A Review on Metal–Organic Frameworks as Technological Excipients: Synthesis, Characterization, Toxicity, and Application in Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
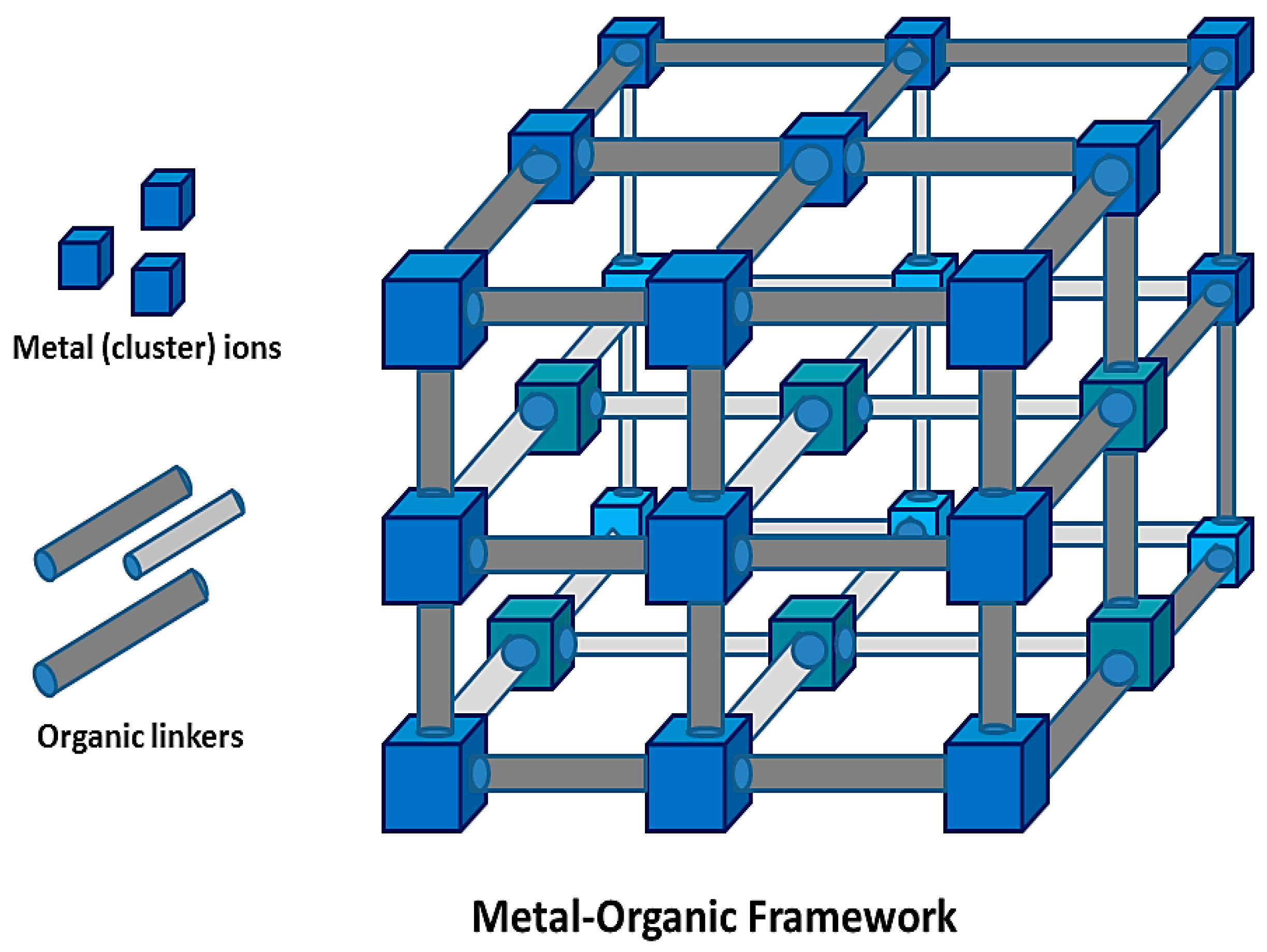
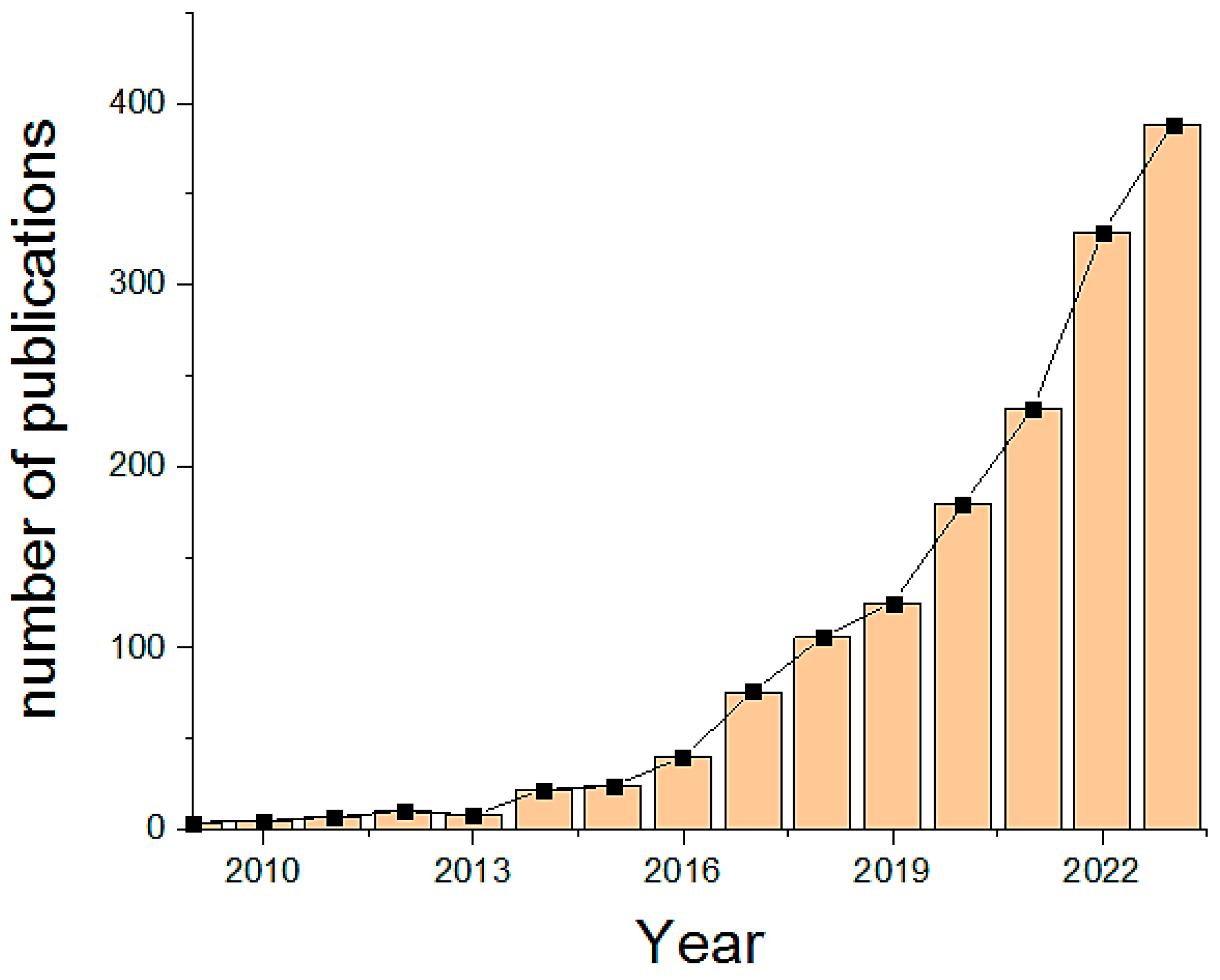
:1. Introduction
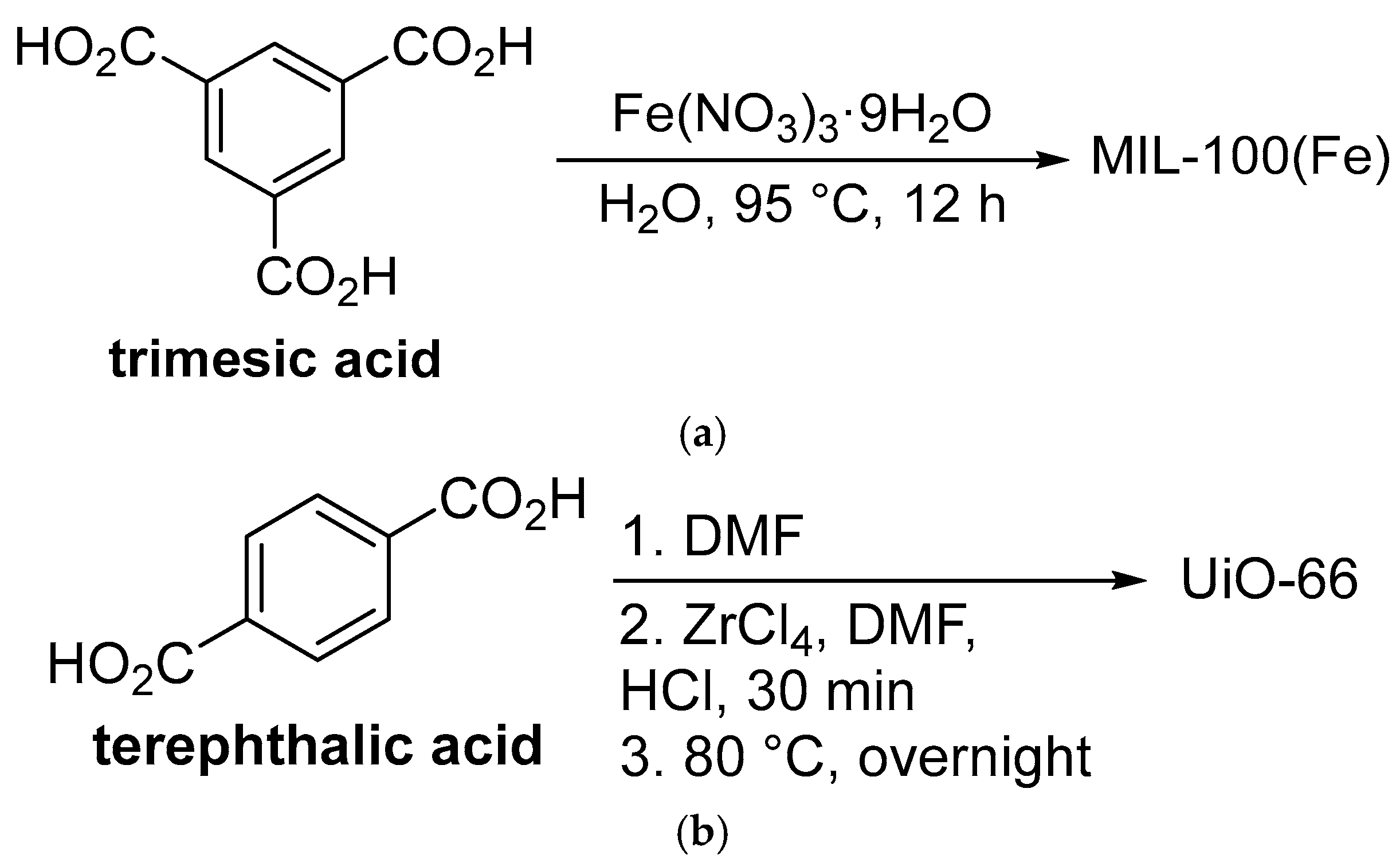
2. Synthesis and Characterization of MOFs
3. Toxicological Compatibility of MOFs for Biological Applications
4. Applications of MOFs as Drug Delivery Systems
4.1. MOFs Used for Prolonged Release
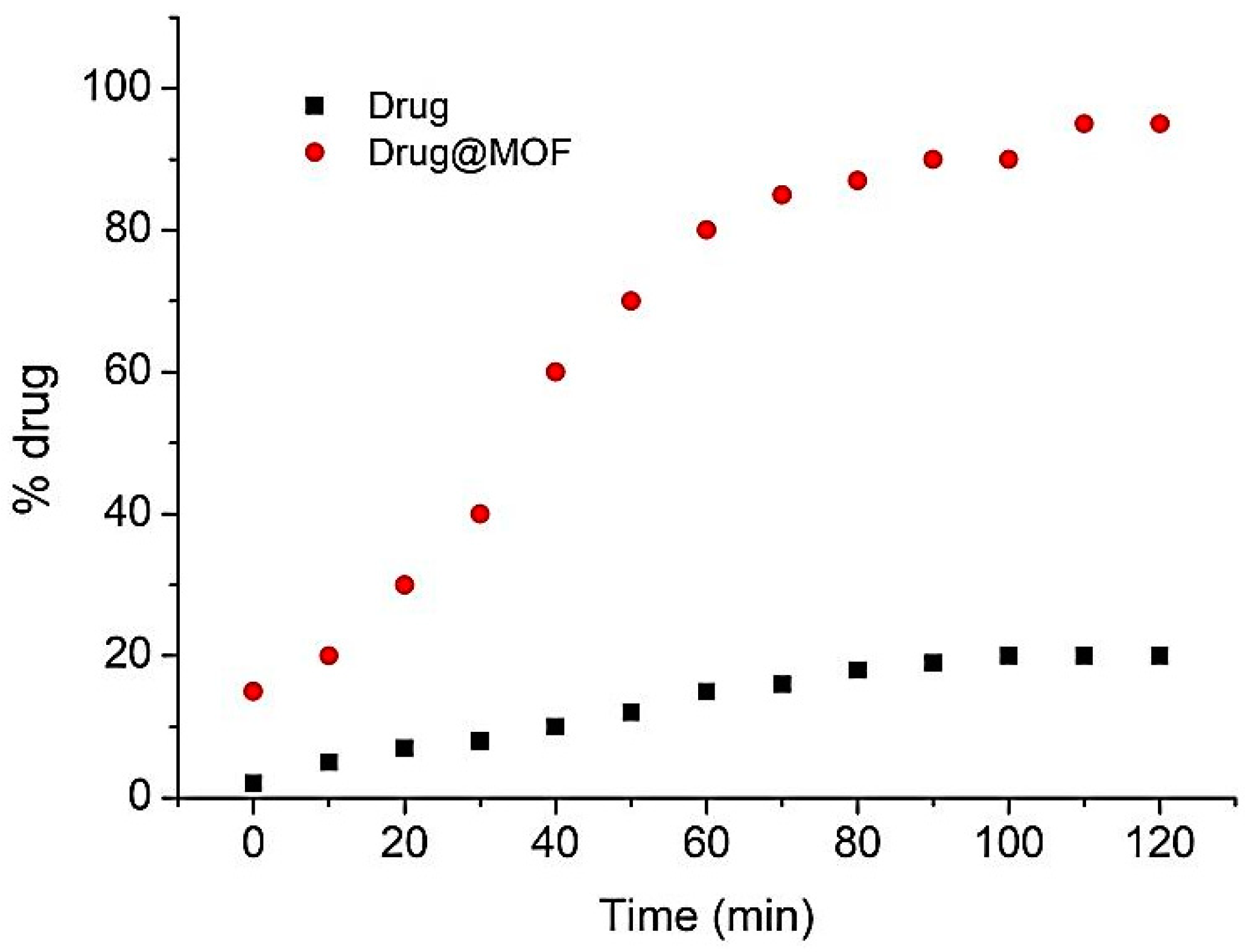
4.2. Solubility Increase
4.3. NanoMOFs
5. Possibilities for MOF Applications in the Healthcare Industry
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, T.; Luo, M.; Zou, M.; Nie, S.; Li, X. Advances in Nano-Sized Metal-Organic Frameworks and Biomedical Applications: A Review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2022, 18, 1707–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, H.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Varma, R.S. 2D and 3D covalent organic frameworks: Cutting-edge applications in biomedical sciences. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 5, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yadav, A.; Zhou, H.; Roy, K.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lee, C. Advances and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) in Emerging Technologies: A Comprehensive Review. Global Chall. 2024, 8, 2300244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Sigalat, J.; Bradshaw, D. Synthesis and applications of metal-organic framework–quantum dot (QD@MOF) composites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liédana, N.; Galve, A.; Rubio, C.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. CAF@ZIF-8: One-Step Encapsulation of Caffeine in MOF. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5016–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.C.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Chemical, thermal and mechanical stabilities of metal–organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Yang, B.; Cai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, S. Bioactive nano-metal–organic frameworks as antimicrobials against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, P.; Serre, C.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Sebban, M.; Taulelle, F.; Férey, G. Metal–Organic Frameworks as Efficient Materials for Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5974–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Ferreira, A.M. Química Supramolecular e Nanotecnologia; Grupo Ateneu: São Paulo, Brazil, 2014; pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cacho-Bailo, F.; Seoane, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.J. ZIF-8 continuous membrane on porous polysulfone for hydrogen separation. Memb. Sci. 2014, 464, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, R. Research Progress on Metal Ion Recovery Based on Membrane Technology and Adsorption Synergy. Materials 2024, 17, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, F.; Dong, W.; Hou, J.; Lu, P.; Gong, J. Self-template synthesis of core–shell ZnO@ZIF-8 nanospheres and the photocatalysis under UV irradiation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 156, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Srinivas, D.; Bhogeswararao, S.; Ratnasamy, P.; Carreon, M.A. Catalytic activity of ZIF-8 in the synthesis of styrene carbonate from CO2 and styrene oxide. Catal. Commun. 2013, 32, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, N.; Yoshimune, M.; Negishi, H.; Haraya, K.; Hara, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Diffusive Separation of Propylene/Propane with ZIF-8 Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 450, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Sun, S.-X.; Kong, L.-B.; Lang, J.-W.; Luo, Y.-C. Investigating metal-organic framework as a new pseudo-capacitive material for supercapacitors. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranescu, B.; Visa, A. Applications of metal-organic frameworks as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, N. Sustainable metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for drug delivery systems. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; An, G.; Yang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Y. Iron− Based Metal–Organic Frameworks as Multiple Cascade Synergistic Therapeutic Effect Nano− Drug Delivery Systems for Effective Tumor Elimination. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Li, G.; Li, H. Selective binding and removal of guests in a microporous metal–organic framework. Nature 1995, 378, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, N.G.; Damhus, T.; Hartshorn, R.M.; Hutton, A.T. Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Batten, S.R.; Champness, N.R.; Chen, X.-M.; Garcia-Martinez, J.; Kitagawa, S.; Öhrström, L.; O’Keeffe, M.; Paik Suh, M.; Reedijk, J. Terminology of metal–organic frameworks and coordination polymers (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zong, B.; Mao, S. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Sensors for Environmental Contaminant Sensing. Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.; Lollar, C.T.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.-C. Recent advances in gas storage and separation using metal–organic frameworks. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröger, H.; Allahverdiyev, A.; Yang, J.; Stiehm, J. Merging MOF Chemistry & Biocatalysis: A Perspective for Achieving Efficient Organic Synthetic Processes and Applications in the Chemical Industry? Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2304794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gates, B.C. Catalysis by Metal Organic Frameworks: Perspective and Suggestions for Future Research. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazari, R.; Sanati, S.; Bajaber, M.A.; Javed, M.S.; Junk, P.C.; Nanjundan, A.K.; Qian, J.; Dubal, D.P. Design and Advanced Manufacturing of NU-1000 Metal–Organic Frameworks with Future Perspectives for Environmental and Renewable Energy Applications. Small 2024, 20, 2306353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, J.; Kroczewska, M.; Baluk, M.; Sowik, J.; Mazierski, P.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. Morphology control through the synthesis of metal-organic frameworks. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 314, 102864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Pant, P.; Rajput, H. Strategies to Synthesize Diverse Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs). In Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) as Catalysts; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 69–97. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, N.; Biswas, S. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to Various MOF Topologies, Morphologies, and Composites. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 933–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemmi, E.; Christian, S.; Stock, N.; Bein, T. High-throughput screening of synthesis parameters in the formation of the metal-organic frameworks MOF-5 and HKUST-1. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouni, R.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. A novel combined manufacturing technique for rapid production of IRMOF-1 using ultrasound and microwave energies. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Su, Z.-M. Metal-organic frameworks as potential drug delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxford, R.C.; Della Rocca, J.; Lin, W. Metal-organic frameworks as potential drug carriers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.J.; Samanta, A.; Mir, M.H.; Dutta, B. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A promising candidate for stimuli-responsive drug delivery. ES Mater. Manuf. 2022, 19, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, P.; Haponiuk, J.; Saeb, M.R.; Rabiee, N.; Bencherif, S.A. Mitigating metal-organic framework (MOF) toxicity for biomedical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehipour, M.; Nikpour, S.; Rezaei, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Rezaei, M.; Ilbeygi, D.; Hosseini-Chegeni, A.; Mogharabi-Manzari, M. Safety of metal–organic framework nanoparticles for biomedical applications: An in vitro toxicity assessment. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 152, 110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Davis, L.; Tissot, A.; Shepard, W.; Marrot, J.; Martineau-Corcos, C.; Hamdane, D.; Maurin, G.; Devautour-Vinot, S.; et al. A robust zirconium amino acid metal-organic framework for proton conduction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterrieth, J.W.M.; Fairen-Jimenez, D. Metal–Organic Framework Composites for Theragnostics and Drug Delivery Applications. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 16, e2000005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Wang, Z. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) for drug delivery: A critical review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 15, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.N.; Bollini, P. Structure, characterization, and catalytic properties of open-metal sites in metal organic frameworks. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.F.; Sherman, E.; Vajo, J.J. Aqueous room temperature synthesis of cobalt and zinc sodalite zeolitic imidizolate frameworks. Dalt. Trans. 2012, 41, 5458–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravillon, J.; Münzer, S.; Lohmeier, S.-J.; Feldhoff, A.; Huber, K.; Wiebcke, M. Rapid Room-Temperature Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystals of a Prototypical Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-N.; Ahn, W.-S. High yield 1-L scale synthesis of ZIF-8 via a sonochemical route. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 169, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, F.; Williams, J.D.; Linares-Moreau, M.; Parise, C.; Liang, W.; Amenitsch, H.; Doonan, C.; Kappe, C.O.; Falcaro, P. Continuous-Flow Synthesis of ZIF-8 Biocomposites with Tunable Particle Size. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8123–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beldon, P.J.; Fábián, L.; Stein, R.S.; Thirumurugan, A.; Cheetham, A.K.; Friščić, T. Rapid Room-Temperature Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks by Using Mechanochemistry. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9640–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X. MIL-100(Fe) and its derivatives: From synthesis to application for wastewater decontamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4703–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinlay, A.C.; Morris, R.E.; Horcajada, P.; Férey, G.; Gref, R.; Couvreur, P.; Serre, C. BioMOFs: Metal-organic frameworks for biological and medical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6260–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Xing, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Hou, X. UiO-66(Zr) as sorbent for porous membrane protected micro-solid-phase extraction androgens and progestogens in environmental water samples coupled with LC-MS/MS analysis: The application of experimental and molecular simulation method. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Serre, C.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Millange, F.; Surblé, S.; Dutour, J.; Margiolaki, I. A hybrid solid with giant pores prepared by a combination of targeted chemistry, simulation, and powder diffraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6296–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Surblé, S.; Serre, C.; Hong, D.-Y.; Seo, Y.-K.; Chang, J.-S.; Grenèche, J.-M.; Margiolaki, I.; Férey, G. Synthesis and catalytic properties of MIL-100(Fe), an iron(iii) carboxylate with large pores. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2820–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Purkait, M.K.; Gumma, S. Doxorubicin Loading Capacity of MIL 100(Fe): Efect of Synthesis Conditions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2366–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, W. Facile synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) under HF-free conditions and its application in the acetalization of aldehydes with diols. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhung, S.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, J.W.; Serre, C.; Férey, G.; Chang, J.-S. Microwave synthesis of chromium terephthalate MIL-101 and its benzene sorption ability. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Xu, W. Rapid Synthesis of Metal–Organic Frameworks MIL-101(Cr) Without the Addition of Solvent and Hydrofluoric Acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.J.; Brown, Z.J.; Colón, Y.J.; Siu, P.W.; Scheidt, K.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9449–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Užarević, K.; Wang, T.C.; Moon, S.-Y.; Fidelli, A.M.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K.; Friščić, T. Mechanochemical and solvent-free assembly of zirconium-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2133–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Garibay, S.J.; Cohen, S.M. Microwave-Assisted Cyanation of an Aryl Bromide Directly on a Metal−Organic Framework. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; D’Alessandro, D.M. Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of zirconium oxide based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3706–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; Qi, H.; Wang, M.; Pei, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Gong, P.; et al. Development of a bacteria-nanosapper for the active delivery of ZIF-8 particles containing therapeutic genes for cancer immune therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2024, 14, 5418–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; You, Y.; Zha, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.; Kwan, H.Y.; et al. Biotin decorated celastrol-loaded ZIF-8 nano-drug delivery system targeted epithelial ovarian cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhou, C.; Luo, X.; Pang, H.; Han, C.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Nong, Y.; Lu, C. Tumor Targeting with Apatinib-loaded Nanoparticles and Sonodynamic Combined Therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2024, 24, 648–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Ren, J.; Ye, H.; Chu, W.; Ding, X.; Ding, L.; Fu, Y. Thymosin beta 10 loaded ZIF-8/sericin hydrogel promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis for bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yang, J.; Tu, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, L. Facile synthesis of ZIF-8@ poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly (4-styrenesulfonate) and its application as efficient electrochemical sensor for the determination dichlorophenol. Synth. Met. 2021, 277, 116769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, D.; Wang, Z. ZIF-8 based porous liquids with high hydrothermal stability for carbon capture. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, L.; Dendy, D.; Lestari, W.W.; Suharbiansah, R.S.; Firdaus, M.; Masykur, A.; Wibowo, F.R. Rapid and Facile Electrochemical Synthesis of MIL-101 (Fe)-NH2 and Its Curcumin Loading and Release Studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 34, 4039–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W.; Khan, M.Z.H.; Liu, X. Molecularly Imprinting Polymers (MIP) Based on Nitrogen Doped Carbon Dots and MIL-101(Fe) for Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Delivery. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, U.; Khan, M.E.; Sadiq, S.; Aamir, M.; Ullah, Z.; Bhatti, M.H.; Sher, M.; Chaudhry, G.-E. Methotrexate-loaded Fe-metal organic frameworks: Synthesis, characterizations, and drug release investigations. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2024, 97, 105790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yu, H.-M.; Wu, M.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y.; Sun, M.; Qin, J.-C.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y.-W. AuNRs@ MIL-101-based stimuli-responsive nanoplatform with supramolecular gates for image-guided chemo-photothermal therapy. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Cai, L.; Li, G.; Ren, Y.; Li, E.; Deng, K.; Zhu, M.; Han, S.; Che, X.; Li, X.; et al. Res@ ZIF-90 suppress gastric cancer progression by disturbing mitochondrial homeostasis. Transl. Oncol. 2025, 51, 102179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Qin, T.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L. Anti-inflammatory and anti-biotic drug metronidazole loaded ZIF-90 nanoparticles as a pH responsive drug delivery system for improved pediatric sepsis management. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 176, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, T.; Ameri, A.; Talebian-Kiakalaieh, A.; Mojtabavi, S.; Ameri, A.; Forootanfar, H.; Tarighi, S.; Faramarzi, M.A. Lipase@ zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-90: A highly stable and recyclable biocatalyst for the synthesis of fruity banana flavour. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2021, 166, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Zhu, W.; He, Z.; Xu, J.; Fang, F.; Gao, Z.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. ATP-triggered drug release system based on ZIF-90 loaded porous poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 126255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandara-Loe, J.; Ortuño-Lizarán, I.; Fernández-Sanchez, L.; Alió, J.L.; Cuenca, N.; Vega-Estrada, A.; Silvestre-Albero, J. Metal-Organic Frameworks as Drug Delivery Platforms for Ocular Therapeutics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bindary, A.A.; Toson, E.A.; Shoueir, K.R.; Aljohani, H.A.; Abo-Ser, M.M. Metal–organic frameworks as efficient materials for drug delivery: Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant, anticancer, antibacterial and molecular docking investigation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.T.; Bi, J.; Wu, J.; Kumar, A. Zirconium based nano metal-organic framework UiO-67-NH2 with high drug loading for controlled release of camptothecin. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, G.E.; Stillman, Z.; Attia, L.; Fromen, C.A.; Bloch, E.D. Controlling Size, Defectiveness, and Fluorescence in Na-noparticle UiO-66 Through Water and Ligand Modulation. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4831–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajevardi, A.; Hossaini Sadr, M.; Badiei, A.; Armaghan, M. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@MIL-100(Fe) nanocomposite: A nanocarrier for loading and release of celecoxib. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, T.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. MOF Capacitates Cyclodextrin to Mega-Load Mode for High-Efficient Delivery of Valsartan. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, S.; Hemmati, A.; Namazi, H.; Heydari, A. Carboxymethylcellulose-coated 5-fluorouracil@MOF-5 nano-hybrid as a bio-nanocomposite carrier for the anticancer oral delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, F.; Motaghi, M.; Chauhan, N.P.S.; Sargazi, G. A novel synthesis of new antibacterial nanostructures based on Zn-MOF compound: Design, characterization and a high performance application. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijani, H.; Noori, A.; Faridi, N.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Mousav, M.F. Aptamer-functionalized Fe3O4@MOF nanocarrier for targeted drug delivery and fluorescence imaging of the triple-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 292, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, S.; Newport, K.; Schueddig, K.; Rownaghi, A.A.; Rezaei, F. Optimizing Ibuprofen Concentration for Rapid Pharmacokinetics on Biocompatible Zinc-Based MOF-74 and UTSA-74. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulton, M.E.; Taylor, K.M.G. Delineamento de Formas Farmacêuticas, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016; 855p. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Kulkarni, S.; Vincent, A.P.; Nannuri, S.H.; George, S.D.; Mutalik, S. Hyaluronic acid-drug conjugate modified core-shell MOFs as pH responsive nanoplatform for multimodal therapy of glioblastoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pander, M.; Żelichowska, A.; Bury, W. Probing mesoporous Zr-MOF as drug delivery system for carboxylate functionalized molecules. Polyhedron 2018, 156, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, Q.; Mei, L. pH-Sensitive nanoscale materials as robust drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, C.; Patil, K.M.; Wilson, B.H.; Hermanspahn, L.; Harvey-Reid, N.C.; Howard, B.I.; Kleinjan, C.; Kolien, J.; Payet, F.; Telfer, S.G.; et al. The thermal stability of metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 419, 213388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, L.; Sohrabnezhad, S. Drug delivery by micro and meso metal-organic frameworks. Polyhedron 2020, 180, 114321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peikert, K.; McCormick, L.J.; Cattaneo, D.; Duncan, M.J.; Hoffmann, F.; Khan, A.H.; Bertmer, M.; Morris, R.E.; Fröba, M. Tuning the nitric oxide release behavior of amino functionalized HKUST-1. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 216, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Molton, B. Recent advances of discrete coordination complexes and coordination polymers in drug delivery. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinks, N.J.; McKinlay, A.C.; Xiao, B.; Wheatley, P.S.; Morris, R.E. Metal organic frameworks as NO delivery materials for biological applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 129, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, M.; Jeng, J.-M.; Malavolta, M.; Mocchegiani, E.; Sensi, S.L. Zinc dyshomeostasis: A key modulator of neuronal injury. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2005, 8, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, R.A.; Atwood, C.S.; Xilinas, M.E.; Gray, D.N.; Jones, W.D.; McLean, C.A.; Barnham, K.J.; Volitakis, I.; Fraser, F.W.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Treatment with a copper-zinc chelator markedly and rapidly inhibits beta-amyloid accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Neuron 2001, 30, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-Y.; Cheng, T.-J.; Yang, D.-M.; Wang, C.-T.; Chiung, Y.-M.; Liu, P.-S. Demonstration of an olfactory bulb-brain translocation pathway for ZnO nanoparticles in rodent cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 48, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Geib, S.J.; Rosi, N.L. Cation-triggered drug release from a porous zinc-adeninate metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8376–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaldone, R.A.; Forgan, R.S.; Furukawa, H.; Gassensmith, J.J.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Yaghi, O.M.; Stoddart, J.F. Metal-organic frameworks from edible natural products. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8630–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Yang, G.-S.; Shao, K.-Z.; Lan, Y.-Q.; Su, Z.-M.; Huang, P.; Wang, C.-G.; Wang, E.-B. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as efficient pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicle. Dalt. Trans. 2012, 41, 6906–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Leung, A.W.; Hua, H.; Xu, C. pH-responsive polymer-drug conjugates: Design and progress. J. Control. Release 2016, 222, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Chalati, T.; Serre, C.; Gillet, B.; Sebrie, C.; Baati, T.; Eubank, J.F.; Heurtaux, D.; Clayette, P.; Kreuz, C.; et al. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, L.R.D.M.; Alves, A.É.G.; Nascimento, D.D.S.d.S.; Amariz, I.A.; Ferreira, A.S.; Costa, S.P.M.; Rolim, L.A.; Lima, Á.A.N.d.; Rolim Neto, P.J. Technological innovation strategies for the specific treatment of Chagas disease based on benznidazole. Acta Trop. 2018, 185, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.C.F.; Esteso, M.A. Transport properties for pharmaceutical controlled-release systems: A brief review of the importance of their study in biological systems. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairen-Jimenez, D.; Moggach, S.A.; Wharmby, M.T.; Wright, P.A.; Parsons, S.; Düren, T.J. Opening the gate: Framework flexibility in ZIF-8 explored by experiments and simulations. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8900–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Hong, Y.; Geng, R.; Li, X.; Qu, A.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z. Amine-functionalized ZIF-8 as a fluorescent probe for breath volatile organic compound biomarker detection of lung cancer patients. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3478–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, C.; Das, A.; Chakraborty, A. Zeolitic imidazole framework (ZIF) nanospheres for easy encapsulation and controlled release of an anticancer drug doxorubicin under different external stimuli: A way toward smart drug delivery System. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3158–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z. Coordination polymer nanocapsules prepared using metal–organic framework templates for pH-responsive drug delivery. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 275601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Singh, A.; Garg, N.; Randhawa, J.K. Curcumin encapsulated zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as stimuli responsive drug delivery system and their interaction with biomimetic environment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, H.; Wang, C.; Qi, J.; Liu, K.; Cao, R.; Zheng, H. A protein@metal–organic framework nanocomposite for pH-triggered anticancer drug delivery. Dalt. Trans. 2018, 47, 10223–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettlinger, R.; Moreno, N.; Volkmer, D.; Kerl, K.; Bunzen, H. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 as pH-Sensitive Nanocarrier for “Arsenic Trioxide” Drug Delivery. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 13189–13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava Gallis, D.F.; Butler, K.S.; Agola, J.O.; Pearce, C.J.; McBride, A.A. Antibacterial countermeasures via metal-organic framework-supported sustained therapeutic release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7782–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakeçili, A.; Topuz, B.; Korpayev, S.; Erdek, M. Metal-organic frameworks for on-demand pH controlled delivery of vancomycin from chitosan scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.; Han, W.; Li, J.; Lv, Y.J. Doxorubicin-loaded Fe3O4-ZIF-8 nano-composites for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-M.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.-J.; Liu, M.; Yang, D.-D.; Liu, X.; Wei, J.-Z. Postsynthetic Modification of ZIF-90 for Potential Targeted Codelivery of Two Anticancer Drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27332–27337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yuan, B.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, A. Dual ATP and pH responsive ZIF-90 nanosystem with favorable biocompatibility and facile post-modification improves therapeutic outcomes of triple negative breast cancer in vivo. Biomaterials 2019, 197, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Serre, C.; Maurin, G.; Ramsahye, N.A.; Balas, F.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Sebban, M.; Taulelle, F.; Férey, G.J. Flexible porous metal-organic frameworks for a controlled drug delivery. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6774–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singco, B.; Liu, L.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Shih, Y.-H.; Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Approaches to drug delivery: Confinement of aspirin in MIL-100(Fe) and aspirin in the de novo synthesis of metal–organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 223, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi Alavijeh, R. Biocompatible MIL-101(Fe) as a smart carrier with high loading potential and sustained release of curcumin. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 3570–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. MIL-53(Fe), MIL-101, and SBA-15 porous materials: Potential platforms for drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 47, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Gumma, S.; Purkait, M.K. Fe3O4 promoted metal organic framework MIL-100(Fe) for the controlled release of doxorubicin hydrochloride. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Shi, J. Inherent anchorages in UiO-66 nanoparticles for efficient capture of alendronate and its mediated release. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8779–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Matzger, A.J. Enhanced Drug Delivery by Dissolution of Amorphous Drug Encapsulated in a Water Unstable Metal–Organic Framework (MOF). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16790–16794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, W.; Guo, T.; Zhang, G.; Qin, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, W.; Yang, M.; Hu, X.; et al. Drug nanoclusters formed in confined nano-cages of CD-MOF: Dramatic enhancement of solubility and bioavailability of azilsartan. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhuri, A.R.; Laha, D.; Chandra, S.; Karmakar, P.; Sahu, S.K. Synthesis of multifunctional upconversion NMOFs for targeted antitumor drug delivery and imaging in triple negative breast cancer cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.S.F.; Silva, J.Y.R.; de Sá, G.F.; Araújo, S.S.; Filho, M.A.G.; Ronconi, C.M.; Santos, T.C.; Júnior, S.A. Multifunctional System Polyaniline-Decorated ZIF-8 Nanoparticles as a New Chemo-Photothermal Platform for Cancer Therapy. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12147–12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Langner, E.H.G. The effect of synthesis temperature on the particle size of nano-ZIF-8. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 221, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nune, S.K.; Thallapally, P.K.; Dohnalkova, A.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Exarhos, G.J. Synthesis and properties of nano zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4878–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, B.; Nabipour, H.; Nasab, N.A. Efficient storage of gentamicin in nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanocarrier for pH-responsive drug release. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schejn, A.; Balan, L.; Falk, V.; Aranda, L.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. Controlling ZIF-8 nano- and microcrystal formation and reactivity through zinc salt variations. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4493–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Guan, X.; Xie, Z. One-Step Synthesis of Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks with High Curcumin Loading for Treatment of Cervical Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22181–22187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Chu, C.-C.; Liu, G.; Wáng, Y.-X.J. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Nanomedicine Platforms for Drug Delivery and Molecular Imaging. Small 2015, 11, 4806–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, H.; Sadr, M.H.; Bardajee, G.R. Synthesis and characterization of nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with ciprofloxacin and their applications as antimicrobial agents. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7364–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lu, K.; Liu, D.; Lin, W.J. Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Co-Delivery of Cisplatin and Pooled siRNAs to Enhance Therapeutic efficacy in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5181–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chou, L.-Y.; Liu, D.-Y.; Weerapana, E.; Tsung, C.-K. Optimized metal-organic-framework nanospheres for drug delivery: Evaluation of small-molecule encapsulation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y. Simple synthesis of multifunctional zeolitic imidazolate frameworks-8/graphene oxide nanocrystals with controlled drug release and photothermal effect. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 237, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, B.A.; Kim, S. Current and emerging applications of nanostructured metal–organic frameworks in cancer-targeted theranostics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-X.; Yang, Y.-W. Metal–organic framework (MOF)-based drug/cargo delivery and cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Q. Metal-Organic Framework Composites for Catalysis. Matter 2019, 1, 57–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ma, D.; Li, S.; Qu, W.; Wang, D. Preparation of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks and Their Application as Flame Retardant and Smoke Suppression Agent for Rigid Polyurethane Foams. Polymers 2020, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia-Kuang, T.; Jeffery, B. Molecular Encapsulation in Metal-Organic Framework Crystals. U.S. Patent 10137429B2, 17 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Yan, X.; Zhaokun, Z.; Weijia, C.; Ping, W.; Caihong, J.; Fang, Z. Preparation Method of pH sensitive and Photothermal Therapeutic Probe Based on Metal Organic Framework ZIF-8. Patent CN109529036A, 29 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhongqiu, L.; Lijie, C. Preparation Method of Metal Polyphenol Vesicle Material with Micrometer/Nanometer Multilayer Composite Structure. CN106565964A, 19 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Song, C.; Huo, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Sun, M.; Jin, B.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Anti-CD155 and anti-CD112 monoclonal antibodies conjugated to a fluorescent mesoporous silica nanosensor encapsulating rhodamine 6G and fluorescein for sensitive detection of liver cancer cells. Analyst 2016, 141, 4933–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.; Schatz, G.C.J. Resonance Raman scattering of rhodamine 6G as calculated using time-dependent density functional theory. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 5973–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim-Neto, P.J.; Ferraz, L.R.M.; Alves, A.E.G.; Nascimento, D.D.S.S.; Amariz, I.A.; Costa, S.P.M.; Rolim, L.A.; Melo, C.; Alves-Junior, S. Formulações Farmacêuticas contendo Associação de Benznidazol e MOFs para Obtenção Tecnológicas de Sistemas Drug Delivery. Patent BR1020160034086, 2 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rolim-Neto, P.J.; Silva, R.M.F.; Rolim, L.A.; Nascimento, D.D.S.S.; Ferraz, L.R.M.; Alves, A.E.G.; Ferreira, A.S.; Oliveira, F.F.F.G.; Oliveira, R.S.; Alves-Junior, S.; et al. Uso da MOF como protetor térmico em formulações farmacêuticas à base de carbamazepina. Patent BR1020190159219, 31 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J. Surface Functionalization Modification Method for Metal Organic Framework (MOF) Material Based on Liposome Membrane. Patent CN107189074(A), 22 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fairen-Jimenez, D.; Kaminski, G.; Teplensky, M.; Colin, H.; Salame, H. Metal Organic Framework—Based Compositions and Uses Thereof. Patent WO2019086542A1, 9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. MOF-Manganese Dioxide Microspheres, and Preparation Method and Application Thereof. CN108219155A, 29 June 2018. [Google Scholar]


| MOF | Synthesis Method | Encapsulated Substance/ MOF-Based System | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | room-temperature aqueous synthesis | interleukin 2 (Il2)/ Il2/ZIF-8@salmonella | [60] |
| celastrol (CEL)/ CEL@ZIF-8@PEG-BIO | [61] | ||
| apatinib/ apatinib/Ce6@ZIF-8@cytomembrane (ACZ@M) | [62] | ||
| thymosin beta 10 (TMSB10)/ TMSB10@ZIF-8 | [63] | ||
| electrochemical | dichlorophene (2, 2-methylenebis (4-chlorophenol), Dcp) /ZIF-8@PEDOT:PSS | [64] | |
| hydrothermal | shell–ligand exchange reaction (SLER)/ ZIF-8-SLER-PLs | [65] | |
| MIL-101 (Fe) | solvothermal (S)/electrochemical (E) | curcumin@MIL-101(Fe)-NH2—(S)/ curcumin@MIL-101(Fe)-NH2—(E) | [66] |
| hydrothermal | doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX)/ DOX@MIL-101(Fe)@molecularly imprinting polymer | [67] | |
| methotrexate (MTX)/ MTX@MIL-101(Fe) | [68] | ||
| solvothermal (polar solvent) + hydrothermal | 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu)/ (5-Fu)-loaded gold nanorods@MIL-101(Fe)–NH2 @carboxylatopillar [5] arene | [69] | |
| ZIF-90 | dissolution (polar solvent) | resveratrol (Res)/ Res@ZIF-90 | [70] |
| hydrothermal | metronidazole (MI)/ MI@ZIF-90 | [71] | |
| solvothermal | porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL)/ PPL@ZIF-90 | [72] | |
| doxorubicin (Dox)/ (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)@ZIF-90)@PLGA | [73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sampaio, P.A.; Pereira, E.C.V.; Sá, P.G.S.; Alencar Filho, J.M.T.; Ferraz, L.R.M.; Nishimura, R.H.V.; Ferreira, A.S.; Rolim Neto, P.J.; Araújo, E.S.; Rolim, L.A. A Review on Metal–Organic Frameworks as Technological Excipients: Synthesis, Characterization, Toxicity, and Application in Drug Delivery Systems. Compounds 2025, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5010001
Sampaio PA, Pereira ECV, Sá PGS, Alencar Filho JMT, Ferraz LRM, Nishimura RHV, Ferreira AS, Rolim Neto PJ, Araújo ES, Rolim LA. A Review on Metal–Organic Frameworks as Technological Excipients: Synthesis, Characterization, Toxicity, and Application in Drug Delivery Systems. Compounds. 2025; 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSampaio, Pedrita A., Emanuella C. V. Pereira, Pedro G. S. Sá, José Marcos T. Alencar Filho, Leslie R. M. Ferraz, Rodolfo H. V. Nishimura, Aline S. Ferreira, Pedro J. Rolim Neto, Evando S. Araújo, and Larissa A. Rolim. 2025. "A Review on Metal–Organic Frameworks as Technological Excipients: Synthesis, Characterization, Toxicity, and Application in Drug Delivery Systems" Compounds 5, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5010001
APA StyleSampaio, P. A., Pereira, E. C. V., Sá, P. G. S., Alencar Filho, J. M. T., Ferraz, L. R. M., Nishimura, R. H. V., Ferreira, A. S., Rolim Neto, P. J., Araújo, E. S., & Rolim, L. A. (2025). A Review on Metal–Organic Frameworks as Technological Excipients: Synthesis, Characterization, Toxicity, and Application in Drug Delivery Systems. Compounds, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5010001






