Checklist of Medico-Veterinary Important Biting Flies (Ceratopogonidae, Hippoboscidae, Phlebotominae, Simuliidae, Stomoxyini, and Tabanidae) and Their Associated Pathogens and Hosts in Maghreb
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
3. Main Biting Fly Groups of Medical and Veterinary Importance in the Maghreb
3.1. Stomoxyini
3.2. Hippoboscidae
3.3. Ceratopogonidae
3.4. Tabanidae
3.5. Phlebotominae
3.6. Simuliidae
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nizam, N.; Najib, C.M.; Yusof, N.M.; Naser, N.M.; Hatta, S.M. Preliminary Study on the Distribution and Diversity of Diptera at Tuba Island Reserve Forest, Langkawi Malaysia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1019, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Mayfield, M.M. Diptera species and functional diversity across tropical Australian countryside landscapes. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 191, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaux Torres, M.-C.; Pellot, C.; Somwang, P.; Khositharattanakool, P.; Vongphayloth, K.; Randrianambinintsoa, F.J.; Mathieu, B.; Siriyasatien, P.; Gay, F.; Depaquit, J. Phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera, Psychodidae) from Pha Tong cave, Northern Thailand with a description of two new species and taxonomical thoughts about Phlebotomus stantoni. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limsopatham, K.; Klong-Klaew, T.; Fufuang, N.; Sanit, S.; Sukontason, K.L.; Sukontason, K.; Somboon, P.; Sontigun, N. Wing morphometrics of medically and forensically important muscid flies (Diptera: Muscidae). Acta Trop. 2021, 222, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Lopez, A.; Ruiz, C.; Galian, J.; Romera, E. Molecular identification of forensically important fly species in Spain using COI barcodes. Sci. Justice 2020, 60, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotonirina, A.; Pol, M.; Kainiu, M.; Barsac, E.; Tutagata, J.; Kilama, S.; O’connor, O.; Tarantola, A.; Colot, J.; Dupont-Rouzeyrol, M. MALDI-TOF MS: Optimization for future uses in entomological surveillance and identification of mosquitoes from New Caledonia. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.D.; Blodorn, E.; Zafalon-Silva, Â.; Domingues, W.; Marques, R.; Krolow, T.K.; Greif, G.; Campos, V.F.; Krüger, R.F. Molecular detection of Trypanosoma kaiowa in Tabanus triangulum (Diptera: Tabanidae) from the coastal plain of Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansens, E.J. Tabanidae of the east coast as an economic problem. J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 1979, 87, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Malta, L.G.F.; Sant’anna, M.R.V.; Pereira, M.H.; Gontijo, N.F. A brief look at sexual dimorphism in the midgut morphology of lower Diptera and its implications for hematophagy. Zool. Anz. 2024, 313, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mann, B.K. Insect bite reactions. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2013, 79, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiodorova, O.; Sivkova, E. Blood-sucking midges’ ecology in pastures and cattle farms Of the Tyumen Region. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2020, 10, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soviana, S.; Hadi, U.K.; Putra, A.K. Diversity and activity of bloodsucking flies (Diptera: Muscidae) in Cibungbulang dairy farm, Bogor regency Indonesia. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 738–741. [Google Scholar]
- González, M.; López, S.; Alarcón-Elbal, P.M. Blood-feeding Diptera (Culicidae and Ceratopogonidae) in an urban park of the city of Vitoria-Gasteiz (Basque Country, Spain). J. Eur. Mosq. Control Assoc 2015, 33, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Yu, M.-T.; Kuo, T.-W.; Lam, K.-I.; Yang, J.-T. Does Culicoides spp. (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) not suck human blood in Riparian Habitat of a National Park. Adv. Entomol. 2017, 5, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, X.-Q.; Yu, Y.-X.; Zheng, W.-Q.; Ma, H.-M.; Fu, R.-L.; Chen, H.-Y. An investigation and study of biting midges (Ceratopogonidae) in nine major tourist attractions in Jiangxi Province, China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2020, 31, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Khyatti, M.; Trimbitas, R.-D.; Zouheir, Y.; Benani, A.; El Messaoudi, M.-D.; Hemminki, K. Infectious diseases in North Africa and north African immigrants to Europe. Eur. J. Public Health 2014, 24, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaara, D.; Haouas, N.; Dedet, J.P.; Babba, H.; Pratlong, F. Leishmaniases in Maghreb: An endemic neglected disease. Acta Trop. 2014, 132, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githeko, A.K.; Lindsay, S.W.; Confalonieri, U.E.; Patz, J.A. Climate change and vector-borne diseases: A regional analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Hotez, P.J. Southern Europe’s coming plagues: Vector-borne neglected tropical diseases. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, V.; Günay, F.; Le Goff, G.; Boussès, P.; Sulesco, T.; Khalin, A.; Medlock, J.M.; Kampen, H.; Petrić, D.; Schaffner, F. Distribution chart for Euro-Mediterranean mosquitoes (western Palaearctic region). J. Eur. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 2019, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Merabti, B.; Boumaza, M.; Ouakid, M.; Carvajal, T.M.; Harbach, R.E. An updated checklist of the mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) present in Algeria, with assessments of doubtful records and problematic species. Zootaxa 2021, 5027, 515–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebbak, A.; Almeras, L.; Parola, P.; Bitam, I. Mosquito vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) and mosquito-borne diseases in North Africa. Insects 2022, 13, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkent, A.; Dominiak, P. Catalog of the biting midges of the world (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4787, 1–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettani, K.; Ebejer, M.J.; Ackland, D.M.; Bächli, G.; Barraclough, D.; Barták, M.; Carles-Tolrá, M.; Černý, M.; Cerretti, P.; Chandler, P. Catalogue of the Diptera (Insecta) of Morocco—An annotated checklist, with distributions and a bibliography. ZooKeys 2022, 1094, 1–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.H. World Blackflies (Diptera: Simuliidae): A Comprehensive Revision of the Taxonomic and Geographical Inventory; Clemson University: Clemson, SC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Moucha, J. Horse-flies (Diptera: Tabanidae) of the world, synoptic catalogue. Acta Entom. Mus. Nat. Pragae Suppl. 1976, 7, 1–319. [Google Scholar]
- Duvallet, G.; Hogsette, J.A. Global Diversity, Distribution, and Genetic Studies of Stable Flies (Stomoxys sp.). Diversity 2023, 15, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendzele, S.S.; Aubin, K.A.; Roland, Z.-K.C.; Rodrigue, M.-N.; Mavoungou, J.F. Apparent Densities of Stomoxys Species (Diptera, Muscidae) of Different Physiological Ages Caught with Vavoua Trap Differ With Landscape and Trapping Period. J. Zool. Res. 2021, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleba, S.B.; Torto, B.; Masiga, D.; Getahun, M.N.; Weldon, C.W. Stable flies, Stomoxys calcitrans L. (Diptera: Muscidae), improve offspring fitness by avoiding oviposition substrates with competitors or parasites. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issimov, A.; Taylor, D.B.; Zhugunissov, K.; Kutumbetov, L.; Zhanabayev, A.; Kazhgaliyev, N.; Akhmetaliyeva, A.; Nurgaliyev, B.; Shalmenov, M.; Absatirov, G. The combined effects of temperature and relative humidity parameters on the reproduction of Stomoxys species in a laboratory setting. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machtinger, E.; Geden, C.; Hogsette, J.; Leppla, N. Development and oviposition preference of house flies and stable flies (Diptera: Muscidae) in six substrates from Florida equine facilities. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Broce, A.; Zurek, L. Role of bacteria in the oviposition behaviour and larval development of stable flies. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2006, 20, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solórzano, J.-A.; Gilles, J.; Bravo, O.; Vargas, C.; Gomez-Bonilla, Y.; Bingham, G.V.; Taylor, D.B. Biology and trapping of stable flies (Diptera: Muscidae) developing in pineapple residues (Ananas comosus) in Costa Rica. J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, P.E.; Burgess IV, E.R.; Weeks, E.N. Stable Fly Stomoxys calcitrans (L.) (Insecta: Diptera: Muscidae): EENY642/IN1114, 10/2022. EDIS 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcpheron, L.J.; Broce, A.B. Environmental components of pupariation-site selection by the stable fly (Diptera: Muscidae). Environ. Entomol. 1996, 25, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochon, K.; Hogsette, J.; Kaufman, P.; Olafson, P.; Swiger, S.; Taylor, D. Stable fly (Diptera: Muscidae)—Biology, management, and research needs. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2021, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.A.; Bravo-Barriga, D.; Fernández, E.B.; Frontera, E.; Ruiz-Arrondo, I. Severe Skin lesions caused by persistent bites of the stable fly Stomoxys calcitrans (Diptera: Muscidae) in a donkey sanctuary of Western Spain. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 116, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreki, J.C.; Tjinyeka, K.; Makore, J.; Tlotleng, K.; Moseki, M.I. The impact of stable flies (Stomoxys calcitrans L.) on small stock production in Bodibeng, Bothatogo and Sehithwa in the North West district, Botswana; a survey study. Online J. Anim. Feed. Res. 2022, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Jacquiet, P.; Prevot, F.; Grisez, C.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Semin, M.; Geffré, A.; Trumel, C.; Franc, M.; Bouhsira, É. Stomoxys calcitrans, mechanical vector of virulent Besnoitia besnoiti from chronically infected cattle to susceptible rabbit. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2019, 33, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, J.; Simons, X.; Humblet, M.-F.; Saegerman, C. Lumpy skin disease: A systematic review of mode of transmission, risk of emergence and risk entry pathway. Viruses 2023, 15, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjeibi, M.R.; Hamida, T.B.; Dalgatova, Z.; Mahjoub, T.; Rejeb, A.; Dridi, W.; Gharbi, M. First report of surra (Trypanosoma evansi infection) in a Tunisian dog. Parasite 2015, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihok, S.; Maramba, O.; Munyoki, E.; Kagoiya, J. Mechanical transmission of Trypanosoma spp. by African Stomoxynae (Diptera: Muscidae). Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1995, 46, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sumba, A.L.; Mihok, S.; Oyieke, F.A. Mechanical transmission of Trypanosoma evansi and T. congolense by Stomoxys niger and S. taeniatus in a laboratory mouse model. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1998, 12, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounioko, F.; Maganga, G.D.; Mavoungou, J.F.; Koumba, C.R.Z.; Koumba, A.A.; Sevidzem, S.L.; Tamesse, J.L.; Simo, G.; M’batchi, B. Molecular screening of Trypanosoma spp. in Glossina, Stomoxys and tabanids in the Moukalaba Doudou National Park (South-West, Gabon). World J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 6, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.A.; Adams, W.; Cook, L.; Wilson, B.; Roth, E. Role of horse fly (Tabanus fuscicostatus Hine) and stable fly (Stomoxys calcitrans L.) in transmission of equine infectious anemia to ponies in Louisiana. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1973, 34, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.; Panella, N.; Hale, K.; Komar, N. Detection of West Nile virus in stable flies (Diptera: Muscidae) parasitizing juvenile American white pelicans. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 47, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, A.S.; Lohse, L.; Hansen, M.F.; Boklund, A.; Halasa, T.; Belsham, G.J.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bøtner, A.; Bødker, R. Infection of pigs with African swine fever virus via ingestion of stable flies (Stomoxys calcitrans). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, M.J.; Dohm, D.J.; Geden, C.J.; Hogsette, J.A.; Linthicum, K.J. Potential for stable flies and house flies (Diptera: Muscidae) to transmit rift valley fever virus1. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2010, 26, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issimov, A.; Taylor, D.B.; Shalmenov, M.; Nurgaliyev, B.; Zhubantayev, I.; Abekeshev, N.; Kushaliyev, K.; Kereyev, A.; Kutumbetov, L.; Zhanabayev, A. Retention of lumpy skin disease virus in Stomoxys spp. (Stomoxys calcitrans, Stomoxys sitiens, Stomoxys indica) following intrathoracic inoculation, Diptera: Muscidae. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0238210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhahlela, N.B.; Liebenberg, D.; Van Hamburg, H.; Taioe, M.O.; Onyiche, T.; Ramatla, T.; Thekisoe, O.M. Detection of pathogens of veterinary importance harboured by Stomoxys calcitrans in South African feedlots. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohier, C.; Haegeman, A.; Mostin, L.; De Leeuw, I.; Campe, W.V.; De Vleeschauwer, A.; Tuppurainen, E.; Van Den Berg, T.; De Regge, N.; De Clercq, K. Experimental evidence of mechanical lumpy skin disease virus transmission by Stomoxys calcitrans biting flies and Haematopota spp. horseflies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mramba, F.; Broce, A.; Zurek, L. Vector competence of stable flies, Stomoxys calcitrans L. (Diptera: Muscidae), for Enterobacter sakazakii. J. Vector Ecol. 2007, 32, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelder, M.P.; Lloyd, J.E.; Loftis, A.D.; Reeves, W.K. Coxiella burnetii in wild-caught filth flies. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turell, M.J.; Knudson, G.B. Mechanical transmission of Bacillus anthracis by stable flies (Stomoxys calcitrans) and mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti and Aedes taeniorhynchus). Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 1859–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversa, D.; Otranto, D.; Iorio, R.; Carluccio, A.; Contri, A.; Paoletti, B.; Bartolini, R.; Giangaspero, A. Identification of the intermediate hosts of Habronema microstoma and Habronema muscae under field conditions. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2008, 22, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.K.; Lloyd, J.E. Louse flies, keds, and bat flies (Hippoboscoidea). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 421–438. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, S.M.; Attia, M.M.; Al-Harbi, M.S.; Saad, A.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Salem, H.M. Low host specificity of Hippobosca equina infestation in different domestic animals and pigeon. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, S.; Sturm, B.P.; Büsse, S.; Büscher, T.H.; Gorb, S.N. Louse flies holding on mammals’ hair: Comparative functional morphology of specialized attachment devices of ectoparasites (Diptera: Hippoboscoidea). J. Morphol. 2022, 283, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Armisén, M.; Bartolomé, B.; Rodriguez, V.; Luna, I. Anaphylaxis to Hippobosca equina (louse fly). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007, 99, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.B.; Attardo, G.M.; Baumann, A.A.; Michalkova, V.; Aksoy, S. Adenotrophic viviparity in tsetse flies: Potential for population control and as an insect model for lactation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.; Otranto, D.; Wall, R. Keds and Louse flies (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). In The Encyclopaedia of Medical and Veterinary Entomology; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2013; pp. 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Selmi, R.; Dhibi, M.; Ben Said, M.; Ben Yahia, H.; Abdelaali, H.; Ameur, H.; Baccouche, S.; Gritli, A.; Mhadhbi, M. Evidence of natural infections with Trypanosoma, Anaplasma and Babesia spp. in military livestock from Tunisia. Trop. Biomed. 2019, 36, 742–757. [Google Scholar]
- Smetanin, A. On the insect fauna of the Kichiga River basin, northeastern Kamchatka. Entomol. Rev. 2013, 93, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobkova, L.V. The Importance of Coastal Ecosystems in Providing Nutrition for Juveniles of Certain Salmon Species in the Freshwaters of Kamchatka. In Proceedings of the Conservation of Biodiversity of Kamchatka and Adjacent Seas, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Russia, 12–13 November 2019; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Boucheikhchoukh, M.; Mechouk, N.; Benakhla, A.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Molecular evidence of bacteria in Melophagus ovinus sheep keds and Hippobosca equina forest flies collected from sheep and horses in northeastern Algeria. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 65, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boularias, G.; Azzag, N.; Gandoin, C.; Bouillin, C.; Chomel, B.; Haddad, N.; Boulouis, H.-J. Bartonella bovis and Bartonella chomelii infection in dairy cattle and their ectoparasites in Algeria. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 101450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; de la Fuente, J.; Biró, N.; Fernández de Mera, I.G.; Meli, M.L.; Elek, V.; Gönczi, E.; Meili, T.; Tánczos, B.; Farkas, R. First molecular evidence of Anaplasma ovis and Rickettsia spp. in keds (Diptera: Hippoboscidae) of sheep and wild ruminants. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 1319–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Espinoza, M.; Em, D.; Shahi-Barogh, B.; Berer, D.; Duscher, G.G.; Van Der Vloedt, L.; Glawischnig, W.; Rehbein, S.; Harl, J.; Unterköfler, M.S. Molecular pathogen screening of louse flies (Diptera: Hippoboscidae) from domestic and wild ruminants in Austria. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, T. A revised checklist and concise host index of Hippoboscidae (Diptera). Pac. Insects Monogr. 1969, 20, 261–299. [Google Scholar]
- Mulugeta, Y.; Yacob, H.T.; Ashenafi, H. Ectoparasites of small ruminants in three selected agro-ecological sites of Tigray Region, Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, R.W. A review of Melophagus ovinus (L.), the sheep ked. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 130, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; He, B.; Li, K.-R.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Li, X.-Q.; Zhao, L. First report of border disease virus in Melophagus ovinus (sheep ked) collected in Xinjiang, China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedke, A.; Jochim, M.; Bowne, J. Preliminary bluetongue transmissions with the sheep ked Melophagus ovinus (L.). Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1965, 29, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Kumsa, B.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D.; Socolovschi, C. Bartonella melophagi in Melophagus ovinus (sheep ked) collected from sheep in northern Oromia, Ethiopia. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 37, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, G.R.; Murphree, C.S. Biting midges (Ceratopogonidae). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 213–236. [Google Scholar]
- Cribb, B. Oviposition and maintenance of Forcipomyia (Lasiohelea) townsvillensis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in the laboratory. J. Med. Entomol. 2000, 37, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.B. Laboratory observations on the biology and life cycle of the Australian biting midge Culicoides subimmaculatus (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1982, 19, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.; López, S.; Mullens, B.A.; Baldet, T.; Goldarazena, A. A survey of Culicoides developmental sites on a farm in northern Spain, with a brief review of immature habitats of European species. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 191, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, P. The behaviour of larvae of Culicoides circumscriptus Kieff. (Dipt., Ceratopogonidae) towards light stimuli as influenced by feeding, with observations on the feeding habits. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1958, 49, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribar, L.J. Mouthpart morphology and feeding behavior of biting midge larvae (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). In Functional Morphology of Insect Feeding; BioOne: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Mazumdar, A. Predatory Behaviour of Larval Alluaudomyia formosana Okada on Alluaudomyia xanthocoma Kieffer (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae)–Video Documentation. Proc. Zool. Soc. 2017, 72, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadziewski, R. Biting midges (Insecta: Diptera). Pr. Muz. Ziemi 1990, 2, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanek, A.; Richert, M.; Giłka, W.; Szadziewski, R. Morphology and histology of secretory setae in terrestrial larvae of biting midges of the genus Forcipomyia (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2011, 40, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardjadj, M.; Luka, P.D. Molecular epidemiology of foot and mouth disease, bluetongue and pest de petites ruminants in Algeria: Historical perspective, diagnosis and control. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 2474–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Dhaou, S.; Sailleau, C.; Babay, B.; Viarouge, C.; Sghaier, S.; Zientara, S.; Hammami, S.; Bréard, E. Molecular characterisation of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus associated with a Tunisian outbreak among cattle in 2006. Acta Vet. Hung. 2016, 64, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, S.; Sailleau, C.; Marcacci, M.; Thabet, S.; Curini, V.; Ben Hassine, T.; Teodori, L.; Portanti, O.; Hammami, S.; Jurisic, L. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus serotype 8 in tunisia, 2021. Viruses 2022, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, H.; Casal, J.; Alba, A.; Allepuz, A.; Cêtre-Sossah, C.; Hafsi, L.; Kount-Chareb, H.; Bouayed-Chaouach, N.; Saadaoui, H.; Napp, S. Animal diseases caused by orbiviruses, Algeria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazrati, A. Identification and typing of horse-sickness virus strains isolated in the recent epizootic of the disease in Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria. Arch. Razi Inst. 1967, 19, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hassine, T.B.; Amdouni, J.; Monaco, F.; Savini, G.; Sghaier, S.; Selimen, I.B.; Chandoul, W.; Hamida, K.B.; Hammami, S. Emerging vector-borne diseases in dromedaries in Tunisia: West Nile, bluetongue, epizootic haemorrhagic disease and Rift Valley fever. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2017, 84, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touil, N.; Cherkaoui, Z.; Lmrabih, Z.; Loutfi, C.; Harif, B.; El Harrak, M. Emerging viral diseases in dromedary camels in the Southern Morocco. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, R.; Doğan, F.; Ataseven, V.S.; Ergün, Y. Antibody detection against Akabane (AKA) and Bluetongue (BT) viruses in Algeriandromedary camels. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2020, 44, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daif, S.; El Berbri, I.; Fassi Fihri, O. First molecular evidence of potential Culicoides vectors implicated in bluetongue virus transmission in Morocco. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardjadj, M.; Luka, P.D.; Benmadhi, M.H. Sero-epidemiology of bluetongue in Algerian ruminants. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 868–871. [Google Scholar]
- Sana, K.; Soufien, S.; Thameur, B.H.; Liana, T.; Massimo, S.; Kaouther, G.; Raja, G.; Haikel, H.; Bassem, B.H.M.; Wiem, K. Risk-based serological survey of bluetongue and the first evidence of bluetongue virus serotype 26 circulation in Tunisia. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, L.; Yaacoub, A.; Bel Hadj, S.; Anene, S.; Kaouech, A.; Kallel, K. Les parasitoses sanguines et urinaires chez les étudiants non résidents permanents en Tunisie [Blood and urinary parasitosis among non-resident students in Tunisia]. Rev. Tun. Infectiol. 2008, 2, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Krolow, T.K.; Lucas, M.; Henriques, A.L. Revisiting the tabanid fauna (Diptera: Tabanidae) of Uruguay: Notes on the species of the genus Tabanus Linnaeus, with the description of a new species. Neotrop. Entomol. 2022, 51, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugasa, C.M.; Villinger, J.; Gitau, J.; Ndungu, N.; Ciosi, M.; Masiga, D. Morphological re-description and molecular identification of Tabanidae (Diptera) in East Africa. ZooKeys 2018, 769, 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, B.A. Horse flies and deer flies (Tabanidae). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 327–343. [Google Scholar]
- Mullens, B.A.; Trout Fryxell, R.; Masonick, P.K.; Yanega, D.A.; Davis, T.M. Hiding in plain sight: An abundant and widespread North American horse fly (Diptera: Tabanidae) in the Tabanus sulcifrons Group, Tabanus variegatus Fabricius, redescribed. J. Med. Entomol. 2022, 59, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husseneder, C.; Delatte, J.R.; Krumholt, J.; Foil, L.D. Development of microsatellites for population genetic analyses of Tabanus nigrovittatus (Diptera: Tabanidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldacchino, F.; Desquesnes, M.; Mihok, S.; Foil, L.D.; Duvallet, G.; Jittapalapong, S. Tabanids: Neglected subjects of research, but important vectors of disease agents! Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 596–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foil, L.; Hogsette, J. Biology and control of tabanids, stable flies and horn flies. Rev. Sci. Tech.-Off. Int. Épizooties 1994, 13, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, F.; Lucas, E.; Gérard, D. Seasonal abundance of Tabanidae (Diptera) on a farm in southern France. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2020, 54, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ganeva, D.; Ivanov, I. Seasonal activity of the horse flies (Diptera, Tabanidae) from the Central Balkan Mountains, Bulgaria. Trakia J. Sci. 2020, 18, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djonguep, A.S.; Mamoudou, A.; Hiol, V.D.; Lebalé, O.; Sevidzem, S.L.; Kohagne, L.T.; Cornel, A.; Nukenine, E.N. Impact of Landscape and Season on the Ecological Distribution of Tabanidae and Stomoxyinae, Mechanical Vectors of Bovine Trypanosomosis in the Forest of Sanaga Maritime and Savanna of Ngaoundere, Cameroon. Res. Sq. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keita, M.L.; Medkour, H.; Sambou, M.; Dahmana, H.; Mediannikov, O. Tabanids as possible pathogen vectors in Senegal (West Africa). Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostygov, A.Y.; Frolov, A.O.; Malysheva, M.N.; Ganyukova, A.I.; Drachko, D.; Yurchenko, V.; Agasoi, V.V. Development of two species of the Trypanosoma theileri complex in tabanids. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotánková, A.; Fialová, M.; Čepička, I.; Brzoňová, J.; Svobodová, M. Trypanosomes of the Trypanosoma theileri group: Phylogeny and new potential vectors. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issel, C.; Foil, L. Equine infectious anaemia and mechanical transmission: Man and the wee beasties. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, C.F.; Santos, A.M.; Cook, R.F.; Victor, R.M.; Câmara, R.J.F.; Gonçalves, G.P.; Lima, J.G.; Maciel e Silva, A.G.; Leite, R.C.; Dos Reis, J.K.P. Low transmission rates of Equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) in foals born to seropositive feral mares inhabiting the Amazon delta region despite climatic conditions supporting high insect vector populations. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, R.-R.; Liu, L.-Y.; Sun, M.; Hong, Y.-H.; Yang, C.-S.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.-J.; Xu, Q.-M. Tabanus hypomacros: A suspected mechanical transmission vector of African swine fever virus in Dabie mountain region of Jinzhai county, Anhui Province in China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2022, 33, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselschwert, D.; French, D.; Hribar, L.; Luther, D.; Leprince, D.; Van der Maaten, M.; Whetstone, C.; Foil, L. Relative susceptibility of beef and dairy calves to infection by bovine leukemia virus via tabanid (Diptera: Tabanidae) feeding. J. Med. Entomol. 1993, 30, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salihi, K. Lumpy skin disease: Review of literature. Mirror Res. Vet. Sci. Anim. 2014, 3, 6–23. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FAO Alerts Countries in the Near East, North Africa and Southern Europe to Enhance Preparedness for Lumpy Skin Disease; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Baldacchino, F.; Desquesnes, M.; Duvallet, G.; Lysyk, T.; Mihok, S. Veterinary importance and integrated management of Brachycera flies in dairy farms. In Pests and Vector-Borne Diseases in the Livestock Industry; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1765–1771. [Google Scholar]
- DeCesare, N.J.; Harris, R.B.; Peterson, C.J.; Ramsey, J.M. Prevalence and Mortality of Moose (Alces alces) Infected with Elaeophora schneideri in Montana, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2023, 59, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVan, I.K.; Fox, K.A.; Miller, M.W. High elaeophorosis prevalence among harvested Colorado moose. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona Zuluaga, E.A. Sarcopromusca pruna (Diptera: Muscidae): Phoretic for Dermatobia hominis (Diptera: Cuterebridae) eggs in Colombia. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pecu. 2011, 24, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.M.M.; Barros, L.M.; Bôlla, D.A.S.; Almeida, M.Q.; Souza, D.d.C.; Souza de Araujo, J.; Sacheto, M.C.; da Silva, D.A.T.; Fonseca, R. Furuncular Myiasis by Dermatobia hominis (Diptera: Oestridae) in Wild Jaguars in the Amazon Rainforest. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1936–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürcan, Ş. Epidemiology of tularemia. Balk. Med. J. 2014, 2014, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasanella, A.; Di Taranto, P.; Garofolo, G.; Colao, V.; Marino, L.; Buonavoglia, D.; Pedarra, C.; Adone, R.; Hugh-Jones, M. Ground Anthrax Bacillus Refined Isolation (GABRI) method for analyzing environmental samples with low levels of Bacillus anthracis contamination. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; Földvári, G.; Elek, V.; Naranjo, V.; Farkas, R.; de la Fuente, J. Molecular identification of Anaplasma marginale and rickettsial endosymbionts in blood-sucking flies (Diptera: Tabanidae, Muscidae) and hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 154, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinsky, W.L. Animal disease agents transmitted by horse flies and deer flies (Diptera: Tabanidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1976, 13, 225–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontigun, N.; Boonhoh, W.; Phetcharat, Y.; Wongtawan, T. First study on molecular detection of hemopathogens in tabanid flies (Diptera: Tabanidae) and cattle in Southern Thailand. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desquesnes, M.; Dia, M.L. Trypanosoma vivax: Mechanical transmission in cattle by one of the most common African tabanids, Atylotus agrestis. Exp. Parasitol. 2003, 103, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, M.N.; Villinger, J.; Bargul, J.L.; Muema, J.M.; Orone, A.; Ngiela, J.; Ahuya, P.O.; Saini, R.K.; Torto, B.; Masiga, D.K. Molecular characterization of pathogenic African trypanosomes in biting flies and camels in surra-endemic areas outside the tsetse fly belt in Kenya. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 3729–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulandane, F.C.; Snyman, L.P.; Brito, D.R.; Bouyer, J.; Fafetine, J.; Van Den Abbeele, J.; Oosthuizen, M.; Delespaux, V.; Neves, L. Evaluation of the relative roles of the Tabanidae and Glossinidae in the transmission of trypanosomosis in drug resistance hotspots in Mozambique. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutellis, A.; Bellabidi, M.; Benaissa, M.H.; Harrat, Z.; Brahmi, K.; Drali, R.; Kernif, T. New haplotypes of Trypanosoma evansi identified in dromedary camels from Algeria. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallemi, S.; Rjeibi, M.R.; Rouatbi, M.; Amairia, S.; Ben Said, M.; Khamassi Khbou, M.; Gharbi, M. Molecular prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of Theileria annulata and Trypanosoma evansi in cattle in Northern Tunisia. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 4, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, P.D. Biology of phlebotomine sand flies as vectors of disease agents. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazanfar, M.; Malik, M.F. Sandfly and leishmaniasis: A review. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2016, 6, 1000207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killick-Kendrick, R. The biology and control of phlebotomine sand flies. Clin. Dermatol. 1999, 17, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcover, M.M.; Ballart, C.; Martín-Sánchez, J.; Serra, T.; Castillejo, S.; Portús, M.; Gállego, M. Factors influencing the presence of sand flies in Majorca (Balearic Islands, Spain) with special reference to Phlebotomus pernicious, vector of Leishmania infantum. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, H. Impact of meteorological and geographical factors on the distribution of Phlebotomus chinensis in northwestern mainland China. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2018, 32, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaoui, A.; Sereno, D.; El Jaafari, S.; Hajji, L. A systematic review and global analysis of the seasonal activity of Phlebotomus (Paraphlebotomus) sergenti, the primary vectors of L. tropica. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniha, E.; Milchram, M.; Dvořák, V.; Halada, P.; Obwaller, A.G.; Poeppl, W.; Mooseder, G.; Volf, P.; Walochnik, J. Ecology, seasonality and host preferences of Austrian Phlebotomus (Transphlebotomus) mascittii Grassi, 1908, populations. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, P.; Shah, H.K.; Ajithlal, P.; Mathew, J.; Kumar, N.P.; Kumar, A.; Saini, P. Development of DNA barcode-based PCR methodology to distinguish two sympatric species viz. Phlebotomus argentipes and Phlebotomus colabaensis (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2023, 43, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Huguenin, A.; Pesson, B.; Kaltenbach, M.L.; Diarra, A.Z.; Parola, P.; Depaquit, J.; Randrianambinintsoa, F.J. MALDI-TOF MS Limits for the Identification of Mediterranean Sandflies of the Subgenus Larroussius, with a Special Focus on the Phlebotomus perniciosus Complex. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, C.; Himmi, O. Clés morphologiques pour l’identification des phlébotomes du Maroc (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae). Bull. Société Pathol. Exot. 2020, 113, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaoud, M.; Es-sette, N.; Hamdi, S.; El-Idrissi, A.L.; Riyad, M.; Lemrani, M. Detection and molecular typing of Leishmania tropica from Phlebotomus sergenti and lesions of cutaneous leishmaniasis in an emerging focus of Morocco. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennai, K.; Tahir, D.; Lafri, I.; Bendjaballah-Laliam, A.; Bitam, I.; Parola, P. Molecular detection of Leishmania infantum DNA and host blood meal identification in Phlebotomus in a hypoendemic focus of human leishmaniasis in northern Algeria. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijón-Robles, P.; Gómez-Mateos, M.; Corpas-López, E.; Abattouy, N.; Merino-Espinosa, G.; Morillas-Márquez, F.; Corpas-López, V.; Díaz-Sáez, V.; Riyad, M.; Martín-Sánchez, J. Morphology does not allow differentiating the species of the Phlebotomus perniciosus complex: Molecular characterization and investigation of their natural infection by Leishmania infantum in Morocco. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubidi, S.; Benallal, K.; Boudrissa, A.; Bouiba, L.; Bouchareb, B.; Garni, R.; Bouratbine, A.; Ravel, C.; Dvorak, V.; Votypka, J. Phlebotomus sergenti (Parrot, 1917) identified as Leishmania killicki host in Ghardaïa, south Algeria. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellahi, A.; Djirar, N.; Cherief, A.; Boudrissa, A.; Eddaikra, N. Zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis and Leishmania infection among Meriones shawi population in Setif Province, Algeria. Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2021, 22, 2547–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benallal, K.E.; Mezai, G.; Mefissel, M.; Klari, N.; Lardjane, C.; Khardine, A.-F.; Kherachi, I.; Dib, Y.; Brahmi, K.; Sadlova, J. Host competence of Algerian Gerbillus amoenus for Leishmania major. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 21, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Pérez, M.; Khaldi, M.; Riera, C.; Mozo-León, D.; Ribas, A.; Hide, M.; Barech, G.; Benyettou, M.; Seghiri, K.; Doudou, S. First report of natural infection in hedgehogs with Leishmania major, a possible reservoir of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Algeria. Acta Trop. 2014, 135, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounaci, A.; Brosse, S.; Thomas, A.; Lek, S. Abundance, diversity and community structure of macroinvertebrates in an Algerian stream: The Sébaou wadi. Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Limnol. 2000, 36, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.H.; Haouchine, S.; Belqat, B.; Lounaci, A. North African Endemism: A New Species of Black Fly (Diptera: Simuliidae) from the Djurdjura Mountains of Algeria. Insects 2024, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Arrondo, I.; Veiga, J.; Adler, P.H.; Collantes, F.; Oteo, J.A.; Valera, F. Integrated taxonomy of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) reveals unexpected diversity in the most arid ecosystem of Europe. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.H.; McCreadie, J.W. Black flies (Simuliidae). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 237–259. [Google Scholar]
- Pramual, P.; Wongpakam, K.; Adler, P.H. Cryptic biodiversity and phylogenetic relationships revealed by DNA barcoding of Oriental black flies in the subgenus Gomphostilbia (Diptera: Simuliidae). Genome 2011, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, P.; Cherairia, M.; Arigue, S.; Samraoui, B.; Belqat, B. Cryptic biodiversity in the cytogenome of bird-biting blackflies in N orth A frica. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2015, 29, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, P.H.; McCreadie, J.W. Insect life: The hidden ecology of black flies: Sibling species and ecological scale. Am. Entomol. 1997, 43, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baužienė, V.; Būda, V.; Bernotienė, R. Mating activity of the mammalophilic blacklies Simulium (Wilhelmia) lineatum (Meigen, 1804) (Diptera: Simuliidae) under laboratory conditions. Acta Zool. Litu. 2004, 14, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.H.; Cheke, R.A.; Post, R.J. Evolution, epidemiology, and population genetics of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.M.; Peterson, B.V. Observations on the mating, feeding, ovarian development, and oviposition of adult black flies (Simuliidae, Diptera). Can. J. Zool. 1956, 34, 615–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viel, P. Characterization of Black Fly (Diptera: Simuliidae) Silk Proteins. Master’s Thesis, Brock University, St. Catharines, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fingerut, J.T.; Hart, D.D.; McNair, J.N. Silk filaments enhance the settlement of stream insect larvae. Oecologia 2006, 150, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bmilly Choumara, H.; Bernard, M.; Grenier, P. Note faunistique sur les Simulies (Diptera, Simuliidae) du. nord de la Tunisie. Cah. O.R.S.T.O.M. Ser. Ent. Méd. Parasitol. 1970, 8, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Papadopoulos, E.; Petrić, D.; Ćupina, A.I.; Bain, O. Tracking the vector of Onchocerca lupi in a rural area of Greece. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
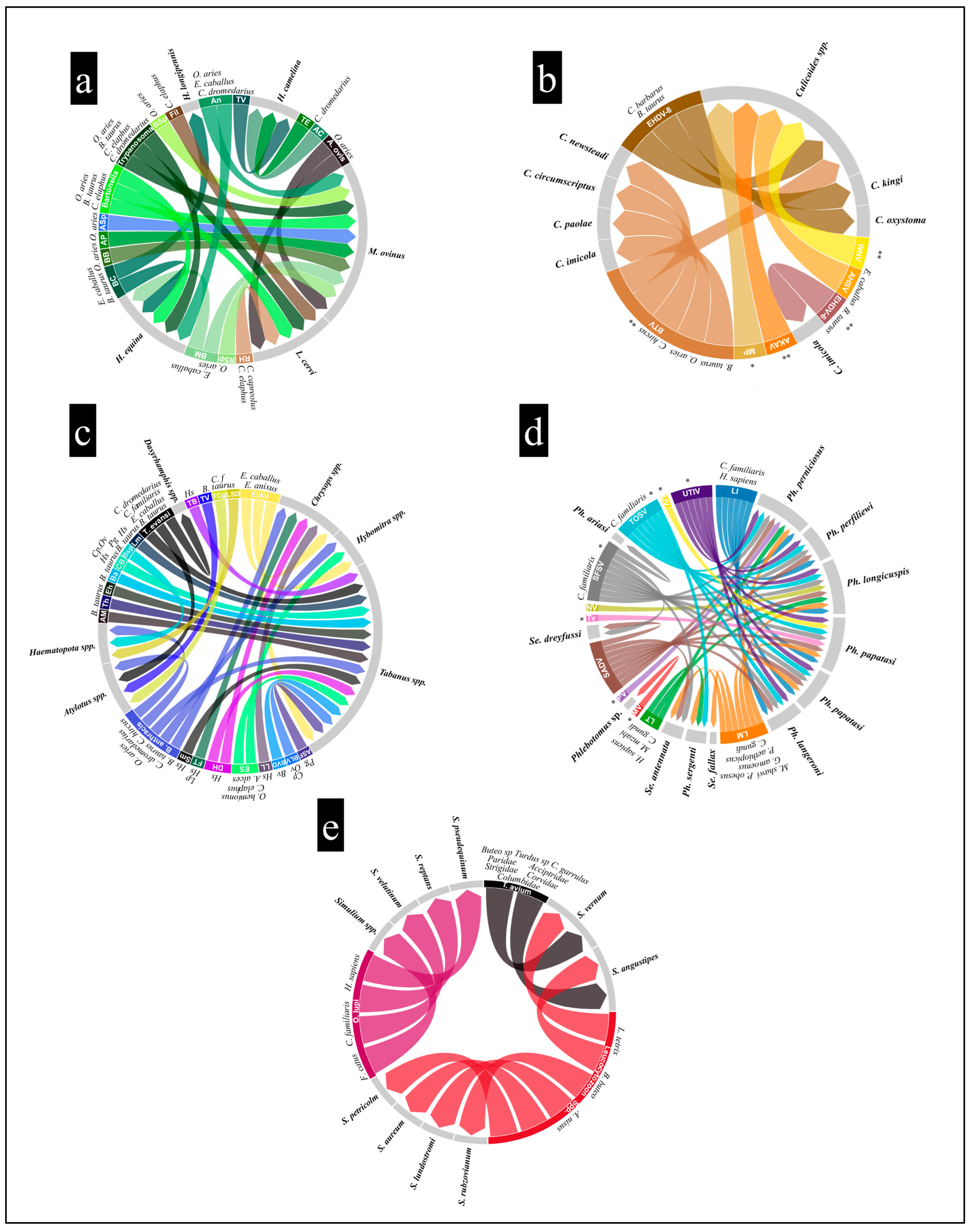
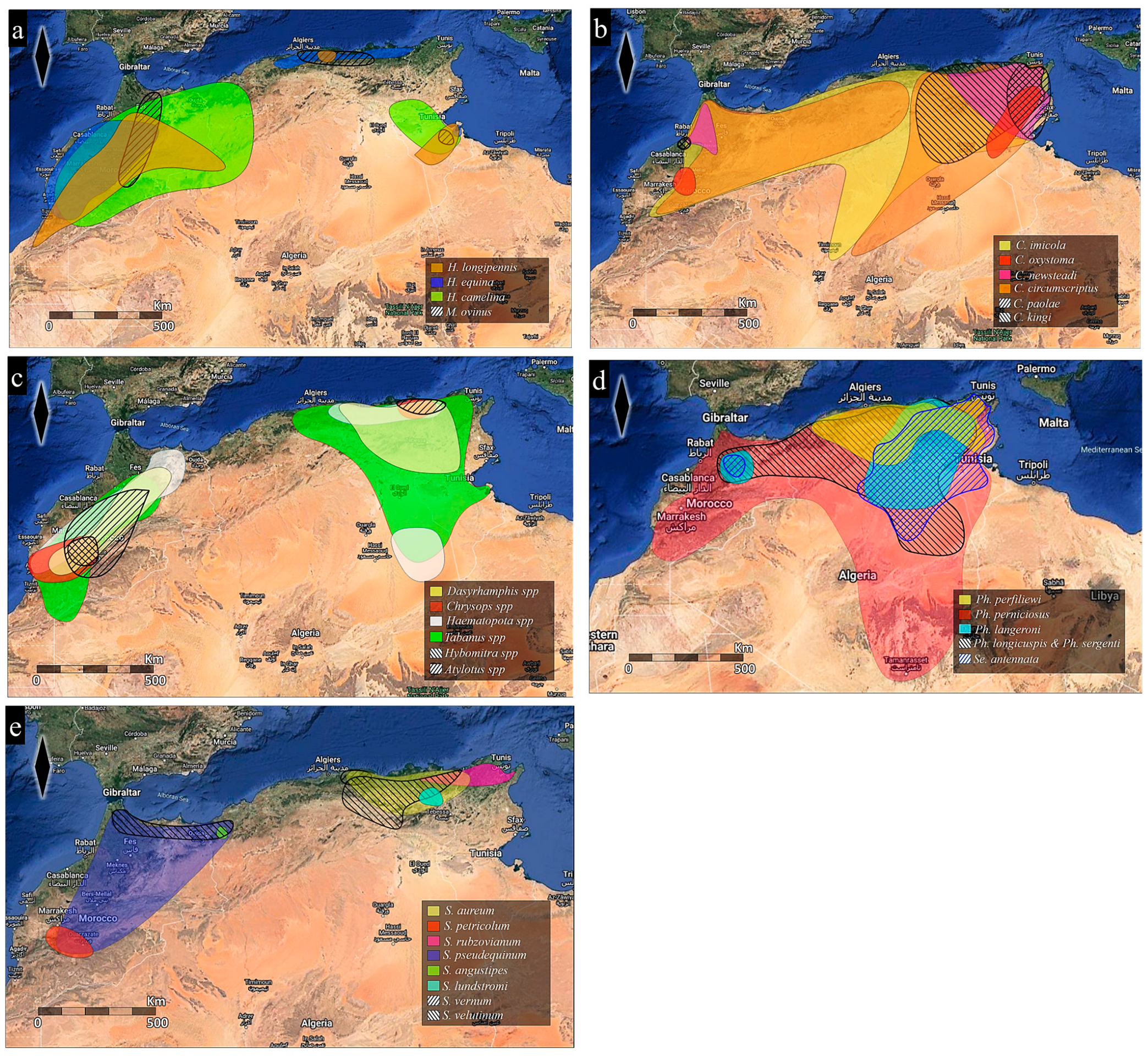
| Genus | Taxon | Taxonomy | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crataerina | Crataerina. acutipennis | Austen, 1926 | M |
| Crataerina pallida | Latreille, 1811 | M | |
| Hippobosca | Hippobosca camelina | Leach, 1817 | M, A, T |
| Hippobosca equina | Linnaeus, 1758 | M, A, T | |
| Hippobosca fulva | Austen, 1912 | M | |
| Hippobosca longipennis | Fabricius, 1805 | M, A, T | |
| Hippobosca variegata | Megerle, 1803 | M | |
| Icosta | Icosta minor | Bigot, 1858 | M |
| Ornithoica | Ornithoica turdi | Olivier in Latreille, 1811 | M |
| Ornithomyia | Ornithomyia avicularia | Linnaeus, 1758 | M |
| Ornithomyia fringilina | Curtis, 1836 | A | |
| Ornithomyia biloba | Dufor, 1827 | M, A | |
| Ornithophila | Ornithophila gestroi | Rondani, 1878 | M, A, T |
| Ornithophila metallica | Schiner, 1864 | M, A | |
| Pseudolynchia | Pseudolynchia canariensis | Macquart, 1839 | M, A |
| Stenepteryx | Stenepteryx hirundinis | Linnaeus, 1758 | M |
| Lipoptena | Lipoptena capreoli | Rondani, 1878 | M |
| Lipoptena cervi | Linnaeus, 1758 | A | |
| Melophagus | Melophagus ovinus | Linnaeus, 1758 | M, A, T |
| Lynchia | Lynchia pilosa | Macquart, 1843 | M |
| Taxon | Taxonomy | Country | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Culicoides achrayi | Kettle & Lawson, 1955 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides albicans | Winnertz, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides algeriensis | Clastrier, 1957 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides azerbajdzhanicus | Dzhafarov, 1962 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides badooshensis | Khalaf, 1961 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides begueti | Clastrier, 1957 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides calloti | Kremer, Delécolle, Bailly-Choumara & Chaker, 1979 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides cataneii | Clastrier, 1957 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides chiopterus | Meigen, 1830 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides circumscriptus | Kiefer, 1918 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides clastrieri | Callot, Kremer & Deduit, 1962 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides corsicus | Kremer, Leberre & Beaucournu-Saguez, 1971 | A, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides derisor | Callot & Kremer, 1965 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides dewulf | Goetghebuer, 1936 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides duddingstoni | Kettle & Lawson, 1955 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides duddingstoni | Kettle & Lawson, 1955 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides dzhafarovi | Remm, 1967 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides faghihi | Navai, 1971 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides fagineus | Edwards, 1939 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides fascipennis | Staeger, 1839 | A, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides festivipennis | Kiefer, 1914 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides foleyi | Kiefer, 1922 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides gejgelensis | Dzhafarov, 1964 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides griseidorsum | Kiefer, 1918 | A, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides grisescens | Edwards, 1939 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides halophilus | Kieffer, 1924 | A | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides helveticus | Callot, Kremer & Deduit, 1962 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides heteroclitus | Kremer & Callot, 1965 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides imicola | Kiefer, 1913 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides indistinctus | Khalaf, 1961 | T | Morphological |
| Culicoides jumineri | Callot & Kremer, 1969 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides jurensis | Callot, Kremer & Deduit, 1962 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides kibunensis | Tokunaga, 1937 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides kingi | Austen, 1912 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing + RFLP |
| Culicoides kurensis | Dzhafarov, 1960 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides landauae | Kremer, 1975 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides langeroni | Kiefer, 1921 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides longipennis | Khalaf, 1957 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides marcleti | Callot, Kremer & Basset, 1968 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoiodes maritimus | Kiefer, 1924 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides montanus | Shakirzjanova, 1962 | A, M | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides navaiae | Lane, 1983 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides newsteadi | Austen, 1921 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides nubeculosus | Austen, 1921 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides nudipennis | Kiefer, 1922 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides. obsoletus | Meigen, 1818 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides odiatus | Austen, 1921 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides oxystoma | Kieffer, 1910 | M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing + RFLP |
| Culicoides pallidicornis | Kiefer, 1919 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides pallidus | Khalaf, 1957 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides paolae | Boorman, Mellor & Scaramozzino, 1996 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides paradoxalis | Ramilo & Delécolle, 2013 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides parroti | Kiefer, 1922 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides pictipennis | Staeger, 1839 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides picturatus | Kremer & Deduit, 1961 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides poperinghensis | Goetghebuer, 1953 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides pseudojumineri | Salma, Chaker, and Babba, 2015 | T | Morphological |
| Culicoides pseudolangeroni | Kremer, Chaker and Delécolle, 1981 | T | Morphological |
| Culicoides pseudopallidus | Khalaf, 1961 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides pulicaris | Linnaeus, 1758 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides pumilus | Winnertz, 1852 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides punctatus | Meigen, 1804 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides puncticollis | Becker, 1903 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides ravus | de Meillon, 1936 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides riethi | Kiefer, 1914 | T | Morphological |
| Culicoides saevus | Kieffer, 1922 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides sahariensis | Kiefer, 1923 | A, M, T | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides santonicus | Callot, Kremer, Rault & Bach, 1966 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides schultzei | Enderlein, 1908 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides scoticus | Downes & Kettle, 1952 | A, M | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides sejfadinei | Dzhafarov, 1958 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides semimaculatus | Clastrier, 1958 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides sergenti | Kiefer, 1921 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides shaklawensis | Khalaf, 1957 | A, M | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides similis | Carter, Ingram & Macfe, 1920 | M | Morphological |
| Culicoides simulator | Edwards, 1939 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides sp. (~C. enderleini) | Enderlein, 1908 | A | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides sphagnumensis | Williams, 1955 | A | Morphological |
| Culicoides subfagineus | Delécolle & Ortega, 1998 | M | Morphological + PCR and sequencing |
| Culicoides subfasciipennis | Kiefer, 1919 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides truncorum | Edwards, 1939 | A, M | Morphological |
| Culicoides univittatus | Vimmer, 1932 | A, M, T | Morphological |
| Culicoides vidourlensis | Callot, Kremer, Molet & Bach, 1968 | M | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia alacris | Winn, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia bipunctata | Lineaus, 1767 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia biskraensis | Kieff, 1923 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia crassipes | Winn, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia formosae | Kieff, 1921 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia frutetorum | Winn, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia fuliginosa | Meigen, 1818 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia litoraurea | Ingram & Macfie, 1924 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia margaritae | Szadziewski, 1983 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia mesasiatica | Remm, 1980 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia monilicornis | Coquillett, 1905 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia murina | Winn, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia nigra | Winn, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia pallidipes | Santos Abreu, 1918 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia paludis | Macfie, 1936 | M | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia phlebotomoides | Bangerter, 1933 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia picheyrei | Harant & Galan, 1942 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia pontica | Remm, 1968 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia psilonota | Kieffer, 1911 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia pulcherrima | Santos Abreu, 1918 | A, T | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia rufescens | Kieffer, 1918 | T | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia rugosa | Chan et Leroux, 1970 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia rustica | Kieff, 1919 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia sahariensis | Kieff, 1923 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia seneveti | Kieffer, 1922 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia striaticornis | Kieff, 1918 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia suberis | Clastrier, 1956 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia tenuisquama | Kieff, 1924 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia velox | Winn, 1852 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia waldemari | Szadziewski, 1983 | A | Morphological |
| Forcipomyia wirthiana | Szadziewski, 1983 | A | Morphological |
| Genus | Species | Taxonomy | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atylotus | Atylotus agricola | Wiedmann, 1828 | M |
| Atylotus agristis | Wiedemann, 1828 | M, A | |
| Atylotus farinosus | Sziliidy, 1915 | A | |
| Atylotus flavipes | Macquart, 1838 | A | |
| Atylotus flavoguttatus | Sziliidy, 1915 | A | |
| Atylotus fulvus | Meigen, 1820 | M, A | |
| Atylotus kroberi | Surcouf, 1923 | M, A | |
| Atylotus latistriatus | Brauer, 1880 | M, A | |
| Atylotus loewianus | Villeneuve, 1920 | M | |
| Atylotus pulchellus | Loew, 1858 | A | |
| Atylotus quadrifarius | Loew, 1874 | M, A | |
| Atylotus sublunaticornis | Zetterstedt, 1842 | M | |
| Chrysops | Chrysops caecutiens | Linnaeus, 1758 | M |
| Chrysops connexus | Loew, 1858 | M | |
| Chrysops flavipes | Meigen, 1804 | M, A | |
| Chrysops italicus | Meigen, 1804 | M, A | |
| Chrysops mauritanicus | Costa, 1893 | M, A | |
| Chrysops pallidiventris | Krober, 1922 | M, A | |
| Chrysops relictus | Meigen, 1820 | M | |
| Chrysops viduatus | Meigen, 1803 | M | |
| Dasyrhamphis | Dasyrhamphis barbata | Coscaron & Philip, 1967 | M |
| Dasyrhamphis algirus | Macquart, 1839 | M, T, A | |
| Dasyrhamphis anthracinus | Meigen, 1820 | M | |
| Dasyrhamphis ater | Rossi, 1790 | M, A | |
| Dasyrhamphis carbonarius | Meigen, 1820 | T | |
| Dasyrhamphis nigritus | Fabricius, 1794 | M, A | |
| Dasyrhamphis tomentosus | Macquart, 1854 | M, A | |
| Dasyrhamphis denticornis | Enderlein, 1925 | A | |
| Dasyrhamphis goleanus | Szilady, 1923 | A | |
| Dasyrhamphis villosus | Macquart, 1839 | A | |
| Ectinocerella | Ectinocerella. surcoufi | Seguy, 1925 | M, A |
| Haematopota | Haematopota algira | Krober, 1922 | M, A |
| Haematopota benoisti | Séguy, 1930 | M | |
| Haematopota bigoti | Gobert, 1881 | M, A | |
| Haematopota crassicornis | Wahlberg, 1848 | M | |
| Haematopota fusicornis | Becker, 1913 | M | |
| Haematopota grandis | Macquart, 1834 | M | |
| Haematopota italica | Meigen, 1804 | M, A | |
| Haematopota lambi | Villeneuve, 1921 | M | |
| Haematopota ocelligera | Krober, 1922 | M, A | |
| Haematopota pandazisi | Krober, 1934 | M, A | |
| Haematopota pluvialis | Linnaeus, 1761 | M, A | |
| Haematopota subcylindrica | Pandellé, 1883 | M | |
| Haematopota saccae | Leclercq, 1966 | T | |
| Heptatoma | Heptatoma pellucens | Fabricius, 1776 | M |
| Heptatomadecora | Loew, 1858 | A (*) | |
| Heptatoma vittata | Fabricius, 1794 | A | |
| Hybomitra | Hybomitra arpadi | Szilády, 1923 | M |
| Hybomitra bimaculata | Macquart, 1826 | M | |
| Hybomitra caparti | Leclercq, 1966 | T | |
| Hybomitra distinguenda | Verrall, 1909 | M | |
| Hybomitra macularis | Fabricius, 1794 | M | |
| Hybomitra vittata | Fabricius, 1794 | M | |
| Silvius | Silvius algirus | Meigen, 1830 | M, A |
| Silviusalpinus | Scopoli, 1763 | M | |
| Silvius variegatus | Fabricius, 1805 | M | |
| Silvius appendiculatus | Macquart, 1846 | A | |
| Surcoufia | Surcoufia paradoxa | Krober, 1922 | A, T |
| Tabanus | Tabanus albifrons | Szilacty, 1914 | A |
| Tabanus algirus | Meigen, 1830 | A, T | |
| Tabanus algeriensis | Peus, 1980 | A | |
| Tabanus autumnalis | Linnaeus, 1761 | M, A | |
| Tabanus barbarus | Coquebert, 1804 | M, A | |
| Tabanus auricpunctatus | Macquart, 1839 | A | |
| Tabanus bifarius | Loew, 1858 | M | |
| Tabanus bovinus | Linnaeus, 1758 | M, A | |
| Tabanus bromius | Linnaeus, 1761 | M, A | |
| Tabanus choumarae | Leclercq, 1967 | M | |
| Tabanus crodiger | Meigen, 1820 | M | |
| Tabanus cordigeroides | Surcouf, 1922 | A | |
| Tabanus darimonti | Leclercq, 1964 | M | |
| Tabanus eggeri | Schiner, 1868 | M, A | |
| Tabanus dorsomaculatus | Macquart, 1847 | A | |
| Tabanus guyonae | Surcouf, 1923 | A | |
| Tabanus leleani | Austen, 1920 | M, A | |
| Tabanus lunatus | Fabricius, 1794 | M, A | |
| Tabanus maculicornis | Zetterstedt, 1842 | M | |
| Tabanus mikii | Brauer, 1880 | M | |
| Tabanus nemoralis | Meigen, 1820 | M, A | |
| Tabanus mitidjensis | Macquart, 1838 | A | |
| Tabanus quatuornotatus | Meigen, 1820 | M | |
| Tabanus regularis | Jeannicke, 1866 | M, A | |
| Tabanus rousseli | Macquart, 1839 | M, A | |
| Tabanus seurati | Surcouf, 1922 | A, T | |
| Tabanus spectabilis | Loew, 1858 | M | |
| Tabanus spodopterus | Olsufjev, Moucha & Chvala, 1967 | M | |
| Tabanus sudeticus | Zeller, 1867 | M | |
| Tabanus unifasciatus | Loew, 1858 | M | |
| Tabanus tinctus | Walker, 1850 | M, A | |
| Tabanus albifacies | Loew, 1856 | A |
| Genus | Taxon | Taxonomy | Country | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phlebotomus | Phlebotomus bergeroti | (Parrot, 1934) | M, A, T | M |
| Phlebotomus papatasi | (Scopoli, 1786) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Phlebotomus ariasi | (Tonnoir, 1921) | M, A, T | M | |
| Phlebotomus chadlii rioux | (Juminer et Gibily, 1966) | M, A, T | M | |
| Phlebotomus langeroni | (Nitzulescu, 1930) | M, A, T | M | |
| Phlebotomus longicuspis | (Nitzulescu, 1930) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Phlebotomus mariae | (Rioux, Croset, Léger et BaillyChoumara, 1974) | M | M | |
| Phlebotomus perfiliewi s.l. | (Parrot, 1930) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Phlebotomus perniciosus | (Newstead, 1911) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Phlebotomus alexandri | (Sinton, 1928) | M, A, T | M | |
| Phlebotomus chabaudi | (Croset, Abonnenc et Rioux, 1970) | M, A, T | M | |
| Phlebotomus kazeruni | (Theodor et Mesghali, 1964) | M, A | M | |
| Phlebotomus riouxi | (Depaquit, Léger et Killick-Kendrick, 1998) | M, A, T | M | |
| Phlebotomus mascittii | (Grassi, 1908) | A | M | |
| Phlebotomus sergenti | (Parrot, 1917) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Sergentomyia | Sergentomyia antennata | (Newstead, 1912) | M, A, T | M |
| Sergentomyia bedfordi | (Newstead, 1914) | M | M | |
| Sergentomyia fallax | (Parrot, 1921) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Sergentomyia minuta | (Rondani, 1843) | M, A, T | M + MT + seq | |
| Sergentomyia schwetzi | (Adler, Theodor et Parrot, 1929) | M, A, T | M | |
| Sergentomyia christophersi | (Sinton, 1927) | M, A, T | M | |
| Sergentomyia clydei | (Sinton, 1928) | M, A, T | M | |
| Sergentomyia a. asiatica | (Newstead, 1912) | M | M | |
| Sergentomyia lewisi | (Parrot, 1948) | M, A, T | M | |
| Sergentomyia dreyfussi | (Parrot, 1933) | M, A, T | M | |
| Sergentomyia a. eremitis | (Parrot et de Jolinière, 1945) | A | M | |
| Sergentomyia hirtus | (Parrot et de Jolinière, 1945) | A | M | |
| Sergentomyia tiberiadis | (Adler, Theodor et Louric, 1930) | A | M | |
| Sergentomyia cincta | (Parrot and Martin 1948) | A | M |
| Genus | Taxon | Taxonomy | Country | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helodon | Helodon laamii | Beaucournu-Saguez & Bailly-Choumara | M | M |
| Metacnephia | Metacnephia blanci | (Grenier & Théodorides, 1953) | M, A, T | M |
| Prosimulium | Prosimulium aculeatum | (Grenier & Bailly-Choumara, 1972) | M | M |
| Prosimulium albense | (Rivosecchi, 1961) | A | M | |
| Prosimulium fungiforme | (Adler, Belqat, Haouchine, 2024) | A | M + CC | |
| Prosimulium hirtipes | (Beaucournu-Saguez & Bailly-Choumara, 1981) | M | M | |
| Prosimulium latimucro | (Enderlein, 1925) | M | M | |
| Prosimulium rufipes | (Meigen, 1830) | M, A (*) | M + CC | |
| Prosimulium tomosvaryi | (Enderlein, 1921) | M | M + CC | |
| Simulium | Simulium angustipes | (Edwards, 1915) | M, A, T | M |
| Simulium angustitarse | (Lundström, 1911) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium argenteostriatum | (Strobl, 1898) | A, T | M | |
| Simulium atlasicum | (Giudicelli & Bouzidi,1989) | M | M | |
| Simulium auricoma | (Meigen, 1818) | M | M | |
| Simulium aureum | (Fries, 1824) | A | M | |
| Simulium berberum | (Giudicelli & Bouzidi 1989) | M | M | |
| Simulium bezzi | (Corti, 1914) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium brevidens | (Rubzov, 1956) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium carthusiense | (Grenier & Dorier, 1959) | M | M | |
| Simulium costatum | (Friederichs, 1920) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium cryophilum | (Rubzov, 1959) | M, A, T | M + CC | |
| Simulium egregium | (Séguy, 1930) | M | M | |
| Simulium erythrocephalum | (De Geer, 1776) | T | M | |
| Simulium equinum | (Linnaeus, 1758) | M, A (*) | M | |
| Simulium galloprovinciale | (Giudicelli, 1963) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium gracilipes | (Edwards, 1921) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium hispaniola | (Grenier & Bertrand, 1954) | A | M | |
| Simulium ibleum | (Rivosecchi, 1966) | M, A, T | M | |
| Simulium intermedium | (Roubaud, 1906) | M, A, T | M | |
| Simulium knidirii | (Doby & David, 1960) | M | M | |
| Simulium lamachei | (Doby & David, 1960) | M | M | |
| Simulium latipes | (Meigen, 1804) | T (*) | M | |
| Simulium lundstromi | (Enderlein, 1921) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium marocanum | (Bouzidi & Giudicelli, 1987) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium mellah | (Santos Abreu, 1922) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium monticola | (Friederichs, 1920) | A | M | |
| Simulium ornatum | (Meigen, 1818) | M, A, T | M | |
| Simulium petricolum | (Rivosecchi, 1953) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium pseudequinum | (Séguy, 1921) | M, A, T | M | |
| Simulium quadrifila | (Grenier, Faure & Laurent, 1957) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium reptans | (Linnaeus, 1758) | T | M | |
| Simulium rubzovianum | (Sherban, 1961) | A, T | M | |
| Simulium ruficorne | (Macquart, 1838) | M, A, T | M | |
| Simulium sergenti | (Edwards, 1923) | M, A, T | M | |
| Simulium toubkal | (Bouzidi & Giudicelli, 1986) | M | M | |
| Simulium trifasciatum | (Curtis, 1839) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium variegatum | (Meigen, 1818) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium velutinum | (Santos Abreu, 1922) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium vernum | (Macquart, 1826) | M, T | M + CC | |
| Simulium weiningense | (Chen & Zhang, 1997) | M, A | M | |
| Simulium xanthinum | (Edwards, 1933) | M, A | M | |
| Urosimulium | Urosimulium faurei | (Bernard, Grenier & Bailly-Choumara, 1972) | M, A | M |
| Urosimulium jucci | (Contini, 1966) | A (*), T | M | |
| Greniera | Greniera fabri | (Doby & David, 1959) | A | M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azzouzi, C.; Rabah-Sidhoum, N.; Boucheikhchoukh, M.; Mechouk, N.; Sedraoui, S.; Benakhla, A. Checklist of Medico-Veterinary Important Biting Flies (Ceratopogonidae, Hippoboscidae, Phlebotominae, Simuliidae, Stomoxyini, and Tabanidae) and Their Associated Pathogens and Hosts in Maghreb. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5010001
Azzouzi C, Rabah-Sidhoum N, Boucheikhchoukh M, Mechouk N, Sedraoui S, Benakhla A. Checklist of Medico-Veterinary Important Biting Flies (Ceratopogonidae, Hippoboscidae, Phlebotominae, Simuliidae, Stomoxyini, and Tabanidae) and Their Associated Pathogens and Hosts in Maghreb. Parasitologia. 2025; 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzzouzi, Chaimaa, Noureddine Rabah-Sidhoum, Mehdi Boucheikhchoukh, Noureddine Mechouk, Scherazad Sedraoui, and Ahmed Benakhla. 2025. "Checklist of Medico-Veterinary Important Biting Flies (Ceratopogonidae, Hippoboscidae, Phlebotominae, Simuliidae, Stomoxyini, and Tabanidae) and Their Associated Pathogens and Hosts in Maghreb" Parasitologia 5, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5010001
APA StyleAzzouzi, C., Rabah-Sidhoum, N., Boucheikhchoukh, M., Mechouk, N., Sedraoui, S., & Benakhla, A. (2025). Checklist of Medico-Veterinary Important Biting Flies (Ceratopogonidae, Hippoboscidae, Phlebotominae, Simuliidae, Stomoxyini, and Tabanidae) and Their Associated Pathogens and Hosts in Maghreb. Parasitologia, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5010001








