Quality Assessment of Medicinal Plants via Chemometric Exploration of Quantitative NMR Data: A Review
Abstract
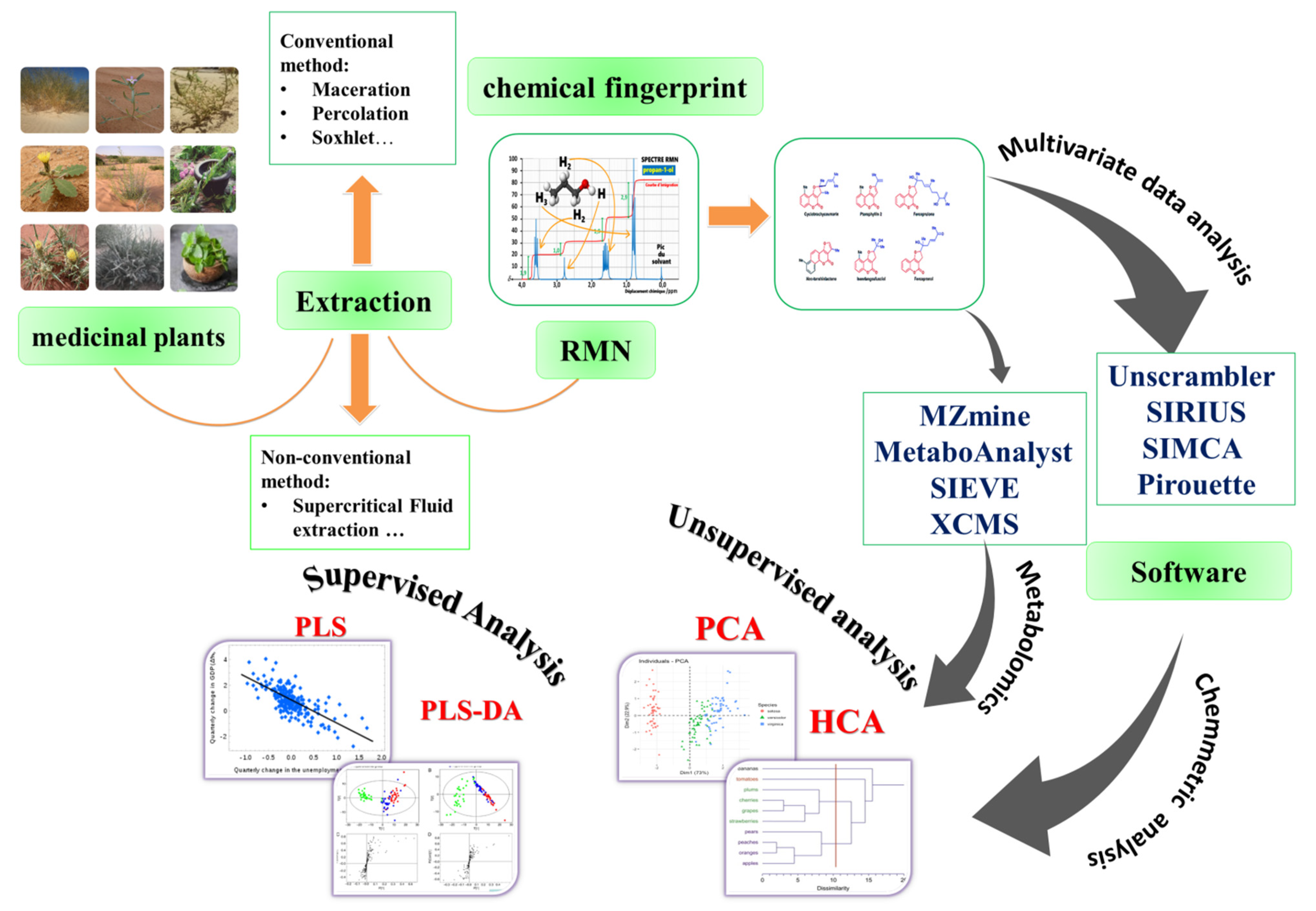
:1. Introduction
2. Herbal Extracts as Therapeutic Agents
3. Quality Control and Quality Assurance (QC/QA) of Herbal Medicine
4. Techniques in Metabolomics
- (a)
- The quantification of specific metabolites via targeted compound analysis.
- (b)
- Metabolic profiling for determining the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of a set of related substances or specific metabolic pathways.
- (c)
- Metabolomic fingerprinting for classifying samples via quick global examination.
- (d)
- Metabolomic study that entails analyzing “all” metabolites quantitatively and qualitatively (which is not yet possible).
5. Plant (Herbal) Metabolomics Experimental Methods
5.1. Herbal Product Collection and Extraction
5.2. NMR Analysis
6. Chemometric Analysis
6.1. Unsupervised Data Exploration by PCA
6.2. Self-Modeling Multivariate Curve Resolution
6.3. Supervised Data Exploration by PLS Regression
6.4. Supervised Classification by PLS-DA Regression
6.5. Improved Supervised Models by Variable Reduction
6.6. Improved Supervised Classification by Orthogonal Factor Extraction
7. Multivariate Data Analysis
7.1. Adaptation of NMR Data for Chemometrics
7.2. Spectral Fingerprinting
7.3. Spectral Profiling
8. Natural Product Metabolomics Using NMR
8.1. Analysis of Complex Pharmaceutical Preparation Using NMR Metabolomics
8.2. Using NMR Metabolomics to Analyze Complex Artemisia Herbal Medicine
8.3. Chemical Profiling of HMs
8.4. Ephedra Metabolic Fingerprinting Using NMR
| No. | Plant Name | Publication Year | Research Aims | Applied Statistical Methods (If Any) | Analytical Techniques | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Panax ginseng (roots) | 2012 | Quality assessment | PCA HCA PLS PLS-DA | 1H-NMR | [102] |
| 2 | Artemisia afra, A. annua (herb) | 2010 | Quality assessment | PCA | 1H-NMR | [103] |
| 3 | Zea mays (seeds) | 2010 | Quality assessment | PCA HCA SIMCA | 1H-NMR | [104] |
| 4 | Echinacea purpurea, E. pallida, E. angustifolia, E. simulate (roots and aerial parts) | 2010 | Taxonomic discrimination | PCA | 1H-NMR | [105] |
| 5 | Ganoderma lucidum (herb) | 2010 | Geographic origins | PCA OPLS-DA | 1H-NMR | [106] |
| 6 | Panax ginseng, P. quinquefolius (roots) | 2009 | Taxonomic discrimination | PCA | 1H-NMR | [107] |
| 7 | Arabidopsis | 2009 | Taxonomic discrimination | PLS-DA | 1H NMR | [108] |
| 8 | Green Tea | 2007 | Quality assessment | PCA PLS OSC | 1H-NMR | [109] |
| 9 | Panax ginseng Panax ginseng C.A. (roots) | 2007 | Quality assessment | PCA | 1H-NMR | [110] |
| 10 | Brassica rapa (leaves) | 2007 | Geographic origins | PCA | 1H-NMR | [111] |
| 11 | Ilex ssp. (arbutin) | 2005 | Discrimination | PCA | 1H-NMR | [112] |
| 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (seeds) | 2003 | Discrimination | PCA | 1H-NMR | [113] |
| 13 | Strychnos nux-vomica (seeds, stem bark, root bark), S. icaja (seeds), S. ignatii (leaves, stem bark, root bark and collar bark) | 2004 | Discrimination | PCA | 1H-NMR | [114] |
| 14 | Artemisia annua (herb) | 2004 | Geographic origins | PCA PLS PLS-DA | 1H-NMR | [115] |
| 15 | Camellia sinensis (green tea leaves) | 2004 | Geographic origins | PCA HCA | 1H-NMR | [116] |
| 16 | Cannabis sativa (flowers) | 2004 | Geographic origins | PCA | 1H-NMR | [117] |
| 17 | Coffee | 2002 | Quality assessment | PCA LDA | 1H-NMR | [118] |
| 18 | Quillaja saponaria (bark/saponins) | 2001 | Structural elucidation | PCA PLS-DA | 1H-NMR | [119] |
| 19 | Propolis | 2016 | Classification | PLS-DA RF | [120] | |
| 20 | Ginseng Radix | 2010 | Evaluation | PCA CA | 1H–NMR | [121] |
| 21 | Isatis tinctoria | 2015 | Comparison | PCA CA k-NN | 1H–NMR | [122] |
| 22 | genus Paeonia L. | 2017 | Determination | PCA | 1H–NMR | [123] |
| 23 | Serenoa repens | 2018 | Authentication of saw palmetto | PCA | 1H–NMR | [124] |
| 24 | Polygoni Multiflori Radix | 2018 | Metabolomics | PLS-DA N3 | 1H–NMR | [125] |
| 25 | Two cinnamon species | 2018 | Authentication | PCA OPLS-DA | 1H–NMR | [126] |
| 26 | Neptunia oleracea | 2016 | Metabolites | PLSR | 1H–NMR | [127] |
| 27 | Orthosiphon stamineus | 2011 | Metabolomics | PLSR OPLSR | 1H–NMR | [128] |
| 28 | Saffron | 2010 | Discrimination | PCA | 1H–NMR | [129] |
| 29 | Angelica gigas | 2011 | Metabolomics | PCA OPLS-DA | 1H–NMR | [130] |
9. NMR-Based Metabolomics: What the Future Holds
9.1. Perspectives on the Economy
9.2. Perspective on Future Developments
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Hsu, C.S. Molecular characterization of sulfur-containing compounds in petroleum. Fuel 2018, 221, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hu, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Rong, R.X.; Li, X.L.; Wang, K.R. Synthesis, self-aggregation and cryopreservation effects of perylene bisimide–Glycopeptide conjugates. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12000–12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofidis, E. Blind source separation: Fundamentals and recent advances (a tutorial overview presented at sbrt-2001). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.03089. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Jafarikukhdan, A.; Hosseini, A.; Armand, R. The application of medicinal plants in traditional and modern medicine: A review of Thymus vulgaris. Int. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 6, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2002: Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Saqib, F.; Janbaz, K.H. Rationalizing ethnopharmacological uses of Alternanthera sessilis: A folk medicinal plant of Pakistan to manage diarrhea, asthma and hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 182, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, H.M.; Meyer, J.J.M. NMR-based metabolomics as a quality control tool for herbal products. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 82, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, A.D.; Ahmad, O.; Guillot, M.; Ferguson, B.D.; Salomon, J.A.; Murray, C.J.L.; Hill, K.H. World Mortality in 2000: Life Tables for 191 Countries; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Mateo, R.; Castells, G.; Green, A.J.; Godoy, C.; Cristofol, C. Determination of porphyrins and biliverdin in bile and excreta of birds by a single liquid chromatography–Ultraviolet detection analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 810, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weathers, P.J.; Arsenault, P.R.; Covello, P.S.; McMickle, A.; Teoh, K.H.; Reed, D.W. Artemisinin production in Artemisia annua: Studies in planta and results of a novel delivery method for treating malaria and other neglected diseases. Phytochem. Rev. 2011, 10, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wills, R.B.; Bone, K.; Morgan, M. Herbal products: Active constituents, modes of action and quality control. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2000, 13, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.M. Synergy and other interactions in phytomedicines. Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.M.; Ribnicky, D.M.; Lipsky, P.E.; Raskin, I. Revisiting the ancient concept of botanical therapeutics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Kotecha, M. A review on the Standardization of herbal medicines. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Patnala, S.; Kanfer, I. Quality control, extraction methods, and standardization: Interface between traditional use and scientific investigation. In Herbal Medicine in Andrology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Ni, H.; Li, P.; Li, H.-J. Discovery of quality control markers from traditional Chinese medicines by fingerprint-efficacy modeling: Current status and future perspectives. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Länger, R.; Stöger, E.; Kubelka, W.; Helliwell, K. Quality standards for herbal drugs and herbal drug preparations—Appropriate or improvements necessary? Planta Med. 2018, 84, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Woo, S.-O.; Koh, H.-L. HPLC and GC–MS screening of Chinese proprietary medicine for undeclared therapeutic substances. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, M.J.; Hassan, H.; Al-Enazi, E.; Ibrahim, Z.; Al-Tufail, M. Application of LC–ESI–MS–MS for detection of synthetic adulterants in herbal remedies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Qu, J.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y. Rapid and reliable determination of illegal adulterant in herbal medicines and dietary supplements by LC/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lu, F.; Yu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Wu, Y. Determination of synthetic drugs used to adulterate botanical dietary supplements using QTRAP LC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. 2009, 26, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xueyi, Z.; Zhonghu, Z.; Feng, L.; Yutian, W.; Yunpeng, Q. Modified local straight-line screening to detect synthetic drugs in adulterated herbal medicines. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, A.; Terauchi, M.; Sugimura, M.; Matsuo, T.; Mochiike, C. Rapid determination of medical components found in the health food for weight loss by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 128, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xiao, S.; Luo, D.; Chen, B.; Yao, S. Simultaneous determination of sibutramine and N-di-desmethylsibutramine in dietary supplements for weight control by HPLC—ESI-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, T.-b.; Hu, X.-h.; Liu, X. Investigation of banned additives in healthy foods for weight control. Chin. J. Food Hyg. 2007, 19, 337–366. [Google Scholar]
- Cianchino, V.; Acosta, G.; Ortega, V.; Martínez, L.; Gomez, M.R. Analysis of potential adulteration in herbal medicines and dietary supplements for the weight control by capillary electrophoresis. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Li, S.; Le, J.; Chen, G.; Cao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chai, Y.; Wu, Y. A new method for testing synthetic drugs adulterated in herbal medicines based on infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 589, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaysse, J.; Balayssac, S.; Gilard, V.; Desoubdzanne, D.; Malet-Martino, M.; Martino, R. Analysis of adulterated herbal medicines and dietary supplements marketed for weight loss by DOSY 1H-NMR. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikam, P.H.; Kareparamban, J.; Jadhav, A.; Kadam, V. Future trends in standardization of herbal drugs. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, M.; Russell, P.J.; Vander Heyden, Y. Similarity analyses of chromatographic herbal fingerprints: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 804, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.A.; Dias, D.A.; Callahan, D.L.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Beale, D.J.; Roessner, U. The use of metabolomics in the study of metals in biological systems. Metallomics 2015, 7, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, M.; Piras, C.; Bassareo, P.P.; Dessalvi, C.C.; Mercuro, G. Metabolomics, a promising approach to translational research in cardiology. IJC Metab. Endocr. 2015, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuro, G.; Bassareo, P.P.; Deidda, M.; Cadeddu, C.; Barberini, L.; Atzori, L. Metabolomics: A new era in cardiology? J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2011, 12, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyur, L.F.; Yang, N.S. Metabolomics for phytomedicine research and drug development. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindon, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Peer reviewed: So what’s the deal with metabonomics? Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 385A–391A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, G.F.; Jaki, B.U.; Lankin, D.C. Quantitative 1H NMR: Development and potential of a method for natural products analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viant, M.R. Improved methods for the acquisition and interpretation of NMR metabolomic data. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, A.; Allnutt, T.; Holmes, S.; Chisholm, J.; Bean, S.; Ellis, N.; Mullineaux, P.; Oehlschlager, S. NMR profiling of transgenic peas. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2004, 2, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaki, B.; Franzblau, S.; Cho, S.; Pauli, G. Development of an extraction method for mycobacterial metabolome analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mushtaq, M.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Wilson, E.G. Extraction for metabolomics: Access to the metabolome. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrawati, O.; Yao, Q.; Kim, H.K.; Linthorst, H.J.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic differentiation of Arabidopsis treated with methyl jasmonate using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.A.; Bouzabata, A. Application of chemometrics in quality control of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) based on Ultra-violet, Fourier transform-infrared and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Connelly, J.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. Metabonomics: A platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, F.; Dorian, V.; Vallance, H.; Wishart, D. Diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism using 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis of urine. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1999, 22, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, J.L.; Walker, L.A.; Garrod, S.; Holmes, E.; Shore, R.F.; Nicholson, J.K. NMR spectroscopy based metabonomic studies on the comparative biochemistry of the kidney and urine of the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus), wood mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus), white toothed shrew (Crocidura suaveolens) and the laboratory rat. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 127, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.; Osborn, D.; Weeks, J.; Lindon, J.; Nicholson, J. An NMR-based metabonomic approach to the investigation of coelomic fluid biochemistry in earthworms under toxic stress. FEBS Lett. 2001, 500, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araníbar, N.; Singh, B.K.; Stockton, G.W.; Ott, K.-H. Automated mode-of-action detection by metabolic profiling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, N.J.; Oven, M.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Zenk, M.H. Metabolomic analysis of the consequences of cadmium exposure in Silene cucubalus cell cultures via 1H NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Rebiai, A.; Sawicka, B.; Atanassova, M.; Ouakouak, H.; Larkem, I.; Egbuna, C.; Awuchi, C.G.; Boubekeur, S.; Ferhat, M.A.; et al. Effect of Extraction Methods on Polyphenols, Flavonoids, Mineral Elements, and Biological Activities of Essential Oil and Extracts of Mentha pulegium L. Molecules 2022, 27, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolomic analysis of Catharanthus roseus using NMR and principal component analysis. In Plant Metabolomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Engelsen, S.B.; Savorani, F.; Rasmussen, M.A. Chemometric exploration of quantitative NMR data. Emagres 2013, 2, 267–278. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, W.S.; Richter, W.; Andreotti, A.H.; Farmer, B.T. Generation of impossible cross-peaks between bulk water and biomolecules in solution NMR. Science 1993, 262, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakach, T.K.; Wentzell, P.D.; Walter, J.A. Characterization of the measurement error structure in 1D 1H NMR data for metabolomics studies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 636, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granato, D.; Santos, J.S.; Escher, G.B.; Ferreira, B.L.; Maggio, R.M. Use of principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for multivariate association between bioactive compounds and functional properties in foods: A critical perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Choosing a subset of principal components or variables. Princ. Compon. Anal. 2002, 47, 111–149. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, T.L.; Duarte, L.M.; Dos Santos, H.F.; de Oliveira, M.A.L. Screening method for simultaneous detection of elaidic and vaccenic trans fatty acid isomers by capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1048, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.E. Principal components and factor analysis: Part I—Principal components. J. Qual. Technol. 1980, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, S.; Palazoglu, A. A data-driven multidimensional visualization technique for process fault detection and diagnosis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 154, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Tutwiler, S.W. The Contradictions of the Legacy of Brown V. Board of Education, a Special Issue of Educational Studies, Topeka (1954); Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014; Volume 37, pp. 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, W.H.; Sylvestre, E.A. Self modeling curve resolution. Technometrics 1971, 13, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauler, R. Multivariate curve resolution applied to second order data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1995, 30, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eads, C.D.; Furnish, C.M.; Noda, I.; Juhlin, K.D.; Cooper, D.A.; Morrall, S.W. Molecular factor analysis applied to collections of NMR spectra. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Williams, A. Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy. Webb GA Ed. 2005, 55, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Martens, H.; Wold, H. The multivariate calibration problem in chemistry solved by the PLS method. In Matrix Pencils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; Volume 973, pp. 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.; Juneja, P.; Kaur, B.; Kumar, P. Pharmaceutical applications of chemometric techniques. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wold, S. Cross-validatory estimation of the number of components in factor and principal components models. Technometrics 1978, 20, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M. Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1974, 36, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhle, L.; Wold, S. Partial least squares analysis with cross-validation for the two-class problem: A Monte Carlo study. J. Chemom. 1987, 1, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemsley, E.K.; Le Gall, G.; Dainty, J.R.; Watson, A.D.; Harvey, L.J.; Tapp, H.S.; Colquhoun, I.J. Multivariate techniques and their application in nutrition: A metabolomics case study. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Anibal, C.V.; Callao, M.P.; Ruisánchez, I. 1H NMR variable selection approaches for classification. A case study: The determination of adulterated foodstuffs. Talanta 2011, 86, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E.; Foca, G.; Vignali, M.; Tassi, L.; Ulrici, A. Adulteration of the anthocyanin content of red wines: Perspectives for authentication by Fourier Transform-Near InfraRed and 1H NMR spectroscopies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 701, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winning, H.; Roldán-Marín, E.; Dragsted, L.O.; Viereck, N.; Poulsen, M.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Cano, M.P.; Engelsen, S.B. An exploratory NMR nutri-metabonomic investigation reveals dimethyl sulfone as a dietary biomarker for onion intake. Analyst 2009, 134, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savorani, F.; Picone, G.; Badiani, A.; Fagioli, P.; Capozzi, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Metabolic profiling and aquaculture differentiation of gilthead sea bream by 1H NMR metabonomics. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, L.; Saudland, A.; Wagner, J.; Nielsen, J.P.; Munck, L.; Engelsen, S.B. Interval partial least-squares regression (i PLS): A comparative chemometric study with an example from near-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. XV—The correlation between relatives on the supposition of Mendelian inheritance. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1919, 52, 399–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Velzen, E.J.; Westerhuis, J.A.; van Duynhoven, J.P.; van Dorsten, F.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Jacobs, D.M.; Smit, S.; Draijer, R.; Kroner, C.I.; Smilde, A.K. Multilevel data analysis of a crossover designed human nutritional intervention study. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4483–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, C.A. Direct orthogonalization. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1999, 47, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; De Jong, S.; Smilde, A.K. Direct orthogonal signal correction. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 56, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, J.-M.; Chauchard, F.; Bellon-Maurel, V. EPO–PLS external parameter orthogonalisation of PLS application to temperature-independent measurement of sugar content of intact fruits. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2003, 66, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cloarec, O.; Dumas, M.-E.; Craig, A.; Barton, R.H.; Trygg, J.; Hudson, J.; Blancher, C.; Gauguier, D.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. Statistical total correlation spectroscopy: An exploratory approach for latent biomarker identification from metabolic 1H NMR data sets. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapp, H.S.; Kemsley, E.K. Notes on the practical utility of OPLS. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedemann, A.; von Malotky, L.; Erban, A.; Kopka, J. TagFinder: Preprocessing software for the fingerprinting and the profiling of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry based metabolome analyses. In Plant Metabolomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 860, pp. 255–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.; Beale, M. NMR spectroscopy in plant metabolomics. In Plant Metabolomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 57, pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, J.; Tenke, C.E. Optimizing PCA methodology for ERP component identification and measurement: Theoretical rationale and empirical evaluation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 2307–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosipal, R.; Kramer, N. Overview and Recent Advances in Partial Least Squares. Subspace, Latent Structure and Feature Selection: Statistical and Optimization Perspectives Workshop (SLSFS 2005), Revised Selected Papers (Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3940); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Geană, E.-I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Apetrei, C.; Artem, V. Application of spectroscopic UV-Vis and FT-IR screening techniques coupled with multivariate statistical analysis for red wine authentication: Varietal and vintage year discrimination. Molecules 2019, 24, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, J.L.; Baker, J.M.; Beale, M.H. Recent applications of NMR spectroscopy in plant metabolomics. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodacre, R.; Broadhurst, D.; Smilde, A.K.; Kristal, B.S.; Baker, J.D.; Beger, R.; Bessant, C.; Connor, S.; Capuani, G.; Craig, A.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.T.; Athersuch, T.J.; Ebbels, T.M.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Keun, H.C. Robust algorithms for automated chemical shift calibration of 1D 1H NMR spectra of blood serum. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7158–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.; Foxall, P.; Nicholson, L.; Neild, G.; Brown, S.; Beddell, C.R.; Sweatman, B.C.; Rahr, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Spraul, M.; et al. Automatic data reduction and pattern recognition methods for analysis of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of human urine from normal and pathological states. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 220, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, N.; Carstensen, J.; Smedsgaard, J. Aligning of single and multiple wavelength chromatographic profiles for chemometric data analysis using correlation optimised warping. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 805, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselkov, K.A.; Lindon, J.C.; Ebbels, T.M.; Crockford, D.; Volynkin, V.V.; Holmes, E.; Davies, D.B.; Nicholson, J.K. Recursive segment-wise peak alignment of biological 1H NMR spectra for improved metabolic biomarker recovery. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savorani, F.; Tomasi, G.; Engelsen, S.B. Icoshift: A versatile tool for the rapid alignment of 1D NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 202, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloarec, O.; Dumas, M.E.; Trygg, J.; Craig, A.; Barton, R.H.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E. Evaluation of the orthogonal projection on latent structure model limitations caused by chemical shift variability and improved visualization of biomarker changes in 1H NMR spectroscopic metabonomic studies. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamud, E.; Vastag, L.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Metabolomic analysis and visualization engine for LC—MS data. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9818–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, B.; Cloarec, O.; Tang, H.; Stærk, D.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Multivariate analysis of integrated and full-resolution 1H-NMR spectral data from complex pharmaceutical preparations: St. John’s wort. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Kooy, F.; Verpoorte, R.; Meyer, J.M. Metabolomic quality control of claimed anti-malarial Artemisia afra herbal remedy and A. afra and A. annua plant extracts. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2008, 74, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, T.; Kamo, K. Seasonal changes of floral frequency and composition of flower in two cool temperate secondary forests in Japan. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 175, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic fingerprinting of Ephedra species using 1H-NMR spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.-O.; Shin, Y.-S.; Hyun, S.-H.; Cho, S.; Bang, K.-H.; Lee, D.; Choi, S.P.; Choi, H.-K. NMR-based metabolic profiling and differentiation of ginseng roots according to cultivation ages. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 58, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.Q.; Cao, M.; Frédérich, M.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; van der Kooy, F. Metabolomic investigation of the ethnopharmacological use of Artemisia afra with NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnen, S.; Bernardi Ogliari, J.; Dias, P.F.; da Silva Santos, M.; Ferreira, A.G.; Bonham, C.C.; Wood, K.V.; Maraschin, M. Metabolic fingerprint of Brazilian maize landraces silk (stigma/styles) using NMR spectroscopy and chemometric methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frédérich, M.; Jansen, C.; De Tullio, P.; Tits, M.; Demoulin, V.; Angenot, L. Metabolomic analysis of Echinacea spp. by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry and multivariate data analysis technique. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 21, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Kang, S.; Song, Y.; Song, Y.; Sung, S.H.; Park, S. Differentiation of cultivation sources of Ganoderma lucidum by NMR-based metabolomics approach. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 21, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Shaykhutdinov, R.; Weljie, A.M.; Vogel, H.J.; Facchini, P.J.; Park, S.-U.; Kim, Y.-K.; Yang, T.-J. Quality assessment of ginseng by 1H NMR metabolite fingerprinting and profiling analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7513–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, T.; Peng, Y.; Xia, B.; Qu, L.-J. Distinguishing transgenic from non-transgenic Arabidopsis plants by 1H NMR-based metabolic fingerprinting. J. Genet. Genom. 2009, 36, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarachiwin, L.; Ute, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Fukusaki, E. 1H NMR based metabolic profiling in the evaluation of Japanese green tea quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9330–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-S.; Bang, K.-H.; In, D.-S.; Kim, O.-T.; Hyun, D.-Y.; Ahn, I.-O.; Ku, B.C.; Kim, S.-W.; Seong, N.-S.; Cha, S.-W. Fingerprinting analysis of fresh ginseng roots of different ages using 1H-NMR spectroscopy and principal components analysis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Farid, I.B.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic characterization of Brassica rapa leaves by NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7936–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; Sertic, S.; Kim, H.K.; Wilson, E.G.; Michopoulos, F.; Lefeber, A.W.; Erkelens, C.; Prat Kricun, S.D.; Verpoorte, R. Classification of Ilex species based on metabolomic fingerprinting using nuclear magnetic resonance and multivariate data analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frédérich, M.; Choi, Y.H.; Angenot, L.; Harnischfeger, G.; Lefeber, A.W.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolomic analysis of Strychnos nux-vomica, Strychnos icaja and Strychnos ignatii extracts by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry and multivariate analysis techniques. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, N.J.; Wang, Y.; Sampson, J.; Davis, W.; Whitcombe, I.; Hylands, P.J.; Croft, S.L.; Holmes, E. Prediction of anti-plasmodial activity of Artemisia annua extracts: Application of 1H NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, G.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Defernez, M. Metabolite profiling using 1H NMR spectroscopy for quality assessment of green tea, Camellia sinensis (L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.K.; Hazekamp, A.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolomic Differentiation of Cannabis sativa Cultivars Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Harris, C.; Lewis, J.; Beale, M.H. Assessment of 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis as a technique for metabolite fingerprinting of Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, A.J.; Farrington, W.H.; Brereton, P. Application of 1H NMR and multivariate statistics for screening complex mixtures: Quality control and authenticity of instant coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3098–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nord, L.I.; Kenne, L.; Jacobsson, S.P. Multivariate analysis of 1H NMR spectra for saponins from Quillaja saponaria Molina. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 446, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschin, M.; Somensi-Zeggio, A.; Oliveira, S.K.; Kuhnen, S.; Tomazzoli, M.M.; Raguzzoni, J.C.; Zeri, A.C.; Carreira, R.; Correia, S.; Costa, C. Metabolic profiling and classification of propolis samples from Southern Brazil: An NMR-based platform coupled with machine learning. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.-N.; Lu, H.-Y.; Lee, M.-S.; Yang, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Chang, Y.-S.; Chang, W.T. Evaluation of the cultivation age of dried ginseng radix and its commercial products by using 1H-NMR fingerprint analysis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldbrandsen, N.; Kostidis, S.; Schäfer, H.; De Mieri, M.; Spraul, M.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Mikros, E.; Hamburger, M. NMR-Based metabolomic study on Isatis tinctoria: Comparison of different accessions, harvesting dates, and the effect of repeated harvesting. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Rong, Z.-M.; Ma, C.-X.; Zhao, X.-F.; Xiao, C.-N.; Zheng, X.-H. Distribution of metabolites in root barks of seven tree peony cultivars for quality assessment using nmr-based metabolomics. Chin. Herb. Med. 2017, 9, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Paolini, M.; Camin, F.; Appendino, G.; Vitulo, F.; De Combarieu, E.; Sardone, N.; Martinelli, E.M.; Pace, R. Combined use of isotopic fingerprint and metabolomics analysis for the authentication of saw palmetto (Serenoa repens) extracts. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, M.; Ren, X.; Jiang, M.; Deng, Y. Rapid authentication and differentiation of herbal medicine using 1H NMR fingerprints coupled with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Labib, R.M.; Noleto, C.; Porzel, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. NMR approach for the authentication of 10 cinnamon spice accessions analyzed via chemometric tools. LWT 2018, 90, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Abas, F.; Khatib, A.; Ismail, I.S.; Shaari, K.; Zawawi, N. Metabolite profiling of Neptunia oleracea and correlation with antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities using 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 16, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliana, N.D.; Khatib, A.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Comprehensive extraction method integrated with NMR metabolomics: A new bioactivity screening method for plants, adenosine A1 receptor binding compounds in Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6902–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Nyberg, N.T.; Mølgaard, P.; Asili, J.; Jaroszewski, J.W. 1H NMR metabolic fingerprinting of saffron extracts. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kwon, J.; Park, S.H.; Park, C.; Seo, Y.-B.; Shin, H.-K.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, K.-S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Ryu, D.H. Metabolite profiling of Angelica gigas from different geographical origins using 1H NMR and UPLC-MS analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8806–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moing, A.; Maucourt, M.; Renaud, C.; Gaudillère, M.; Brouquisse, R.; Lebouteiller, B.; Gousset-Dupont, A.; Vidal, J.; Granot, D.; Denoyes-Rothan, B.; et al. Quantitative metabolic profiling by 1-dimensional 1H-NMR analyses: Application to plant genetics and functional genomics. Funct. Plant Biol. 2004, 31, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based plant metabolomics: Where do we stand, where do we go? Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebiai, A.; Seghir, B.B.; Hemmami, H.; Zeghoud, S.; Amor, I.B.; Kouadri, I.; Messaoudi, M.; Pasdaran, A.; Caruso, G.; Sharma, S.; et al. Quality Assessment of Medicinal Plants via Chemometric Exploration of Quantitative NMR Data: A Review. Compounds 2022, 2, 163-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2020012
Rebiai A, Seghir BB, Hemmami H, Zeghoud S, Amor IB, Kouadri I, Messaoudi M, Pasdaran A, Caruso G, Sharma S, et al. Quality Assessment of Medicinal Plants via Chemometric Exploration of Quantitative NMR Data: A Review. Compounds. 2022; 2(2):163-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebiai, Abdelkrim, Bachir Ben Seghir, Hadia Hemmami, Soumeia Zeghoud, Ilham Ben Amor, Imane Kouadri, Mohammed Messaoudi, Ardalan Pasdaran, Gianluca Caruso, Somesh Sharma, and et al. 2022. "Quality Assessment of Medicinal Plants via Chemometric Exploration of Quantitative NMR Data: A Review" Compounds 2, no. 2: 163-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2020012
APA StyleRebiai, A., Seghir, B. B., Hemmami, H., Zeghoud, S., Amor, I. B., Kouadri, I., Messaoudi, M., Pasdaran, A., Caruso, G., Sharma, S., Atanassova, M., & Pohl, P. (2022). Quality Assessment of Medicinal Plants via Chemometric Exploration of Quantitative NMR Data: A Review. Compounds, 2(2), 163-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2020012











