Social Determinants of Narcotics Use Susceptibility among School-Attending Adolescents in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Determinants of Engagement
1.2. Background to Study
1.3. Aims of the Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey Implementation
2.2. Dependent Variable Modelling
2.3. Statistical Methods
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Cross-Sectional Statistics
4. Discussion
4.1. Determinants of AOD Use
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Development Programme. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2017; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/files/report/2017/thesustainabledevelopmentgoalsreport2017.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. International Youth Day, 12 August 2019; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/youth/wp-content/uploads/sites/21/2019/08/WYP2019_10-Key-Messages_GZ_8AUG19.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Patton, G.C.; Sawyer, S.M.; Santelli, J.S.; Ross, D.A.; Afifi, R.; Allen, N.B.; Arora, M.; Azzopardi, P.; Baldwin, W.; Bonell, C.; et al. Our Future: A Lancet Commission on Adolescent Health and Wellbeing. Lancet 2016, 387, 2423–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2019. Executive Summary; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://wdr.unodc.org/wdr2019/prelaunch/WDR19_Booklet_1_EXECUTIVE_SUMMARY.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- National Institute on Drug Use. Media Guide: How to Find What You Need to Know about Drug Use and Addiction. 2018. Available online: https://www.drugabuse.gov/sites/default/files/media_guide.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Yu, J. Alcohol, Cocaine, and Criminality: Specifying an Interaction Effect Model. J. Crim. Justice 1998, 26, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.; Hayhurst, K.; Bird, S.M.; Hickman, M.; Seddon, T.; Dunn, G.; Millar, T. Insights into the Link between Drug Use and Criminality: Lifetime Offending of Criminally-Active Opiate Users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 179, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.F.; Laurent, S.; Roque, S. The International Cocaine Trade in Guinea-Bissau: Current Trends and Risks. Noref Working Paper. 2011, pp. 1–18. Available online: https://www.files.ethz.ch/isn/137866/international%20cocaine%20trade.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Csete, J.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Kazatchkine, M.; Altice, F.; Balicki, M.; Buxton, J.; Cepeda, J.; Comfort, M.; Goosby, E.; Goulão, J.; et al. Public Health and International Drug Policy. Lancet 2016, 387, 1427–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United States Department of Health & Human Services. Preventing Drug Use among Children and Adolescents. A Research Based Guide for Parents, Educators and Community Leaders, 2nd ed.; United States Department of Health & Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.drugabuse.gov/sites/default/files/preventingdruguse_2.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Medina-Mora, M.E. Prevention of Substance Abuse: A Brief Overview. World Psychiatry 2005, 4, 25–30. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1414714/ (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Stockings, E.; Hall, W.D.; Lynskey, M.; Morley, K.I.; Reavley, N.; Strang, J.; Patton, G.; Degenhardt, L. Prevention, Early Intervention, Harm Reduction, and Treatment of Substance Use in Young People. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, L.L.; Toal, S.B.; Swahn, M.; Behrens, C.B. Measuring Violence-Related Attitudes, Behaviors, and Influences among Youths: A Compendium of Assessment Tools, 2nd ed.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/YV_Compendium.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Treatment and Care for People with Drug Use Disorders in Contact with the Criminal Justice System. Alternatives to Conviction or Punishment; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/justice-and-prison-reform/UNODC_WHO_Alternatives_to_Conviction_or_Punishment_2018.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- International Narcotics Control Board. Primary Prevention of Drug Use. 2009. Available online: https://www.incb.org/documents/Publications/AnnualReports/Thematic_chapters/English/AR_2009_E_Chapter_I.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Masquelier, B.; Hug, L.; Sharrow, D.; You, D.; Mathers, C.; Gerland, P.; Alkema, L. Global, Regional, and National Mortality Trends in Youth Aged 15–24 Years between 1990 and 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e409–e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embleton, L.; Mwangi, A.; Vreeman, R.; Ayuku, D.; Braitstein, P. The Epidemiology of Substance Use among Street Children in Resource-Constrained Settings: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Street Children and Substance Use: A Review. Addiction 2013, 108, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. International Standards on Drug Use Prevention, 2nd ed.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/prevention/UNODC-WHO_2018_prevention_standards_E.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Csete, J.; Sanchez, C. Telling the Story of Drugs in West Africa: The Newest Front in a Losing War? Global Drug Policy Observatory Swansea: Swansea, UK, 2013; pp. 1–18. Available online: https://www.swansea.ac.uk/media/West-Africa-A-New-Front-in-a-Losing-War.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Terminology and Information on Drugs; United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC): New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Terminology_and_Information_on_Drugs-E_3rd_edition.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Aslam, N. Drug Addiction, Criminality and Birth Order. J. Alcohol Drug Depend. 2014, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aaltonen, M.; Kivivuori, J.; Martikainen, P. Social Determinants of Crime in a Welfare State: Do They Still Matter? Acta Sociol. 2011, 54, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjeruldsen, S.R.; Myrvang, B.; Opjordsmoen, S. Criminality in Drug Addicts: A Follow-Up Study over 25 Years. Eur. Addict. Res. 2004, 10, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Health & Human Services. Facing Addiction in America. The Surgeon General’s Report on Alcohol, Drugs and Health; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell, M.; Bachand, A.; Peel, J.; Brown, M. Familial, Social, and Individual Factors Contributing to Risk for Adolescent Substance Use. J. Addict. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odejide, A.O. Status of Drug Use/Abuse in Africa: A Review. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2006, 4, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsdóttir, H.; Bragadóttir, R. Crime and Criminal Policy in Iceland: Criminology on the Margins of Europe. Eur. J. Criminol. 2006, 3, 221–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervishi, E.; Ibrahimi, S. Risk Factors Related to Juvenile Drug Use. OJPR 2018, 2, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.A.; Joe, G.W.; Dwayne Simpson, D. Prediction of Long-Term Alcohol Use, Drug Use, and Criminality among Inhalant Users. Hisp. J. Behav. Sci. 1991, 13, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Keenan, K.; Tremblay, R.E.; Coie, J.D.; Herrenkohl, T.I.; Loeber, R.; Petechuk, D. Risk and Protective Factors of Child Delinquency. 2003. Available online: https://www.ojp.gov/pdffiles1/ojjdp/193409.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Cocaine Trafficking in West Africa. The Threat to Stability and Development (with Special Reference to Guinea-Bissau); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/data-and-analysis/West%20Africa%20cocaine%20report_10%2012%2007.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- United Nations Development Programme. Human Development Report 2020. The Next Frontier Human Development and the Anthropocene; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2020.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Chabal, P.; Green, T. Guinea-Bissau. Micro-State to “Narco-State”; Hurst & Company: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fragile States Index. Country Dashboard. 2021. Available online: https://fragilestatesindex.org/country-data/ (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Crundall, I.A. Student Perceptions of the Danger of Drug Use: A Factor Analysis. J. Drug Educ. 1992, 22, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIA. Guinea-Bissau—The World Factbook. 2021. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/guinea-bissau/#people-and-society (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- United Nations Children’s Fund. Education. 2021. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/guineabissau/education (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Kristjánsson, A.L.; Mann, M.J.; Sigfússon, J.; Thorisdóttir, I.E.; Allegrante, J.P.; Sigfúsdóttir, I.D. Implementing the Icelandic Model for Preventing Adolescent Substance Use. Health Promot. Pract. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prichard, J.; Payne, J. Alcohol, Drugs and Crime: A Study of Juveniles in Detention; Research and Public Policy Series: No. 67; Australian Institute of Criminology: Canberra, Australia, 2005; Available online: https://www.aic.gov.au/sites/default/files/2020-05/rpp067.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Webster, C. Predicting Criminality? Risk Factors, Neighbourhood Influence and Desistance. Youth Justice 2006, 6, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM. Pooled Results Not Produced for R-Square and SEE Values with Multiple Imputation. 2021. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/support/pages/pooled-results-not-produced-r-square-and-see-values-multiple-imputation (accessed on 24 March 2021).
- United Nations Children’s Fund. Convention on the Rights of the Child Text. 2021. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/child-rights-convention/convention-text (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Einarsdóttir, J. Tired of Weeping: Mother Love, Child Death, and Poverty in Guinea-Bissau, 2nd ed.; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-299-20134-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnlaugsson, G.; Whitehead, T.A.; Baboudóttir, F.N.; Baldé, A.; Jandi, Z.; Boiro, H.; Einarsdóttir, J. Use of Digital Technology among Adolescents Attending Schools in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, S.; Vlahov, D. Social Determinants and the Health of Drug Users: Socioeconomic Status, Homelessness, and Incarceration. Public Health Rep. 2002, 117, 135–145. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1913691/ (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation. Guinea-Bissau: Education and Literacy. 2021. Available online: http://uis.unesco.org/en/country/gw (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Sachsida, A.; de Mendonça, M.J.C.; Loureiro, P.R.A.; Gutierrez, M.B.S. Inequality and Criminality Revisited: Further Evidence from Brazil. Empir. Econ. 2010, 39, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of State. Guinea-Bissau 2018 Human Rights Report Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2018. Available online: https://www.state.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Guinea-Bissau-2018.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- United Nations Children’s Fund. Republic of Guinea Bissau Executive Summary. 2017. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/about/annualreport/files/Guinea_Bissau_2017_COAR.PDF (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Aguirre-Molina, M.; Gorman, D.M. Community-Based Approaches for the Prevention of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drug Use. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1996, 17, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, J.; Babor, T.; Caulkins, J.; Fischer, B.; Foxcroft, D.; Humphreys, K. Drug Policy and the Public Good: Evidence for Effective Interventions. Lancet 2012, 379, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C.B.; White, H.R.; Catalano, R.F. Romantic Relationships and Substance Use in Early Adulthood: An Examination of the Influences of Relationship Type, Partner Substance Use, and Relationship Quality. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2010, 51, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodin, M.C.; Strandberg, A.K. The Örebro Prevention Programme Revisited: A Cluster-Randomized Effectiveness Trial of Programme Effects on Youth Drinking. Addiction 2011, 106, 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, I.M.; van den Eijnden, R.J.; Verdurmen, J.E.; Engels, R.C.; Vollebergh, W.A. Long-Term Effects of a Parent and Student Intervention on Alcohol Use in Adolescents: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 40, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armiya’u, A.Y. Topic: Drug Abuse and Crime in West Africa. What Prospects? Drugs West Afr. Insight 2015, 4, 3–10. Available online: https://cddelibrary.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/West%20Africa%20Insight%20edition%20on%20Drugs%202015.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- International Centre for the Prevention of Crime. Prevention of Drug-Related Crime Report. 2015. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/ungass2016/Contributions/Civil/ICPC/Rapport_FINAL_ENG_2015.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Slutkin, G.; Ransford, C.; Decker, R.B. Cure violence: Treating violence as a contagious disease. In Envisioning Criminology: Researchers on Research as a Process of Discovery; Maltz, M.D., Rice, S.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
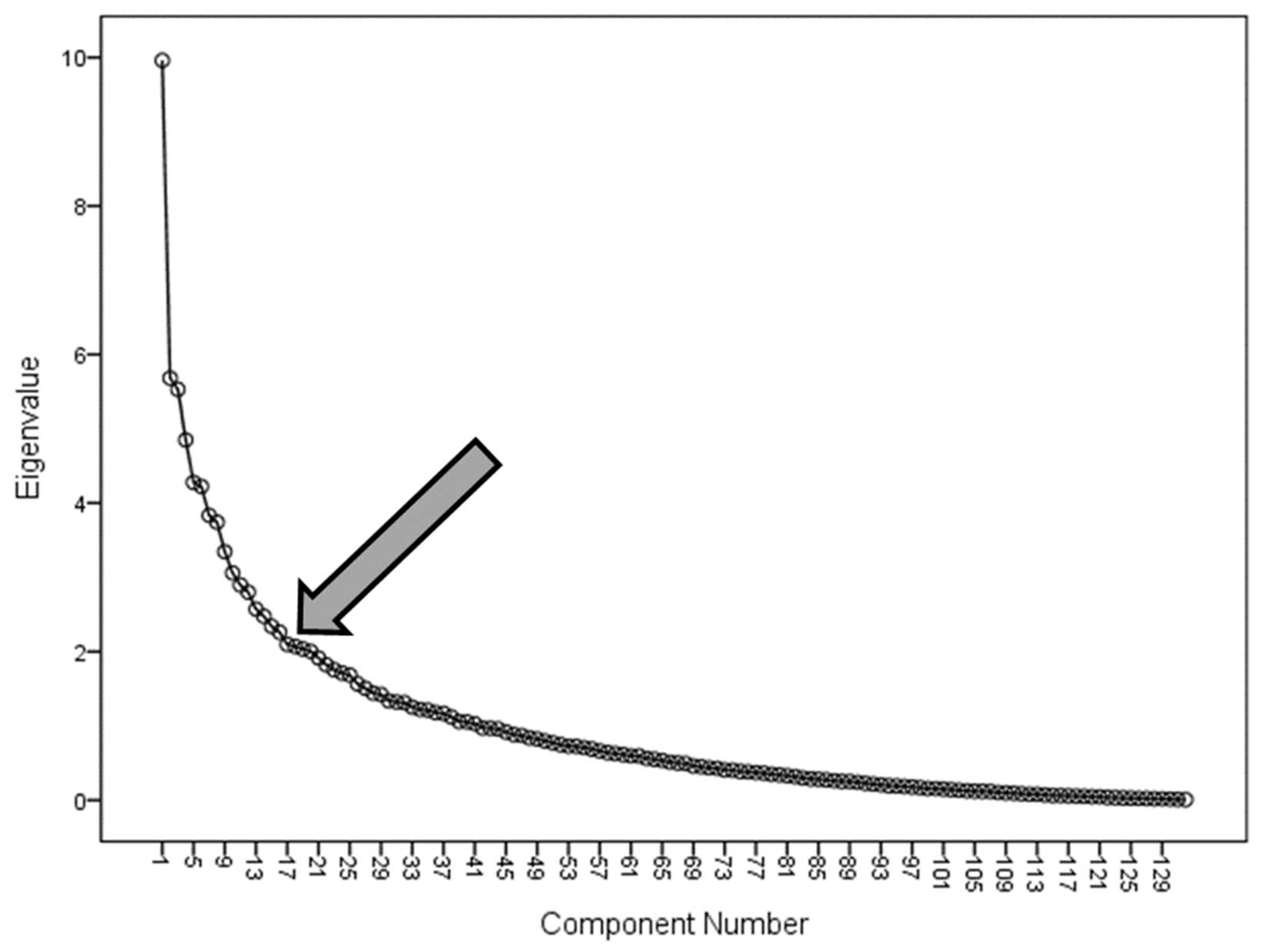
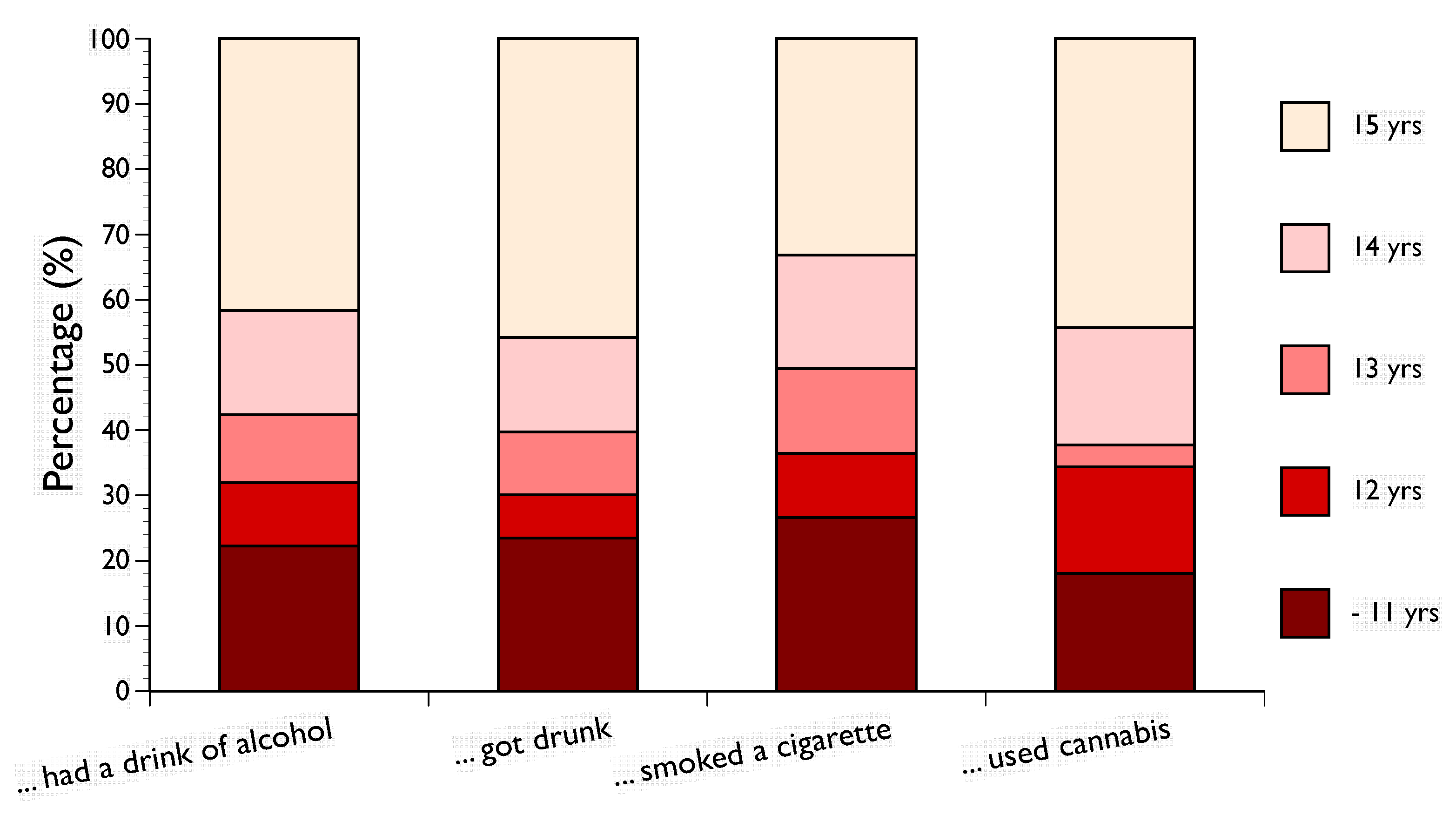
| Variable | Component |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| Q72a. How many of your friends do the following? Smoke cigarettes | 0.857 |
| Q72b. How many of your friends do the following? Drink alcohol | 0.836 |
| Q72c. How many of your friends do the following? Become drunk at least once a month | 0.801 |
| Q72d. How many of your friends do the following? Smoke hash or marijuana | 0.731 |
| Q72e. How many of your friends do the following? Fight with somebody | 0.532 |
| Q72f. How many of your friends do the following? Pick fights or search out fights | 0.502 |
| Q64b. At what age (if ever) did you do the following for the first time? Got drunk | 0.482 |
| Q55. How often have you smoked cigarettes in your lifetime? | 0.450 |
| Q66f. How often have you done the following in the last 12 months? Committed another offence | 0.402 |
| Q61a. How often have you had an alcoholic drink of any kind? In your lifetime | 0.448 |
| Q64e. At what age (if ever) did you do the following for the first time? Used cannabis (hash/marijuana) | 0.317 |
| Variable | Total (%) | Boy (%) | Girl (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q25c. How many whole days have you been absent from school during the last 30 days for other reasons [than (a) because of illness and (b) you “skipped” or “cut” classes]? | |||
| None/Never | 606 (49) | 325 (50) | 281 (49) |
| 1 day | 326 (27) | 169 (26) | 157 (27) |
| 2 days | 182 (15) | 94 (14) | 88 (15) |
| 3–4 days | 53 (4) | 33 (5) | 20 (3) |
| 5–6 days | 20 (2) | 10 (2) | 10 (2) |
| 7 days or more | 40 (3) | 20 (3) | 20 (3) |
| Total | 1227 (100) | 651 (100) | 576 (100) |
| Q47k. Have you ever experienced a breakup with a boyfriend/girlfriend? | |||
| Yes, during the last 30 days | 246 (15) | 119 (15) | 127 (16) |
| Yes, during the last 12 months | 212 (13) | 109 (14) | 103 (13) |
| Yes, more than 12 months ago | 203 (13) | 112 (14) | 91 (11) |
| Never | 937 (59) | 451 (57) | 486 (60) |
| Total | 1598 (100) | 791 (100) | 807 (100) |
| Q47p. Have you ever been dismissed from class or sent to the disciplinary board? | |||
| Yes, during the last 30 days | 121 (8) | 63 (8) | 58 (7) |
| Yes, during the last 12 months | 73 (5) | 40 (5) | 33 (4) |
| Yes, more than 12 months ago | 93 (6) | 59 (7) | 34 (4) |
| Never | 1304 (82) | 633 (80) | 671 (84) |
| Total | 1591 (100) | 795 (100) | 796 (100) |
| Q67a. Have you been a victim of physical violence during the last 12 months? | |||
| Never | 1498 (84) | 719 (82) | 779 (85) |
| Once | 211 (12) | 109 (13) | 102 (11) |
| 2 to 5 times | 47 (3) | 29 (3) | 18 (2) |
| 6 to 9 times | 12 (0.7) | 8 (1) | 4 (0.4) |
| 10 to 13 times | 6 (0.3) | 2 (0.2) | 4 (0.4) |
| 14 to 17 times | 4 (0.2) | 3 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) |
| 18 times or more | 9 (0.5) | 4 (0.5) | 5 (0.5) |
| Total | 1787 (100) | 874 (100) | 913 (100) |
| Q69f. How often, during the last 12 months, have you been in a group that was attacked by another group? | |||
| Never | 1425 (86) | 700 (87) | 725 (87) |
| Once | 141 (9) | 70 (9) | 71 (9) |
| Twice | 36 (2) | 21 (3) | 15 (2) |
| 3 to 4 times | 13 (1) | 9 (1) | 4 (1) |
| 5 times or more | 33 (2) | 17 (2) | 16 (2) |
| Total | 1648 (100) | 817 (100) | 831 (100) |
| Imputation Number | Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Change Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R Square Change | F Change | df1 | df2 | Sig. F Change | ||||||
| Original data | 1 | 0.767 a | 0.589 | 0.526 | 0.41371 | 0.589 | 9.472 | 45 | 298 | 0.000 |
| 1 | 1 | 0.775 b | 0.601 | 0.592 | 0.46255 | 0.601 | 66.779 | 45 | 1993 | 0.000 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.769 c | 0.592 | 0.582 | 0.46185 | 0.592 | 64.135 | 45 | 1993 | 0.000 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.764 d | 0.584 | 0.575 | 0.45911 | 0.584 | 62.276 | 45 | 1993 | 0.000 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.766 e | 0.587 | 0.578 | 0.45816 | 0.587 | 62.996 | 45 | 1993 | 0.000 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.761 f | 0.578 | 0.569 | 0.46502 | 0.578 | 60.781 | 45 | 1993 | 0.000 |
| Variable | Total (%) | Boy (%) | Girl (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q1. Are you a boy or a girl? | |||
| 1978 (100) | 954 (48) | 1024 (52) | |
| Q2. How old are you? (years) | |||
| 14 | 130 (7) | 55 (6) | 75 (8) |
| 15 | 346 (19) | 166 (19) | 180 (19) |
| 16 | 435 (24) | 194 (22) | 241 (26) |
| 17 | 581 (32) | 305 (35) | 276 (29) |
| 18 | 288 (16) | 139 (16) | 149 (16) |
| 19+ | 45 (2) | 22 (3) | 23 (2) |
| Total | 1825 (100) | 881 (100) | 944 (100) |
| Q3. Grade/Class in school | |||
| 7th grade 8th grade | 40 (2) 757 (39) | 19 (2) 354 (38) | 21 (2) 403 (40) |
| 9th grade | 908 (47) | 442 (48) | 466 (47) |
| 10th grade | 224 (12) | 112 (12) | 112 (11) |
| Total | 1929 (100) | 927 (100) | 1002 (100) |
| Type of school | |||
| Public | 1033 (52) | 530 (56) | 503 (49) |
| Private | 945 (48) | 424 (44) | 521 (51) |
| Total | 1978 (100) | 954 (100) | 1024 (100) |
| Q5Q7. Both parents educated | |||
| Neither parent educated | 604 (36) | 298 (37) | 306 (34) |
| One parent educated | 538 (32) | 277 (34) | 261 (29) |
| Both parents educated | 553 (32) | 231 (29) | 322 (36) |
| Total | 1695 (100) | 806 (100) | 889 (100) |
| Q9Q10. Both parents work outside of the home | |||
| Neither parent outside the home | 283 (15) | 146 (16) | 137 (14) |
| One parent works outside the home | 844 (45) | 408 (45) | 436 (45) |
| Both parents work outside the home | 751 (40) | 351 (39) | 400 (41) |
| Total | 1878 (100) | 905 (100) | 973 (100) |
| Unstandardised Coefficients | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval for B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| (Constant) | 0.425 | 0.236 | 1.800 | 0.074 | −0.041 | 0.890 |
| Economic crime | 0.171 | 0.033 | 5.174 | 0.000 | 0.102 | 0.240 |
| Violent crime | 0.059 | 0.016 | 3.671 | 0.000 | 0.027 | 0.091 |
| Cannabis risk perception | 0.000 | 0.008 | −0.019 | 0.985 | −0.016 | 0.015 |
| Parental oversight | 0.042 | 0.015 | 2.731 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.072 |
| Drinking | 0.395 | 0.015 | 25.559 | 0.000 | 0.364 | 0.426 |
| Age | −0.003 | 0.010 | −0.281 | 0.779 | −0.023 | 0.017 |
| Gender | −0.061 | 0.023 | −2.695 | 0.007 | −0.106 | −0.017 |
| A breakup with a boyfriend/girlfriend | −0.035 | 0.010 | −3.491 | 0.001 | −0.055 | −0.015 |
| Been dismissed from class, or sent to the disciplinary board | −0.048 | 0.018 | −2.705 | 0.016 | −0.086 | −0.010 |
| Been a victim of physical violence during the last 12 months | 0.072 | 0.019 | 3.760 | 0.001 | 0.033 | 0.112 |
| Been in a group that was attacked by another group during the last 12 months | 0.094 | 0.019 | 4.836 | 0.000 | 0.055 | 0.133 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bollom, J.E.; Baldé, A.; Jandi, Z.; Boiro, H.; Einarsdóttir, J.; Gunnlaugsson, G. Social Determinants of Narcotics Use Susceptibility among School-Attending Adolescents in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Adolescents 2021, 1, 306-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/adolescents1030023
Bollom JE, Baldé A, Jandi Z, Boiro H, Einarsdóttir J, Gunnlaugsson G. Social Determinants of Narcotics Use Susceptibility among School-Attending Adolescents in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Adolescents. 2021; 1(3):306-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/adolescents1030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleBollom, Jon Edmund, Aladje Baldé, Zeca Jandi, Hamadou Boiro, Jónína Einarsdóttir, and Geir Gunnlaugsson. 2021. "Social Determinants of Narcotics Use Susceptibility among School-Attending Adolescents in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau: A Cross-Sectional Analysis" Adolescents 1, no. 3: 306-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/adolescents1030023
APA StyleBollom, J. E., Baldé, A., Jandi, Z., Boiro, H., Einarsdóttir, J., & Gunnlaugsson, G. (2021). Social Determinants of Narcotics Use Susceptibility among School-Attending Adolescents in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Adolescents, 1(3), 306-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/adolescents1030023








