Abstract
Adult-acquired flatfoot has been considered to arise from tibialis posterior tendon deficiency. Recent evidence shows that arch stability is mainly maintained by structures such as plantar fascia and spring ligament. The dysfunction of these ’passive’ stabilizers results in loss of arch integrity that causes forefoot pronation and reactive tendon overload, especially in the tibialis posterior tendon and peroneus longus tendon. The peroneus longus tendon (PLT) spans several midfoot joints and overloads with arch lengthening. The biomechanical stress/changes that occurs in this tendon are not well recognized. This study evaluates the biomechanical consequences that fusions have on peroneus longus tendon stresses in soft-tissue deficiencies associated with flatfoot deformity. A complete computational human foot model was used to simulate different scenarios related to the flatfoot deformity and associated common midfoot/hindfoot fusions, to quantify the biomechanical changes in the peroneus longus tendon. The results showed that the stress of the peroneus longus tendon is especially affected by the fusion of hindfoot joints and depends on the soft tissue types that fail, causal in generating the flatfoot. These results could be useful to surgeons when evaluating the causes of flatfoot and the secondary effects of surgical treatments on tissues such as the peroneus longus tendon.
1. Introduction
The clinical literature has traditionally related flatfoot deformities as synonymous with tibialis posterior tendon (TPT) deficiency [1]. However, recent studies have shown that passive structures such as the plantar fascia and spring ligament have a significant role in medial foot arch collapse [2]. The dysfunction of these passive stabilizers results in loss of arch integrity, causing forefoot pronation and overload in the tibialis posterior tendon and peroneus longus tendon [2,3]. Treatment options to restore foot arch integrity depend on the deformity stage and the flexibility of the arch. In some advanced cases (stage IIb or III), midfoot and hindfoot fusions are common procedures used to stabilize joints and reduce arch collapse.
Just as the tibialis posterior tendon (TPT) does, the peroneus longus tendon (PLT) spans several midfoot joints and suffers overload with arch collapse. The PLT’s common synovial sheath with peroneus brevis lies 4 cm proximal and 1 cm distal to the lateral malleolus tip. The peroneal tubercle separates the two synovial sheaths. The peroneus longus continues through the fibro-osseous cuboid tunnel, formed by the long plantar ligament and the groove under the cuboid. The PLT changes course from a vertical to an oblique direction in the plantar foot acting across several joints and both medial and lateral sagittal foot columns. The peroneus longus and brevis plantar flex the ankle and evert the subtalar joint. They play a dynamic role in restraining the ankle against sudden inversion. The oblique axis of insertion of the PLT on the plantar medial cuneiform and the base of the first metatarsal causes a frontal plane rotation of the medial column to lock the first ray joint including the cuneo metatarsal and the navicular–cuneiform joints. At the maximum point of eversion motion at each tarsal joint, a torsional load is transferred to more proximal segments, forming a series of links that stabilize the medial column. The PLT supports the lateral arch at the cuboid tunnel and enhances the transverse foot arch. PLT contraction increases Meary’s axis, and PLT contraction decreases foot stiffness and increases energy storage in the foot, stabilizing the first ray.
Some authors have reported increased EMG activity reflecting increased muscle activity in the PLT [4]. Recent studies have shown that in adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD), the dysfunction of several muscles, including the intrinsic muscles, occurs [5]. However, the biomechanical stress changes that the PLT suffers are not well recognized [5]. PLT overload is overlooked or masked by pain from the reactive tibialis posterior or valgus impingement pain. Although fusions improve stability and offload the TPT, their effect on the PLT is not defined. The PLT spans the longitudinal and transverse foot arches. Therefore, selective midfoot/hindfoot fusions affect tendon function differently.
Cavus and anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) instability [5] are recognized causes of peroneal overload. Spring ligament laxity in AAFD has also recently been identified as a cause of peroneus longus overload [3]. The effects that midfoot/hindfoot fusions have on PLT function when restoring foot stability are not known. Previous studies have demonstrated that midfoot fusions may have negative biomechanical effects on soft tissues associated with AAFD [5]. The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the biomechanical consequences that fusions have on PLT stresses in soft-tissue deficiencies associated with AAFD. We used a human foot model to evaluate the biomechanical stress changes experienced by the PLT in different foot fusion scenarios, allowing the evaluation of PLT stress, which cannot be achieved through clinical studies or cadaveric modeling. Our model included a complete geometry reconstruction of the main issues related to AAFD development. The results of the simulations generally show that the stress in the peroneus longus tendon is affected by the fusion of hindfoot joints and depends on the type of deficiencies that are causal to flatfoot. In this study, the weakening of both the plantar fascia and the spring ligament were evaluated. Alterations in the mechanical capacity of the plantar fascia had a greater influence on tension changes in the PLT. These results demonstrate that the plantar component of the peroneus longus tendon must work more when the fascia reduces its mechanical contribution in maintaining the arch, and tension in the PLT tendon is reduced when hindfoot joint fusion is included as part of the treatment. This study evaluated scenarios related to soft-tissue deficiencies in AAFD and the biomechanical effects that common fusions/combination of fusions used in surgical strategies when treating flatfoot have on the peroneus longus tendon. To date, these have not been fully evaluated. This enables greater understanding and better treatment decisions when correcting flatfoot.
2. Materials and Methods
The reconstruction was performed with computed tomography (CT) images using the MIMICS V.10 (Materialize) software in conjunction with anatomical guides. The resultant model depicts the structure of an unloaded, healthy human foot from a 49-year-old male, weighing 73.4 kg, and with a height of 170 cm. This model takes into account 26 cortical tissues and 24 trabecular bones, cartilages, the plantar fascia (PF), spring ligament (SL), long plantar ligament (LPL), short plantar ligament (SPL), talocalcaneal ligament, metatarsal ligament, Achilles tendon (AT), peroneus brevis tendon (PB), tibialis posterior tendon (TPT), flexor digitorum longus (FDL), flexor hallucis longus (FHL), and peroneus longus tendon (PLT). (See Figure 1). The computational model was used in further research associated with AAFD and its modifications in biomechanical stress in soft tissues [1,2,3,4,5].
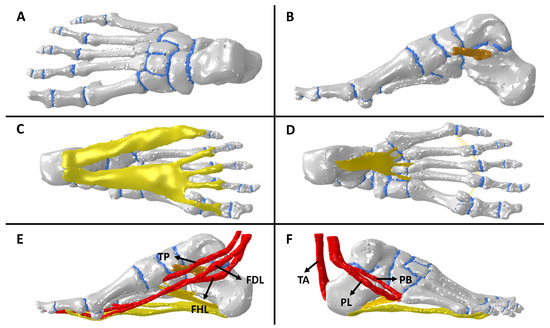
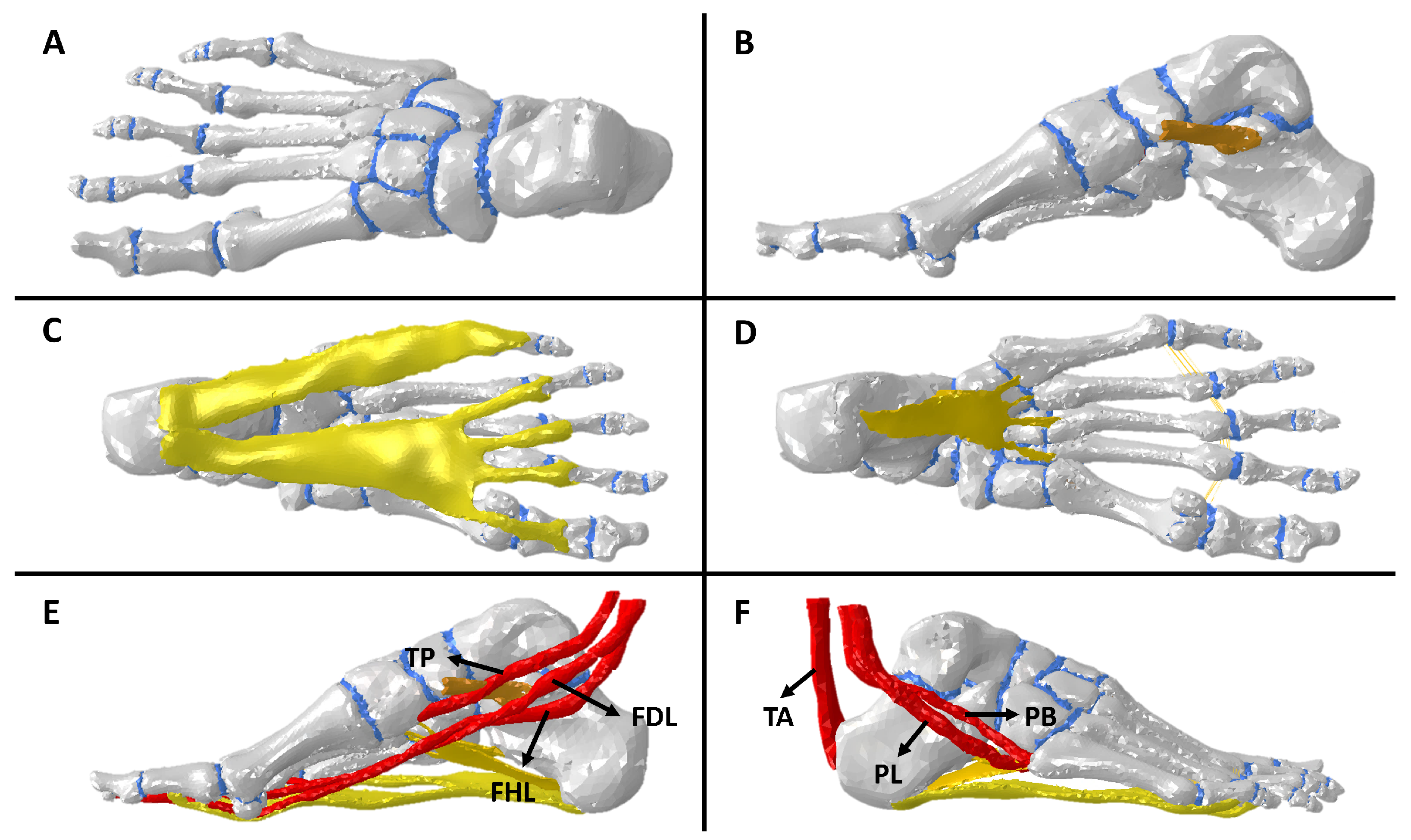
Figure 1.
Computational model: (A) top view bones and cartilages, (B) sagittal view of spring ligament, (C) bottom view of fascia plantar, (D) bottom view of plantar ligaments, (E) sagittal view of medial foot tendons, and (F) sagittal view of lateral foot tendons.
2.1. Meshing
The meshing process was executed using the software Ansys V.21 (Canonsburg, PA, USA). A trial–error approach was used to optimize the mesh size of each tissue in the model. The previous conditions were considered to achieve a reasonable mesh size without compromising the calculation time. The mesh size and type of elements of structures of the foot model are shown in Table 1. Moreover, to avoid inadequate mesh quality, a mesh accuracy of more than 95% of the elements being better than 0.2 mesh quality (Jacobians) was used, and poor elements were located away from the studied region [6].

Table 1.
Mesh size and element type for segments of finite element model.
The model has a total of 269.338 linear tetrahedral elements (C3D4). It is important to note that C3D4 elements are a suitable choice for analyzing stress and tension in finite element models because they can accurately represent complex geometries and are generated automatically by meshing software [7]. All parameters were within good mesh quality ratios (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Mesh quality metrics according to Burkhart et al.’s criteria [6].
2.2. Tissue Modeling and Boundary Conditions
2.2.1. Tissue Modeling
The tissues in the model were treated as elastic linear materials, except for cartilage and tendons. Based on the literature, we used the following mechanical properties: cortical bone (E = 17,000 MPa, = 0.3), trabecular bone (E = 700 MPa, = 0.30), ligaments (E = 700 MPa, = 0.28), and plantar fascia (E = 250 MPa, = 0.28) [8,9,10], where E represent Young’s modulus, and is the mean poison ratio. A non-linear and hyperelastic Ogden model was used to describe the mechanical properties of cartilage tissue. The composition of human cartilage consists of approximately 80% water, principally in the exterior layer. The water and collagen fibers’ orientation contributes to distributing compression and shear stress [11]. Thus, it is not entirely correct to consider cartilage a linear material. For this reason, the mechanical behavior of cartilage is quasi-incompressible material generally used in similar models [12,13]. Its strain energy density function (U) is presented in the following equation:
where is the initial shear modulus, J is the determinant of the deformation tensor, is the strain-hardening exponent, and D is the compressibility parameter. The parameters used for the cartilaginous part were = 4.4, = 2, and D = 0.45.
2.2.2. Boundary Conditions
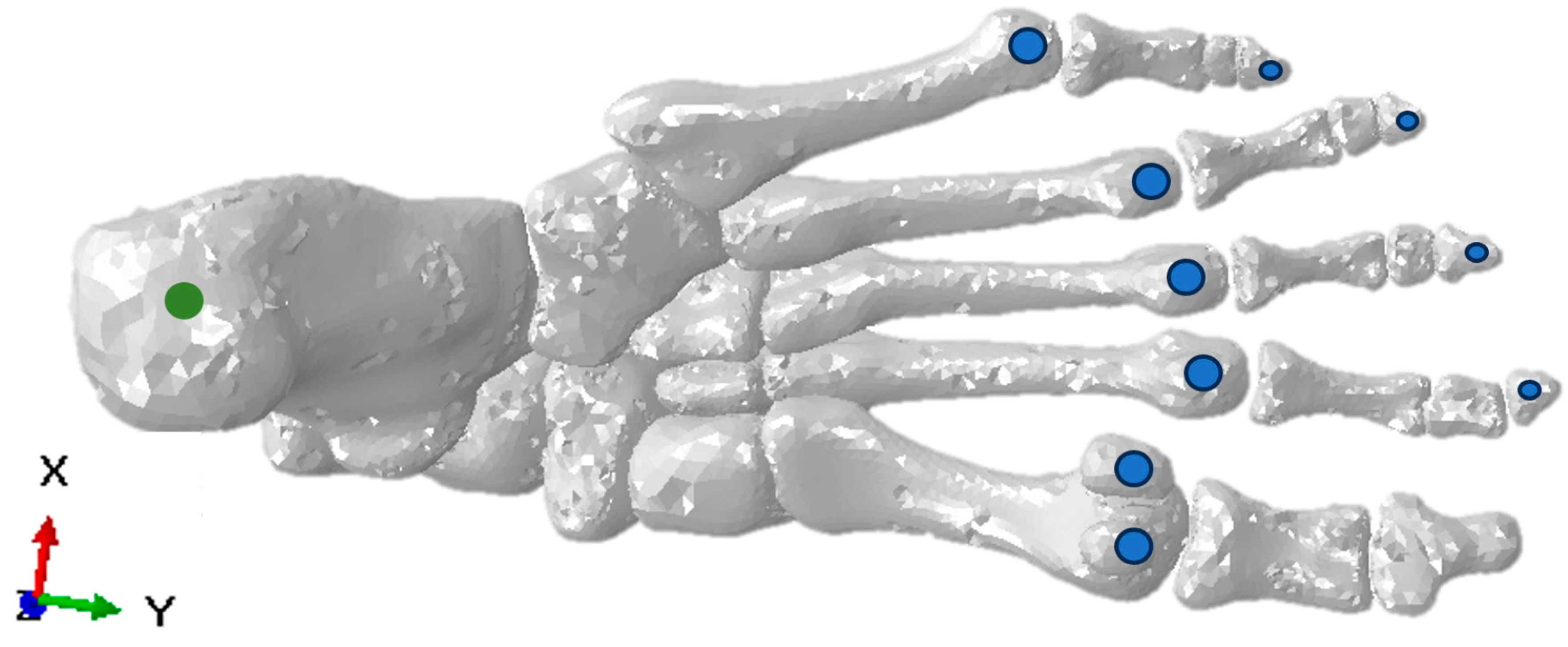
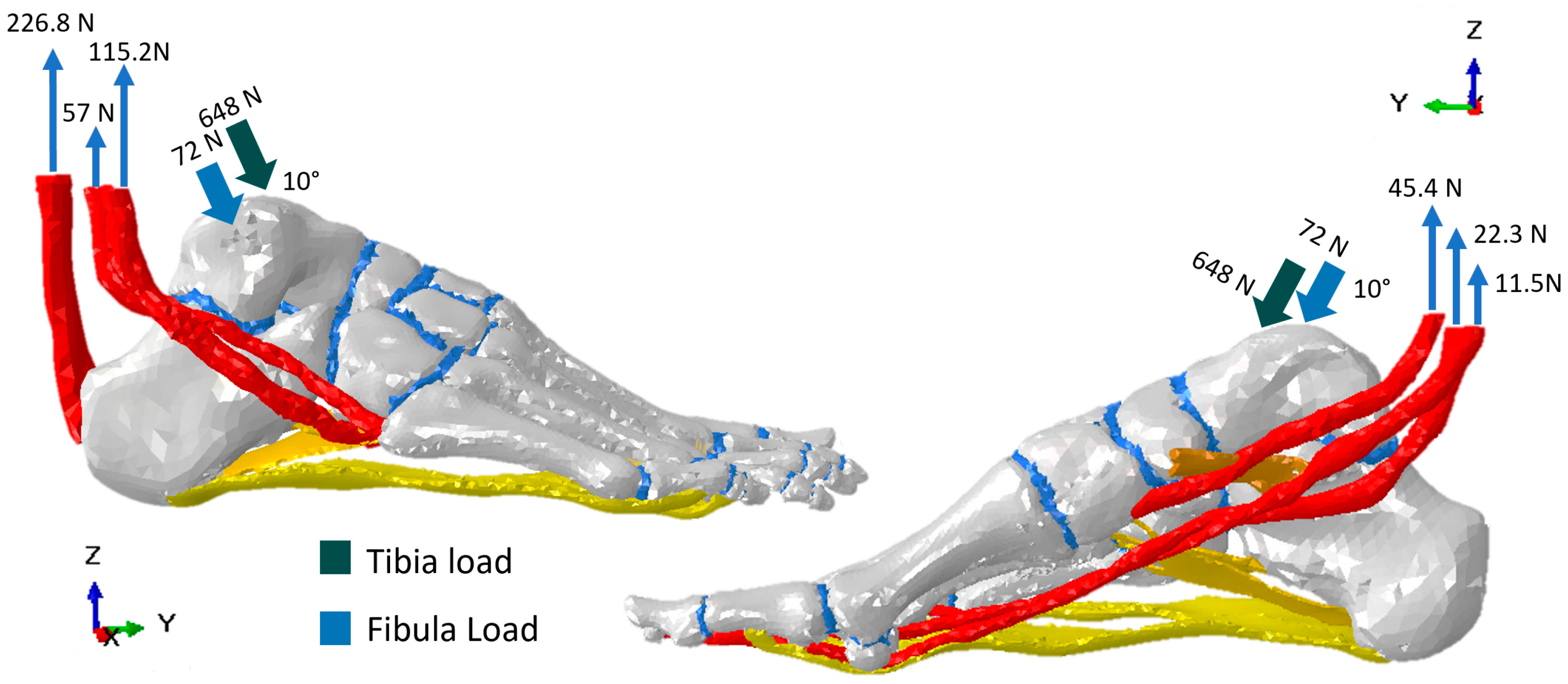
The model was simulated by applying a 720 N load representing the full weight of an adult person of 73.4 kgs during the mid-stance phase, leaning on one foot. The foot load was orientated in a dropping vertical direction, with 10° of inclination distributed in the region of contact tibia–talus (90%) and fibula–talus (10%) [14]. The load used for the tendons in the model was reported in a cadaveric study [15]. The fixed nodes were in four regions for mid- and terminal-stance simulation. The first region was the calcaneus, where fixed nodes restricted movement and displacements in the X, Y, and Z directions. The second, third, and fourth regions were the heads of the metatarsal bones, sesamoids, and distal phalanges, which avoided constraint displacements in the Z axis. This was set to simulate the ground effect. The above descriptions of load conditions and fixed nodes can be seen in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively.
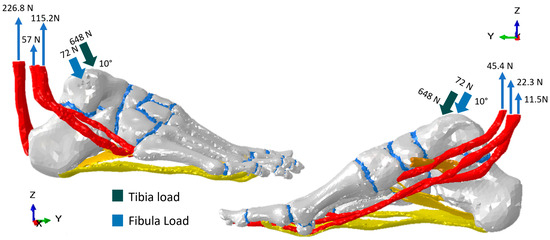
Figure 2.
Load conditions for simulation of the mid-stance phase of the gait cycle.

Figure 3.
Fixed nodes (green) and displacement constraint (blue) locations for the simulation of the mid-stance of the gait cycle.
2.3. Flatfoot, Arthrodesis, and Fusion Representations in the Computational Model
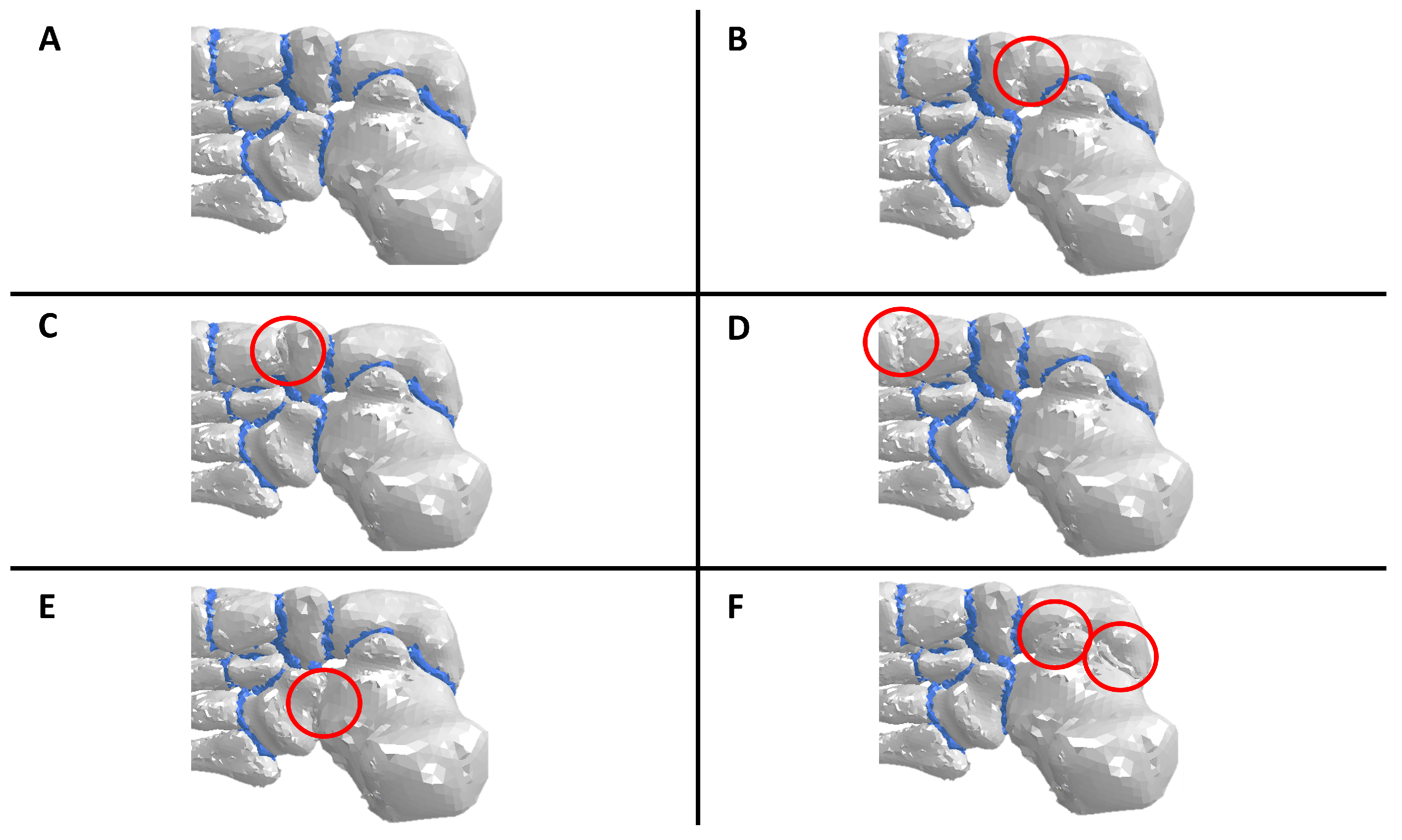
The computational model allowed studying six scenarios: adult-acquired flatfoot deformity, subtalar arthrodesis (STA), talonavicular arthrodesis (TNA), first tarsometatarsal fusion (TMF), calcaneocuboid fusion (CCF), and cuneonavicular fusion (CNF). The loads and fixed-node conditions used to simulate all scenarios were the same. To represent the flatfoot condition, Young’s modulus of the plantar fascia and spring ligament were reduced because the disease is associated with the loss of the biomechanical properties of passive stabilizers of the plantar arch. In surgical scenarios, the cartilages in the joints of interest changed their mechanical properties. The new mechanical characteristics of the cartilage were the same as cortical bone because arthrodesis involves joining two bones. Thus, this change in mechanical properties adequately represents total joint fusion (Figure 4). All simulations assumed complete arthrodesis of the joint surfaces. These changes were implemented before starting the simulations.
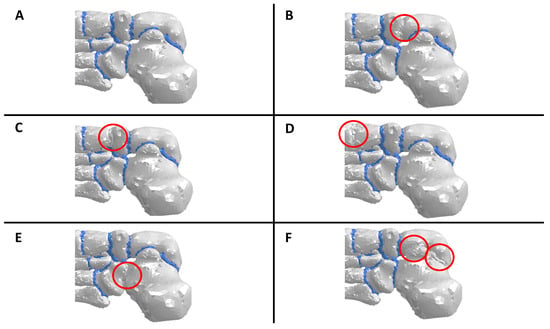
Figure 4.
Clarification of how the arthrodesis and fusions were simulated. The cartilage material was changed to a cortical bone in each fused joint. (A) Flatfoot condition, (B) talonavicular arthrodesis, (C) cuneonavicular fusion, (D) first tarsometatarsal fusion, (E) calcaneocuboid fusion, and (F) subtalar arthrodesis.
2.4. Model Analysis and Evaluation Criteria
The variable used to evaluate the tension in soft tissues was the maximum principal stress (S Max). During the mid-stance and toe-off phases, the plantar fascia and spring ligament elongate due to the support of the foot in the ground. For this reason, the main forces that support the soft tissues are related to traction efforts, and the most appropriate variable for measuring these changes is the maximum principal stress. This study focused on evaluating how stress tension changes during healthy, diseased, and surgical scenarios. The simulations were conducted in Abaqus/CAE 6.14-1 utilizing the non-linear solver to consider surface contacts between bone and soft tissues.
2.5. Foot Model Validation
The validation of the model employed in this study adhered to the guidelines proposed by Tao et al. (2010) [9]. It involved the assessment of specific anatomical landmarks under two distinct loading conditions (light loading and normal standing) from a lateral perspective. Analyzing the variations in these points enabled a comparison of vertical displacements observed in radiographic images of a typical foot with the predictions performed by the finite element (FE) model. Measurements included foot lengthening (FL) and the vertical distances from the highest points of the talus (T) and the navicular (NAV), the midpoint of the cuneiform (CUN), and the highest point of the first metatarsal head (MTH1). These measurements were conducted on 12 radiographic images from 6 healthy patients, encompassing both light-loading and full-load conditions. The obtained normalized average and standard deviation facilitated an objective comparison with the predictions generated by the model. The validation of the computational model was used in more research associated with AAFD and its modifications in biomechanic stress in soft tissues [1,2,3,4,5].
3. Results
3.1. About Model Validation
The validation process results are shown in Table 3. The model produced a bone structure variation akin to what is anticipated in a typical patient. This accounts for foot deformations observed from a side view with minimal load (absence of soft tissue tension) and regular weight-bearing (soft tissue tension under normal circumstances). Additional information on validation results can be found in previous papers [1,2,3,4,5].

Table 3.
The results of the validation process. The values correspond to the difference between the measured distance from each point to the ground, in two different loading conditions: light loading and normal standing load.
3.2. Peroneus Longus Analysis
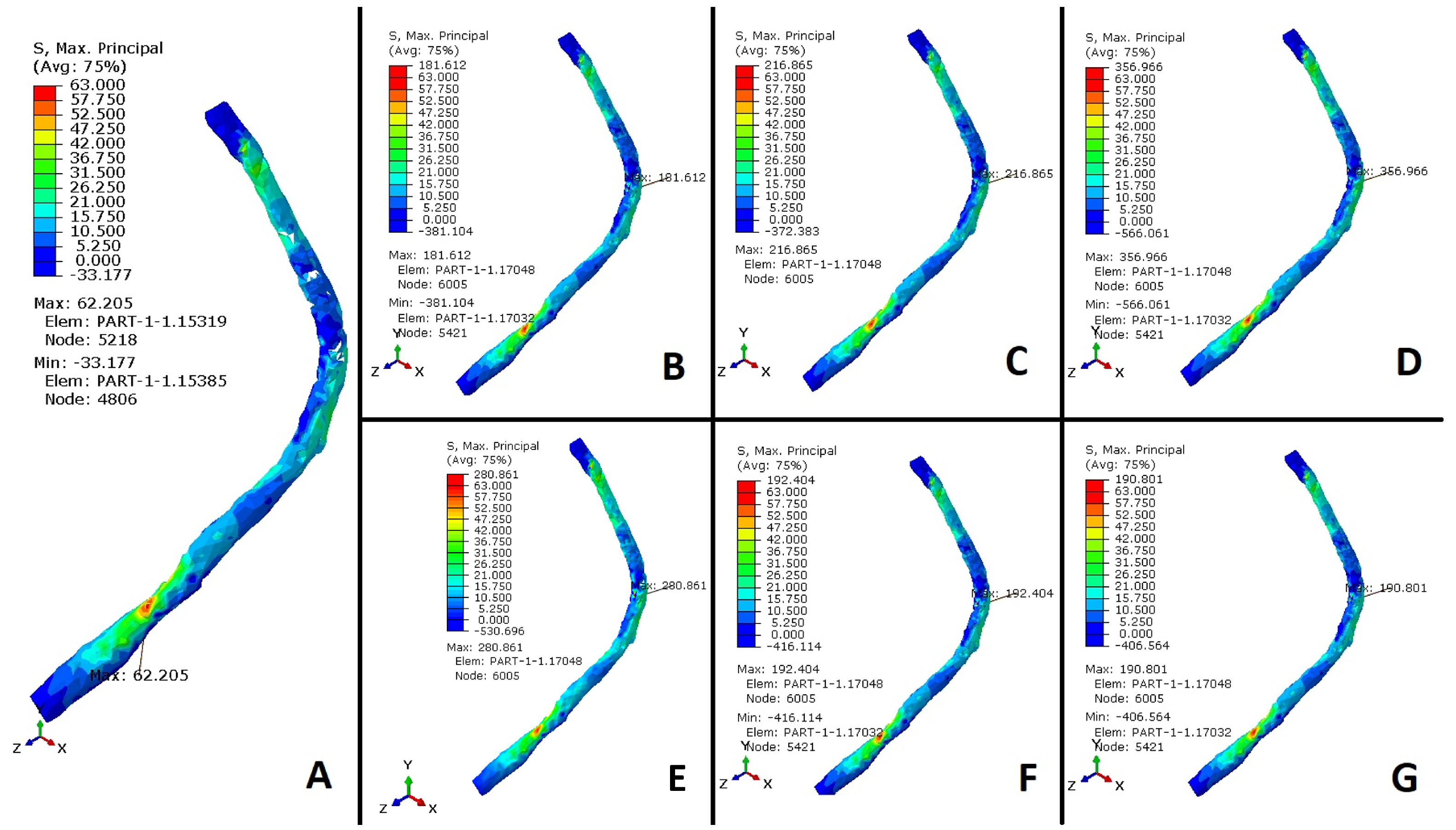
The plantar fascia and spring ligament are the main tissues associated with the maintenance of the plantar arch. A failure in the passive stabilizers increases the tension in PL during mid-stances and terminal stances. The results of the maximum principal stress of the peroneus long tendon are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
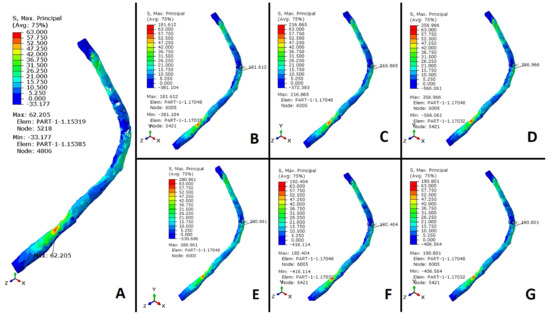
Figure 5.
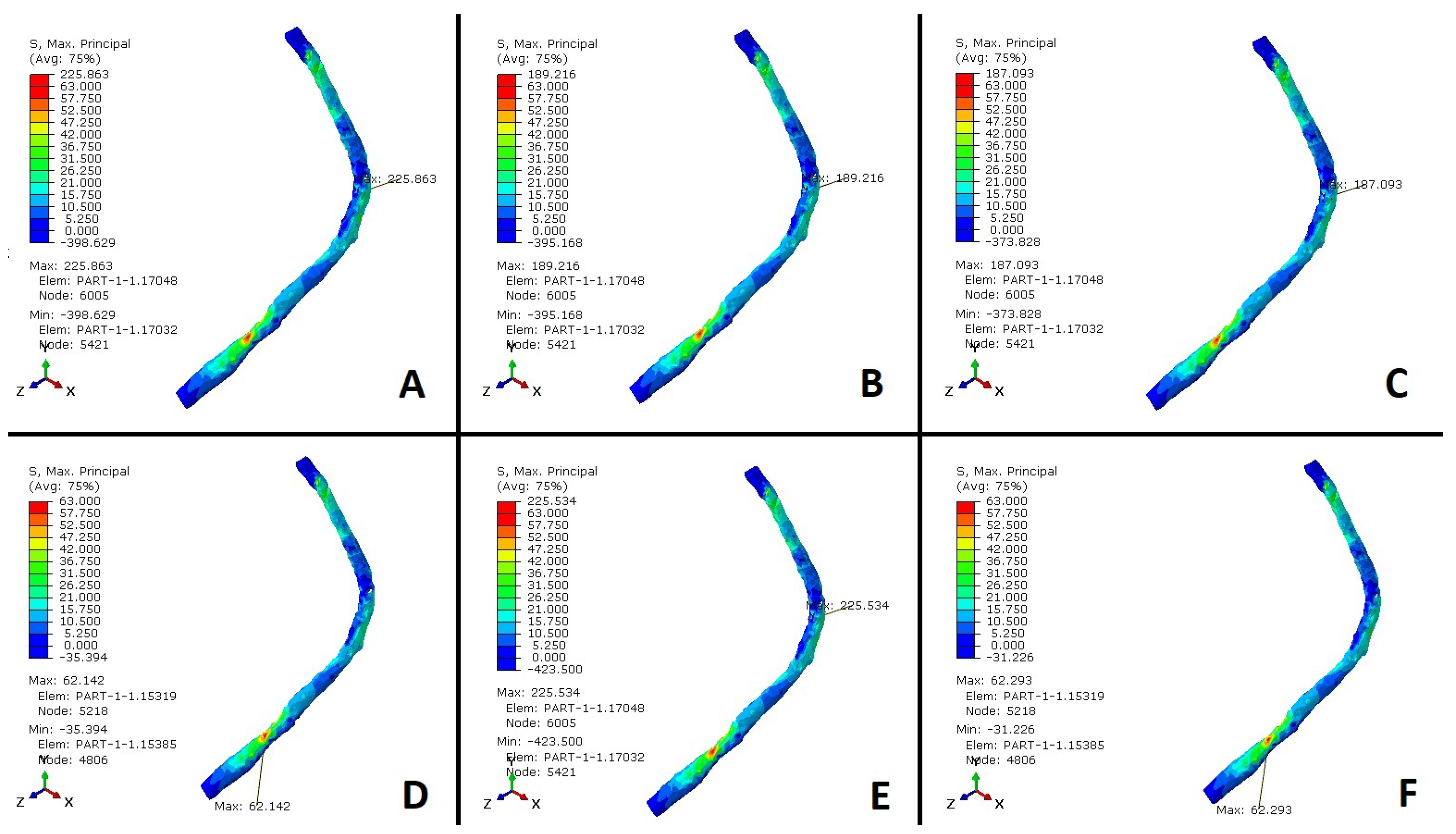
Stress values (MPa) in the peroneus longus tendon. (A) Healthy foot. (B) Plantar fascia weakness. (C) Alterations in the spring ligament and plantar fascia weakness. (D) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, and CCF. (E) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, TNA, and CCF. (F) Plantar fascia weakness and STA. (G) Plantar fascia weakness and TMF.
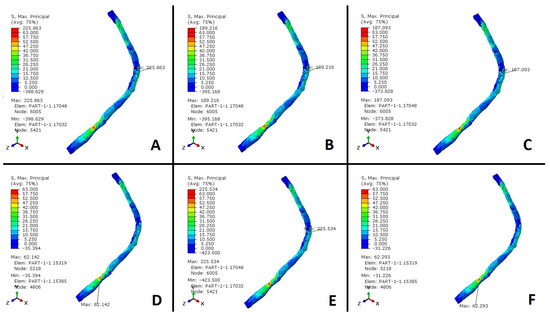
Figure 6.
Stress values (MPa) in the peroneus longus tendon. (A) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, and CNF. (B) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, TMF, and CNF. (C) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, and CNF. (D) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, and TNA. (E) Alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, and STA. (F) Posterior tibial dysfunction.
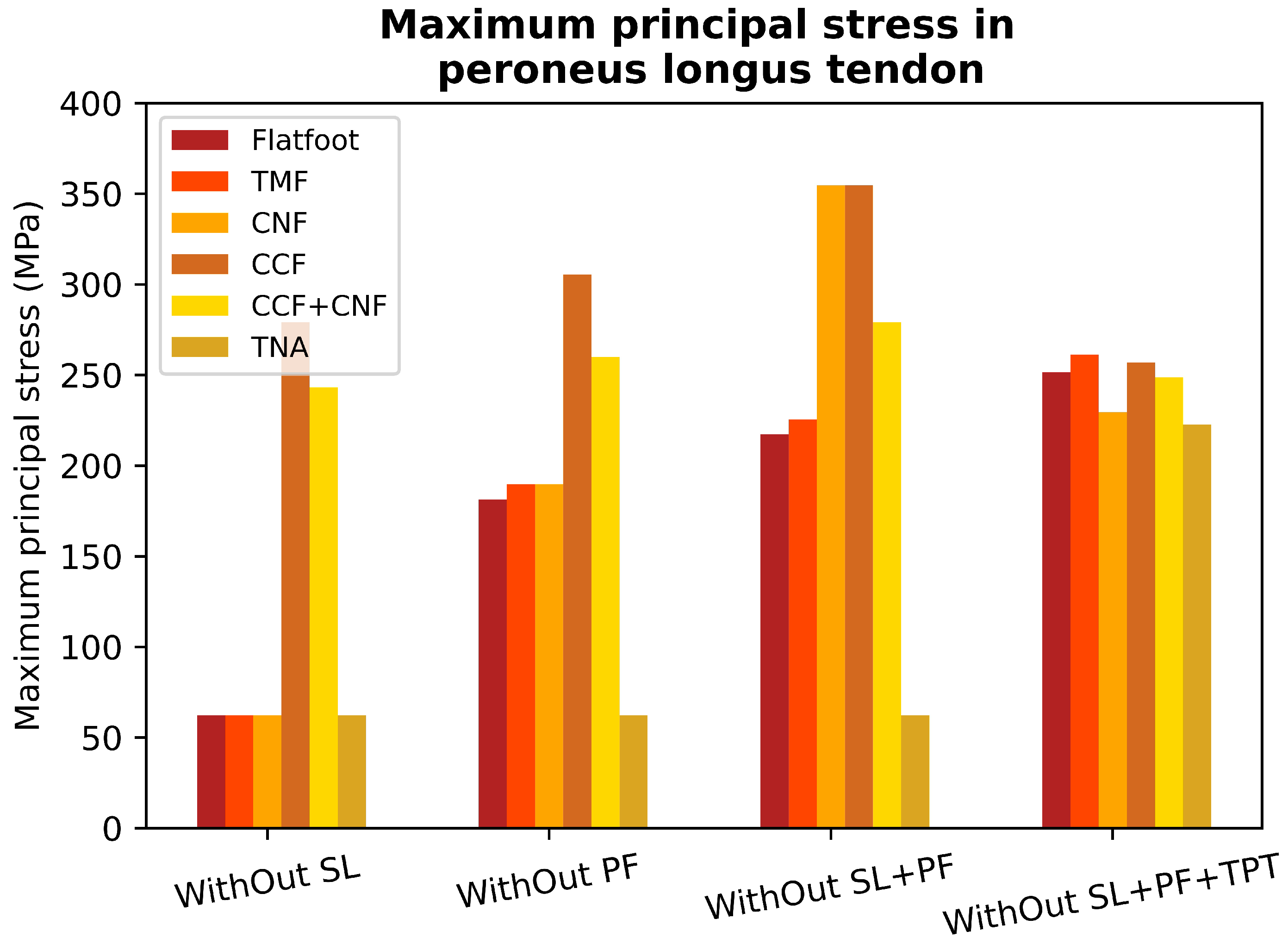
The results were normalized with the maximum value of a healthy scenario (0 to 63 MPa) and compared to simulations of a flatfoot situation caused by weakness in the plantar fascia, used as a reference (Figure 7), to evaluate the stress generated in the PLT and surrounding tissues. The simulations indicate that the stress in the PLT increases nearly threefold during flatfoot conditions resulting from plantar fascia weakness, compared to the stress observed in the healthy case. Furthermore, the results demonstrate an additional approximately 19% increase in PLT stress when both the SL and plantar fascia weaken compared to when only the plantar fascia is weakened. This exacerbates the maintenance of the plantar arch due to increased activity in the tibialis posterior tendon (TPT). Stresses generated within the PLT grow from 63 to 181 MPa (Figure 5B), an increase of almost three times. Also, the additional sectioning of both passive stabilizers of the plantar arch increased the PLT stresses from 63 to 216 MPa (Figure 5C), an increase of more than 3.5 times, as mentioned. Clinical dysfunctions of the TPT and subsequent overloads and synovitis may develop, significantly impacting the PLT’s role in supporting the medial arch. These findings highlight a substantial increase in PLT tension when the PF, SL, and TPT are compromised. Lapidus joint arthrodesis decreases stress on the peroneus longus tendon by approximately 10% in the absence of planus, enhancing medial arch stability and offloading the tendon. However, when the plantar fascia is sectioned, both passive stabilizers lose their mechanical properties, or passive stabilizers and the tibialis posterior tendon fail, the cuneometatarsal joint arthrodesis increases PLT stress by 3%, 4.1%, and 4%, respectively (Figure 5G and Figure 6A). In these scenarios, the additional fusion of the cuneonavicular joint does not drop PLT stress (see Figure 7). The effects of a CNF were also analyzed to determine if additional stability of the medial column would help reduce traction forces on the peroneus longus (PL). PL pronates the first ray and locks it, altering the moment arm of both the PLT and the TPT. Additionally, stabilizing the CM joint may reduce planus and thereby alleviate strain on the PLT beneath the cuboid. Our results demonstrate increased PLT stress when CNF is fused in flatfoot conditions.
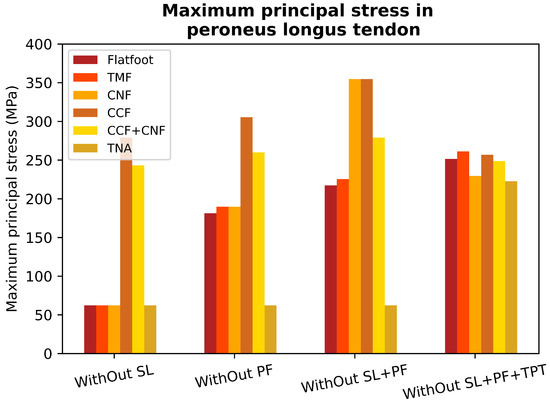
Figure 7.
Maximum stress values in the peroneus longus tendon for a healthy foot (HF); alterations in the spring ligament (SL); plantar fascia weakness (PF); alterations in the Spring ligament and plantar fascia weakness (SL, PF); alterations in the spring ligament, plantar fascia weakness, and posterior tibial dysfunction (SL, PF, TPT).
4. Discussion
The behavior and reactivity of the PLT are difficult to fully define especially in the presence of pathological stiffness, and its behavior and role vary depending on the presence of foot pathology and stiffness. The peroneus longus and brevis plantar flex the ankle and evert the subtalar joint preveting sudden inversion [16]. Johnson and Christensen showed the first metatarsal base generates eversion torque that the PLT generates, causing frontal plane rotation of the medial column to lock the first ray joint [17,18]. The cuneometatarsal joint maximally everts 8.06°, and the navicular–cuneiform joint everts 7.44°. The peroneus longus also generates 3.8° and 2.97° of plantarflexion at the first metatarsal and cuneiform, respectively [18]. Sumal also showed a decrease in the transverse and longitudinal arch with PLT contraction [19].
We used a computational model of the human foot designed to quantify stress changes in the peroneus longus tendon across 10% to 50% of the gait cycle. Using this mode to evaluate flatfoot conditions characterized by weakened plantar fascia and spring ligament in the presence of different midfoot and hindfoot arthrodesis scenarios, we were able to generate a more complete picture of how the PLT behaves.
Traditionally, it was believed that the main injury in adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) was the loss of the tibialis posterior. However, recent evidence challenges this notion, indicating that such loss alone does not lead to a flatfoot condition [20,21]. Cadaveric and clinical studies now acknowledge that the primary lesion in AAFD is the loss of static restraints, particularly involving the spring ligament and fascia plantar. The flatfoot condition associated with SL weakness causes medial talar head subluxation and reciprocal foot pronation, which is resisted by the ground reaction force through a stable first ray [22]. The first ray destabilization in the presence of spring ligament laxity progresses the flatfoot condition [22,23]. An excess talar head internal rotation produces an internal rotation of the subtalar joint axis, which lateralizes the ground reaction force contributing to lateral column overload and instability [24]. Also, the flatfoot condition decreases the cuneometatarsal joint height, diminishing the plantarflexion vector of the peroneus longus tendon. Consequently, this transforms it into a predominantly valgus vector. The dorsiflexion instability of the first ray and lateral column height loss overload the peroneus longus tendon. Therefore, the reduction in mechanical properties of SL produces overloads, consequently causing tendinopathy in tendons like the peroneus longus tendon [20]. This affirmation is consistent with Ringleb’s findings in early AAFD [25]. Ringleb showed an increase in EMG amplitude in the tibialis posterior tendon and the peroneus longus tendon when looking at peroneal activity in acute symptomatic stage 2 of flatfoot (significant TPT pain as confirmed on MRI with synovitis and tears). The peroneus brevis exhibits reduced activity, emphasizing its role as an evertor that exacerbates the flatfoot. In AAFD, the relative height loss and foot length increase in the loaded foot were directly proportional to the relative dorsiflexion motion in midfoot joints [19].
Peroneal overload in the early AAFD can produce lateral-sided symptoms in addition to valgus impingement pain. Understanding PLT behavior in AAFD has important clinical implications. In our model, the flatfoot condition was induced by plantar fascia sectioning. Cyclical loading cadaver studies have shown a growth strain in SL and long plantar ligaments after plantar fascia sectioning [26]. Huang demonstrated in 12 freshly frozen axially loaded cadaver feet (sectioning plantar fascia, plantar ligaments, SL) that the highest relative contribution (25%) to arch stiffness was the plantar fascia [27,28]. The relative height loss and foot length increase in the loaded foot were directly proportional to the relative dorsiflexion motion in midfoot joints [19]. Whittaker’s cadaveric study revealed that the talonavicular joint contributes 9.68 degrees, the navicular cuneiform joint provides 12.28 degrees, and the cuneometatarsal joint offers 5.68 degrees of dorsiflexion, contributing to the total sagittal plane motion of 27.48 degrees [27].
New-onset isolated peroneus longus tendon dysfunction in chronic cavus feet [27], where the PLT may already be overloaded, can be driven by associated new-onset SL failure or medial arch instability, which must be assessed for and identified to ensure appropriate treatment.
Fusions of the medial column and hindfoot are routinely used to restore stability in AAFD. Arch stability offloads the TPT and improves foot function. However, it is not possible to ascertain the effects that these fusions have on the function and potential overload of the PLT. Clinical and cadaver studies that try to evaluate stress in the PLT have limitations [19]. The calcaneocuboid joint arthrodesis has been used to control the talonavicular joint abduction, often performed as part of a triple fusion or in isolation as a distraction arthrodesis. In our results, calcaneocuboid fusion increased the peroneus longus stress despite its potential beneficial effect of increasing lateral longitudinal arch stability (Figure 5C and Figure 7). This may be important if pre-existing peroneal symptoms are present. After a lateral column lengthening degenerative changes that arise from the calcaneocuboid joint’s increased pressure result in radiographic arthrosis and stiffness [27]. Zhang demonstrated decreased foot eversion by fifty-five percent with a calcaneocuboid fusion [27]. Foot eversion offloads the PLT tendon as its motion is in the same direction as the action of the tendon. Fusions act like coalitions causing foot stiffening and peroneal symptoms. Medial arch weakening in the presence of calcaneocuboid fusion risks further overloading the PLT.
As the medial column destabilizes, the dorsiflexion instability of the first ray overloads the PLT. This scenario increases stresses in the peroneus longus tendon (Figure 7). Therefore, lateral arch stiffness with medial arch laxity overloads the PLT. Surgically medial-sided procedures are performed concomitantly in AAFD to stabilize the arch and offload the peroneus longus tendon. Another principal fusion used to stabilize the first ray in AAFD is the cuneometatarsal joint (Lapidus) fusion [27]. This surgery has shown minimal negative effects on PLT function [18], but how SL integrity would further influence PLT performance in the presence of a Lapidus fusion has never been looked at [18]. Lapidus joint arthrodesis decreases stress on the peroneus longus tendon by approximately 10% in the absence of planus, as it enhances and offloads the tendon. However, without the associated loss of the passive stablisers and tibialis posterior tendon, loss as shown in the results, the cuneometatarsal joint arthrodesis increases PLT stress by 3%, 4.1%, and 4%, respectively (Figure 5G and Figure 6A). In these scenarios, the additional fusion of the cuneonavicular joint does not drop PLT stress (see Figure 7). Reasons may be multiple and related to its anatomy. A Lapidus fusion may interfere with the locking mechanism of the first ray [26]. This fusion increases the dorsal ground reaction moment exerted at the first ray metatarsal head as the pivot point is brought more proximally, shifting the center of dorsal rotation back to the navicular–cuneiform joint and increasing the total moment generated. Therefore, this increased moment generated would have to be further counteracted at least partially by PLT action. However, the oblique insertion places the peroneus longus tendon at a disadvantage when attempting to generate plantarflexion force or moment along the sagittal axis, consequently increasing its stresses. The loss of any lateral or medial column height may also decrease the PLT’s plantarflexion vector generated. In the absence of other identifiable causes, such as ATFL instability, peroneal retinaculum tears, or foot cavus, SL laxity is a known cause of PLT overload pain [5]. In the presence of multiple causes of PLT overload, such as foot cavus with SL laxity, further stabilization of the cuneometatarsal joint may increase PLT pain. The foot pronation decreases if controlling talonavicular joint laxity. The possible options for this goal are SL reinforcement or talonavicular arthrodesis. Consequently, it decreases the first ray dorsiflexion GRF, which may help offload the PLT.
The cuneonavicular joint has almost 12 degrees of motion in the sagittal plane. Therefore, the isolated fusion of the cuneonavicular joint improves arch stability and stiffens the arch in the sagittal plane [27]. Nevertheless, simulated arch weakening by plantar fascia despite a cuneonavicular fusion does not offload PLT. We advocate caution infusing the cuneonavicular joint due to a potential adverse increase in stresses that may occur in the PLT. Further stiffening of the medial arch with CNF significantly reduces tensile stresses in the PLT. The results exhibit that an isolated STA with a weak plantar fascia increases PLT stress (Figure 5F) due to the continued stability in the TN articulation. STA still allows 55% motion at the TN axis, stabilized by the SL [27]. STA is performed in AAFD to contribute to stability in fixed deformity and instability. The model indicates a little increase in the PLT stress with STA and flatfoot by plantar fascia weakness in comparison with the flatfoot condition caused by a loss of mechanical properties of plantar fascia (Figure 5B,F). The initial position of the foot is crucial for establishing hindfoot stability. Arch weakening leads to subtalar joint eversion and pronation, aligning with the direction of the peroneal tendons and consequently reducing the length of the peroneus longus tendon, thereby offloading it. A subtalar arthrodesis would not allow this aspect of offloading to happen. TNA decreases tensile forces through the PLT when there is a flatfoot condition (Figure 6D). Cadaver studies have demonstrated that the weakness of the plantar fascia induces planus and strain in the SL demonstrating a decrease in the talus first ray declination angle [23]. Furthermore, clinical studies demonstrate a high incidence of TNA laxity in patients with plantar fasciitis (tensile overload of the plantar fascia). Therefore, weakening either the SL or the plantar fascia increases stress in the other. TNA prevents the pronation of the foot, relieving stress on the SL and enhancing arch stiffness to reduce traction forces in the PLT. Pronation tends to increase the ground reaction force (GRF) in the first ray, a tendency counteracted by the PLT. The peroneus longus must still counteract first-ray instability in the presence of arch instability. This tendon is offloaded in the valgus, as this foot position reduces the working length of the peroneus longus. Additionally, a maximally dorsiflexed first ray in a flatfoot decreases the plantarflexion vector of the PLT. Therefore, realigning a hindfoot fusion may not alleviate stress in the PLT when restoring the foot position from a flatfoot. Persistent first-ray instability during the restoration of the hindfoot to the neutral axis from a flatfoot may augment the function and stress on the peroneus longus. This is due to the elongation of the working length and the restoration of arch height, consequently amplifying the plantarflexion vector of the PLT (Figure 6E). The loss of the tibialis posterior tendon does not increase peroneus longus tendon stress, as shown in Figure 6F. Dynamic restraints compensate and overload in the absence of static restraints. PLT stresses virtually remain unchanged even with the absence of tibialis posterior. This clinical scenario arises, for instance, when the TPT is transferred for foot drop. Additionally, if the foot is stabilized in the treatment of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) and the TPT is sacrificed, there is no additional increase in PLT stress. While fusions reestablish stability, they do not return the foot to its pre-pathological state. Different fusions may affect the load differently through the tendons.
We consider that the main limitation of our model was not including the plantar pad or arch muscles. Clinical studies have shown that these tissues have a minor role in AAFD development and foot arch stability, compared to the tissues included in the model used [1]. Additionally, we used an isotropic characterization for plantar fascia and ligament tissues, which could lead to non-real calculations of stress in the tissues. A further study with analysis would show how sensitive the model predictions are to the material properties chosen. Finally, the biomechanical stress values generated cannot be assumed as true stress values for all individuals due to inter-subject variability.
5. Conclusions
AAFD is known to cause PLT overload, particularly in cavoid foot types that further overload it. PLT overload in AAFD is less well recognized. Our results show that variation in PLT anatomy compared to TPT anatomy means different midfoot/hindfoot fusions affect it differently, aiming to improve alignment and restore stability. Our model shows that some common arthrodesis such as CCF fusions increase peroneal stress. Isolated STA does not decrease peroneal stress in the presence of soft tissue in SL instability. TMF joint fusions significantly increase PLT stresses if more proximal ligament deficiencies are not addressed. We advocate restoring SL integrity when performing a TMF/STA in the context of AAFD to help offload stress in the PLT.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Y.-M., C.P., R.L.-G. and C.C.-D.l.P.; Methodology, B.D.S.Q., R.L.-G. and J.B.; Software, J.B. and C.C.-D.l.P.; Validation, N.Y.-M. and C.C.-D.l.P.; Formal analysis, N.Y.-M. and B.D.S.Q.; Writing—Review & editing, C.P. and I.A.; Project administration, J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AAFD | Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity; |
| PF | Plantar fascia; |
| SL | Spring ligament; |
| ATFL | Cavus and anterior talofibular ligament; |
| LPL | Long plantar ligament; |
| SPL | Short plantar ligament; |
| AT | Achilles tendon; |
| PBT | Peroneus brevis tendon; |
| TPT | Tibialis posterior tendon; |
| PLT | Peroneal longus tendon; |
| FDL | Flexor digitorum longus; |
| FHL | Flexor hallucis longus; |
| STA | Subtalar arthrodesis; |
| TNA | Talonavicular arthrodesis; |
| TMF | First tarsometatarsal fusion; |
| CCF | Calcaneocuboid fusion; |
| CNF | Cuneonavicular fusion; |
| FE | Finite element; |
| FL | Foot lengthening; |
| AST | Astragalus; |
| NAV | Navicular; |
| CUN | Cuneiform; |
| MTH1 | First metatarsal head. |
References
- Johnson, K.A.; Strom, D.E. Tibialis posteroir tendon dysfunction. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1989, 239, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, M.M.; Christenson, J. The The effects of sectioning the spring ligament on rearfoot stability and posterior tibial tendon efficiency. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008, 47, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-De la Portilla, C.; Larrainzar-Garijo, R.; Bayod, J. Analysis of biomechanical stresses caused by hindfoot joint arthrodesis in the treatment of adult acquired flatfoot deformity: A finite element study. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murley, S.G.; Menz, B.H.C.; Landorf, K.B. Foot posture influences the electromyographic activity of selected lower limb muscles during gait. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2009, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes-De la Portilla, C.; Pasapula, C.; Gutiérrez-Narvarte, B.; Larrainzar-Garijo, R.; Bayod, J. Peroneus Longus overload caused by soft tissue deficiencies associated with early adult acquired flatfoot: A finite element analysis. Clin. Biomech. 2021, 86, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, T.A.; Andrews, D.M.; Dunning, C.E. Finite element modeling mesh quality, energy balance and validation methods: A review with recommendations associated with the modeling of bone tissue. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Hu, Y.; Gao, X.; Dumas, J.; Zorin, D.; Panozzo, D. A large-scale comparison of tetrahedral and hexahedral elements for solving elliptic pdes with the finite element method. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2022, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aznar, J.M.; Bayod, J.; Rosas, A.; Larrainzar, R.; García-Bógalo, R.; Doblaré, M.; Llanos, L.F. Load transfer mechanism for different metatarsal geometries: A finite element study. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Ji, W.T.; Wang, D.M.; Wang, C.T.; Wang, X. Relative contributions of plantar fascia and ligaments on the arch static stability: A finite element study. Biomed. Eng. Tech. 2010, 55, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.G.; Rennels, D.C. A study of the elastic properties of plantar Fascia. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1964, 46, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forriol Campos, F. El cartílago articular: Aspectos mecánicos y su repercusión en la reparación tisular. Rev. Ortop. Traumatol. 2002, 380–390. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, J.M. Biomechanics of cartilage. In Kinesiology: The Mechanics and Pathomechanics of Human Movement; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 66–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Nonlinear finite element analysis for musculoskeletal biomechanics of medial and lateral plantar longitudinal arch of Virtual Chinese Human after plantar ligamentous structure failures. Clin. Biomech. 2007, 22, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Orcajo, E.; Barbosa de las Casas, E.; Bayod López, J. Computational Foot Modeling for Clinical Assessment. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Zaragoza, Zaragoza, España, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arangio, G.A.; Salathe, E.P. A biomechanical analysis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, medial displacement calcaneal osteotomy and flexor digitorum longus transfer in adult acquired flat foot. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louwerens, J.W.K.; Linge, B.V.; de Klerk, L.W.; Mulder, P.G.; Snijders, C.J. Peroneus longus and tibialis anterior muscle activity in the stance phase: A quantified electromyographic study of 10 controls and 25 patients with chronic ankle instability. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1995, 66, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, C.F.; Dawson, J.M.; Philbin, T.M.; Berlet, G.C.; Lee, T.H. The peroneal tubercle: Description, classification, and relevance to peroneus longus tendon pathology. Foot Ankle Int. 2005, 26, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Christensen, J.C. Biomechanics of the first ray part I. The effects of peroneus longus function: A three-dimensional kinematic study on a cadaver model. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 1999, 38, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumal, A.S.; Jarvis, G.E.; Norrish, A.R.; Brassett, C.; Whitaker, R.H. The role of the angle of the fibularis longus tendon in foot arch support. Clin. Anat. 2021, 34, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecheva, M.; Devany, A.; Nourallah, B.; Cutts, S.; Pasapula, C. Long-term follow-up of patients undergoing tibialis posterior transfer: Is acquired pes planus a complication? Foot 2018, 34, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, J.S.; Singh, D.; Birch, R. Tibialis posterior tendon dysfunction: A primary of secondary problem? Foot Ankle Int. 2001, 22, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasapula, C.; Ali, A.; Kiliyanpilakkil, B.; Hardcastle, A.; Koundu, M.; Ghaooni, A.; Kabwama, S.; Cutts, S. High Incidence of spring ligament laxity in ankle fractures with complete deltoid ruptures and secondary first ray instabilty. Foot 2021, 46, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, I.T.; Myerson, M.S.; Nyska, M.; Parks, B.G. Experimental flatfoot model: The contribution of dynamic loading. Foot Ankle Int. 2001, 22, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, K.A. Subtalar joint axis location and rotational equilibrium theory of foot function. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2001, 91, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringleb, S.I.; Kavros, S.J.; Kotajarvi, B.R.; Hansen, D.K.; Kitaoka, H.B.; Kaufman, K.R. Changes in gait associated with acute stage II posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, J.L.; Hollis, J.M.; Manoli, A. The effect of plantar fascia release on strain in the spring and long plantar ligaments. Foot Ankle Int. 2003, 24, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Qiang, M.; Hao, Y. Effects of five hindfoot arthrodeses on foot and ankle motion: Measurements in cadaver specimens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.K.; Kitaoka, H.B.; An, K.N.; Chao, E.Y. Biomechanical evaluation of longitudinal arch stability. Foot Ankle 1993, 14, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).