Bandages Static Stiffness Index Is Not Influenced by Calf Mechanical Properties but Only by Geometrical Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Compression Bandages
2.3. Characterization of the Lower Leg Soft Tissue Global Stiffness
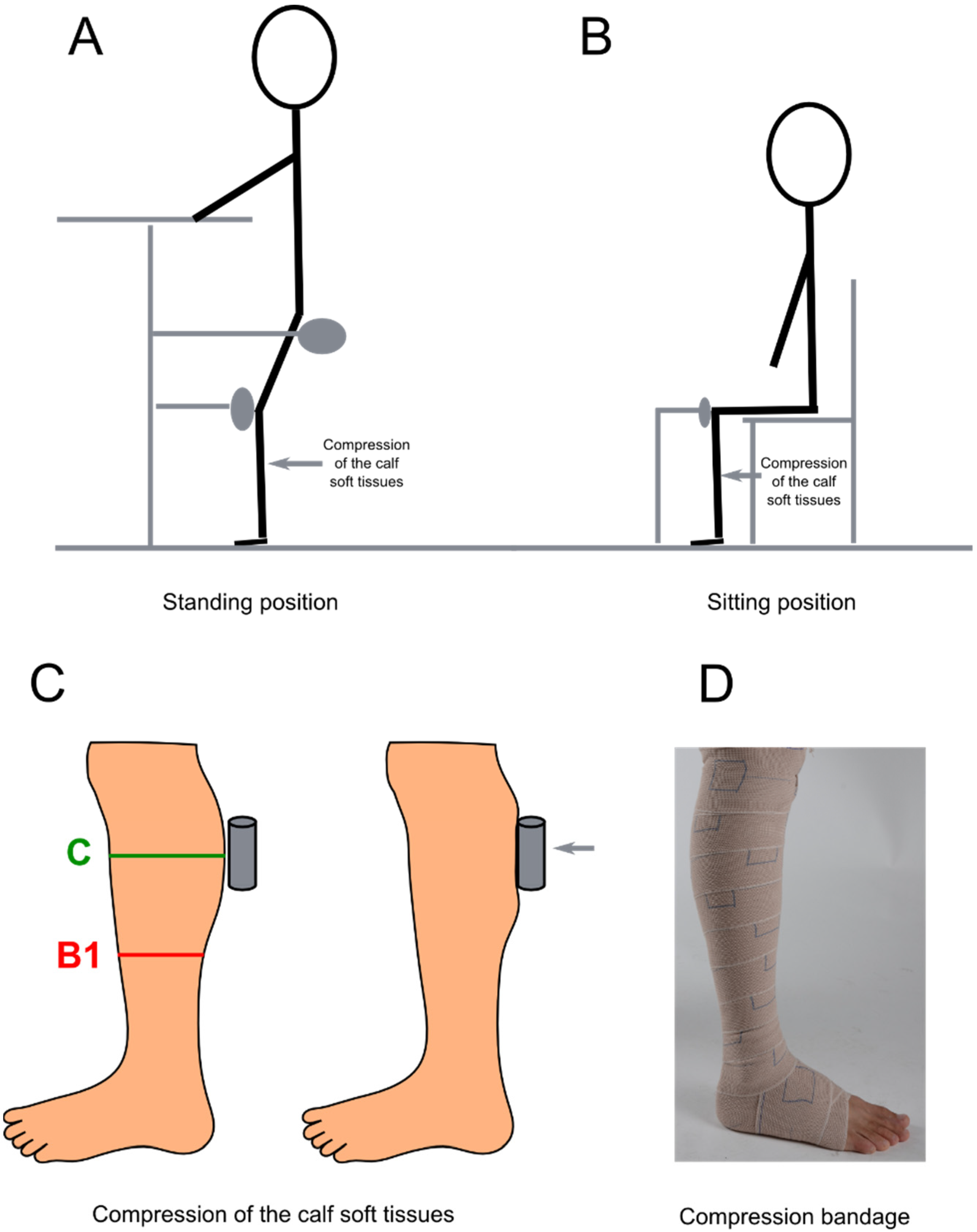
2.3.1. Compression of the Calf Soft Tissues
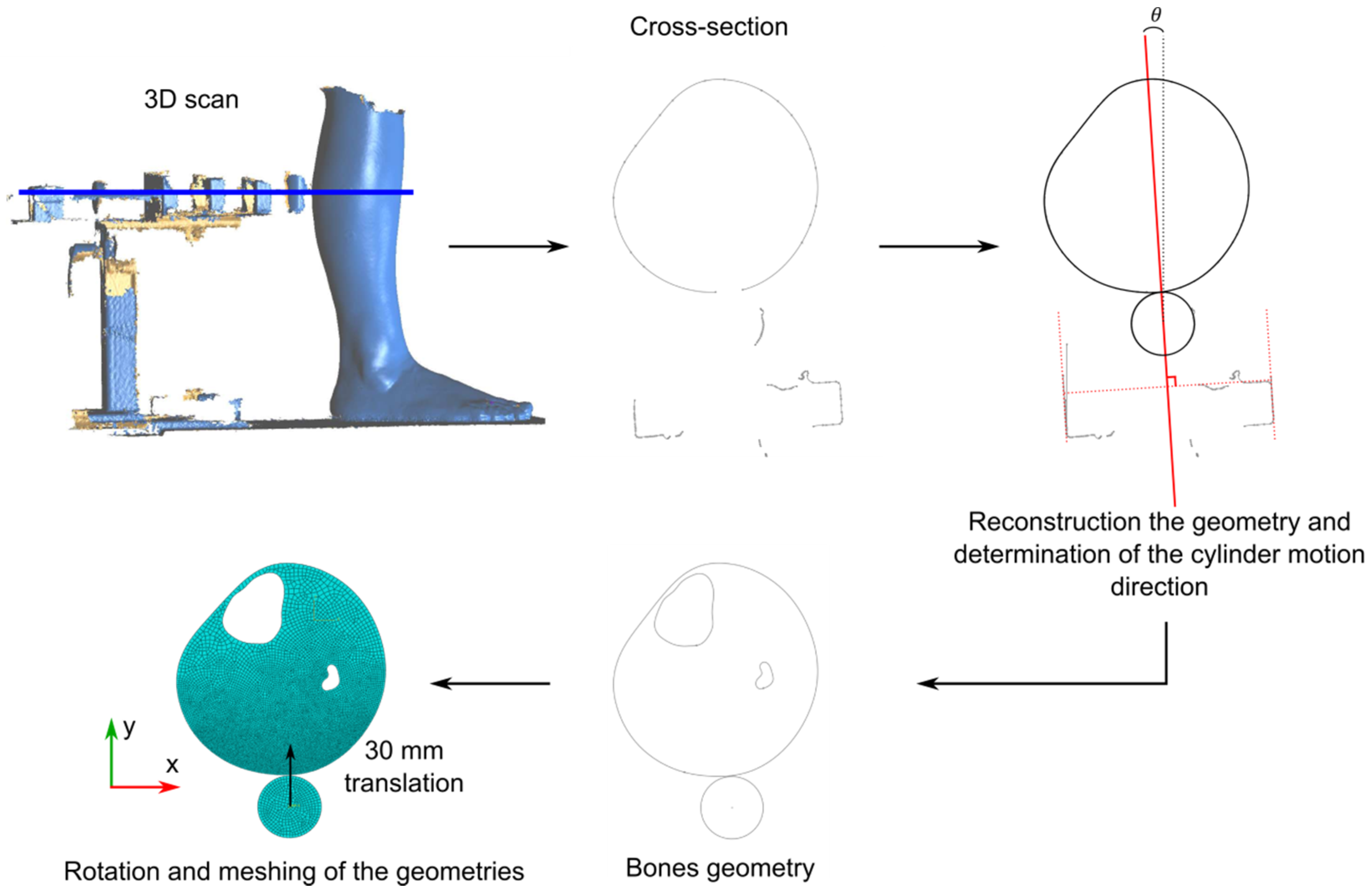
2.3.2. Finite Element Model Updating
2.4. Interface Pressure Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Compression Test and Calf Soft Tissue Global Stiffness
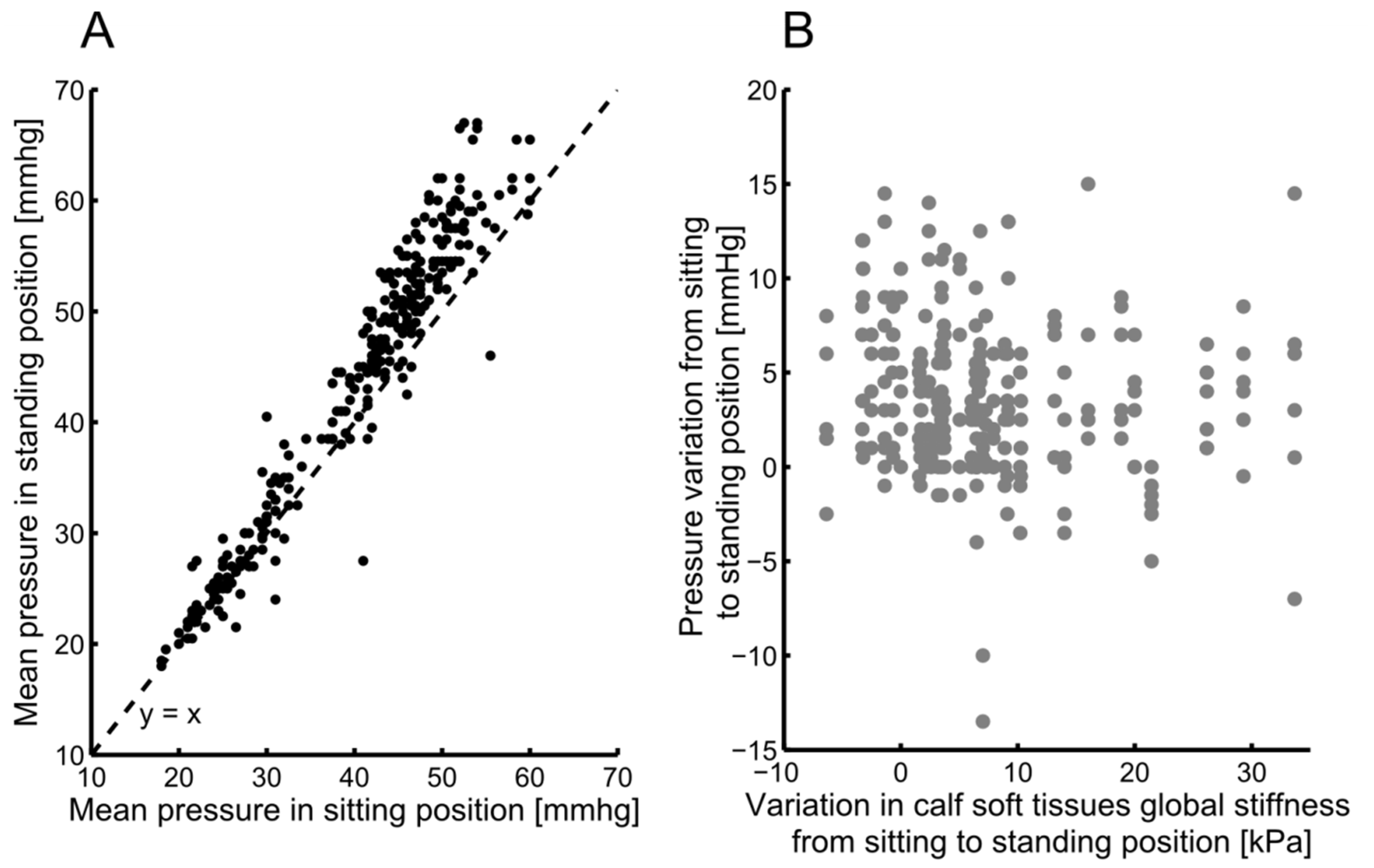
3.2. Calf Soft Tissue Global Stiffness and Interface Pressure
4. Discussion
4.1. Compression Test and Calf Soft Tissue Global Stiffness
4.2. Calf Soft Tissue Global Stiffness and Interface Pressure
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Partsch, H. Compression for the management of venous leg ulcers: Which material do we have? Phlebology 2014, 29 (Suppl. 1), 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partsch, H.; Clark, M.; Mosti, G.; Steinlechner, E.; Schuren, J.; Abel, M.; Benigni, J.-P.; Coleridge-Smith, P.; Cornu-ThéNard, A.; Flour, M.; et al. Classification of Compression Bandages: Practical Aspects. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassagne, F.; Martin, F.; Badel, P.; Convert, R.; Giraux, P.; Molimard, J. Experimental Investigation of Pressure Applied on the Lower Leg by Elastic Compression Bandage. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 2967–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partsch, H. The use of pressure change on standing as a surrogate measure of the stiffness of a compression bandage. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2005, 30, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partsch, H. The static stiffness index: A simple method to assess the elastic property of compression material in vivo. Derm. Surg. 2005, 31, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partsch, H.; Schuren, J.; Mosti, G.; Benigni, J.P. The Static Stiffness Index: An important parameter to characterise compression therapy in vivo. J. Wound Care 2016, 25, S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berszakiewicz, A.; Sieroń, A.; Krasiński, Z.; Cholewka, A.; Stanek, A. Compression therapy in venous diseases: Physical assumptions and clinical effects. Postepy Derm. Alergol. 2020, 37, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebruers, N.; Hendriks, J.M.H.; Tjalma, W.; Verbelen, H.; Van Soom, T.; van Breda, E.; De Vrieze, T. Pressure Curves, Static and Dynamic Stiffness of Different Two-Component Compression Systems for the Treatment of Chronic Edema of the Lower Limbs. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loram, I.D.; Maganaris, C.N.; Lakie, M. Paradoxical muscle movement in human standing: Paradoxical muscle movement in standing. J. Physiol. 2004, 556, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassagne, F.; Helouin-Desenne, C.; Molimard, J.; Convert, R.; Badel, P.; Giraux, P. Superimposition of elastic and nonelastic compression bandages. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2017, 5, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frauziols, F.; Chassagne, F.; Badel, P.; Navarro, L.; Molimard, J.; Curt, N.; Avril, S. In vivo Identification of the Passive Mechanical Properties of Deep Soft Tissues in the Human Leg: In vivo Identification of Passive Mechanical Properties of Leg Soft Tissues. Strain 2016, 52, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Partsch, H.; Clark, M.; Bassez, S.; Benigni, J.-P.; Becker, F.; Blazek, V.; Caprini, J.; Cornu-Thénard, A.; Hafner, J.; Flour, M.; et al. Measurement of lower leg compression in vivo: Recommendations for the performance of measurements of interface pressure and stiffness: Consensus statement. Derm. Surg. 2006, 32, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaud, J.-C.; Hersch, R.D. Visible human slice sequence animation Web server. In Proceedings of the Photonics West 2001-Electronic Imaging, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–26 January 2001; pp. 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bouten, L. Identification des Propriétés Mécaniques des Tissus Constitutifs du Mollet pour L’étude Mécanique de la Contention. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Saint-Etienne, Saint-Étienne, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Joo, S.Y.; Seo, C.H. Comparison between the portable pressure measuring device and PicoPress® for garment pressure measurement on hypertrophic burn scar during compression therapy. Burns 2021, 47, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimaud, D.; Convert, R.; Calmels, P. In vivo measurement of compression bandage interface pressures: The first study. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 57, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partsch, H.; Mosti, G. Comparison of three portable instruments to measure compression pressure. Int. Angiol. 2010, 29, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fridén, J.; Lieber, R.L. Spastic muscle cells are shorter and stiffer than normal cells: Spastic Muscle Cell Properties. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugh, A.B.; Pandyan, A.D.; Johnson, G.R. A systematic review of the Tardieu Scale for the measurement of spasticity. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohan, P.-Y.; Badel, P.; Lun, B.; Rastel, D.; Avril, S. Prediction of the Biomechanical Effects of Compression Therapy on Deep Veins Using Finite Element Modelling. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| # Patient | C10 (kPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sitting Position | Standing Position | |||
| Right Leg | Left Leg | Right Leg | Left Leg | |
| #1 | 1.61 | 1.48 | 3.33 | 5.85 |
| #2 | 1.33 | 1.12 | 2.54 | 2.23 |
| #3 | 1.36 | 2.00 | 1.98 | 1.46 |
| #4 | 1.70 | 1.97 | 3.40 | 2.32 |
| #5 | 1.32 | 1.14 | 1.60 | 1.72 |
| #6 | 1.23 | 1.12 | - | 1.40 |
| #7 | 1.16 | 1.74 | 4.73 | 3.45 |
| #8 | 2.10 | 1.46 | 2.53 | 2.63 |
| #9 | 1.02 | 1.51 | 1.63 | 1.51 |
| #10 | 1.86 | 2.10 | 1.75 | 1.98 |
| #11 | 2.79 | 2.18 | 2.24 | 5.32 |
| #12 | 1.93 | 1.65 | 1.70 | 2.05 |
| #13 | 1.27 | 1.44 | 2.59 | 2.92 |
| #14 | 3.08 | 2.68 | 8.69 | 7.56 |
| #15 | 1.61 | 1.51 | 2.68 | 5.87 |
| #16 | 1.22 | 1.62 | 1.51 | 2.20 |
| #17 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 2.39 | 2.50 |
| #18 | 2.24 | 2.08 | 3.32 | 2.34 |
| #19 | 1.24 | 1.72 | 1.82 | 3.24 |
| #20 | 1.42 | 2.52 | - | 1.46 |
| #21 | 2.18 | 2.14 | 4.37 | 5.47 |
| #22 | 1.39 | 1.48 | 2.40 | 2.01 |
| #23 | 2.43 | 2.65 | 3.96 | 3.49 |
| #24 | 1.59 | 1.82 | 3.92 | - |
| #25 | 1.66 | 1.49 | 4.33 | 2.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chassagne, F.; Molimard, J.; Convert, R.; Helouin-Desenne, C.; Badel, P.; Giraux, P. Bandages Static Stiffness Index Is Not Influenced by Calf Mechanical Properties but Only by Geometrical Changes. Biomechanics 2022, 2, 87-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics2010009
Chassagne F, Molimard J, Convert R, Helouin-Desenne C, Badel P, Giraux P. Bandages Static Stiffness Index Is Not Influenced by Calf Mechanical Properties but Only by Geometrical Changes. Biomechanics. 2022; 2(1):87-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleChassagne, Fanette, Jérôme Molimard, Reynald Convert, Clothilde Helouin-Desenne, Pierre Badel, and Pascal Giraux. 2022. "Bandages Static Stiffness Index Is Not Influenced by Calf Mechanical Properties but Only by Geometrical Changes" Biomechanics 2, no. 1: 87-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics2010009
APA StyleChassagne, F., Molimard, J., Convert, R., Helouin-Desenne, C., Badel, P., & Giraux, P. (2022). Bandages Static Stiffness Index Is Not Influenced by Calf Mechanical Properties but Only by Geometrical Changes. Biomechanics, 2(1), 87-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics2010009







