A CMOS-Based Power Management Circuit with a Reconfigurable Rectifier and an LDO Regulator for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting in IoT Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
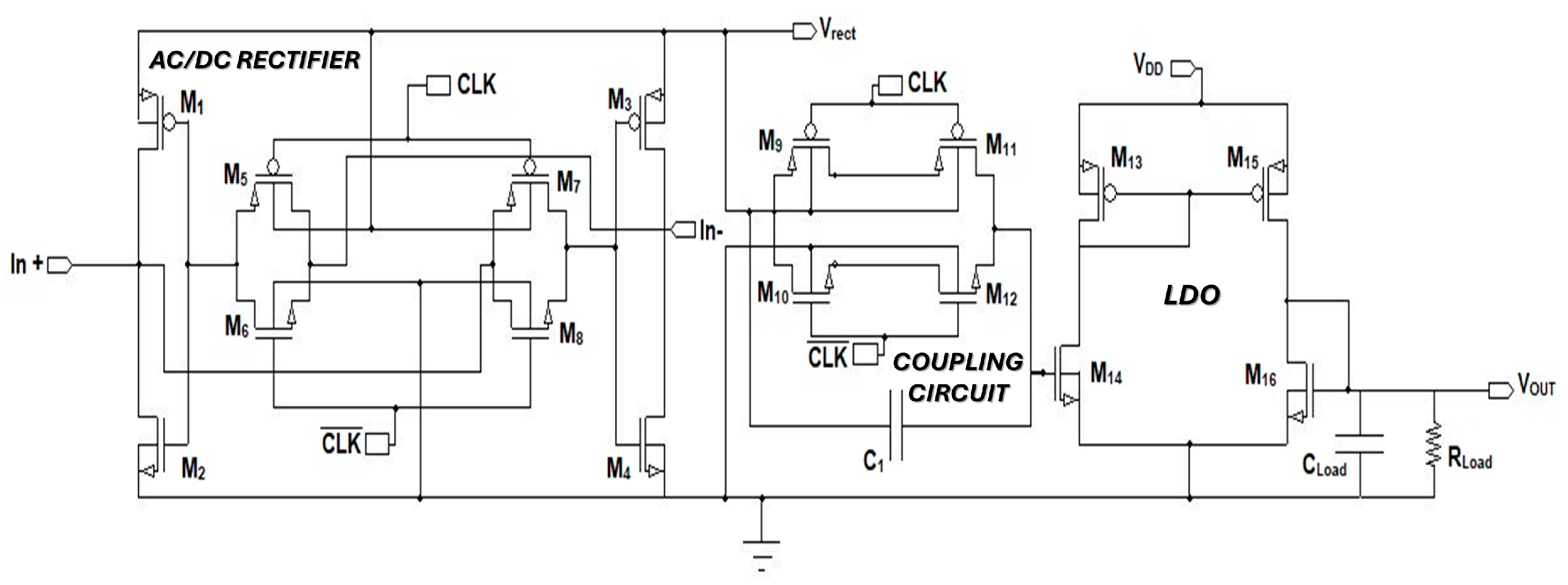
- Introduces a novel reconfigurable rectifier–coupling–regulator architecture fabricated in 0.18 µm from Taiwan semiconductor manufacturing company (TSMC) for piezoelectric harvester CMOS technology.
- (ii)
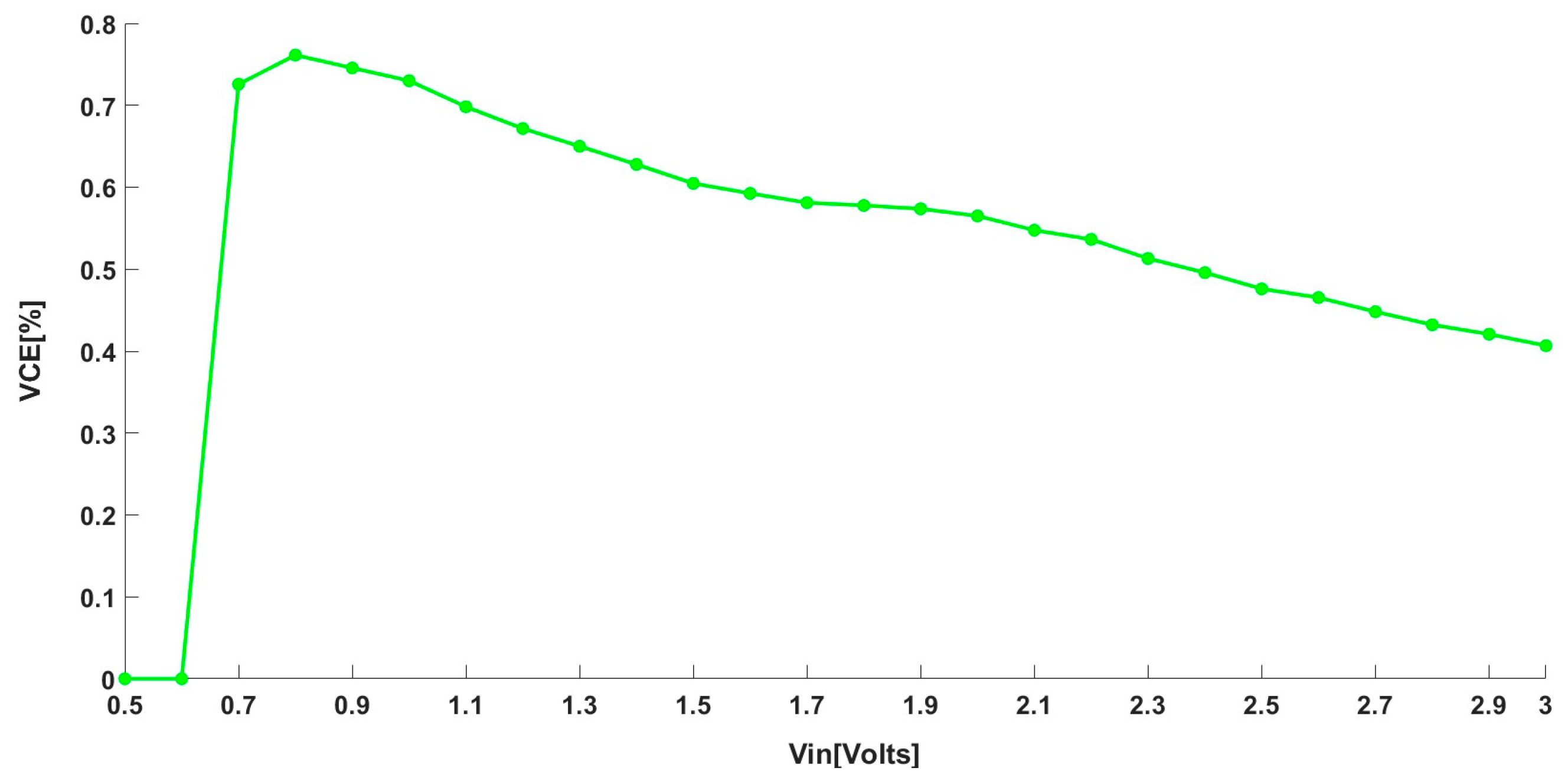
- Achieves wide-range input operation from 0.7 V to 2.8 V, maintaining high VCE (72.8% to 43.21%).
- (iii)
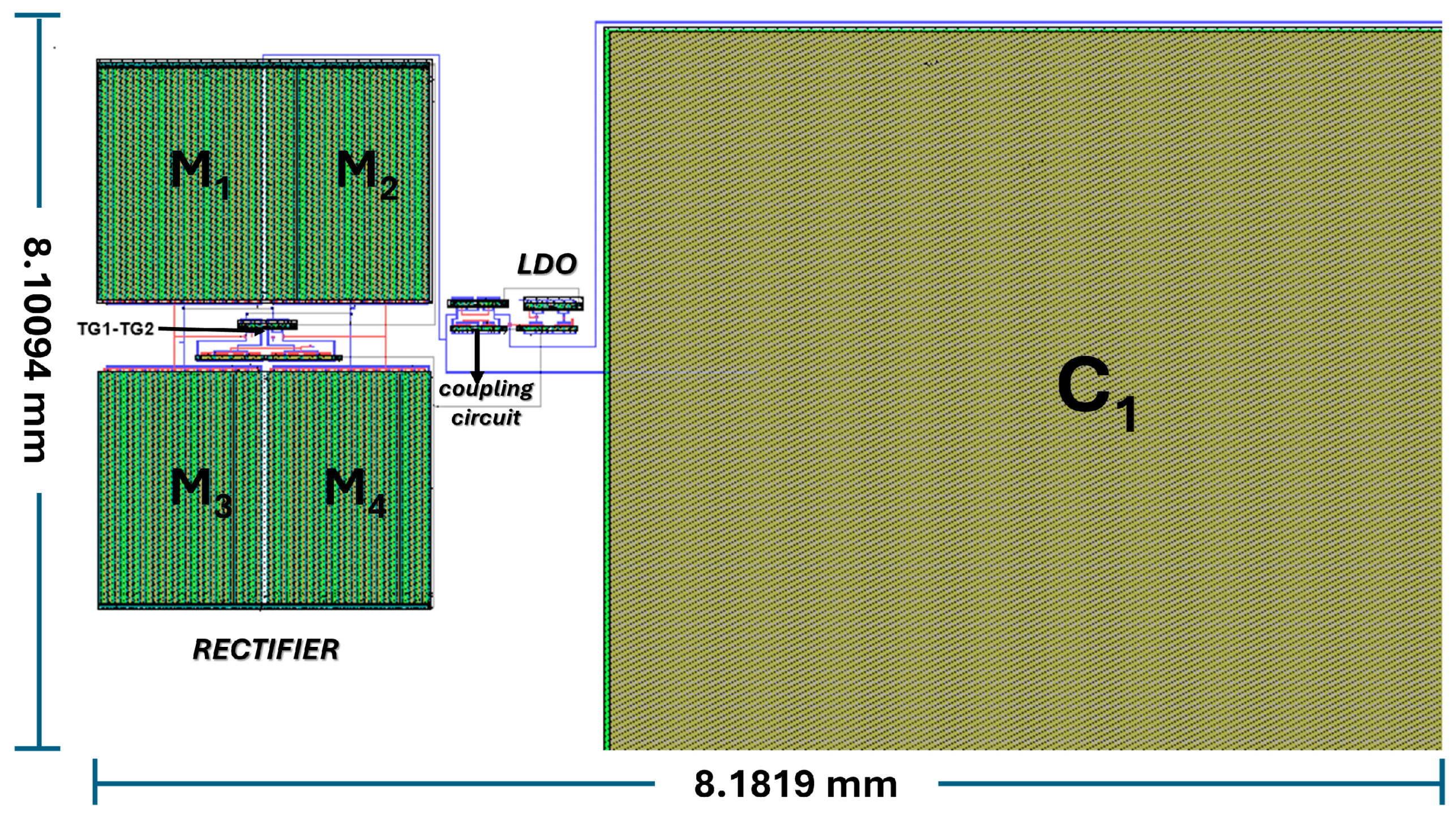
- Demonstrates compact area efficiency with a silicon footprint of 66.28 mm2.
- (iv)
- Incorporates a coupling network that significantly reduces voltage losses between rectification and regulation stages (~10% gain).
- (v)
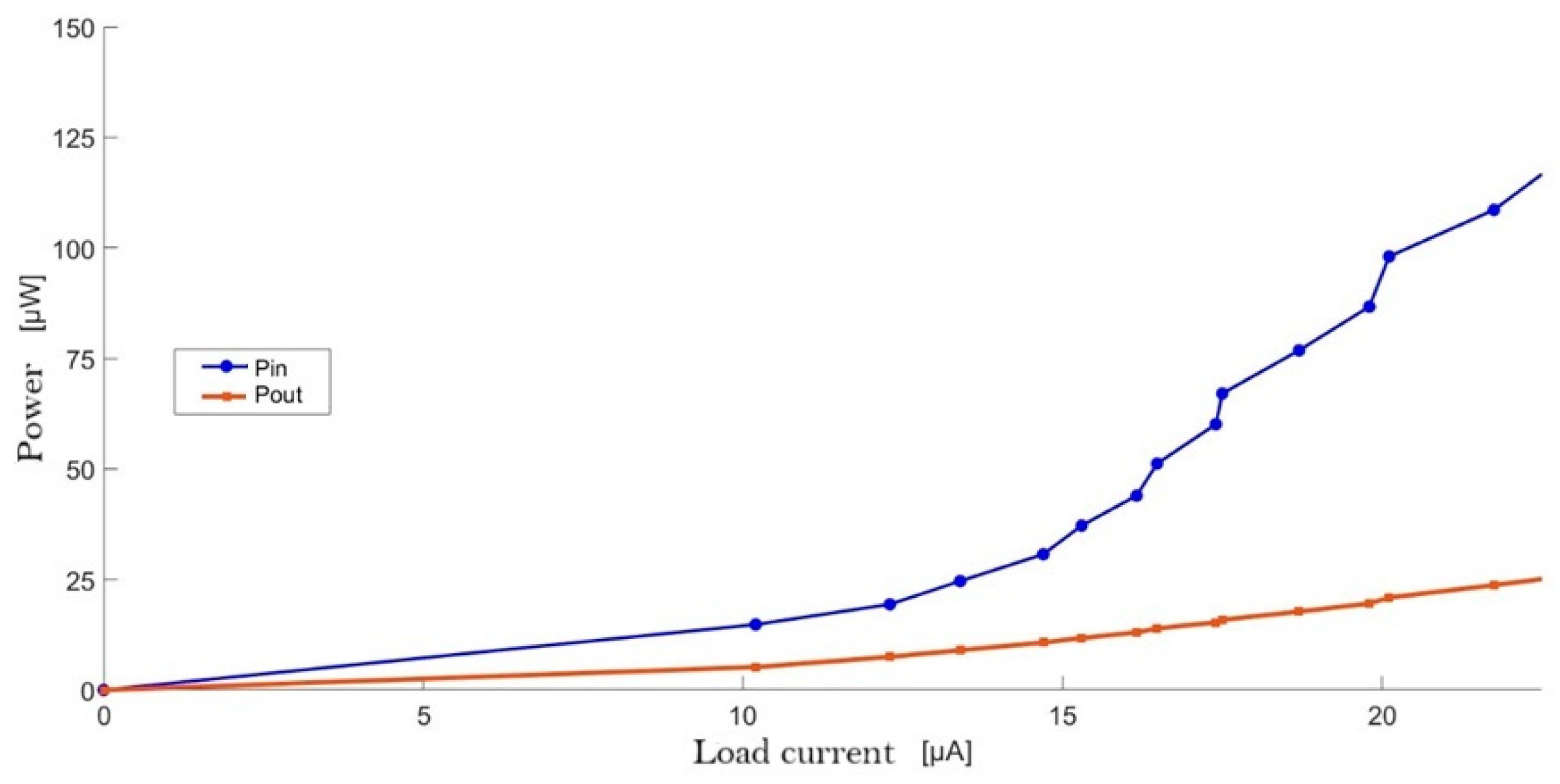
- Supports power conversion efficiencies above 35% at typical load conditions for IoT sensor nodes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Requirements for the IoT Sensors
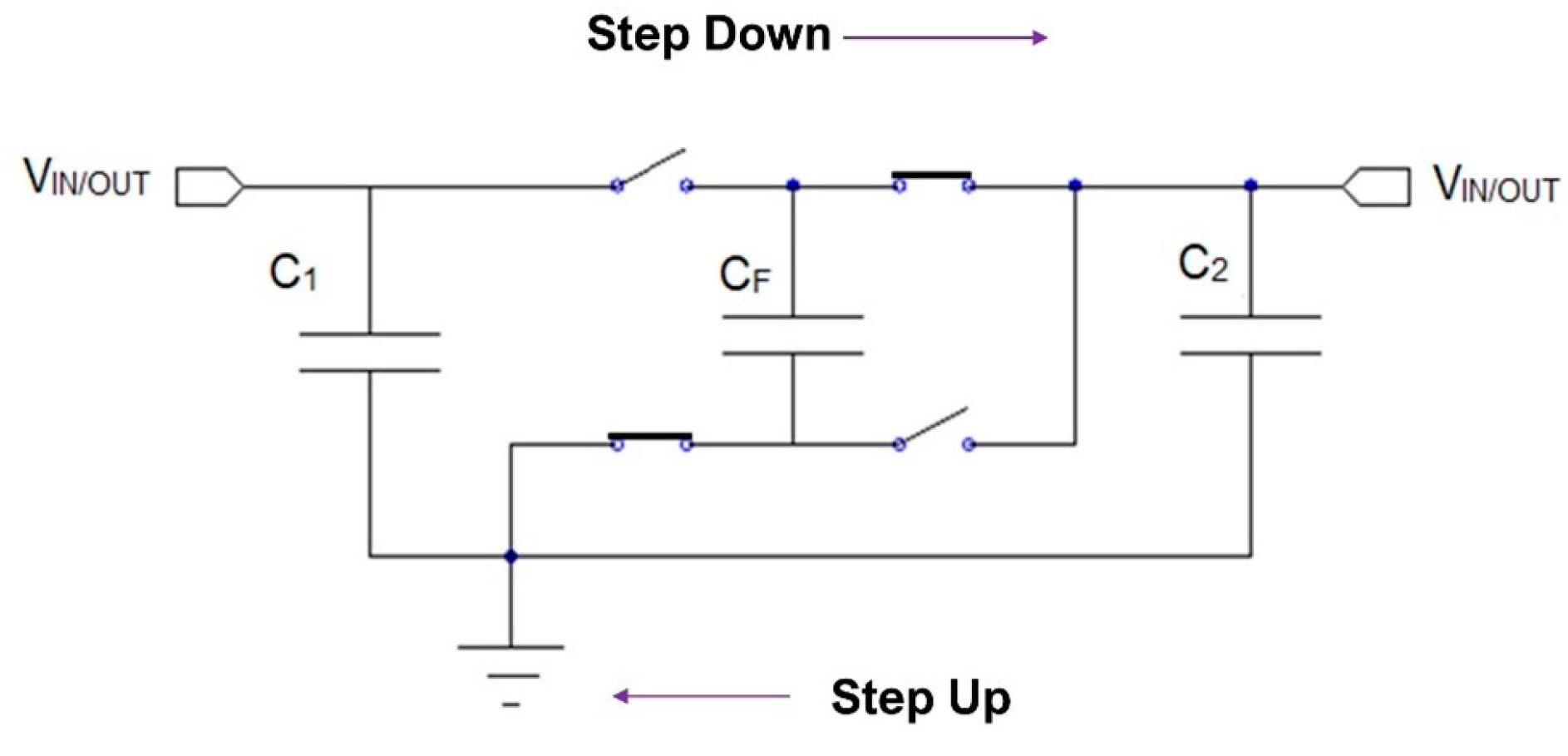
2.2. DC-DC Converter Topologies
2.3. Power Management Circuits for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters
3. Results and Discussions
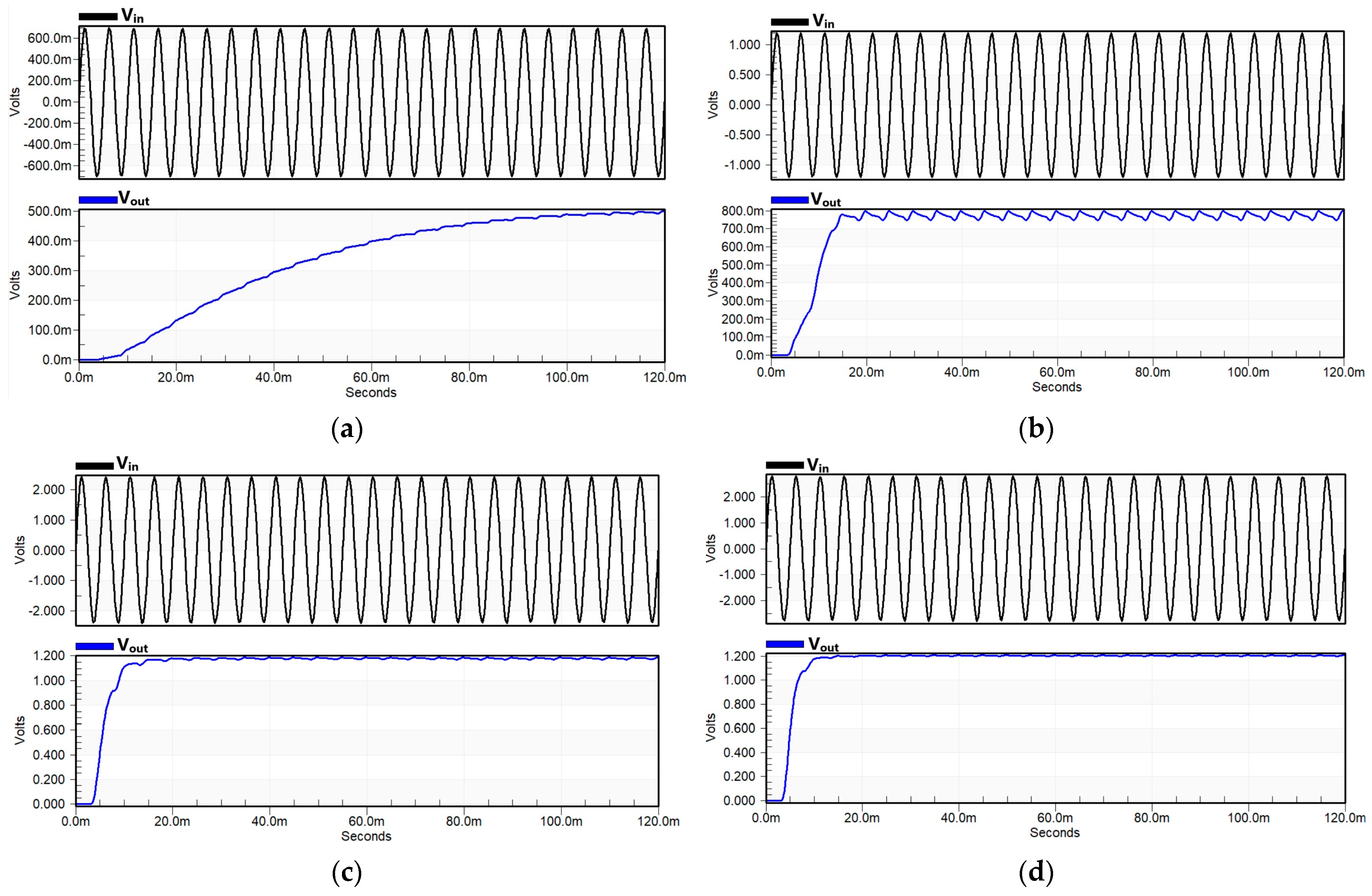
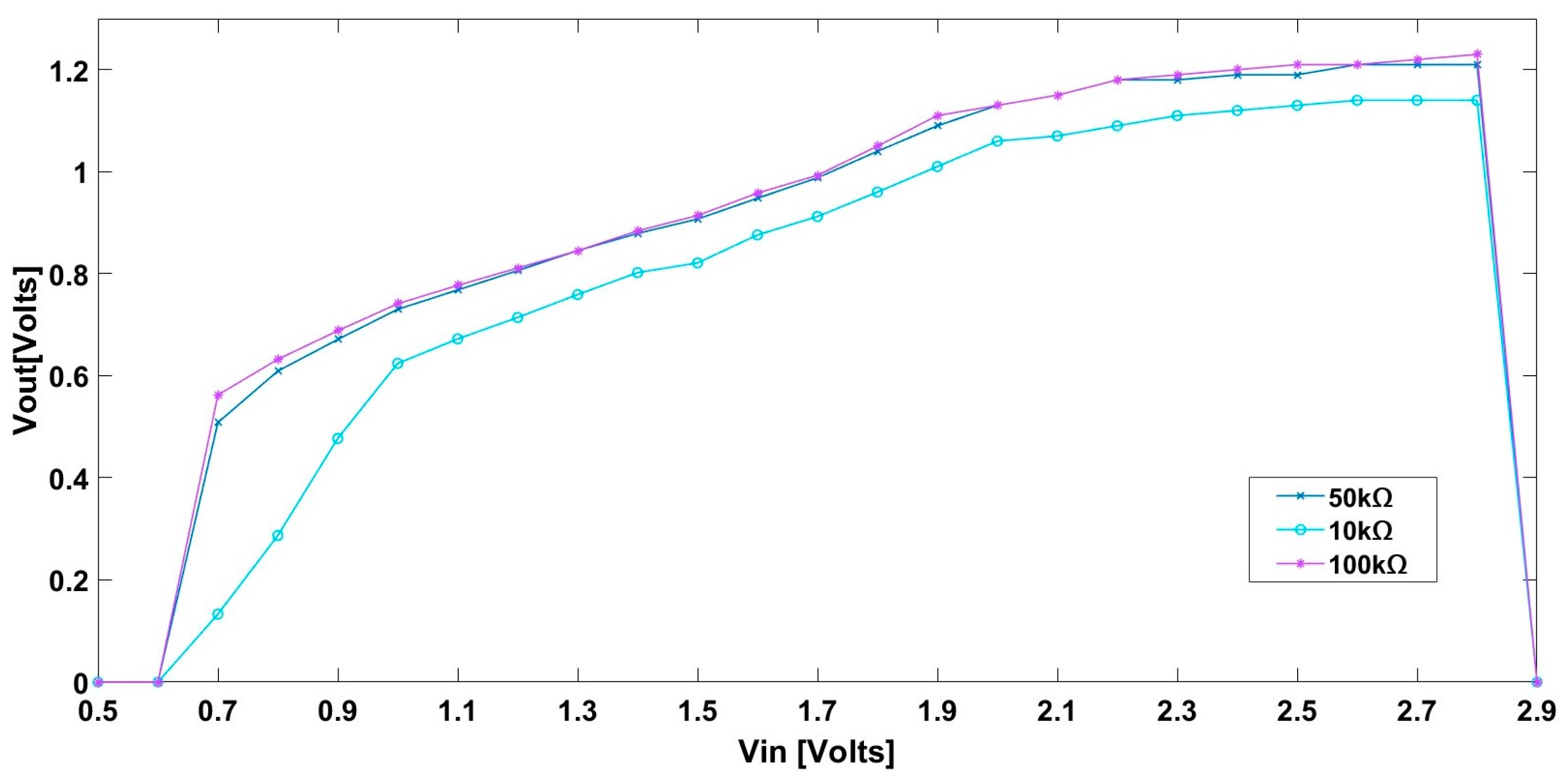
3.1. Output Voltage Regulation
3.2. Voltage Conversion Efficiency and Power Conversion Efficiency
3.3. Output Voltage as a Function of Input Voltage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, T.; Kundu, S.; Nag, A.; Xu, Y. 3D Printed Sensors for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Rajaboina, R.K.; Jho, Y.-D. Review on the Hierarchical Improvement of Zinc Sulfide-Based Nanogenerator Systems and Their Various IoT Applications. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, 8, 1918–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Redouté, J.-M.; Yuce, M.R. A Wireless Implantable Sensor Design with Subcutaneous Energy Harvesting for Long-Term IoT Healthcare Applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35801–35808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Han, Q.; Wu, N. Piezoelectric energy harvesting: A review of energy sources, structures, and working mechanisms in high-frequency excitations and operations. Smart Mater. Struct. 2025, 34, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bhat, G.; NK, A.; Geyik, C.S.; Ogras, U.Y.; Lee, H.G. Energy per Operation Optimization for Energy-Harvesting Wearable IoT Devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, D.; Domingos, I.; Carvalho, N.; Pinho, P.; Alves, H. Harvesting circuits for triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable applications. iScience 2022, 25, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edla, M.; Lim, Y.Y.; Mikio, D.; Padilla, R. A Single-Stage Rectifier-Less Boost Converter Circuit for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, L.G. A Recursive N-Path Switched-Capacitor Rectifier for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2025, 60, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.B.; Sahnoun, S.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. Design of a DC-DC Boost Converter of Hybrid Energy Harvester for IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–16 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghage, K.; Gunawardane, K.; Kularatna, N. Supercapacitor-Assisted Low-Dropout Regulator Technique for Low Output Ripple DC-DC Conversion. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2022, 3, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Liang, J.; Zeng, X. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters: An Overview on Design Strategies and Topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvanimoghaddam, M.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Abolhasani, M.M.; Farhangi, M.; Barsari, V.Z.; Liu, H. Towards a Green and Self-Powered Internet of Things Using Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 94533–94556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiev, I.; Tomchev, N.; Kurtev, N.; Aleksandrova, M. Analysis of the Methods for Realization of Low-Power Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Circuits for Wearable Battery-Free Power Supply Devices. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Rial, O.; Cabrini, A.; Torelli, G.; Lopez, P.; Carrillo, J.M. Ultra-Low-Power Low-Input-Voltage Charge Pump for Micro-Energy Harvesting Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaci, C.; Gontean, A. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Solutions: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Chung, H.S.-H. Self-Powered SSDCI Array Interface for Multiple Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 9093–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, F.; Migliorini, M.; Pozzebon, A. Piezoelectric Sensors as Energy Harvesters for Ultra Low-Power IoT Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadgoshasb, I. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting towards Self-Powered Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors in Smart Cities. Sensors 2021, 21, 8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, F.; Lu, Z.; Yu, X. A High-Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting and Management Circuit Based on Full-Bridge Rectification. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2024, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, P.; Khanna, G. A broadband piezoelectric energy harvester for IoT based applications. Microelectron. J. 2019, 93, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.-K.; Jiang, Y.; Mak, P.-I.; Martins, R.P. Miniaturized Energy Harvesting Systems Using Switched-Capacitor DC-DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wu, F.; Redouté, J.-M.; Yuce, M.R. An autonomous wireless body area network implementation towards IoT-connected healthcare applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 11413–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Song, H.-C.; Zhou, Y.; Varghese, R.; Chopra, A.; Kim, S.-G.; Kanno, I.; Wu, L.; Ha, D.S.; Ryu, J.; et al. A review on piezoelectric energy harvesting: Materials, methods, and circuits. Energy Harvest. Syst. 2019, 4, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Cao, D.; Li, M.; Chuai, X.; Peng, Y.; Mei, X.; et al. Mutualistic symbiotic wireless node for next-era smart transportation. Nano Energy 2025, 136, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wu, F.; Qiu, C.; Redoute, J.M.; Yuce, M.R. A Rigid-Flex Wearable Health Monitoring Sensor Patch for IoT-Connected Healthcare Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6932–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, A.; Biswas, D.K.; Mahbub, I.; Adhikari, P.R.; Reid, R.C. Highly efficient rectifier and DC-DC converter designed in 180 nm CMOS process for ultra-low frequency energy harvesting applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 Dallas Circuits and Systems Conference (DCAS) 2020, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.U.; Sandhie, Z.T.; Chowdhury, M.H. An implementation of external capacitor-less low-dropout voltage regulator in 45 nm technology with output voltage ranging from 0.4 V–1.2 V. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 38th International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Harford, CT, USA, 18–21 October 2020; pp. 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Chung, W.G.; Kwon, Y.W.; Kim, S.; Hong, Y.-M.; Park, W.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; et al. Smart Contact Lenses as Wearable Ophthalmic Devices for Disease Monitoring and Health Management. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 11488–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Tan, J.S.Y.; Wu, H.; Dong, Y.; Yoo, J. 1225-Channel Neuromorphic Retinal-Prosthesis SoC with Localized Temperature-Regulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Lim, J.; Nolan, J.K.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H. Wearable Glucose Monitoring and Implantable Drug Delivery Systems for Diabetes Management. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yi, Z.; Yang, B.; Lee, C. Making use of nanoenergy from human—Nanogenerator and self-powered sensor enabled sustainable wireless IoT sensory systems. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Closson, A.B.; Jin, C.; Nie, Y.; Cabe, A.; Escobedo, D.; Huang, S.; Trase, I.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; et al. Multifunctional Pacemaker Lead for Cardiac Energy Harvesting and Pressure Sensing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Huang, B.; Gong, H.; et al. Monitoring of the central blood pressure waveform via a conformal ultrasonic device. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gljušćić, P.; Zelenika, S.; Blažević, D.; Kamenar, E. Kinetic Energy Harvesting for Wearable Medical Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Azad, A.N.M.W.; Baidya, S.; Khan, F. A Comprehensive Review on Rectifiers, Linear Regulators, and Switched-Mode Power Processing Techniques for Biomedical Sensors and Implants Utilizing in-Body Energy Harvesting and External Power Delivery. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 12721–12745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmmod, B.M.; Naser, M.A.; Al-Sudani, A.H.S.; Alsabah, M.; Mohammed, H.J.; Alaskar, H. Patient Monitoring System Based on Internet of Things: A Review and Related Challenges With Open Research Issues. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 132444–132479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Khanbareh, H.; Halim, M.A.; Feeney, A.; Zhang, X.; Heidari, H.; Ghannam, R. Piezoelectric energy harvesting for self-powered wearable upper limb applications. Nano Select. 2021, 2, 1459–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.A.; Manchi, P.; Paranjape, M.V.; Kurakula, A.; Kavarthapu, V.S.; Lee, J.K.; Yu, J.S. Multifunctional Thermochromic Dye-Integrated Hybrid Nanogenerators for Mechanical Energy Harvesting and Real-Time IoT Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2409608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, S.A.Z.; Harun, A.; Isa, M.N.M.; Marzuki, A.; Sapawi, R. A Linear 0.98 mV Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator in 0.18-μm CMOS Technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1755, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan Bhuiyan, M.A.; Hossain, M.R.; Minhad, K.N.; Haque, F.; Hemel, M.S.K.; Md Dawi, O.; Ibne Reaz, M.B.; Ooi, K.J.A. CMOS Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator Design Trends: An Overview. Electronics 2022, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ye, D.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Luo, Z. An adaptive Gm cell compensation technique for fast transient and high efficiency LDO without on/off-chip capacitor. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2025, 190, 155640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Mejia, G.; Gomez-Garcia, D.E.; Giron-Nieto, H.; Martinez-Castillo, J.; Moreno-Coria, L.A.; Rocha-Perez, J.M.; Diaz-Sanchez, A. A 0.18 μm CMOS capacitor-less Low-Drop Out Voltage Regulator Compensated via the Bootstrap Flipped-Voltage Follower. Microelectron. J. 2020, 101, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicea-Morales, P.M.; Ortiz-Villanueva, C.J.; Pérez, R.; Palomera-Garcia, R.; Jiménez, M. Design of an adjustable, low voltage, low dropout regulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Caracas Conference on Devices, Circuits and Systems (ICCDCS) 2004, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 3–5 November 2004; pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, J.; Brenk, D.; Essel, J.; Heinrich, M.; Jung, M.; Hofer, G. Design of a low-power voltage regulator for RFID applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Region 8 International Conference on Computational Technologies in Electrical and Electronics Engineering (SIBIRCON), Irkutsk, Russia, 11–15 July 2010; pp. 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbet, D.; Potocny, M.; Kovac, M.; Nagy, L.; Stopjakova, V. Fully On-Chip Low-Drop Regulator for Low-Power Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 44th International Convention on Information, Communication and Electronic Technology (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilani, D.; Alhawari, M.; Mohammad, B.; Saleh, H.; Ismail, M. Reconfigurable, Switched-Capacitor Power Converter for IoT. In The IoT Physical Layer; Elfadel, I., Ismail, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran Kumar, G.; Kobaku, T.; Sahoo, S.; Subudhi, B.; Elangovan, D.; Blaabjerg, F. An Overview of Fully Integrated Switching Power Converters Based on Switched-Capacitor versus Inductive Approach and Their Advanced Control Aspects. Energies 2021, 14, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, S.; Ravi, S. Effect of physical variations of inductor and capacitor on peak current in DC-DC converter. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Smart Structures and Systems (ICSSS), Chennai, India, 9 October 2014; pp. 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ki, W.-H. CMOS Integrated Circuit Design for Wireless Power Transfer; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.U.; Sandhie, Z.T.; Ali, L.; Chowdhury, M.H. A Brief Overview of On-Chip Voltage Regulation in High-Performance and High-Density Integrated Circuits. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.F.; Tofoli, F.L.; Ribeiro, E.R. Switched Capacitor DC-DC Converters: A Survey on the Main Topologies, Design Characteristics, and Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Gangineni, M.; Huerta-Chua, J. Low Voltage CMOS Class AB Current Mirror/Precision Rectifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE 66th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Tempe, AZ, USA, 6–9 August 2023; pp. 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Pandey, R.; Tu, T.Y.; Cheng, Y.-P.; Chao, P.C.P. An efficient energy harvesting circuit for batteryless IoT devices. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, Z. A 15 mV-input and 71%-efficiency boost converter with 22 mV output ripple for thermoelectric energy harvesting application. Microelectron. J. 2022, 121, 105353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Liu, X.; Wan, Q.; Kuai, Q.; Teh, Y.-K.; Mok, P.K.T. A 0.3-V Ultralow-Supply-Voltage Boost Converter for Thermoelectric Energy Harvesting with Time-Domain-Based MPPT. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2021, 4, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, H.M.P.C.; Pathirana, W.P.M.R.; Muhtaroğlu, A. An on-die ultra-low voltage DC–DC step-up converter with voltage doubling LC-tank. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Device | Electrical Parameters | Power Level |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial pacemakers | 10–15 μW | Ultra-low [32] |
| Blood pressure sensors | ~4.6–24 mW | Low [33,34] |
| Temperature sensors | ~38.5–241 µW | Ultra-low [34] |
| Pulse oximeter sensors | ~68 µW–4.8 mW | Low [34] |
| Drug pump | ~100 μW–2 mW | Ultra-low [35] |
| Retinal stimulator | ~1–100 mW | Low [35] |
| Neural stimulator | ~10–200 mW | Low [35] |
| AC/DC Rectifier Transistors | W/L (µm) | Factor | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 36/0.4 | 25 | PMOS |
| M2 | 36/0.4 | 25 | NMOS |
| M3 | 36/0.4 | 25 | PMOS |
| M4 | 36/0.4 | 25 | NMOS |
| M5 | 0.5/0.18 | 4 | PMOS |
| M6 | 0.5/0.18 | 4 | PMOS |
| M7 | 0.5/2 | 4 | NMOS |
| M8 | 0.5/2 | 4 | NMOS |
| M9 | 2.5/2 | 4 | PMOS |
| M10 | 2.5/2 | 4 | NMOS |
| M11 | 2.5/2 | 4 | PMOS |
| M12 | 2.5/2 | 4 | NMOS |
| M13 | 2.5/2 | 4 | PMOS |
| M14 | 2.5/2 | 4 | NMOS |
| M15 | 2.5/2 | 4 | PMOS |
| M16 | 2.5/2 | 4 | NMOS |
| Parameters | In This Work |
|---|---|
| Technology (µm) | 0.18 µm TSMC |
| Vin (V) | 0.7–2.8 V |
| Vout (V) | 0.508–1.21 V |
| Frequency (Hz) | 200 Hz |
| VCE (%) | 72.57%@50 kΩ |
| PCE (%) | 35%@50 kΩ |
| C1 (µF) | 1 |
| Area (mm2) | 66.28108 |
| Reference | CMOS Technology | Vin Range (V) | Vout (V) | VCE (%) | PCE (%) | Area (mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Work | 0.18 µm | 0.7–2.8 | 1.8 | 43–72.8 | 35 | 66.28 |
| Gunti et al. [26] | 0.18 µm | 0.5–2.0 | 1.2 | 50–70 | 25–35 | 70 |
| Ahmed et al. [27] | 0.45 µm | 0.4–1.2 | 1.0 | 35–60 | 20–30 | 60 |
| Paul et al. [52] | 0.18 µm | 1.0–2.5 | 1.8 | 40–65 | 30–40 | 80 |
| Yihan et al. [54] | 0.18 µm | 0.15–2.4 | 1.25 | 45–71 | 30–38 | 65 |
| Liu et al. [19] | 0.11 µm | 0.5–2.5 | 1.8 | 50–75 | 40–50 | 0.6 |
| Wu et al. [55] | 0.13 µm | 0.3 | 0.3 | 72 | 28 | 1.16 |
| Jayaweera et al. [56] | 0.18 µm | 0.20 | 1.6 | 15–35 | 32–40 | 1.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez-Valdés, S.E.; Argüelles-Lucho, P.; Woo-García, R.M.; Osorio-de-la-Rosa, E.; López-Huerta, F.; Herrera-May, A.L. A CMOS-Based Power Management Circuit with a Reconfigurable Rectifier and an LDO Regulator for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting in IoT Applications. Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5020007
Vázquez-Valdés SE, Argüelles-Lucho P, Woo-García RM, Osorio-de-la-Rosa E, López-Huerta F, Herrera-May AL. A CMOS-Based Power Management Circuit with a Reconfigurable Rectifier and an LDO Regulator for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting in IoT Applications. Nanoenergy Advances. 2025; 5(2):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez-Valdés, Suany E., Primavera Argüelles-Lucho, Rosa M. Woo-García, Edith Osorio-de-la-Rosa, Francisco López-Huerta, and Agustín L. Herrera-May. 2025. "A CMOS-Based Power Management Circuit with a Reconfigurable Rectifier and an LDO Regulator for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting in IoT Applications" Nanoenergy Advances 5, no. 2: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5020007
APA StyleVázquez-Valdés, S. E., Argüelles-Lucho, P., Woo-García, R. M., Osorio-de-la-Rosa, E., López-Huerta, F., & Herrera-May, A. L. (2025). A CMOS-Based Power Management Circuit with a Reconfigurable Rectifier and an LDO Regulator for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting in IoT Applications. Nanoenergy Advances, 5(2), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5020007









