Abstract
Background: Anabolic–androgenic steroids (AASs) are commonly used for performance enhancement but have been linked to significant neurobiological consequences. This review explores the impact of AASs on neurochemical pathways, cognitive function, and psychiatric disorders, highlighting their potential neurotoxicity. Methods: A narrative review of current literature was conducted to examine AASs-induced alterations in neurotransmitter systems, structural and functional brain changes, and associated psychiatric conditions. The interplay between AASs use and other substances was also considered. Results: Chronic AASs exposure affects serotonin and dopamine systems, contributing to mood disorders, aggression, and cognitive deficits. Structural and functional changes in the prefrontal cortex and limbic regions suggest long-term neurotoxicity. AASs use is associated with increased risks of depression, anxiety, and psychosis, potentially driven by hormonal dysregulation and neuroinflammation. Co-occurring substance use exacerbates neurocognitive impairments and behavioral disturbances. Discussion: While evidence supports the link between AASs use and neurotoxicity, gaps remain in understanding the precise mechanisms and long-term effects. Identifying biomarkers of brain damage and developing targeted interventions are crucial for mitigating risks. Increased awareness among medical professionals and policymakers is essential to address AASs-related neuropsychiatric consequences. Conclusions: AASs abuse poses significant risks to brain health, necessitating further research and prevention efforts. Evidence-based strategies are needed to educate the public, enhance early detection, and develop effective interventions to reduce the neuropsychiatric burden of AASs use.
1. Introduction
Anabolic–androgenic steroids (AASs) are synthetic derivatives of testosterone that have been widely used for their ability to promote muscle growth, enhance athletic performance, and, in some cases, treat medical conditions such as delayed puberty and muscle-wasting diseases [1,2,3,4]. Despite their intended benefits, the misuse of AASs has become a significant public health concern, particularly among athletes, bodybuilders, and recreational users seeking to enhance physical appearance and strength [5,6,7]. While much research has focused on the physiological consequences of AASs use—such as cardiovascular complications, liver toxicity, and endocrine disruptions—there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that AASs can also have profound and lasting effects on the brain.
AASs influence the central nervous system (CNS) through complex mechanisms, affecting neuroanatomy, neurotransmitter balance, and behavioral regulation [8]. Chronic exposure to these substances has been linked to structural brain changes, cognitive impairments, and an increased risk of psychiatric disorders, including aggression, anxiety, depression, and even suicidal tendencies [9,10,11]. These effects are particularly concerning given the increasing prevalence of AASs use among young adults and adolescents, whose brains are still in crucial developmental stages. Recent epidemiological data reinforce the concern over adolescent substance use, including AASs. According to the 2024 Monitoring the Future Survey in the United States, adolescent drug use has remained at historically low levels since the COVID-19 pandemic, with alcohol, nicotine vaping, and cannabis being the most reported substances. However, global trends reveal a more nuanced picture. A 2025 WHO/Europe report found that over 50% of 15-year-olds across Europe had experimented with alcohol, and 1 in 5 had recently used e-cigarettes, indicating a persistent culture of experimentation with psychoactive substances. Furthermore, a 2025 global burden analysis showed that while the overall burden of adolescent substance use disorders (SUDs) has declined, high-income regions, including the U.S. and parts of Europe, have seen increasing disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) linked to adolescent SUDs [12]. These trends are compounded by the influence of social media, where fitness influencers and online forums often glamorize AASs use, downplaying associated risks and promoting unregulated access.
The neurobiological impact of AASs is mediated through several pathways. First, AASs can alter neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine, serotonin, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which play essential roles in mood regulation, cognition, and impulse control. Disruptions in these systems can contribute to aggressive behavior, impulsiveness, and mood disturbances, commonly observed in long-term AASs users [13]. Additionally, AASs use has been associated with oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, both of which can lead to neuronal damage and cognitive dysfunction [14]. Animal studies and human neuroimaging research indicate that prolonged exposure to AASs may result in structural changes in key brain regions, such as the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus—areas responsible for decision making, emotional processing, and memory [15,16,17]. Other anabolic compounds, such as Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs), are gaining attention due to their purported ability to selectively target anabolic pathways in muscle and bone with fewer androgenic side effects compared to traditional AASs. This selectivity makes them attractive to users seeking muscle growth with a reduced risk of virilization or other adverse effects. However, long-term safety data are still limited, and their use is associated with various risks, including potential liver toxicity and hormonal suppression [18].
One of the most widely discussed psychological effects of AASs misuse is “roid rage,” a term used to describe the heightened aggression and irritability reported by many users [19]. While some studies have suggested that increased aggression may stem from personality traits or environmental factors, experimental evidence supports the idea that AASs-induced alterations in the brain contribute significantly to aggressive and impulsive behavior [8,20]. This has major implications for public safety, particularly among individuals who engage in high-risk activities or occupations requiring emotional regulation and self-control [21].
Beyond aggression, AASs use has been linked to an increased prevalence of psychiatric conditions such as anxiety and depression. While some users report a temporary sense of euphoria or increased confidence, prolonged AASs exposure can lead to dysregulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, which plays a central role in stress response and mood stability [22,23,24].
AASs influence the CNS through a dual action. First, they directly engage their own intracellular receptors. Second, they act indirectly by either altering binding at neurotransmitter receptor sites or by prompting the release of neuropeptides. These processes are, consequently, impacted by the presence of inhibitory GABA receptors and 5-HT receptors [25]. These receptors are particularly prevalent in brain regions linked to mood disorders, stress responses, aggression, and sexual function. Research has consistently demonstrated a notable interplay between the 5-HTT-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) and neuroticism, particularly in athletes prone to anxiety and depression. Furthermore, circulating AAS in the periphery can undergo conversion into estrogen derivatives, subsequently activating secondary messenger systems [26]. Most AAS primarily bind to androgen receptors. They can also undergo aromatization into estrogenic metabolites, which then interact with both estrogen receptor-alpha (ERα) and estrogen receptor-beta (ERβ). Beyond this, AAS can signal through ERα, ERβ, and progesterone receptors even without metabolic conversion to estrogen. Brain areas implicated in the development of anxiety and aggression observed with AAS misuse appear to exhibit a high concentration of steroid receptors and associated enzymes [27].
Withdrawal from AASs can exacerbate these symptoms, leading to severe mood disturbances and even suicidal ideation in some cases. The dependency potential of AASs further complicates this issue, as individuals who develop tolerance may escalate their usage, increasing their risk of neurotoxicity and long-term cognitive deficits [28]. The acute bouts of resistance exercise (like weightlifting) can cause a transient increase in circulating total and free testosterone levels. This increase typically peaks around the end of exercise and returns to resting concentrations within a few hours. The evidence for chronically elevated resting endogenous androgen levels in natural bodybuilders compared to the general population is less clear-cut and not consistently supported across all studies. Some research indicates that while exercise is a potent stimulus, the sustained impact on resting endogenous hormone levels might be limited, and sometimes even a decline in testosterone can be observed with excessive training or inadequate energy intake (overtraining) [29].
Despite growing evidence highlighting the risks associated with AASs use, awareness of these dangers remains limited, particularly among young people and non-competitive users. Social media, fitness influencers, and online forums often portray AASs as relatively safe when used “responsibly,” failing to emphasize the potential consequences for brain health [1,30]. Given the long-term implications of AASs-related neurotoxicity, there is an urgent need for educational initiatives aimed at dispelling misconceptions and providing evidence-based information on the risks of steroid misuse [14,31,32,33].
This review aims to synthesize the existing literature on AASs and brain damage, exploring the neurobiological mechanisms underlying their effects on brain structure and function. We will discuss the cognitive and behavioral consequences of AASs use, as well as the potential for recovery after cessation. Additionally, we will examine current strategies for prevention, intervention, and harm reduction, emphasizing the importance of early detection and mental health support for AASs users. By increasing awareness of the neurological risks associated with AASs, we hope to contribute to a more informed dialogue on the responsible use of these substances and the need for stricter regulations in their distribution and consumption.
This review was conducted by searching the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (WOS) databases using the keywords “Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids” AND “Brain Damage” AND “Medico-Legal.” Articles extracted from this search were subsequently analyzed and included based on the following criteria: English language publications, covering the period between 2000 and 2025, classified as original articles or meta-analyses, and focusing on specific models (in vivo/in vitro). Exclusion criteria included studies published before 2000, case reports, articles not available in full text, studies with significant methodological weaknesses, and non-English language articles.
2. Neuroanatomical Effects of Anabolic–Androgenic Steroids
Chronic use of AASs has been linked to significant structural and functional changes in the brain, particularly in regions involved in memory, emotional regulation, and executive functioning [34,35]. Neuroimaging studies suggest that prolonged AASs exposure can alter brain morphology, leading to volume reductions, impaired neural connectivity, and changes in neurochemical signaling. The hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex—three critical brain areas responsible for learning, emotion processing, and decision making—appear to be particularly vulnerable to AASs-induced neurotoxicity (Table 1) [36,37].

Table 1.
This table summarizes the structural and functional changes observed in key brain regions following the use of AASs.
In comparison to individuals who are not dependent on AASs, dependent users of AASs display a markedly reduced cortical thickness across three distinct clusters in the right hemisphere and five in the left hemisphere. These affected areas encompass the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes. Notably, substantial disparities are evident within the frontal regions [15]. Overall, AASs users seem to exhibit diminished cortical thickness in numerous brain areas, with a particular concentration in the prefrontal cortex, which plays a crucial role in inhibitory control and emotional regulation, when contrasted with non-dependent AASs users [15,34]. Drawing upon existing research and established models of reward processing and addictive behaviors, key brain structures of significant interest include the nucleus accumbens (NA), which is deeply involved in reward mechanisms, and the prefrontal cortex, essential for higher-order cognitive functions such as impulse suppression and affect regulation [38] (Figure 1).
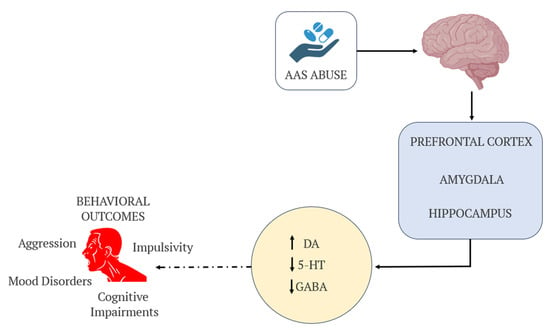
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the neurochemical pathways affected by AASs use. AASs influence key brain regions (prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus) and disrupt neurotransmitter systems, including increased dopamine (DA), decreased serotonin (5-HT), and reduced GABA activity. These alterations contribute to behavioral outcomes such as aggression, mood disorders, cognitive impairments, and impulsivity.
The hippocampus, a key region for learning and memory, has been shown to shrink in volume following chronic AASs abuse [37,39]. This atrophy may be linked to hippocampal neurogenesis suppression, where AASs disrupt the generation of new neurons, impairing cognitive flexibility and memory retention. Several studies have demonstrated that AASs users perform poorly on memory-related tasks compared to non-users, suggesting that the hippocampal deterioration translates to functional deficits. The glucocorticoid and androgen receptor (AR) interactions in the hippocampus may be partially responsible, as AASs can disrupt stress hormone regulation, further exacerbating cognitive dysfunction [40].
The amygdala, a structure central to emotion processing and aggression, also exhibits notable changes in AASs users. Animal and human studies indicate that AASs can induce hypertrophy (enlargement) of the amygdala, potentially leading to heightened aggression, impulsivity, and anxiety. This phenomenon is often referred to as “roid rage,” a well-documented behavioral manifestation of AASs abuse. The increase in amygdala activity and volume correlates with dysregulated emotional responses, making AASs users more prone to irritability, violent outbursts, and heightened stress reactivity. Furthermore, disruptions in serotoninergic and dopaminergic pathways within the amygdala may contribute to mood instability, fostering symptoms of anxiety and depression [8,41,42].
The prefrontal cortex, a region governing executive function, impulse control, and decision making, is also significantly affected by AASs [43]. Structural abnormalities in this area are associated with reduced self-regulation, increased risk-taking behaviors, and poor judgment, common traits observed among AASs users. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have demonstrated lowered activity in the prefrontal cortex of long-term AASs users, suggesting impaired top-down control over aggressive and impulsive behaviors [34,44]. This dysfunction may explain the higher incidence of reckless decision making, substance abuse, and antisocial tendencies in individuals who misuse AASs. The prefrontal cortex’s susceptibility to androgen-induced neurotoxicity may stem from both hormonal imbalances and disrupted neurotransmitter systems, particularly involving dopamine, serotonin, and GABA [44,45].
At a cellular level, multiple mechanisms contribute to AASs-induced neurotoxicity. One prominent factor is oxidative stress, where an excessive buildup of reactive oxygen species (ROS) leads to neuronal damage and apoptosis (cell death). The brain is particularly vulnerable to oxidative damage due to its high metabolic demand and lipid-rich composition. Studies have shown that chronic AASs exposure reduces antioxidant enzyme activity, increasing susceptibility to oxidative stress-related neurodegeneration (Table 2) [46,47]. Apoptosis is a caspase-dependent cell demise process initiated when pro-apoptotic ligands, such as FAS/CD95 ligand (FASL/CD95L), bind to the FAS/CD95 death receptor. This resultant complex then recruits various intracellular components, including FAS-associated protein with a death domain (FADD), cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (cIAPs), c-FLIPs, and procaspase 8. This sophisticated molecular assembly regulates the activation of caspase-8. Once activated, caspase-8 can directly initiate the caspase cascade by facilitating the proteolytic maturation of caspase-3, or it can induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization through the cleavage of the BH3-interacting domain (BID) [14].

Table 2.
This table outlines the principal biological mechanisms by which AASs exert neurotoxic effects.
Another key mechanism is neuroinflammation, where chronic AASs use triggers pro-inflammatory responses in the brain [48]. Elevated levels of cytokines and microglial activation have been observed in AASs users, suggesting that prolonged exposure induces chronic low-grade inflammation, which can compromise synaptic integrity and neuronal function [46,47]. This inflammation is particularly pronounced in the prefrontal cortex and limbic system, regions responsible for cognitive and emotional regulation. Over time, sustained neuroinflammation can accelerate gray matter deterioration, contributing to long-term cognitive and psychiatric disorders [49].
AASs also disrupt neurotransmitter homeostasis, significantly affecting dopaminergic, serotonergic, and GABAergic signaling pathways [8]. By modulating dopamine release, AASs can create an imbalance in reward processing, increasing susceptibility to addiction and compulsive behaviors. Serotonin, a neurotransmitter essential for mood stabilization and emotional regulation, is also negatively affected, with AASs use leading to decreased serotonin receptor expression and function. This decline may explain the increased prevalence of depression, anxiety, and mood swings among AASs users [50]. The GABAergic system, which plays a crucial role in inhibitory control, is also impaired, reducing impulse suppression and increasing aggression levels [51].
Collectively, these neuroanatomical and cellular alterations paint a concerning picture of AASs-related brain damage. The structural degeneration of key brain regions, compounded by oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurotransmitter imbalances, underscores the long-term cognitive and psychological risks associated with AASs misuse. Given the growing prevalence of AASs abuse, further research is essential to fully understand the extent of these neurotoxic effects and develop effective prevention and intervention strategies.
3. Cognitive Impairments Associated with Anabolic–Androgenic Steroid Use
The impact of AASs use on cognitive function has been a growing concern, as evidence suggests that chronic abuse can significantly impair various aspects of memory, attention, and executive decision making [52,53]. These cognitive deficits appear to stem from the neurotoxic effects of AASs on key brain regions such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, which are critical for information processing, concentration, and behavioral regulation [34,37].
One of the most well-documented cognitive impairments associated with AASs use is memory dysfunction. Users often report difficulties in recall and retention, struggling with both short-term and long-term memory. This impairment is largely attributed to hippocampal atrophy, as AASs-induced neurotoxicity can disrupt neuronal plasticity and synaptic function within this brain region [54]. Research indicates that long-term AASs users perform poorly on verbal and spatial memory tasks, suggesting deficits in episodic and working memory. Furthermore, studies in both human and animal models have shown that AASs can reduce hippocampal neurogenesis, limiting the brain’s ability to form new connections necessary for learning and memory consolidation [52,54]. This may explain why chronic AASs users often experience learning difficulties and struggle with cognitive flexibility in problem-solving scenarios.
In addition to memory deficits, AASs abuse is associated with significant attention and concentration impairments [55]. Users frequently report difficulty maintaining focus on tasks, leading to decreased productivity and increased cognitive fatigue [56]. These attentional deficits may result from dysregulation of dopamine and serotonin neurotransmitter systems, both of which play essential roles in maintaining focus and processing relevant information [57]. Studies suggest that dopamine receptor alterations caused by AASs abuse can mimic symptoms of attention-deficit disorders, leading to reduced task efficiency and increased distractibility. Additionally, prefrontal cortex dysfunction—which has been linked to AASs use—may contribute to deficits in selective attention and sustained concentration, impairing an individual’s ability to filter out distractions and stay engaged in cognitively demanding activities [58].
Perhaps the most concerning cognitive consequence of AASs abuse is impaired decision making and impulse control. Chronic users display a higher propensity for risk-taking behaviors, which may be linked to structural and functional abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex—a region responsible for executive function and inhibitory control [59]. Impaired impulse regulation can lead to reckless decision making, financial irresponsibility, substance abuse, and heightened aggression, all of which can significantly impact personal and professional relationships. Neuroimaging studies indicate that AASs users exhibit reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex during decision-making tasks, suggesting compromised neural circuits involved in weighing consequences and exerting self-restraint [34]. This dysfunction aligns with real-world behavioral patterns observed in AASs users, such as impatience, disregard for long-term repercussions, and susceptibility to addictive behaviors [6,19,28].
Collectively, these cognitive impairments highlight the profound impact of AASs on brain function and mental acuity. The disruption of memory, attention, and impulse control mechanisms underscores the long-term cognitive risks associated with steroid misuse, emphasizing the need for increased awareness and early intervention strategies to mitigate neuropsychological damage in chronic users.
4. Behavioral Changes and Mental Health Implications
The psychological and behavioral consequences of AASs use are profound, often manifesting in increased aggression, mood disorders, and dependency-related withdrawal symptoms [60]. These effects can have severe personal, social, and legal ramifications, affecting users’ relationships, occupational stability, and overall quality of life. The neurobiological impact of AASs on key brain regions and neurotransmitter systems plays a crucial role in modulating emotions and behavior, contributing to significant mental health disturbances [59].
One of the most well-documented behavioral changes associated with AASs use is heightened aggression and hostility, often referred to as “roid rage” [61]. This phenomenon is characterized by sudden, intense outbursts of anger, increased irritability, and violent tendencies, sometimes resulting in physical confrontations or legal issues. The underlying mechanisms of AASs-induced aggression involve alterations in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, which regulate emotional responses and impulse control. Animal studies and human reports suggest that AASs use may enhance activity in aggression-related neural pathways while simultaneously impairing executive control mechanisms, making users more prone to reacting impulsively to perceived threats or frustrations. This aggressive behavior can strain personal relationships, leading to conflict with family members, colleagues, or peers. Additionally, some AASs users report an inability to recognize or acknowledge their own aggressive tendencies, further complicating intervention and behavioral regulation [17,20,62,63].
Beyond aggression, mood disorders are another serious psychological consequence of AAS use. Depression, anxiety, and severe mood swings are frequently reported among both active users and individuals experiencing withdrawal from AASs (Figure 2).
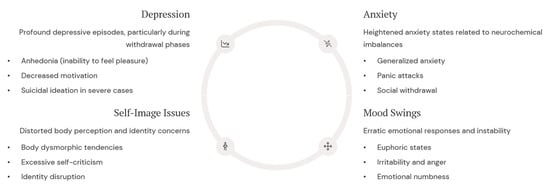
Figure 2.
Mood disorders represent a significant psychological consequence of AASs use, with effects that can persist long after cessation. These emotional disturbances stem from disruptions in serotonergic and dopaminergic systems, particularly affecting reward pathways and emotional processing circuits. These issues include depression (especially during withdrawal), anxiety (linked to neurochemical imbalances), self-image issues (e.g., body dysmorphia), and significant mood swings.
AASs can alter the balance of important neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin in the brain. Studies in animal models have shown that nandrolone abuse, for example, can reduce dopamine and serotonin levels in key brain areas associated with the reward system and mood regulation, contributing to anhedonia and a depressive profile [64]. Steroids, at supraphysiological doses, can enhance dopamine release in the mesolimbic circuit, a key pathway in the brain’s reward system. Dopamine is the primary neurotransmitter associated with the sensation of pleasure, motivation, and euphoria, and an increase in its synaptic availability can generate these effects [65].
AASs can alter the balance of important neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin in the brain. Studies in animal models have shown that abuse of nandrolone, for example, can reduce dopamine and serotonin levels in key brain areas associated with the reward system and mood regulation, contributing to anhedonia and a depressive profile [64].
Chronic AASs use may lead to disruptions in serotonin transmission, increasing susceptibility to depressive episodes and heightened anxiety levels. Furthermore, dopaminergic dysfunction may contribute to anhedonia, or the inability to experience pleasure, which is a hallmark of AASs-induced depressive states. Alarmingly, some long-term users have reported experiencing suicidal ideation, particularly during withdrawal periods when mood instability and emotional distress peak [66]. The psychological burden of AASs-induced mood disorders underscores the need for mental health interventions targeting users who struggle with the emotional repercussions of steroid abuse [8,66,67].
Particularly concerning mental health, the implication of AASs use is dependency and withdrawal syndrome, which can exacerbate psychological distress and lead to a cycle of compulsive drug use. While many individuals begin using AASs for performance enhancement or body image concerns, prolonged exposure can lead to physiological and psychological dependence. Withdrawal symptoms can be severe, often including fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances, and profound depressive episodes, which may drive users to resume steroid use to alleviate discomfort. Withdrawal-related psychological distress can be severe enough to require professional intervention, such as counseling, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), or pharmacological support, to aid individuals in managing the emotional and physiological challenges of cessation [6,68,69].
Existing research, encompassing numerous clinical studies and surveys, frequently points to a correlation between AASs misuse and heightened aggression along with feelings of hostility, sometimes culminating in violent conduct [70]. It has also been observed that a significant number of individuals who abuse AASs concurrently misuse alcohol and/or various illicit substances. Given that substance abuse is an established predictor of violent behavior, it is plausible that the violence perpetrated by AASs users might, in many instances, be primarily attributable to the co-abuse of other drugs [71]. Data further reveal that the likelihood of conviction for a violent crime was at least comparable, if not higher, for groups testing positive for AASs compared to those testing negative. Additionally, when examining a three-year period immediately preceding death, there was a notable surge in the incidence of violent crime and a distinct reduction in property crime rates, particularly when contrasted with the initial three years following a first criminal conviction. These findings suggest that, in certain predisposed individuals, AASs use could contribute to an elevated incidence of violent crime, particularly when combined with the consumption of other illegal substances [72]. Several real-world cases underscore the complex medico-legal implications of AASs misuse. For instance, a forensic case involving a 31-year-old aesthetic weightlifter revealed that chronic AASs abuse may lead to immunodeficiency, contributing to fatal complications such as necrotizing myofasciitis following minor trauma. Despite surgical intervention and hyperbaric therapy, the patient died, and autopsy findings confirmed the role of AASs in compromising immune function [73]. This case highlights the need for clinicians and forensic experts to consider immunosuppression as a potential consequence of AASs use, especially in sudden or unexplained deaths. Additionally, a large-scale forensic study comparing criminal histories of deceased individuals found that AASs users, particularly those not co-abusing other substances, had a significantly higher incidence of violent crimes in the years preceding death, suggesting a direct link between AASs use and aggressive behavior [72]. Together, these cases illustrate the multifaceted legal and forensic challenges posed by AASs, from clinical negligence and criminal liability to the interpretation of cause of death in forensic pathology. The medicolegal landscape surrounding AASs is characterized by strict legal controls, significant liability risks for prescribers who deviate from approved indications and standard medical practice, severe consequences for athletes engaged in doping, and complex ethical considerations that underscore the importance of patient safety and professional responsibility [74].
Jurisdictional differences significantly influence how physicians navigate the ethical dilemma of confidentiality versus disclosure in cases involving AASs or doping. In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) enshrines strict patient confidentiality, allowing disclosure only under specific legal exceptions, such as imminent harm or court orders. However, state laws may impose additional obligations or restrictions, creating variability across jurisdictions (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). In contrast, the United Kingdom adheres to the General Medical Council’s (GMC) guidance, which permits breaching confidentiality when it is in the public interest—such as preventing serious harm to others—but requires careful justification and documentation. Meanwhile, in many European Union countries, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs medical data privacy, emphasizing informed consent and proportionality in data sharing [75]. However, national laws may further refine these principles, especially in sports medicine or forensic contexts. Notably, under the World Anti-Doping Code (WADC), healthcare professionals globally are prohibited from assisting athletes in doping practices and may face sanctions if they fail to report such behavior, even if doing so conflicts with local confidentiality norms. These discrepancies underscore the ethical and legal complexity faced by clinicians, who must balance professional duties, patient trust, and regulatory compliance across diverse legal landscapes.
Overall, the behavioral and mental health consequences of AASs misuse highlight the urgent need for education, early intervention, and accessible psychological support (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Early intervention is crucial, as prolonged AASs use can lead to more severe and potentially irreversible psychological and endocrine effects. Treatment should be tailored to individual needs, with particular attention to underlying factors that initially motivated steroid use. Psychotherapy (e.g., CBT, motivational interviewing), pharmacotherapy (for symptoms and hormone restoration), support systems (peer and family therapy), and endocrine monitoring can be used to track physiological recovery.
The link between AASs use and aggression, mood instability, and dependency underscores the importance of screening steroid-related mental health issues in both athletic and non-athletic populations. Addressing these risks through awareness campaigns, psychological counseling, and harm reduction strategies is essential to mitigating the long-term neuropsychiatric damage associated with AAS abuse.
Research indicates that long-term AASs use is associated with structural brain differences, including thinner cortex in widespread regions and smaller neuroanatomical volumes (e.g., total gray matter, cerebral cortex, and putamen). The reversibility of these structural changes is largely unknown and requires more longitudinal studies [76]. Furthermore, experimental and animal studies strongly suggest that AASs can induce neurotoxicity, involving mechanisms such as oxidative stress and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Whether neurons damaged through these pathways can fully recover or be replaced is a critical question [14]. Bertozzi et al. state that irritability, anxiety, and depressive symptoms are commonly reported. While some acute behavioral effects may subside with discontinuation, long-term psychiatric sequelae and the underlying neurobiological alterations are less clear regarding reversibility [8].
The long-term neurodegenerative effects of AAS use may remain clinically silent during young age, as most illicit users are under 50, an age too early for clear symptomatic manifestations of potential neurotoxic effects. However, early exposure during a critical developmental window like adolescence could predispose individuals to more severe or earlier onset of issues later in life [77]. Experimental animal studies have shown that supraphysiological doses of steroids can cause considerable damage to nervous tissue, leading to ultrastructural and behavioral impairment. For example, a significant decrease in neuronal density was observed in both male and female mice treated with anabolic steroids, with specific steroids (e.g., stanozolol) causing greater reductions in certain brain areas compared to others. Another animal model demonstrated remarkable modifications in GABA A receptor subunit mRNA levels depending upon the dose of AAS [78].
5. Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency in Medical Record Management with AI
AASs are synthetic derivatives of testosterone designed to enhance muscle growth and promote masculinizing effects [28]. Their dual action is reflected in their nomenclature: the anabolic component refers to their ability to stimulate protein synthesis, increase nitrogen retention, and promote muscle hypertrophy, while the androgenic component is responsible for the development and maintenance of male secondary sexual characteristics such as increased body hair, deepened voice, and enhanced bone density [29,30,31,32,33]. AASs can be classified into various categories based on their chemical structure, mode of administration, and potency. They are commonly consumed in either oral or injectable forms, with each mode having distinct pharmacokinetic properties [34,35,36].
Different administration protocols in non-medical settings could be adopted by the users (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
The administration protocols in non-medical settings are summarized, highlighting each characteristic: cycling (intermittent use for recovery and HPG axis mitigation), stacking (concurrent use of multiple compounds for maximal effect), pyramiding (gradual dose adjustment for adaptation and withdrawal management), and post-cycle therapy (PCT) (aimed at restoring natural hormone production post-use).
Oral AASs, such as oxandrolone, stanozolol, and methandrostenolone, undergo extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, which can lead to hepatotoxicity with prolonged use. Injectable AASs, such as testosterone enanthate, nandrolone decanoate, and trenbolone acetate, bypass the liver to a greater extent and have longer half-lives, leading to more sustained physiological effects [79,80].
AASs were initially developed for medical use and remain valuable in clinical settings. They are prescribed for conditions such as hypogonadism, muscle-wasting diseases (e.g., AIDS-related cachexia and cancer-related muscle loss), and certain types of anemia [3]. In these contexts, AASs help restore hormonal balance, improve muscle mass, and enhance overall quality of life. However, their non-medical use, particularly among athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts, has surged dramatically over the past few decades. Many users engage in supraphysiological dosing, consuming doses several times higher than therapeutic recommendations in pursuit of enhanced muscularity and physical performance [81,82]. This widespread misuse has been fueled by the portrayal of hyper-muscular physiques in media, the availability of AASs through illicit markets, and the influence of social media figures who advocate for their use while downplaying the associated risks [83,84,85]. In this context, pharmacogenetics plays a pivotal role in the AASs metabolism [86], and post mortem investigations are vital in order to clarify the cause of death [73,87].
The use of AASs extends beyond professional athletes and bodybuilders, permeating recreational fitness communities and even reaching adolescents seeking quick physical transformations. Many users adopt complex regimens, including cycling, stacking, and pyramiding [1]. Cycling involves alternating periods of AASs use with drug-free intervals, purportedly to reduce side effects and avoid detection in drug testing [79]. Stacking refers to the simultaneous use of multiple AASs, often in combination with other performance-enhancing substances like human growth hormone (hGH) and insulin, to maximize anabolic effects [88,89]. Pyramid entails gradually increasing AASs dosage over several weeks, reaching a peak, and then tapering down to minimize withdrawal effects. Despite these strategies, there is little scientific evidence to suggest that they effectively mitigate the long-term risks of AASs use, particularly their neuropsychological and neurotoxic effects [19,90].
Beyond their well-documented impact on muscle hypertrophy and athletic performance, AASs exert profound effects on multiple organ systems. Endocrine disruptions are among the most immediate consequences, as exogenous AASs suppress the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis, leading to reduced endogenous testosterone production [91,92]. This suppression can result in testicular atrophy, infertility, gynecomastia (breast tissue development in males), and sexual dysfunction. In women, AASs use can cause menstrual irregularities, voice deepening, clitoral hypertrophy, and male pattern baldness, some of which may be irreversible [31,93,94,95,96]. Cardiovascular complications are another major concern, as AASs increase low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, decrease high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and elevate blood pressure, thereby heightening the risk of atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke [97,98]. Additionally, the liver is highly susceptible to cholestatic hepatotoxicity, particularly with the use of 17α-alkylated oral AASs, which can lead to conditions such as hepatic adenomas and, in severe cases, hepatocellular carcinoma [99].
While the somatic side effects of AASs have been extensively studied, their impact on the CNS and brain function remains a growing area of research. AASs interact with ARs in the brain, particularly in regions such as the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus, which play crucial roles in cognition, emotional regulation, and impulse control [100,101]. Chronic AASs exposure has been associated with mood disturbances, cognitive deficits, increased aggression, and dependency, suggesting that their effects extend well beyond muscle enhancement. Given the increasing prevalence of AASs use and the potential for severe neurological and psychiatric consequences, a deeper understanding of their impact on brain function is essential [19,102,103].
6. AASs Use Among Women
Although AASs use is more prevalent among men, recent studies indicate a growing trend among women, particularly in competitive bodybuilding and strength sports. The use of AASs among women remains an area of active research, but it is not yet fully understood. This is primarily because most studies exploring the various facets of AASs use in females rely on small cohorts of women involved in competitive fitness, bodybuilding, and strength sports. Women typically administer AASs in cycles, either orally or via injection [104]. For some, initiating AASs use is an impulsive decision, while others seek to overcome training plateaus and/or prepare for fitness competitions. Many users are often unprepared for the undesirable virilizing effects; however, some report that these are counterbalanced by the desired outcomes. Clitoral enlargement frequently leads to feelings of shame and a reduction in self-esteem. Conversely, an increased libido is a common effect, resulting in both positive and negative experiences depending on an individual’s life circumstances, partner status, whether the partner also uses AASs, and the presence of any accompanying genital alterations [81]. AASs produce fetal virilization and changes in fetal growth through one of three mechanisms. Furthermore, the drugs can exert an indirect effect by stimulating other glands, such as the adrenal cortex, which in turn produce androgens. AASs can also produce changes in the placenta and significant modifications [105].
The global lifetime prevalence of androgen abuse in women is estimated between 0.1 and 1.6%, with most research limited to small, qualitative samples [106]. Women often use fewer substances at lower doses to minimize virilizing effects yet still face significant physical and psychosocial consequences. Recent qualitative studies have revealed that motivations for AAS use among women include body dissatisfaction, eating disorders, and the pursuit of external validation through muscularity and performance [81]. Many women report being introduced to AASs by male partners or coaches, often without adequate information about the risks. Common adverse effects include menstrual irregularities, voice deepening, clitoral hypertrophy, and female pattern hair loss (FPHL), which is often underdiagnosed and under-researched compared to male pattern baldness. FPHL can have profound psychosocial impacts, including anxiety, shame, and body image distress [107]. Moreover, women may use the return or absence of menstruation as a self-monitoring tool for perceived safety, despite the lack of clinical validation [108]. These findings highlight the need for gender-specific education, harm reduction strategies, and access to informed medical care. Medico-legal challenges also arise, particularly in cases involving misinformed consent, underreported side effects, and the societal stigma surrounding female androgen use. Addressing these gaps requires further research and tailored clinical guidelines to ensure safe and ethical care for female AAS users.
7. Conclusions
Although AASs are widely used for their muscle-enhancing and performance-boosting properties, their adverse effects on brain health and mental well-being cannot be overlooked. The evidence reviewed highlights the potential for neurotoxicity, cognitive impairments, and significant behavioral alterations, all of which can have lasting consequences on an individual’s psychological and neurological integrity. The disruption of key brain structures, such as the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex, combined with oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurotransmitter imbalances, underscores the serious risks associated with prolonged AASs use. Furthermore, the psychological toll, including increased aggression, mood disorders, and dependency-related withdrawal symptoms, presents additional challenges that necessitate targeted intervention strategies.
Given these profound implications, raising awareness and implementing preventive measures should be a priority in both clinical and athletic settings. Educational programs must be developed to inform potential users about the long-term risks of AASs use, ensuring that individuals make informed decisions regarding their health. Additionally, regular psychological screening should be integrated into sports medicine protocols, particularly for those engaged in competitive sports or high-risk environments where AASs use is prevalent. Counseling services and structured support systems should be readily available to individuals struggling with AASs dependency, offering professional guidance on cessation strategies and mental health management.
Interactive online sessions for parents, coaches, physical education teachers, and youth, led by health professionals (doctors, psychologists, and dietitians) and law enforcement, should be organized to openly discuss the risks and answer questions. Furthermore, it is important to create and distribute clear guidelines for gym staff on how to respond to suspected AAS use, thus promoting a safe and supportive environment, and establish or designate specialized clinics and outpatient services for the treatment of AAS abuse, offering medical care for managing side effects, psychological support for addiction, and nutritional and exercise counseling for healthy lifestyle maintenance. Self-help and peer support groups (online and offline) should be established, where individuals can share experiences and cessation strategies in a safe and confidential environment. Given the uncertainty surrounding the reversibility of AAS-induced neuroanatomical changes, there is a pressing need for longitudinal human studies to clarify the extent and duration of these effects, particularly in younger populations and chronic users.
Ultimately, understanding the detrimental effects of AASs on the brain is crucial for fostering healthier, more responsible practices within both professional and recreational fitness communities. By prioritizing mental health alongside physical fitness, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and sports organizations can work toward reducing AASs-related harm and promoting safer alternatives for enhancing athletic performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.C. and L.D.M.; methodology, M.G.C., M.E., S.A., S.F., M.F., G.V., R.R., N.D.F. and L.D.M.; validation, M.G.C. and L.D.M.; data curation, M.G.C., M.E., S.A., S.F., M.F., G.V., R.R., N.D.F. and L.D.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G.C., M.E., S.A., S.F. and M.F.; writing—review and editing, G.V., R.R., N.D.F. and L.D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AASs | Anabolic–androgenic steroids. |
| ARs | Androgen receptors. |
| CNS | Central nervous system. |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging. |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid. |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal. |
| HPG | Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal. |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein. |
| HDLs | High-density lipoprotein. |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species. |
References
- Wenbo, Z.; Yan, Z. The Uses of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids Among Athletes; Its Positive and Negative Aspects-A Literature Review. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2023, 16, 4293–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, A.; Basaria, S. Adverse Health Effects of Androgen Use. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 464, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauchen, J.; Jurášek, M.; Huml, L.; Rimpelová, S. Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited. Molecules 2021, 26, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agriesti, F.; Tataranni, T.; Pacelli, C.; Scrima, R.; Laurenzana, I.; Ruggieri, V.; Cela, O.; Mazzoccoli, C.; Salerno, M.; Sessa, F.; et al. Nandrolone Induces a Stem Cell-like Phenotype in Human Hepatocarcinoma-Derived Cell Line Inhibiting Mitochondrial Respiratory Activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadah, K.; Gopi, G.; Lingireddy, A.; Blumer, V.; Dewald, T.; Mentz, R.J. Anabolic Androgenic Steroids and Cardiomyopathy: An Update. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1214374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacentino, D.; Kotzalidis, G.D.G.; Casale, A.; Aromatario, M.; Pomara, C.; Girardi, P.; Sani, G.; del Casale, A.; Aromatario, M.; Pomara, C.; et al. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Use and Psychopathology in Athletes. A Systematic Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 13, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Bertozzi, G.; Cipolloni, L.; Messina, G.; Aromatario, M.; Polo, L.; Turillazzi, E.; Pomara, C. MiRNAs as Novel Biomarkers of Chronic Kidney Injury in Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Users: An Experimental Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 563756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertozzi, G.; Sessa, F.; Albano, G.D.G.D.; Sani, G.; Maglietta, F.; Roshan, M.H.K.M.H.K.; Volti, G.L.G.L.; Bernardini, R.; Avola, R.; Pomara, C.; et al. The Role of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids in Disruption of the Physiological Function in Discrete Areas of the Central Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 55, 5548–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas-Iniguez, C.; Burnor, E.; Herting, M.M. Neurotoxicants, the Developing Brain, and Mental Health. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2022, 2, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zundel, C.G.; Ryan, P.; Brokamp, C.; Heeter, A.; Huang, Y.; Strawn, J.R.; Marusak, H.A. Air Pollution, Depressive and Anxiety Disorders, and Brain Effects: A Systematic Review. Neurotoxicology 2022, 93, 272–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, R.; Pitruzzella, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Rappa, F.; Salerno, M.; Barone, F.; Sangiorgi, C.; D’Amico, D.; Locorotondo, N.; Di Gaudio, F.; et al. Nandrolone Decanoate Interferes with Testosterone Biosynthesis Altering Blood–Testis Barrier Components. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Woo, S.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Kim, T.; Fond, G.; Boyer, L.; Rahmati, M.; Smith, L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Trends in Drug Use Disorder Mortality Rates across 73 Countries from 1990 to 2021, with Projections up to 2040: A Global Time-Series Analysis and Modelling Study. eClinicalMedicine 2025, 79, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzer, J.J.; Ricci, L.A.; Melloni, R.H. Interactions between the Dopaminergic and GABAergic Neural Systems in the Lateral Anterior Hypothalamus of Aggressive AAS-Treated Hamsters. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 203, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomara, C.; Neri, M.; Bello, S.; Fiore, C.; Riezzo, I.; Turillazzi, E. Neurotoxicity by Synthetic Androgen Steroids: Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Neuropathology: A Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 13, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauger, L.E.; Westlye, L.T.; Fjell, A.M.; Walhovd, K.B.; Bjørnebekk, A. Structural Brain Characteristics of Anabolic–Androgenic Steroid Dependence in Men. Addiction 2019, 114, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, R.L.; Lumia, A.R.; McGinnis, M.Y. Androgenic Anabolic Steroid Exposure during Adolescence: Ramifications for Brain Development and Behavior. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Esposito, M.; Salerno, M. Experimental Studies on Androgen Administration in Animal Models: Current and Future Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 566–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, Z.J.; Mirabal, J.R.; Mazur, D.J.; Kohn, T.P.; Lipshultz, L.I.; Pastuszak, A.W. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators: Current Knowledge and Clinical Applications. Sex. Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanayama, G.; Brower, K.J.; Wood, R.I.; Hudson, J.I.; Pope, H.G. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Dependence: An Emerging Disorder. Addiction 2009, 104, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, T.R.; Sikes, R.W.; Melloni, R.H. Anabolic Steroids Alter the Physiological Activity of Aggression Circuits in the Lateral Anterior Hypothalamus. Neuroscience 2016, 315, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, N.H.; Sullivan, T.P.; Tull, M.T. Explicating the Role of Emotion Dysregulation in Risky Behaviors: A Review and Synthesis of the Literature with Directions for Future Research and Clinical Practice. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2015, 3, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, J.A.; Sanchez, E.R. The Role of the Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) Axis in Test-Induced Anxiety: Assessments, Physiological Responses, and Molecular Details. Stresses 2022, 2, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, O.; Raz, M.; Tendler, A.; Bar, A.; Korem Kohanim, Y.; Milo, T.; Alon, U. A New Model for the HPA Axis Explains Dysregulation of Stress Hormones on the Timescale of Weeks. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Polito, R.; Li Rosi, G.; Salerno, M.; Esposito, M.; Pisanelli, D.; Ministeri, F.; Messina, A.; Carotenuto, M.; Chieffi, S.; et al. Neurobiology and Medico-Legal Aspects of Suicides among Older Adults: A Narrative Review. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1449526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, K.L.; Porter, D.M.; Henderson, L.P. Anabolic Androgenic Steroids Induce Age-, Sex-, and Dose-Dependent Changes in GABAA Receptor Subunit MRNAs in the Mouse Forebrain. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masonis, A.E.T.; McCarthy, M.P. Effects of the Androgenic/Anabolic Steroid Stanozolol on GABAA Receptor Function: GABA-Stimulated 36Cl- Influx and [35S] TBPS Binding. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 279, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petito, A.; Altamura, M.; Iuso, S.; Padalino, F.A.; Sessa, F.; D’Andrea, G.; Margaglione, M.; Bellomo, A. The Relationship between Personality Traits, the 5HTT Polymorphisms, and the Occurrence of Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms in Elite Athletes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertozzi, G.; Salerno, M.; Pomara, C.; Sessa, F. Neuropsychiatric and Behavioral Involvement in Aas Abusers. A Literature Review. Medicina 2019, 55, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Copeland, J.L.; Van Helder, W. Effect of Training Status and Exercise Mode on Endogenous Steroid Hormones in Men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, H.G.; Kanayama, G.; Hudson, J.I. Risk Factors for Illicit Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Use in Male Weightlifters: A Cross-Sectional Cohort Study. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Di Mizio, G.; Bertozzi, G.; Messina, G.; Tomaiuolo, B.; Pisanelli, D.; Maglietta, F.; Ricci, P.; Pomara, C. Anabolic Androgenic Steroids: Searching New Molecular Biomarkers. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, M.; Cascio, O.; Bertozzi, G.; Sessa, F.; Messina, A.; Monda, V.; Cipolloni, L.; Biondi, A.; Daniele, A.; Pomara, C. Anabolic Androgenic Steroids and Carcinogenicity Focusing on Leydig Cell: A Literature Review. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19415–19426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Franco, S.; Picciocchi, E.; Geraci, D.; Chisari, M.G.; Marsala, G.; Polito, A.N.; Sorrentino, M.; Tripi, G.; Salerno, M.; et al. Addictions Substance Free during Lifespan. Acta Medica Mediterr. 2018, 34, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Westlye, L.T.; Kaufmann, T.; Alnæs, D.; Hullstein, I.R.; Bjørnebekk, A. Brain Connectivity Aberrations in Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Users. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 13, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarth, M.; Bjørnebekk, A. Androgen Abuse and the Brain. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2021, 28, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørnebekk, A.; Kaufmann, T.; Hauger, L.E.; Klonteig, S.; Hullstein, I.R.; Westlye, L.T. Long-Term Anabolic–Androgenic Steroid Use Is Associated With Deviant Brain Aging. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, M.J.; Janes, A.C.; Hudson, J.I.; Brennan, B.P.; Kanayama, G.; Kerrigan, A.R.; Jensen, J.E.; Pope, H.G. Brain and Cognition Abnormalities in Long-Term Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Users. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2015, 152, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, C.M. Natural Rewards, Neuroplasticity, and Non-Drug Addictions. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S.; Nasca, C.; Gray, J.D. Stress Effects on Neuronal Structure: Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Prefrontal Cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, J.M.; Sips, H.C.M.; Viho, E.M.G.; Kroon, J.; Meijer, O.C. Restricted Effects of Androgens on Glucocorticoid Signaling in the Mouse Prefrontal Cortex and Midbrain. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1292024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinine, E.; Zimmer, E.R.; Zenki, K.C.; Kalinine, I.; Kazlauckas, V.; Haas, C.B.; Hansel, G.; Zimmer, A.R.; Souza, D.O.; Müller, A.P.; et al. Nandrolone-Induced Aggressive Behavior Is Associated with Alterations in Extracellular Glutamate Homeostasis in Mice. Horm. Behav. 2014, 66, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, B.S.; Hildebrandt, T.; Wallisch, P. Anabolic–Androgenic Steroid Use Is Associated with Psychopathy, Risk-Taking, Anger, and Physical Problems. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin-Miller, K.; Li, G.; Kelishani, D.; Wood, R.I. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids Alter Decision Making in a Balanced Rodent Model of the Iowa Gambling Task. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 132, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Raine, A. Prefrontal Structural and Functional Brain Imaging Findings in Antisocial, Violent, and Psychopathic Individuals: A Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2009, 174, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, C.; Villringer, A.; Sacher, J. Sex Hormones Affect Neurotransmitters and Shape the Adult Female Brain during Hormonal Transition Periods. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olufunmilayo, E.O.; Gerke-Duncan, M.B.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS Function in Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J. Microglia and Neuroinflammation: Crucial Pathological Mechanisms in Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 825086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Hui, E.S.; Kranz, G.S.; Chang, J.R.; de Luca, K.; Pinto, S.M.; Chan, W.W.; Yau, S.Y.; Chau, B.K.; Samartzis, D.; et al. Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Accelerated Cognitive Decline in People with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Scoping Review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 82, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, J.; Juszczyk, G.; Gawrońska-Grzywacz, M.; Herbet, M. Hpa Axis in the Pathomechanism of Depression and Schizophrenia: New Therapeutic Strategies Based on Its Participation. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, F.; Yang, L.; Tuolihong, L.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, K.; et al. Involvement of the GABAergic System in PTSD and Its Therapeutic Significance. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1052288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramey, T.; Regier, P.S. Cognitive Impairment in Substance Use Disorders. CNS Spectr. 2019, 24, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Cocimano, G.; Ministrieri, F.; Rosi, G.L.; Nunno, N.D.; Messina, G.; Sessa, F.; Salerno, M. Smart Drugs and Neuroenhancement: What Do We Know? Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2021, 26, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.S.; Mitre, M.C.; Brinck-Johnsen, T. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid and Adrenal Steroid Effects on Hippocampal Plasticity. Brain Res. 1995, 679, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, A. Cognitive Control, Motivation and Fatigue: A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective. Brain Cogn. 2022, 160, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimgampalle, M.; Chakravarthy, H.; Sharma, S.; Shree, S.; Bhat, A.R.; Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Devanathan, V. Neurotransmitter Systems in the Etiology of Major Neurological Disorders: Emerging Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 89, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhillaj, E.; Morgese, M.G.; Tucci, P.; Bove, M.; Schiavone, S.; Trabace, L. Effects of Anabolic-Androgens on Brain Reward Function. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomides, L.; Oliveira, L.A.; Mayers, N.; Lacerda, F.B.; Santos, J.P.B.; Borcard Filho, B.; Assunção, I.N.; Cupertino, M.; Santana, M.G. Neurological consequences of abusive use of anabolic-androgenic steroids. Tempus–Actas Saúde Coletiva 2019, 13, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, H.G.; Wood, R.I.; Rogol, A.; Nyberg, F.; Bowers, L.; Bhasin, S. Adverse Health Consequences of Performance-Enhancing Drugs: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 341–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.I.; Armstrong, A.; Fridkin, V.; Shah, V.; Najafi, A.; Jakowec, M. ’Roid Rage in Rats? Testosterone Effects on Aggressive Motivation, Impulsivity and Tyrosine Hydroxylase. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 110–111, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, M.Y. Anabolic Androgenic Steroids and Aggression: Studies Using Animal Models. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1036, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, N.A.; Alnahdi, H.S. The Impact of Nandrolone Decanoate Abuse on Experimental Animal Model: Hormonal and Biochemical Assessment. Steroids 2020, 153, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanayama, G.; Hudson, J.I.J.I.; Pope, H.G.H.G. Long-Term Psychiatric and Medical Consequences of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Abuse: A Looming Public Health Concern? Drug Alcohol Depend 2008, 98, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiblin, I.; Finn, A.; Ross, S.B.; Stenfors, C. Increased Dopaminergic and 5-Hydroxytryptaminergic Activities in Male Rat Brain Following Long-Term Treatment with Anabolic Androgenic Steroids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 126, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagun, B.; Altug, S. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids Are Linked to Depression and Anxiety in Male Bodybuilders: The Hidden Psychogenic Side of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2337717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, C.; Harries, R.L.; Reid, R.; Nisbet, L.A.; Nic Daéid, N. Changing Trends in Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Use within Scottish Prisons: Detection, Prevalence, and Quantitation. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 17, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutz, J.; Potemkin, M.; Shah, H.; Lam, D.; Patel, P.; Doyle-Baker, P.K. A Qualitative Exploration of Family Physicians and People Who Use Anabolic Steroids: Barriers to Accessing Evidence-Based Care. Perform. Enhanc. Health 2025, 13, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoob Carter, B.N.; Boardley, I.D. Development and Validation of Dependence and Craving Measures Specific to Athletes Who Use Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1347211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagatell, C.J.; Bremner, W.J. Androgens in Men—Uses and Abuses. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madea, B.; Grellner, W.; Musshoff, F.; Dettmeyer, R. Medico-Legal Aspects of Doping. J. Clin. Forensic Med. 1998, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klötz, F.; Petersson, A.; Isacson, D.; Thiblin, I. Violent Crime and Substance Abuse: A Medico-Legal Comparison between Deceased Users of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids and Abusers of Illicit Drugs. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 173, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertozzi, G.; Sessa, F.; Maglietta, F.; Cipolloni, L.; Salerno, M.; Fiore, C.; Fortarezza, P.; Ricci, P.; Turillazzi, E.; Pomara, C. Immunodeficiency as a Side Effect of Anabolic Androgenic Steroid Abuse: A Case of Necrotizing Myofasciitis. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2019, 15, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, R.; McNamee, M.; Phillips, N. On the Duty of the Doctor Not to Disclose Athlete Doping Data without Consent. Int. J. Sport. Policy 2011, 3, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, J. The Policy Effect of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) on the Digital Public Health Sector in the European Union: An Empirical Investigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørnebekk, A.; Walhovd, K.B.; Jørstad, M.L.; Due-Tønnessen, P.; Hullstein, I.R.; Fjell, A.M. Structural Brain Imaging of Long-Term Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Users and Nonusing Weightlifters. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 82, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, T.; Langenbucher, J.W.; Flores, A.; Harty, S.; Berlin, H.A. The Influence of Age of Onset and Acute Anabolic Steroid Exposure on Cognitive Performance, Impulsivity, and Aggression in Men. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2014, 28, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damião, B.; Rossi-Junior, W.C.; Guerra, F.D.R.; Marques, P.P.; Nogueira, D.A.; Esteves, A. Anabolic Steroids and Their Effects of on Neuronal Density in Cortical Areas and Hippocampus of Mice. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, P.; Smit, D.L.; de Ronde, W. Anabolic–Androgenic Steroids: How Do They Work and What Are the Risks? Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 1059473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelleroth, S.; Stam, F.; Nylander, E.; Kjellgren, E.; Gising, J.; Larhed, M.; Grönbladh, A.; Hallberg, M. The Decanoate Esters of Nandrolone, Testosterone, and Trenbolone Induce Steroid Specific Memory Impairment and Somatic Effects in the Male Rat. Horm. Behav. 2024, 161, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havnes, I.A.; Jørstad, M.L.; Innerdal, I.; Bjørnebekk, A. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Use among Women—A Qualitative Study on Experiences of Masculinizing, Gonadal and Sexual Effects. Int. J. Drug Policy 2021, 95, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, J.R.; Binmadi, N.O.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.H.; Paoli, A.; Proia, P. Supraphysiological Doses of Performance Enhancing Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids Exert Direct Toxic Effects on Neuron-like Cells. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif-Nia, H.; Sivarajan Froelicher, E.; Gorgulu, O.; Osborne, J.W.; Błachnio, A.; Rezazadeh Fazeli, A.; Goudarzian, A.H.; Kaveh, O. The Relationship among Positive Body Image, Body Esteem, and Eating Attitude in Iranian Population. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1304555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baceviciene, M.; Jankauskiene, R. Changes in Sociocultural Attitudes towards Appearance, Body Image, Eating Attitudes and Behaviours, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Students before and during COVID-19 Lockdown. Appetite 2021, 166, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, Z.; O’Dea, J.A. Relationships between Body Image, Nutritional Supplement Use, and Attitudes towards Doping in Sport among Adolescent Boys: Implications for Prevention Programs. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunno, N.D.; Esposito, M.; Argo, A.; Salerno, M.; Sessa, F. Pharmacogenetics and Forensic Toxicology: A New Step towards a Multidisciplinary Approach. Toxics 2021, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertozzi, G.; Maglietta, F.; Sessa, F.; Scoto, E.; Cipolloni, L.; Di Mizio, G.; Salerno, M.; Pomara, C. Traumatic Brain Injury: A Forensic Approach. A Literature Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Girolamo, F.G.; Biasinutto, C.; Mangogna, A.; Fiotti, N.; Vinci, P.; Pisot, R.; Mearelli, F.; Simunic, B.; Roni, C.; Biolo, G. Metabolic Consequences of Anabolic Steroids, Insulin, and Growth Hormone Abuse in Recreational Bodybuilders: Implications for the World Anti-Doping Agency Passport. Sports Med. Open 2024, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnecaze, A.K.; O’Connor, T.; Burns, C.A. Harm Reduction in Male Patients Actively Using Anabolic Androgenic Steroids (AAS) and Performance-Enhancing Drugs (PEDs): A Review. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bishi, K.A.; Afify, A. Prevalence and Awareness of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids (AAS) among Gymnasts in the Western Province of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 6050–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ronde, W.; Smit, D.L. Anabolic Androgenic Steroid Abuse in Young Males. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R102–R111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.B.; Ng, M.Z.; Huang, S.S.; Ding, M.; Hu, K. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Misuse: Mechanisms, Patterns of Misuse, User Typology, and Adverse Effects. J. Sports Med. 2021, 2021, 7497346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieschlag, E.; Vorona, E. Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Medical Consequences of Doping with Anabolic Androgenic Steroids: Effects on Reproductive Functions. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, R47–R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, J.M.; Avant, R.A.; Charchenko, C.M.; Westerman, M.E.; Ziegelmann, M.J.; Miest, T.S.; Trost, L.W. Impact of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids on Sexual Function. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Salerno, M.; Calvano, G.; Agliozzo, R.; Ficarra, V.; Sessa, F.; Favilla, V.; Cimino, S.; Pomara, C. Impact of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids on Male Sexual and Reproductive Function: A Systematic Review. Panminerva Med. 2023, 65, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Licciardello, G.; Privitera, F.; Iannuzzi, S.; Liberto, A.; Sessa, F.; Salerno, M. Forensic Post-Mortem Investigation in AAS Abusers: Investigative Diagnostic Protocol. A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhares, B.L.; Miranda, E.P.; Cintra, A.R.; Reges, R.; Torres, L.O. Use, Misuse and Abuse of Testosterone and Other Androgens. Sex. Med. Rev. 2022, 10, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyksen, T.S.; Vanberg, P.; Gjesdal, K.; von Lueder, T.G.; Bjørnerheim, R.; Steine, K.; Atar, D.; Halvorsen, S. Cardiovascular Phenotype of Long-Term Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Abusers Compared with Strength-Trained Athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, A.; Vukadin, S.; Sikora, R.; Bojanic, K.; Smolic, R.; Plavec, D.; Wu, G.Y.; Smolic, M. Anabolic Androgenic Steroid-Induced Liver Injury: An Update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Cipolloni, L.; Bertozzi, G.; Messina, G.; Di Mizio, G.; Asmundo, A.; Pomara, C. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids and Brain Injury: MiRNA Evaluation in Users Compared to Cocaine Abusers and Elderly People. Aging 2020, 12, 15314–15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, G.D.; Amico, F.; Cocimano, G.; Liberto, A.; Maglietta, F.; Esposito, M.; Rosi, G.L.; Di Nunno, N.; Salerno, M.; Montana, A. Adverse Effects of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids: A Literature Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.I. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Dependence? Insights from Animals and Humans. Front. Neuroendocr. 2008, 29, 490–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanayama, G.; Brower, K.J.; Wood, R.I.; Hudson, J.I.; Pope, H.G. Treatment of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Dependence: Emerging Evidence and Its Implications. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2010, 109, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahin, O.; Félix Souza, N.S.; de Sousa, E.C.; Santos, A.M.; Bahrke, M.S. Anabolic–Androgenic Steroid Use among Brazilian Women: An Exploratory Investigation. J. Subst. Use 2016, 22, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.M.; Mason, J.I.; Sharpe, R.M. Steroidogenesis in the Fetal Testis and Its Susceptibility to Disruption by Exogenous Compounds. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 883–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatkowski, T.; Whiteside, B.; Robertson, J.; Henning, A.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Dunn, M. What Is the Prevalence of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Use among Women? A Systematic Review. Addiction 2024, 119, 2088–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinks, A.L.; Needle, C.D.; Spindler, A.J.; Brody, A.M.; Scandagli, I.; Oh, C.; Shapiro, J.; Lo Sicco, K.I.; Tawanwongsri, W. Alopecia in Female Athletes Using Androgenic and Anabolic Steroids: Pathophysiology and Management. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnolini, R.; Kaeppeli, M.; Schori, D.; Bruggmann, P.; Senn, O. Evaluation of Implementing Drug Checking Services for Anabolic Androgenic Steroids in Switzerland: A Pilot Study. Harm Reduct. J. 2025, 22, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).