Effect of Rainfall Intensity on Landslide Initiation: Flume Tests and Numerical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Used
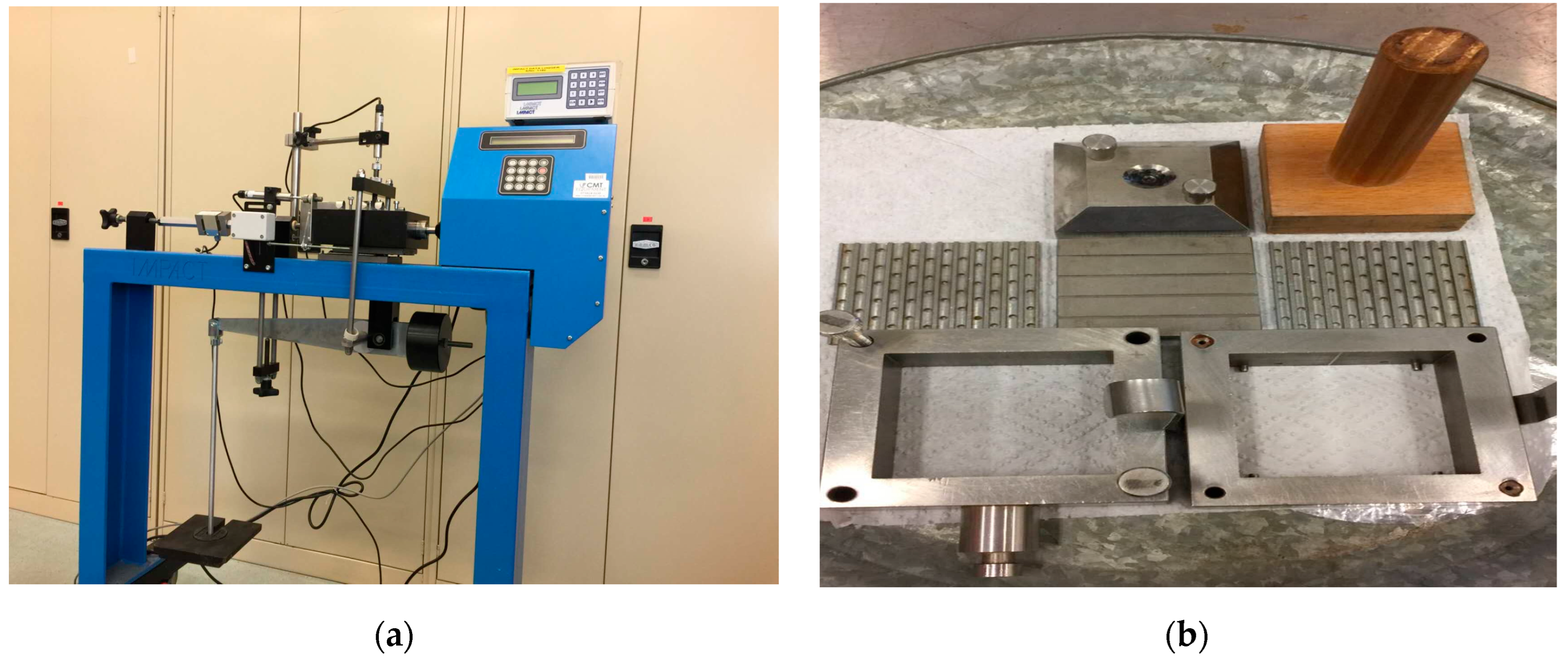
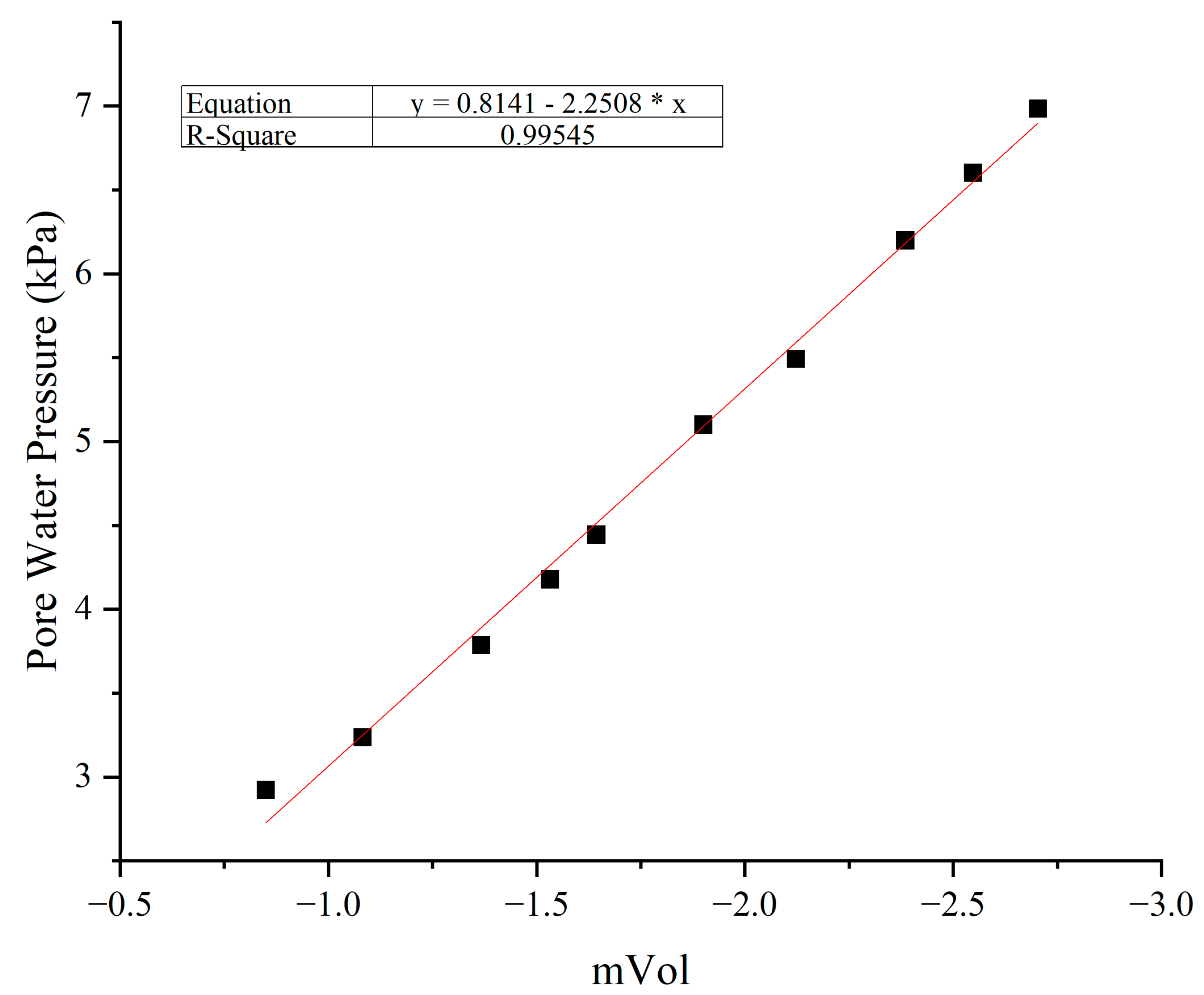
2.2. Shear Box Tests
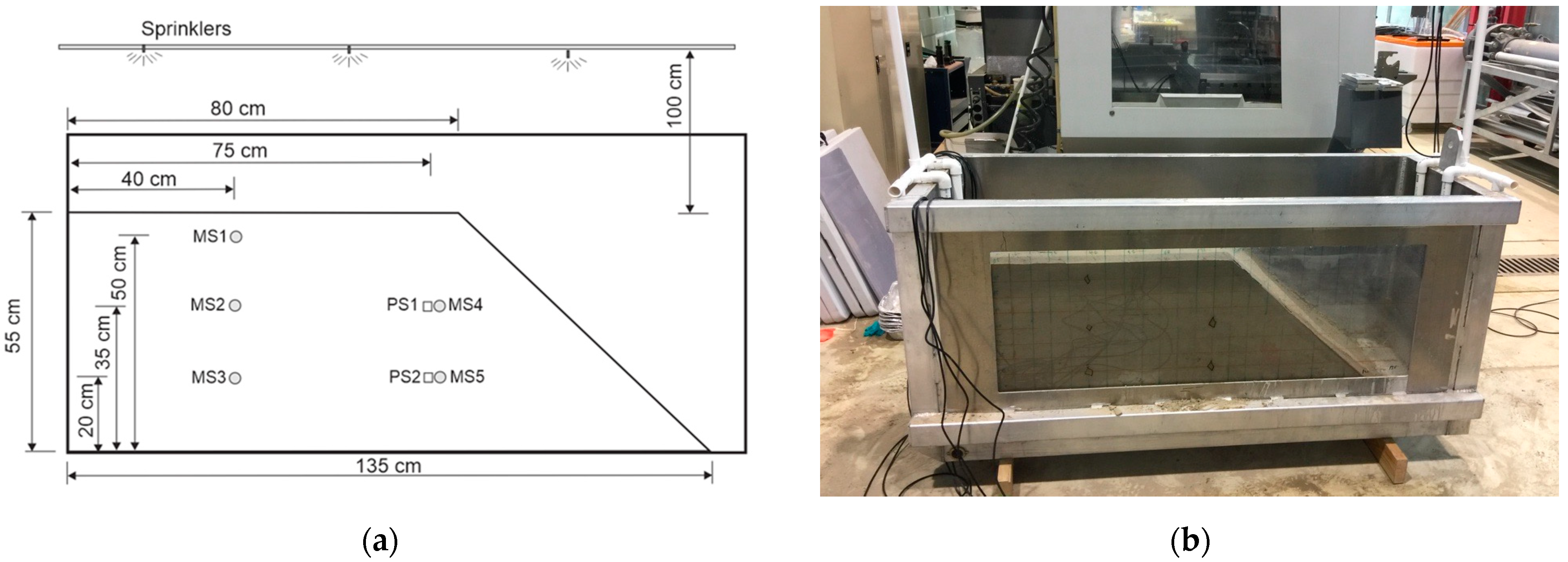
2.3. Flume Apparatus and Experimental Setup
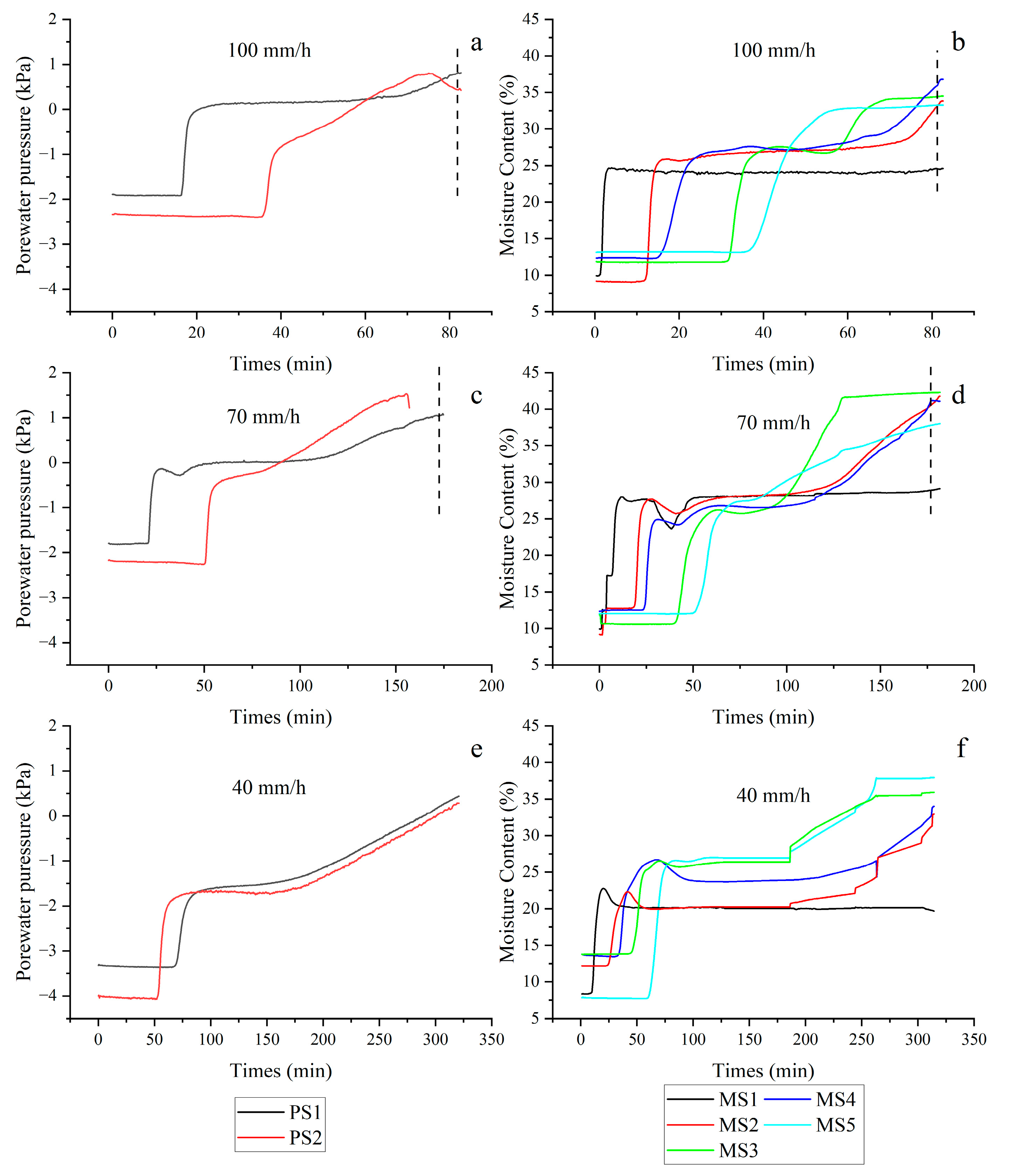
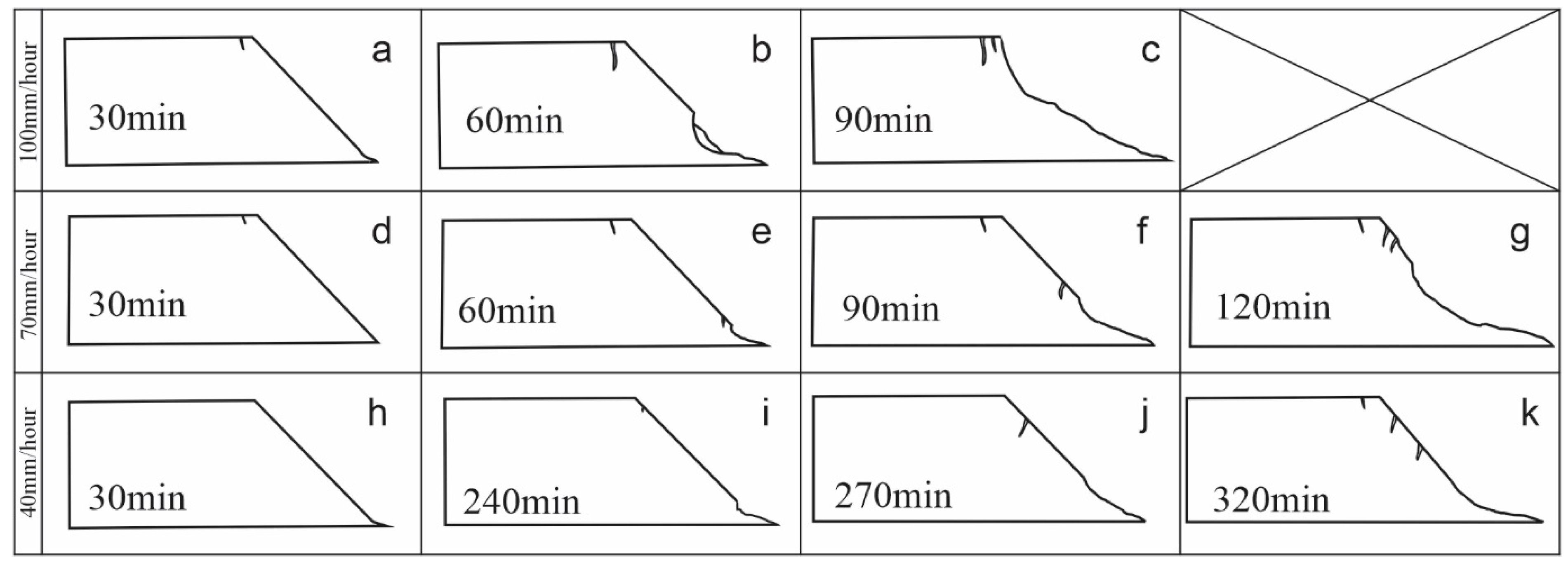
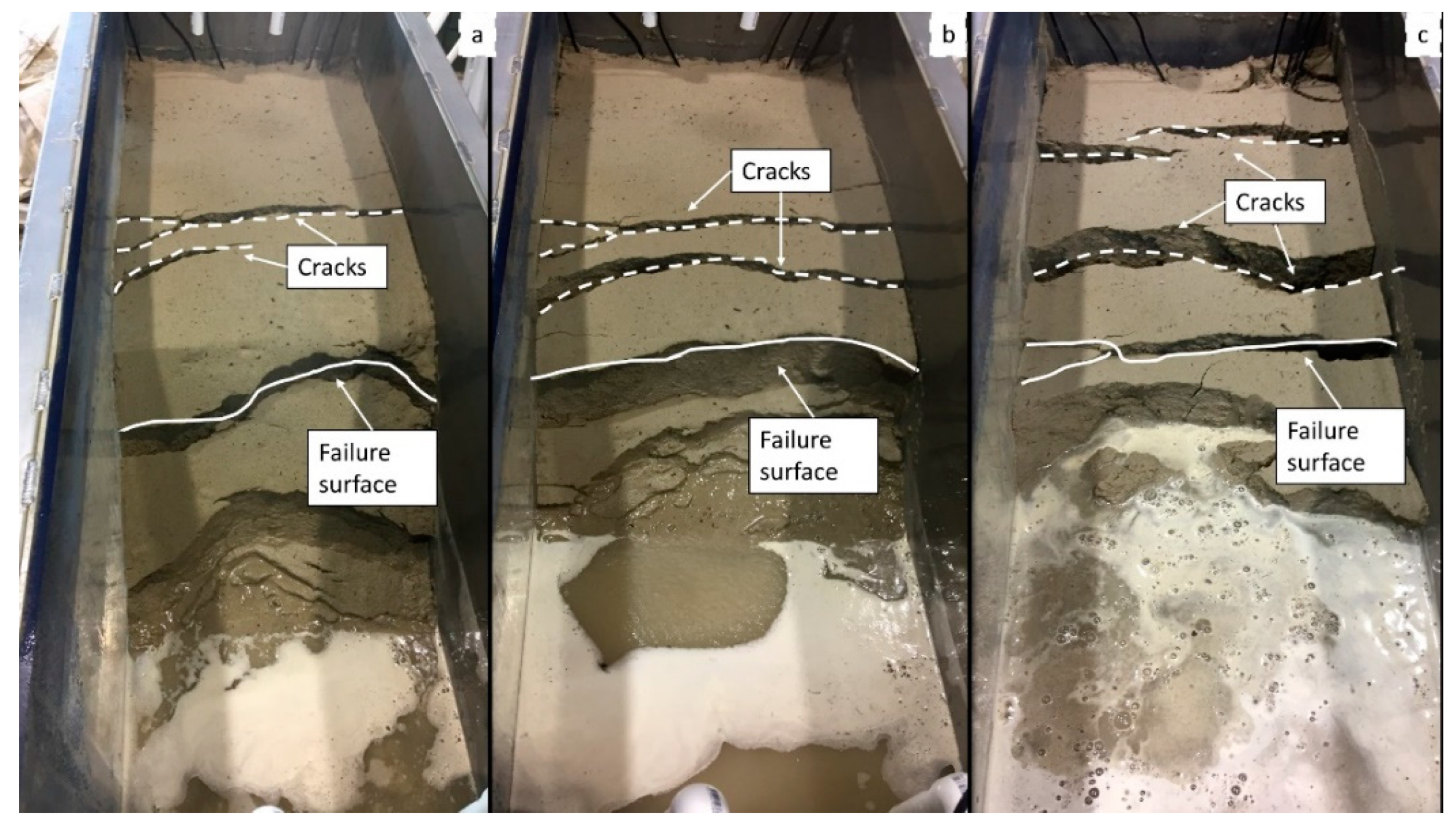
3. Results and Discussion
4. Numerical Analysis
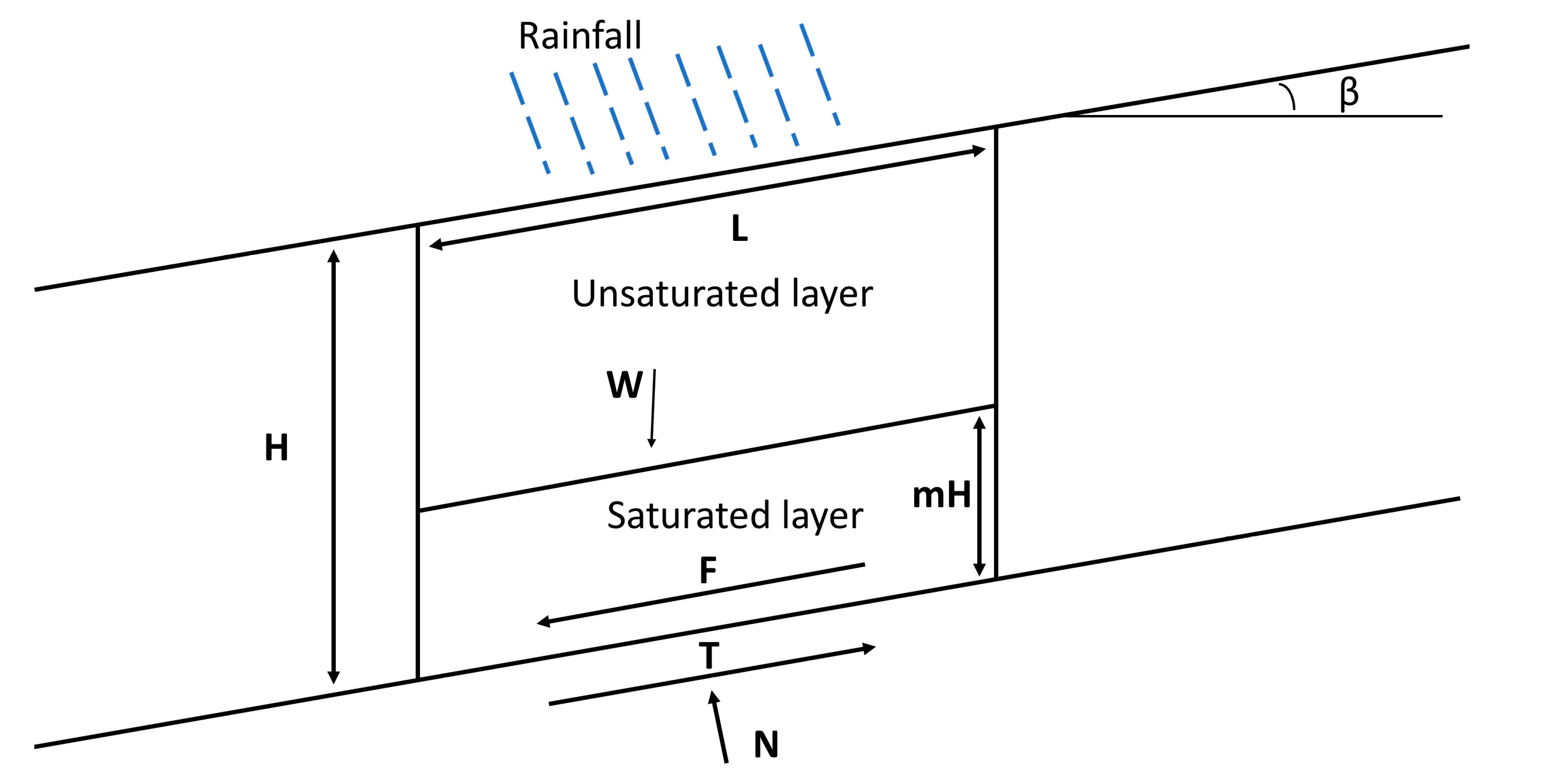
4.1. Theoretical Considerations
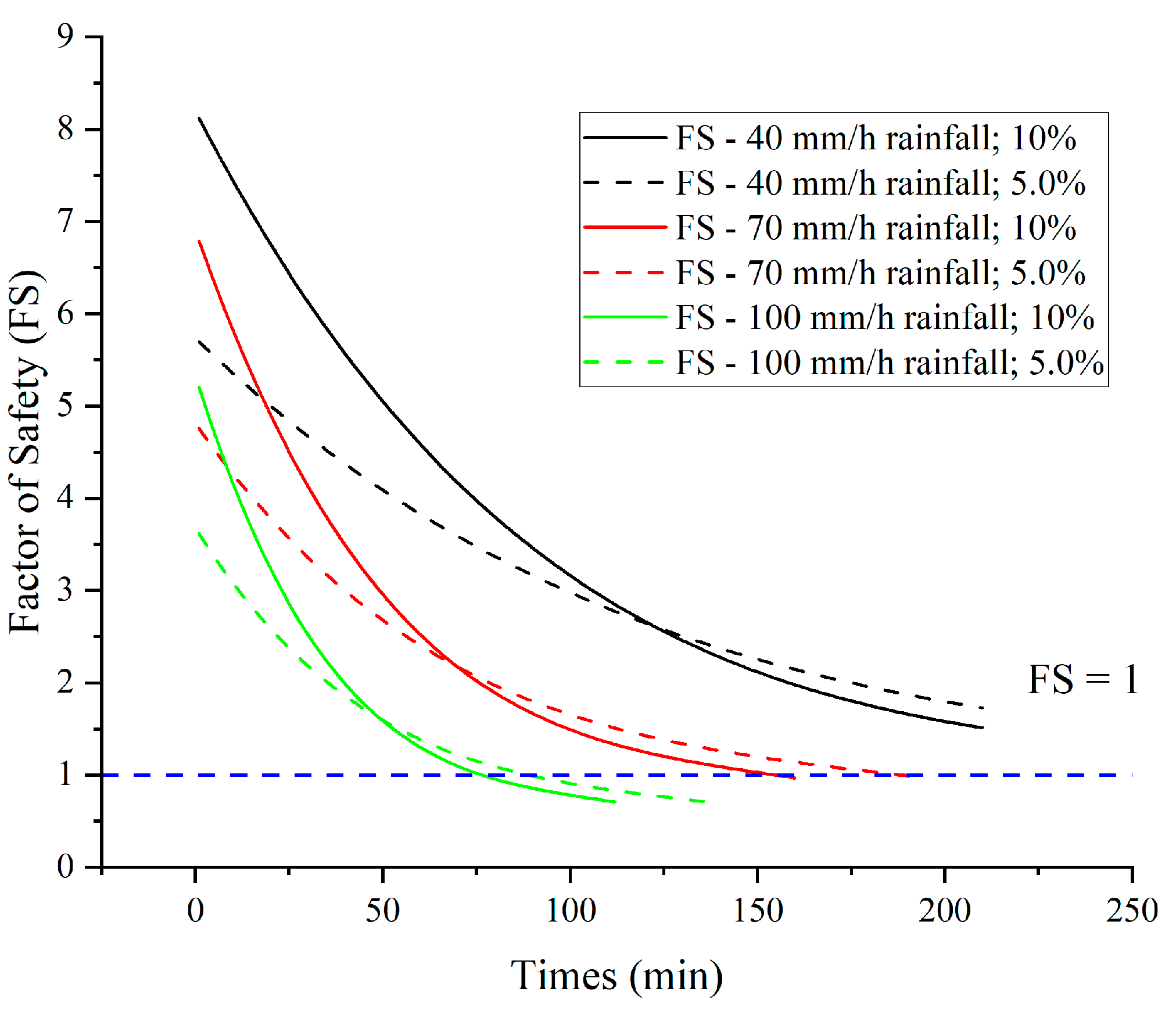
4.2. Comparison of Flume Test Results and Numerical Data
4.3. Limitations of the Numerical Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.W. Assessment of landslide susceptibility on the natural terrain of Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L.; Cuomo, S.; Della Sala, M. Spatial and temporal occurrence of rainfall-induced shallow landslides of flow type: A case of Sarno-Quindici, Italy. Geomorphology 2011, 126, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, C.; Kamal, S.A.; Shanahan, P.; Bras, R.L. Rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility zonation of Puerto Rico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.M.; Glade, T. Characteristics of earthquake- and rain-induced landslides near the epicenter of Wenchuan earthquake. Eng. Geol. 2014, 175, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, J.; Gratchev, I.; Wang, G. Rainfall-induced shallow landslides caused by ex-Tropical Cyclone Debbie, 31st March 2017. Landslides 2018, 15, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, S.; Gratchev, I.; Jeng, D.S. Analysis of Rainfall-Induced Landslides in Northern New South Wales, Australia. Aust. Geomech. 2019, 54, 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, S.; Gratchev, I. Prediction of Shallow Rainfall-Induced Landslides Using Shear Strength of Unsaturated Soil. Indian Geotech. J. 2021, 51, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratchev, I.; Ravindran, S.; Kim, D.H.; Cui, C.; Tang, Q. Mechanisms of Shallow Rainfall-Induced Landslides from Australia: Insights into Field and Laboratory Investigations; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Okura, Y.; Kitahara, H.; Ochiai, H.; Sammori, T.; Kawanami, A. Landslide fluidization process by flume experiments. Eng. Geol. 2002, 66, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Inokuchi, T.; Hattanji, T.; Sassa, K.; Ochiai, H.; Wang, G. Failure processes in a full-scale landslide experiment using a rainfall simulator. Landslides 2004, 1, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, L.; Damiano, E.; Greco, R.; Zeni, L.; Picarelli, L.; Minardo, A.; Guida, A.; Bernini, R. An Instrumented Flume to Investigate the Mechanics of Rainfall-induced Landslides in Unsaturated Granular Soils. Geotech. Test. J. 2009, 32, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Sassa, K. Factors affecting rainfall-induced flowslides in laboratory flume tests. Geotechnique 2001, 51, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Sassa, K. Pore-pressure generation and movement of rainfall-induced landslides: Effects of grain size and fine-particle content. Eng. Geol. 2003, 69, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.D.N.; Sassa, K.; Fukuoka, H. Failure process and hydrologic response of a two layer physical model: Implications for rainfall-induced landslides. Geomorphology 2006, 73, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakro, M.R.; Harahap, I.S.H. Laboratory experiments on rainfall-induced flowslide from pore pressure and moisture content measurements. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 3, 1575–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Z.; Huang, R.Q.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Li, H.L. Analysis of physical testing of rainfall-induced soil slope failures. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8519–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, G.; Cochrane, T.A.; Davies, T.; Bowman, E. The influence of shallow landslides on sediment supply: A flume-based investigation using sandy soil. Eng. Geol. 2009, 109, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Adli, M.; Huvaj, N.; Toker, N.K. Rainfall-triggered landslides in an unsaturated soil: A laboratory flume study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, J.; Gratchev, I. A study on the effect of rainfall and slope characteristics on landslide initiation by means of flume tests. Landslides 2019, 16, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. Landslides in a changing climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Oppenheimer, M.; Warren, R.; Hallegatte, S.; Kopp, R.E.; Portner, H.O.; Scholes, R.; Birkmann, J.; Foden, W.; Licker, R.; et al. IPCC reasons for concern regarding climate change risks. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R.; Losi, G.L. Rainfall-induced shallow landslides: A model for the triggering mechanism of some case studies in Northern Italy. Landslides 2009, 6, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, S.; Gratchev, I. Effect of Water Content on Apparent Cohesion of Soils from Landslide Sites. Geotechnics 2022, 2, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R. A model for triggering mechanisms of shallow landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R.; Meisina, C. Soil Saturation and Stability Analysis of a Test Site Slope Using the Shallow Landslide Instability Prediction (SLIP) Model. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Rahardjo, H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Xing, A.Q.; Fredlund, M.D.; Barbour, S.L. The relationship of the unsaturated soil shear strength to the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R.; Losi, G.L. Towards a real-time susceptibility assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslides on a regional scale. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1927–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotisankasa, A.; Tapparnich, J. Shear and soil-water retention behaviour of a variably saturated residual soil and its implication on slope stability. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Unsaturated Soils UNSAT 2010, Barcelona, Spain, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]

| Moisture Content (%) | Apparent Cohesion (kPa) | Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 27 | 39 |
| 12 | 18 | 39 |
| 17 | 14 | 34 |
| 31 | 0 | 34 |
| Notation | How It Is Obtained | Value |
|---|---|---|
| H | Flume test | 0.55 |
| ß* | According to Ravindran and Gratchev [7] | 0.95 |
| n | Calculations using lab data | 0.46 |
| Sr | Calculations using lab data | 15 |
| c’ | Shear box test | 0 |
| ϕ’ | Shear box test | 34 |
| cψ | Equation (4) | |
| α | According to Montrasio, Valentino and Losi [22] | 3.4 |
| λ | According to Montrasio, Valentino and Losi [22] | 0.4 |
| A | Estimation from shear box tests | 45.2 |
| G | Lab tests | 2.63 |
| L | Constant factor for converting forces to line loads | 1 |
| kt | Lab tests | 2.00 × 10−5 |
| c*ψ | Equation (4) | 6.43 |
| nw | Equation (10) | 0.39 |
| Ω | Equation (11) | 0.41 |
| Г | Equation (7) | 1.48 |
| Test No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall intensity (mm/h) | 40 | 40 | 70 | 70 | 100 | 100 |
| Initial moisture content (%) | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 |
| Time to failure (min) from flume tests | No failure | No failure | 210 | 180 | 90 | 85 |
| Time to failure (min) predicted by the numerical model | No failure | No failure | 145 | 122 | 102 | 86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Q.; Gratchev, I.; Ravindran, S. Effect of Rainfall Intensity on Landslide Initiation: Flume Tests and Numerical Analysis. Geotechnics 2023, 3, 104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics3010007
Tang Q, Gratchev I, Ravindran S. Effect of Rainfall Intensity on Landslide Initiation: Flume Tests and Numerical Analysis. Geotechnics. 2023; 3(1):104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics3010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Qianhao, Ivan Gratchev, and Sinnappoo Ravindran. 2023. "Effect of Rainfall Intensity on Landslide Initiation: Flume Tests and Numerical Analysis" Geotechnics 3, no. 1: 104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics3010007
APA StyleTang, Q., Gratchev, I., & Ravindran, S. (2023). Effect of Rainfall Intensity on Landslide Initiation: Flume Tests and Numerical Analysis. Geotechnics, 3(1), 104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics3010007







