Mechanical Conversion and Transmission Systems for Controlling Triboelectric Nanogenerators
Abstract
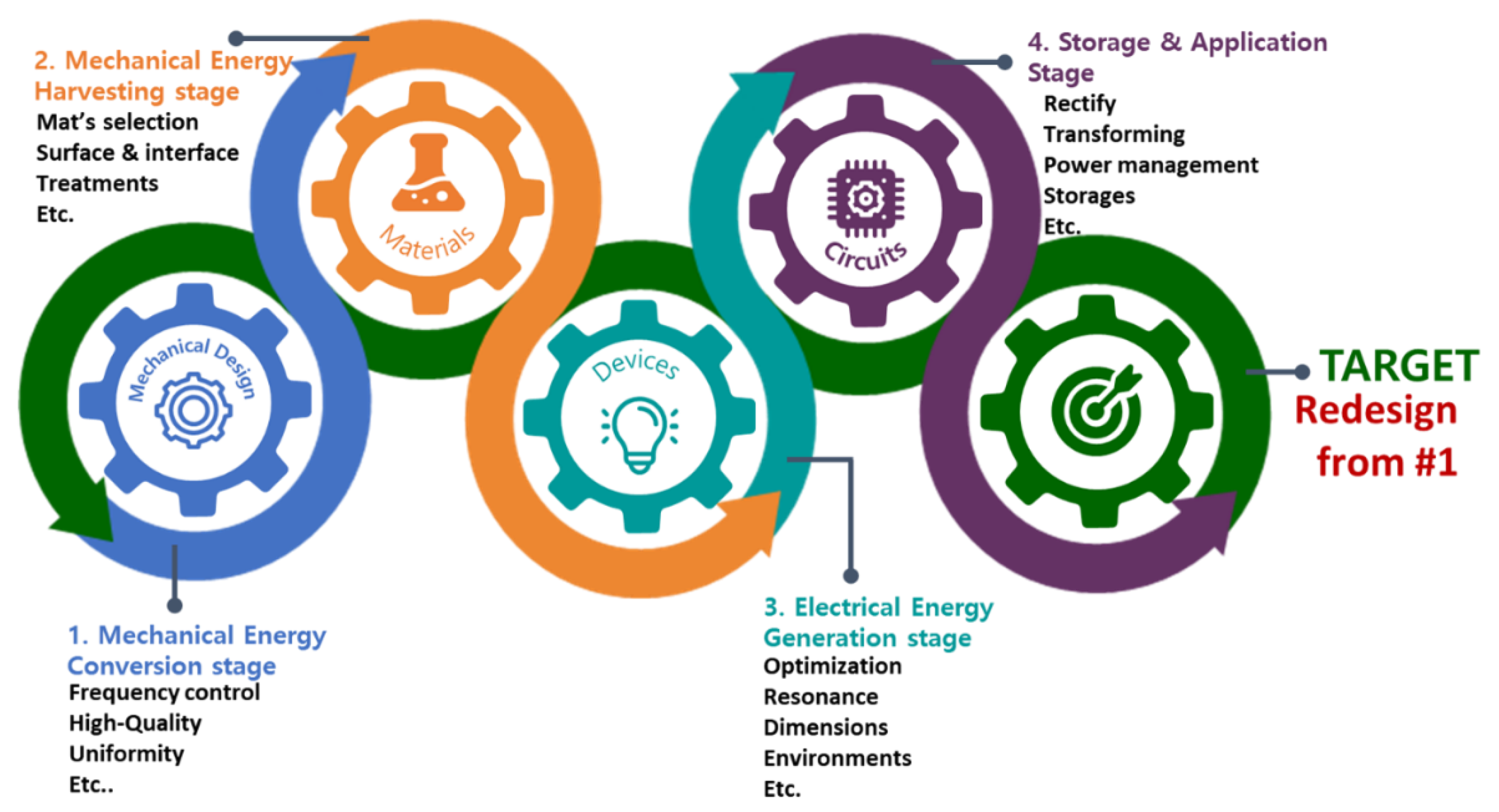
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Simple Machines and TENG Basics
2.1. Simple Machines: An Overview
2.1.1. Force Controlled
2.1.2. Velocity-Frequency Controlled
2.2. Basic Working Principle of TENGs
2.2.1. Basic Principle of the Triboelectric Effect
2.2.2. Basic Working Modes of TENGs
2.2.3. Governing Equations of TENG
3. Gear-Based Mechanical Control Systems
4. Cam-Based Mechanical Control Systems
5. Flywheel/Governor-Based Mechanical Control Systems
6. Gear- and Cam-Based Mechanical Control Systems
7. Gear-, Spiral-Spring- and Flywheel-Based Mechanical Systems
8. Mechanical Systems to Control the Input Flow
9. Summary and Perspective
- (1)
- To obtain higher efficiency TENG systems, miniaturization, high adaptability, sustainability, endurance, and friction are big problems that need to be solved for the development of TENGs and hybrid system devices.
- (2)
- Due to the irregular and intermittent external energy sources, TENGs and hybrid systems based on a rotary system design should be adapted for bi-directional rotation to easily harvest surrounding energy, such as wind, from multiple directions.
- (3)
- For automatic and continuously operating TENG systems, MECSs should be designed to use unmanned device technology. TENGs integrated with such MECS designs could power Internet-of-Things systems and sensing networks automatically and precisely. We hope these problems can soon be solved and that TENGs can soon begin contributing to smart cities and other industrial applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Su, Y.; Wen, Z.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Automatic Mode Transition Enabled Robust Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12334–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhong, X.; Lin, Z.-H.; Su, Y.; Bai, P.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Wind Energy and as Self-Powered Wind Vector Sensor System. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9461–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Pan, H.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; et al. Lawn Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Scavenging Sweeping Wind Energy on Rooftops. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Disk-Based Hybridized Electromagnetic–Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Sustainably Powering Wireless Traffic Volume Sensors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6241–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Han, C.B.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Robust Thin Films-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Harvesting Bidirectional Wind Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Hwang, H.J.; Huynh, N.D.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Nam, Y.; Kim, J.-G.; Choi, D. Continuous scavenging of broadband vibrations via omnipotent tandem triboelectric nanogenerators with cascade impact structure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, D. Tandem triboelectric nanogenerators for optimally scavenging mechanical energy with broadband vibration frequencies. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Yi, F.; Yin, Y.; Hao, C.; Dai, K.; Zhang, Y.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Ambient Vibration Energy over a Wide Frequency Range for Self-Powered Electronics. ACS Nano. 2017, 11, 1728–1735. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.6b07633 (accessed on 29 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, F.G. Vibration energy harvesting by magnetostrictive material. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Quantitative measurements of vibration amplitude using a contact-mode freestanding triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12004–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Yang, Y.; Hou, T.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harmonic-resonator-based triboelectric nanogenerator as a sustainable power source and a self-powered active vibration sensor. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6094–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Jing, Q.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting energy from the natural vibration of human walking. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11317–11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Yang, W.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting broadband kinetic impact energy from mechanical triggering/vibration and water waves. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7405–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Wen, X.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Z. Harvesting vibration energy by a triple-cantilever based triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Lin Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Broadband Vibrational Energy Harvesting Based on a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Adams, K.; Lee, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Vibration Energy in Full Space and as Self-Powered Acceleration Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J. Design of Bionic Cochlear Basilar Membrane Acoustic Sensor for Frequency Selectivity Based on Film Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-based organic film nanogenerator for acoustic energy harvesting and self-powered active acoustic sensing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrathin, rollable, paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator for acoustic energy harvesting and self-powered sound recording. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitcheson, P.D.; Yeatman, E.M.; Rao, G.K.; Holmes, A.S.; Green, T.C. Energy harvesting from human and machine motion for wireless electronic devices. Proc. IEEE 2008, 96, 1457–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators for harvesting energy from a moving object or human motion in contact and non-contact modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.H.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated multilayered triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting biomechanical energy from human motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zou, H.; Liu, R.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, J.; Du, J.; Fan, X.; Tao, C.; Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; et al. A Wearable All-Solid Photovoltaic Textile. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Kempa, T.J.; Lieber, C.M. Single nanowire photovoltaics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, S. Experimental study on low-temperature waste heat thermoelectric generator. J. Power Sources 2009, 188, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, P.-K.; Yi, F.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric–Pyroelectric–Piezoelectric Hybrid Cell for High-Efficiency Energy-Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wong, C.P.; Wang, Z.L. A hybrid energy cell for self-powered water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2429–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Yin, Y.; Yi, F.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Fully Enclosed Rolling Spherical Structure for Harvesting Low-Frequency Water Wave Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. A novel hybridized blue energy harvester aiming at all-weather IoT applications. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Cheng, P.; Chen, R.; Xie, L.; Sun, N.; Shen, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator for Harvesting Blue Energy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.M.; Han, C.B.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Multilayer wavy-structured robust triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water wave energy. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Lin Wang, Z. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Gu, L.; Lei, Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, Y.; Ma, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Dynamic Behavior of the Triboelectric Charges and Structural Optimization of the Friction Layer for a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6131–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated flywheel and spiral spring triboelectric nanogenerator for improving energy harvesting of intermittent excitations/triggering. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Jang, S.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D. Exo-shoe triboelectric nanogenerator: Toward high-performance wearable biomechanical energy harvester. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, W.; Bhatia, D.; Hwang, H.J.; Lee, S.; Choi, D. Cam-based sustainable triboelectric nanogenerators with a resolution-free 3D-printed system. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, H.G.; Huynh, N.D.; Hwang, H.J.; Han, S.; Choi, D.; Park, Y.T. Designable Skin-like Triboelectric Nanogenerators Using Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembled Polymeric Nanocomposites. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.; Park, H.; Bhatia, D.; Jee, E.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, D. An Ultra-Mechanosensitive Visco-Poroelastic Polymer Ion Pump for Continuous Self-Powering Kinematic Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, W.; Hwang, H.J.; Hong, H.; Choi, K.H.; Song, A.; Chung, K.B.; Choi, D. Effects of embedded TiO2-x nanoparticles on triboelectric nanogenerator performance. Micromachines 2018, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.-W.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.; Nam, Y.; Lee, S.; Chung, K.-B.; Choi, D. Electron blocking layer-based interfacial design for highly-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudem, B.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D.; Yu, J.S. Nanopillar-array architectured PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator integrated with a windmill model for effective wind energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2017, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Yang, Y.; Lin, L.; Lin, Z.H.; Hwang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting pendulum oscillation energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Han, M.-D.; Wang, R.-X.; Zhu, F.-Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.-X. Frequency-Multiplication High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Sustainably Powering Biomedical Microsystems. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.-R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors Based on Micropatterned Plastic Films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthu, M.; Pandey, R.; Wang, X.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Palani, I.A.; Singh, V. Enhancement of triboelectric nanogenerator output performance by laser 3D-Surface pattern method for energy harvesting application. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Vivekananthan, V.; Khandelwal, G.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, S.J. Green energy from working surfaces: A contact electrification–enabled data theft protection and monitoring smart table. Mater. Today Energy 2020, 18, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Khandelwal, G.; Rao Alluri, N.; Vivekananthan, V.; Kim, S.-J. Battery-Free Electronic Smart Toys: A Step toward the Commercialization of Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudem, B.; Ko, Y.H.; Leem, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, J.S. Highly Transparent and Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Subwavelength-Architectured Polydimethylsiloxane by a Nanoporous Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20520–20529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoscale Triboelectric-Effect-Enabled Energy Conversion for Sustainably Powering Portable Electronics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6339–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Grating-Structured Freestanding Triboelectric-Layer Nanogenerator for Harvesting Mechanical Energy at 85% Total Conversion Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6599–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered active sensors. Nano Energy 2015, 11, 436–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chun, J.; Ye, B.U.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, D.; Kang, C.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Baik, J.M. Boosted output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via electric double layer effect. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, F.; Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Dai, K.; Zhang, G.; Lin, L.; Wen, Z.; Guo, H.; et al. A highly shape-adaptive, stretchable design based on conductive liquid for energy harvesting and self-powered biomechanical monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Yeh, M.H.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Bai, Y.; Feng, L.; Lai, M.; Ho, K.C.; Guo, H.; et al. Whirligig-inspired triboelectric nanogenerator with ultrahigh specific output as reliable portable instant power supply for personal health monitoring devices. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Dai, G.; Zou, H.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. An Ultra-Low-Friction Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Rotation Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Sensor. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9433–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Mu, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, C.; Gu, A.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Flow-Driven Triboelectric Generator for Directly Powering a Wireless Sensor Node. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Cho, S.; Yun, Y.; La, M.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. A highly sensitive magnetic configuration-based triboelectric nanogenerator for multidirectional vibration energy harvesting and self-powered environmental monitoring. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 18262–18274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zou, H.; Wu, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Rationally designed rotation triboelectric nanogenerators with much extended lifetime and durability. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Kim, Y.; Mehmood, M.U.; Shaislamov, U.; Chun, W. Power generation by a thermomagnetic engine by hybrid operation of an electromagnetic generator and a triboelectric nanogenerator. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 5852–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Meng, L.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Magnetic switch structured triboelectric nanogenerator for continuous and regular harvesting of wind energy. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.W.; Kim, J.N.; Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Bui, V.T.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, D.; Oh, I.K. Long-Lasting and Steady Triboelectric Energy Harvesting from Low-Frequency Irregular Motions Using Escapement Mechanism. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2002929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcho, I.W.; Jeon, S.B.; Park, S.J.; Kim, W.G.; Jin, I.K.; Han, J.K.; Kim, D.; Choi, Y.K. Disk-based triboelectric nanogenerator operated by rotational force converted from linear force by a gear system. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Bhatia, D.; Jeong, S.; Choi, D. Mechanical energy conversion systems for triboelectric nanogenerators: Kinematic and vibrational designs. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Hwang, H.J.; Bhatia, D.; Lee, Y.; Baik, J.M.; Choi, D. Kinematic design for high performance triboelectric nanogenerators with enhanced working frequency. Nano Energy 2016, 21, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hwang, H.J.; Huynh, N.D.; Pham, K.D.; Choi, K.; Ahn, D.; Choi, D. Magnetic Force Enhanced Sustainability and Power of Cam-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Research 2021, 2021, 6426130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, K.D.; Bhatia, D.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, H.; Baik, J.M.; Lin, Z.H.; Choi, D. Automatically switchable mechanical frequency regulator for continuous mechanical energy harvesting via a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Lee, J.; Hwang, H.J.; Baik, J.M.; Kim, S.; Choi, D. Design of Mechanical Frequency Regulator for Predictable Uniform Power from Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ouyang, H.; Shi, B.; Zou, Y.; Tan, P.; Qu, X.; Chao, S.; Xi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fan, Y.; et al. A wearable noncontact free-rotating hybrid nanogenerator for self-powered electronics. InfoMat 2020, 2, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, N.D.; Lin, Z.H.; Choi, D. Dynamic balanced hybridization of TENG and EMG via Tesla turbine for effectively harvesting broadband mechanical pressure. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Chung, J.; Choi, D.; Jung, D.; Cho, M.; Lee, S. Highly reliable wind-rolling triboelectric nanogenerator operating in a wide wind speed range. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, S.; Kien, P.T.; Dong, J.; Mi, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, M. Multi-functional wind barrier based on triboelectric nanogenerator for power generation, self-powered wind speed sensing and highly efficient windshield. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chen, X.; Han, C.B.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Study of Rotary Freestanding Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2928–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Han, C.; Fan, F.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical comparison, equivalent transformation, and conjunction operations of electromagnetic induction generator and triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting mechanical energy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3580–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Noncontact free-rotating disk triboelectric nanogenerator as a sustainable energy harvester and self-powered mechanical sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, T.; Liu, G.; Pang, Y.; Wu, B.; Xi, F.; Zhao, J.; Bu, T.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Compressible hexagonal-structured triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting tire rotation energy. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhou, T.; Wang, B.; Yin, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Sleeve Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for High Efficiency of Harvesting Mechanical Energy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8370–8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.; Yu, J.; Kim, I.; Chae, Y.; Kim, D. Dynamic Analysis to Enhance the Performance of a Rotating-Disk-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Injected Gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25170–25178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-disk-based hybridized electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator for scavenging biomechanical energy as a mobile power source. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Lei, S.; Wang, W. Wind energy harvester based on coaxial rotatory freestanding triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered water splitting. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Segmentally structured disk triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting rotational mechanical energy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Cao, S.; Zhang, H. Cylinder-based hybrid rotary nanogenerator for harvesting rotational energy from axles and self-powered tire pressure monitoring. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Meng, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator with double rocker structure design for ultra-low-frequency wave full-stroke energy harvesting. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2021, 46, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Lu, X.; Qiao, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Mechanical Regulation Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Controllable Output Performance for Random Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Jo, S.H.; Ryu, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, H.S. Wearable triboelectric nanogenerator based exercise system for upper limb rehabilitation post neurological injuries. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Vertical C-S Mode | Controllability by Mechanical Energy Conversion Systems | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Material selection | Material thickness | Material gap | Surface roughness | Contact area | Contact force | Contact velocity | Contact frequency |
| X | X | X | X | X | O | O | O | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huynh, N.D.; Choi, D. Mechanical Conversion and Transmission Systems for Controlling Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanoenergy Adv. 2022, 2, 29-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2010002
Huynh ND, Choi D. Mechanical Conversion and Transmission Systems for Controlling Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanoenergy Advances. 2022; 2(1):29-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuynh, Nghia Dinh, and Dukhyun Choi. 2022. "Mechanical Conversion and Transmission Systems for Controlling Triboelectric Nanogenerators" Nanoenergy Advances 2, no. 1: 29-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2010002
APA StyleHuynh, N. D., & Choi, D. (2022). Mechanical Conversion and Transmission Systems for Controlling Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanoenergy Advances, 2(1), 29-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2010002






