SCAPS-1D Simulation of Various Hole Transport Layers’ Impact on CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells Under Indoor Low-Light Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Device Structure and Simulation Parameters
2.1. Device Structure
2.2. Numerical Method
3. Results and Discussion
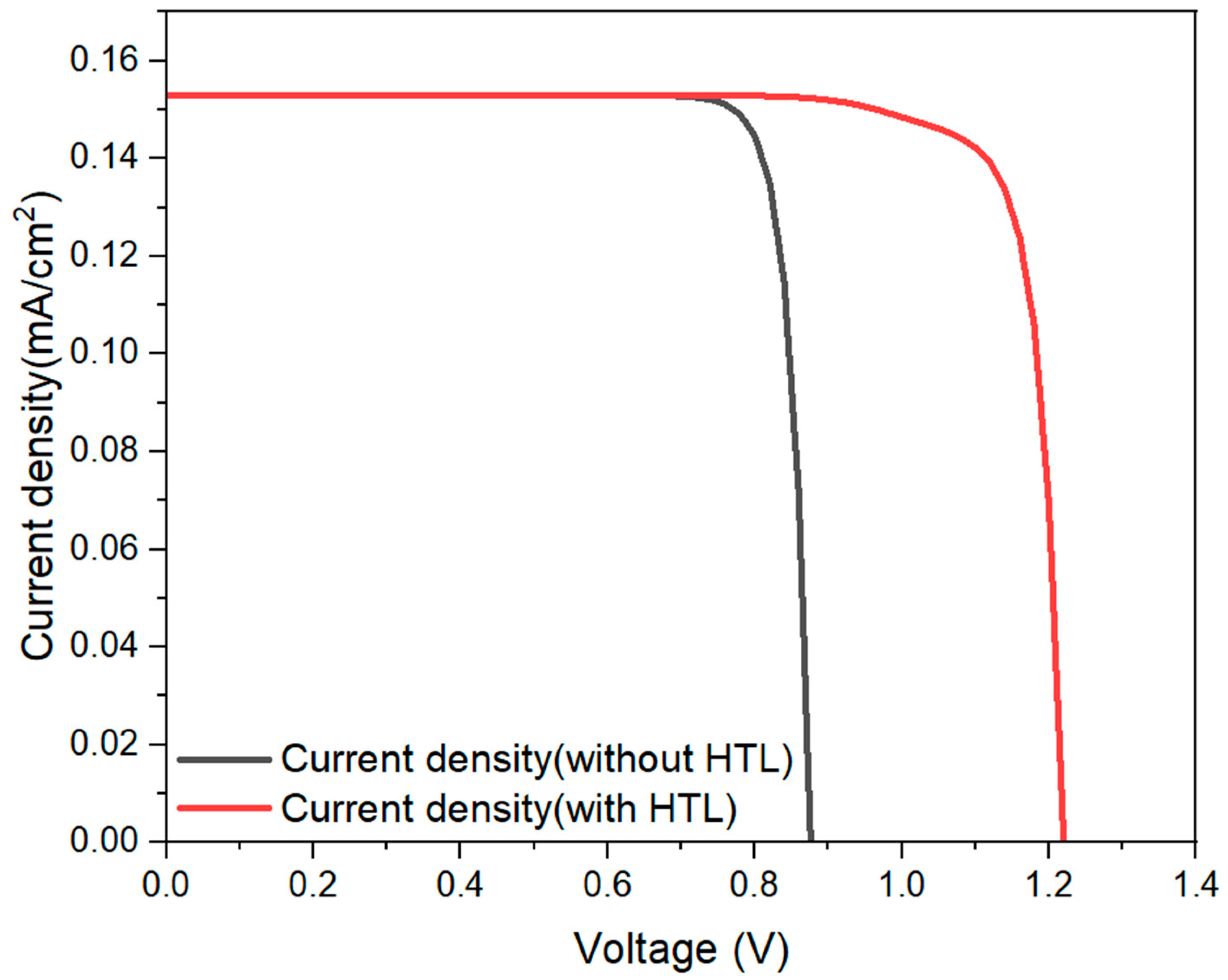
3.1. CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cell Energy Band Diagram and Performance Comparison of Different HTLs
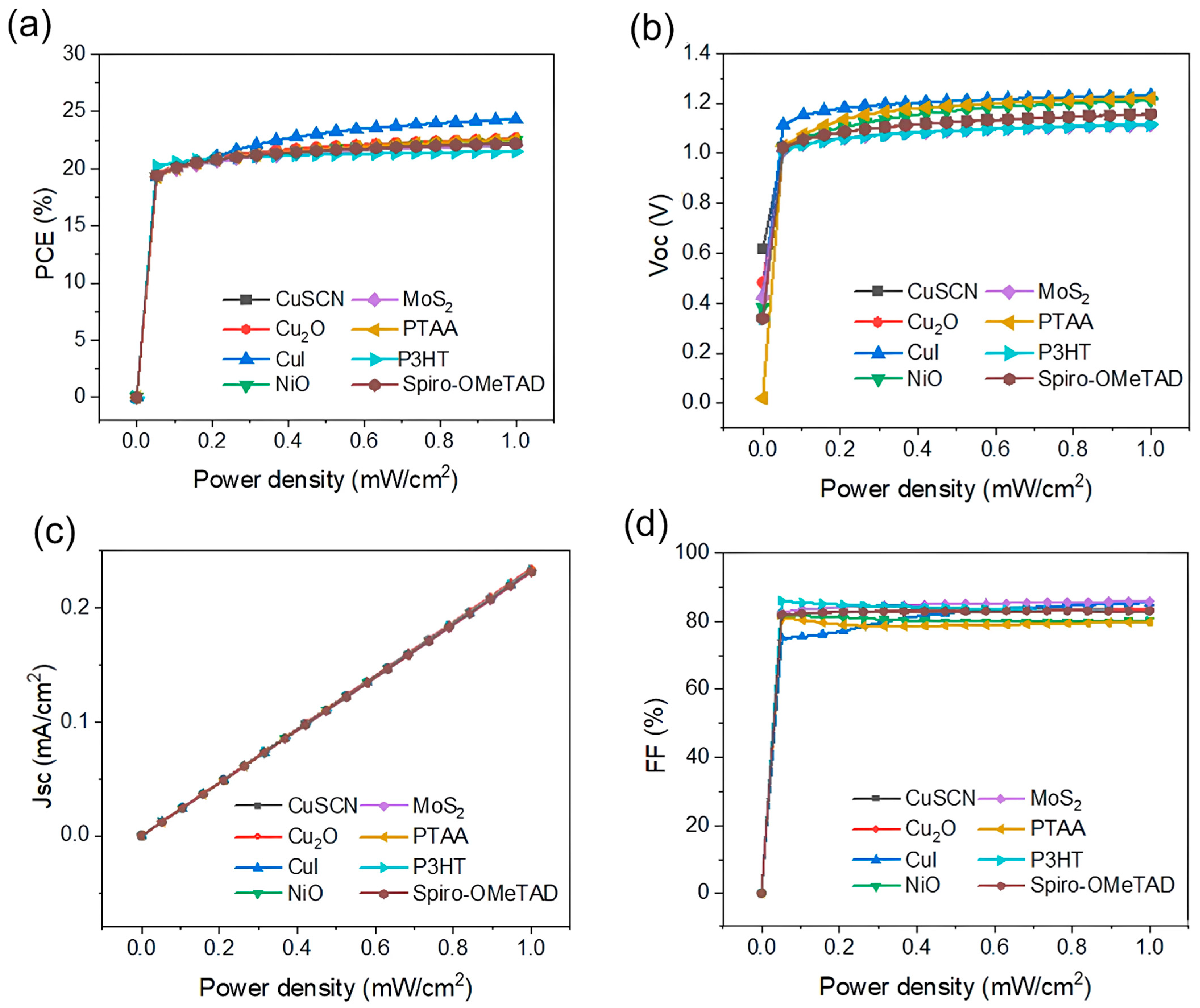
3.2. Performance Parameter Optimization and Structure Analysis of CsPbI2Br Solar Cells
3.3. Literature Comparison
| Device Structure | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTO/SnO2/CsPbI2Br/CuI/Au | 1.376 | 16.35 | 86.57 | 19.48 | This work |
| ITO/ZnO/CsPbI2Br/P3HT/Au | 1.220 | 14.88 | 75.70 | 13.74 | Bahadur [8] |
| ITO/NiOx/CsPbI2Br/PC61BM/BCP/Ag | 1.10 | 15.75 | 75.13 | 13.01 | Chen [27] |
| FTO/TiO2/CsPbI2Br/MoO2-PTAA/Carbon | 1.21 | 15.07 | 80.44 | 14.67 | Lee [23] |
| FTO/TiO2/CsPbI2Br/Carbon | 1.15 | 13.87 | 64 | 10.21 | Dong [28] |
| FTO/TiO2/CsPbI2Br/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 1.21 | 15.67 | 80 | 15.03 | Chen [24] |
| Device Structure (Illumination Intensity) | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTO/SnO2/CsPbI2Br/CuI/Au (0.661mW/cm2) | 1.2468 | 0.17043 | 88.90 | 28.57 | This work |
| ITO/SnO2/ZnO/CsPbI2Br/P3HT/Au (0.382 mW/cm2) | 1.051 | 0.110 | 76.79 | 23.24 | Bahadur [26] |
| ITO/SnO2/CsPbI2Br/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au (0.3098 mW/cm2) | 0.95 | 0.114 | 70 | 23.51 | Kim [25] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alanazi, T.I.; Shaker, A.; Zein, W. Design and Simulation of 2D Ruddlesden-Popper Perovskite Solar Cells under LED Illumination: Role of ETL and Front Contact Band Alignment. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2024, 274, 112992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Kuo, C.; Jhuang, L.; Chen, P.; Lai, Y.; Chen, F. Bandgap engineering enhances the performance of mixed-cation perovskite materials for indoor photovoltaic applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kim, D.; Park, Y. High-efficiency perovskite solar cells for indoor photovoltaic applications: Recent progress and challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Spectral response optimization of perovskite photovoltaics for indoor light harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100332. [Google Scholar]
- Pinzón, C.; Martínez, N.; Casas, G.; Alvira, F.C.; Denon, N.; Brusasco, G.; Chanduví, H.M.; Gil Rebaza, A.V.; Cappelletti, M.A. Optimization of Inverted All-Inorganic CsPbI3 and CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells by SCAPS-1D Simulation. Solar 2022, 2, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xue, J.; Wang, K.L. Phase stability engineering of CsPbI2Br perovskites for photovoltaic applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y. Comparative study of all-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskites for indoor photovoltaic ap-plications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 43833–43841. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadur, J.; Cho, S.; Pandey, P.; Yoon, S.; Lee, D.-G.; Ryu, J.; Meena, V.; Kang, D.-W. Fully hot Air-Processed All-Inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells for outdoor and indoor applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 684, 161909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lang, K.; Han, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Zou, P.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yao, J. Crystallization management of CsPbI2Br perovskites by PbAc2-incorporated twice spin-coating process for efficient and stable CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 97, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jena, A.K.; Takei, I.; Ikegami, M.; Ishii, A.; Numata, Y.; Miyasaka, T. Dopant-free polymer HTM-based CsPbI2Br solar cells with efficiency over 17% in sunlight and 34% in indoor light. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Lou, Y.-H.; Wang, Z.-K. Perovskite indoor photovoltaics: Opportunity and challenges. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 11936–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huy, V.P.H.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Bark, C.W. Recent Advances of Doped SnO2 as Electron Transport Layer for High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells. Materials 2023, 16, 6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Duan, J.; Luo, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Gao, Y. Interface optimization of CsPbI2Br based perovskite solar cells by device simulation. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Niu, X.; Ding, L. Emerging dopant-free hole transport materials for perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 3608–3620. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Zhao, J.; Du, M. Long-term stable inorganic hole transport layers for efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002674. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Varo, P.; Jiménez-Tejada, J.A.; García-Rosell, M.; Ravishankar, S.; Garcia-Belmonte, G.; Bisquert, J.; Almora, O. Device Physics of Hybrid Perovskite Solar cells: Theory and Experiment. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Multi-scale simulation approaches for perovskite photovoltaics: From material properties to device performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 17545–17570. [Google Scholar]
- Khatoon, S.; Chakraborty, V.; Yadav, S.K.; Diwakar, S.; Singh, J.; Singh, R.B. Simulation study of CsPbIxBr1-x and MAPbI3 heterojunction solar cell using SCAPS-1D. Sol. Energy 2023, 254, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, A.; Singh, U.P. Numerical modelling and analysis of earth abundant Sb2S3 and Sb2Se3 based solar cells using SCAPS-1D. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 230, 111184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.; Sultan, M.; Safeer, S.H. Device Optimization of CsPbI2Br-based Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells using Different Hole and Electron Transport Layers via SCAPS-1D. Next Mater. 2025, 8, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Mehra, R.; Raj, B. Comparative study of hole transporting layers commonly used in high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 21172–21191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoui, Y.; Ez-Zahraouy, H.; Ahmad, S.; Kazim, S. Unravelling the theoretical window to fabricate high performance inorganic perovskite solar cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Ki, M.J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.K.; Hong, S.Y.; Kim, B.W.; Heo, J.H.; Im, S.H. Fully Scalable and Stable CsPbI2Br Solar Cells Realized by an All-Spray-Coating Process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7926–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, G.; Du, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Improving the stability and efficiency of inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskite via surface reconstruction strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Jin, I.S.; Park, S.H.; Lim, S.J.; Jung, J.W. Methylammonium Iodide-Mediated Controlled Crystal Growth of CsPbI2Br Films for Efficient and Stable All-Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 36228–36236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, J.; Cho, S.; Pandey, P.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, S.; Lee, D.-G.; Song, J.T.; Cho, J.S.; Kang, D.-W. Surface defect passivation of All-Inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskites via fluorinated ionic liquid for efficient Outdoor/Indoor photovoltaics processed in ambient air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 637, 157901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, X. Performance enhancement of inverted CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells via butylammonium cation additive modification. Mater. Lett. 2025, 379, 137643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Han, X.; Li, W.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, J. Anti-solvent assisted multi-step deposition for efficient and stable carbon-based CsPbI2Br all-inorganic perovskite solar cell. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

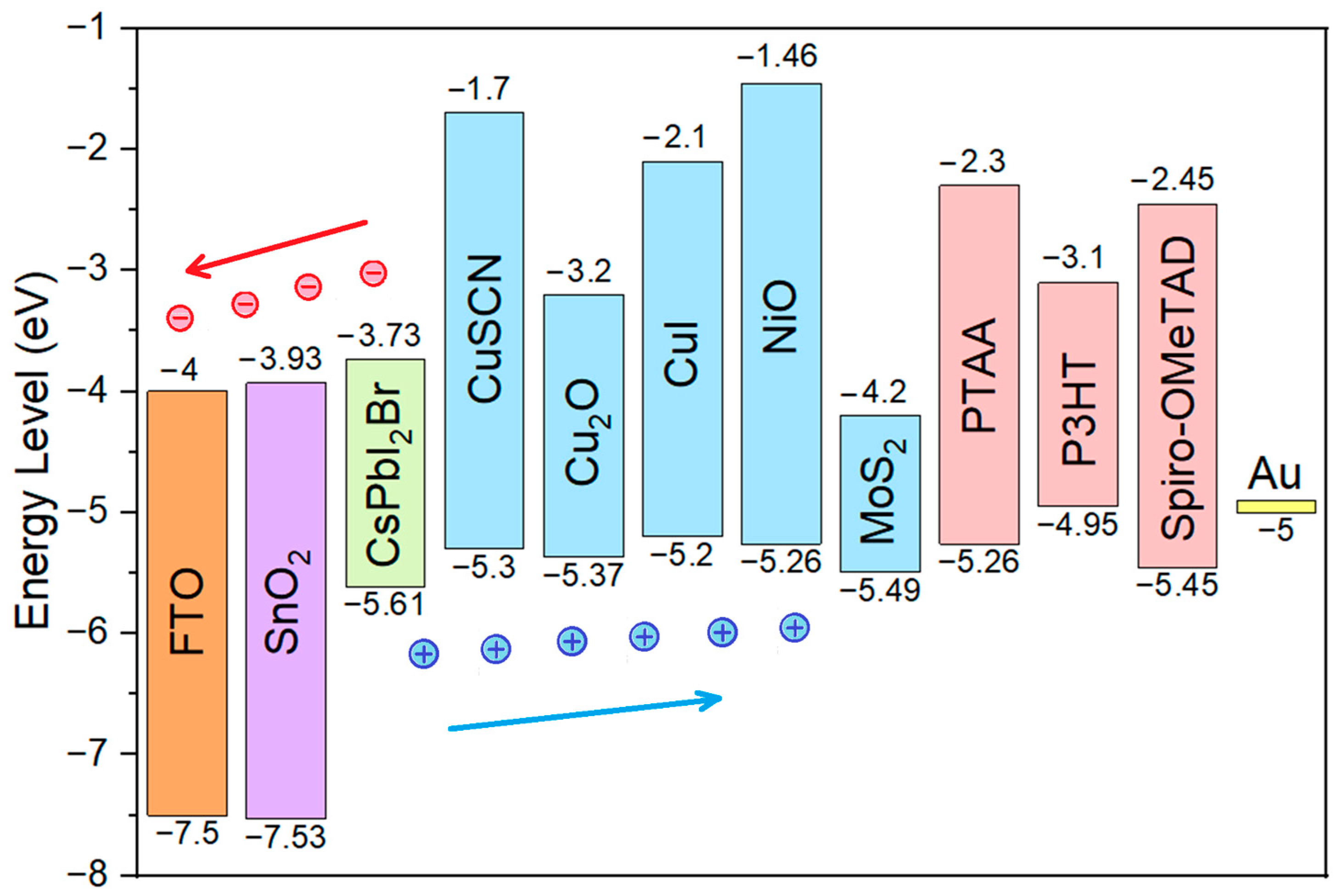


| Parameters | FTO | SnO2 | CsPbI2Br |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (μm) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Bandgap (eV) | 3.5 | 3.6 | 1.88 |
| Relative permittivity | 9 | 9 | 8.6 |
| Electron affinity (eV) | 4 | 3.93 | 3.73 |
| Effective DoS at CB (cm−3) | 2.2 × 1018 | 3.16 × 1018 | 1.9 × 1018 |
| Effective DoS at VB (cm−3) | 1.8 × 1019 | 2.5 × 1019 | 2.370 × 1019 |
| Mob. of electrons (cm2/V·s) | 20 | 20 | 200 |
| Mob. of holes (cm2/V·s) | 10 | 10 | 200 |
| Dop. conc. of acceptor (cm−3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Dop. conc. of donor (cm−3) | 2.0 × 1018 | 1.0× 1018 | 1.0 × 1015 |
| Defect density (cm−3) | 1.0 × 1015 | 1.0 × 1015 | 3.64 × 1015 |
| Parameters | CuSCN | Cu2O | CuI | NiO | MoS2 | PTAA | P3HT | Spiro-OMeTAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (μm) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Bandgap (eV) | 3.6 | 2.17 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 1.29 | 2.96 | 1.85 | 3 |
| Relative permittivity | 10 | 7.1 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 4.26 | 9 | 3.4 | 3 |
| Electron affinity (eV) | 1.7 | 3.2 | 2.1 | 1.46 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 2.45 |
| Effective DoS at CB (cm−3) | 2.29 × 1019 | 2 × 1017 | 2.8 × 1019 | 2.8 × 1019 | 2.2 × 1018 | 2 × 1018 | 2 × 1020 | 2.2 × 1018 |
| Effective DoS at VB (cm−3) | 1.8 × 1018 | 1.1 × 1019 | 1 × 1019 | 1 × 1019 | 1.8 × 1019 | 1 × 1019 | 2 × 1020 | 1.9 × 1019 |
| Mob. of electrons (cm2/V·s) | 100 | 200 | 100 | 12 | 100 | 1 | 1 × 10−4 | 2 × 10−4 |
| Mob. of holes (cm2/V·s) | 25 | 80 | 43.9 | 3.8 | 150 | 40 | 1 × 10−3 | 2 × 10−4 |
| Dop. conc. of acceptor (cm−3) | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 | 1 × 1018 |
| Defect density (cm−3) | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 | 1 × 1015 |
| Parameters | SnO2/CsPbI2Br | CsPbI2Br/CuI |
|---|---|---|
| Defect types | Neutral | Neutral |
| Capture cross section electrons (cm2) | 1.0 × 10−19 | 1.0 × 10−19 |
| Capture cross section holes (eV) | 1.0 × 10−19 | 1.0 × 10−19 |
| Energy distributions | Single | Single |
| Ref for defect energy level | Above the highest Ev | Above the highest Ev |
| Energy with respect to reference (eV) | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Total density (cm−3) | 1.0 × 109 | 1.0 × 109 |
| HTLs/Performances | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuSCN | 1.1381 | 0.153 | 83.35 | 21.96 |
| Cu2O | 1.1379 | 0.154 | 83.43 | 22.21 |
| CuI | 1.2191 | 0.153 | 83.84 | 23.66 |
| NiO | 1.1891 | 0.153 | 79.85 | 21.98 |
| MoS2 | 1.0908 | 0.152 | 85.63 | 21.57 |
| PTAA | 1.2044 | 0.153 | 79.04 | 22.05 |
| P3HT | 1.1016 | 0.153 | 83.39 | 21.34 |
| Spiro-OMeTAD | 1.1379 | 0.153 | 82.91 | 21.84 |
| HTLs/Performances | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuSCN | 1.1131 | 0.0889 | 83.04 | 21.4 |
| Cu2O | 1.1132 | 0.0898 | 83.12 | 21.64 |
| CuI | 1.202 | 0.0889 | 81.1 | 22.57 |
| NiO | 1.1521 | 0.0889 | 80.2 | 21.39 |
| MoS2 | 1.0825 | 0.0887 | 84.75 | 21.19 |
| PTAA | 1.1784 | 0.0889 | 78.52 | 21.43 |
| P3HT | 1.0817 | 0.0892 | 84.12 | 21.14 |
| Spiro-OMeTAD | 1.1136 | 0.0889 | 82.82 | 21.35 |
| HTLs/Performances | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuSCN | 1.0313 | 0.0153 | 82.01 | 19.58 |
| Cu2O | 1.0321 | 0.0154 | 82.05 | 19.81 |
| CuI | 1.1282 | 0.0153 | 74.99 | 19.59 |
| NiO | 1.0362 | 0.0153 | 81.43 | 19.54 |
| MoS2 | 1.0197 | 0.0152 | 82.84 | 19.51 |
| PTAA | 1.0433 | 0.0153 | 80.88 | 19.54 |
| P3HT | 1.0202 | 0.0153 | 85.75 | 20.33 |
| Spiro-OMeTAD | 1.0333 | 0.0153 | 82.05 | 19.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-C. SCAPS-1D Simulation of Various Hole Transport Layers’ Impact on CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells Under Indoor Low-Light Conditions. Solids 2025, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6030031
Peng C-H, Lin Y-C. SCAPS-1D Simulation of Various Hole Transport Layers’ Impact on CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells Under Indoor Low-Light Conditions. Solids. 2025; 6(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6030031
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Chih-Hsi, and Yi-Cheng Lin. 2025. "SCAPS-1D Simulation of Various Hole Transport Layers’ Impact on CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells Under Indoor Low-Light Conditions" Solids 6, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6030031
APA StylePeng, C.-H., & Lin, Y.-C. (2025). SCAPS-1D Simulation of Various Hole Transport Layers’ Impact on CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells Under Indoor Low-Light Conditions. Solids, 6(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6030031






