Automatic Unfolding of CityGML Buildings to Paper Models
Abstract
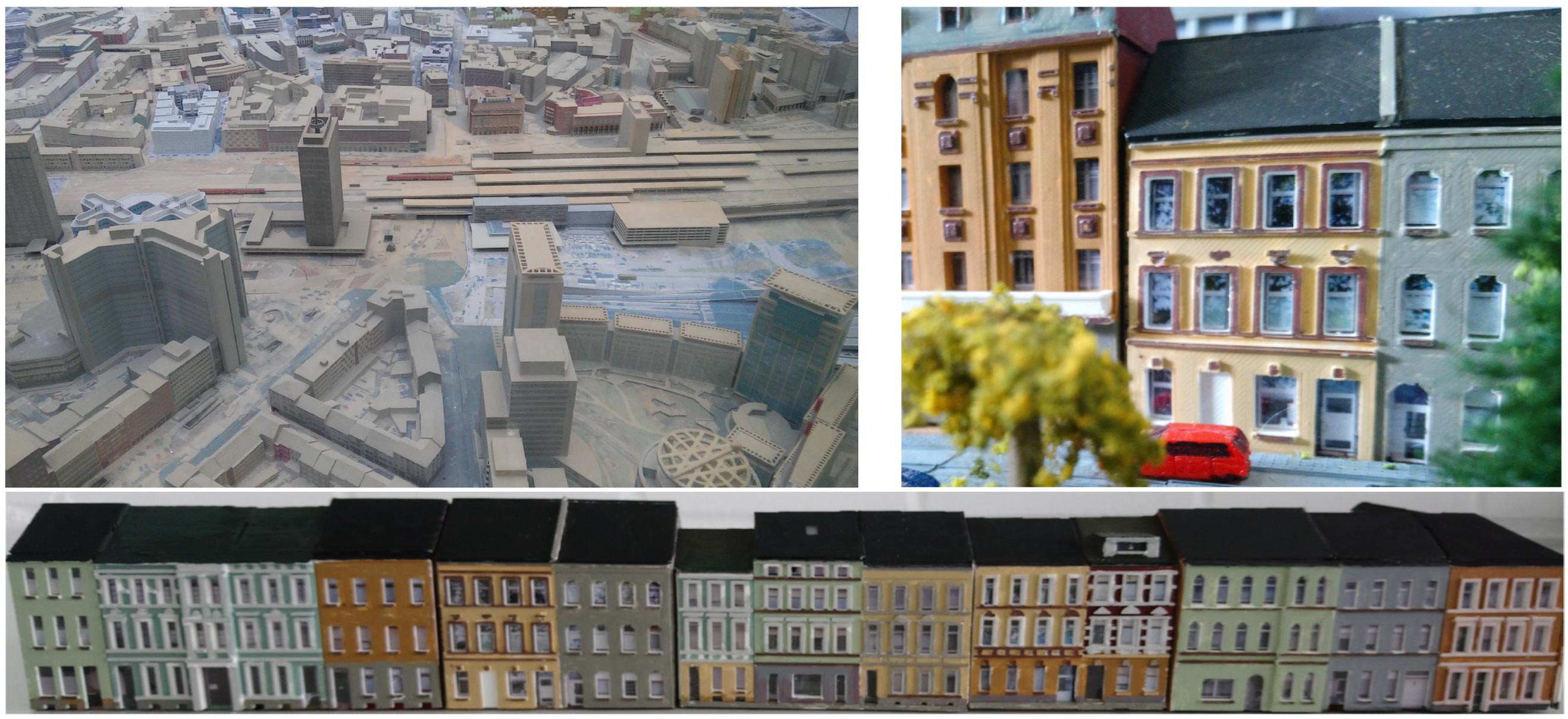
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
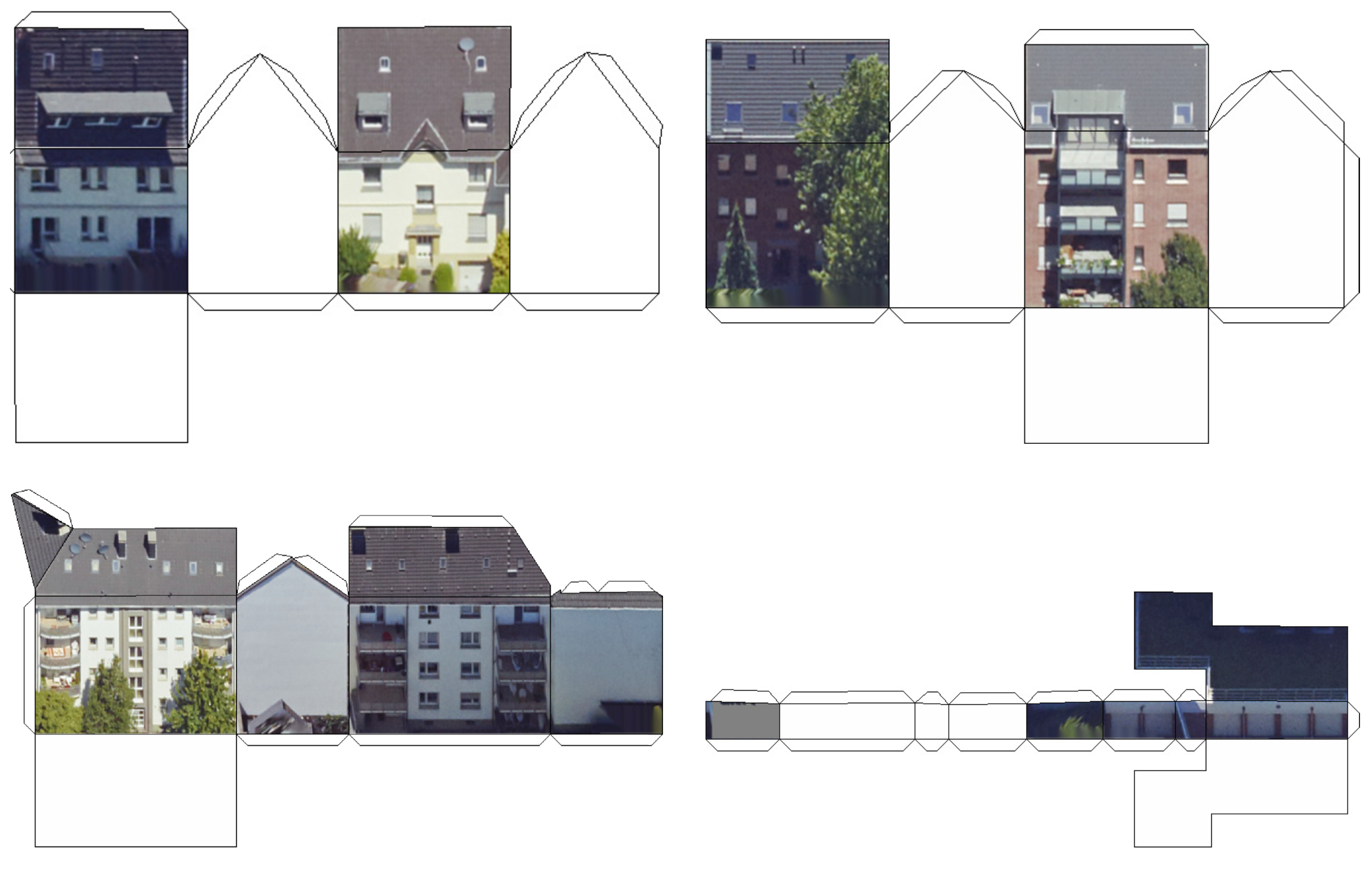
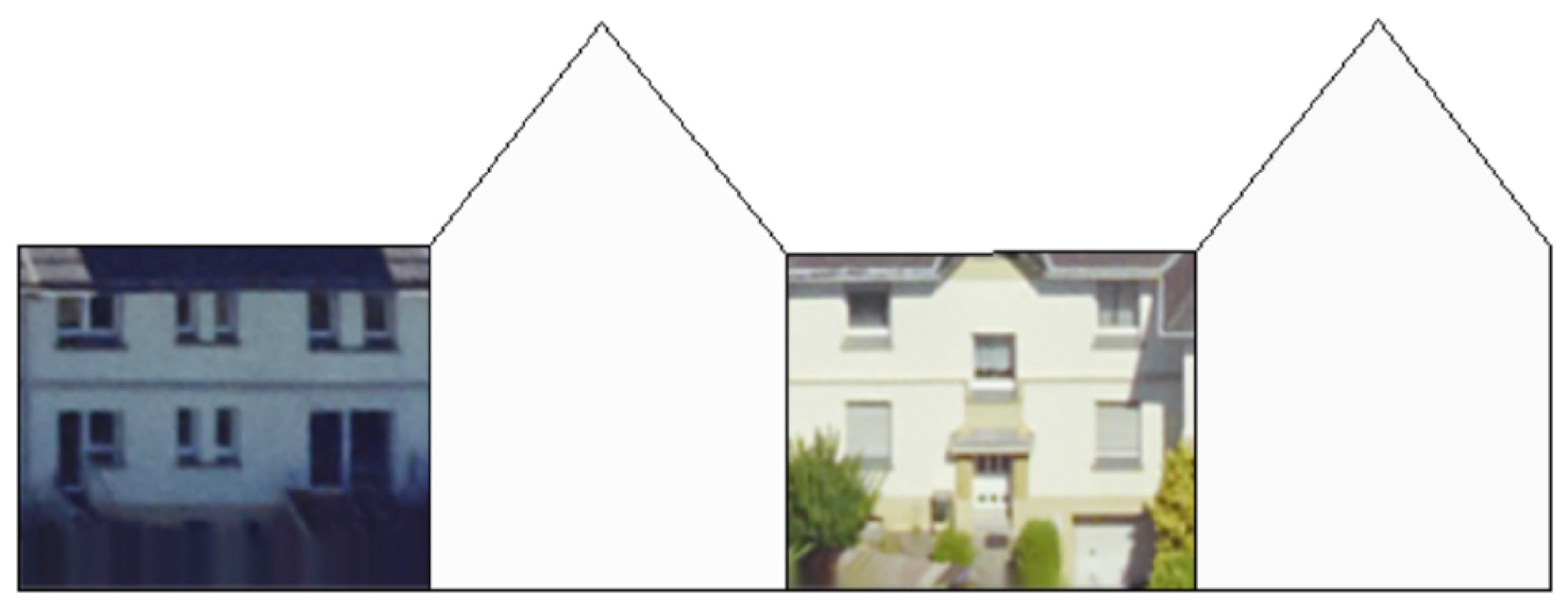
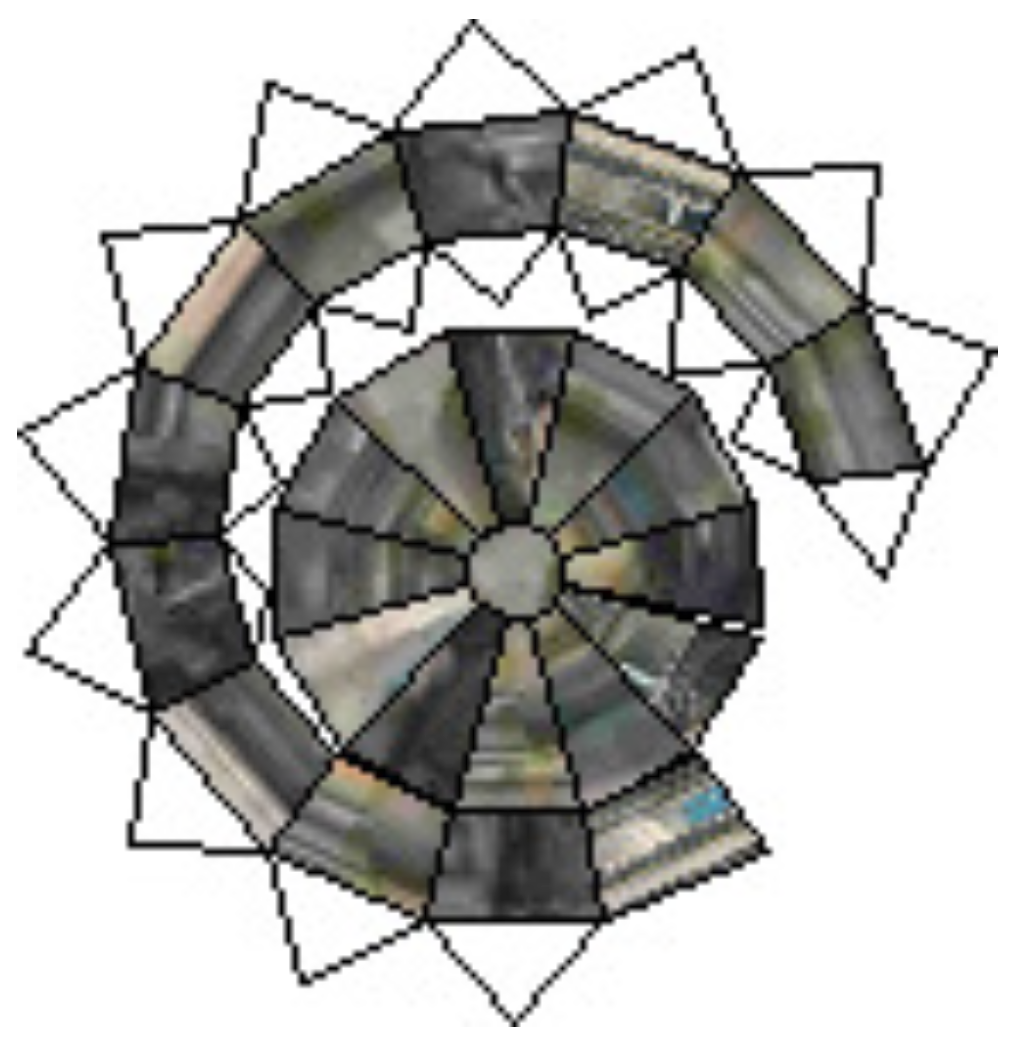
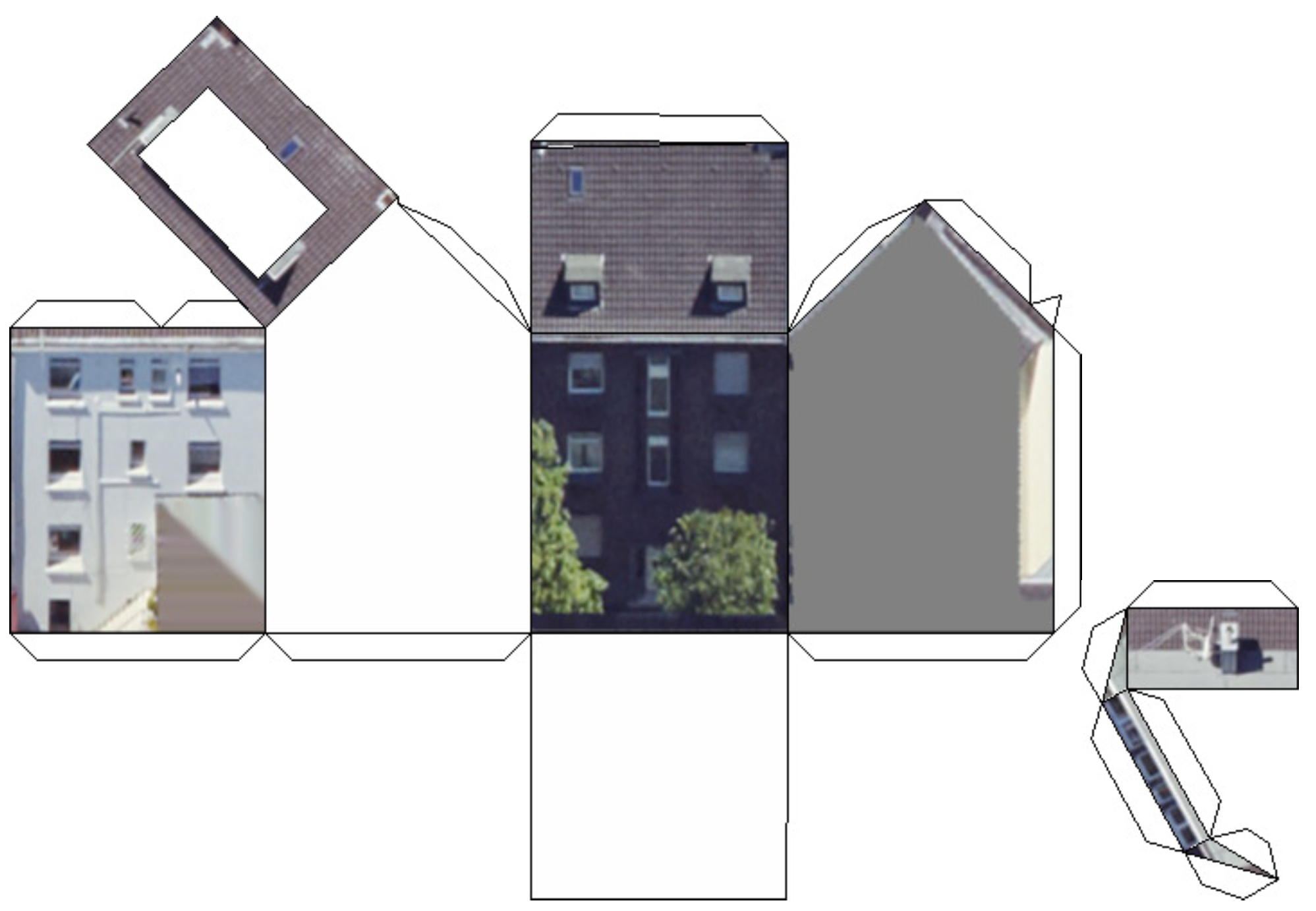
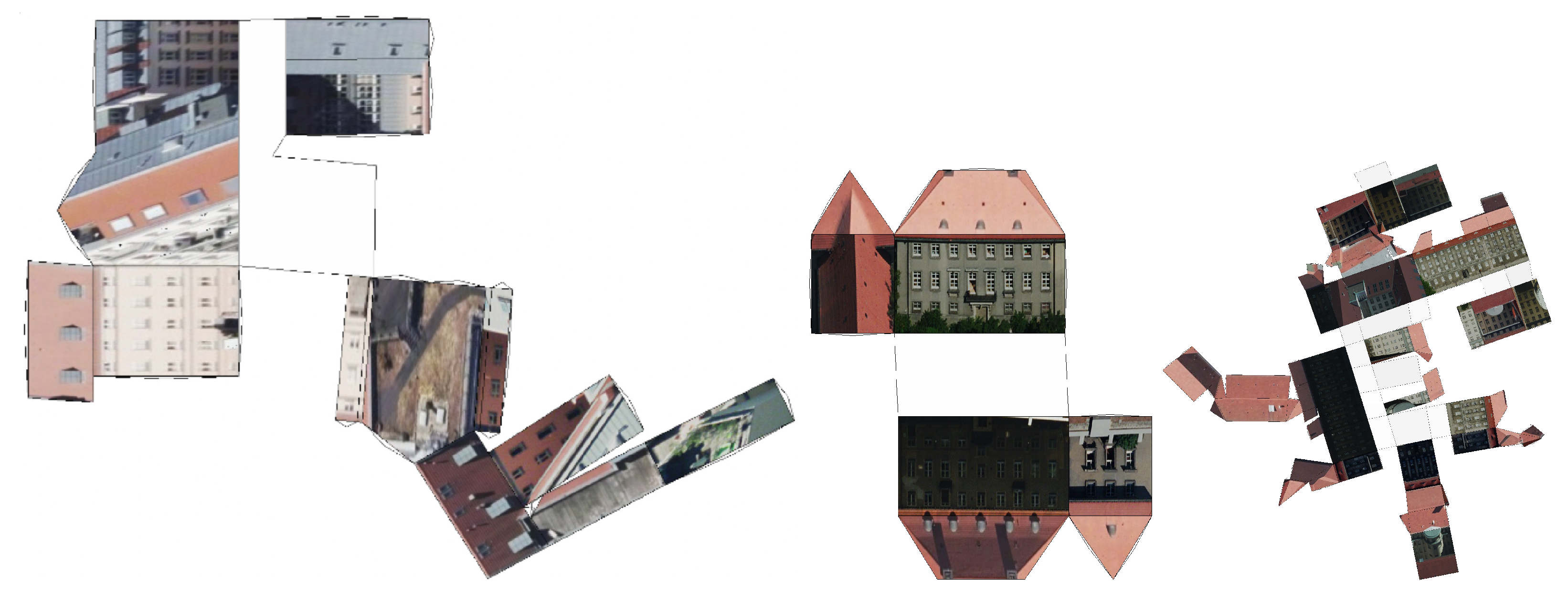
2.1. The Greedy Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Greedy Unfolding |
|
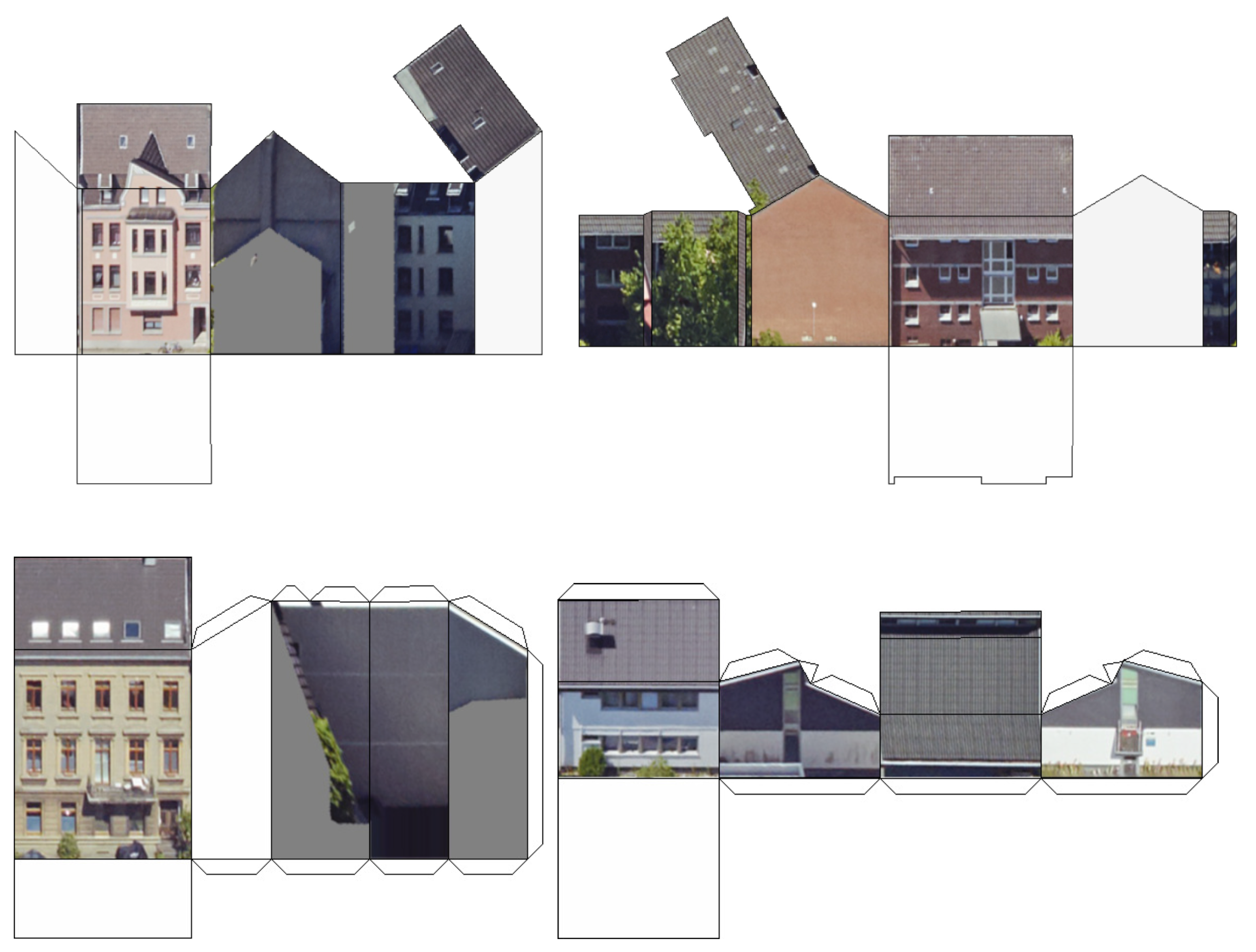
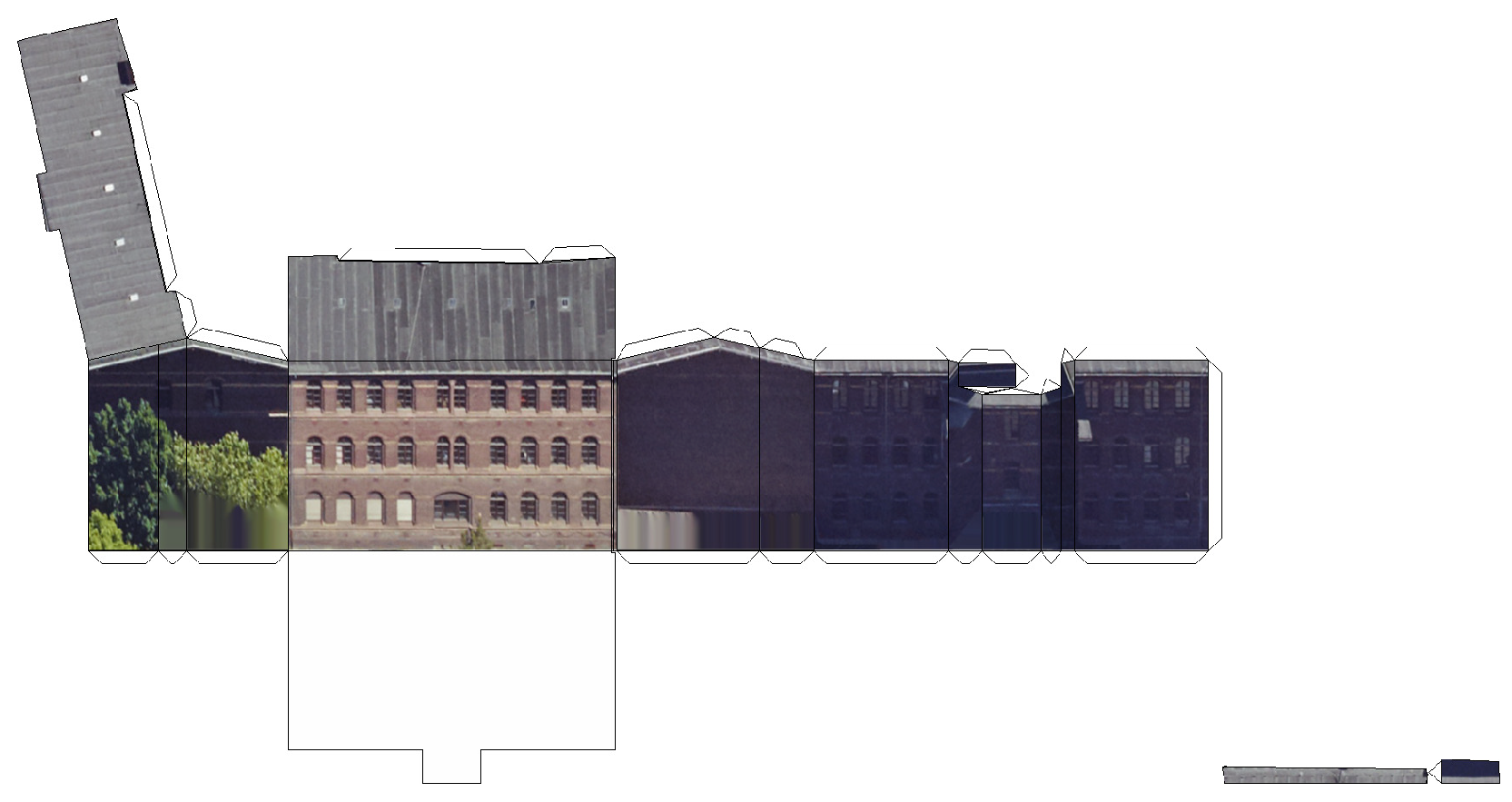
2.2. Data Preparation
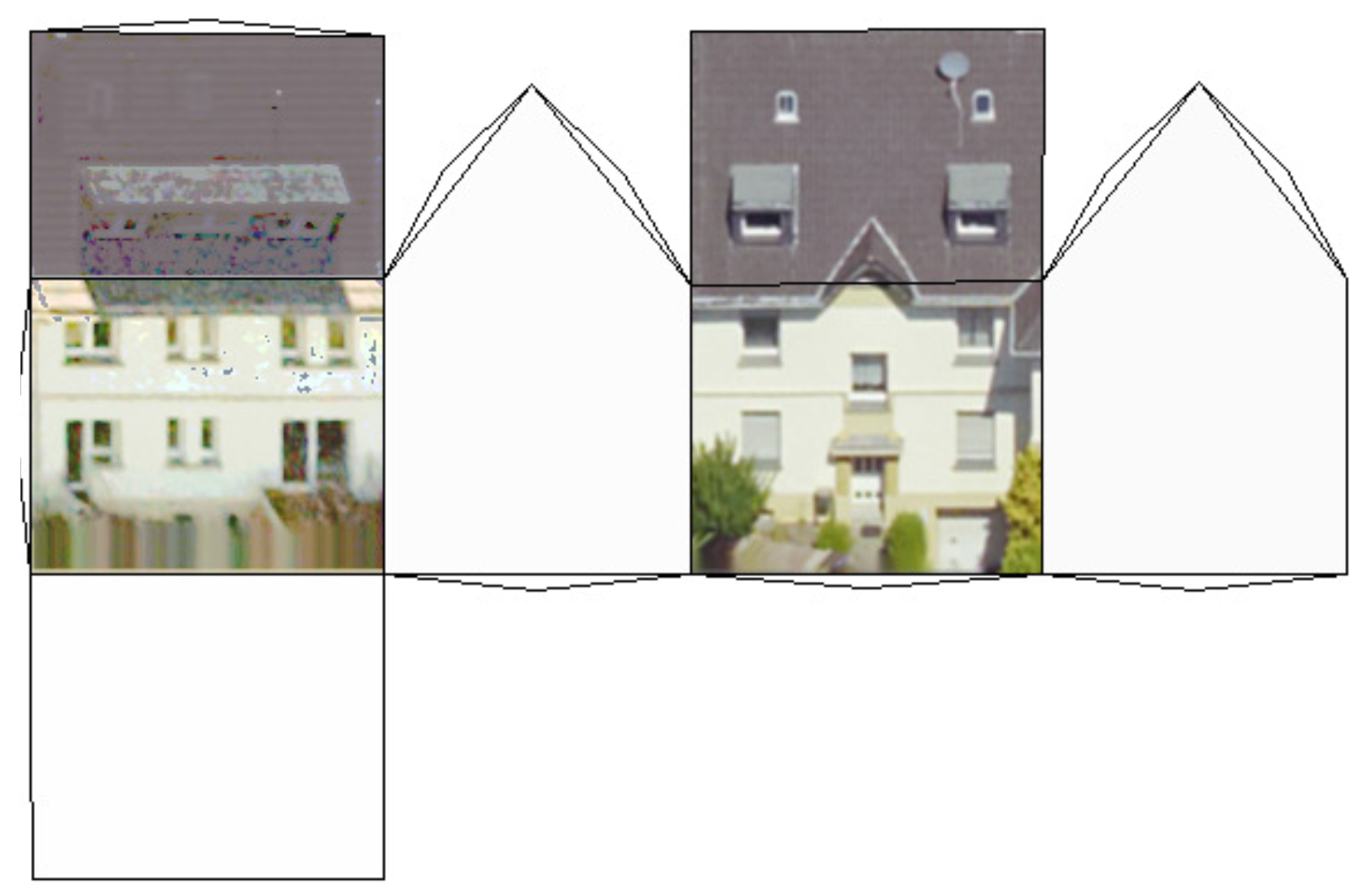
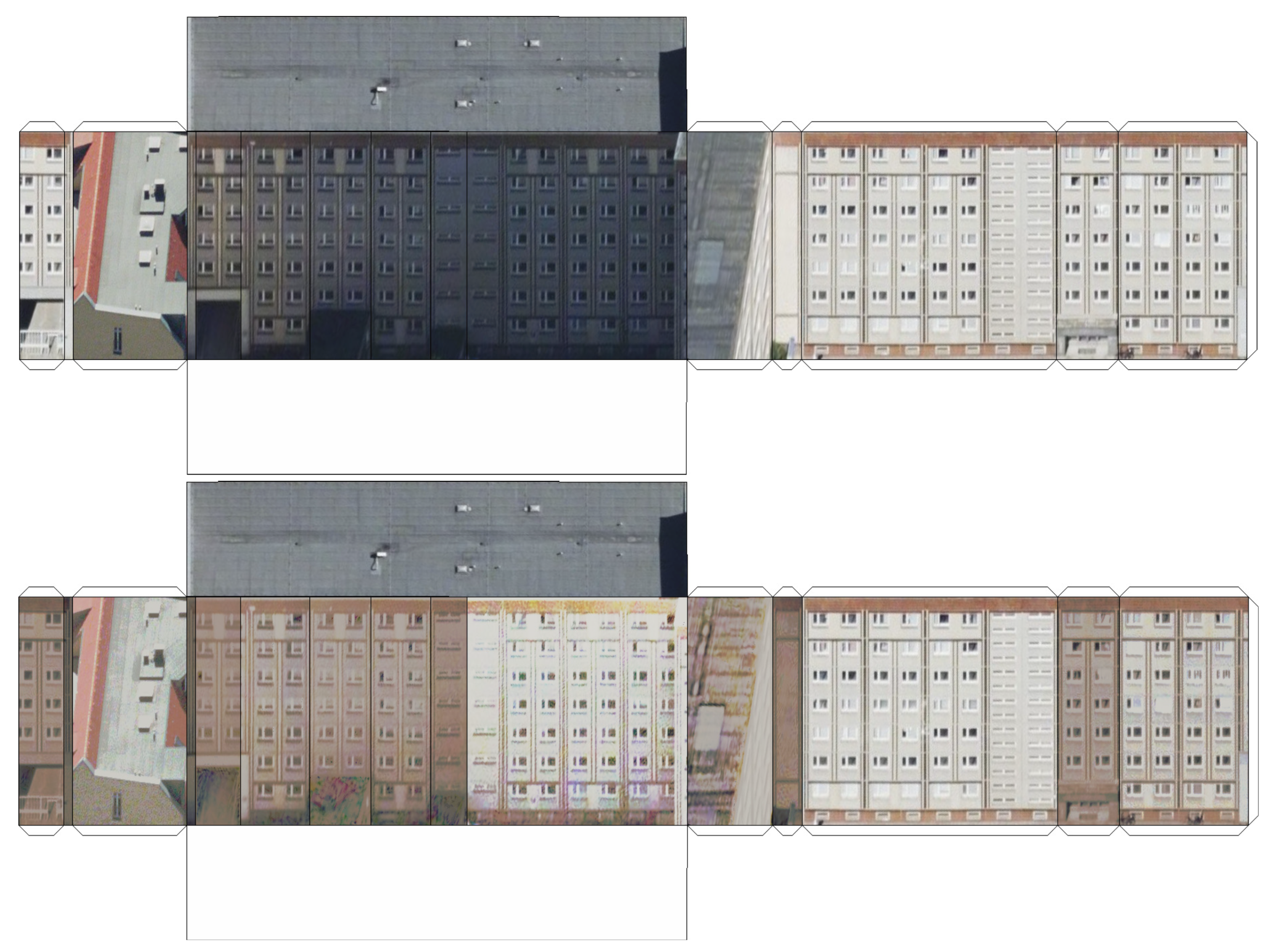
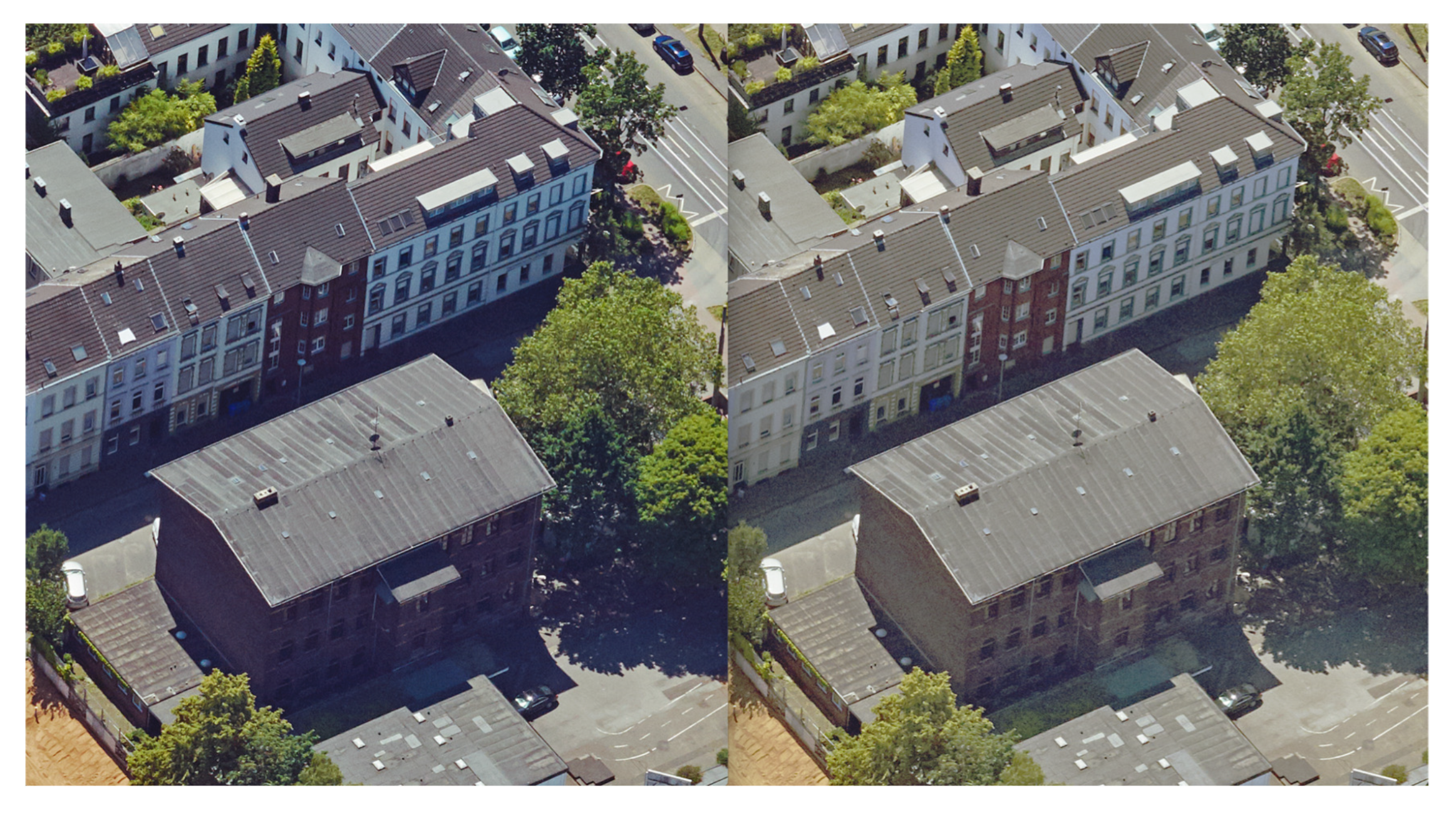
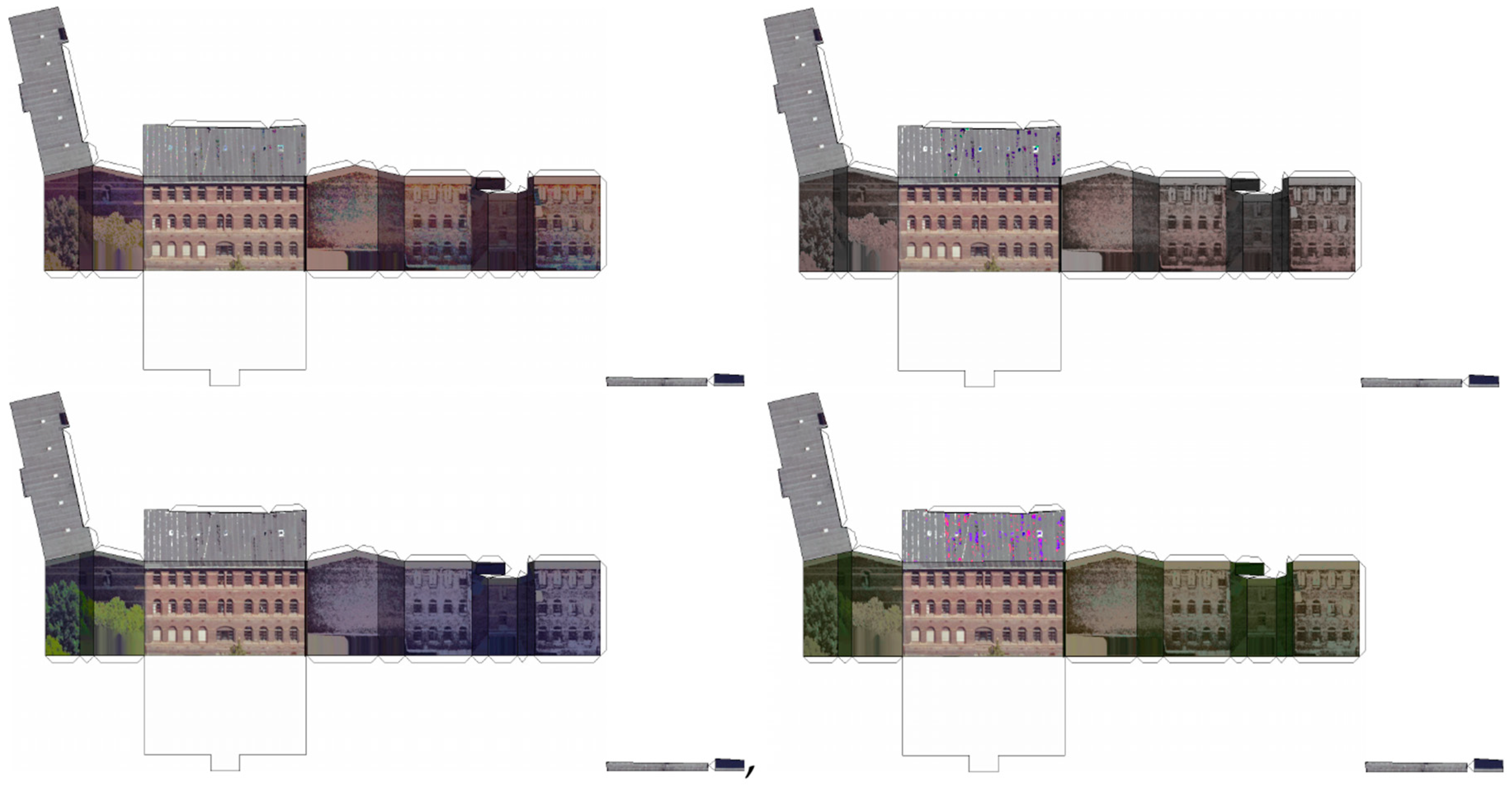
2.3. Histogram Matching
2.4. Implementation
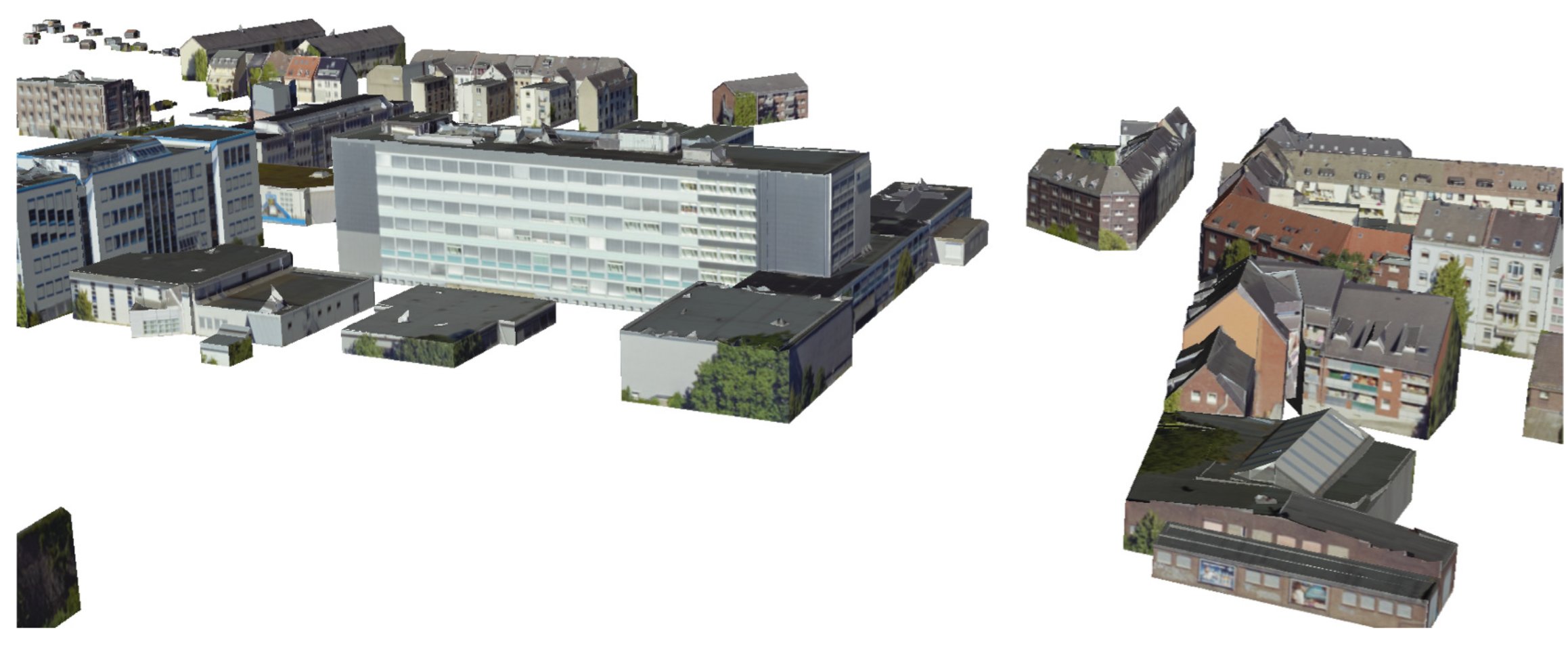
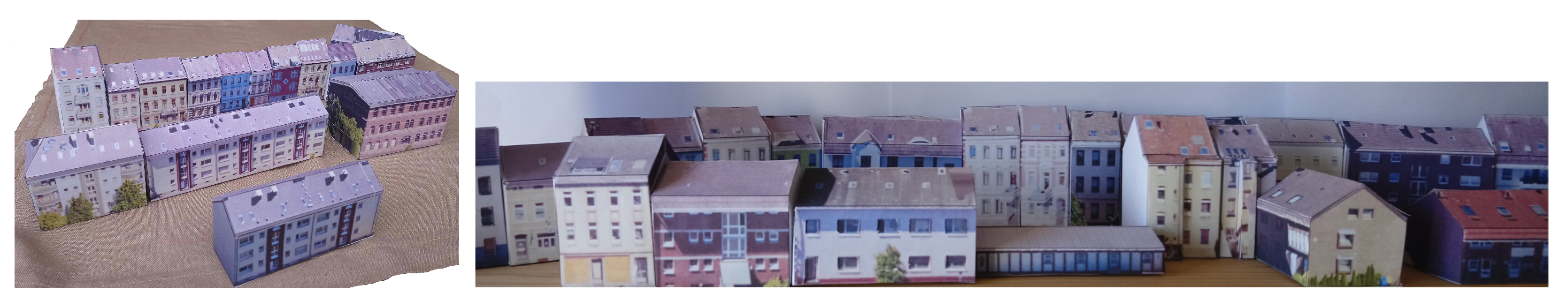
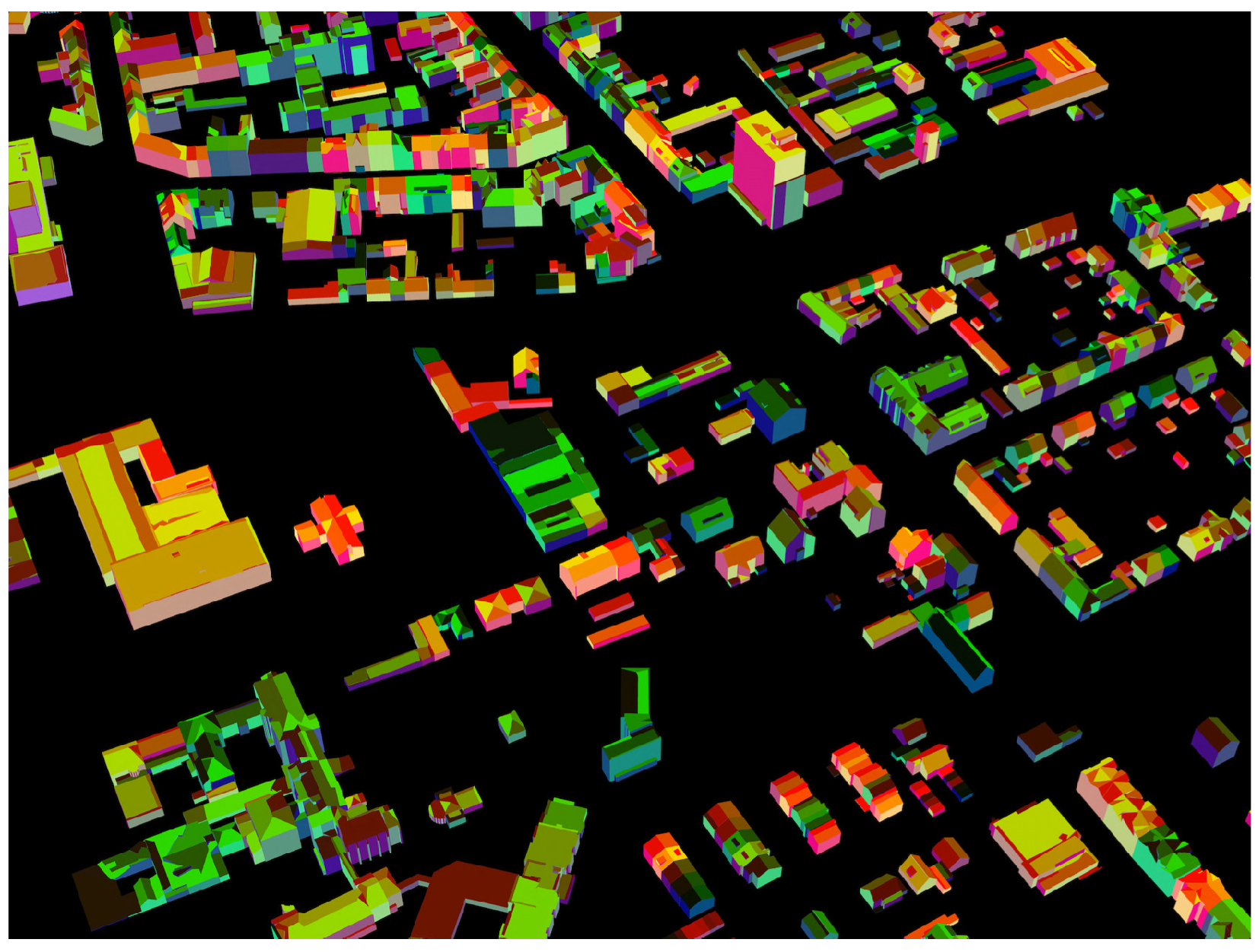
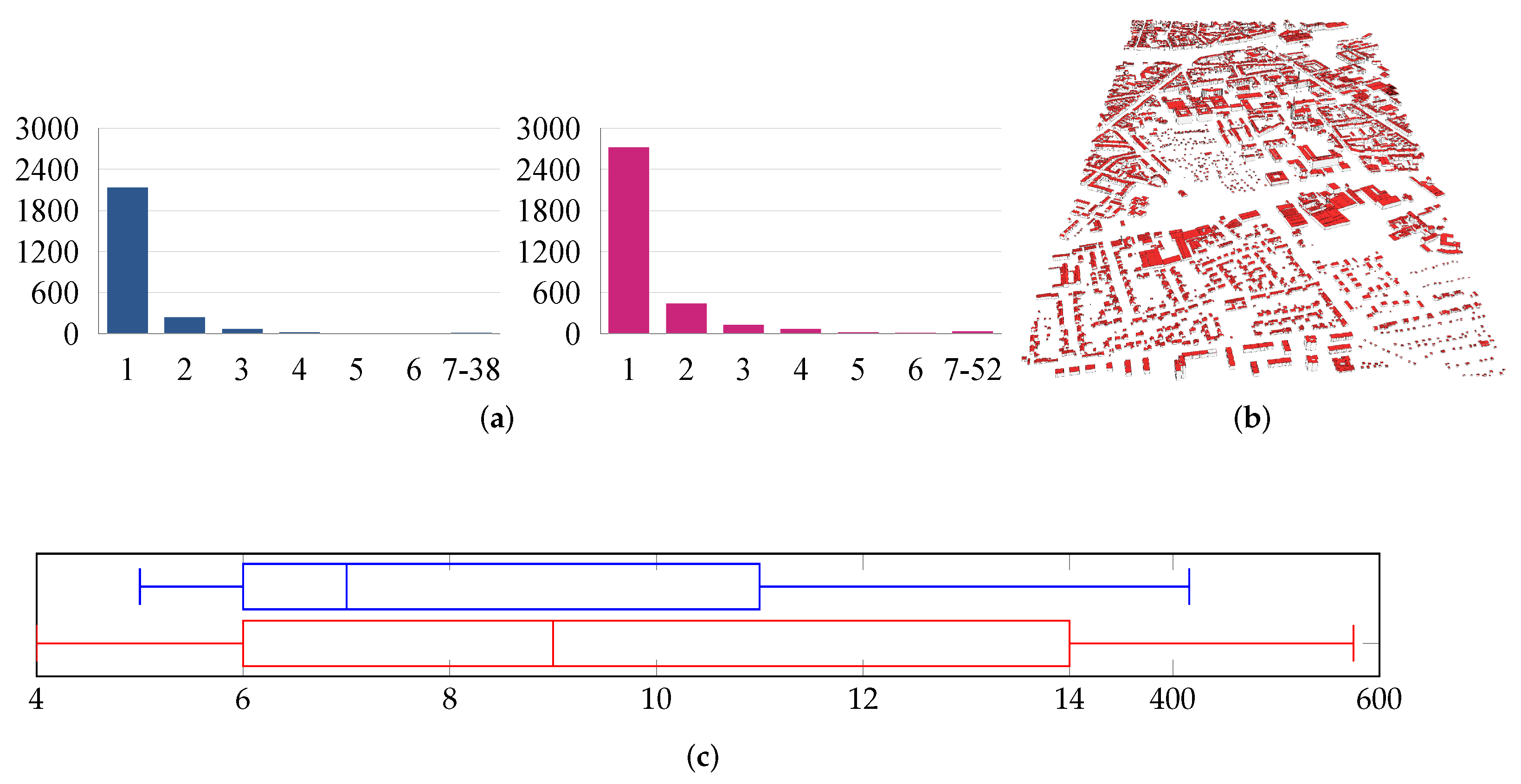
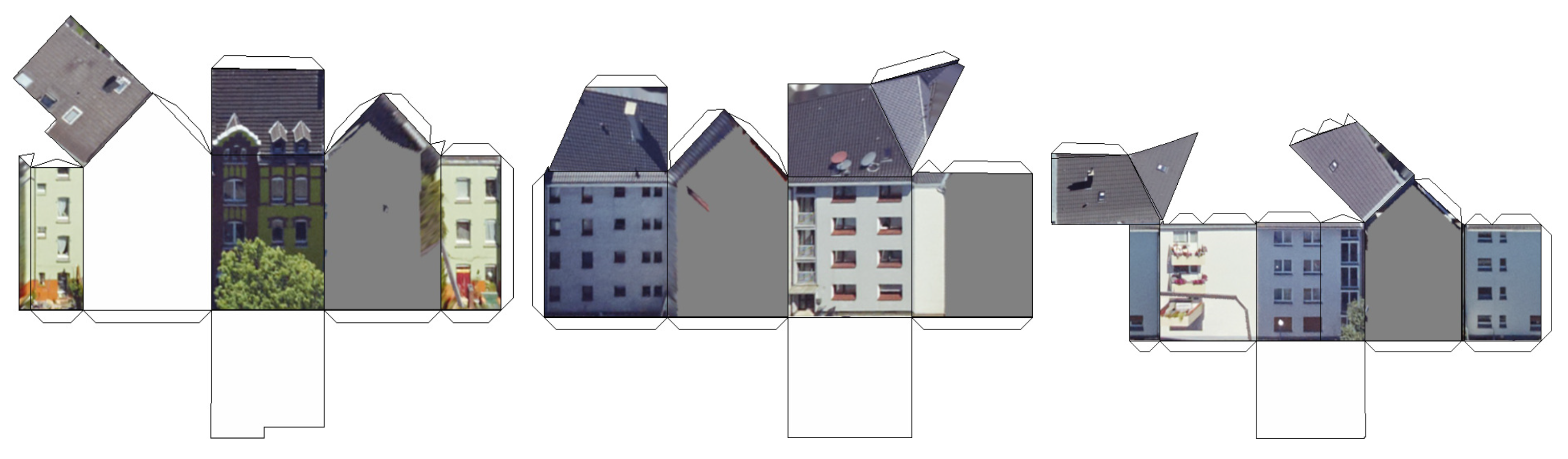
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biljecki, F.; Stoter, J.; Ledoux, H.; Zlatanova, S.; Çöltekin, A. Applications of 3D City Models: State of the Art Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 2842–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, T.; Donaubauer, A. Semantic 3D City Modeling and BIM; Urban Informatics. The Urban Book Series; Shi, W., Goodchild, M., Batty, M., Kwan, M., Zhang, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 609–636. [Google Scholar]
- Gröger, G.; Kolbe, T.H.; Nagel, C.; Häfele, K.H. OpenGIS City Geography Markup Language (CityGML) Encoding Standard. Version 2.0.0; Open Geospatial Consortium: Arlington, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, P.; Stattmann, N. Unfolded; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kodmany, K. Visualization tools and methods for participatory planning and design. J. Urban Technol. 2001, 8, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, C.; Willett, W. Building with Data: Architectural Models as Inspiration for Data Physicalization. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1217–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, A.L. Feeling It Out: The Use of Haptic Visualization for Exploratory Geographic Analysis. Cartogr. Perspect. 2001, 39, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, A. Architektur und Modellbau: Konzepte-Methoden-Materialien; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pottmann, H.; Asperl, A.; Hofer, M.; Kilian, A. Die Erstellung von Modellen im Kontext der Architektur. In Architekturgeometrie; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 423–453. [Google Scholar]
- Bañón, C.; Raspall, F. 3D Printing Architecture: Workflows, Applications, and Trends; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, R.; Prautzsch, H. Creating Optimized Cut-Out Sheets for Paper Models from Meshes. KarlsRuhe Rep. Inform. 2011, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cankova, K.; Dovramadjiev, T.; Jecheva, G.V. Methodology for creating 3D paper unfolded models with complex geometry using open-source software and resources with free personal and commercial license. Annu. J. Tech. Univ. Varna Bulg. 2018, 2, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Haenselmann, T.; Effelsberg, W. Optimal strategies for creating paper models from 3D objects. Multimed. Syst. 2012, 18, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpitsch, T.; Takahashi, S.; Gröller, E.; Wu, H.Y. Simulated Annealing to Unfold 3D Meshes and Assign Glue Tabs. J. WSCG 2020, 28, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, H.; Falconer, K.; Guy, R. Unsolved Problems in Geometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bern, M.; Demaine, E.; Eppstein, D.; Kuo, E.; Mantler, A.; Snoeyink, J. Unfoldable polyhedra with convex faces. Comput. Geom. 2003, 24, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goebbels, S.; Pohle-Fröhlich, R. Roof reconstruction from airborne laser scanning data based on image processing methods. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebbels, S. Convergence rates for Fourier partial sums of polygons and periodic splines. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2019, 25, 1902–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitalis, S.; Arroyo Ohori, K.; Stoter, J. CityJSON in QGIS: Development of an open-source plugin. Trans. GIS 2020, 24, 1147–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Paper Model | Color Powder 3D Print | FFF with Multiple Filaments Colors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| time needed for model creation | |||
| manual interaction | |||
| costs of materials and equipment | |||
| stability of models | |||
| quality of color | |||
| number of colors | |||
| durability of structure | |||
| durability of colors | |||
| precision of scale | |||
| applicability for simple geometries | |||
| applicability for complex geometries | |||
| scalability of models |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goebbels, S.; Pohle-Fröhlich, R. Automatic Unfolding of CityGML Buildings to Paper Models. Geographies 2021, 1, 333-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies1030018
Goebbels S, Pohle-Fröhlich R. Automatic Unfolding of CityGML Buildings to Paper Models. Geographies. 2021; 1(3):333-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies1030018
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoebbels, Steffen, and Regina Pohle-Fröhlich. 2021. "Automatic Unfolding of CityGML Buildings to Paper Models" Geographies 1, no. 3: 333-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies1030018
APA StyleGoebbels, S., & Pohle-Fröhlich, R. (2021). Automatic Unfolding of CityGML Buildings to Paper Models. Geographies, 1(3), 333-345. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies1030018






