Particles in the Eluate from Double Filtration Plasmapheresis—A Case Study Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (FE-SEM/EDX)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
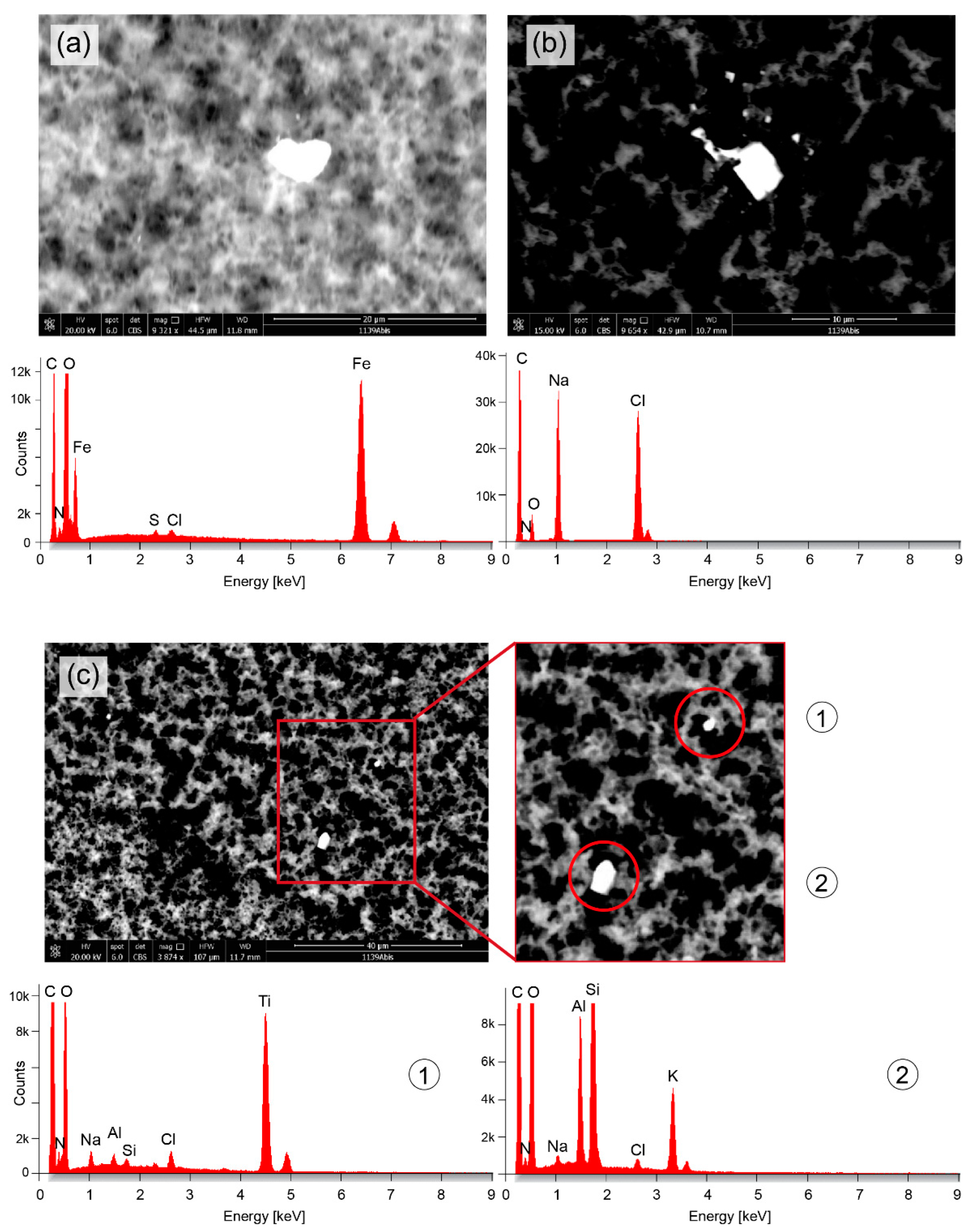
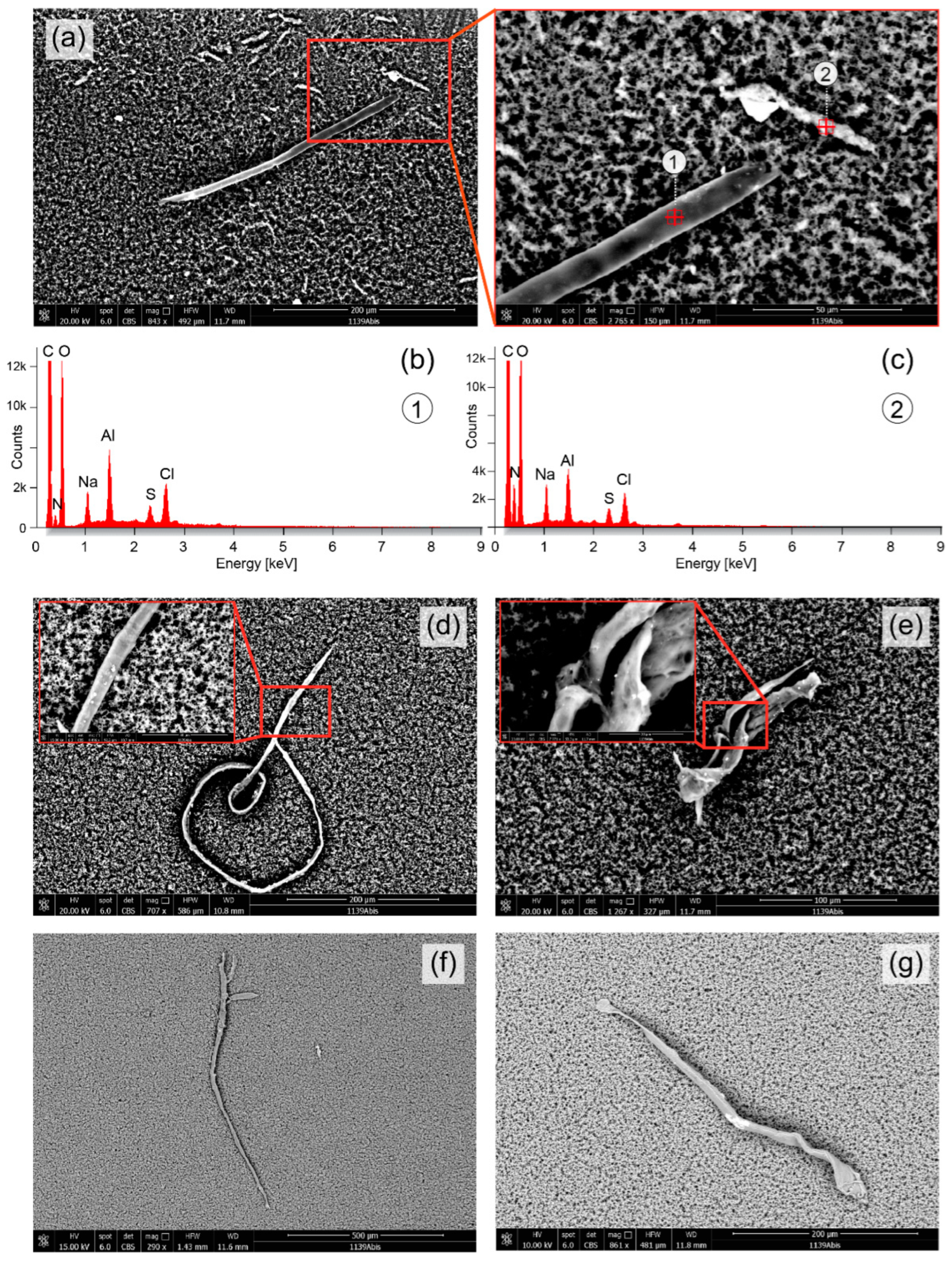
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agishi, T.; Kaneko, I.; Hasuo, Y.; Hayasaka, Y.; Sanaka, T.; Ota, K.; Amemiya, H.; Sugino, N.; Abe, M.; Ono, T.; et al. Double Filtration Plasmapheresis. ASAIO J. 1980, 26, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, R.; Namazuda, K.; Hirata, N. Double filtration plasmapheresis: Review of current clinical applications. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2020, 25, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, J.; Jiang, S.; Xu, P.; Han, H.; Wang, L. A Controlled Study of Double Filtration Plasmapheresis in the Treatment of Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 13, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Tsuda, H.; Takasaki, Y.; Hashimoto, H. Double Filtration Plasmapheresis for the Treatment of a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient with Extremely High Level of C-reactive Protein. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2004, 8, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-D.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.-S.; Lun, L.-D. Double Filtration Plasmapheresis for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Study of 21 Cases. Artif. Organs 2008, 21, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Odaka, M.; Tabata, Y.; Soeda, K.; Hayashi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Sato, T.; Yamane, S.; Isono, K. Clinical Experience of Double Filtration Plasmapheresis for Drug Refractory Neurological Diseases. Biomater. Artif. Cells Immobil. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.-K.; Chen, W.-H.; Hsieh, S.-T. Plasma Exchange Versus Double Filtration Plasmapheresis in the Treatment of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2002, 6, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Tu, K.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tian, Y.-C.; Yu, C.-C.; Hung, C.-C.; Fang, J.-T.; Yang, C.-W.; Chang, M.-Y. Prognostic factors and complication rates for double-filtration plasmapheresis in patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2015, 52, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.-C.; Chang, W.-N.; Chen, J.-B.; Chee, E.C.-Y.; Huang, C.-R.; Lu, C.-H.; Chang, C.-J.; Hung, P.-L.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-T.; et al. Long-term prognosis for Guillain-Barré syndrome: Evaluation of prognostic factors and clinical experience of automated double filtration plasmapheresis. J. Clin. Apher. 2003, 18, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Yeh, J.-H.; Chiu, H.-C. Experience of double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of Guillain-Barre syndrome. J. Clin. Apher. 1999, 14, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramunni, A.; De Robertis, F.; Brescia, P.; Saliani, M.T.; Amoruso, M.; Prontera, M.; Dimonte, E.; Trojano, M.; Coratelli, P. A Case Report of Double Filtration Plasmapheresis in an Acute Episode of Multiple Sclerosis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2008, 12, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Masi, R.; Orlando, S.; Accoto, S. Double Filtration Plasmapheresis Treatment of Refractory Multiple Sclerosis Relapsed on Fingolimod: A Case Report. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, H. Plasmapheresis in acute phase of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Nihon Rinsho. Jpn. J. Clin. Med. 2014, 72, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.-H.; Chiu, H.-C. Comparison between double-filtration plasmapheresis and immunoadsorption plasmapheresis in the treatment of patients with myasthenia gravis. J. Neurol. 2000, 247, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennani, H.N.; Lagrange, E.; Noble, J.; Malvezzi, P.; Motte, L.; Chevallier, E.; Rostaing, L.; Jouve, T. Treatment of refractory myasthenia gravis by double-filtration plasmapheresis and rituximab: A case series of nine patients and literature review. J. Clin. Apher. 2020, 36, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-F.; Wang, W.-X.; Xue, J.; Zhao, C.-B.; You, H.-Z.; Lu, J.-H.; Gu, Y. Comparing the Autoantibody Levels and Clinical Efficacy of Double Filtration Plasmapheresis, Immunoadsorption, and Intravenous Immunoglobulin for the Treatment of Late-onset Myasthenia Gravis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2010, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J.; Xue, J.; Gu, Y.; Hao, C.; Lin, S.; Lv, C. Double filtration plasmapheresis benefits myasthenia gravis patients through an immunomodulatory action. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.H.; Chiu, H.C. Double filtration plasmapheresis in myasthenia gravis-analysis of clinical efficacy and prognostic parameters. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 100, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.H.; Chen, W.H.; Chiu, H.C. Double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of myasthenic crisis-analysis of prognostic factors and efficacy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 104, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podestà, M.A.; Gennarini, A.; Portalupi, V.; Rota, S.; Alessio, M.G.; Remuzzi, G.; Ruggenenti, P. Accelerating the Depletion of Circulating Anti-Phospholipase A<sub>2</sub> Receptor Antibodies in Patients with Severe Membranous Nephropathy: Preliminary Findings with Double Filtration Plasmapheresis and Ofatumumab. Nephron 2020, 144, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Yeh, J.-H. Double Filtration Plasmapheresis in the Treatment of Inflammatory Polyneuropathy. Ther. Apher. 1997, 1, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, K.; Yuasa, N.; Mitsuma, T.; Nagamatsu, M.; Sobue, G. Double filtration plasmapheresis (DFPP) in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP). Rinsho Shinkeigaku = Clin. Neurol. 1998, 38, 719–723. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, R.; Voit-Bak, K.; Gor, A.; Steinmeier, T.; Chrousos, G.P.; Boehm, B.O.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Barbir, M.; Balanzew, W.; Bornstein, S.R. Lipid Profiles in Lyme Borreliosis: A Potential Role for Apheresis? Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Voit-Bak, K.; Rosenthal, P.; Tselmin, S.; Julius, U.; Schatz, U.; Boehm, B.O.; Thuret, S.; Kempermann, G.; Reichmann, H.; et al. Extracorporeal apheresis therapy for Alzheimer disease—Targeting lipids, stress, and inflammation. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 25, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, R.; Müller, G.; Voit-Bak, K.; Tselmin, S.; Julius, U.; Schatz, U.; Rietzsch, H.; Reichmann, H.; Chrousos, G.P.; Schürmann, A.; et al. Metabolic and Non-Metabolic Peripheral Neuropathy: Is there a Place for Therapeutic Apheresis? Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Voit-Bak, K.; Donate, T.; Rodionov, R.N.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Tselmin, S.; Kanczkowski, W.; Müller, G.M.; Achleitner, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Chronic post-COVID-19 syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome: Is there a role for extracorporeal apheresis? Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 27, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Takov, K.; Straube, R.; Voit-Bak, K.; Graessler, J.; Julius, U.; Tselmin, S.; Rodionov, R.; Barbir, M.; Walls, M.; et al. Precision Medicine Approach for Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Therapeutic Apheresis. Horm. Metab. Res. = Horm.-Und Stoffwechs. = Horm. Et Metab. 2022, 54, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Tsenkova, R. Changes in Water Properties in Human Tissue after Double Filtration Plasmapheresis-A Case Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Dubey, S.P.; Sillanpää, M.; Kwon, Y.-N.; Lee, C.; Varma, R.S. Fate of engineered nanoparticles: Implications in the environment. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 287, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Wick, P.; Nowack, B. Placing nanoplastics in the context of global plastic pollution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, M.; Neculae, A.; Bunoiu, M.; Biris, C. Nanoparticles’ Promises and Risks. In Nanoparticles’ Promises and Risks: Characterization, Manipulation, and Potential Hazards to Humanity and the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, A.M.; Montanari, S. Nanopathology: The Nano-Bio-Interaction of Nanoparticles Inside the Human Body; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallelian, F.; Buehler, P.W.; Schaer, D.J. Hemolysis, free hemoglobin toxicity and scavenger protein therapeutics. Blood 2022, 140, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, D.J.; Buehler, P.W.; Alayash, A.I.; Belcher, J.D.; Vercellotti, G.M. Hemolysis and free hemoglobin revisited: Exploring hemoglobin and hemin scavengers as a novel class of therapeutic proteins. Blood 2013, 121, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MSD-Manual. Representative Laboratory Reference Values: Blood, Plasma, and Serum. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/multimedia/table/representative-laboratory-reference-values-blood-plasma-and-serum (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Sonwani, S.; Madaan, S.; Arora, J.; Suryanarayan, S.; Rangra, D.; Mongia, N.; Vats, T.; Saxena, P. Inhalation Exposure to Atmospheric Nanoparticles and Its Associated Impacts on Human Health: A Review. Front. Sustain. Cities 2021, 3, 690444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, T.; Choi, J.; Park, D. Sources and Characteristics of Particulate Matter in Subway Tunnels in Seoul, Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golokhvast, K.S.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Chaika, V.V.; Ugay, S.M.; Zelinskaya, E.V.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Karakitsios, S.P.; Sarigiannis, D.A. Size-segregated emissions and metal content of vehicle-emitted particles as a function of mileage: Implications to population exposure. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, E.; Varghese, Z. Differences in the calcium concentration of serum and plasma initially and after storage. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1977, 14, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efsa Panel on Food Contact Materials; Enzymes and Processing Aids; Lambre, C.; Barat Baviera, J.M.; Bolognesi, C.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; et al. Safety assessment of the substance nano precipitated calcium carbonate for use in plastic food contact materials. EFSA J. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. 2022, 20, e07135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Degli Esposti, L.; Adamiano, A.; Iafisco, M. The Use of Calcium Phosphates in Cosmetics, State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Materials 2021, 14, 6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Firestein, B.L. DNA transfection: Calcium phosphate method. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1018, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.; Murase, J. Titanium Dioxide in Sunscreen. In Application of Titanium Dioxide; Janus, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicka, Z.A.; Benedetto, A.F.; Benoit, D.N.; Yu, W.W.; Fortner, J.D.; Colvin, V.L. The structure, composition, and dimensions of TiO2 and ZnO nanomaterials in commercial sunscreens. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 3607–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropers, M.-H.; Terrisse, H.; Mercier-Bonin, M.; Humbert, B. Titanium Dioxide as Food Additive. In Application of Titanium Dioxide; Janus, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, S. TiO2 particles in seafood and surimi products: Attention should be paid to their exposure and uptake through foods. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudefoi, W.; Terrisse, H.; Popa, A.F.; Gautron, E.; Humbert, B.; Ropers, M.-H. Evaluation of the content of TiO2 nanoparticles in the coatings of chewing gums. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 35, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golja, V.; Dražić, G.; Lorenzetti, M.; Vidmar, J.; Ščančar, J.; Zalaznik, M.; Kalin, M.; Novak, S. Characterisation of food contact non-stick coatings containing TiO2 nanoparticles and study of their possible release into food. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Fabricius, L.; Hristovski, K.; von Goetz, N. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Dietary Exposure to Aluminium-Containing Food Additives; European Food Safety Authority, EFSA Supporting Publications: Parma, Italy, 2013; Volume 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zahhar, A.A.; Idris, A.M.; Fawy, K.F.; Arshad, M. SEM, SEM-EDX, µ-ATR-FTIR and XRD for urban street dust characterisation. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 101, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, C. Human exposure to aluminium. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.W.; Chung, S.W.; Kwong, K.P.; Yin Ho, Y.; Xiao, Y. Dietary exposure to aluminium of the Hong Kong population. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2010, 27, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, S. Aluminium Exposure Through the Diet. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, G.; La Joie, E.; Thomas, P.; Lyons-Weiler, J. Acute exposure and chronic retention of aluminum in three vaccine schedules and effects of genetic and environmental variation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 58, 126444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.M.; Kassis, T.; Rogers, A.M.; Schudel, A.; Weil, J.; Evans, C.C.; Moorhead, A.R.; Thomas, S.N.; Dixon, J.B. Optimization of culture and analysis methods for enhancing long-term Brugia malayi survival, molting and motility in vitro. Parasitol. Open 2018, 4, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Menezes, A.; Lins, R.; Noroes, J.; Dreyer, G.; Lanfredi, R.M. Comparative analysis of a chemotherapy effect on the cuticular surface of Wuchereria bancrofti adult worms in vivo. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paily, K.P.; Hoti, S.L.; Das, P.K. A review of the complexity of biology of lymphatic filarial parasites. J. Parasit. Dis. Off. Organ Indian Soc. Parasitol. 2009, 33, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namrata, P.; Miller, J.; Shilpa, M.; Reddy, P.; Bandoski, C.; Rossi, M.; Sapi, E. Filarial Nematode Infection in Ixodes scapularis Ticks Collected from Southern Connecticut. Vet. Sci. 2014, 1, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, T.C.; Orr, J.M.; Smith, J.D.; Arias, J.R.; Rasgon, J.L.; Norris, D.E. Discovery of filarial nematode DNA in Amblyomma americanum in Northern Virginia. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Möller, W. Health implications of nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scholkmann, F.; Gatti, A.M. Particles in the Eluate from Double Filtration Plasmapheresis—A Case Study Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (FE-SEM/EDX). Compounds 2022, 2, 367-377. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040030
Scholkmann F, Gatti AM. Particles in the Eluate from Double Filtration Plasmapheresis—A Case Study Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (FE-SEM/EDX). Compounds. 2022; 2(4):367-377. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleScholkmann, Felix, and Antonietta M. Gatti. 2022. "Particles in the Eluate from Double Filtration Plasmapheresis—A Case Study Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (FE-SEM/EDX)" Compounds 2, no. 4: 367-377. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040030
APA StyleScholkmann, F., & Gatti, A. M. (2022). Particles in the Eluate from Double Filtration Plasmapheresis—A Case Study Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (FE-SEM/EDX). Compounds, 2(4), 367-377. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040030






