Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Layman, 1930) (Digenea: Hemiuridae) in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: A Morphological and Phylogenetic Study Based on Specimens Found in Nebris microps (Actinopterygii: Sciaenidae) off the Brazilian Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Host Family | Host Species | Locality | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acipenseridae | Acipenser transmontanus | Columbia River, Washington, DC, USA | Becker [19] |
| Huso dauricus | Amur River basin, Russia | Akhmerov [20] | |
| Congridae | Conger conger (=Leptocephalus conger) | Puerto Real, Porto Rico, Atlantic Ocean | Siddiqi and Cable [21] |
| Muraenesocidae | Cynoponticus ferox (=Phyllogramma regani) | Tema, Ghana, Atlantic Ocean; Gulf of Guinea, Nigeria, Atlantic Ocean | Fischthal and Thomas, [22]; Siddiqi and Hafeezullah [23] |
| Anguillidae | unidentified eel | Pelado Island, Panama, Pacific Ocean | Sogandares-Bernal [9] |
| Synodontidae | Saurida tumbil | South China Sea, Pacific Ocean; Gulf of Mannar, Indian Ocean | Shen [24]; Gupta and Sehgal [25] |
| Synodus sp. | Panama Bay, Panama, Pacific Ocean | Sogandares-Bernal [9] | |
| Batrachoididae | Porichthys notatus | Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Arai [26] * |
| Hemiramphidae | Hyporhamphus sajori | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] |
| Echeneidae | Echeneis naucrates | South China Sea, Pacific Ocean | Parukhin [28] |
| Alestidae | Hydrocyon brevis | Volta River, Ghana | Fischthal and Thomas [22] |
| Sparidae | Pagrus sp. (=Pagrosomus unicolar) | Inland Sea, Japan, Pacific Ocean | Yamaguti [29] * |
| Sparus macrocephalus | Inland Sea, Japan, Pacific Ocean | Yamaguti [7] * | |
| Gadidae | Gadus chalcogrammus (=Theragra chalcogramma) | Friday Harbor, Washington, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] |
| Gadus macrocephalus (Gadus morhua macrocephalus) | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Lophiidae | Lophiomus setigerus | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] |
| Lophius litulon | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Machida et al. [31] | |
| Lophius piscatorius | Indian Ocean | Parukhin [28] | |
| Embiotocidae | Cymatogaster aggregata | Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Arai [26] * |
| Hyperprosopon ellipticum | Tomales and Bodega Bays, USA, Pacific Ocean | Rodella and Nahhas [32] | |
| Agonidae | Hemitripterus villosus | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] |
| Anarhichadidae | Anarrhichthys ocellatus | Bering Sea, Russia, Pacific Ocean | Gordeev and Sokolov [33] |
| Cottidae | Enophrys bison | Dillon’s Beach, USA, Pacific Ocean; Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean | Park [34] **; McCauley, [12] |
| Hemilepidotus hemilepidotus | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] | |
| Leptocottus armatus | San Quintín Bay, Baja California, Mexico, Pacific Ocean; Friday Harbor, Washington, USA, Pacific Ocean; Newport, Oregon, USA, Pacific Ocean; Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | King [35]; Ching [30]; McCauley [12]; Arai [26] | |
| Myoxocephalus brandtii (=Myoxocephalus brandti) | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Myoxocephalus polyacanthocephalus | Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Arai [26,36] | |
| Oligocoitus maculosus | Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Arai [26] | |
| Synchirus gilli | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] | |
| Gasterosteidae | Gasterosteus aculeatus | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] |
| Hexagrammidae | Ophiodon elongatus | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean; Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean; Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30]; McCauley [12]; Arai [26,36] |
| Pleurogrammus azonus | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Jordaniidae | Scorpaenichthys marmoratus | Departure Bay, Canada, Pacific Ocean | McFarlane [37] *** |
| Platycephalidae | Platycephalus indicus | Yellow Sea and Bo-hai Sea, China, Pacific Ocean | Li et al. [38]; Shen and Qiu [39] |
| Scorpaenidae | Scorpaena madurensis | Ilha da Madeira (Origin) Collected in an aquarium in NY | Nigrelli [6] **** |
| Sebastidae | Sebastes alutus | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai [40,41] |
| Sebastes brevispinis | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai, [41] | |
| Sebastes borealis | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai, [41] | |
| Sebastes caurinus (=Sebastodes caurinus) | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean; Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Ching [30]; Sekerak and Arai [41] | |
| Sebastes crameri | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai [41] | |
| Sebastes maliger | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai [41] | |
| Sebastes melanops (=Sebastodes melanops) | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] | |
| Sebastes nigrocinctus (=Sebastodes nigrocinctus) | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] | |
| Sebastes paucispinis | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai [41] | |
| Sebastes pinniger | Northeastern Pacific Ocean | Sekerak and Arai [41] | |
| Sebastes serranoides | Off Central California, Pacific Ocean | Love et al. [42] | |
| Sebastes trivittatus | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Stichaeidae | Anoplarchus purpurescens | Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean | McCauley [12] |
| Stichaeus grigorjewi | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Cyclopsettidae | Citharichthys sordidus | Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean | McCauley [12] |
| Citharichthys stigmaeus | Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean; Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | McCauley [12]; Arai [26,36] | |
| Paralichthyidae | Platichthys bicoloratus (=Kareius bicoloratus) | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] |
| Paralichchthys californicus | San Quintín Bay, Mexico, Pacific Ocean; San Quintín Bay, Todos Santos Bay and Estero de Punta Banda, Mexico, Pacific Ocean | King [35]; Castillo-Sánchez et al. [43] | |
| Paralichthys olivaceus | Sagami Sea, Japan, Pacific Ocean | Kuramochi [44] | |
| Paralichthys stellatus (=Pleuronectes stellatus) | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Pleuronectidae | Atheresthes stomias | Bering Sea, Russia, Pacific Ocean | Mamaev [45] |
| Cleisthenes pinetorum (=Cleisthenes herzensteini) | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Eopsetta grigorjewi | Sagami Sea, Japan, Pacific Ocean | Kuramochi [44] | |
| Hippoglossus hippoglossus | Bering Sea, Russia, Pacific Ocean | Mamaev [45] | |
| Hippoglossus stenolepis | Japan, Pacific Ocean; Canada, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27]; Machida et al. [30]; Blaylock et al. [46] | |
| Limanda aspera | Peter the Great Bay, Russia, Pacific Ocean | Tsimbalyuk [47] | |
| Pleuronichthys guttulatus (=Hypsopsetta guttalata) | San Quintín Bay, Mexico, Pacific Ocean | King [35] | |
| Isopsetta isolepis | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] | |
| Lepidopsetta bilineata | Netarts Bay, USA, Pacific Ocean | McCauley [12] | |
| Parophrys vetulus | Departure Bay, Canada, Pacific Ocean; Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | McFarlane [37] ***; Ching [29] | |
| Platichthys stellatus | Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean; Far Eastern Seas, Pacific Ocean | McCauley [12]; Mamaev et al. [48] | |
| Psettichthys melanostictus | Newport, USA, Pacific Ocean; Puget Sound, USA, Pacific Ocean | McCauley [12] | |
| Pseudopleuronectes herzensteini | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Pseudopleuronectes obscurus (=Liopsetta obscura) | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Unidentified | Peter the Great Bay, Russia, Pacific Ocean | Layman [8] ***** | |
| Verasper moseri | Hokkaido, Japan, Pacific Ocean | Machida et al. [30] | |
| Psettodidae | Psettodes eruei | Gulf of Tonkin, Vietnam, Pacific Ocean | Parukhin [49] |
| Salmonidae | Oncorhynchus keta | Amur River, Russia; British Columbia coast, Canada, Pacific Ocean; Indian Ocean | Akhmerov [20]; Strelkov [50]; Margolis and Boyce [51]; Parukhin [31] |
| Oncorhynchus gorbuscha | British Columbia coast, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Margolis and Boyce [51] | |
| Oncorhynchus kisutch | Friday Harbor, USA, Pacific Ocean | Ching [30] | |
| Oncorhynchus tschawytscha | Alsea Bay, USA, Pacific Ocean; Mad River, California, USA | McCauley [12]; Jennings and Hendrickson [52] | |
| Salvelinus leucomaenis | Japan, Pacific Ocean | Zhukov [27] | |
| Salvelinus malma | Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Arai [26,36] | |
| Syngnathidae | Syngnathus califoniensis (=Syngnathus griseolineatus) | Burke Channel, Canada, Pacific Ocean | Arai [26,36] |
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
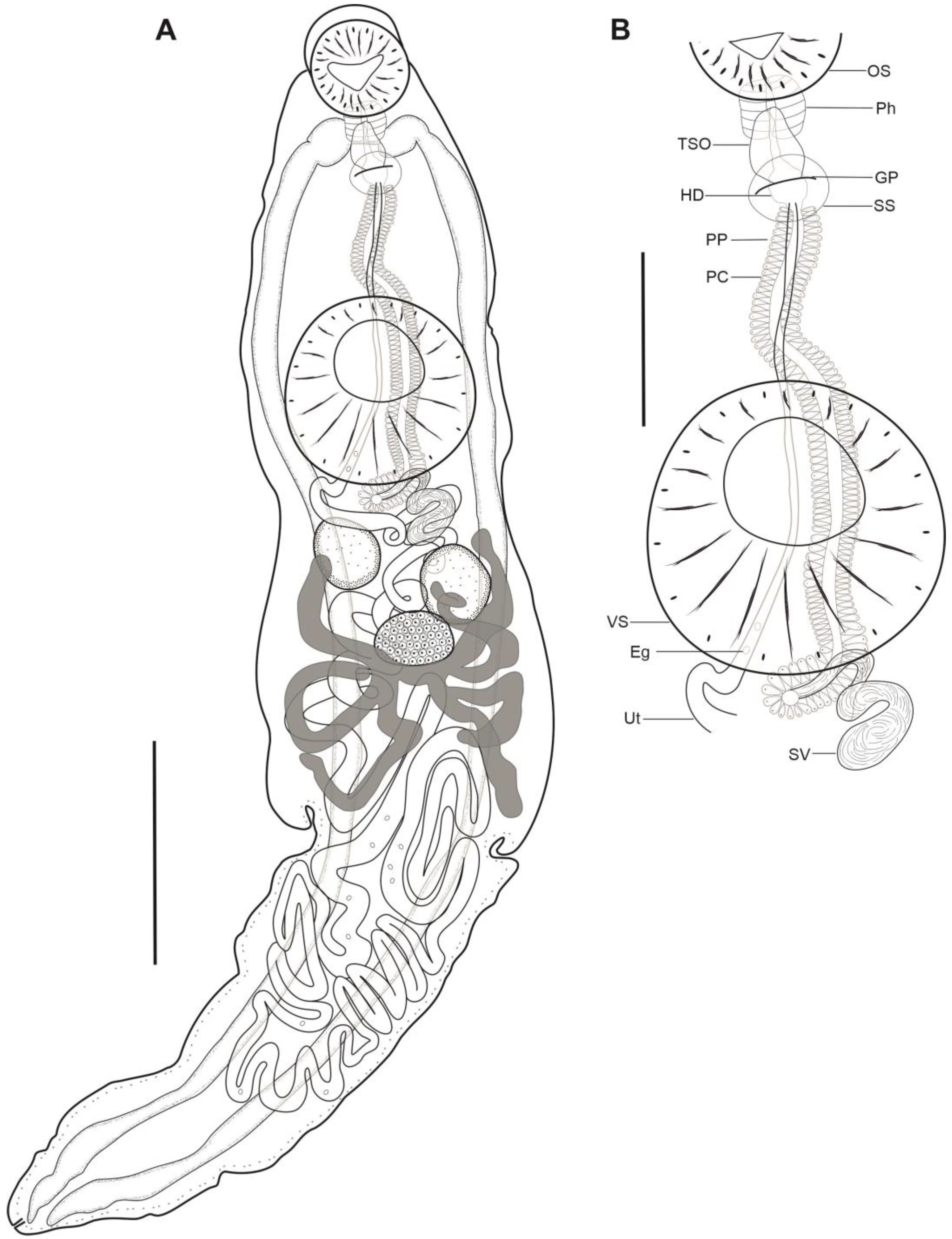
3.1. Morphological Description
3.2. Molecular Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilqees, F.M.; Khalil, B.; Khatoon, N.; Perveen, S. Tubulovesicula dorabi, new species (Trematoda: Hemiuridae Looss, 1899: Dinurinae Looss, 1907) from the fish Chirocentous dorab (Forsk.) of Karachi Coast. Pak. J. Zool. 2010, 42, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, R.A. Hemiuridae (Digenea) from marine fishes of the southern Indian Ocean: Dinurinae, Elytrophallinae, Glomericirrinae and Plerurinae. Syst. Parasitol. 1990, 17, 183–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.I. Family Hemiuridae Looss, 1899. In Keys to the Trematoda; Gibson, D.I., Jones, A., Bray, R.A., Eds.; CAB International and the Natural History Museum: London, UK, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 305–340. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavi, R.; Bray, R.A. Digenetic Trematodes of Indian Marine Fishes; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.B.; De Silva, M.L.I.; Pathirana, E.; Rajapakse, R.P.V.J. Polyphyly of the Dinurinae Looss, 1907 (Digenea: Hemiuridae) and resurrection of the Mecoderinae Skrjabin & Guschanskaja, 1954 based on novel collection of Tubulovesicula laticaudi Parukhin, 1969 from marine elapid snakes in Sri Lanka. Parasitol. Int. 2023, 97, 102776. [Google Scholar]
- Nigrelli, R.F. Two new species of trematodes from the deep Sea Scorpion Fish, Scorpaena madurensis Cuv. & Val. Zoologica 1940, 25, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguti, S. Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 2. Trematodes of fishes, I. Jpn. J. Zool. 1934, 5, 249–541. [Google Scholar]
- Layman, E.M. Parasitic worms from the fishes of Peter the Great Bay. Bull. Pac. Sci. Fish. Res. Stn. 1930, 3, 1–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sogandares-Bernal, F. Digenetic trematodes of marine fishes from the Gulf of Panama and Bimini, British West Indies. Tulane Stud. Zool. 1959, 7, 69–117. [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS Editorial Board. World Register of Marine Species. 2022. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Manter, H.W. Some digenetic trematodes from fishes of New Zealand. Trans. R. Soc. N. Z. 1954, 82, 475–568. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, J.E. Some hemiurid trematodes of Oregon marine fishes. J. Parasitol. 1960, 46, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.C.; Velloso, A.L.; Pereira, J. Parasitos de Peixes Marinhos da América do Sul; FURG: Rio Grande, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja, C.; Kudlai, O. Hemiurid trematodes (Digenea: Hemiuridae) from marine fishes off the coast of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, with novel molecular data. Animals 2022, 12, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho Filho, A. Fishes of the Brazilian Coast; Literare Books International: São Paulo, Brazil, 2023; 424p. [Google Scholar]
- Marceniuk, A.P.; Caires, R.A.; Carvalho-Filho, A.; Rotundo, M.M.; Santos, W.C.R.; Klautau, A.G.C.M. Peixes Teleósteos da Costa Norte do Brasil; Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi: Belém, Brazil, 2021; 775p. [Google Scholar]
- Vincente, J.J.; Santos, E. Alguns helmintos de peixe do litoral norte Fluminense—I. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1973, 71, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chero, J.D.; Cruces, C.L.; Sáez, G.; Luque, J.L. Six new species of Rhamnocercus Monaco, Wood & Mizelle, 1954 (Monogenea: Diplectanidae) infecting the gills from South American sciaenid fishes. Syst. Parasitol. 2022, 99, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.D. Marine trematode Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Digenea: Hemiuridae) from resident White sturgeon in the Columbia River. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1970, 27, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmerov, A.H. On the trematode fauna of fishes in the basin of the River Amur. Tr. Gelmintol. Lab. 1961, 11, 22–31. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, A.H.; Cable, R.M. Digenetic trematodes of marine fishes of Puerto Rico. Sci. Surv. P. R. Virg. Isl. 1960, 17, 257–369. [Google Scholar]
- Fischthal, J.H.; Thomas, J.D. Additional hemiurid and other trematodes of fishes from Ghana. Bull. L’IFAN 1972, 34, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, A.H.; Hafeezullah, M. Some digenetic trematodes of marine fishes of Nigeria. Family Hemiuridae Luhe, 1907. Dr B. S. Chauhan Commem. Vol. 1975, 1975, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.W. Digenetic Trematodes of Marine Fishes from Hainan Island; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; 228p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.K.; Sehgal, S.K. Studies on some hemiurid trematodes from marine food fishes in India. Res. Bull. Panj. Univ. Sci. 1970, 21, 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, H.P. Preliminary report on the parasites of certain marine fishes of British Columbia. J. Fish Res. Board Can. 1969, 26, 2319–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, E.V. Endoparasitic worms of the fishes in the Sea of Japan and South-Kuril shallow-waters. Tr. Zool. Inst. Leningr. 1960, 28, 3–146. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Parukhin, A.M. Parasitic Worms of Food Fishes of the Southern Seas; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1976; p. 183. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguti, S. Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 26. Trematodes of fishes, VI. JPN J. Zool 1939, 211–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ching, H.L. Some digenetic trematodes of fishes of Friday Harbor, Washington. J. Parasitol. 1960, 46, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, M.; Araki, J.; Kamiya, H.; Ohbayashi, M. Trematodes collected from sea fishes of the Hidaka District, Hokkaido. Mem. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 1972, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rodella, T.D.; Nahhas, F.M. Some digenetic trematodes of embiotocid fishes from Tomales and Bodega Bays, California. J. Parasitol. 1969, 55, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeev, I.I.; Sokolov, S.G. Helminths of epipelagic fish in the western Bering Sea and southern Sea of Okhotsk. Invert. Zool. 2023, 20, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.T. Two new trematodes, Sterrhurus magnatestis and Tubulovesicula californica (Hemiuridae) from littoral fishes of Dillon’s Beach, California. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1936, 55, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.E. A new species of Parahemiurus and notes on Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Trematoda: Hemiuridae) from fishes of Bahia de San Quintin, Baja California. Pac. Nat. 1962, 10, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, H.P. A preliminary report on a study of the parasites of marine fishes of Burke Channel, British Columbia. FRB Manuscr. Rep. Ser. 1967, 925, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane, S.H. A study of the endoparasitic trematodes from marine fishes of Departure Bay, BC. J. Biol. Board Can. 1936, 2, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K.; Qiu, Z.Z.; Zhang, R.S. Digenetic trematodes of fishes from the Bo-Hai Sea, China VI (Trematoda: Opecoelidae). Acta Zootaxon. Sin. 1989, 1, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.W.; Qiu, Z.Z. Studies on the Trematodes of Fishes from the Yellow Sea and the Bo Hai Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1995; 207p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sekerak, A.D.; Arai, H.P. Helminths of Sebastes alutus (Pisces: Teleostei) from the northeastern Pacific. Can. J. Zool. 1973, 51, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekerak, A.D.; Arai, H.P. Some metazoan parasites of rockfishes of the genus Sebastes from the northeastern Pacific Ocean. Syesis 1977, 10, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.S.; Shriner, K.; Morris, P. Parasites of olive rockfish, Sebastes serranoides, (Scorpaenidae) off central California. Fish. Bull. U.S. 1984, 82, 530–537. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Sánchez, E.; Rosales-Casián, J.A.; Pérez-Ponce de León, G. Helminth parasites of Paralichthys californicus (Osteichthyes: Paralichthydae) in Estero de Punta Banda, Todos Santos Bay and San Quintín Bay, Baja California, Mexico. Cienc. Mar. 1998, 24, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, T. Digenetic trematodes of fishes caught in the Sagami Sea, Central Japan. Mem. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 2006, 40, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Mamaev, Y.L. Helminths of fish in the Bering Sea. In Parasitic Worms of Domestic and Wild Animals; Leonov, V.A., Leonov, A.A., Mamaev, Y.L., Oshmarin, P.G., Eds.; Akademiya Nauk SSSR: Vladivostok, Russia, 1965; pp. 168–188. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Blaylock, R.B.; Holmes, J.C.; Margolis, L. The parasites of Pacific halibut (Hippoglossus stenolepis) in the eastern North Pacific: Host-level influences. Can. J. Zool. 1998, 76, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimbalyuk, E.M. The helminthofauna of some plaice species of Peter the Great Bay. Izv. Tikhookean. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Rybn. Khozyaistva Okeanogr. 1978, 102, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mamaev, Y.L.; Parukhin, A.M.; Baeva, O.M. Parasitic worms of Pleuronectidae from the Far Eastern Seas. In Parasitic Worms of Animals of the Primorye Region and the Pacific Ocean; Akad. Nauk SSSR: Moscow, Russia, 1963; pp. 82–113. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Parukhin, A.M. Parasitic Worms of Bottom Fishes of the Southern Seas; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1989; 155p. [Google Scholar]
- Strelkov, Y.A. Trematodes of fish in the Amur basin. Parazitol. Sb. 1971, 25, 120–139. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, L.; Boyce, N.P. Life span, maturation, and growth of two hemiurid trematodes, Tubulovesicula lindbergi and Lecithaster gibbosus, in Pacific salmon (Genus Oncorhynchus). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1969, 26, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, M.R.; Hendrickson, G.L. Parasites of chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and coho salmon (O. kisutch) from the Mad River and vicinity, Humboldt County, California. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. 1982, 49, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Pleijel, F.; Jondelius, U.; Norlinder, E.; Nygren, A.; Oxelman, B.; Schander, C.; Sundberg, P.; Thollesson, M. Phylogenies without roots? A plea for the use of vouchers in molecular phylogenetic studies. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 48, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, S.; Soldánová, M.; Pérez-Del-Olmo, A.; Dangel, D.R.; Sitko, J.; Sures, B.; Kostadinova, A. Molecular prospecting for European Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) reveals cryptic diversity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, S.D.; Tkach, V.V. Phylogenetic analysis of the subfamily Neodiplostominae (Digenea: Diplostomidae) based on 28S rDNA sequences. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Tkach, V.V.; Pawlowski, J.; Mariaux, J. Phylogenetic analysis of the suborder Plagiorchiata (Platyhelminthes, Digenea) based on partial lsrDNA sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, J.; Blair, D.; McManus, D.P. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 54, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribb, T.H.; Adlard, R.D.; Bray, R.A. A DNA-based demonstration of a three-host life-cycle for the Bivesiculidae (Platyhelminthes: Digenea). Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1791–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutmore, S.C.; Miller, T.L.; Curran, S.S.; Bennett, M.B.; Cribb, T.H. Phylogenetic relationships of the Gorgoderidae (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda), including the proposal of a new subfamily (Degeneriinae n. subfam). Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, N.Q.-X.; Cribb, T.H.; Bray, R.A.; Cutmore, S.C. Two known and one new species of Proctoeces from Australian teleosts: Variable host-specificity for closely related species identified through multi-locus molecular data. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlewood, D.T.; Curini-Galletti, M.; Herniou, E.A. The interrelationships of Proseriata (Platyhelminthes: Seriata) tested with molecules and morphology. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2000, 16, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlewood, D.T.; Rohde, K.; Clough, K.A. Parasite speciation within or between host species?—Phylogenetic evidence from site-specific polystome monogeneans. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science 1321 Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, R.A.; Diaz, P.E.; Cribb, T.H. Knowledge of marine fish trematodes of Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans. Syst. Parasitol. 2016, 3, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaukat, N. Studies on Digenetic Trematodes of Some Fishes of Karachi Coast. Ph.D. Thesis, Jinnah University for Women, Nazimabad, Karachi, Pakistan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shaukat, N.; Bilqees, F.M.; Haseeb, M.F. A new species Tubulovesicula microcaudum (Trematoda: Hemiuridae looss, 1899) from the fish Otolithus argenteus of Karachi coast. Int. J. Biol. Biotech. 2008, 5, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Shaukat, N.; Bilqees, F.M. New species of the genus Tubulovesicula Yamaguti, 1934 (Digenea: Hemiuridae Looss, 1899) from the fish Pomadasys olivaceum (Day) off Karachi Coast. Pak. J. Zool. 2011, 43, 715–719. [Google Scholar]
- Shaukat, N.; Bilqees, F.M. A new species Tubulovesicula magnacirrosa (Trematoda: Hemiuridae Looss, 1899) from the fish Pseudosciaena diacanthus of Karachi Coast. RADS J. Biol. Res. Appl. Sci. 2011, 2, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, E. Trematodes from fishes mainly from the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1940, 88, 1–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.D.; Shen, J.W. Some dinurid trematodes (subfamily Dinurinae Looss, 1907) from marine fishes of economic importance of China. Acta Zool. Sin. 1978, 24, 373–387. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.Q. Digenetic trematodes of marine fishes in Pingtan county, Fujian Province, South China. Wuyi Sci. J. 1987, 7, 151–163. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.L.; Bray, R.A.; Cribb, T.H. Taxonomic approaches to and interpretation of host specificity of trematodes of fishes: Lessons from the Great Barrier Reef. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claxton, A.T.; Fuehring, A.D.; Andres, M.J.; Moncrief, T.D.; Curran, S.S. Parasites of the vermilion snapper, Rhomboplites aurorubens (Cuvier), from the western Atlantic Ocean. Comp. Parasitol. 2017, 84, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshmarin, P.G. On the trematode fauna of marine and freshwater fishes of Vietnam. In Parasitic Worms of Domestic and Wild Animals; Leonov, A.A., Mamaev, Y.L., Oshmarin, P.G., Eds.; Akademiya Nauk SSSR: Vladivostok, Russia, 1965; pp. 213–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanei-Motlagh, R.J.; Hernández-Orts, J.S.; Fast, M.D.; Whyte, S.K.; El-Matbouli, M.; Saleh, M. Morphological and molecular characterization of Stomachicola muraenesocis Yamaguti, 1934 (Digenea: Hemiuridae) from the daggertooth pike conger Muraenesox cinereus (Forsskål). Parasitology 2024, 151, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Source | Present study | Layman [8] | Yamaguti [7] | Park [34] | McFarlane [37] | Nigrelli [6] | McCauley [12] | Shen [24] | |
| Locality | Maranhão Island, Maranhão, Brazil, Atlantic Ocean | Peter Great Bay, Russia, Pacific Ocean | Inland Sea, Japan, Pacific Ocean | Dillon Beach, California, USA, Pacific Ocean | Departure Bay, Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, Pacific Ocean | New York Aquarium, New York, USA | Newport, Alsea Bay, Netarts Bay, Oregon; Pujet Sound, Washington, USA, Pacific Ocean | Hainan Island, China, Pacific Ocean, | |
| Host | Nebris microps (Sciaenidae) | Variety of fishes (most Pleuronectiformes) | Acanthopagrus schlegelii (= Sparus macrocephalus) (Sparidae) | Enophrys bison (Cottidae) | Parophrys vetulus (Pleuronectidae) and Scorpaenichthys marmoratus (Jordaniidae) | Scorpaena madurensis (Scorpaenidae) | Variety of fishes (most Pleuronectidae) | Saurida tumbil (Synodontidae) | |
| Range (n = 7) | Mean | Range (n = NP) | Range (n = 1) | Range (n = 1) | Range (n = NP) | Range (n = 4) | Range (n = NP) | Range (n = 6) | |
| Body (soma) length | 3356–4645 | 4019 | 2400−3800 | 5570 | 2560 | 1510–2680 | – | 1110–3800 | 2688–5367 |
| Body (soma) width | 1211–1677 | 1370 | 852−1310 | – | – | – | 1630 | 300–1137 | 935–1403 |
| Ecsoma length | 2102–2813 | 2376 | 1147 (maximum) | – | 1530 | – | 2690 | 1600 | 1313–2272 |
| Total length | 5867−6879 | 6395 | 3600−5240 | – | 4090 | – | 7350 | – | 3557–7047 |
| Forebody length | 1232−1725 | 1498 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hindbody length | 1359−2279 | 1758 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Preoral lob length | 24−78 | 61 | − | 74 | – | – | 44 | – | 33–50 |
| Oral sucker length | 403−494 | 452 | 229−327 (diameter) | 300 | 210 | 168–212 | 251 | 100–350 | 184–301 |
| Oral sucker width | 410−516 | 466 | − | 320 | 280 | 336–420 | 287 | 100–380 | 251–334 |
| Pharynx length | 194−227 | 215 | 98−147 | 140 | 110 | 89 (diameter) | 161 | 80–120 (diameter) | 134–167 (diameter) |
| Pharynx width | 182−236 | 205 | 81−147 | 150 | 130 | – | 194 | – | |
| Ventral sucker length | 792−1076 | 934 | 409−606 (diameter) | 640 (diameter) | 460 | – | 643 | 230–380 (diameter) | 434–585 (diameter) |
| Ventral sucker width | 788−1015 | 903 | − | – | 470 | – | 659 | – | – |
| DIBAE * | 501−647 | 584 | − | – | 260 | – | – | – | – |
| Anterior testis (or right) length | 253−370 | 328 | 295−376 (diameter) | 260 | 210 (diameter) | 224 (diameter) | 444 | 120–200 | 248–351 |
| Anterior testis (or right) width | 287−402 | 330 | − | 290 | – | – | 498 | 100–300 | 198–367 |
| Posterior testis (or left) length | 208–380 | 376 | − | 320 | 240 (diameter) | – | 413 | – | 198–367 |
| Posterior testis (or left) width | 290–378 | 334 | − | 360 | – | – | 532 | – | 228–334 |
| DTVS * | 95–378 (n = 6) | 249 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Post-testicular region | 785–1617 | 1164 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Seminal vesicle length | 437−1336 | 842 | 590–655 | 1000 | 670 | – | 465 | – | 835–1336 |
| Seminal vesicle width | 65−208 | 128 | – | 63 | 120 | – | 165 | – | 50–117 |
| Pars prostatica length | 1591−2171 | 1822 | 737−835 | 1000 | 920 | – | 1280 | – | 585–969 |
| Pars prostatica width | 179−270 | 222 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Sinus-sac length | 197–289 | 236 | 376−458 | – | 270 | 224 | 150 | – | 217–418 |
| Sinus-sac width | 204–262 | 229 | − | – | 180 | 112 | 270 | – | 150–284 |
| Ovary length | 216−310 | 251 | 114−229 | 200 | 310 (diameter) | 240 | 348 | 140–350 | 167–267 |
| Ovary width | 201−345 | 290 | 229−360 | 390 | – | 130 | 442 | – | 267–384 |
| Vitellarium length | 777–1332 | 1062 | 653−885 (ray) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Vitellarium width | 821–1160 | 1000 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Egg length | 29–34 (n = 10) | 32 | 27−29 | 32 | 28–32 | 32–36 | 12–15 | 18–23 | 24–27 |
| Egg width | 25–31 (n = 10) | 28 | 18−20 | 21 | 16–24 | 19–20 | 18–25 | 12–22 | 18–20 |
| Body length/body width | 1:2.28–3.56 | 1:2.96 | − | – | 1:1.70 | – | – | – | – |
| Oral/ventral sucker width | 1:1.79−2.06 | 1:1.94 | − | – | – | – | – | – | 1:2.2 |
| Ecsoma/body length, % | 48−84 | 60 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Forebody/body length, % | 31−51 | 38 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Post-testicular region/body length, % | 21–35 | 29 | − | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantoja, C.; Paschoal, F.; Nunes, J.L.S.; Pinto, H.A. Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Layman, 1930) (Digenea: Hemiuridae) in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: A Morphological and Phylogenetic Study Based on Specimens Found in Nebris microps (Actinopterygii: Sciaenidae) off the Brazilian Coast. Taxonomy 2024, 4, 447-463. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4030022
Pantoja C, Paschoal F, Nunes JLS, Pinto HA. Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Layman, 1930) (Digenea: Hemiuridae) in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: A Morphological and Phylogenetic Study Based on Specimens Found in Nebris microps (Actinopterygii: Sciaenidae) off the Brazilian Coast. Taxonomy. 2024; 4(3):447-463. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4030022
Chicago/Turabian StylePantoja, Camila, Fabiano Paschoal, Jorge Luiz Silva Nunes, and Hudson Alves Pinto. 2024. "Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Layman, 1930) (Digenea: Hemiuridae) in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: A Morphological and Phylogenetic Study Based on Specimens Found in Nebris microps (Actinopterygii: Sciaenidae) off the Brazilian Coast" Taxonomy 4, no. 3: 447-463. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4030022
APA StylePantoja, C., Paschoal, F., Nunes, J. L. S., & Pinto, H. A. (2024). Tubulovesicula lindbergi (Layman, 1930) (Digenea: Hemiuridae) in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean: A Morphological and Phylogenetic Study Based on Specimens Found in Nebris microps (Actinopterygii: Sciaenidae) off the Brazilian Coast. Taxonomy, 4(3), 447-463. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4030022








