iraq. Table 5 shows the usual features of PP.Fs. Figure 5 displays an image of polypropylene fibers that were used in this work.

Table 5.
The features of PP.Fs used according to provider.
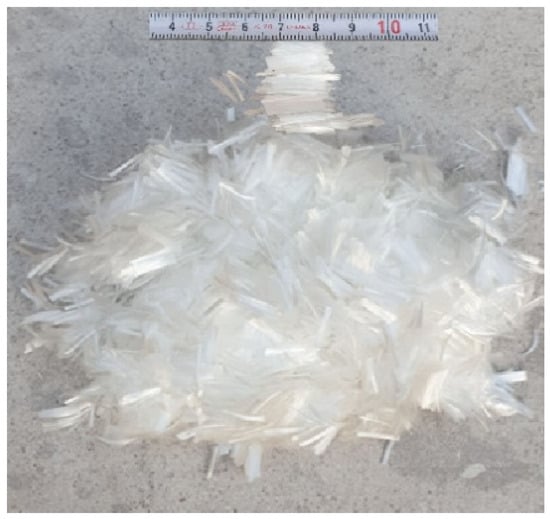

Figure 5.
Polypropylene fibers used in this work.
2.1.5. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs)
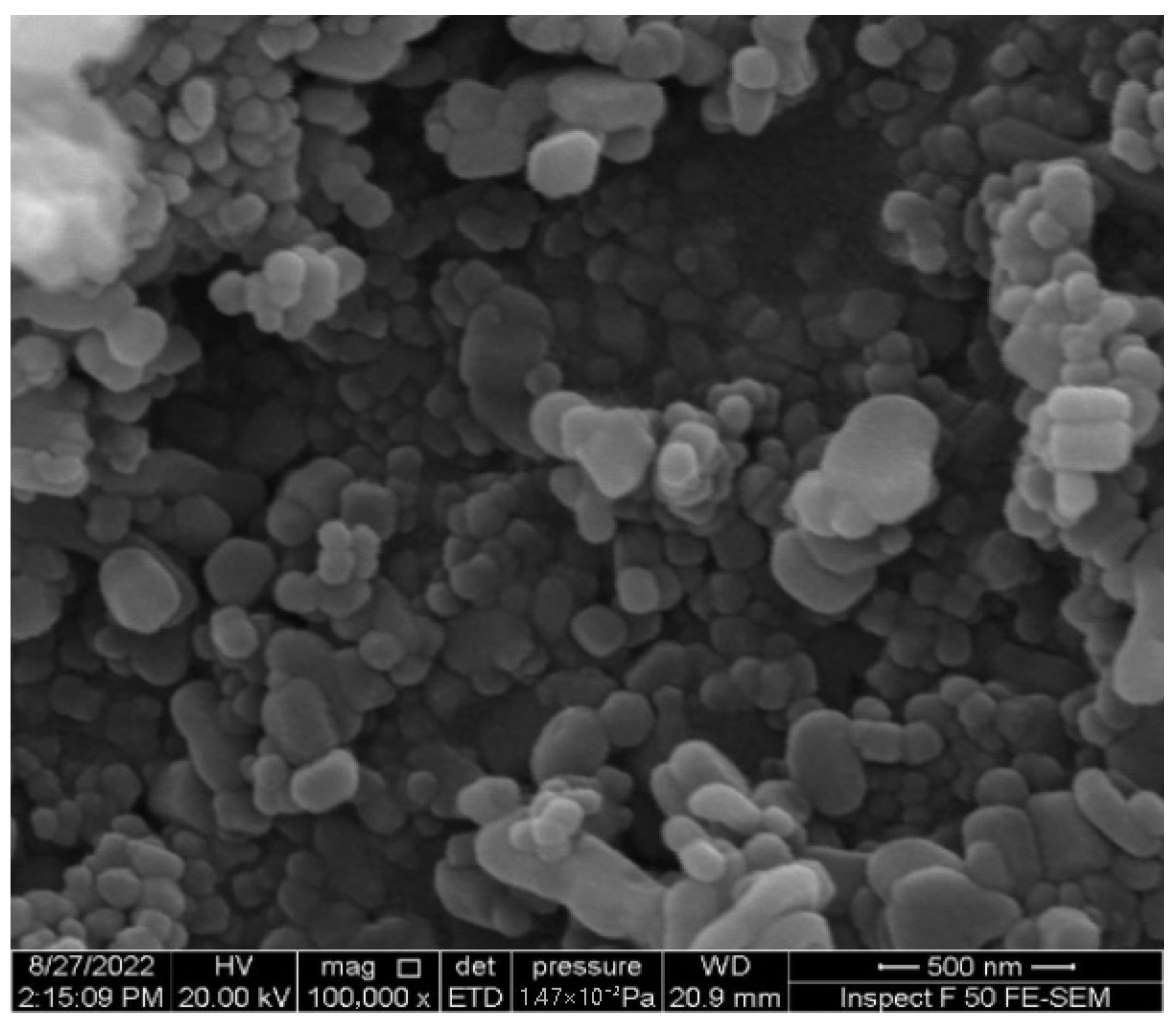
Zinc oxide is an inorganic substance with the appearance of a white powder. ZnO-NPs were sourced from Skyspring Nanomaterials, Inc., Houston, TX 77082, USA. Table 6 showed the properties of ZnO-NPs utilized in this work and Figure 6 showed the SEM image for the ZnO-NPs.

Table 6.
Properties of ZnO-NPs utilized in this work.
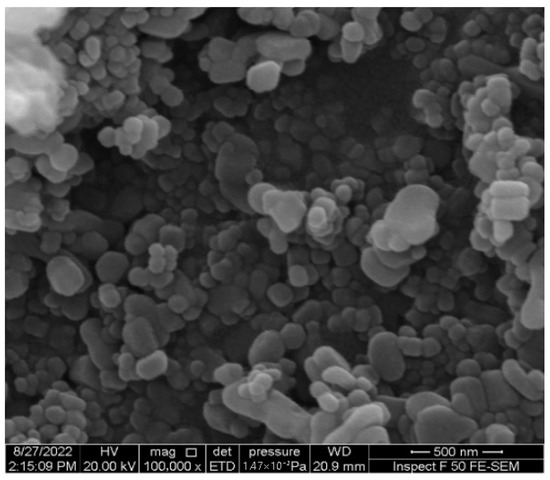
Figure 6.
SEM image of the ZnO-NPs.
2.1.6. Chemical Admixture (S.P)
Polycarboxylate superplasticizer (type F) is utilized as a chemical additive to decrease the water content in the concrete mixtures. The product utilized is designated as Sika ViscoCrete 5930 L, supplied by the Sika branch of construction chemicals in Baghdad/Iraq. This product adheres to BS EN 934, Part 2:2001, and ASTM C494 requirements [32].
2.1.7. Water
All concrete samples were prepared and cured using tap water. The water has a pH of (7.5).
2.2. Preparation of Concrete
Mixing Proportion
Concrete samples were made in accordance with British Standard B.S. (5328-2:1997) [33]. A weight ratio of cement:sand:gravel (1:1.92:2.88) was employed for mixing, with the objective of achieving a goal strength of 30 MPa for reference concrete at four weeks. The preparing of concrete mixes involves three phases: the first phase is the incorporation of WPMs as substitutes for sand at 25%, 50% and 75%. The second phase includes the reinforcement of WPMs modified concrete in phase one by polypropylene fibers with a volume fraction of (0.5). The third phase involves the incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles at 0.5% and 1% as a substitute for cement in concrete mixtures of phase two. The 26 concrete mixing ratios in 1 m3 were depicted in Table 7. All mixes except the reference mix were made using a constant water to cement ratio of 0.5. In all mixes, a superplasticizer admixture of 1.1% of the cementitious materials was utilized to achieve concrete with acceptable workability.

Table 7.
Mixing ratios in 1 m3.
2.3. Mixing, Curing, and Preparation of Samples
A pan-type laboratory mixing machine with a capacity of 250–300 kg was utilized to mix concrete constituents. Dry mixing was employed, followed by the incorporation of water, fibers, and ZnO-NPs suspension. First, the fine aggregate and WPMs (i.e., PWP or BWP) were dry-mixed for two minutes in a mixer, then cement was added to the mix and mixed for one minute. Gravel was added, and the mixer was turned on for 1 min. Then PP.Fs were added to the dry mix and mixed for another 1 min. The method of incorporating ZnO-NPs into the concrete mixture is crucial for assessing its efficacy and influence on the mechanical properties and microstructure of concrete, due to the agglomeration and sensitive nature of nanoparticles. This study employed wet dispersion to achieve excellent particle distribution in mixtures; ultrasonication is employed for five minutes to provide more effective dispersion of ZnO-NPs. This method mitigates agglomerations caused by van der Waals forces among ZnO-NPs. To prepare a solution of ZnO-NPs, it is added to half of the mixing water, and subsequently this solution is added to the other dry mixture (cement, sand, aggregate, WPMs and fibers) in a concrete mixer, adhering to the prescribed mixing sequence. The other half, mixing water, is mixed with superplasticizer and this solution is added after two minutes of continuous mixing by adding the ZnO-NPs solution to the mixer. Finally, mix for 2 min after the complete addition of all constituents to the mixer. Standard operating parameters for the mixing operation included a 27 °C ambient temperature.
Standard molds of cubic (100 × 100 × 100 mm3), prism (100 × 100 × 400 mm3) and cylindrical with diameter × height (100 mm × 200 mm) were employed to produce concrete samples in accordance with BS EN 12390-1 [34]. The interior surfaces of the molds were greased with oil to prevent the concrete from adhering during solidification. The concrete mixture was put into molds and subsequently compacted with an electric vibrating apparatus to eliminate any voids in the structure. This guarantees adequate compaction and eradicates air pockets. This experiment involves casting different sample dimensions using designated molds including cubic, prisms and cylindrical samples. Samples were extracted after 24 h from casting. Subsequently, each concrete sample was placed in water tanks and subjected to ambient temperatures for ages 7, 28, and 91 days.
2.4. Testing Program
This investigation involved carrying out several tests, as illustrated in Table 8 detailed in the following sections.
2.4.1. Fresh Properties
The workability (i.e., slump) test is conducted on fresh concrete for all mixes. The testing procedure is performed on all concrete mixes (i.e., reference and modified) in accordance with the ASTM C143 standard [35].
2.4.2. Hardened Properties Testing
- A.
- Compressive Strength
The test is conducted according to standards BS 1881-116 by using compressive testing machine, MATEST Co., Italy [36]. Each concrete sample with a cube size of 100 mm3 was produced to test the development of compressive strength in different concrete mixtures over time. The compressive strength examined at ages 7, 28 and 91 days. Three cubic samples were casted for each mix and age.
- B.
- Flexural Strength
The flexural strength test is conducted according to ASTM C293 [37]. It was performed on prism samples of 100 × 100 × 400 mm3. Three samples were tested for each mix at 7, 28, and 91 days of age. The test was done using a Center-Point loading machine (150 kN), MATEST Co., Italy. It was conducted in accordance with ASTM C293.
- C.
- Splitting Tensile Strength
The splitting tensile strength test on cylindrical concrete samples is carried out in accordance with ASTM C496 utilizing the compressive testing machine, MATEST Co., Italy [38]. The cylindrical molds with dimensions of 100 mm × 200 mm in diameter and height, respectively. At curing of 7, 28 and 91 days, three samples were tested for every concrete mix.
- D.
- Dry Density, Porosity and Water Absorption Tests
The density, porosity and water absorption were calculated according to the procedures specified in ASTM C642 [39]. The test used concrete samples in the form of cubes of (100 × 100 × 100) mm3 at ages 28 and 91 days. The procedure of measuring dry density, porosity, and water absorption involving: (A) Drying the concrete samples in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h and left them to cool at atmosphere then measured the dry weight, (B) Immersing the samples in water at 24 °C and measured the submerged weight, (C) Measuring the saturated surface dried-weight (SSD) of the samples after wiping the surfaces by smooth cloth. The dry density, porosity, and water absorption were calculated by Equations (1)–(3), respectively. Each result was measured three times to obtain the average value.
w1 indicates the weight of the dry sample (g), w2 represents the weight of the saturated surface-dry sample (g), w3 shows the weight of the submerged sample in water (g), and ρw implies the density of water, quantified as (1 g/cm3).
2.4.3. Microstructural Analysis
- A.
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
This test was employed to investigate the crystalline structure of solid substances through X-ray diffraction. For diffraction studies, the Phillips Xpert Panalytical is manufactured by Malvern Panalytical, UK. It is a multifunctional X-ray diffractometer built with a source of Cu Kα with 2 theta angles in range (10–80°). Accurate phase identification and high-quality data collection are provided. A small piece of concrete sample after curing for 28 days was inspected by XRD [40].
- B.
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and EDS
The SEM test was carried out in accordance with ASTM:C1723-2010. The concrete specimen’s morphology was examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with the MIRA3 model produced by the TESCAN ORSAY HOLDING company, Czech Republic. The cubic specimens that were broken after compression test at 28 days. Approximately 1 × 1 × 0.5 cm in size, the tiny sections of specimens were employed for SEM observation. The energy dispersive spectroscopy technique is employed to identify the relative elemental compositions and the constituent compounds within a substance. EDS analyses were conducted in the series where SEM analysis was executed. This method is utilized for predicting the existence of ingredients that are crucial in the development of concrete strength [41].

Table 8.
A summary of the testing program.
Table 8.
A summary of the testing program.
| Test | Standard |
|---|---|
| Slump | ASTM-C 143 [35] |
| Compressive Strength | BS 1881-Part 116 [36] |
| Flexural Strength | ASTM C293 [37] |
| Splitting Tensile Strength | ASTM C496 [38] |
| Dry density, porosity and water absorption | ASTM C642 [39] |
| Microstructural Analysis | ASTM:C1723-2010 [41] |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Slump Test
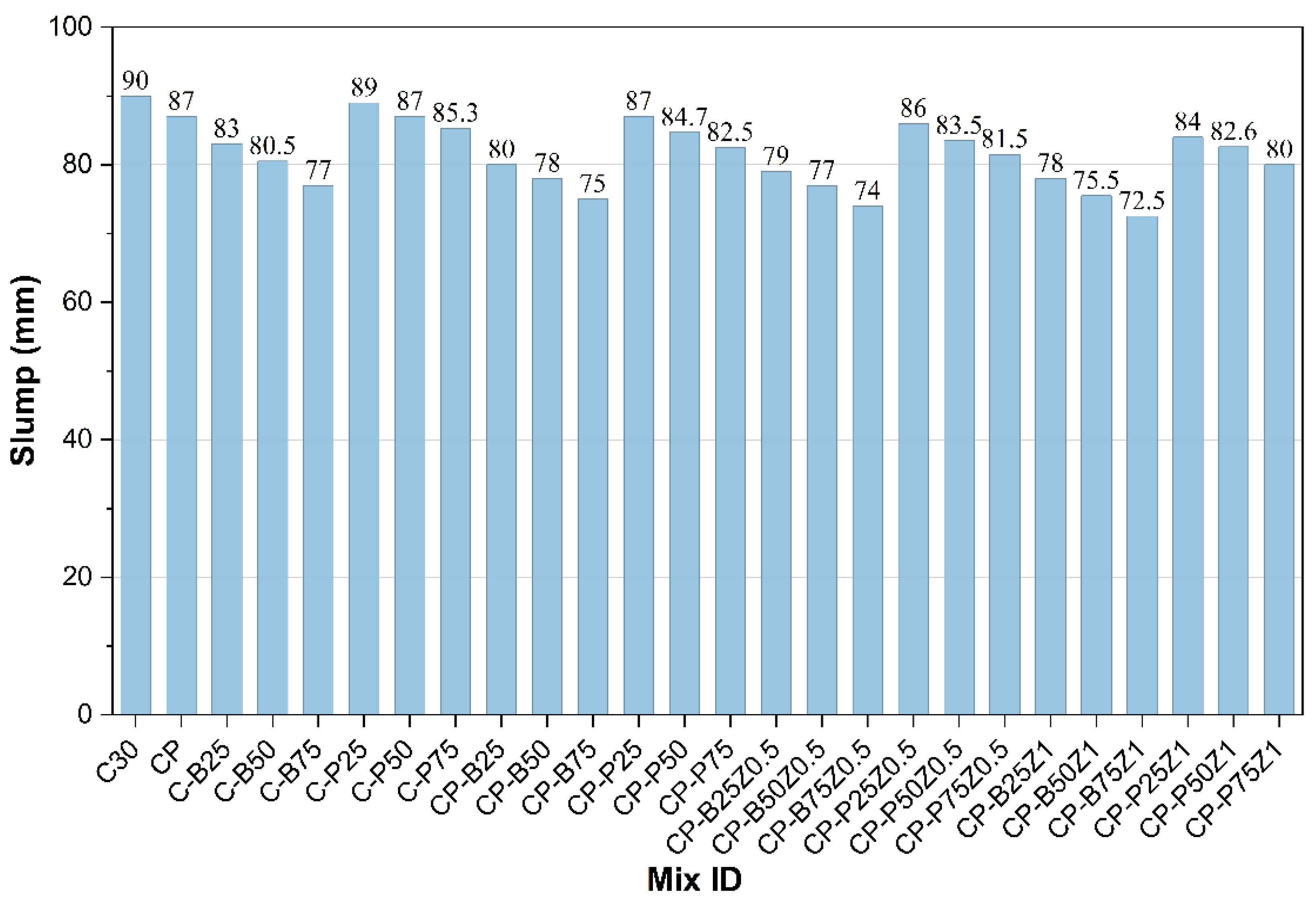
The slump results of the freshly reference concrete mix, along with the modified concrete mixes that included a sand partial replacement of 25%, 50%, and 75% with porcelain and brick, are presented. Also, the mixes modified with PP.Fs and ZnO-NPs as cement replacements with ratios of 0.5% and 1% are presented in Figure 7. Immediately after, the water was added and well-blended. The slump measurement of the C30 mix was determined to be 90 mm. Subsequently, upon beginning the sand replacement process, there was a decrease in the slump value. When the replacement ratios increased, the values of slump dropped due to waste powders like porcelain particles having angular shapes with sharp edges, leading to high friction with other constituents of the mix and hence lower fluidity, then reducing slumps. Brick waste powder, due to its porous nature and water absorption, reduces workability, particularly at higher sand replacement ratios [42,43]. The addition of PP fiber to the reference mix and mixes modified with WPMs that replaced sand led to a reduction of slump due to increased interlock and resistance to the movement of aggregates during mixing and pouring. When the incorporating of ZnO-NPs as a cement replacement in concrete mixes incorporated with PP.Fs and WPMs (sand replacement), the workability is further decreased. ZnO nanoparticles have a substantially greater surface area compared to cement particles. As a result, the mixture became more challenging to work with due to higher water absorption. All mixtures incorporating waste powders maintain slump values within the range of 75–95 mm [43,44].
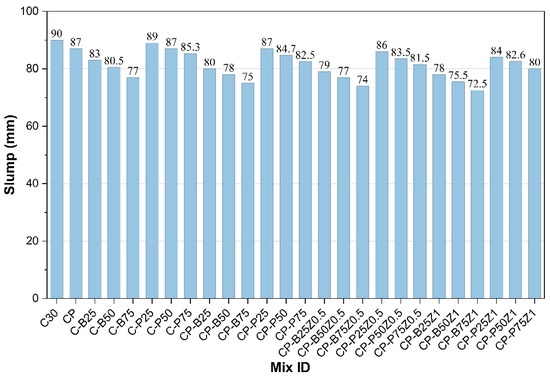
Figure 7.
The slump results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
3.2. Compressive Strength
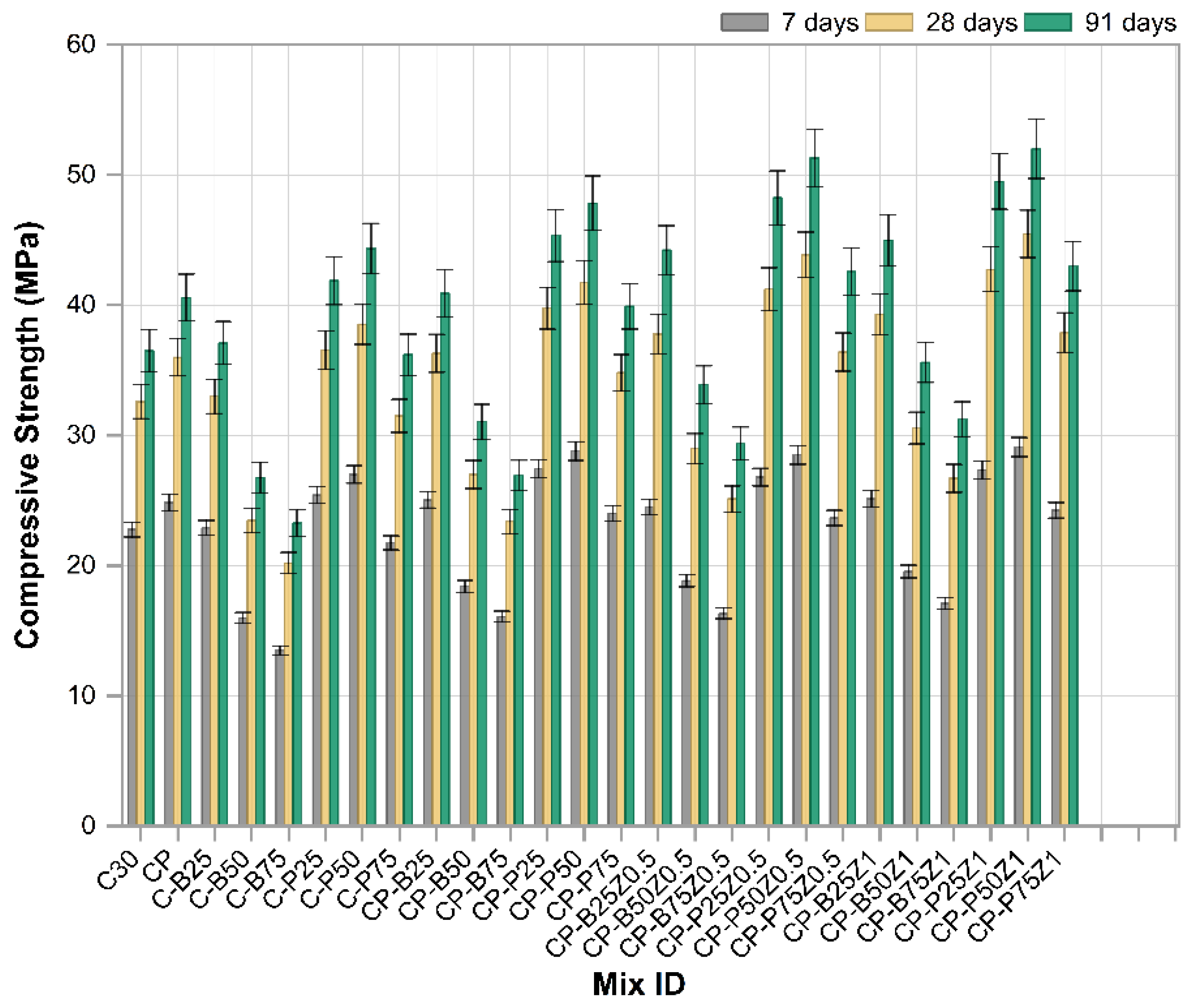
Figure 8 depicts the results of the compressive strength test of cubic concrete samples (10 × 10 × 10 cm3) at 7, 28 and 91 days tested at a rate of loading of 0.35 MPa/s. Each result is derived from the average of three measurements. The findings showed that the mixes with sand replacement (25% and 50%) of PWP have higher compressive strength than the reference sample at all ages, with the increases in compressive strength being 11.5%, 12.25% and 14.8% at 25% and 17.21%, 18.5% and 21.5% at 50%. At 75% of porcelain waste powder (PWP) replacing sand, CS decreased by 4.5%, 3.3%, and 0.82% for three ages (7, 28 and 91 days), respectively, compared to the reference sample. The trend of enhancement in CS of mixes mixed with PWP is attributed to its superior hardness relative to conventional fine aggregates as well as the fact that it contains amorphous silica and alumina, so it may be contributed to in pozzolanic reaction. Also, porcelain tiles are made under high pressure, resulting in superior compressive strength compared to ordinary aggregates. Moreover, porcelain tiles have superior compressive strength due to their distinct composition compared to natural aggregates. Consequently, concretes with PWP demonstrate enhanced compressive strengths as the porcelain waste powder content increases. Conversely, at higher levels of sand substitution, CS undergoes reduced due to the porosity increasing significantly [45]. The compressive strength increased by 0.6%, 1.3%, and 2.1% of 25% replaced sand with BWP, respectively, at 7, 28 and 91 days compared to the reference sample. At higher levels of sand replacement, there are decreases in CS for BWP of (29.7%, 27.9% and 26%) and (40.7%, 38% and 36.2%) for replaced sand at (50% and 75%), respectively, compared to the reference sample at (7, 28 and 91 days), respectively. The decline in CS of mixtures incorporating BWP at higher sand replacement may be attributed to the augmentation of the porous cement paste associated with these recycled aggregates as well as the portion of BWP fine particles which produced during the crushing process. These two variables impart to the BWP increased porosity, elevated water absorption, and reduced density compared to conventional sand, resulting in inferior concrete and thus diminished mechanical strength. It is noteworthy that the CS at 25% is about equivalent to or slightly enhanced to that of the reference sample. This is attributable to the uniform distribution of recycled aggregates within the concrete structure, indicating that the incorporation of 25% BWP does not hinder the effective hydration of the cement particles around the aggregates. On the contrary, finely brick waste aggregate may participate in the pozzolanic reaction of cement and thus improve the mechanical properties. When the replacement increased, BWP affected the mode of failure under compression due to the weak porous structure of clay brick particles [46]. The addition of polypropylene fibers with (Vf = 0.5) to the reference mix and mixes modified with PWP and BWB as sand replacements showed a significant increase in all percentages of sand replacement at all three ages: 7, 28, and 91 days. Addition of PP.Fs to reference concrete led to raising CS by 9%, 10.43% and 11.2% at 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively. Mixes like CP-P25, CP-P50, CP-P75, CP-B25, etc., indicated synergistic effects when fibers and waste materials were used together. Higher strengths are observed in combinations of CP-P50, CP-P25 and CP-B25. The CS values of CP-P50 enhanced by 26%, 28% and 31% for 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively, compared to the reference sample. For the CP-P25 mix, the CS was enhanced by 20.5%, 22% and 24.2% for 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively compared to the reference sample. While the CS values for CP-B25 were enhanced by 10%, 11.35% and 12% for 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively compared to the reference sample. The inclusion of PPFs in the concrete change its brittle characteristics towards ductile properties even with low fractions. So, the addition of PP.Fs led to improved cohesiveness between concrete components and postponed failure. This action led to improvement of mechanical characteristics [47]. The effect of incorporated nano zinc oxide at 0.5% and 1% as a cement replacement into PP.Fs-reinforced concrete modified with PWP and BWP as a sand replacement is investigated. The highest CS were observed in combinations of CP-P50Z1, CP-P25Z1 and CP-B25Z1. The CS values of CP-P50Z1 were enhanced by 35.6%, 39.5% and 42.5% for 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively, compared to the reference sample. For the CP-P25Z1 mix, the CS was enhanced by 25.5%, 31% and 35.6% for 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively, compared to the reference sample. While the CS values for CP-B25Z1 were enhanced by 17.2%, 20.6% and 23.4% for 7, 28 and 91 days, respectively, compared to the reference sample. The incorporation of ZnO-NPs leads to the enhancement of compressive strength for all mixes. This is attributed to the fact that nanoparticles of ZnO offer more active sites for the initiation of C-S-H gel development. Furthermore, nanoparticles of ZnO acted as very fine fillers, leading to a more compact structure of concrete and hence improving the mechanical characteristics. Consequently, ZnO nanoparticles improved hydration and microstructure refinement [48].
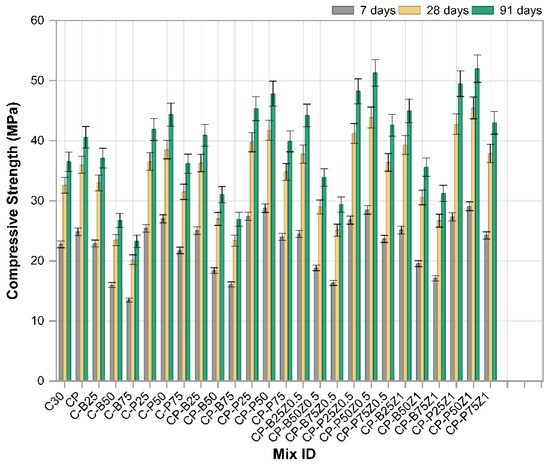
Figure 8.
The compressive strength results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
3.3. Flexural Strength
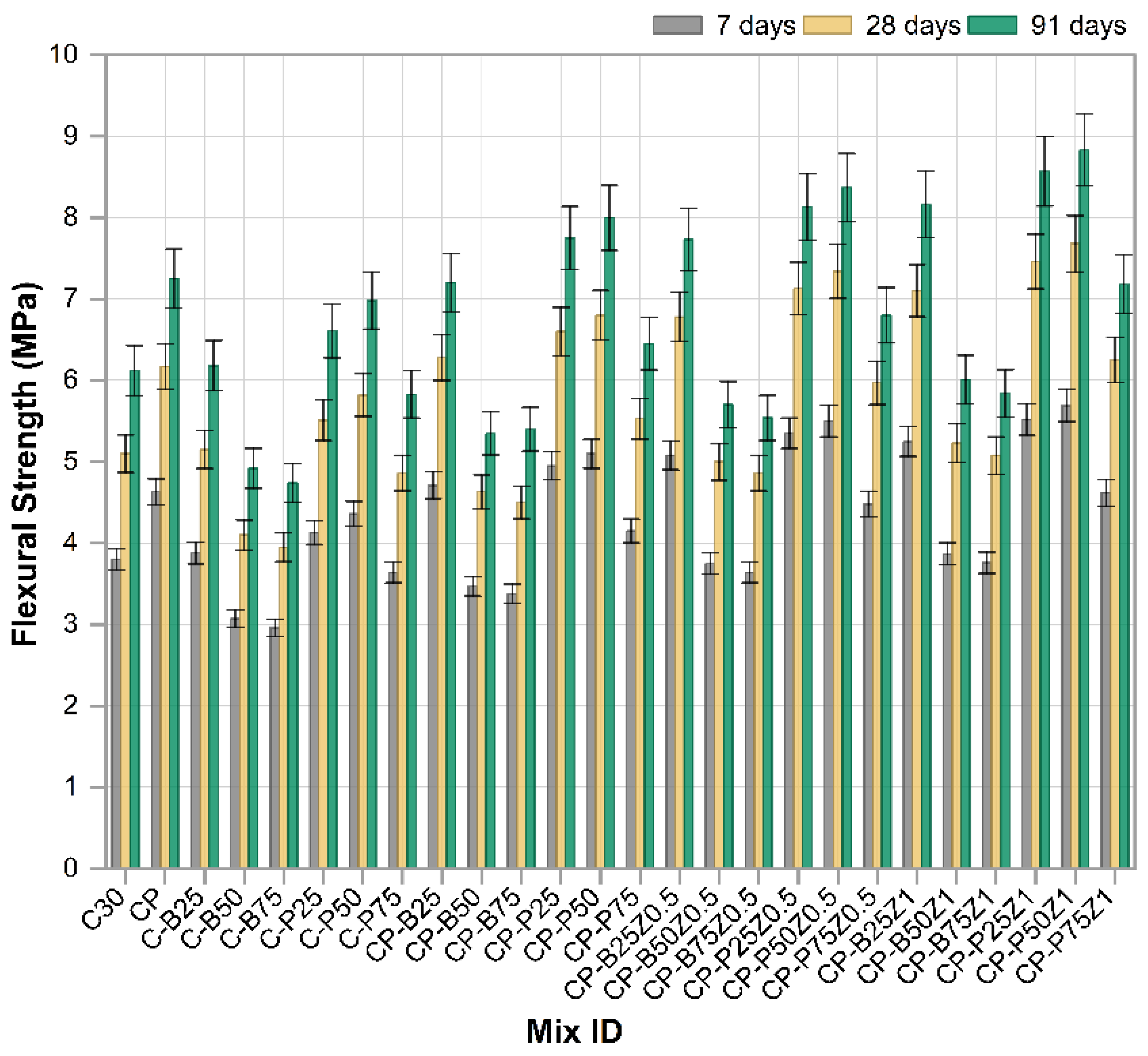
Figure 9 illustrates the development of flexural strength for the reference mix and concrete mixes incorporated with PWP, BWP, PP fibers and ZnO-NPs tested at 7, 28 and 91 days. The findings demonstrated that all mixes showed a distinct trend of increased flexural strength over time, illustrating the gradual development of the concrete microstructure due to continuous chemical reaction processes, notably hydration and pozzolanic reactions, compared to reference sample [49]. The reference mix C30 exhibited the lowest overall performance values, whereas the mechanical properties markedly improved with the implementation of changes. The incorporation of PP.Fs in modified concrete mixes with PWP and BWP as sand replacements resulted in increased flexural strength relative to C30. This is owing to their capacity to promote cement paste cohesiveness and mitigate the formation of microcracks. Mixes with PWP as a sand replacement, like C-P25, C-P50 and C-P75, exhibited notable enhancements in strength, especially at 25% and 50% replacement ratios. This results from the physical and chemical characteristics of porcelain, including its high hardness. Also, PWP consists of amorphous silica and alumina, which facilitate the pozzolanic reaction and enhance the generation of cementitious reaction products such as C-S-H, hence enhancing tensile and flexural strength. Conversely, with a 75% sand replacement ratio, F.S diminished slightly, attributed to increased porosity and diminished interparticle cohesiveness [49]. Mixes containing both fibers and PWP (e.g., CP-P25, CP-P50 and CP-P75) outperformed their single-component mixes, showing a synergistic interaction between the fibers and the pozzolanic additives. The effect reached its maximum level at CP-P50, which demonstrated one of the highest values for flexural strength at all ages [50]. Strength was significantly increased when nano zinc oxide (ZnO) (Z0.5 and Z1) was incorporated as a cement replacement to mixes that contained wastes and fibers. This effect was clear with combinations of CP-P50Z0.5, CP-P50Z1 and CP-P25Z1, where values at 91 days were above 8 MPa. This enhancement is attributed to the function of ZnO nanoparticles in facilitating cementitious interactions and forming a more cohesive microstructure, hence enhancing flexural strength and diminishing crack formation [51]. Conversely, concrete mixes incorporated with brick waste-like combinations (CP-B25, CP-B50 and CP-B75) and their nano-modified variants exhibited comparatively lower strengths than their porcelain-containing equivalents. This is demonstrating that the nature of the replacement material significantly affects performance, with porcelain proving to be more effective in enhancing the mechanical properties of concrete. The incorporation of porcelain fine aggregate, PP.Fs, and zinc oxide nanoparticles into concrete can substantially enhance the flexural strength and other mechanical characteristics. This combination will be useful in construction applications that necessitate resistance to tensile and flexural forces. While also promoting sustainability through the utilization of building waste in new building materials [50,51].
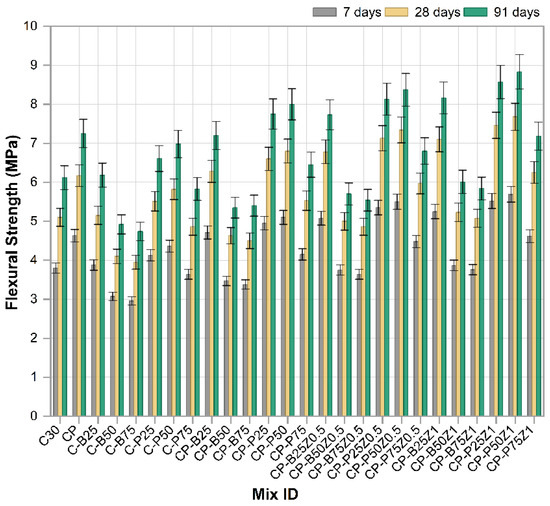
Figure 9.
The flexural strength results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
3.4. Splitting Tensile Strength
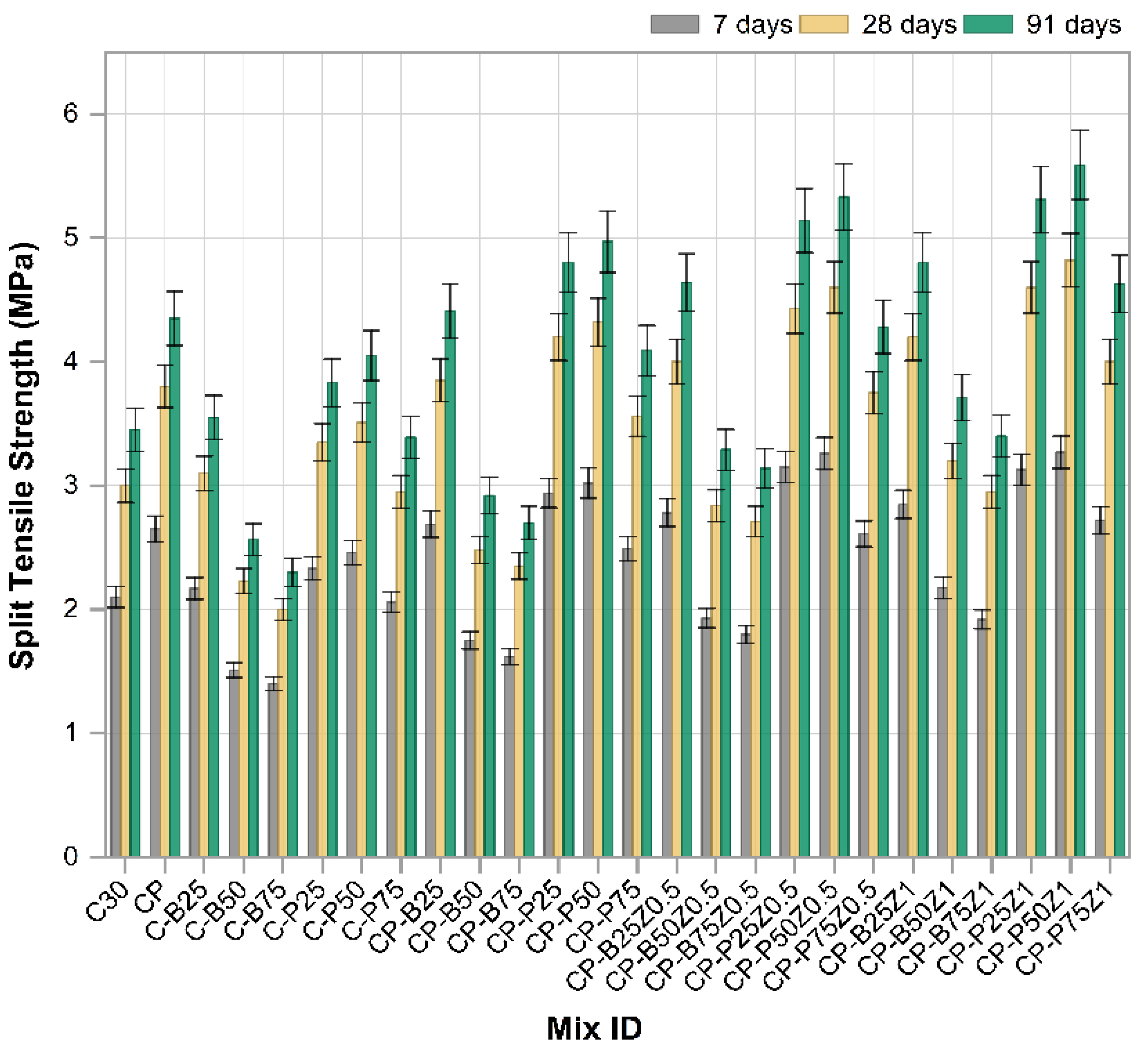
Figure 10 illustrates the development of split tensile strength for the reference mix and concrete mixes incorporated with PWP, BWP, PP.Fs and ZnO-NPs at 7, 28 and 91 days. All mixes demonstrated significant S.T.S. enhancements with age, indicating continuous hydration processes and microstructural evolution of the concrete throughout time. The reference sample (C30) had the lowest performance across all age groups. The incorporation of PP.Fs into the concrete mix resulted in a notable enhancement in tensile strength, thereby confirming the fibers’ effectiveness in enhancing bonding within the concrete and mitigating cracking under tensile stresses. Slight enhancements of S.T.S. were noted at lower replacement ratios when utilizing BWP as sand replacement (C-B25, C-B50 and C-B75). Nonetheless, performance declined at 75% sand replacement, probably due to the higher porosity and insufficient intergranular cohesion of the crushed bricks [52]. Conversely, porcelain waste mixes (C-P25, C-P50 and C-P75) exhibited a superior performance, especially at 25% and 50% percentages. The hardness of porcelain and its chemical composition comprising amorphous silica and alumina improved the pozzolanic reaction and hence enhanced the structural integrity of the cement paste [52,53]. When porcelain or brick wastes were mixed with fibers in mixes such as CP-B25, CP-B50, CP-P25 and CP-P50, distinct synergistic effects were observed, resulting in tensile strength exceeding that of mixes comprising only wastes or fibers. The most significant effect was noted in the CP-P50 and CP-P25 mixes, indicating that porcelain is a superior option compared to brick in this situation [54]. The incorporation of 0.5% and 1% zinc oxide nanoparticles into the composite mixes (CP-BZ and CP-PZ) resulted in the porcelain-containing mixes achieving the highest values, notably CP-P50Z1 and CP-P25Z1, which surpassed 5.5 MPa at 91 days. The enhanced performance is ascribed to the influence of ZnO nanoparticles in expediting cementitious reactions and occluding micropores, hence improving paste cohesiveness and diminishing crack propagation. In contrast, the brick combinations incorporating ZnO did not exhibit a comparable enhancement in strength, reinforcing the theory that the nature of the waste substituted is essential and that the physical and chemical characteristics of porcelain offer an advantage in enhancing the mechanical properties of concrete. In conclusion, the findings indicate that the ideal mix for enhancing the splitting tensile strength of concrete comprises 50% to 75% porcelain waste combined with polypropylene fibers and the incorporation of 1% nano ZnO, demonstrating significant potential for the development of durable and sustainable concrete utilizing recycled materials and efficient nanomaterials [55].
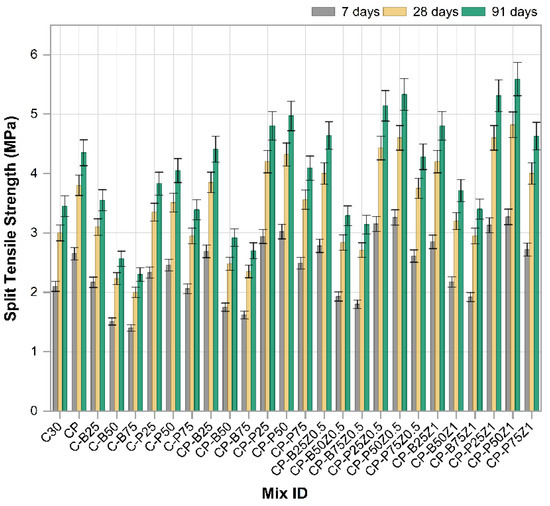
Figure 10.
The splitting tensile strength results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
3.5. Dry Density
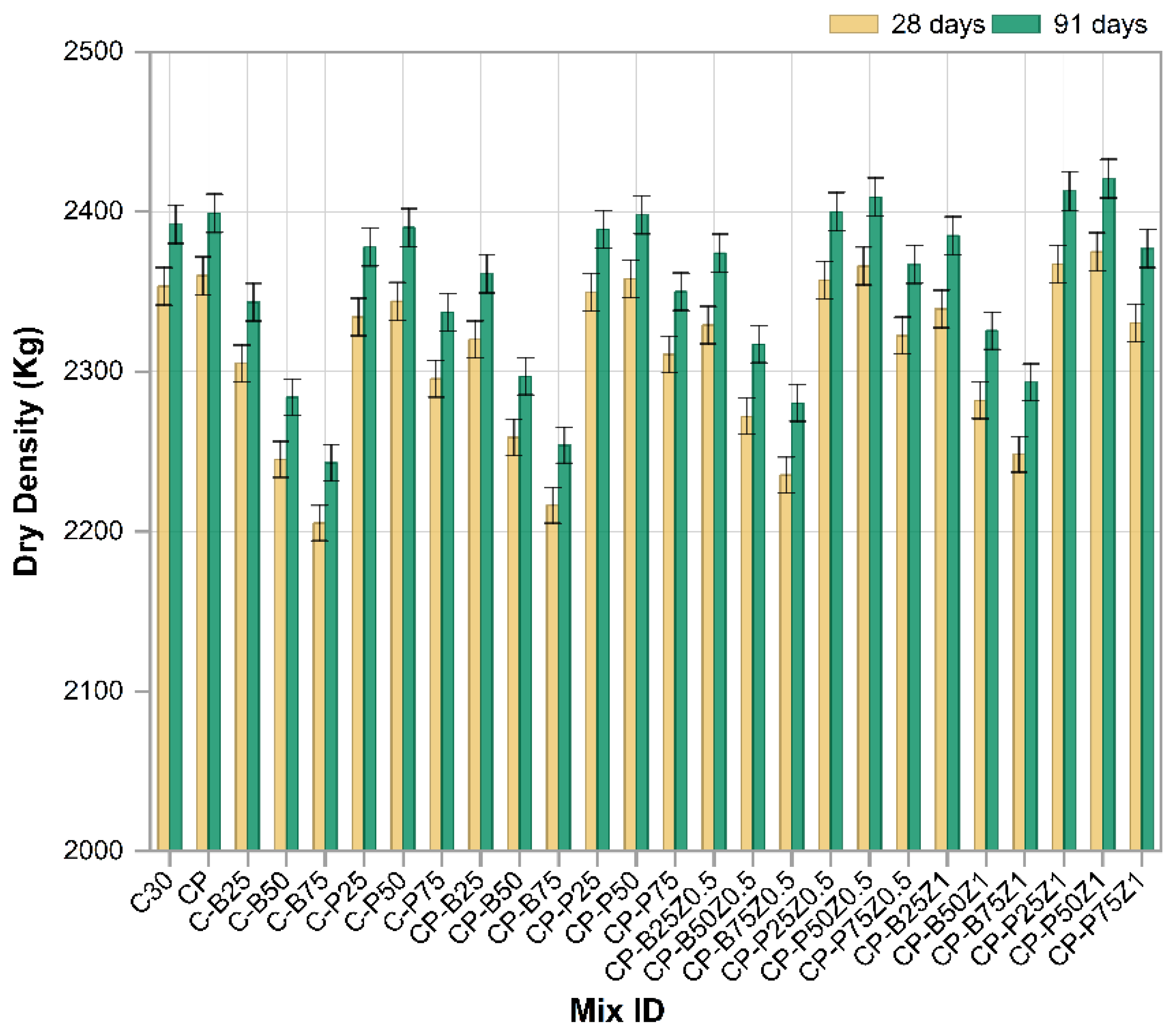
Figure 11 illustrates the dry density values of different modified concrete mixes at 28 and 91 days of age aimed to evaluate the impact of substituting sand with different quantities of porcelain and brick wastes, alongside the incorporation of PP.Fs and ZnO-NPs. Overall, most mixes exhibited a progressive rising in dry density with age attributed to the continuous hydration reactions and the gradual interaction of cement paste components, which reduces voids and enhances bonding within the concrete. Mixes (C-P25, C-P50, C-P75, C-B25, C-B50 and C-B75) exhibited a gradual decrease in dry density as the replacement ratio increased. This phenomenon arises from the lower specific gravity and greater porosity of crushed brick compared to ordinary sand, leading to less cohesive concrete and increased void content [56]. Conversely, PWP mixes exhibited markedly higher densities, particularly at 25% and 50% replacement ratios. This is attributed to their solid composition and higher density derived from production under high pressure and temperature, which diminishes porosity and fosters a more compact structure [57]. At a 75% replacement level, the density of the PWP mixes began to decrease significantly due to the increasing porosity resulting from the extensive utilization of this waste. There is a slight increase in density of the CP mix containing polypropylene fibers due to the role of fibers in reducing cracks and porosity [58]. The CP-P25 and CP-P50 mixes exhibited densities within an acceptable range (2392–2400 kg/m3), whereas the CP-B75 mixes recorded the lowest density among the samples. This proves that the porcelain mixes outperform brick mixes in the presence of fibers. The incorporation of nano-zinc oxide at amounts of 0.5% and 1% as a cement replacement in mixes containing PWP or BWP fine aggregates and PP fibers (e.g., CP-P25Z0.5, CP-B25Z0.5 and CP-P25Z1, etc.). This has resulted in a significant improvement in dry density, especially at 91 days of age. Mixes of CP-P50Z1 and CP-P25Z1 had the highest densities, exceeding that of their sub-nano counterparts. This results from the ability of ZnO-NPs to occupy micro voids and improve the microstructural arrangement of the cement paste. Furthermore, it promotes pozzolanic reactions and creates a more compact C-S-H compound [59].
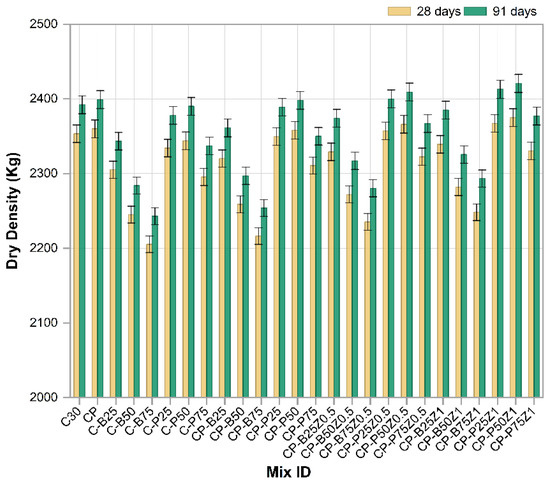
Figure 11.
The dry density results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
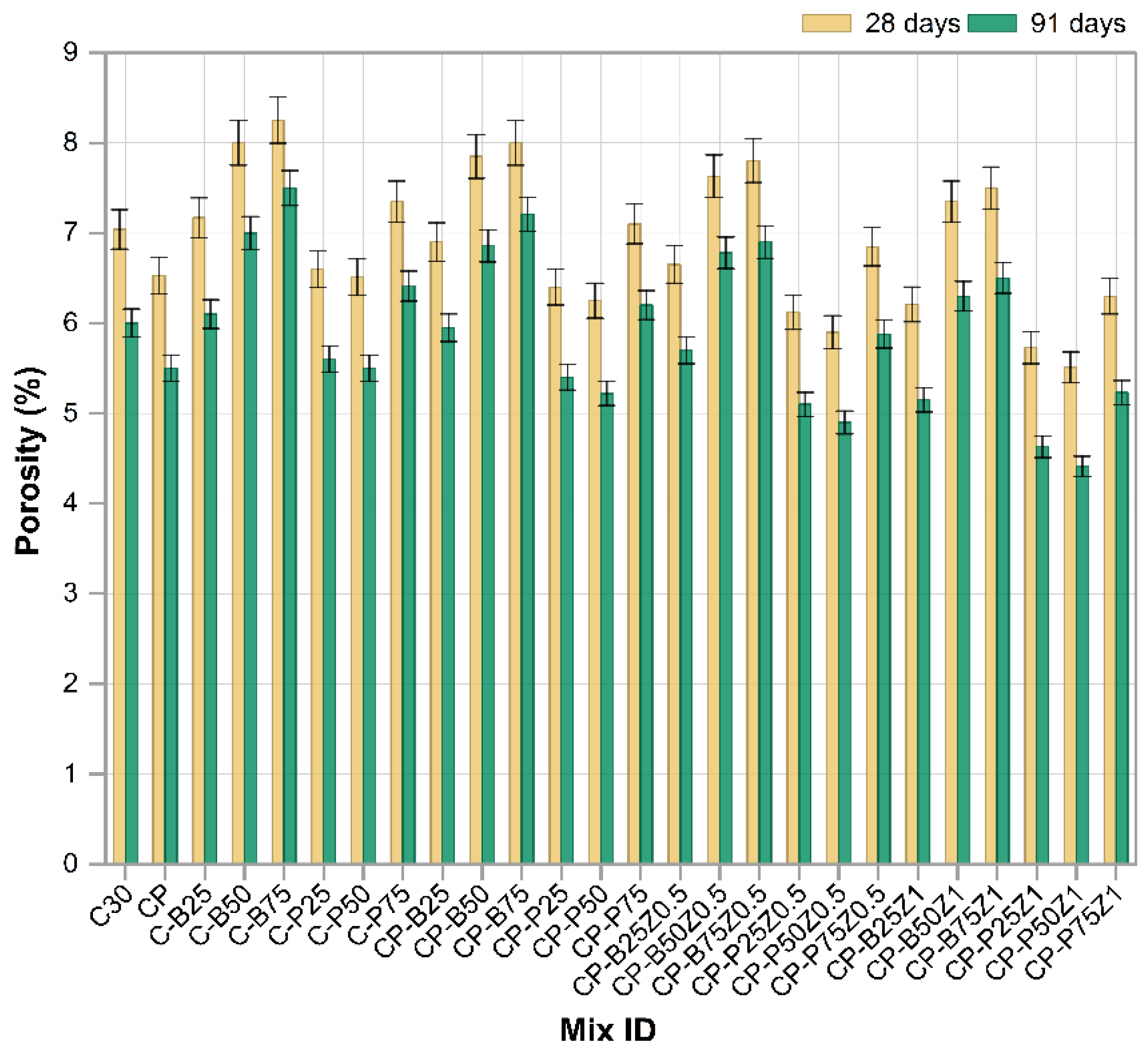
3.6. Porosity
Figure 12 illustrates the porosity values of different modified concrete mixes, including the substitution of sand with construction wastes (PWP and BWP), along with the incorporation of (PP.Fs) and ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 and 91 days. Mixes involving sand substituted with varying quantities of BWP (C-B25, C-B50 and C-B75) exhibited higher porosity relative to the reference sample (C30), with the most significant increase observed at 75% substitution. This increase results from the brick’s low specific gravity and elevated internal porosity, which increase the number of voids inside the concrete matrix [60]. Conversely, mixes using porcelain waste (C-P25, C-P50 and C-P75) exhibited reduced porosity compared to the brick mixes, especially at 25% and 50% replacement ratios. This results from porcelain’s greater density and reduced surface absorption, helping in minimizing voids within the cement paste. Nevertheless, when 75% of the sand was substituted with porcelain, porosity increased correspondingly due to the increased ratio of replacement materials and diminished compaction [61]. The incorporation of fibers as in CP-P25, CP-P50, CP-P75, CP-B25, CP-B50 and CP-B75) resulted in a slight decrease in porosity values relative to their non-fiber equivalents. Concrete mixes including porcelain with fibers (CP-P25 and CP-P50) exhibited lower porosity levels compared to mixes of bricks with fibers (CP-B25 and CP-B50). This highlights that the nature of the building wastes is more significant in controlling porosity. The inclusion of PP.Fs in concrete mixtures diminished porosity and improved fracture resistance relative to concrete without PP.Fs. Consequently, this modification diminished the permeation of water and deleterious substances, thereby improving durability [62]. The incorporation of nano-ZnO at 0.5% and 1% as cement replacements into mixes comprising PWP or BWP wastes and PP fibers (e.g., CP-P25Z0.5, CP-B25Z0.5 and CP-P25Z1, etc.). This ZnO-NPs incorporation led to a substantial decrease in porosity relative to all other samples without NPs. This results from ultra-fine nanoparticles occupying the micropores and capillary gaps in the cement paste, hence decreasing permeability and enhancing microscopic density. The effect was especially significant in porcelain combinations, where ZnO nanoparticles interacted with amorphous silica and alumina to generate extra hydration products (C-S-H), thereby filling the pores and improving paste bonding. The incorporation of ZnO-NPs in brick mixes resulted in an enhancement of porosity; nevertheless, this effect was a little due to the bricks’ inherently high initial porosity, which is challenging to significantly diminish even with nano-additives [59].
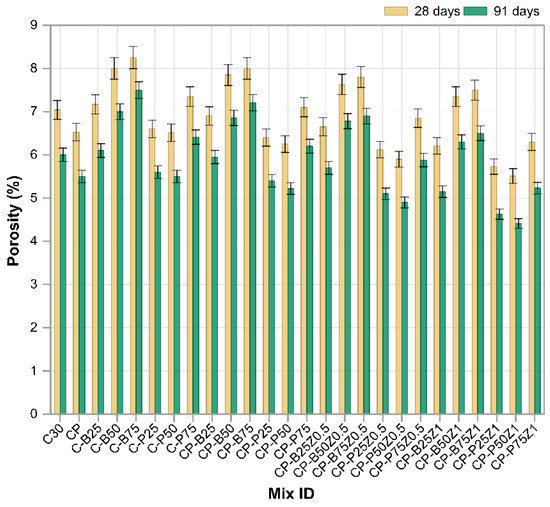
Figure 12.
The porosity results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
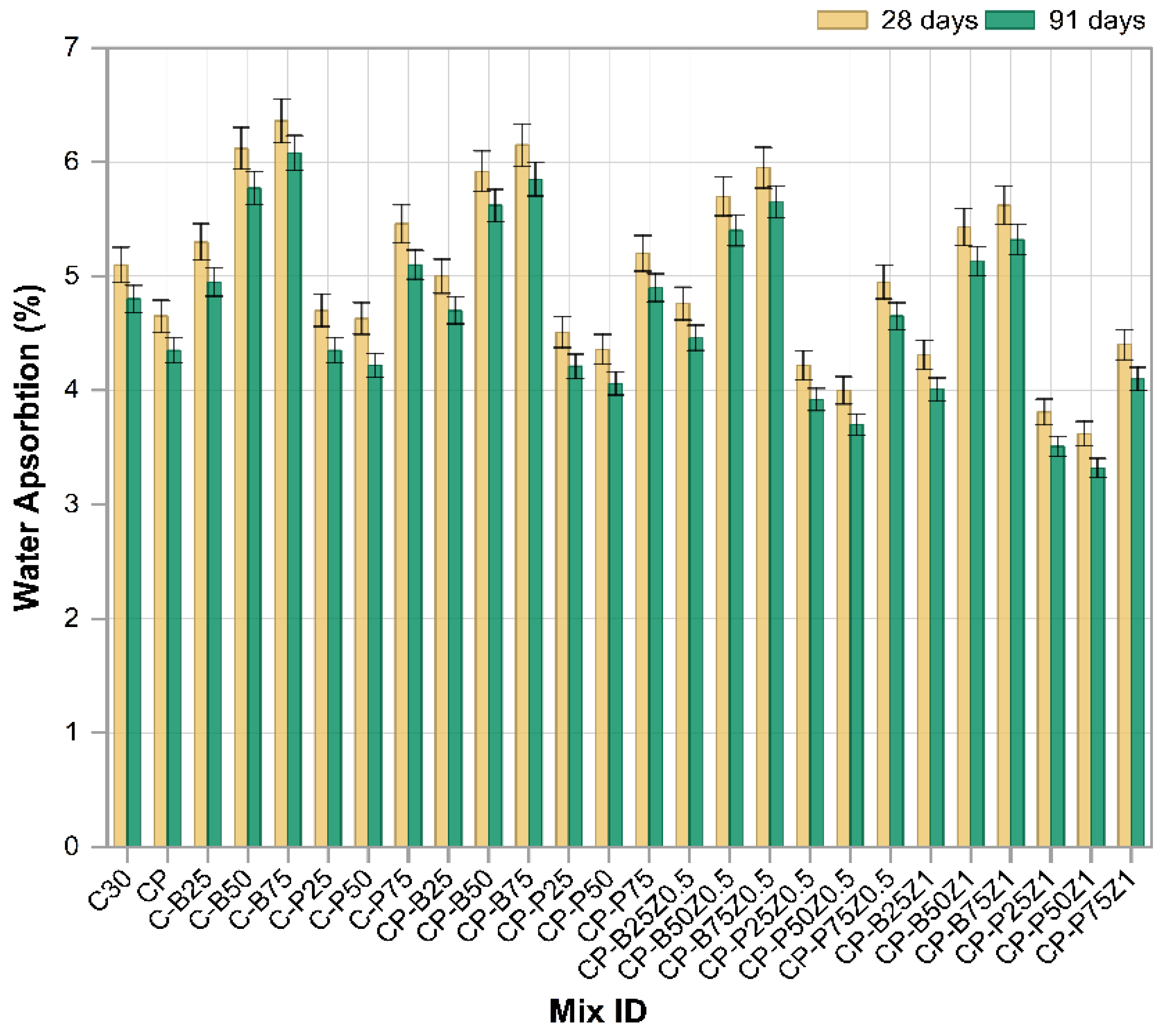
3.7. Water Absorption
Figure 13 shows the water absorption rates of various modified concrete mixes, including the substitution of sand with construction wastes (PWP and BWP), along with the incorporation of (PP.Fs) and ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 and 91 days of age, respectively. Mixes like C-B25, C-B50 and C-B75 involving sand substituted with varying quantities of BWP exhibited higher water absorption relative to the reference sample (C30), with the most significant increase observed at 75% of substitution. This increase results from the brick’s low specific gravity and higher internal porosity, which increase the number of voids inside the matrix of concrete [63]. Conversely, mixes incorporating PWP like C-P25, C-P50 and C-P75, exhibited reduced water absorption compared to the brick mixes, especially at 25% and 50% replacement ratios. This results from porcelain’s greater density and reduced surface absorption, helping in minimizing voids within the cement paste. Nevertheless, 75% of the sand was substituted with porcelain waste. The water absorption and porosity increased correspondingly due to the increased ratio of replacement materials and diminished compaction [61]. The mixing of (0.5 Vf) PP.Fs into concrete mixes diminishes water absorption by bridging microcracks and obstructing capillary pores. PP.Fs can enhance the cohesiveness of the cement paste with the aggregate, hence diminishing permeability and water absorption [64]. The incorporation of nano-ZnO at 0.5% and 1% as cement replacements into mixes comprising PWP or BWP wastes and PP fibers (e.g., CP-P25Z0.5, CP-B25Z0.5 and CP-P25Z1, etc.). This incorporation of nano-ZnO at 0.5% and 1% markedly diminishes the water absorption due to more effectively filling micro-voids, promoting further C-S-H production, and enhancing the interfacial transition zone between the cement paste and aggregate/waste [65].
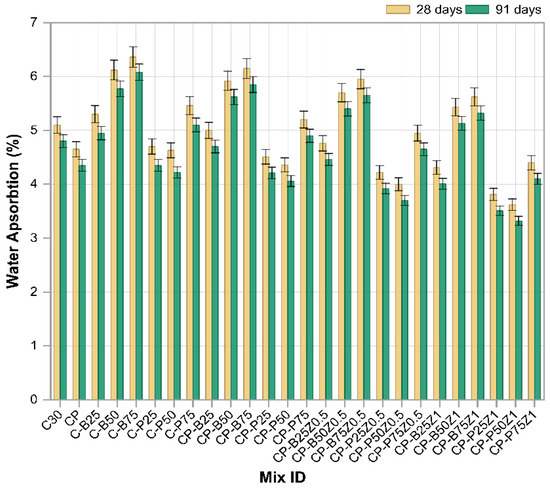
Figure 13.
The water absorption results of reference and modified concrete mixes.
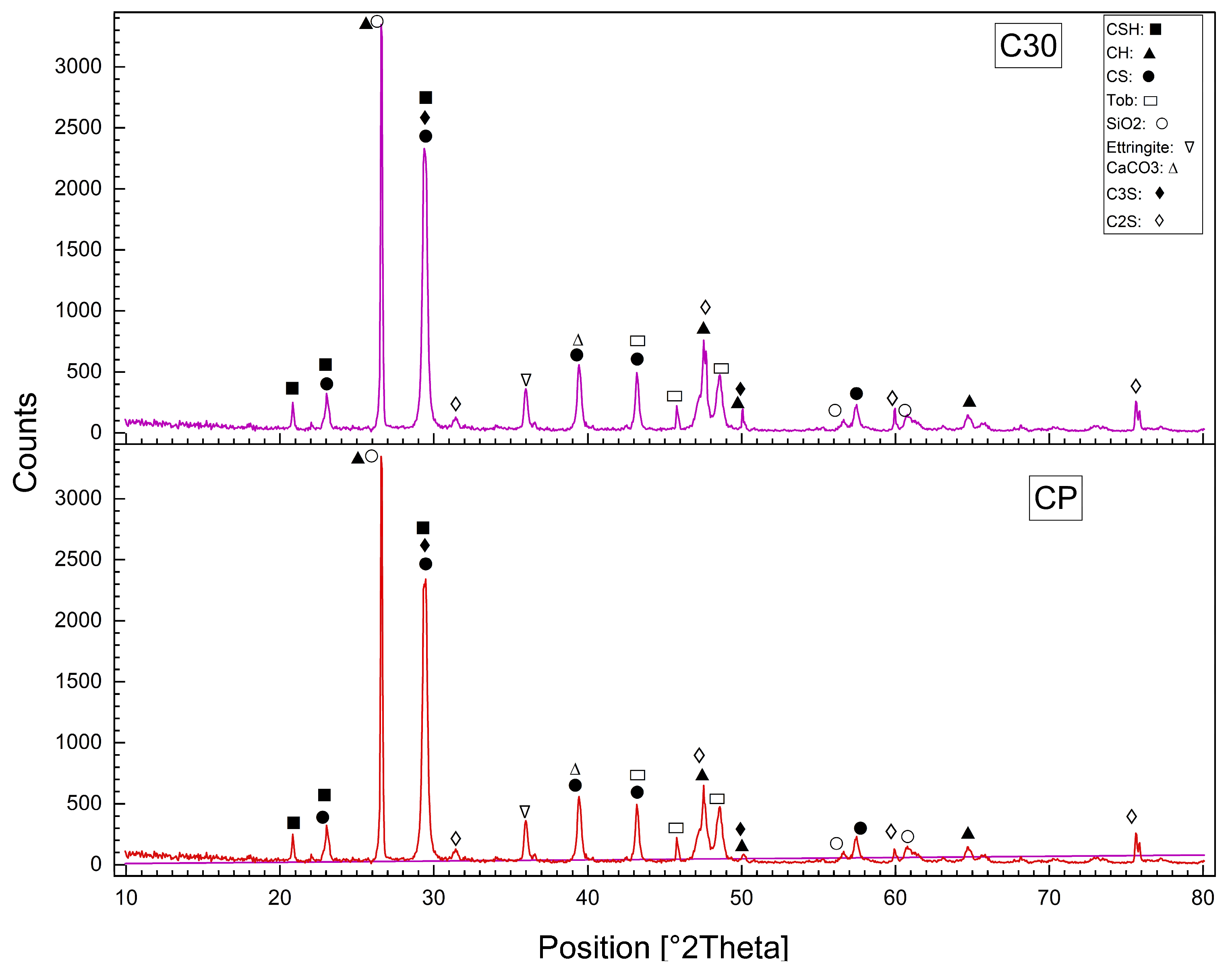
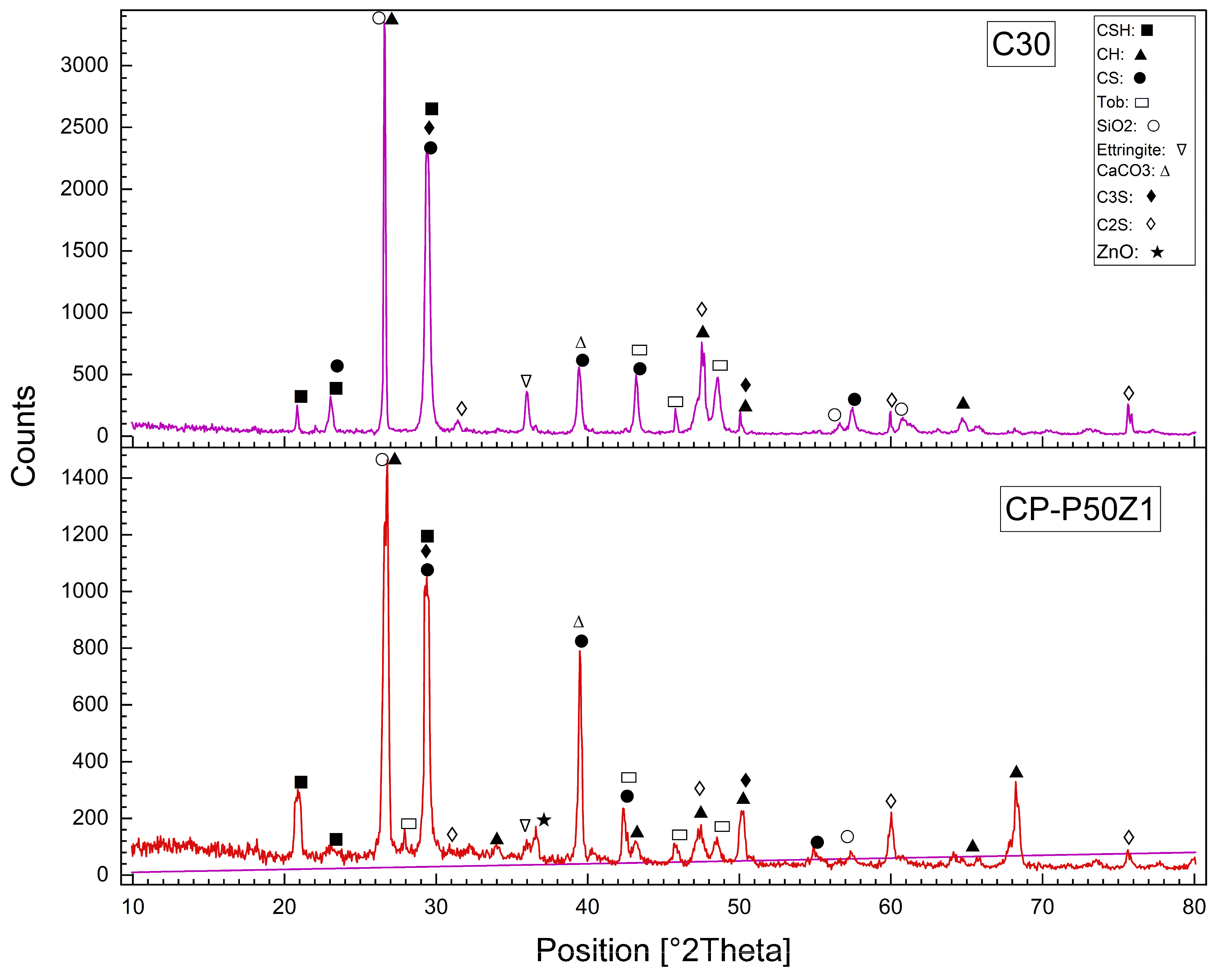
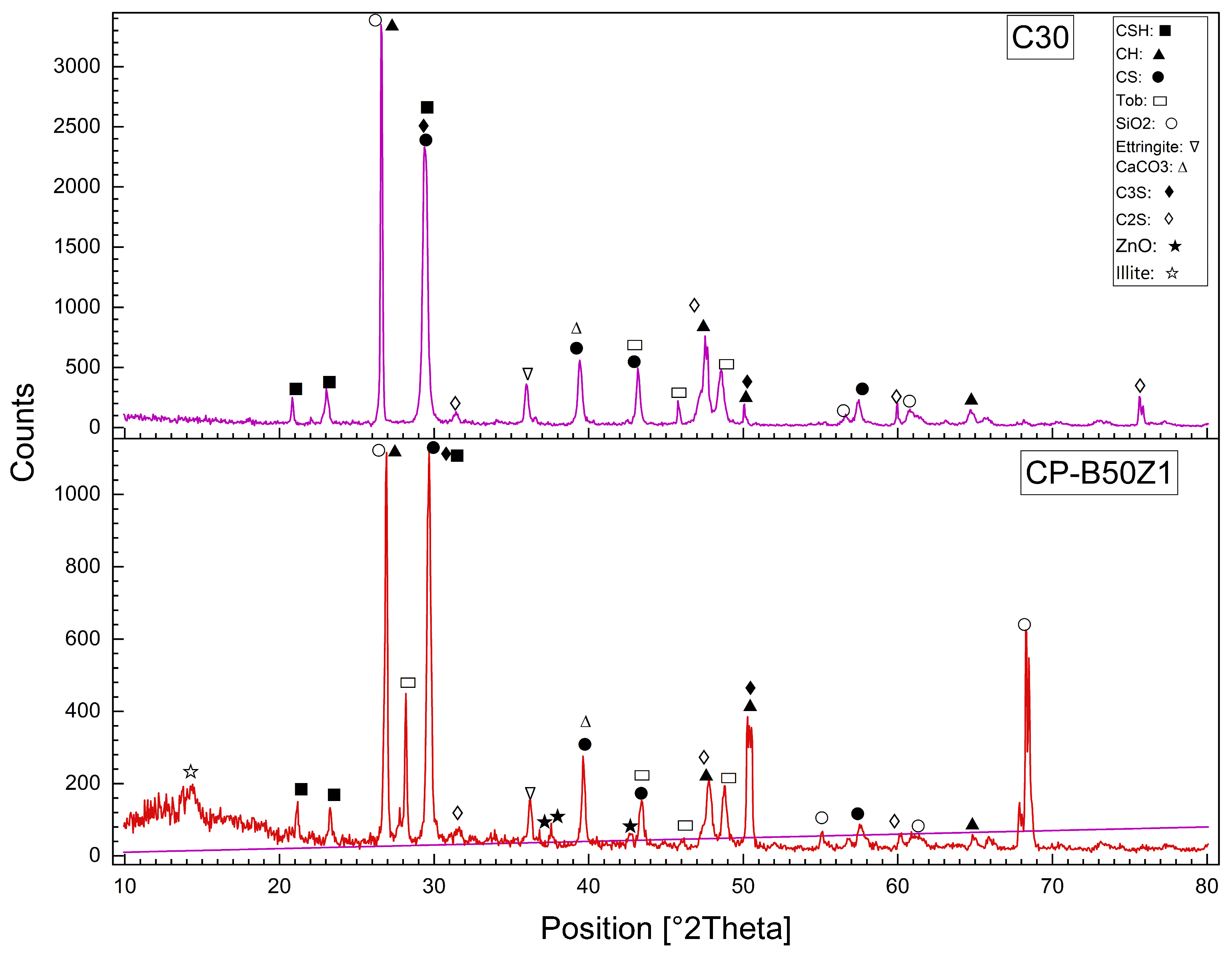
3.8. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) of Reference and Modified Concrete Samples
Using of the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) to determine the structural and mineralogical changes caused by modifications such as WPM sand replacements, ZnO-NPs cement replacements, and PP.Fs on concrete. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) is used for the identification of crystalline phases and monitoring the chemical reactions associated with hydration. XRD patterns showed the possibility to identify important compounds (such as C-S-H, ettringite, and other hydration products), providing useful information about the effect of waste materials, PP.Fs and ZnO-NPs on the microstructure of the cementitious matrix [66]. Figure 14 showed the XRD patterns of the reference concrete mix (C30) and PP.Fs-reinforced concrete (CP) at 28 days at a curing time of 28 days. Figure 15 showed the XRD patterns of the reference concrete mix (C30) and PP.Fs-reinforced concrete including 50% PWP as sand replacement and 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 days. Figure 16 showed the XRD patterns of the reference concrete mix (C30) and PP.Fs-reinforced concrete, including 50% BWP as sand replacement and 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 days. Regarding the referenced and modified concrete mixes with PP.Fs, WPMs sand replacements, and ZnO-NPs as cement replacements after 28 days of curing, the components of the phases are enumerated in Table 9.
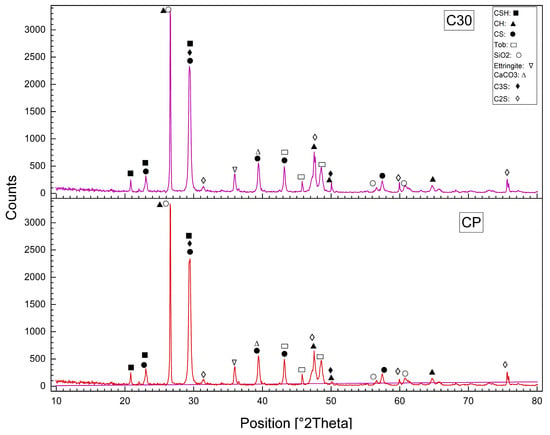
Figure 14.
XRD patterns of the reference concrete mix (C30) and PP.Fs-reinforced concrete (CP) at 28 days.
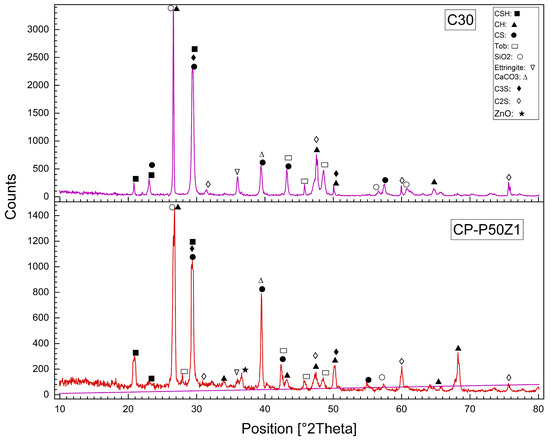
Figure 15.
XRD patterns of the reference concrete mix (C30) and PP.Fs-reinforced concrete including 50% PWP as sand replacement and 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 days.
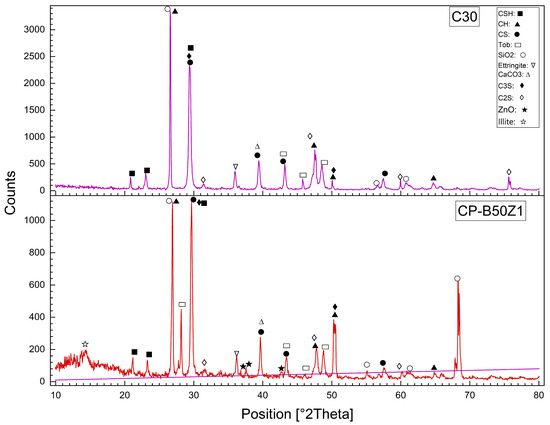
Figure 16.
XRD patterns of the reference concrete mix (C30) and PP.Fs reinforced concrete including 50% BWP as sand replacement and 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 days.

Table 9.
Diagnosis of the phases appeared in reference concrete and modified concrete with PP.Fs, ZnO-NPs and (PWP or BWP).
The all-concrete mixes, including the reference, PP.Fs-reinforced concrete, and PP.Fs-reinforced concrete with 1% ZnO and 50% (PWP or BWP), exhibit the primary phases of CH, CSH, and CS peaks in XRD patterns. Quartz content attributable to the presence of sand and the substantial crystalline silica content in WPMs (PWP and BWP). Calcite is synthesized through the carbonation of calcium hydroxide (lime). Patterns indicated that the peak intensity of CH compounds in the reference sample is higher than that of concrete samples incorporated with ZnO-NPs and WPMs. This is attributed to the fact that the ZnO-NPs and ultrafine particles from porcelain and brick waste powders participate in pozzolanic reactions by interacting with CH compounds generated from cement hydration. This led to the production of additional CSH gel during the secondary hydration process. The mechanical properties of PP.Fs-reinforced concrete samples, incorporating ZnO-NPs as a cement substitute and WPMs (PWP or BWP) as a sand substitute, were dramatically enhanced [67,68].
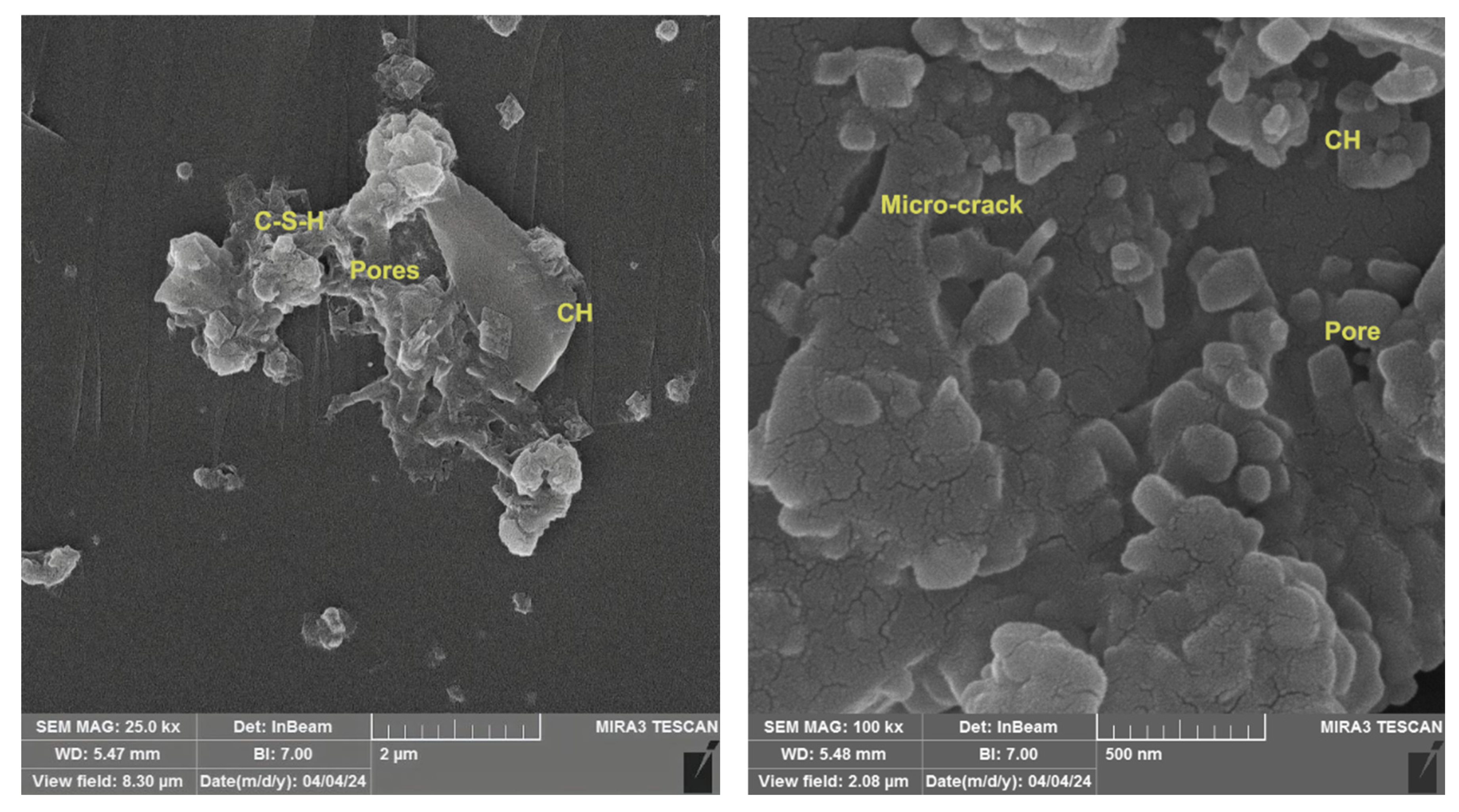
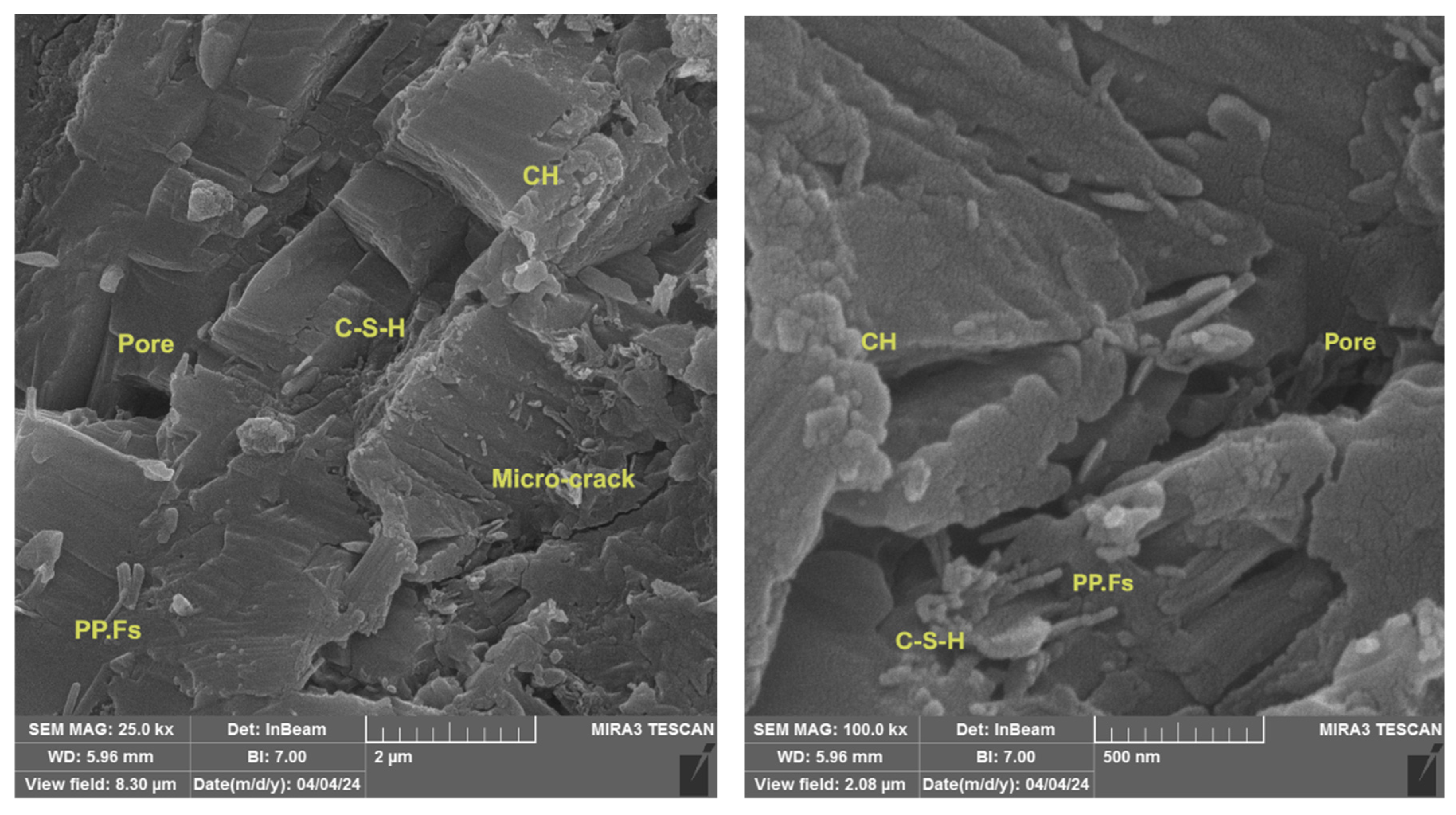
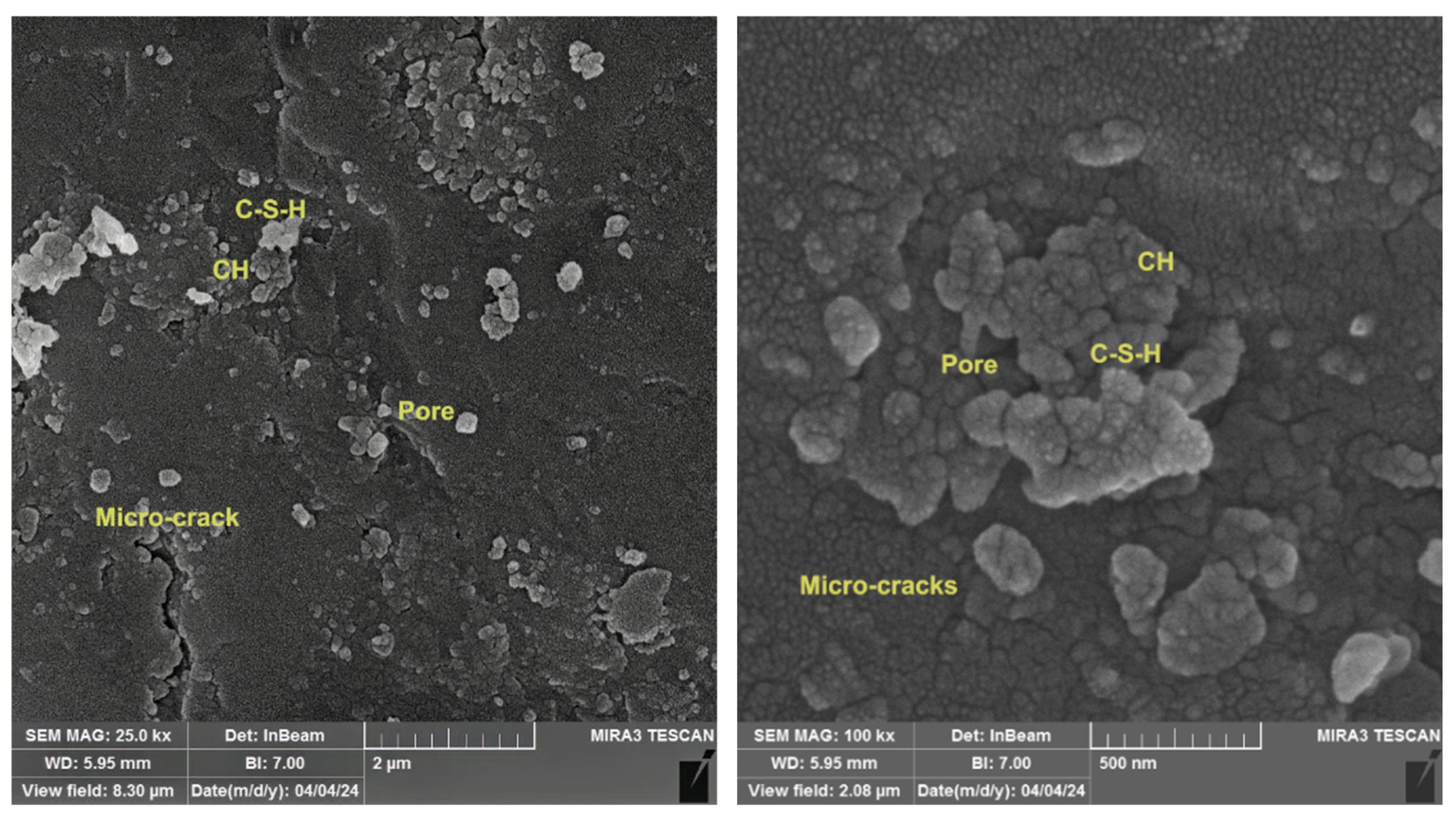
3.9. SEM Imaging of Reference and Modified Concrete Samples
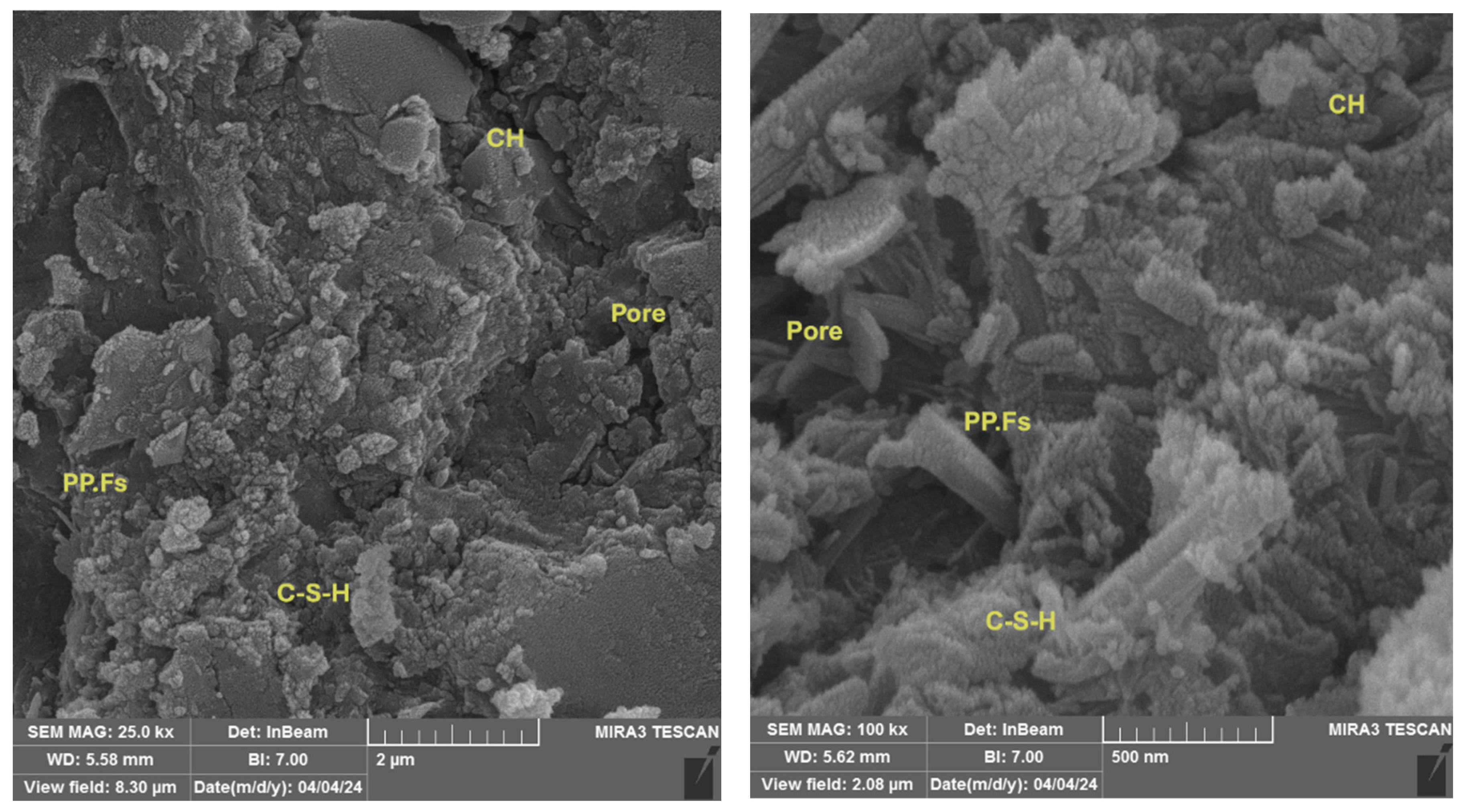
The SEM examination of broken surfaces after the compression test at 28 days is essential in research as it relates to the assessment of microstructural characteristics, including voids and micro-cracks, along with the identification of developed phases. Figure 17 showed the microstructure of reference concrete mix at 28 days, which appears to include the main constituents of cement hydration, including CH with large crystals, little C-S-H poorly crystallized gel and many pores inside the structure of concrete. Figure 18 illustrated the micrograph of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete mixture with 0.5 volume fraction of polypropylene fibers at 28 days of curing. The microstructure exhibits increased density and a reduced number of cracks and pores due to the incorporation of PP.Fs, which facilitate bridging and minimize small cracks in concrete when properly distributed [69]. Figure 19 showed the micrograph of PP.Fs-reinforced concrete mixed with 50% porcelain as sand replacement and 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 days. The structure looks to be denser and more compact than the reference sample due to the role of ZnO-NPs to refine the structure of concrete through its role as filler and offer active sites due to its higher surface area, which react with CH to produce more C-S-H in cement paste. As well as the very fine PWP particles may promote the hydration reaction due to it containing the main components of the pozzolanic reaction, Fe2O3, SiO2 and Al2O3, in accordance with ASTM C614. The bigger particles have good interlocking with cement paste lead to give a compact structure and hence good mechanical properties [70]. Figure 20 showed the imaging of PP.Fs-reinforced concrete mixed with 50% brick powder as fine aggregate replacement and 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement at 28 days. Similar to other replacements, PP.Fs appear as threads randomly distributed in the matrix, not chemically reacting, but they work as a bridge to connect the constituents of concrete. Brick particles have irregular shapes with rough surfaces due to their inherently porous nature, offering surfaces for mechanical adhesion with cement paste, as well as the very fine particles that may react with CH to produce additional C-S-H due to their containing silica, alumina and ferric oxide [71]. On the other hand, the effect of ZnO-NPs is the same with other concrete samples.
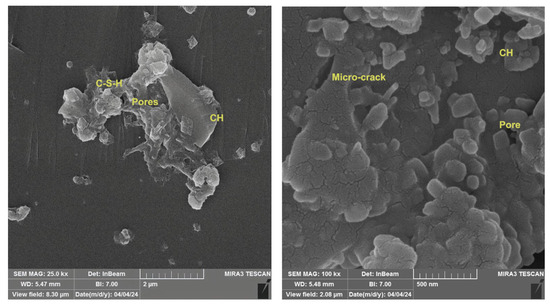
Figure 17.
SEM micrograph of the reference concrete mix at 28 days.

Figure 18.
SEM micrograph of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete samples without WPMs or ZnO-NPs at 28 days.

Figure 19.
SEM micrograph of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete sample incorporated with 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement and 50% sand replacement of PWP at 28 days.

Figure 20.
SEM micrograph of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete sample incorporated with 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement and 50% sand replacement of BWP at 28 days.
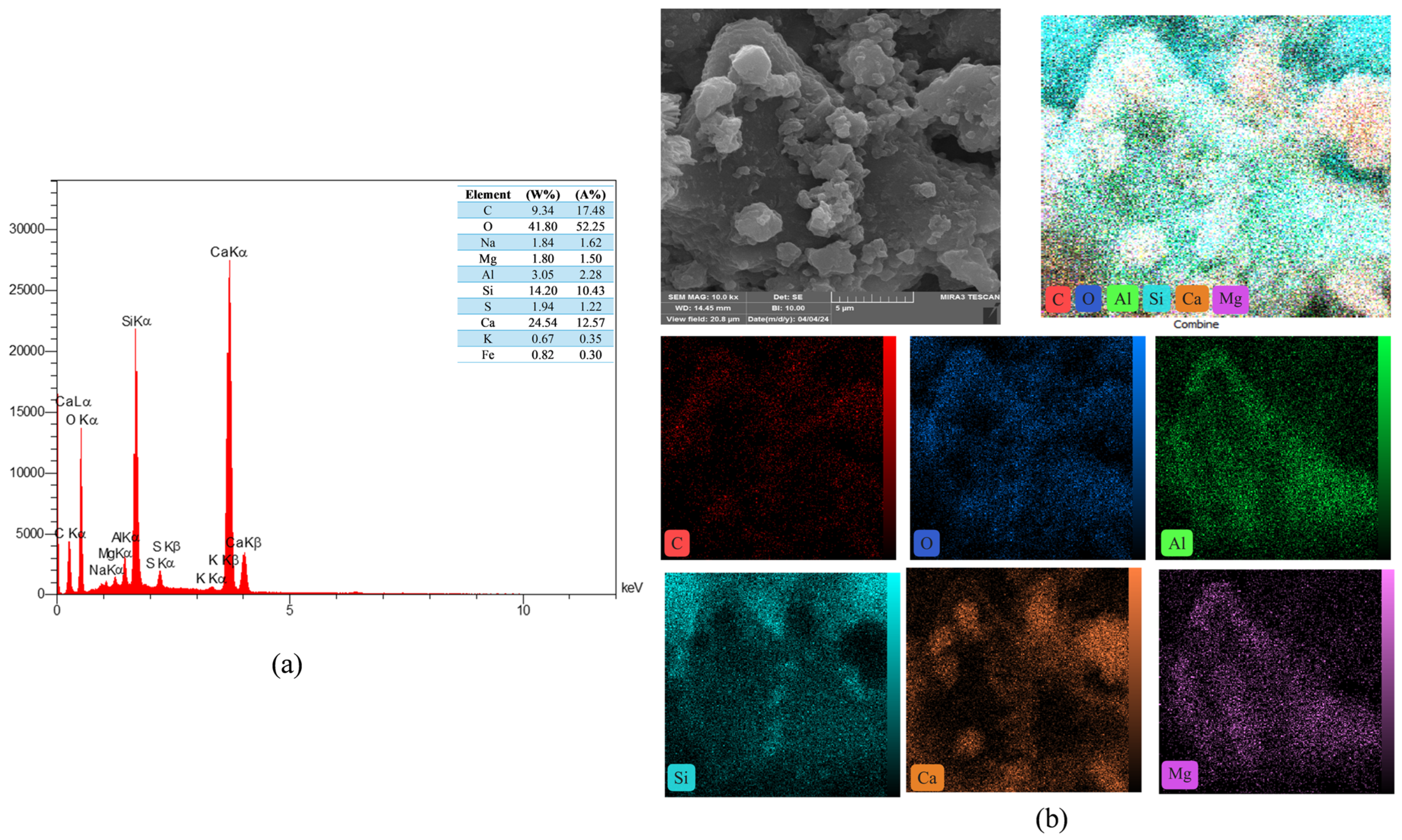
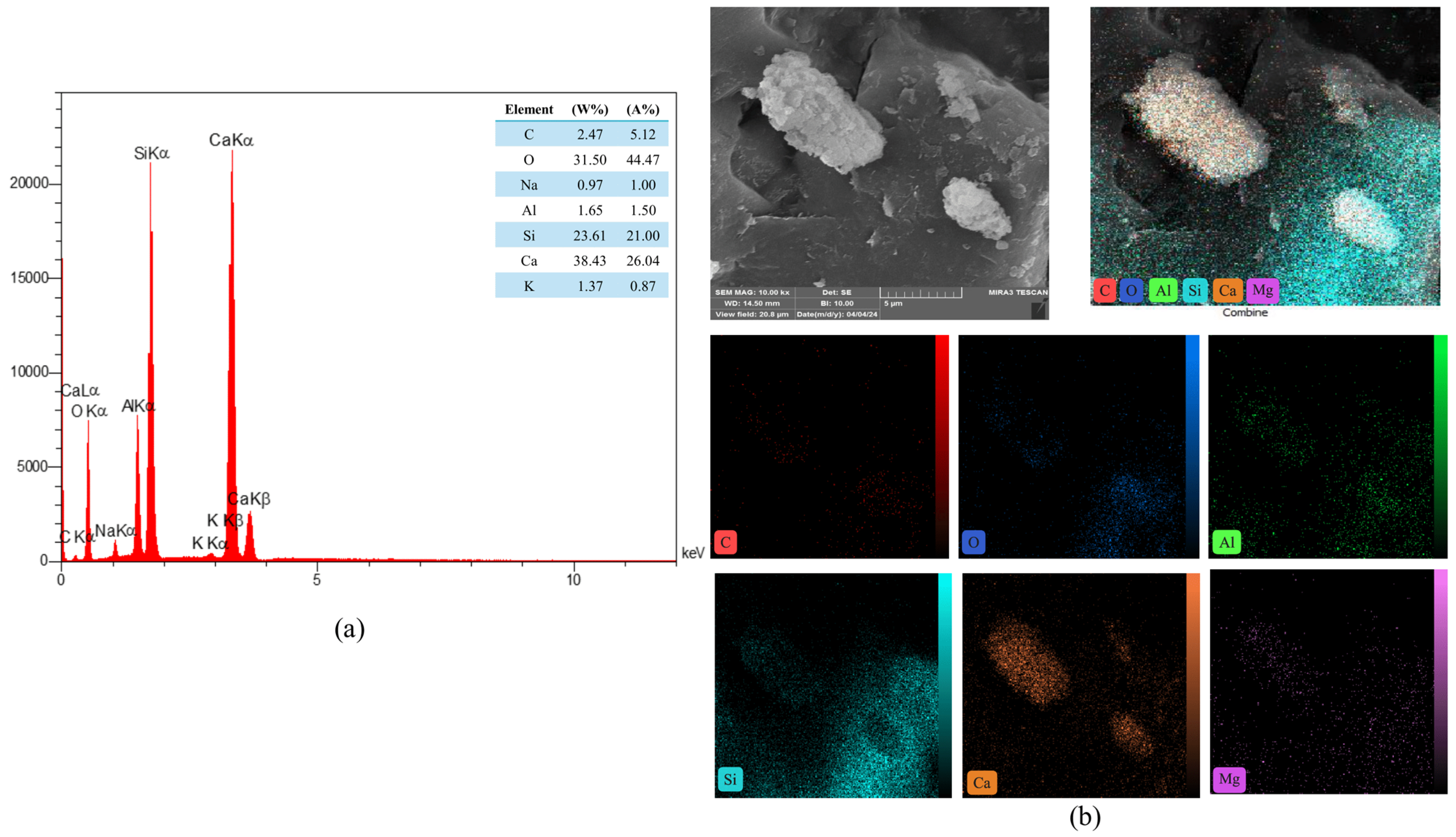
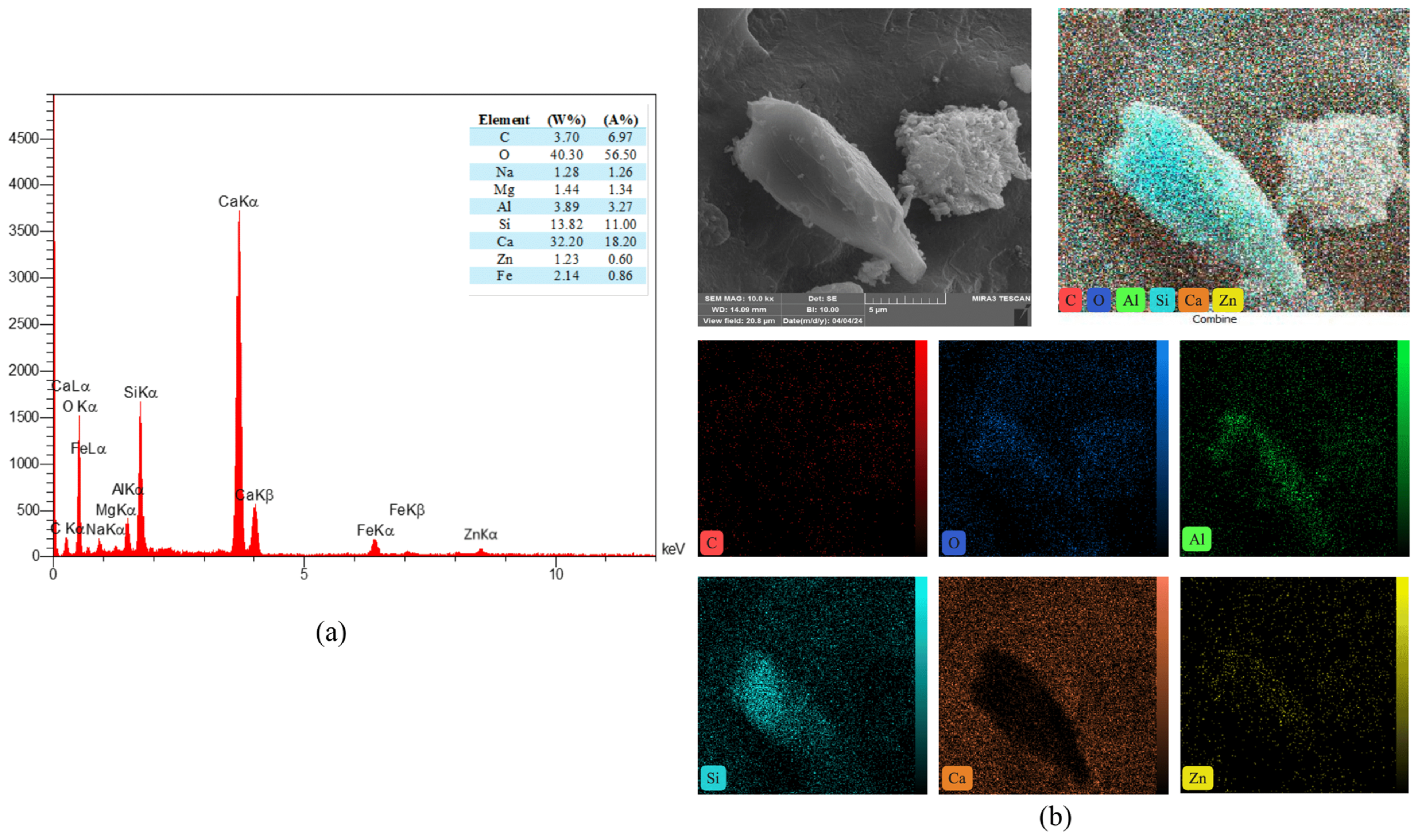
3.10. EDS Mapping of Reference and Modified Concrete Samples
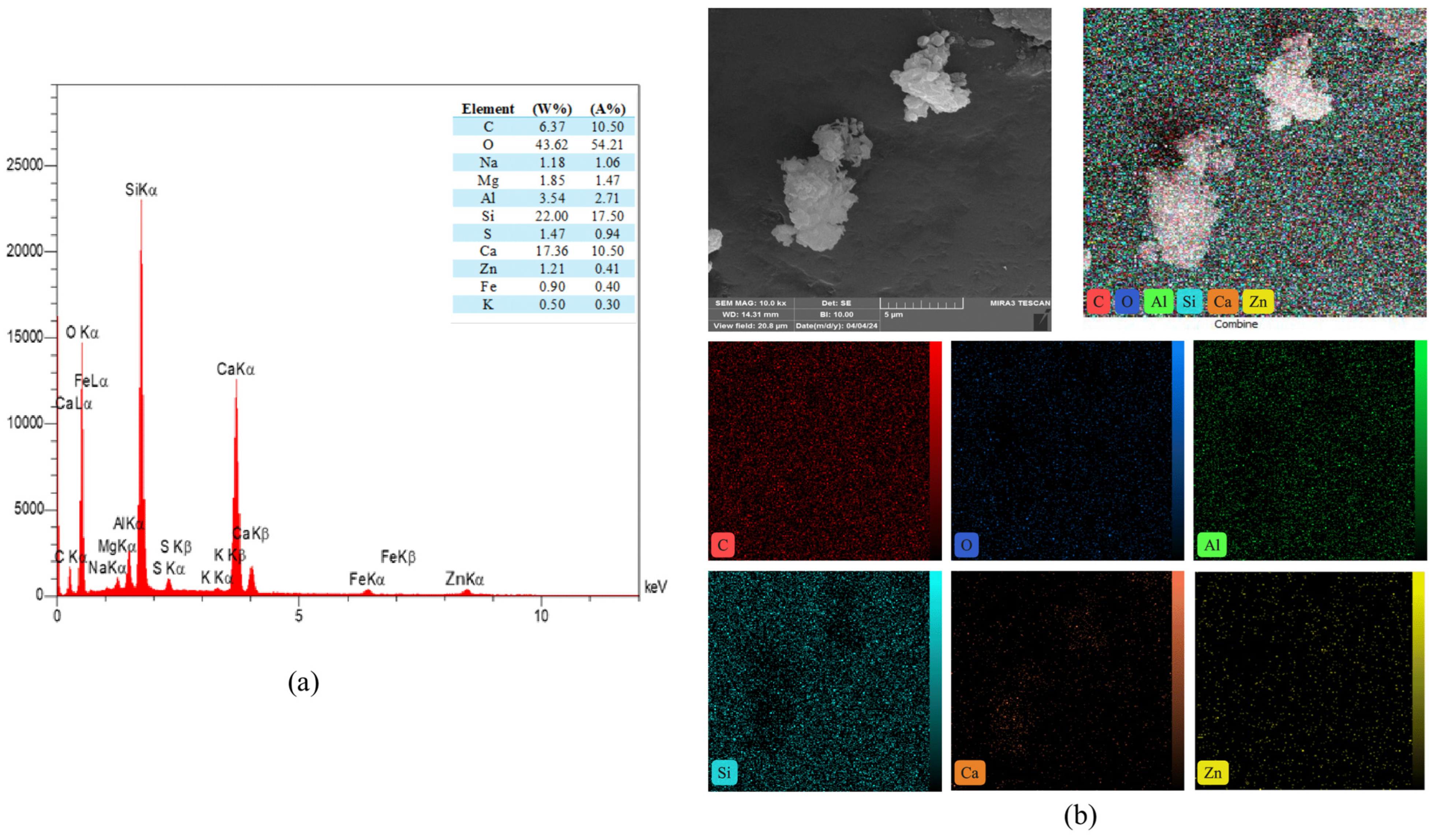
The study of the energy dispersive spectroscopy technique (EDS) was employed to provide quantitative data for a complete clarification of the produced chemical phases. The atomic ratio of calcium to silicon (Ca/Si) was utilized to assess the hydration level of calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) gels [72]. Figure 21 showed the EDS mapping analysis of reference concrete at 28 days. While Figure 22 illustrated the EDS mapping analysis of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete mixture with 0.5 volume fraction of polypropylene fibers at 28 days of curing. Figure 23 and Figure 24 showed the EDS mapping analysis of PP.Fs-reinforced concrete incorporated with 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement and 50% of (porcelain and brick) waste powder as fine aggregates replacement at 28 days. EDS analysis showed that the most effective elements (Ca and Si) contributing to the strength of concrete were present in all concrete samples with high concentrations. It revealed the presence of oxygen in all samples due to it being the main constituent of the main oxides such as Ca(OH)2, SiO2, and Al2O3 as well as aluminum and other trace elements like Fe, Mg, K, S and Na. Furthermore, analysis revealed that the presence of the zinc element due to ZnO mixed as a cement replacement in modified concrete mixes. Also, the appearance of the carbon element is attributed to the reinforcing of concrete mixes by polypropylene fibers [73]. The chemical analysis of the waste powders indicated that porcelain and brick powders are rich in silica and alumina. Consequently, the calcium-to-silicon ratio in BWP mixes is diminished and for PWP, it’s increased but still in an acceptable range compared to the reference sample. This is attributed to their pozzolanic activity in conjunction with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nonetheless, the influence of ZnO-NPs continues in the pozzolanic hydration of cement. Incorporating PWP and BWP in designated ratios as a sand substitute in concrete alongside the mixing of ZnO-NPs as a cement replacement results in an enhancement of calcium and silicon levels in the mixture. This signifies an enhancement in the production of CH and C-S-H compounds hence improving or preserving the mechanical characteristics with higher sand replacement ratios [74].
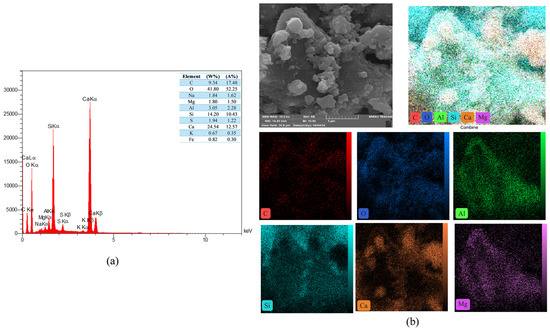
Figure 21.
(a) EDS and (b) mapping of the reference concrete mix at 28 days.
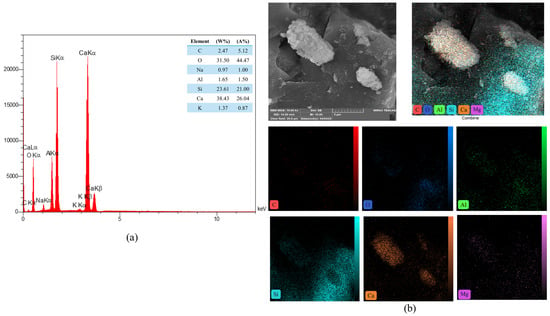
Figure 22.
(a) EDS and (b) mapping of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete samples without (PWP/BWP) or ZnO-NPs at 28 days.
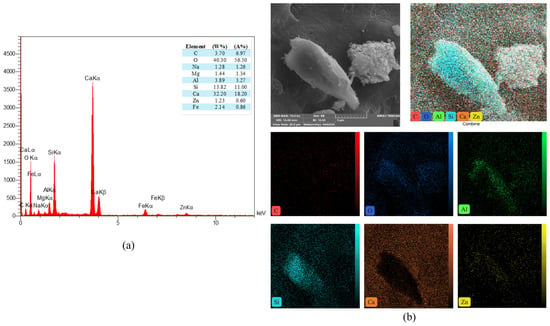
Figure 23.
(a) EDS and (b) mapping of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete sample incorporated with 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement and 50% sand replacement of PWP at 28 days.
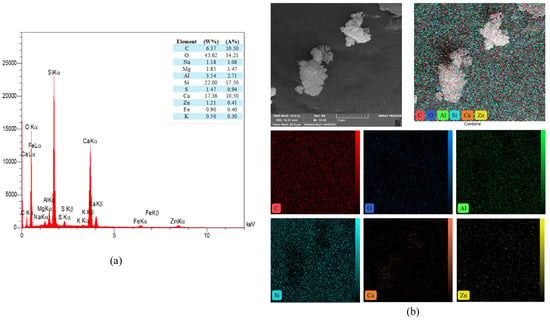
Figure 24.
(a) EDS and (b) mapping of the PP.Fs-reinforced concrete sample incorporated with 1% ZnO-NPs as cement replacement and 50% sand replacement of BWP at 28 days.
3.11. Cost Evaluation of Natural Sand, Porcelain and Brick Waste Powders
A comparison of the expected production costs of one ton of natural sand with porcelain waste powder (PWP) and brick waste powder (BWP) is shown in Table 10. Including extraction, transportation, and processing, natural sand costs around $20 USD per ton. Conversely, using waste-based resources is more cost-effective because the raw materials are regarded as byproducts and have very low beginning costs. The procedures of collecting, crushing, and milling are the primary costs. PWP’s production cost is therefore projected to be 14 ± 3 USD/ton, while BWP’s is considerably cheaper at about 10 ± 3 USD/ton. Depending on processing needs and energy costs, this suggests that using porcelain or brick waste in place of natural sand can result in immediate cost savings of between 30% and 50%. Utilizing these wastes not only lowers the cost of raw materials but also lessens landfill loads and promotes the circular economy, which helps the environment and the economy [75].

Table 10.
Cost of 1 ton for sand, porcelain and brick aggregates.
3.12. Carbon Emissions Estimation
To assess the environmental performance of the recommended combinations, a simplified estimation of the embodied carbon (estimated in kg CO2e per cubic meter of concrete) was conducted for the natural sand and the alternative waste materials (porcelain and brick). Life cycle inventory (LCI) data indicates that the extraction, processing, and transportation of natural sand often result in emissions of 4–6 kg CO2e per m3 of concrete. Conversely, porcelain and brick wastes are by-products of demolition or building wastes with the primary environmental impact already attributed to the original product. Consequently, only collection, crushing, and sieving are considered, leading to markedly reduced impacts estimated at roughly 1–2 kg CO2e per m3. Replacing natural sand with porcelain or brick waste may diminish the carbon footprint of concrete mixtures by 60–70% at the aggregate level. This reduction highlights the dual advantages of utilizing building and demolition waste: reducing landfill disposal and mitigating the environmental effects linked to raw material extraction [76,77].
4. Conclusions
This study sought to assess the mechanical and physical performance of sustainable concrete formulated with alternative materials, especially waste building materials (porcelain and brick). WPMs are used as a partial substitute for sand, alongside the incorporation of polypropylene fibers in a constant ratio to enhance the internal structure and load-supporting ability of the concrete. Furthermore, the mix is augmented by mixing of zinc oxide nanoparticles as a partial substitute for cement. The principal conclusions drawn from this study can be briefly summarized below:
- SEM images of the powders revealed that porcelain exhibited irregular angular shapes with sharp angles. The brick particles exhibited a semi-elongated shape characterized by higher surface roughness and finer-grained agglomerates than porcelain particles.
- The mechanical test findings, including compressive strength, flexural strength, and splitting tensile strength of samples using waste powders, indicated that the optimal percentage for improving properties was 50% for PWP. The optimum amount for BWP was 25%. Conversely, increasing the proportion of natural sand substitution with waste powders to 75% resulted in a significant decline in mechanical characteristics.
- The dry density findings indicated that substituting sand with porcelain led to a slight reduction in concrete density. While it diminished further upon replacement with brick due to its higher porosity and water absorption.
- The porosity ratio results of the concrete mixes containing PWP at 25% and 50% sand replacement ratio showed that porosity decreased. While mixes contain 25% BWP, porosity exhibited a modest rise. Increasing the sand replacement ratio with waste materials led to a notable increase in porosity, with the exception of porcelain, for which the optimal replacement ratio was 50%.
- The water absorption rate for mixes incorporating PWP at 25% and 50% sand replacement is diminished. However, the water absorption rate increases for mixes that incorporate 25% BWP sand replacement. Increasing the sand replacement ratio led to a notable increase in water absorption, but with the exception of porcelain, for which the optimal replacement ratio was 50%.
- Trials have demonstrated that incorporating polypropylene fibers into concrete mixes, alongside varying amounts of building wastes significantly enhances compressive, flexural, and tensile strength. The physical characteristics indicated a minor increase in density, accompanied by a decrease in absorption and porosity for the fiber-reinforced concretes.
- Experimental findings have demonstrated that partially substituting of cement with zinc oxide nanoparticles in fiber-reinforced concrete samples included PWP or BWP at different sand replacement ratios. It led to a marked enhancement in mechanical characteristics, density, reduced porosity and water absorption at all ages.
- XRD analysis indicated that samples reinforced with polypropylene fibers, PWP or BWP as a sand substitute and nano ZnO as a partial cement substitute exhibited an increase in hydration products. It characterized by a reduction in calcium hydroxide compounds and an elevation in CSH compounds.
- SEM images indicated that the concrete mixes reinforced with fibers, PWP or BWP as a sand substitute and nano ZnO as a partial cement substitute exhibited more cohesiveness and reduced porosity compared to the reference sample. This is attributable to the filling effect of the fine particles and the role of nano ZnO in filling the micro-voids within the structure.
- EDS analysis revealed that the concrete mixes reinforced with polypropylene fibers, PWP or BWP sand substitutes and nano ZnO as a partial cement substitute exhibited an increase in hydration products. This is due to porcelain and brick wastes have high amounts of silica and alumina. Furthermore, nano zinc oxide promoted the pozzolanic reaction.
- In general, the concrete mix including sand replacement with 50% of PWP showed the best performance compared to the other mixes, whether or not additives were used including polypropylene fibers and zinc oxide nanoparticles. This substitution enhanced microstructure and diminished porosity, hence improving the concrete’s resistance to cracking.
- The production cost for one ton from porcelain or brick wastes as fine aggregate is lower than for sand.
5. Recommendations for Future Research
This research investigated the utilization of building waste as a value-enhancing component in concrete. It also investigated the application of fiber reinforcement and the substitution of cement with ZnO-NPs. The newly produced sustainable concrete was evaluated for its mechanical and physical characteristics, exhibiting enhanced features relative to conventional concrete. Nevertheless, additional research is required to incorporate findings regarding the impact of substituting waste with natural materials in concrete. The following recommendations provide for future research:
- Utilizing a composite of (porcelain and brick) wastes to examine their combined influence on the performance of the resulting concrete.
- Investigating the impact of higher PP.Fs percentages on the performance of concrete containing various amounts of waste materials.
- Utilizing of higher dosages of ZnO-NPs and investigating their impact on the characteristics of mixes exclusively composed of fibers without of waste materials.
- Investigating the influence of several additives or replacements on the characteristics like resistance to corrosion, wear resistance and impact resistance.
- Assessment of long-term performance regarding shrinkage, contraction and water permeability.
- As already reported, it is better to investigate in depth one type of each modified concrete. Long term studies need to know preliminary results on each modified concrete.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T.H.; methodology, M.T.H.; validation, M.T.H. and A.A.A.-H.; formal analysis, M.T.H.; investigation, M.T.H.; data curation, M.T.H.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T.H.; writing—review and editing, A.A.A.-H. and F.M.O.; supervision, A.A.A.-H. and F.M.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study were obtained from experimental work and are available from the corresponding author, Mustafa Thaer Hasan, upon reasonable request. Due to privacy/ethical restrictions, the data are not publicly available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Papamichael, I.; Voukkali, I.; Loizia, P.; Zorpas, A.A. Construction and demolition waste framework of circular economy: A mini review. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2023, 41, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmi, N.; Sayhood, E.; Mohammed, N. Impact of recycled aggregate on bond behavior between concrete and steel bars: A systematic review. Eng. Technol. J. 2025, 43, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, A.; Hassan, M.; Atiyah, A. Evaluation of the Performance of Steel Slag and Waste Glass as a Cement Replacement. Eng. Technol. J. 2023, 41, 1568–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Haque, M.; Sakib, M.N.; Mita, A.F.; Rahman, M.M.; Tanmoy, B.B. Use of ceramic wastes as aggregates in concrete production: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngayakamo, B.H. Sustainable concrete production: The role of ceramic waste as a partial coarse aggregate substitute. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2025, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.A.; Anaee, R.A.; Nasr, M.S. Durability, Mechanical, and Corrosion Characteristics of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Utilizing Locally Sourced Waste and Ultrafine Cerium Oxide. J. Appl. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2025, 5, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besklubova, S.; Kravchenko, E.; Tan, B.Q.; Zhong, R.Y. A feasibility analysis of waste concrete powder recycling market establishment: Hong Kong case. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, I.; Al-Awsi, G.R.L.; Hasan, Y.M.; Almotlaq, S.S.K. Mechanical properties of concrete containing recycled aggregate from construction waste. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belebchouche, C.; Temami, O.; Khouadjia, M.L.K.; Hamlaoui, S.; Berkouche, A.; Chouadra, T. Recycling of Brick and Road Demolition Waste in the Production of Concrete. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2024, 4, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, M.A.; Sudheer, M. Effect of recycled porcelain-ceramic aggregates on concrete: A review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Development in Civil Engineering, Jamshoro, Pakistan, 16–18 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Roig-Flores, M.; Reig, L.; Albero, V.; Hernández-Figueirido, D.; Melchor-Eixea, A.; Pitarch, Á.M.; Piquer, A. Utilisation of ceramic stoneware tile waste as recycled aggregate in concrete. Buildings 2023, 13, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shen, A.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Yao, C.; Wu, J. Research progress on recycled clay brick waste as an alternative to cement for sustainable construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 122113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, T.A.; Sičáková, A.; Kuzielová, E.; Kušnír, Š.; Eštoková, A.; Bálintová, M.; Junáková, N. Sustainable reuse of waste ceramic tiles powder and waste brick powder as a replacement for cement on green high strength concrete properties. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Beushausen, H.; Alexander, M. The Use of Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste in Low-Strength Concrete Brick and Block Production: A South African Perspective. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Net-Zero Built Environment, Cape Town, South Africa, 5–7 November 2025; Kioumarsi, M., Shafei, B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, M.; Xia, H. Effects of elevated temperature on the mechanical properties of concrete with aggregate of waste porcelain tile. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105585. [Google Scholar]
- Şenol, A.F.; Karakurt, C. High-strength self-compacting concrete produced with recycled clay brick powders: Rheological, mechanical and microstructural properties. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 88, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, K.; Bărbulescu, A. Sustainable Concrete Using Ceramic Tile Waste as a Substitute for Brick Aggregate. Materials 2025, 18, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, R. Research on different types of fiber reinforced concrete in recent years: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Jia, Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure of glass fiber and polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete: An experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapoñan Inoñan, J.J.; Delgado Fernández, E.; Muñoz Pérez, S.P.; Garcia Chumacero, J.M.; Sánchez Diaz, E.; Diaz Ortiz, E.A.; Rodriguez Laffite, E.D.; Villena Zapata, L.I.; Malpartida Iturregui, J.D.D. Influence of polypropylene fibers on the microstructure and physical and mechanical properties of concrete. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.T.; Yew, M.K.; Yew, M.C.; Lee, F.W.; Lim, S.K.; Beh, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Lim, J.H. Mechanical property enhancement in concrete composites with hybrid polypropylene fibre reinforcement. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, R.; Nithiyanantham, S. Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on cement mortar for enhancing the physico-chemical, mechanical and related properties. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2020, 12, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Dwivedi, A. Impact of nano ZnO particles on the characteristics of the cement mortar. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2021, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Garg, R. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on mechanical properties of silica fume-based cement composites. Mater. Today: Proc. 2021, 43, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IQS 5/1984; Portland Cement. Iraqi Standard Specifications: Baghdad, Iraq, 1984.
- ASTM C150-04; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- IQS 45/1984; Aggregates from Natural Sources for Concrete and Building Construction. Iraqi Standard Specifications: Baghdad, Iraq, 1984.
- ASTM C33; Method for Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- Alotaibi, J.G.; Alajmi, A.E.; Alsaeed, T.; Khalaf, J.A.; Yousif, B.F. On the incorporation of waste ceramic powder into concrete. Front. Mech. Eng. 2024, 10, 1469727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Xiao, J.; Duan, Z. Effect of pore structure and morphological characteristics of recycled fine aggregates from clay bricks on mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 358, 129455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1116; Standard Specification for Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- BS EN 934-2:2001; Admixtures for Concrete, Mortar and Grout, Concrete Admixtures, Definitions, Requirements, Conformity, Marking and Labeling. British Standard Institution: London, UK, 2001.
- BS EN 5328-2; Concrete-Part 2, Methods for Specifying Concrete Mixes. British Standard Institution: London, UK, 1997.
- Baranov, A.N.; Sokolov, P.S.; Solozhenko, V.L. ZnO under pressure: From nanoparticles to single crystals. Crystals 2022, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C143/C143M; Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- BS 1881-116; Testing Concrete. Method for Determination of Compressive Strength of Concrete Cubes. British Standard Institution: London, UK, 1983.
- ASTM C293; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Center-Point Loading). American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- ASTM C496; Standard Test Method for Splitting Tensile of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- ASTM C642; Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- ASTM C856; Standard Practice for Petrographic Examination of Hardened Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- ASTM C1723; Standard Guide for Examination of Hardened Concrete Using Scanning Electron Microscopy. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Elaqra, H.A.; Haloub, M.A.A.; Rustom, R.N. Effect of new mixing method of glass powder as cement replacement on mechanical behavior of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadbad, K.R.; Foroughi-Asl, A.; Talatahari, S.; Mohasseb, S. The effects of nanoparticle additives on thermophysical properties of concrete mixtures. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 12, 587–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nejati, F.; Edalatpanah, S.A.; Goudarzi Karim, R. Experimental study to compare the strength of concrete with different amounts of polypropylene fibers at high temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz, Z.; Mostofinejad, D. Porcelain and red ceramic wastes used as replacements for coarse aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 195, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raini, I.; Jabrane, R.; Mesrar, L.; Akdim, M. Evaluation of mortar properties by combining concrete and brick wastes as fine aggregate. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, M.R.; Biricik, Ö.; Mardani Aghabaglou, A. Effect of the addition of polypropylene fiber on concrete properties. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 345–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Ashour, A.; Zhang, W.; Han, B. Effect and mechanisms of nanomaterials on interface between aggregates and cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Zhao, J.; Pang, S.D.; Zhao, S. Durability and microstructural properties of concrete with recycled brick as fine aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wen, B.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Polypropylene–Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Desert Sand Concrete. Polymers 2023, 15, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Bansal, M.; Garg, R. An overview of beneficiary aspects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on performance of cement composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, J.; AL-Mwanes, A.O. Performance Evaluation of Eco-Friendly Ultra-High-Performance Concrete Incorporated with Waste Glass-A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1094, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahim Zai, A.; Salhotra, S. Effect of waste foundry sand and glass fiber on mechanical properties and fire resistance of high-strength concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji Azandariani, M.; Vajdian, M.; Asghari, K.; Mehrabi, S. Mechanical properties of polyolefin and polypropylene fibers-reinforced concrete—An experimental study. Compos. Part C Open Access 2023, 12, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rbaihat, R.; Al-Marafi, M.N.I. Combined Effect of Silicon Dioxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Concrete Properties. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 319–335. Available online: https://www.jeeng.net/Combined-Effect-of-Silicon-Dioxide-and-Titanium-Dioxide-Nanoparticles-on-Concrete,173210,0,2.html (accessed on 27 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ortiz, R.S.; Díaz, S.A.; Del Angel-Meraz, E.; Magaña-Hernández, F. Recycled Fine Aggregates from Mortar Debris and Red Clay Brick to Fabricate Masonry Mortars: Mechanical Analysis. Materials 2022, 15, 7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanash, A.O.; Muthusamy, K.; Budiea, A.M.A.; Fauzi, M.A.; Jokhio, G.; Jose, R. A review on the utilization of ceramic tile waste as cement and aggregates replacement in cement based composite and a bibliometric assessment. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 17, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos Cotrina, J.A.; Cubas Benavides, E.A.; Garcia Chumacero, J.M. Analysis of the combination of glass and polypropylene fibers on the mechanical properties of mortar. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2025, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangapandi, K.; Anuradha, R.; Archana, N.; Muthuraman, P.; Awoyera Paul, O.; Gobinath, R. Experimental Study on Performance of Hardened Concrete Using Nano Materials. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, D. Research Progress on Fiber-Reinforced Recycled Brick Aggregate Concrete: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemam, W.E.; Agwa, I.S.; Tahwia, A.M. Reusing Ceramic Waste as a Fine Aggregate and Supplemental Cementitious Material in the Manufacture of Sustainable Concrete. Buildings 2023, 13, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ding, W.; Qiao, Y. An experimental investigation on the integral waterproofing capacity of polypropylene fiber concrete with fly ash and slag powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klak, F.S.; Saleh, H.; Tais, A.S. Recycling of crushed clay bricks as fine aggregate in concrete and cement mortar. Aust. J. Struct. Eng. 2023, 24, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, K.; Sun, L. Review on the Durability of Polypropylene Fibre-Reinforced Concrete. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6652077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, F.; Baudys, M.; Racova, Z.; Scheinherrová, L.; Ingrisova, L.; Hajek, P. Contribution of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles to the hydration of Portland cement and photocatalytic properties of High Performance Concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.; Exposito, C.; Toshimi Ishikawa, T.; Yuuki Koga, G. X-ray diffraction study of the early hydration of Portland cements containing calcium carbonate by in-situ and ex-situ approaches. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 129947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, J.; Singh, A. Utilization potential of aerated concrete block powder and clay brick powder from C&D waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, S.; Yu, X.; Han, B.; Ou, J. Multifunctional cementitious composites modified with nano titanium dioxide: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 111, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J. Comparative Study of Concrete with Polypropylene and Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste Plastic as Partial Replacement of Coarse Aggregate. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4928065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, Y.; Mohammadyan-Yasouj, S.E. Utilization of Porcelain Polishing Residues and Metakaolin in Self-Consolidating Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 420, 135588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulghebar, K.; Sadok, A.H.; Brahma, A. Effect of recycled brick sand on mechanical and transfer properties of roller compacted concrete “RCC” used for dams. Matéria 2025, 30, 20240703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunther, W.; Ferreiro, S.; Skibsted, J. Influence of the Ca/Si ratio on the compressive strength of cementitious calcium–silicate–hydrate binders. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17401–17412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fly ash blended cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, O.; Alakara, E.H.; Guzelkucuk, S. Fresh and Hardened Properties of Cementitious Composites Incorporating Firebrick Powder from Construction and Demolition Waste. Buildings 2023, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, S.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Bai, X. Sustainable reuse of ceramic waste powder as a supplementary cementitious material in recycled aggregate concrete: Mechanical properties, durability and microstructure assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampanis, I.; Vasilatos, C. Recycling Concrete to Aggregates, Implications on CO2 Footprint. Mater. Proc. 2023, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Deng, C.; Tang, Z. Carbon Emission Evaluation of Recycled Fine Aggregate Concrete Based on Life Cycle Assessment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).