Abstract
Glycine receptors (GlyRs) are essential for inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system (CNS) and represent promising targets against neurological disorders. Several indole alkaloids from Gelsemium species have been shown to modulate GlyRs. Notably, the anxiolytic and analgesic properties of certain Gelsemium alkaloids appear to depend on GlyR modulation. However, prior studies have focused on only a few indole alkaloids, leaving the activity of other Gelsemium compound classes unexplored. This study employed an integrative in silico approach to investigate the interactions between GlyR α1 and α3 subtypes and 162 structurally diverse Gelsemium compounds. Physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, and toxicological analyses identified compounds with favorable bioavailability in the CNS. Molecular docking revealed that indolic alkaloids bind the GlyR orthosteric site with profiles comparable to the reference Gelsemium compound, gelsemine. Molecular dynamics simulations confirmed the stability and conformational integrity of selected ligand-receptor complexes. Overall, novel potential GlyR modulators were identified, with several compounds showing a promising selectivity profile towards GlyR α1 and α3 subtypes. These findings further support the therapeutic potential of Gelsemium alkaloids and provide a foundation for further pharmacological and toxicological validation.
1. Introduction
Gelsemium species, belonging to the family Loganiaceae, comprise five known species endemic to North America and East Asia. These plants have long held a prominent place in traditional Asian medicine, where their extracts have been used for centuries to treat a variety of conditions, particularly pain, sciatica, and inflammatory disorders [1,2,3,4]. The ethnomedicinal use of Gelsemium is especially well documented in central and southeastern China, where its pharmacological effects were harnessed through traditional remedies [5,6].
Phytochemical investigations have attributed the therapeutic properties of Gelsemium to a structurally diverse array of natural products [3]. To date, over 100 compounds have been isolated from the genus. The indole alkaloids gelsemine, koumine, gelsevirine, and gelsenicine (also known as humantenmine) have been consistently identified as the four major constituents [7]. Despite their pharmacological potential, these compounds exhibit significant toxicity in mammals, particularly affecting the central nervous system (CNS). Adverse effects include respiratory depression, convulsions, and, in severe cases, asphyxia and death [8].
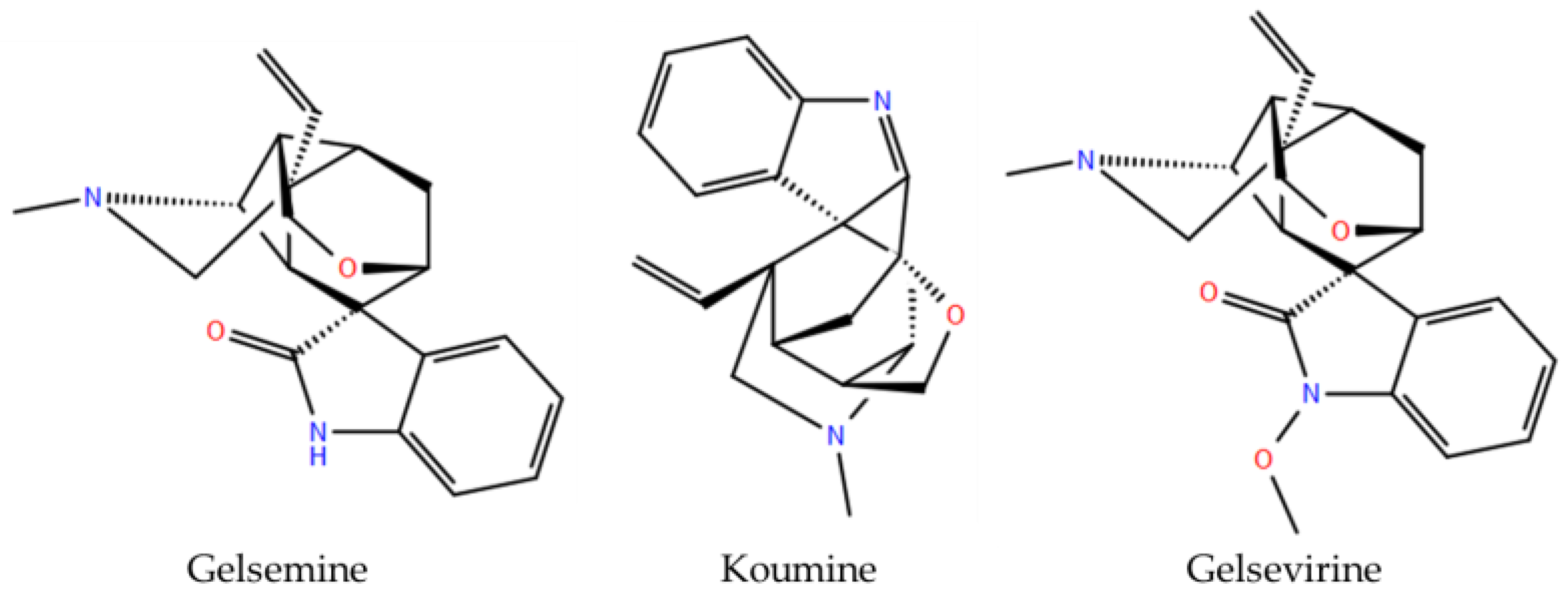
The molecular targets underlying both the medicinal and toxic effects of Gelsemium alkaloids remain largely undefined. However, functional studies have demonstrated that gelsemine modulates inhibitory glycine receptors (GlyRs), a key neurotransmitter-gated channel regulating CNS excitability. Gelsemine exhibits concentration-dependent negative modulatory effects on most subtypes of GlyRs [9,10,11]. These effects are primarily explained by competitive inhibition and molecular interactions at the orthosteric binding sites [9,12]. In addition to gelsemine, the indole alkaloids koumine and gelsevirine also show activity on GlyRs (Figure 1), while gelsenicine did not exhibit any detectable functional effects [12]. These observations propose that structurally related Gelsemium alkaloids possess diverse modulatory profiles on GlyRs, suggesting that other uncharacterized compounds derived from these natural sources may display subunit selective actions on different GlyR subtypes. Alterations in glycinergic inhibition, arising from either genetic mutations or post-translational modifications of GlyR subunits, underlying pathologies such as hyperekplexia, epilepsy, autism, and chronic pain. Consequently, the development of subunit-selective compounds may provide valuable research tools and foster innovative therapeutic strategies [13,14,15,16,17,18].
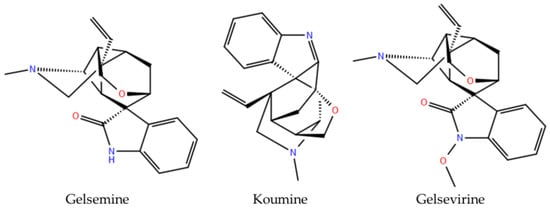
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of Gelsemium alkaloids functionally validated as modulators of glycine receptor.
As the experimental evaluations discussed above have been performed on the four major Gelsemium alkaloids, the potential target interactions and pharmacological potential of other phytochemicals generated by these plants with GlyRs remain majorly unexplored. This knowledge gap hinders a comprehensive pharmacological and toxicological evaluation of Gelsemium bioactive constituents. In particular, in silico assessment of minor components, such as iridoids, terpenes, sterols, glycosides, and flavonoids, may yield novel insights into their pharmacological potential on GlyRs and on other biological CNS targets. Recent advances in structure-based modeling, large-scale virtual screening, and physics-based simulations further accelerate hit identification, reduce costs, and enhance binding predictions, thereby streamlining early-stage discovery and guiding focused in vitro and in vivo validation with greater precision [19].
The present study aims to systematically investigate whether 162 Gelsemium related compounds can interact with the orthosteric site of GlyR α1 and α3 subtypes. Physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, and toxicological analyses identified compounds with favorable bioavailability in the CNS. These studies showed, for example, that 50.5% of the indolic compounds (46 out of 91) were predicted to be permeable to the blood–brain barrier, but conversely, only 21.1% (15 out of 71) of the non-indolic molecules were classified as permeable. Molecular docking revealed that many Gelsemium alkaloids potentially bind the GlyR orthosteric site. Indolic compounds preferentially bind to the closed state of the channel, but the non-indolic molecules show a more diverse profile for both open and close conformations. A total of 34 indolic and 24 non-indolic compounds showed the most favorable docking scores (i.e., <−8.0 kcal/mol) to the closed confirmation of α1GlyRs. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations confirmed the stability and conformational integrity of 3 reference indole alkaloids with confirmed functional activity on GlyRs and 5 selected compounds forming promising in silico ligand-receptor complexes. Mostly all these compounds display RMSD values lower than 6 Å along the 200 ns of simulation, suggesting the formation of stable interactions with the orthosteric site. By integrating these datasets, we selected novel compounds with promising selectivity profiles towards specific GlyR subtypes for further experimental validation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Library Preparation
To investigate the potential interactions between Gelsemium compounds and GlyRs, a total of 162 structurally diverse molecules were selected based on the comprehensive review by Jin et al. [3]. These compounds represent a wide array of phytochemical compound classes naturally occurring in the Gelsemium genus. Structural data was obtained from public repositories including PubChem [20] and ChEMBL [21].
All Gelsemium-derived compounds included in this study were categorized into two primary groups, indole and non-indole alkaloids (Table 1). All indole-type Gelsemium alkaloids share a conserved tetracyclic indole core that provides a rigid polycyclic framework enriched in nitrogen and frequent oxygen substituents. Across all groups, oxidation at positions such as C14, C15, or C19 is common, often producing hydroxyl, methoxy, or N-oxide derivatives. This conserved architecture confers a three-dimensional character and supports diverse stereochemistry while maintaining the fundamental indolic scaffold. Within this shared backbone, each structural group exhibits distinctive modifications. Gelsedine-type (GS, n = 33) compounds possess a tetracyclic indole fused to a highly oxidized, rearranged cyclopentane ring, frequently showing oxygenated groups and sometimes incorporating an additional nitrogen or strained oxazolidine ring. Gelsemine-type (GM, n = 9) alkaloids feature a rigid cage-like tetracycle with a cyclopropane bridge between the indole and piperidine rings, commonly oxidized at C19 or at tertiary amine. Humantenmine-type (HT, n = 24) molecules lack this cyclopropane, instead incorporating an extra six-membered ring and extensive oxygenation, providing greater conformational flexibility. Koumine-type (KO, n = 10) alkaloids are defined by a distinctive pentacyclic cage, to which an additional furan ring may be fused, and they generally lack extensive oxygen-based functional groups. Sarpagine-type (SA, n = 12) members retain a polycyclic azabicyclo[3.3.1]-nonane core, with diversity introduced by dehydration, hydroxylation, or stereochemical variation at C19. Finally, Yohimbane-type (YO, n = 3) derivatives present the most compact architecture, a planar pentacyclic yohimbane skeleton that contrasts with the more open frameworks of the other subgroups. This combination of a conserved indole core with subgroup-specific rearrangements highlights both the chemical cohesion and remarkable diversity of Gelsemium alkaloids [2,3,22,23].

Table 1.
List of indole-type and non-indole compounds derived from Gelsemium plants, organized by structural classification into specific chemical subgroups.
The non-indole compounds lack the indole core but share high oxygenation, frequent hydroxyl or methoxy substitutions, and a strong tendency toward glycosylation, which enhances polarity and solubility. Within this profile, each group exhibits distinct structural hallmarks. Iridoids (IR, n = 25) are monoterpenoids built on a cyclopentane iridoid skeleton, almost always present as glycosides and further diversified by hydroxylation or esterification. Megastigmane glycosides (MG, n = 6) derive from C13 nor-isoprenoids formed by carotenoid degradation, with a cyclohexane core and diglycosidic linkages that strongly influence solubility and activity. Steroids (ST, n = 7) possess the classical tetracyclic sterane framework of three fused cyclohexane rings and a cyclopentane, occurring as pregnane derivatives lacking the sterol side chain or as phytosterols with a full alkyl side chain. Lignin–Phenolic acids–Flavonoids (LPF, n = 16) encompass polyphenolic metabolites, including lignans linked through their side-chain carbons, simple phenolic acids with C6–C1 or C6–C3 skeletons (often as esters), and flavonoids composed of two aromatic rings joined by a heterocyclic pyran ring. Coumarin–Terpenoid–Fructose and its derivatives (CTF, n = 9) combine benzopyrone-based coumarins, one ursane-type terpenoid with a carboxylic acid, a hydroxy group, and an esterification, and alkylated fructose derivatives, which are fructofuranose and fructopyranose sugars bearing alkyl groups. Finally, the other type (OT, n = 8) group is chemically heterogeneous, containing unique structures such as the highly rearranged, cage-like alkaloid gelsenine, primary metabolites like uridine, fatty acid esters such as 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl heptadecanoate, plasticizers like bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, and rare peroxide-bridged gelebolines. This classification highlights a common foundation of oxygenated secondary metabolites while underscoring an important structural diversity of the non-indole Gelsemium compounds [24,25,26,27,28,29]. The full set of compound structures is available in Supplementary Table S1.
All selected Gelsemium compounds were prepared using LigPrep (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, USA). The preparation protocol involved generating the appropriate ionization states at pH 7.0 ± 0.2 using the Epik tool (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, USA), the prediction of structures of tautomers, stereoisomers, and protonation states. All molecules were energy-minimized using the OPLS4 force field (Schrödinger 2024, NY, USA) to ensure accurate geometrical optimization and chemical consistency.
2.2. ADMET and Toxicologic Profiling Gelsemium Compounds
A comprehensive in silico assessment of the physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, toxicological, and drug-likeness properties of the 162 Gelsemium compounds was carried out using three predictive platforms. The main physicochemical descriptors were obtained using QikProp (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, USA), including molecular weight, predicted lipophilicity (WlogP), and aqueous solubility (logSw). Oral absorption potential was assessed using SwissADME [30] and pkCSM [31], focusing on gastrointestinal absorption classifications and predicted human oral absorption percentages (PHOA). To further characterize drug-likeness and oral bioavailability, Lipinski’s Rule of Five (LIP) and Veber’s Rules (VEB) were applied [32,33]. Blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability was estimated using QPlogBB values obtained from QikProp, where values ranging from −3.0 to +1.2 indicate limited but possible permeability across the BBB. An additional indicator of CNS penetration was the predicted central nervous system activity score, where values between 0 and +2.0 suggest effective CNS accessibility. Potential interactions with the main human cytochrome P450 isoforms—CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, were predicted using SwissADME and pkCSM [30,31]. Compounds were classified based on their likelihood of acting as substrates or inhibitors of these enzymes. This analysis was used to anticipate metabolic stability and the risk of drug–drug interactions [34]. Total body clearance values were predicted using pkCSM, providing an estimate of the rate at which each compound would be eliminated from systemic circulation. Compounds with extremely low predicted clearance values should be deprioritized due to their potential for prolonged retention or toxicity [35]. Predictions for the potential toxicological risks associated with the Gelsemium compounds were performed using pkCSM-Pharmacokinetics, focusing on three clinically relevant endpoints: AMES mutagenicity, hERG channel inhibition, and drug-induced liver injury (DILI) [36]. Compounds predicted to be negative for all three endpoints were considered safer candidates for further computational and experimental validation.
2.3. Protein Selection and Preparation
The three-dimensional structures of GlyRs α1β and α3 were obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). For GlyR α1β, the open and closed conformations were retrieved from Danio rerio using PDB IDs 7TVI and 7TU9 [37], respectively. For GlyR α3, the open and closed structures were selected from Homo sapiens using PDB IDs 5TIO and 5CFB [38,39]. All protein structures were prepared using the Protein Preparation Wizard in Maestro (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, USA), which included bond order assignment, addition of hydrogens, optimization of side chains and hydrogen bonding networks, and restrained minimization under the OPLS4 force field [40]. Water molecules beyond 5 Å from the binding site were removed unless they were involved in ligand interactions.
2.4. Protein-Ligand Docking
Receptor grids were generated using Glide (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, USA) for both open and closed states of GlyR α1β and α3. Grid boxes were placed on the orthosteric binding site. In all cases, a cubic grid box of 15 × 15 × 15 Å was defined. Docking was performed using Glide under extra precision (XP) configuration. All complexes were evaluated using an empirical scoring function known as docking score, which integrates energetic and structural components relevant to molecular recognition. The best-ranked poses were selected based on docking score and visual inspection of key binding interactions with known functional residues. The docking protocol was validated by redocking strychnine or glycine into its respective binding site in the prepared GlyR α1β and α3 structures, resulting in RMSD values below 2.0 Å, thus confirming the accuracy of the docking setup.
To estimate the binding affinity of selected Gelsemium compounds toward glycine receptors, MM-GBSA (Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area) calculations were performed using Prime (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, USA). These calculations were applied directly to the best-ranked docking poses, selected based on docking score and key interaction criteria. All structures were treated as rigid during MM-GBSA energy evaluation. Calculations were performed using the OPLS4 force field and the Generalized Born (GB) solvation model. These ∆G bind values were used as an initial estimate of binding affinities and to prioritize compound–receptor complexes for subsequent molecular dynamics simulations [40,41]. Conceptually, docking scores represent the predicted binding affinities of a compound for a specific protein binding site, whereas ∆Gbind values denote the Gibbs free energy associated with the formation of each ligand–protein complex. Quantitatively, more negative values indicate a more favorable binding capacity, reflecting a potential stronger and more stable ligand–protein interaction. Based on these principles, we ranked the Gelsemium compounds according to their docking scores, as we consider this parameter a more reliable descriptor of the stability of a molecule within a protein binding site [19,41].
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
To evaluate the dynamic stability and interaction profiles of selected Gelsemium compounds with glycine receptors, MD simulations were conducted using Desmond (Schrödinger 2024, New York, NY, 2024). Protein–ligand complexes involving GlyR α1β and α3, previously selected based on docking scores, were embedded in a hydrated lipid bilayer model and simulated under physiologically relevant conditions. The system was embedded in a POPE lipid bilayer and solvated using the SPC model. To maintain electrostatic neutrality, 0.15 M NaCl was added. The system underwent a relaxation phase involving a 20 ns restrained simulation, where harmonic positional restraints of 10 kcal/mol·Å2 were applied to the protein backbone and ligand atoms. Following this, all restraints were removed, and production simulations were carried out for 200 ns under semi-isotropic NPT ensemble conditions, with temperature maintained at 300 K using the Nosé–Hoover chain thermostat and pressure set at 1.01325 bar using the Martyna–Tobias–Klein barostat. The OPLS4 force field was used throughout. Trajectory data were collected over the full simulation time, and quantitative analyses including RMSD and RMSF were calculated. We also summarize parameters like the residue contact profiles and ligand–receptor interaction fingerprints.
3. Results
3.1. Pharmacokinetic and Toxicological Profile of Gelsemium Compounds
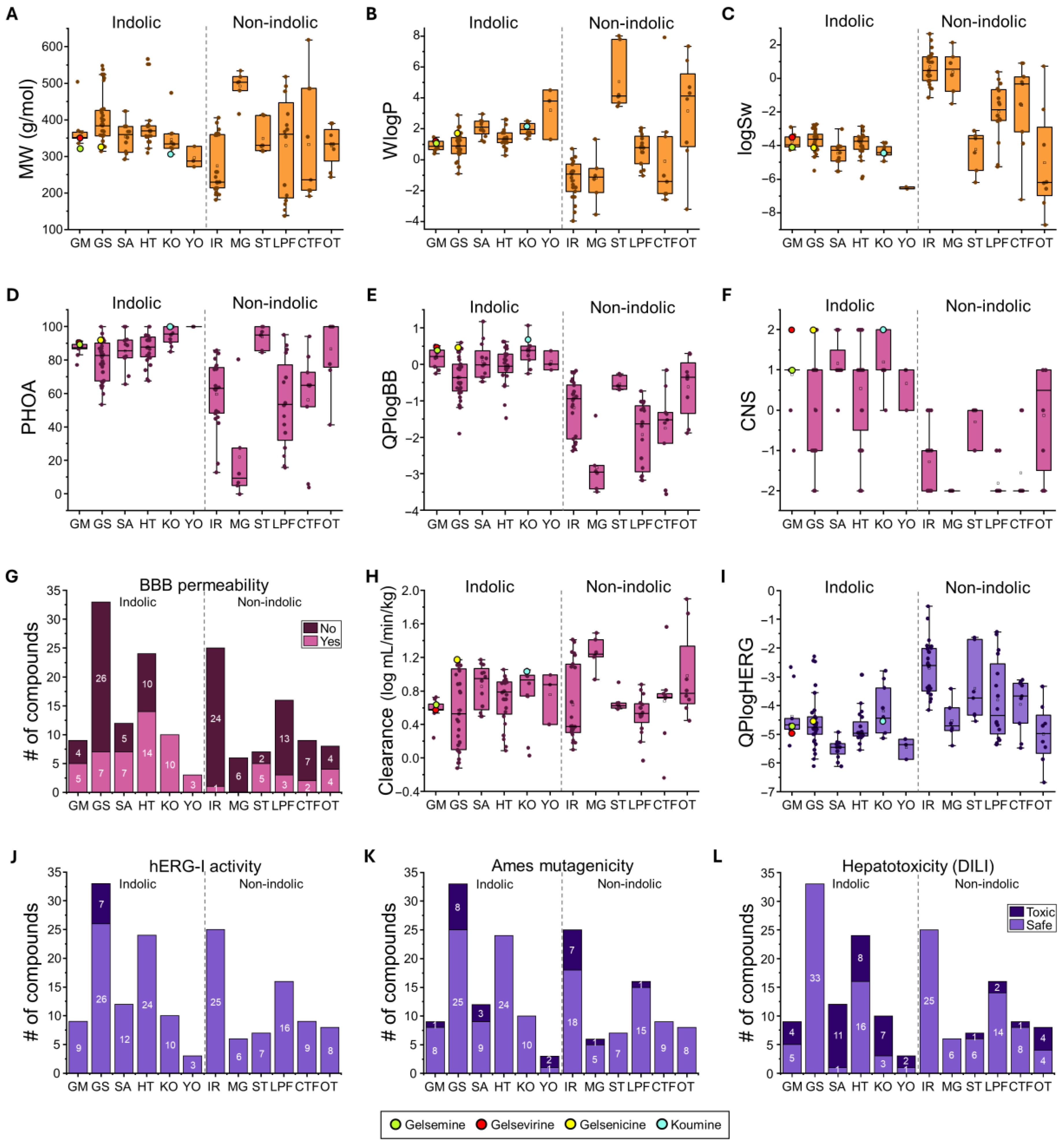
To characterize the pharmacokinetic behavior and potential toxicological actions of Gelsemium compounds, we start our analysis by characterizing the four major indole Gelsemium alkaloids (i.e., gelsemine, koumine, gelsevirine, and gelsenicine). These reference molecules are highlighted in Figure 2, to facilitate comparisons with other less characterized Gelsemium derivatives (gelsemine (green), gelsevirine (red), gelsenicine (yellow), and koumine (cyan)). These compounds exhibited molecular weights ranging from 306 to 352 g/mol, consistent with polyhydroxylated structures (Figure 2A). The predicted lipophilicity (WLogP) of these molecules spanned from 1.08 to 2.17, while aqueous solubility (LogS) ranged between −4.42 and −3.48. These properties suggest moderate hydrophobic character and limited solubility (Figure 2B,C). Oral absorption was uniformly high (89–100%) across these compounds, with no violations of Lipinski’s or Veber’s rules (Figure 2D). Blood–brain barrier permeability (QPlogBB) values ranged 0.414 to 0.701, and the CNS activity scores were between 1 and 2 (Figure 2E,F). In terms of metabolism, most of these compounds were predicted to inhibit CYP2D6. Interestingly, this analysis indicates that koumine may also inhibit CYP1A2, whereas gelsenicine inhibits CYP3A4 (Supplementary Table S2). These results are in line with previous reports [42,43]. The predicted clearance values ranged from 0.638 to 1.174 Log mL/min/kg. In silico toxicity profiling (AMES, DILI, hERG I) did not detect potential genotoxic or cardiotoxic liabilities for gelsenicine and gelseverine, while gelsemine and koumine were predicted to be hepatotoxic.
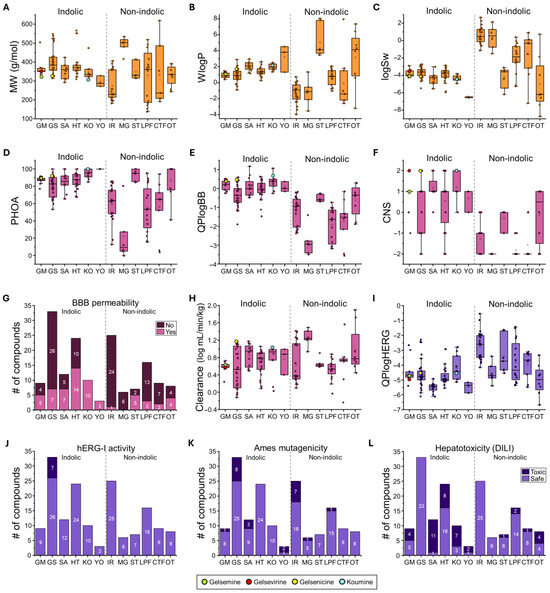
Figure 2.
ADMET properties of Gelsemium compounds. Summary of physicochemical (orange), pharmacokinetic (magenta), and toxicological (purple) properties for the indolic and non-indolic groups of Gelsemium compounds. Panels include box plots (A–F,H,I) and bar graphs (G,J–L) representing key descriptors: (A). Molecular weight (MW), (B). Water partition coefficient (WlogP), (C). Water solubility (logSw), (D). Percentage of human oral absorption (PHOA), (E). Brain-to-blood partition coefficient (QPlogBB), (F). Central nervous system activity (CNS), (G). Blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability, (H). Total clearance (logCLtot), (I). Predicted IC50 for hERG K+ channel blockage (QPlogHERG), (J). hERG inhibition, (K). AMES toxicity, and (L). Drug-induced liver injury (DILI). Highlighted values correspond to gelsemine (green), gelsevirine (red), gelsenicine (yellow), and koumine (cyan). The boxed graphs (A–F,H–I) display the parameter values for each compound (dots), with group medians indicated by the central line, interquartile ranges (25–75%) by the box borders, and whiskers representing the minimum and maximum values within each group. The histograms (G,J–L) illustrate the distribution of compounds across groups.
The physicochemical analysis of the whole indole-type group (n = 91) revealed a relatively narrow distribution of molecular weights, ranging from 272 g/mol (Sempervirine, from the YO group) to 566 g/mol (Humantenidine, from the HT group). Calculated WLogP values ranged from 0.29 (Rankiniridine from the HT group) to 4.52 (Sempervirine, from the YO group). Interestingly, the koumine group exhibited an elevated average lipophilicity (1.99 ± 0.12, n = 10). Predicted solubility values (LogSw) were uniformly low (−4.23 ± 0.11, n = 91), with YO displaying the lowest solubility (>−6.45 in all cases) and GM and KO groups showing similar average values (GM = −3.73 ± 0.15, n = 9; KO = −4.35 ± 0.12, n = 10) (Figure 2B,C and Supplementary Table S2). These findings suggest that indole-type compounds tend to combine high polarity and moderate to high lipophilicity, with generally poor aqueous solubility. In contrast, the group of non-indole compounds displayed a wide variability in molecular weight and physicochemical properties. The individual molecular weight values of the whole group range from 138 (3,4-Dihydroxyphenylaldehyde, LPF group) to 619 g/mol (3-Hydroxy-27-p-(E)-coumaroyloxy ursan-12-en-28-oic acid, CTF group) (Figure 2A and Supplementary Table S2). This group of compounds exhibited low lipophilicity (mean WLogP = 0.43 ± 0.33, n = 71) and moderate aqueous solubility (mean LogSw = −1.34 ± 0.31, n = 71). Iridoids (IR) showed minor lipophilicity (mean WLogP = −1.32 ± 0.25, n = 25) and higher predicted solubility (mean LogSw = 0.70 ± 0.2, n = 25). Compounds of the LPF group presented moderate lipophilicity (mean WLogP = 0.67 ± 0.25), and moderate solubility (mean LogSw = −1.96 ± 0.41, n = 16). The CTF group had the highest distribution of molecular weight (between 192.12 and 618.85 g/mol) among these non-indolic compounds and exhibited moderate to high solubility (mean LogSw = 0.39 ± 0.55, n = 6). The OT group encompassed the widest range of lipophilicity values (WLogP values from −3.18 to 7.35), while Steroids (ST) were characterized by high lipophilicity (mean WLogP = 5.06 ± 0.74, n = 7) and a low predicted solubility (−4.22 ± 0.45). Collectively, these data highlight the noticeable structural and physicochemical heterogeneity of the non-indole compounds. These analyses suggest a considerable variability in their absorption and distribution profiles within biological systems.
A major part of the indole type compounds exhibited moderate to high oral absorption, consistent with their favorable lipophilicity (Figure 2D). Koumine (KO) and yohimbine (YO) groups showed the highest predicted oral absorption (averages group values higher than 95%), while gelsedine (GS) showed the lowest average (80.1% ± 2.0, n = 33). Several violations of Lipinski rules were detected within compounds of the GS (6), HT (3) and GM (1) groups (Supplementary Table S2). Conversely, the non-indole compounds exhibited a broader range of oral absorption properties (Figure 2D). Steroids (ST) and compounds of the OT group showed high oral absorption values (averages group values higher than 87%), while the MG compounds showed a particularly low absorption (22.0 ± 12, n = 6). Although a large variability was detected in these parameters, violations of Lipinski and Veber rules were present in all non-indolic derivatives (Supplementary Table S2). Regarding blood–brain barrier permeability and neuroactive potential, the indole type compounds exhibited high QPlogBB and CNS activity scores. Predicted QPlogBB values for the indole group (average −0.05 ± 0.06, n = 91), while CNS activity scores were mostly positive (mean: 0.55 ± 0.12, n = 91) (Figure 2E,F). Particularly high CNS activity values for the SA (1.17 ± 0.16, n = 12) and KO (1.2 ± 0.2, n = 10) subgroups were detected. By contrast, non-indole molecules displayed significantly lower predicted blood–brain barrier penetration (average QPlogBB = −1.41 ± 0.12, n = 71) and poor CNS activity scores (mean scores = −1.27 ± 0.11, n = 71) (Figure 2E,F). Additional distribution analyses confirm that the proportion of indolic compounds potentially active in the CNS (50.1%) is higher than the non-indolic compounds (21.1%, Figure 2G). Altogether, these analyses suggest that indole type compounds possess high predicted oral bioavailability and more likely CNS activity, with minimal liability warnings. On the other hand, the non-indole group showed a high heterogeneity in oral uptake, less potential as CNS active molecules, and some liability profiles.
The indole-type compounds exhibited diverse profiles of cytochrome P450 inhibition, with several predicted to inhibit clinically relevant enzymes such as CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 (Supplementary Table S2). Notably, CYP2D6 inhibition was the most consistent concern among indole scaffolds, with additional limitations for CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 in some compound subgroups. On the other hand, non-indole compounds generally showed lower overall CYP inhibition and more selective interactions, involving one or two isoforms. However, certain scaffolds (such as OT and LPF) exhibited variable potential CYP inhibitory actions. The predicted systemic clearance (CL) analysis indicated that the indole-type compounds showed moderate and similar clearance rates, whereas non-indole scaffolds demonstrated greater variability (Figure 2H). Within the indole group, SA and KO were associated with relatively faster clearance, while MG belonging to the non-indole group, showed the highest predicted clearance values.
The toxicological safety profiling was conducted using in silico predictions for three key endpoints: hERG channel inhibition (HERG I) (Figure 2I,J), mutagenicity (AMES test) (Figure 2K), and drug-induced liver injury (DILI) (Figure 2L). HERG I inhibition risk was minimal for non-indole scaffolds (i.e., no potential toxicity detected within the whole 71 compounds). The indolic compounds were also majorly safe, except for several specific GS compounds (7 of 33 of this group) that exhibited elevated risk (Figure 2I,J). The AMES test revealed a variable genotoxic risk profile within the indole class (Figure 2K). KO and HT groups were predicted to be largely non-mutagenic (100% safe), whereas gelsemine (GM) and gelsedine (GS) groups exhibited moderate mutagenic potential (11.1% and 24.2%, respectively). Yohimbine (YO) compounds were predicted to be mostly mutagenic (2 out of 3). On the other hand, CTF, OT and ST compounds showed no potential mutagenicity, while MG and LPF exhibited low toxicity (16.7% and 6.3%, respectively). The IR derivatives showed intermediate AMES toxicity (28.0%) in comparison with the whole non-indolic group values. Finally, DILI predictions were generally favorable across all classes of non-indolic compounds. The IR and MG groups showed no toxicity, while ST, LPF and CTF displayed a large proportion of compounds cataloged as safe (Figure 2L). Conversely, the indolic derivatives showed a more diverse profile. Only the GS group displayed no potential hepatotoxicity, while the SA, KO and YO showed a high number of compounds (>56.3%) tagged as toxic. Overall, our toxicological profiling indicated that non-indole scaffolds exhibited a consistently favorable safety profile, while certain indolic derivatives, particularly the GS, SA, KO, and YO groups, demonstrated variable risks of cardiotoxicity, genotoxicity, and hepatotoxicity.
3.2. Glycine Receptors Binding Predictions for Gelsemium Compounds
Our next step aims to determine whether these Gelsemium compounds can bind the orthosteric site of GlyRs. Using systematic molecular docking simulations of GlyRs composed by α1β and α3 in both closed and open conformations, we first analyzed docking scores and ΔGbind for the 162 Gelsemium derivatives (Table 2 and Table 3 and Supplementary Tables S3 and S4). The ligands were docked to the orthosteric binding site, located at the interface between two adjacent α subunits. From this dataset, the four major indole Gelsemium alkaloids (i.e., gelsemine, koumine, gelsevirine, and gelsenicine) showed favorable energetic profiles in the closed state of the channels, but not in the open state, consistent with a previous report showing functional competitive inhibition [12]. Our docking simulations suggest that a major part of the Gelsemium compounds, regardless of being indolic or non-indolic, may interact with the orthosteric site of both GlyR subtypes (Figure 3 and Figure 4, and Supplementary Tables S3 and S4). Nevertheless, indolic compounds displayed a consistent preference for the closed state in both α1 and α3 GlyRs, showing more favorable binding values than in open state. On the other hand, the non-indolic derivatives displayed a dispersed preference for the open and close states but still showed favorable binding parameters (Figure 3 and Figure 4). In addition, non-indolic compounds showed a more variable distribution of both docking scores and free binding energies within specific groups, while the indolic molecules displayed more compact patterns (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Representative binding poses are illustrated in Figure 5 and Figure 6, and details of the interacting amino acids and their corresponding contacts are provided in Supplementary Figures S1 and S2. Additionally, corresponding individual docking scores and ΔGbind across the open and closed states are summarized in Supplementary Tables S3 and S4.

Table 2.
Docking scores and ΔGbind values for best ranked indole- and non-indole compounds derived from Gelsemium species docked to GlyR α1β receptor structures in open (PDB: 7TVI) and closed (PDB: 7TU9) conformations.

Table 3.
Docking scores and ΔGbind values for best ranked indole- and non-indole compounds derived from Gelsemium species docked to GlyR α3 receptor structures in open (PDB: 5TIO) and closed (PDB: 5CFB) conformations.
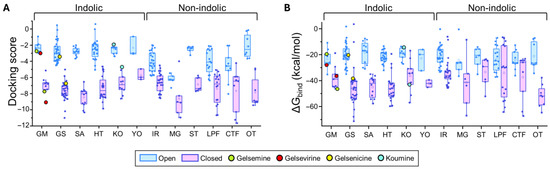
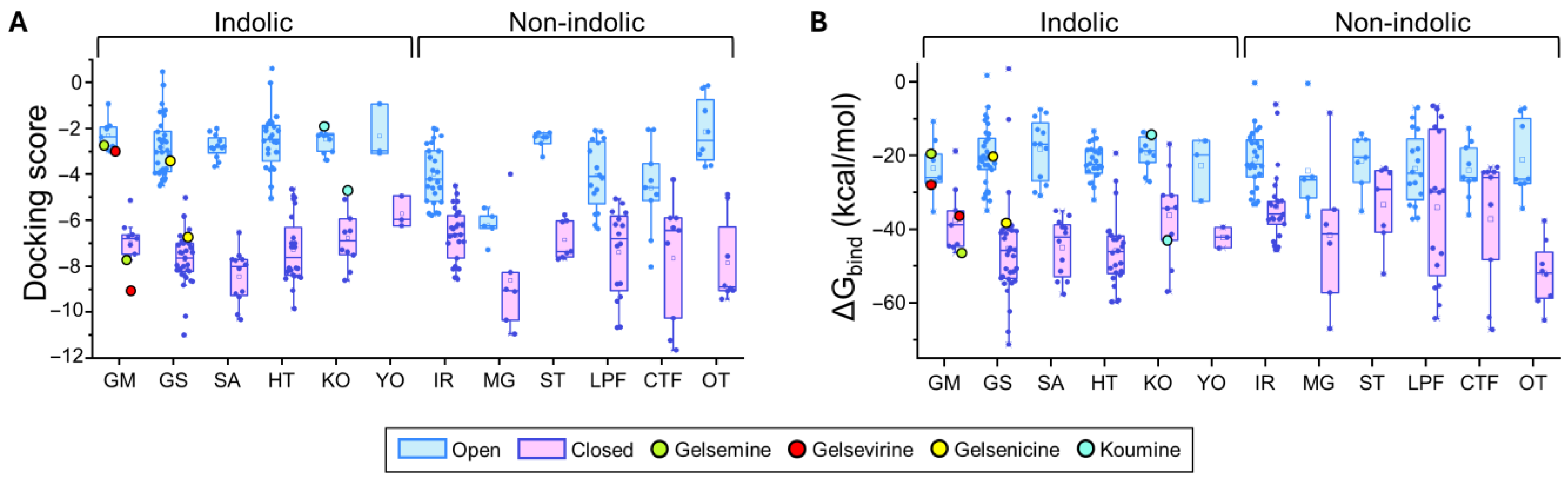
Figure 3.
Predicted binding energies of Gelsemium compounds in the orthosteric site of α1β glycine receptor. (A). Docking scores for the indole and non-indole compound groups. (B). ∆Gbind values calculated using MM-GBSA for the indole and non-indole groups. Highlighted values correspond to gelsemine (green), gelsevirine (red), gelsenicine (yellow), and koumine (cyan). Open conformation (PDB: 7TVI, light blue); closed conformation (PDB: 7TU9, light magenta). The box plots summarize the distributions of individual docking scores (A) and ∆Gbind (B) for the best-ranked poses of each ligand within the orthosteric site of α1β glycine receptors. Medians are represented by the central line, interquartile ranges (25–75%) by the box borders, and whiskers denote the minimum and maximum values within each group.
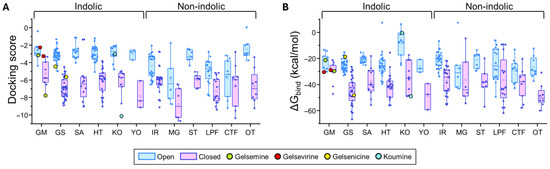
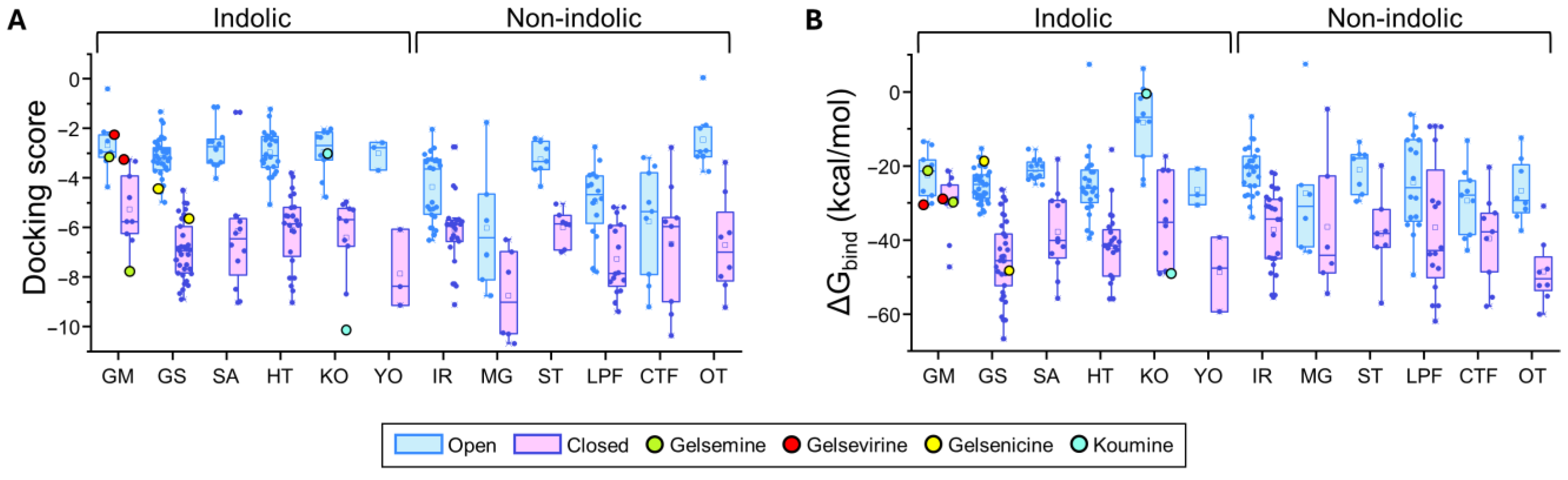
Figure 4.
Predicted binding energies of Gelsemium compounds in the orthosteric site of α3 glycine receptor. (A). Docking scores for the indole and non-indole compound groups. (B). ∆Gbind values calculated using MM-GBSA for the indole and non-indole groups. Highlighted values correspond to gelsemine (green), gelsevirine (red), gelsenicine (yellow), and koumine (cyan). Open conformation (PDB: 5TIO, light blue); closed conformation (PDB: 5CFB, light magenta). The box plots summarize the distributions of individual docking scores (A) and ∆Gbind (B) for the best-ranked poses of each ligand within the orthosteric site of α3 glycine receptors. Medians are represented by the central line, interquartile ranges (25–75%) by the box borders, and whiskers denote the minimum and maximum values within each group.
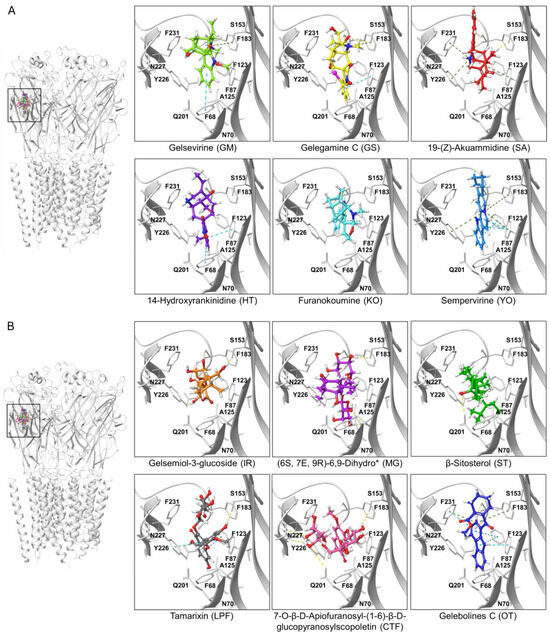
Figure 5.
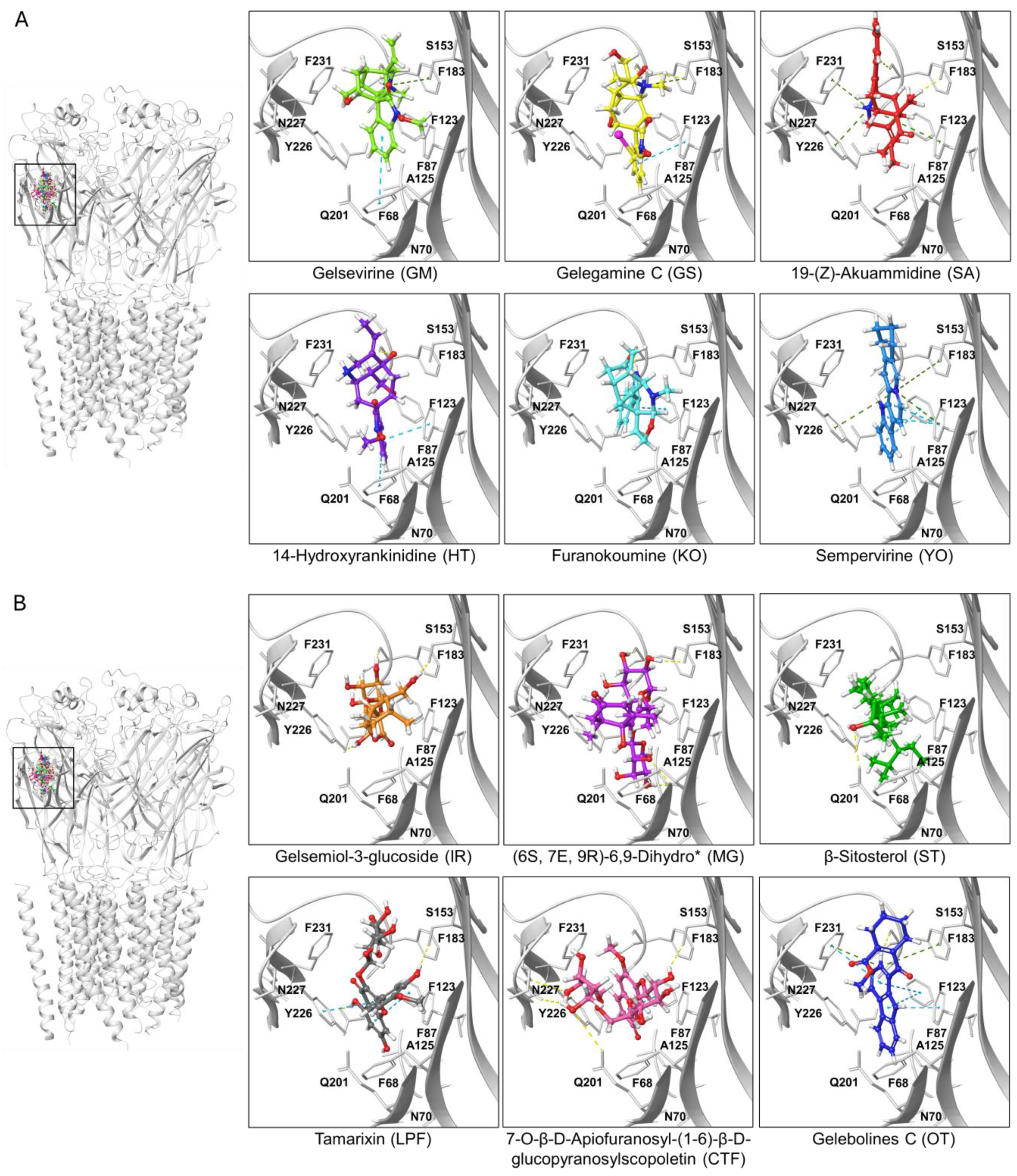
Ligand-protein complexes of representative indolic and non-indolic Gelsemium compounds docked to the α1β glycine receptor in closed conformation. (A). Indolic compounds. (B). Non-indolic compounds. For both datasets, the left panel depicts a pentameric α1β GlyR (i.e., the functional conformation of the receptor) with the six representative indolic (A) or non-indolic (B) compounds bound to the orthosteric site. Right panels show enhanced views of each ligand-receptor complex. Residues forming the orthostheric site are schematically represented and labeled. The molecules presented belong to the groups GM (light green), GS (yellow), SA (red), HT (violet), KO (cyan), YO (blue), IR (orange), MG (purple), ST (green), LPF (gray), CTF (faded salmon) and OT (navy blue). A detailed representation of the interacting amino acids and their corresponding contacts for these ligand-protein complexes are provided in Supplementary Figure S1. The * symbol denotes an abbreviated molecule name. The complete name can be found in Table 1.
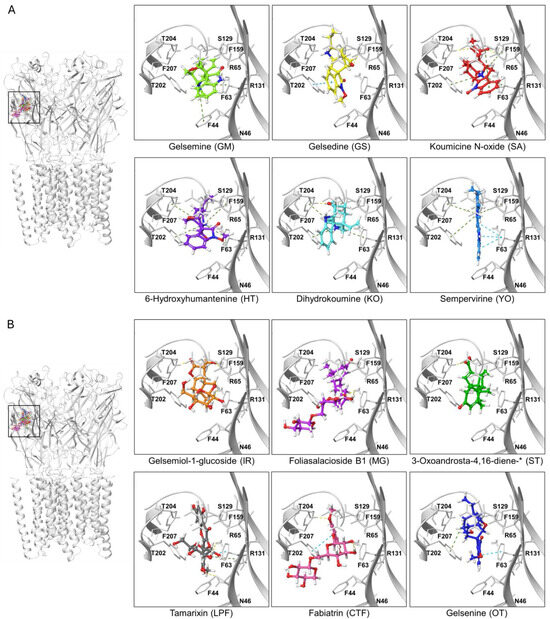
Figure 6.
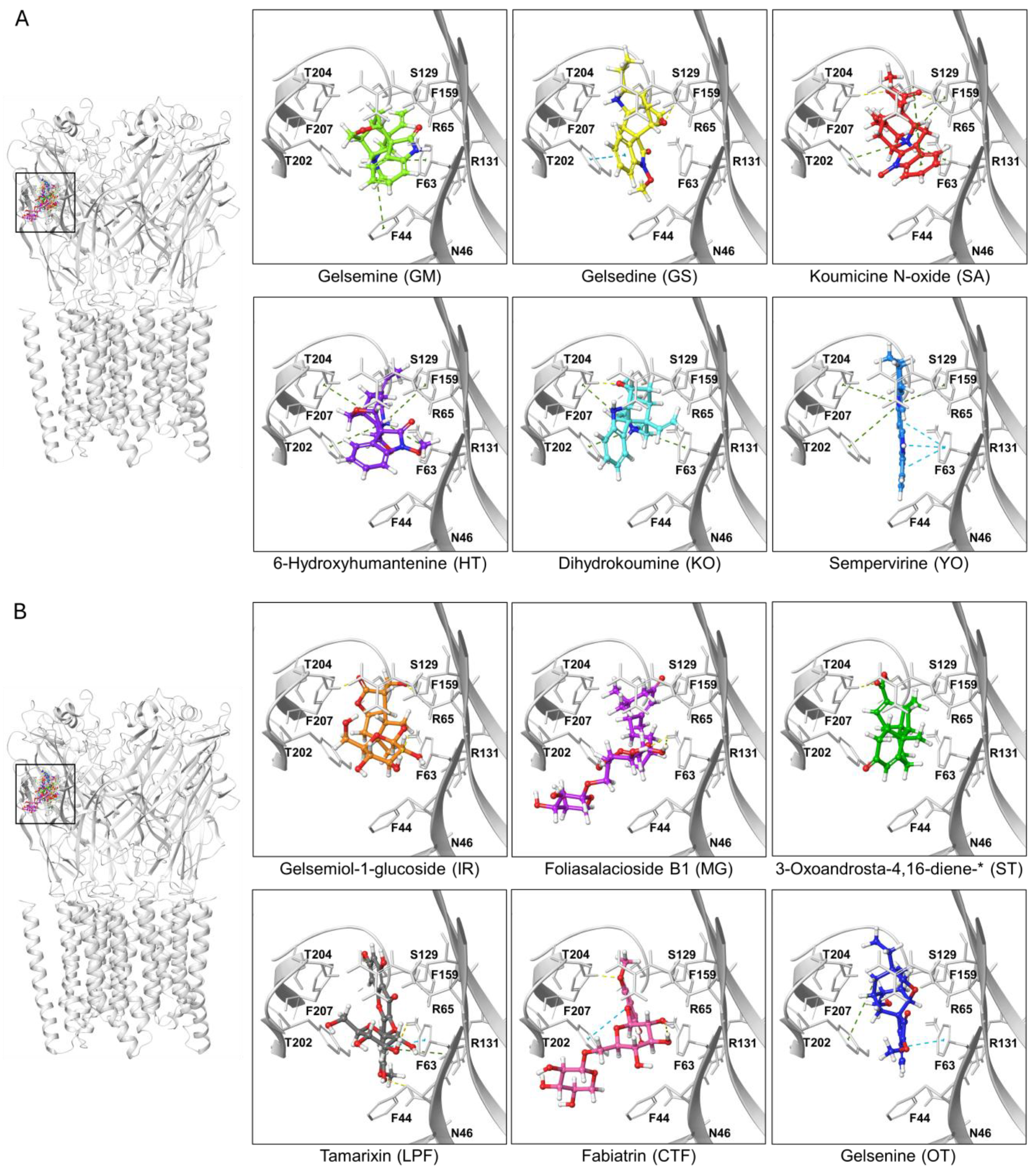
Ligand-protein complexes of representative indolic and non-indolic Gelsemium compounds docked to the α3 glycine receptor in closed conformation. (A). Indolic compounds. (B). Non-indolic compounds. For both datasets, the left panel depicts a pentameric α3 GlyR (i.e., the functional conformation of the receptor) with the six representative indolic (A) or non-indolic (B) compounds bound to the orthosteric site. Right panels show enhanced views of each ligand-receptor complex. Residues forming the orthostheric site are schematically represented and labeled. The molecules presented belong to the groups GM (light green), GS (yellow), SA (red), HT (violet), KO (cyan), YO (blue), IR (orange), MG (purple), ST (green), LPF (gray), CTF (faded salmon) and OT (navy blue). A detailed representation of the interacting amino acids and their corresponding contacts for these ligand-protein complexes are provided in Supplementary Figure S2. The * symbol denotes an abbreviated molecule name. The complete name can be found in Table 1.
For GlyR α1β, indole-type compounds exhibited significantly stronger predicted binding in the closed conformation, with docking scores ranging from −11.95 to −4.63 kcal/mol, compared to less favorable values in the open conformation, ranging from −5.03 to −2.6 kcal/mol. Non-indole molecules showed a similar trend, with docking scores of −11.65 to −4.49 kcal/mol in the closed state and −8.03 to −0.13 kcal/mol in the open state. A similar analysis was performed in the α3 orthosteric interface. The more stable interactions (i.e., more negative docking scores) were detected in the closed state for both indole-type and non-indolic compounds, highlighting the values of the yohimbane group (YO average: −7.85 ± 0.91 kcal/mol, n = 3) and megastigmane group (MG average: −8.73 ± 0.76 kcal/mol, n = 6). In the open state, indole compounds showed markedly less favorable docking scores, whereas non-indole ligands showed variable tendencies. While some of these groups retained favorable but dispersed average docking score values (MG = −6.24 ± 1.13 kcal/mol, n = 6), others considerably decreased their values (e.g., ST, IR, LPF and OT groups). Further analysis of the ΔGbind values were consistent with the distribution patterns of docking scores (Figure 3 and Figure 4 and Supplementary Tables S2 and S3).
Based on the docking results obtained for Gelsemium compounds on the GlyR orthosteric site on the closed state, we selected ten top-ranked ligands from indolic and non-indolic compound classes for further analysis. Thus, a set of 20 lead compounds preferentially targeting either the α1GlyR and α3 GlyR orthosteric site was compiled (Table 2 and Table 3). Interestingly, these candidate molecules displayed a promising binding profile for GlyR but span diverse chemical families, pointing out the structural heterogeneity of the Gelsemium dataset. A major part of them were predicted to be non-toxic according to the in silico toxicity models employed, reinforcing their potential for further experimental evaluation. To further sort the molecules, we analyzed their predicted pharmacokinetic profiles, and we prioritized compounds that showed optimal BBB permeability together with high CNS score activity (Table 2 and Table 3).
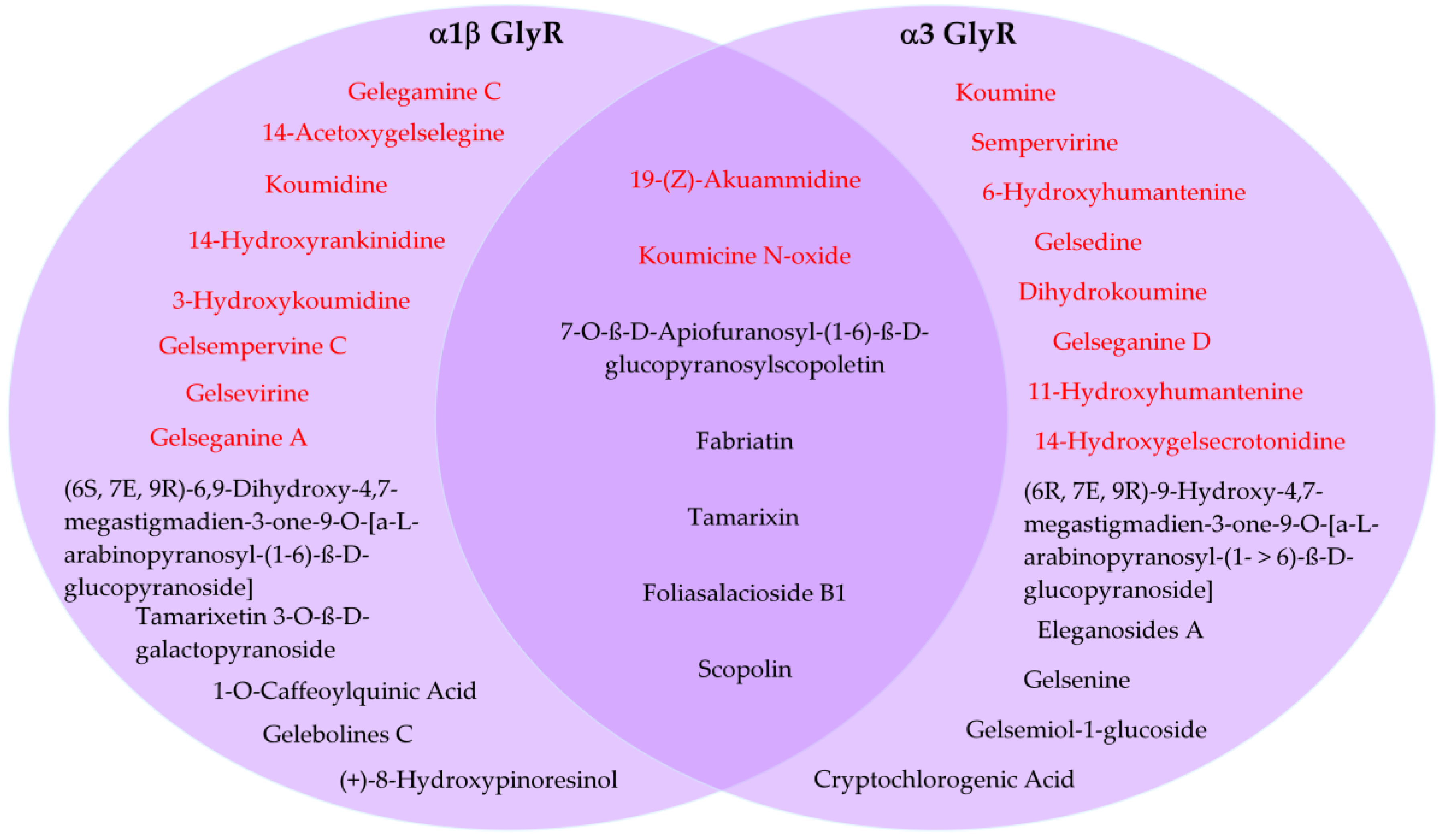
Despite several of these compounds having limitations in their pharmacokinetic profiles, we also analyzed whether these molecules may show potential subunit specificity towards α1 and α3 GlyR subtypes. A Venn diagram showed that, from these 20 compounds, 7 were cataloged as mixed α1/α3 modulators (2 indolic + 5 non indolic compounds), while 13 were grouped as α1 GlyR preferent (8 indolic + 5 non indolic) and another 13 as α3 GlyR preferent (8 indolic + 5 non indolic) (Figure 7).
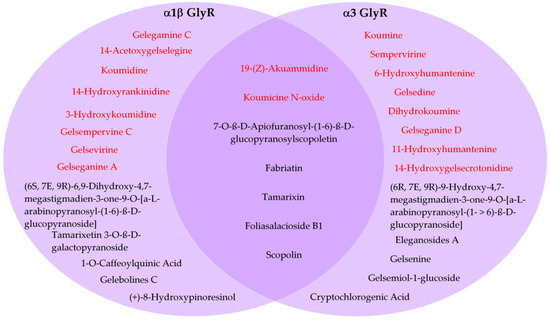
Figure 7.
Predicted subunit preference of selected compounds for α1- and α3 glycine receptors. Venn diagram showing the distribution of 20 compounds classified as α1-preferent, α3-preferent, or mixed α1/α3 GlyR modulators based on in silico docking analysis. Indolic and non indolic compounds were colored red and black, respectively.
This comparative evaluation provides a rational basis for prioritizing compounds for downstream molecular dynamic (MD) simulations, which would be valuable before experimental validation. Considering the previously described properties, we performed (MD) simulations of the four Gelsemium alkaloids selected as reference molecules for their functional characterization: gelsemine, koumine, gelseverine and gelsenicine [12]. In addition, we included two compounds that exhibited favorable interactions with the α1β GlyR (i.e., koumidine and 14-hydroxyrankinidine); two compounds with preferential binding to the α3 GlyR (i.e., 6-hydroxyhumantenine and Gelsenine); and one compound displaying favorable interactions with both receptor subtypes (i.e., 19-(Z)-Akuammidine) (Figure 8). These compounds were selected based on their potential BBB permeability, positive CNS scores, and favorable oral absorption, as well as considerations of commercial availability, ongoing purification, and cost.
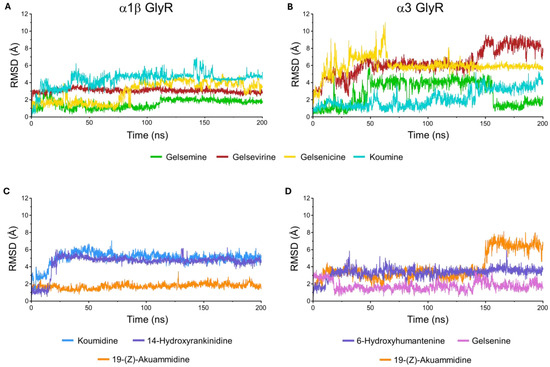
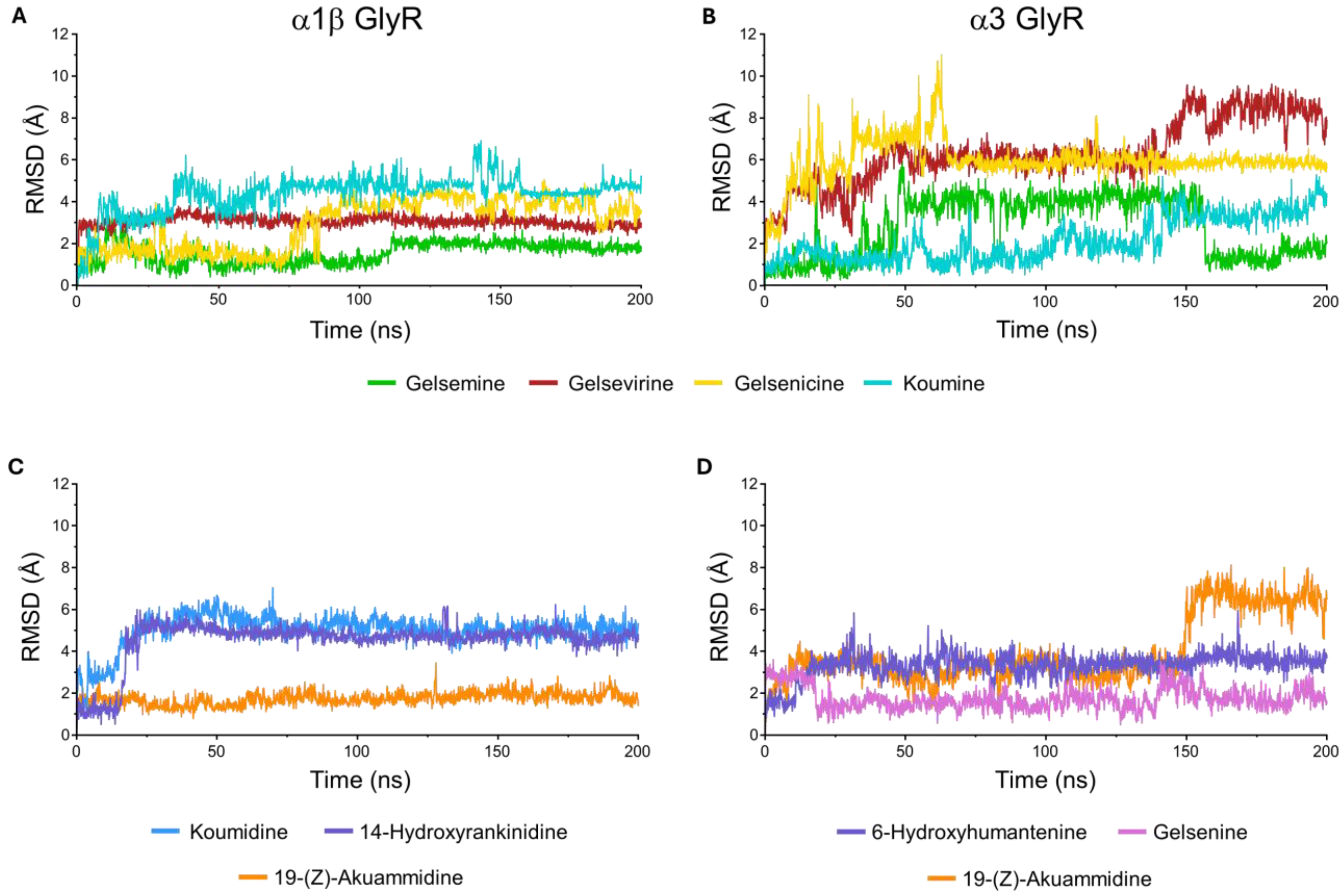
Figure 8.
Root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) trajectories of ligand–glycine receptor complexes in the closed conformation during molecular dynamics simulations. (A) Reference Gelsemium alkaloids, gelsemine (green), gelsevirine (red), gelsenicine (yellow), and koumine (cyan), bound to the α1β GlyR. (B) The same reference compounds bound to the α3 GlyR. (C) Selected molecules 19-(Z)-akuammidine (orange), koumidine (blue), and 14-hydroxyrankinidine (purple) in complex with the α1β GlyR. (D) Selected molecules 19-(Z)-akuammidine (orange), 6-hydroxyhumantenine (purple), and gelsenine (violet) in complex with the α3 GlyR.
For α1β GlyR, the RMSD values show that all complexes reach stable conformations after initial fluctuations, converging to plateaus between 2 and 3.5 Å. While gelsenicine exhibits delayed stabilization, the others reference molecules (gelsemine, gelseverine and koumine) display consistently low RMSD values, indicating stable binding throughout the simulation. Overall, the α1β GlyR complexes demonstrate structural stability with moderate flexibility (Figure 8A). The MD simulations of α1β GlyR revealed that ligand binding involves the concerted contribution of residues from two neighboring subunits at the α/α interface. For the reference molecules, multiple residues within the orthosteric site participated in stabilizing interactions with the ligands. Hydrophobic contacts with F44, F63, Y202, and F207 contributed substantially to complex stabilization over a large fraction of the simulation time, accompanied by hydrogen bonds and water-mediated bridges involving R65, E157, and T204. Notably, residue E157 also engaged in ionic interactions with the tested molecules (Supplementary Figure S3). Interestingly, a subtle yet significant difference was observed for gelsenicine compared with the other reference alkaloids, as hydrogen-bond and water-mediated interactions involving E157 and its surrounding environment were drastically reduced.
For the α3 GlyR complexes, RMSD profiles are more heterogeneous (Figure 8B). Gelsenicine exhibits the greatest mobility, with an early spike and persistent fluctuations, while gelsevirine shows a progressive RMSD drift toward higher values late in the trajectory, suggesting ongoing rearrangement. By contrast, gelsemine exhibits moderate fluctuations throughout the simulation, whereas koumine remains the most stable, maintaining an RMSD close to 2 Å for the majority of the trajectory. Overall, α3 GlyR complexes display higher conformational sensitivity, with the gelsenicine being the most flexible and least stable. Interaction patterns were largely conserved relative to the α1β GlyR, with the additional observation that T204 consistently contributed to hydrogen bonding and water-mediated bridges, while E157 also retained its ability to form ionic interactions (Supplementary Figure S3). Similarly, the interactions involving E157 were reduced in the presence of gelsenicine.
We subsequently analyzed the molecular dynamics simulations for the selected molecules bound to each glycine receptor conformation. For the α1β GlyR complex (Figure 8C), the RMSD trajectories reveal distinct ligand-dependent dynamics. Koumidine achieves a stable equilibrium after a brief initial equilibration phase. For its part, 14-Hydroxyrankinidine exhibits a progressive drift toward higher RMSD values, suggesting a slower conformational rearrangement of the protein-ligand complex, while 19-(Z)-akuammidine is characterized by moderate fluctuations throughout the simulation timeline. In complexes with α3 GlyR (Figure 8D), 19-(Z)-akuammidine again shows flexibility with persistent oscillations at the end of simulation. Furthermore, 6-Hydroxyhumantenine and gelsenine are stable, maintaining a low RMSD, although gelsenine undergoes an initial conformational shift before stabilizing.
A more detailed analysis of the protein-ligand interactions revealed a high degree of conservation in the key amino acids involved in binding compared to those described for the reference functionally active alkaloids (gelsemine, gelsevirine, and koumine). The conserved interaction network consisted of hydrogen bonds and water-mediated bridges with residues R65, S129, and E157, alongside significant hydrophobic contacts with F44, F63, Y202, and F207. The most notable difference was observed for 19-(Z)-akuammidine (19-akua) between the α1β and α3 GlyR isoforms. Specifically, the complex with the α3 isoform was characterized by a more pronounced reliance on hydrophobic interactions (Supplementary Figures S3–S5).
Despite variations in the magnitude of fluctuations and the time required to achieve equilibrium, all simulated complexes with GlyRs reached a stable conformational state. The observed RMSD profiles are consistent with typical ligand-protein binding behavior, where each ligand induces a distinct but stable dynamic signature in the protein structure. These results predict that the selected molecules could exert functional effects on GlyR activity, as the formation of a stable ligand-receptor complex represents the fundamental first step for potential allosteric modulation.
4. Discussion
An increasing body of research has highlighted the biological activity of natural compounds derived from Gelsemium species. Among these, the major indole alkaloids have been the most extensively studied, primarily due to their involvement in pathological conditions and their toxicity in mammals [1,44,45,46,47]. However, likely due to the prominence of these major alkaloids, other classes of Gelsemium derivatives have received considerably less attention. To date, only a limited number of studies have explored their pharmacological potential or biological effects. Given that these lesser-known compound classes encompass more than 150 structurally diverse chemical entities, comprehensive analyses of their biological activities remain challenging. In addition, the requirement for purified compounds adds another layer of complexity, limiting the ability to experimentally assess the effects of such diverse compounds with precision and reliability. In this study, we adopted an in silico approach to first characterize the physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of 162 structurally distinct Gelsemium compounds, to then examine their potential molecular interactions with two major GlyR subtypes. As GlyR represents one of the few molecular targets functionally validated for Gelsemium indole alkaloids [1,44,45,46,47], we believe our analyses contribute to the broader understanding of the activity of over a hundred chemically diverse natural compounds from Gelsemium species.
The physicochemical characterization showed that the 91 indole-based compounds form a relatively homogeneous group in terms of molecular weight, aqueous solubility, and lipophilicity—although the three YO compounds may represent exceptions. In contrast, the 71 non-indole scaffolds exhibited substantial variability across these parameters. Differences in molecular weight were somewhat expected, given the pronounced structural divergence among these compounds (see Supplementary Table S1). However, the broad range of LogS and WLogP values observed both between and within the non-indole groups suggests that potential CNS activity is likely to be limited to specific individual molecules, rather than attributable to structural classes. These physicochemical profiles were closely reflected in the predicted oral absorption potential and blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability of the analyzed molecules. Most of the indole-based compounds exhibited PHOA (percent human oral absorption) values above 80%, along with logBB and CNS activity scores greater than zero. Notably, these predictions align with the reported CNS activity of gelsemine, koumine, and gelsenidine in rodent behavioral models [48,49,50,51,52,53,54] and are also consistent with their known toxicological profiles, which include prominent CNS-related effects [55,56,57,58,59]. In contrast, most of the non-indole compounds appear to have limited BBB permeability. Nevertheless, a considerable number still displayed PHOA values exceeding 80%, and several exhibited CNS activity scores equal to or greater than zero. These findings suggest that, while their potential to modulate CNS function may be restricted, it cannot be entirely ruled out. Given the relative scarcity of studies on the biological actions of non-indole Gelsemium compounds, our results may serve as a useful guide for selecting promising candidates from this group for further experimental validation. However, the pronounced chemical diversity of the non-indole compounds, coupled with their more limited profiles as CNS modulators, suggests that their potential biological activity may instead be directed toward other physiological systems, such as the cardiovascular, respiratory, or endocrine systems [60,61,62,63,64,65,66].
Our toxicological analyses revealed an unexpected classification pattern among the Gelsemium compounds. While the mutagenicity profiles (i.e., AMES test) of both indolic and non-indolic derivatives were similarly distributed across groups, hepatotoxicity (i.e., DILI index) and cardiotoxicity (i.e., hERG-I modulation) were more prominently associated with several indolic compounds, with only a few potentially risky derivatives identified among the non-indolic group. Regarding hepatotoxicity specifically, gelsemine and koumine were classified as potentially harmful, gelsevirine was predicted to be safe, whereas gelsenicine consistently emerged as potentially toxic. These findings are consistent with prior reports showing comparatively lower systemic toxicity for gelsemine and koumine relative to other indole alkaloids, very high acute toxicity for gelsenicine, and a favorable safety profile for gelsevirine in cellular and in vivo contexts. Moreover, they align with broader medicinal-chemistry guidance that associates hERG liability with specific physicochemical features often enriched in indole scaffolds (e.g., high lipophilicity and aromaticity) [57,67,68,69].
Our binding prediction results suggest that both indolic and non-indolic groups have the potential to interact with the orthosteric site of GlyRs. However, the interactions of indolic compounds were noticeably more favorable in the closed state of both α1 and α3 GlyRs. These findings are in agreement with functional studies showing that gelsemine, koumine, and gelsevirine inhibit GlyRs containing α1 and α3 subunits [9,12], and are further supported by 3H-strychnine displacement assays in rat spinal cord demonstrating gelsemine and koumine binding to native GlyRs [50,70]. Given that docking scores and free binding energies were similarly distributed within the GS and KO groups (Figure 3 and Figure 4), it is likely that other derivatives from these groups may also function as GlyR modulators. In contrast, the binding profiles of non-indolic compounds suggest the presence of molecules that may preferentially bind to the orthosteric site of GlyRs either in the open or closed state. This raises the intriguing possibility of identifying novel compounds with agonistic activity. Since no synthetic or plant-derived agonists for GlyRs have been established to date, our findings could contribute to expanding GlyR pharmacology with such candidates in the future.
The highest-ranked indole alkaloids across both GlyR α1 and α3 receptors consistently belong to scaffolds enriched in nitrogen and capable of forming multiple hydrogen-bonding and hydrophobic contacts. Compounds such as gelegamine C, koumidine, and 14-acetoxygelselegine (α1β) or koumine, sempervirine, and gelsedine (α3) share complex polycyclic frameworks (GS, SA, KO types) possessing oxygenated substituents at positions such as C14–C19. These features provide both polarity and three-dimensional rigidity, favoring tight binding in the closed channel conformation (Table 2 and Table 3). Particularly, the presence of additional nitrogen atoms (e.g., oxazolidine rings in GS-type) and moderate lipophilicity appear advantageous for stabilizing interactions within the orthosteric site. Flexible frameworks such as HT-type also rank well when coupled to extensive oxygenation, suggesting that balanced polarity, heteroatom density, and a constrained polycyclic architecture collectively drive the high docking scores observed for indole compounds. Likewise, among non-indole compounds, top-ranked ligands such as 7-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1-6)-β-D-glucopyranosylscopoletin, fabiatrin, foliasalacioside B1, and several megastigmane glycosides (Table 2 and Table 3) show a consistent pattern of high glycosylation and oxygenation described for CTF, MG, and LPF groups. Diglycosidic linkages, multiple hydroxyl or methoxy groups, and nor-isoprenoid or benzopyrone cores provide a favorable combination of hydrogen-bond donors/acceptors and hydrophilic surface area, enabling strong binding despite the absence of the indole nucleus. Conversely, less polar classes such as steroids are underrepresented among the top scorers, reinforcing the importance of sugar conjugation and extensive heteroatom substitution in driving affinity for the GlyR binding pocket.
Although it is tempting to speculate that many molecules from both the indolic and non-indolic groups, which display favorable binding profiles to the orthosteric site, could act as GlyR modulators, such assumptions should be made with extreme caution. Indeed, previous studies have shown that the indole alkaloid gelsenicine, despite exhibiting a favorable energetic binding profile at the orthosteric sites of α1, α2, and α3 GlyRs, failed to produce any detectable functional effect on these receptors [12]. Interestingly, subsequent pharmacophore modeling analyses suggested that the absence of a key charged nitrogen group in gelsenicine may destabilize its interaction with the orthosteric site, potentially rendering the binding less stable and functionally ineffective.
Considering these limitations, we propose that molecular dynamics (MD) simulations can provide valuable insights into the likelihood that a given Gelsemium compound stably interacts with the orthosteric site of GlyRs, thereby suggesting potential functional activity. Our MD results demonstrated that koumine maintained a stable interaction with the orthosteric site of the α1 and α3 GlyRs, in line with its reported functional activity on GlyRs using electrophysiolgical recordings and binding displacement assays in rat spinal cord [12,70]. In contrast, gelsenicine exhibited a less stable interaction under comparable simulation conditions, suggesting that while it may transiently engage the orthosteric site, the interaction is insufficiently stable to mediate functional modulation of the receptor.
More detailed analysis shows that the MD simulations of Gelsemium-derived compounds complexed with GlyR α1β reveal stable orthosteric binding, anchored by persistent hydrophobic and polar interactions involving key residues such as F44, F63, Y202, F207, and particularly E157. The diminished engagement of E157 observed with gelsenicine, correlated with elevated RMSD and reduced hydrogen-bonding, underscores how even subtle perturbations in residue interactions can produce measurable effects on complex stability and potentially receptor dynamics, echoing similar findings in intracellular domain simulations that linked altered residue behavior to functional modifications. Additionally, this pattern is consistent with recent GlyR studies showing that specific side-chain networks stabilize inter-subunit pockets and shape binding energetics, and that subtle changes in local hydrogen-bonding can shift dynamic equilibria without compromising overall complex stability. Similar residue-level determinants have been implicated in allosteric modulation by lipids and small molecules, underscoring how orthosteric and peri-orthosteric contacts co-operate to stabilize active-like conformations [71,72,73].
The analysis of GlyR α3 revealed higher conformational sensitivity, with gelsenicine displaying elevated RMSD fluctuations, while gelsemine maintained a notably stable complex. Isoform-specific dynamic responses have been reported for GlyR under diverse modulatory regimes, including cannabinoid potentiation and lipid/cholesterol engagement, and are also reflected in MD studies linking sequence variation to altered conformational transitions [74,75]. Together, these insights reinforce the utility of MD simulations not only in validating docking predictions but also in uncovering the mechanistic basis for isoform-selective ligand behavior, guiding the prioritization of candidates for future functional assays.
5. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive in silico assessment of Gelsemium-derived compounds, combining molecular docking, dynamics simulations, and ADMET predictions to evaluate their interactions with two major GlyR subtypes. The results demonstrate that both indole and non-indole scaffolds can engage the orthosteric site of GlyRs, with subtype- and conformation-dependent differences that reflect the chemical and pharmacological diversity of the genus. Importantly, the integration of docking, energetic, and pharmacokinetic analyses allowed us to discriminate between compounds with favorable stability, bioavailability, and safety profiles, thereby enabling the rational selection of candidates most likely to exhibit modulatory activity on GlyRs. Overall, these findings establish a predictive framework that not only refines the understanding of Gelsemium phytochemistry but also guides the identification of promising molecules for future experimental validation and therapeutic exploration.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/compounds5040040/s1, Figure S1: Ligand–protein interaction diagrams of Gelsemium compounds bound to the α1β GlyR in the closed conformation (PDB ID: 7TU9). The selected alkaloids are shown docked within the orthosteric site, with their interactions with key receptor residues highlighted using a 4 Å cutoff. Purple arrows indicate hydrogen bonds, red lines denote π–cation interactions, and green lines represent π–π contacts. Numbered residues are marked by colored drops, where the color code corresponds to amino-acid properties (green, hydrophobic; red, negatively charged; blue, positively charged; cyan, polar; light yellow, glycine). The compounds illustrated are (A) Gelsevirine (GM), (B) Gelegamine C (GS), (C) 19-(Z)-Akuammidine (SA), (D) 14-Hydroxyrankinidine (HT), (E) Furanokoumine (KO), (F) Sempervirine (YO), (G) Gelsemiol-3-glucoside (IR), (H) (6S, 7E, 9R)-6,9-Dihydroxy-4,7-megastigmadien-3-one-9-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1->6)-β-D-glucopyranoside] (MG), (I) β-Sitosterol (ST), (J) Tamarixin (LPF), (K) 7-O-β-D-Apiofuranosyl-(1->6)-β-D-glucopyranosylscopoletin (CTF), and (L) Gelebolines C (OT); Figure S2: Ligand–protein interaction diagrams of Gelsemium compounds bound to the α3 GlyR in the closed conformation (PDB ID: 5CFB). The selected alkaloids are shown docked within the orthosteric site, with their interactions with key receptor residues highlighted using a 4 Å cutoff. Purple arrows indicate hydrogen bonds, red lines denote π–cation interactions, and green lines represent π–π contacts. Numbered residues are marked by colored drops, where the color code corresponds to amino-acid properties (green, hydrophobic; red, negatively charged; blue, positively charged; cyan, polar; light yellow, glycine). The compounds illustrated are (A) Gelsemine (GM), (B) Gelsedine (GS), (C) Koumicine N-oxide (SA), (D) 6-Hydroxyhumantenine (HT), (E) Dihydrokoumine (KO), (F) Sempervirine (YO), (G) Gelsemiol-1-glucoside (IR), (H) Foliasalacioside B1 (MG), (I) 3-Oxoandrosta-4,16-diene-17-carboxylic acid (ST), (J) Tamarixin (LPF), (K) Fabiatrin (CTF), and (L) Gelsenine (OT); Figure S3: Fraction of protein–ligand contacts during MD simulations of reference Gelsemium alkaloids bound to glycine receptors in the closed conformation. Molecular dynamics simulations of 200 μs were performed using docking-derived complexes of α1β GlyR (left panels) and α3 GlyR (right panels), including the following ligands: (A–B) gelsemine, (C–D) gelsevirine, (E–F) koumine, and (G–H) gelsenicine. Interaction types are categorized as hydrogen bonds (green), hydrophobic contacts (violet), ionic interactions (pink), and water bridges (blue). Values greater than 1.0 indicate residues forming multiple simultaneous contacts. For the analysis, the receptor–ligand interactions at the α/α interface of chains B–C (α1β) and C–D (α3) were considered; Figure S4: Fraction of protein–ligand contacts during MD simulations of reference Gelsemium alkaloids bound to the α1β glycine receptors in the closed conformation. Molecular dynamics simulations of 200 μs were performed using docking-derived complexes of α1β GlyR, including the following ligands: (A) Koumidine, (B) 14-Hydroxyrankinidine, and (C) 19-(Z)-Akuammidine). Interaction types are categorized as hydrogen bonds (green), hydrophobic contacts (violet), ionic interactions (pink), and water bridges (blue). Values greater than 1.0 indicate residues forming multiple simultaneous contacts. For the analysis, the receptor–ligand interactions at the α/α interface of chains C–D were considered; Figure S5: Fraction of protein–ligand contacts during MD simulations of reference Gelsemium alkaloids bound to the α3 glycine receptors in the closed conformation. Molecular dynamics simulations of 200 μs were performed using docking-derived complexes of α3 GlyR, including the following ligands: (A) 6-Hydroxyhumantenine, (B) Gelsenine, and (C) 19-(Z)-Akuammidine). Interaction types are categorized as hydrogen bonds (green), hydrophobic contacts (violet), ionic interactions (pink), and water bridges (blue). Values greater than 1.0 indicate residues forming multiple simultaneous contacts. For the analysis, the receptor–ligand interactions at the α/α interface of chains A–E and B/C were considered; Table S1. Structures of Gelsemium plant compounds. Structures of indole-type and non-indole-type compounds derived from Gelsemium, organized by structural classification into specific chemical subgroups; Table S2: ADMET properties for indolic and non-indolic Gelsemium compounds. ADMET summary of physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, and toxicological properties for indolic and non-indolic compound groups; Table S3: Docking scores and binding free energy values for Gelsemium compounds docked to α1β GlyR structures in open and closed conformations; Table S4: Docking scores and binding free energy values for Gelsemium compounds docked to α3 GlyR structures in open and closed conformations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.M., J.F., G.E.Y. and C.F.B.; methodology, C.M.-O., V.G.-M., B.S.-M. and K.G.-R.; formal analysis, A.M.M., O.R.-M., P.A.G., G.E.Y. and C.F.B.; validation, C.M.-O., V.G.-M., G.E.Y. and C.F.B.; investigation, A.M.M., O.R.-M. and P.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.-O., V.G.-M., G.E.Y. and C.F.B.; funding acquisition, G.E.Y., C.F.B. and J.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by ANID-FONDECYT 1250856 (to G.E.Y.) as well as ANID-FONDECYT 11221211 (to C.F.B.), and ANID-FONDECYT Postdoctoral 3230515 (to P.A.G.). K.G.R., was supported by an ANID doctoral fellowship 21251365. O.R-M. was supported by an ANID doctoral fellowship 21211001. B.S-M. and K.G.R. were supported by the University of Concepcion through Graduate School Fellowships (MSc program in Neurobiology).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank S. Quintana (University of Concepcion) for his technical assistance. During the preparation of this manuscript the authors used ChatGPT (OpenAI, 2025) for the purpose of improving the language and clarity of the manuscript. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADMET | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity |
| AMES | Ames test for mutagenicity |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CL | Clearence |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DILI | Drug-Induced Liver Injury |
| PHOA | Predicted Human Oral Absorption |
| HERG I | Human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene inhibition (Kv11.1 potassium channel) |
| MM-GBSA | Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area |
| RMSD | Root Mean Square Deviation |
| RMSF | Root Mean Square Fluctuation |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| ΔGbind | Binding Free Energy |
| Pgp | P-glycoprotein |
| LIP | Lipinski’s Rule of Five violations |
| VEB | Veber’s Rule violations |
| OA | Oral Absorption |
| QPlogBB | Predicted log of Brain/Blood Partition Coefficient |
References
- Lin, H.; Qiu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Que, Y.; Que, W. Gelsemium elegans Benth: Chemical Components, Pharmacological Effects, and Toxicity Mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Gao, X.; Liang, X.; Lv, W.; Zhang, D.; Jin, X. Recent progress in chemistry and bioactivity of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids from the genus gelsemium: A comprehensive review. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2155639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.L.; Su, Y.P.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, K.J.; Yu, C.X. Medicinal plants of the genus Gelsemium (Gelsemiaceae, Gentianales)—A review of their phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and traditional use. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujjanawate, C.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Panthong, A. Pharmacological effect and toxicity of alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans Benth. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, M.; van Andel, T. Revisiting traditional Chinese materia medica from European historical collections and perspective for current use. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2022, 12, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellavite, P.; Magnani, P.; Zanolin, E.; Conforti, A. Homeopathic Doses of Gelsemium sempervirens Improve the Behavior of Mice in Response to Novel Environments. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 362517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.L.; Liang, J.J.; Xue, Y.; Khan, A.; Zhang, P.P.; Feng, T.T.; Song, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, X. Genus Gelsemium and its Endophytic Fungi—Comprehensive Review of their Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 2452–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W. Gelsemium elegans Poisoning: A Case with 8 Months of Follow-up and Review of the Literature. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, C.O.; Murath, P.; Munoz, B.; Marileo, A.M.; Martin, L.S.; San Martin, V.P.; Burgos, C.F.; Mariqueo, T.A.; Aguayo, L.G.; Fuentealba, J.; et al. Functional modulation of glycine receptors by the alkaloid gelsemine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Xiao, N.; Jia, W.D.; Li, X.R.; Zheng, X.F.; Sun, Z.L. The Effectiveness of Flumazenil-Epinephrine Combination on Treatment for Acute Gelsemium elegans Poisoning. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2022, 53, 938–946. [Google Scholar]
- Marileo, A.M.; Gavilan, J.; San Martin, V.P.; Lara, C.O.; Sazo, A.; Munoz-Montesino, C.; Castro, P.A.; Burgos, C.F.; Leiva-Salcedo, E.; Aguayo, L.G.; et al. Modulation of GABA(A) receptors and of GABAergic synapses by the natural alkaloid gelsemine. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1083189. [Google Scholar]
- Marileo, A.M.; Lara, C.O.; Sazo, A.; Contreras, O.V.; Gonzalez, G.; Castro, P.A.; Aguayo, L.G.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Fuentealba, J.; Burgos, C.F.; et al. Molecular Pharmacology of Gelsemium Alkaloids on Inhibitory Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, A.; Lynch, J.W. The impact of human hyperekplexia mutations on glycine receptor structure and function. Mol. Brain 2014, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmann, A.; Maggio, N.; Eller, J.; Caliskan, G.; Semtner, M.; Haussler, U.; Juttner, R.; Dugladze, T.; Smolinsky, B.; Kowalczyk, S.; et al. Changes in neural network homeostasis trigger neuropsychiatric symptoms. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilorge, M.; Fassier, C.; Le Corronc, H.; Potey, A.; Bai, J.; De Gois, S.; Delaby, E.; Assouline, B.; Guinchat, V.; Devillard, F.; et al. Genetic and functional analyses demonstrate a role for abnormal glycinergic signaling in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martin, V.P.; Sazo, A.; Utreras, E.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Yevenes, G.E. Glycine Receptor Subtypes and Their Roles in Nociception and Chronic Pain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 848642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilhofer, H.U.; Werynska, K.; Gingras, J.; Yevenes, G.E. Glycine Receptors in Spinal Nociceptive Control-An Update. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, C.L. Modulation of Glycine-Mediated Spinal Neurotransmission for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2652–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadybekov, A.V.; Katritch, V. Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery. Nature 2023, 616, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2025 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1516–D1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdrazil, B.; Felix, E.; Hunter, F.; Manners, E.J.; Blackshaw, J.; Corbett, S.; de Veij, M.; Ioannidis, H.; Lopez, D.M.; Mosquera, J.F.; et al. The ChEMBL Database in 2023: A drug discovery platform spanning multiple bioactivity data types and time periods. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1180–D1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, H.; Wei, K.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H. Structure units oriented approach towards collective synthesis of sarpagine-ajmaline-koumine type alkaloids. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.B.; Zhang, G.R.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, J.K. Three new oxygenated yohimbane-type alkaloids from Ophiorrhiza japonica. Fitoterapia 2023, 166, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, M.E.; Franks, A.E.; Phillips, M.A. Biosynthesis, natural distribution, and biological activities of acyclic monoterpenes and their derivatives. Phytochem. Rev. 2023, 22, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.M.; Rasheed, D.M.; Mahrous, E.A.; Abdel-Sattar, E. C(13)-Norisoprenoid megastigmanes: Biosynthesis, classification, natural sources, biological activities, and structure-activity relationship—A comprehensive review. Fitoterapia 2025, 183, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litzenburger, M.; Bernhardt, R. Selective oxidation of carotenoid-derived aroma compounds by CYP260B1 and CYP267B1 from Sorangium cellulosum So ce56. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4447–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, J.C.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Steroids in natural matrices. In Biotechnology of Bioactive Compounds; Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 395–431. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, M.; Liang, Q. Naturally occurring furofuran lignans: Structural diversity and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1357–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.C.; Hua, W.; Zhang, L.; Guo, T.; Zhao, M.H.; Yan, M.; Wu, L.J. Two new alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimoszek, D.; Jelen, M.; Dolowy, M.; Morak-Mlodawska, B. Study of the Lipophilicity and ADMET Parameters of New Anticancer Diquinothiazines with Pharmacophore Substituents. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulsat, J.; Lopez-Nieto, B.; Estrada-Tejedor, R.; Borrell, J.I. Evaluation of Free Online ADMET Tools for Academic or Small Biotech Environments. Molecules 2023, 28, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.E.; Taranu, I. Using In Silico Approach for Metabolomic and Toxicity Prediction of Alternariol. Toxins 2023, 15, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, E.; Klemm, E.; Seiferth, D.; Kumar, A.; Ilca, S.L.; Biggin, P.C.; Chakrapani, S. Conformational transitions and allosteric modulation in a heteromeric glycine receptor. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shaffer, P.L.; Ayube, S.; Bregman, H.; Chen, H.; Lehto, S.G.; Luther, J.A.; Matson, D.J.; McDonough, S.I.; Michelsen, K.; et al. Crystal structures of human glycine receptor alpha3 bound to a novel class of analgesic potentiators. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Michelsen, K.; Schneider, S.; Shaffer, P.L. Crystal structure of human glycine receptor-alpha3 bound to antagonist strychnine. Nature 2015, 526, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, T.H.; Abdelmoniem, N.; Mukhtar, R.M.; Alqhtani, A.T.; Alalawi, A.L.; Alawaji, R.; Althubyani, M.S.; Mohamed, S.G.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; et al. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Studies Reveal the Anticancer Potential of Medicinal-Plant-Derived Lignans as MDM2-P53 Interaction Inhibitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zuo, M.T.; Huang, S.J.; Ma, X.; Qi, X.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. Effect of cytochrome P450 3A4 on tissue distribution of humantenmine, koumine, and gelsemine, three alkaloids from the toxic plant Gelsemium. Toxicol. Lett. 2024, 397, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xia, B.; Tang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Ye, L. Oxidative metabolism of koumine is mainly catalyzed by microsomal CYP3A4/3A5. Xenobiotica 2017, 47, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.; Zhang, M. Toxicokinetics of 11 Gelsemium Alkaloids in Rats by UPLC-MS/MS. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8247270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Qiu, J.; He, X.; Yu, X. Toxicokinetics, in vivo metabolic profiling, and in vitro metabolism of gelsenicine in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Yang, W.J.; Huang, Y.J.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, Z.Y. The metabolism of gelsevirine in human, pig, goat and rat liver microsomes. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 2086–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, G.; Yang, R.; Wei, Y.; Hu, W.; Gan, L.; Xie, C.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liao, R.; Ye, L. The detoxification effect of cytochrome P450 3A4 on gelsemine-induced toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 353, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tang, M.H.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Huang, S.J.; Zheng, X.F.; Liu, Z.Y. Suppressive Effects of Gelsemine on Anxiety-like Behaviors Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress in Mice. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.E.; Li, Y.D.; Luo, Y.J.; Wang, T.X.; Wang, H.J.; Chen, S.N.; Qu, W.M.; Huang, Z.L. Gelsemine alleviates both neuropathic pain and sleep disturbance in partial sciatic nerve ligation mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Gong, N.; Huang, J.L.; Guo, L.C.; Wang, Y.X. Gelsemine, a principal alkaloid from Gelsemium sempervirens Ait., exhibits potent and specific antinociception in chronic pain by acting at spinal α3 glycine receptors. PAIN® 2013, 154, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Boujedaini, N.; Patte-Mensah, C.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.G. Pharmacological effect of gelsemine on anxiety-like behavior in rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 253, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.B.; Tang, M.H.; Long, J.Y.; Wang, W.W.; Qin, J.Y.; Qi, X.J.; Liu, Z.Y. Antinociceptive effect of gelsenicine, principal toxic alkaloids of gelsemium, on prostaglandin E2-induced hyperalgesia in mice: Comparison with gelsemine and koumine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 681, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, H.H.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.P.; Lin, H.W.; Lin, L.Q.; Liao, W.J.; Yu, C.X. The active alkaloids of Gelsemium elegans Benth. are potent anxiolytics. Psychopharmacology 2013, 225, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Lin, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, C. The anxiolytic effect of koumine on a predatory sound stress-induced anxiety model and its associated molecular mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2022, 103, 154225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zuo, M.T.; Liu, Z.Y. The Metabolism and Disposition of Koumine, Gelsemine and Humantenmine from Gelsemium. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.J.; Zuo, M.T.; Huang, S.J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. Metabolic profile and tissue distribution of Humantenirine, an oxindole alkaloid from Gelsemium, after oral administration in rats. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1181, 122901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Yang, K.; Long, X.M.; Xiao, G.; Huang, S.J.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Sun, Z.L. Toxicity assessment of gelsenicine and the search for effective antidotes. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 09603271211062857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zuo, M.T.; Yang, K.; Sun, Z.L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.Y. Excretion, Metabolism, and Tissue Distribution of Gelsemium elegans (Gardn. & Champ.) Benth in Pigs. Molecules 2022, 27, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, M.; Jiang, C.; Jin, M.; Xie, B.; Ma, C.; Cong, B.; Wen, D. Decoding gelsenicine-induced neurotoxicity in mice via metabolomics and network toxicology. Phytomedicine 2025, 142, 156753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G. Anti-hyperlipidemic and anti-oxidative effects of gelsemine in high-fat-diet-fed rabbits. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W.; Jia, N. Nephroprotective effect of gelsemine against cisplatin-induced toxicity is mediated via attenuation of oxidative stress. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.L.; Liu, H.P.; Huang, Y.X.; Zeng, Q.Q.; Chen, J.X.; Lan, X.B.; Xin, Z.M.; Xiong, B.J.; Yue, R.C.; Yu, C.X. Koumine regulates macrophage M1/M2 polarization via TSPO, alleviating sepsis-associated liver injury in mice. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.R.; Zheng, F.T.; Xiong, B.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, S.T.; Fang, C.N.; Yu, C.X.; Yang, J. Koumine alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by regulating macrophage polarization. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 311, 116474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lin, Y.R.; Xiong, B.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Luo, Y.F.; Xu, Y.; Su, Y.P.; Huang, H.H.; Yu, C.X. Regulation effect of koumine on T-helper cell polarization in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 937, 175387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, R.; Jin, G.; Wei, S.; Huang, H.; Su, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Chu, Z.; et al. Immunoregulatory Effect of Koumine on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 8325102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Kong, D.; Guo, H.; Xing, C.; Lv, J.; Bian, H.; Lv, N.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Gelsevirine improves age-related and surgically induced osteoarthritis in mice by reducing STING availability and local inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 198, 114975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Tang, M.; Zuo, M.; Xu, W.; Meng, S.; Liu, Z. The antianxiety effects of koumine and gelsemine, two main active components in the traditional Chinese herbal medicine Gelsemium: A comprehensive review. Brain-X 2023, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Shi, L. The toxic components, toxicological mechanism and effective antidote for Gelsemium elegans poisoning. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 4872–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-J.; Yu, H.; Tang, M.-H.; Liu, Z.-Y. The toxicology and detoxification of Gelsemium: Traditional and modern views. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2024, 12, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, R.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Mao, X.F.; Wang, Y.X. Gelsemine and koumine, principal active ingredients of Gelsemium, exhibit mechanical antiallodynia via spinal glycine receptor activation-induced allopregnanolone biosynthesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 161, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kindig, K.; Rao, S.; Zaki, A.-M.; Basak, S.; Sansom, M.S.; Biggin, P.C.; Chakrapani, S. Structural basis for cannabinoid-induced potentiation of alpha1-glycine receptors in lipid nanodiscs. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalypour, F.; Howard, R.J.; Lindahl, E. Allosteric cholesterol site in glycine receptors characterized through molecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 4996–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Beaudoin, C.A.; Lummis, S.C. Modelling and molecular dynamics predict the structure and interactions of the glycine receptor intracellular domain. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartocci, A.; Grazzi, A.; Awad, N.; Corringer, P.-J.; Souza, P.C.; Cecchini, M. A millisecond coarse-grained simulation approach to decipher allosteric cannabinoid binding at the glycine receptor α 1. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhashal, A.R.; Yoluk, O.; Orellana, L. Exploring the Conformational Impact of Glycine Receptor TM1-2 Mutations Through Coarse-Grained Analysis and Atomistic Simulations. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 890851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).