Influence of Germanium Sulfide on the Structure, Ag-Ion Conductivity and Stability of Glasses in the GeS2-Sb2S3-AgI System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Glass Formation and Short-Range Order Structure
3.2. Differential Thermal Analysis
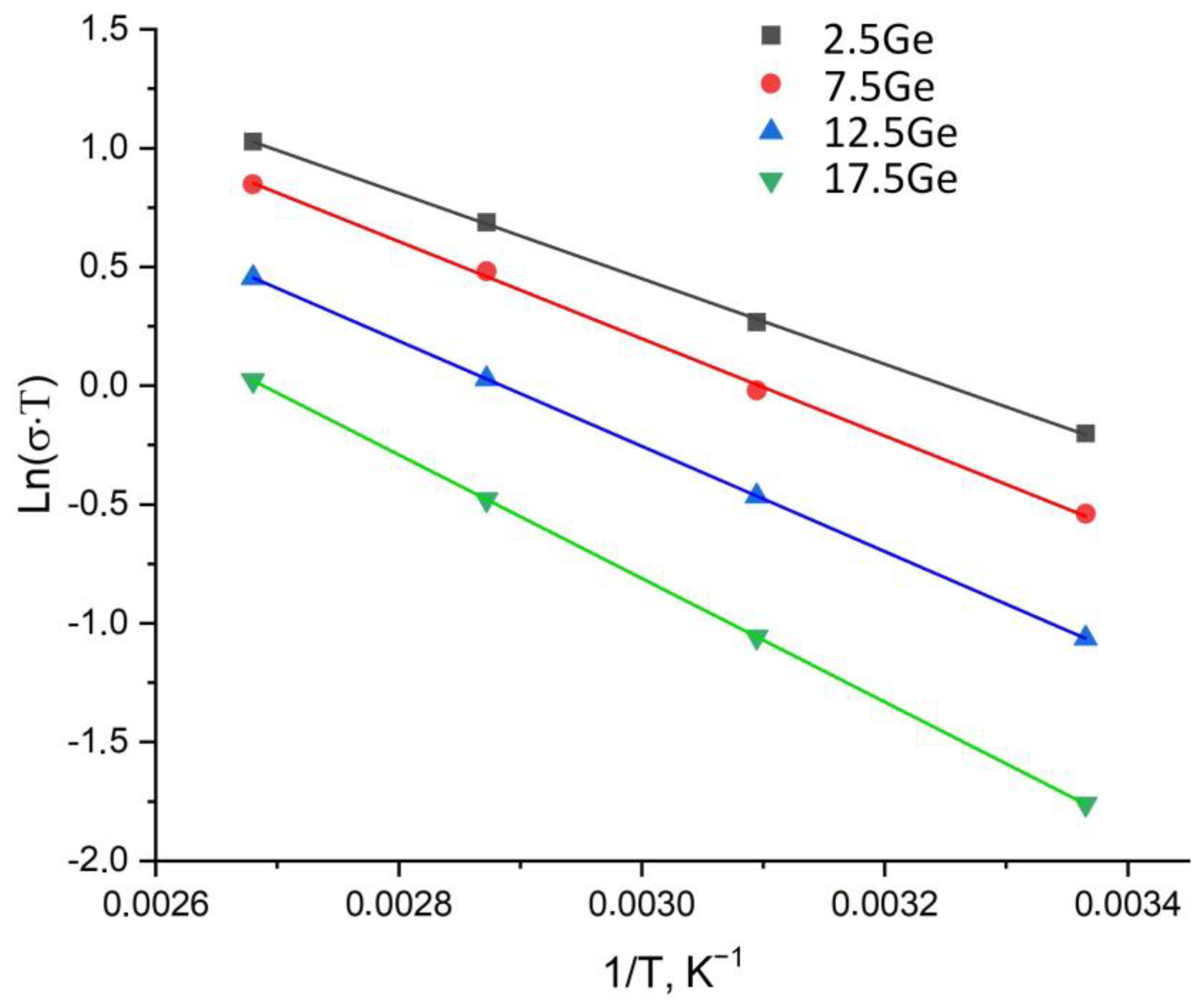
3.3. Ionic Transport Properties
3.4. Microscopic Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escher, C.; Thomann, S.; Andreoli, C.; Fink, H.-W.; Toquant, J.; Pohl, D.W. Vacuum ion emission from solid electrolytes: An alternative source for focused ion beams. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 053513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, A.B.; Belykh, S.F.; Gololobov, G.P.; Gurov, V.S.; Gusev, S.I.; Suvorov, D.V.; Taganov, A.I.; Fud, D.J.; Ai, Z.; Liu, C.S. Ion-Beam Sources Based on Solid Electrolytes for Aerospace Applications and Ion-Beam Technologies (Review). Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2018, 61, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiko, Y.; Segawa, K.; Honda, S.; Iwamoto, Y. Ag+ ion emission from a sharp Ag2O-Al2O3-P2O5-SiO2 glass-fiber emitter. Solid State Ion. 2018, 322, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstogouzov, A.; Aguas, H.; Ayouchi, R.; Belykh, S.F.; Fernandes, F.; Gololobov, G.P.; Moutinho, A.M.C.; Schwarz, R.; Suvorov, D.V.; Teodoro, O.M.N.D. Vacuum solid-state ion-conducting silver source for application in field emission electric propulsion systems. Vacuum 2016, 131, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrosati, B.; Ricci, A.; Lazzari, M. Electrochemical properties of a new solid electrolyte in the system silver iodide? silver dichromate. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1976, 6, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodelli, G.; Magistris, A.; Schiraldi, A. Some solid electrolyte cells. Electrochim. Acta 1974, 19, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Qu, G.; Calvez, L.; Dai, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, T.; Nie, Q. Formation and properties of chalcogenide glasses based on GeS2–Sb2S3–AgI system. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Zhu, E.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, F.; Dai, S. Fast Ag-Ion-Conducting GeS2–Sb2S3–AgI Glassy Electrolytes with Exceptionally Low Activation Energy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Jiao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Dai, S.; Jia, G. Conductivity and structural properties of fast Ag-ion-conducting GaGeSbS–AgI glassy electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 24882–24886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilenko, G.V.; Arif, M.; Blinov, L.N. Phase Diagram and Glass Formation in the Sb2S3-AgI System. Glas. Phys. Chem. 2005, 31, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmidis-Petrović, A.F. Theoretical analysis of relative changes of the Hruby, Weinberg, and Lu–Liu glass stability parameters with application on some oxide and chalcogenide glasses. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 499, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yan, Q.; Wagner, T.; Zima, V.; Frumar, M.; Frumarova, B.; Chen, G. Conductivity study on GeS2-Ga2S3-AgI-Ag chalcohalide glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 023701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, H.C.; Chen, R.K.; Vass, H.; Clark, S.J.; Ackland, G.J.; Poon, W.C.-K.; Crain, J. Compression mechanisms in quasimolecular. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 14812–14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghera, J.S.; Heo, J.; Mackenzie, J.D. Chalcohalide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 103, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Long, N.; Sun, X.; Yin, G.; Jiao, Q.; Liu, X.; Dai, S.; Lin, C. Relationship between composition, crystallization, and phase separation behavior of GeS2–Sb2S3–CsCl chalcogenide glasses. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 102978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.W.; Tanguy, B.; Reau, J.-M.; Videau, J.J.; Portiek, J. Investigations on glasses in the Sb2S3 Agl system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 99, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Siegel, D.J. Grain Boundary Contributions to Li-Ion Transport in the Solid Electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO). Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9639–9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Lin, C.; Xu, Y.; Nie, Q.; Chen, F.; Dai, S. Glass formation and properties of novel GeS2–Sb2S3–In2S3 chalcogenide glasses. Opt. Mater. 2011, 33, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Yang, A.; Tao, H.; Tang, D. The effects of germanium addition on properties of Ga-Sb-S chalcogenide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 452, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Hanashima, T.; Ohara, K.; Simon, A.-A.A.; Mitkova, M. Structural transformation in. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019, 3, 035601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudelka, L.; Frumar, M.; Pisárčik, M. Raman spectra of Ge-Sb-S system glasses in the S-rich region. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1980, 41, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Yoon, J.M.; Ryou, S.-Y. Raman spectroscopic analysis on the solubility mechanism of La3+ in GeS2–Ga2S3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 238, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.; Benmore, C.J.; Tverjanovich, A.; Usuki, T.; Khomenko, M.; Fontanari, D.; Sokolov, A.; Ohara, K.; Bokova, M.; Kohara, S.; et al. Glassy and liquid Sb2S3: Insight into the structure and dynamics of a promising functional material. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 4654–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, Z.; Ying, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Dai, S.; Xu, T.; Nie, Q. Network Structure in GeS2–Sb2S3 Chalcogenide Glasses: Raman Spectroscopy and Phase Transformation Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5862–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mentus, S.V.; Šušić, M.V.; Gajinov, S.P. Electrical conductivity of the solid system AgI-Sb2S3. Solid State Ion. 1983, 11, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiliakos, A.; Iordache, M.; Răceanu, M.; Marinoiu, A. Remediation of activation energy anomalies, scaling distortions, and bandwidth limitations in superionic conductivity modeling of NZSP NaSICON synthesized by an augmented SSR method. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10588–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souquet, J.L. Ionic transport in glassy electrolytes. In Solid State Electrochem; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, C.; Chowdari, B.V.; Rao, G.V.S.; Souquet, J. Lithium conducting glass ceramic with Nasicon structure. Mater. Res. Bull. 2002, 37, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
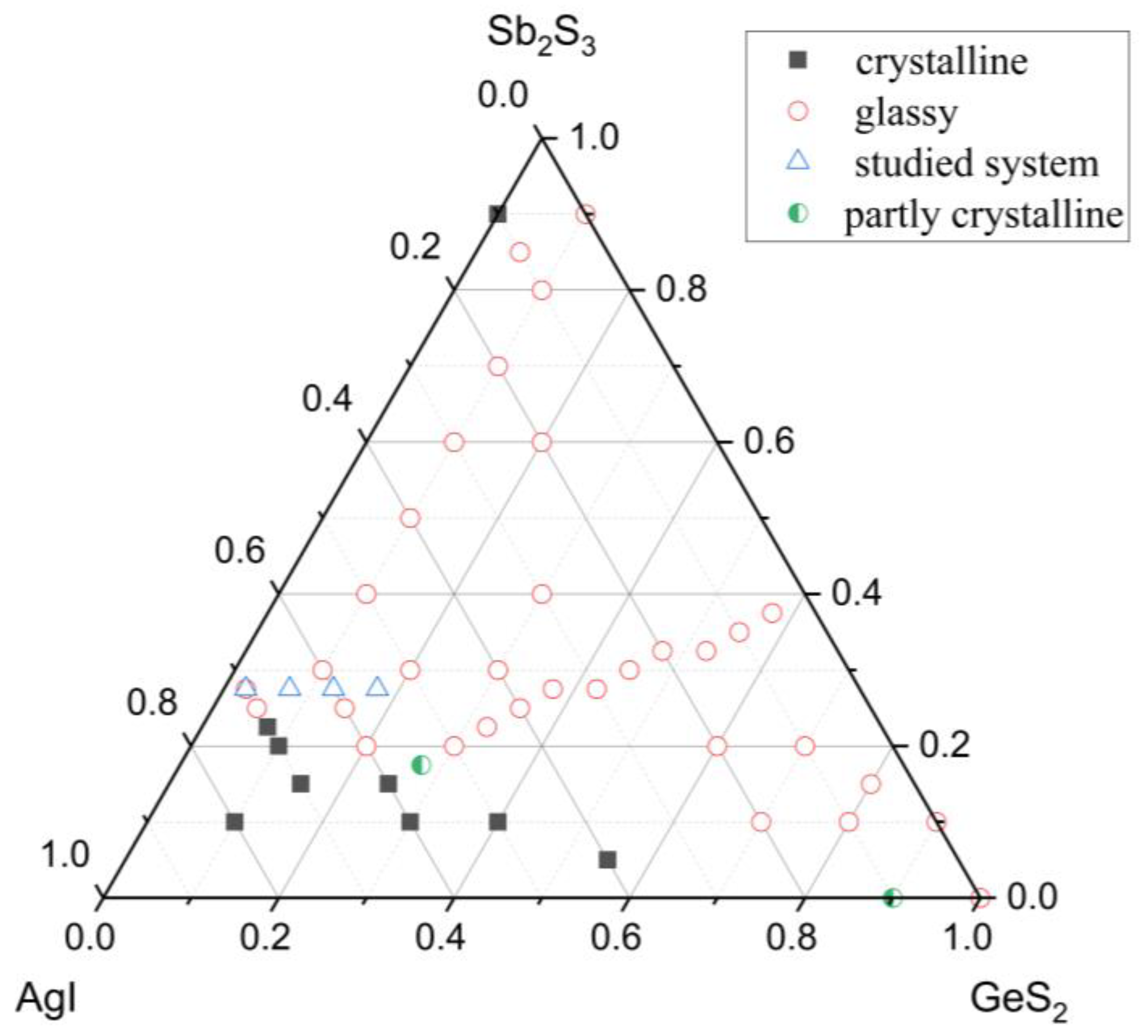
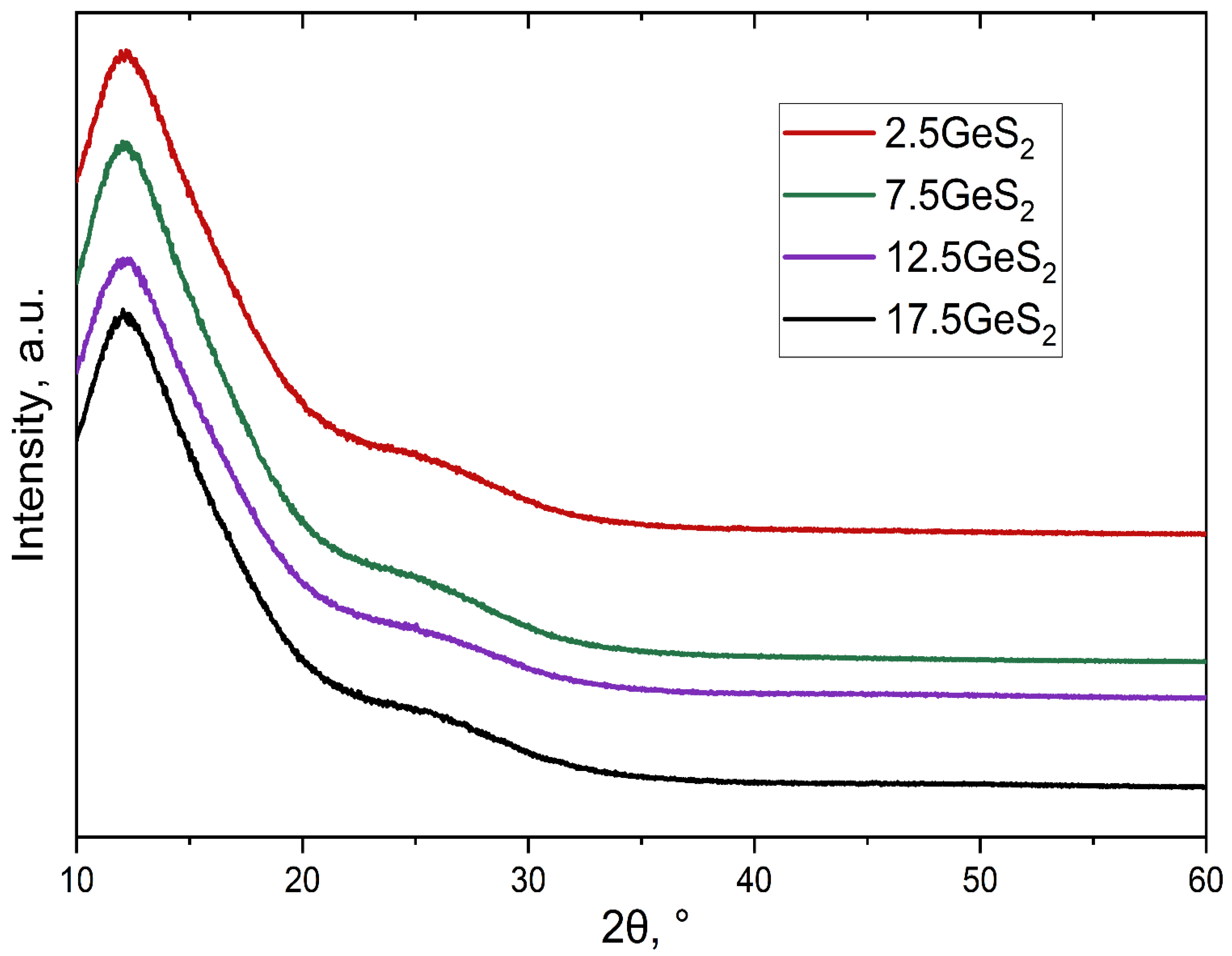
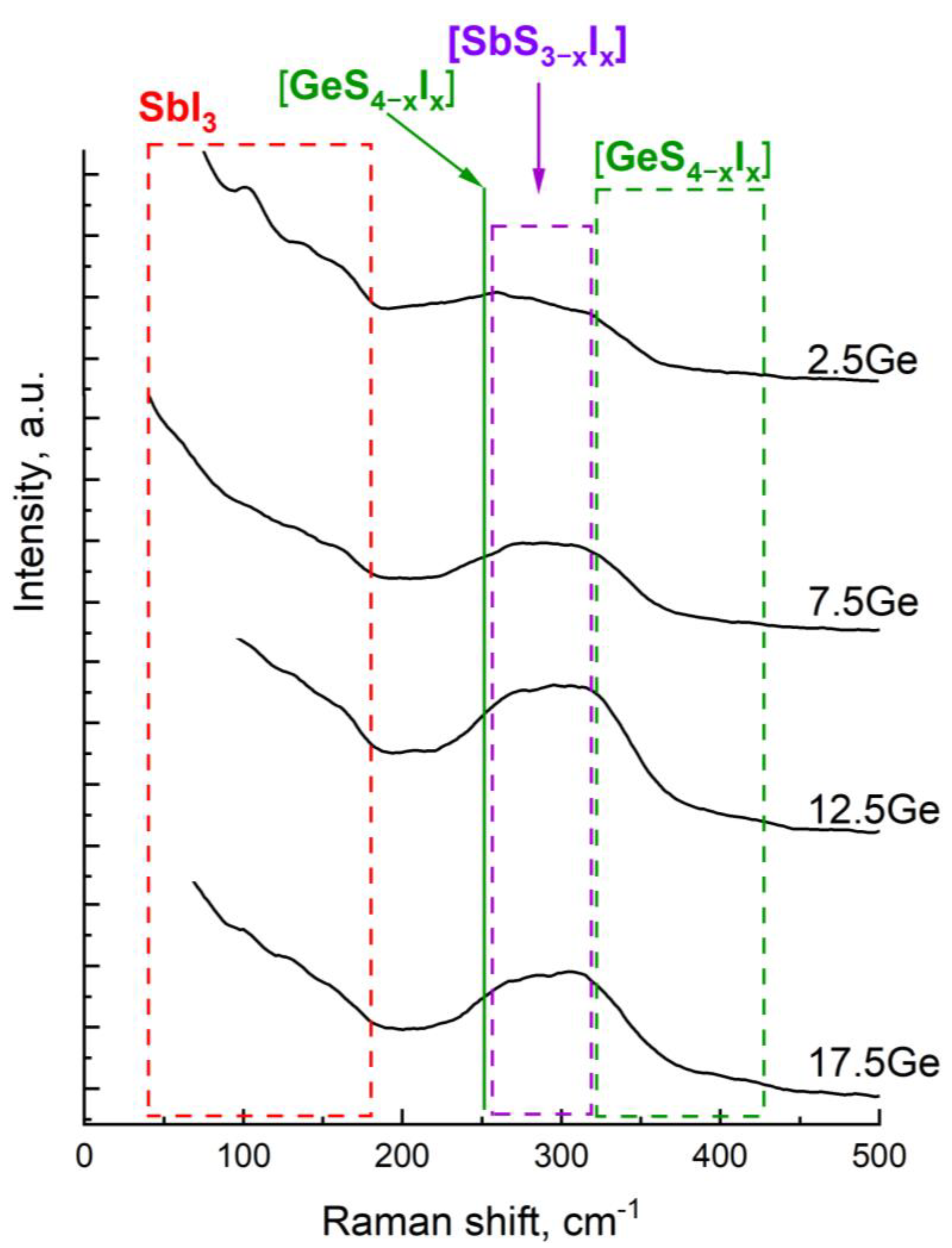

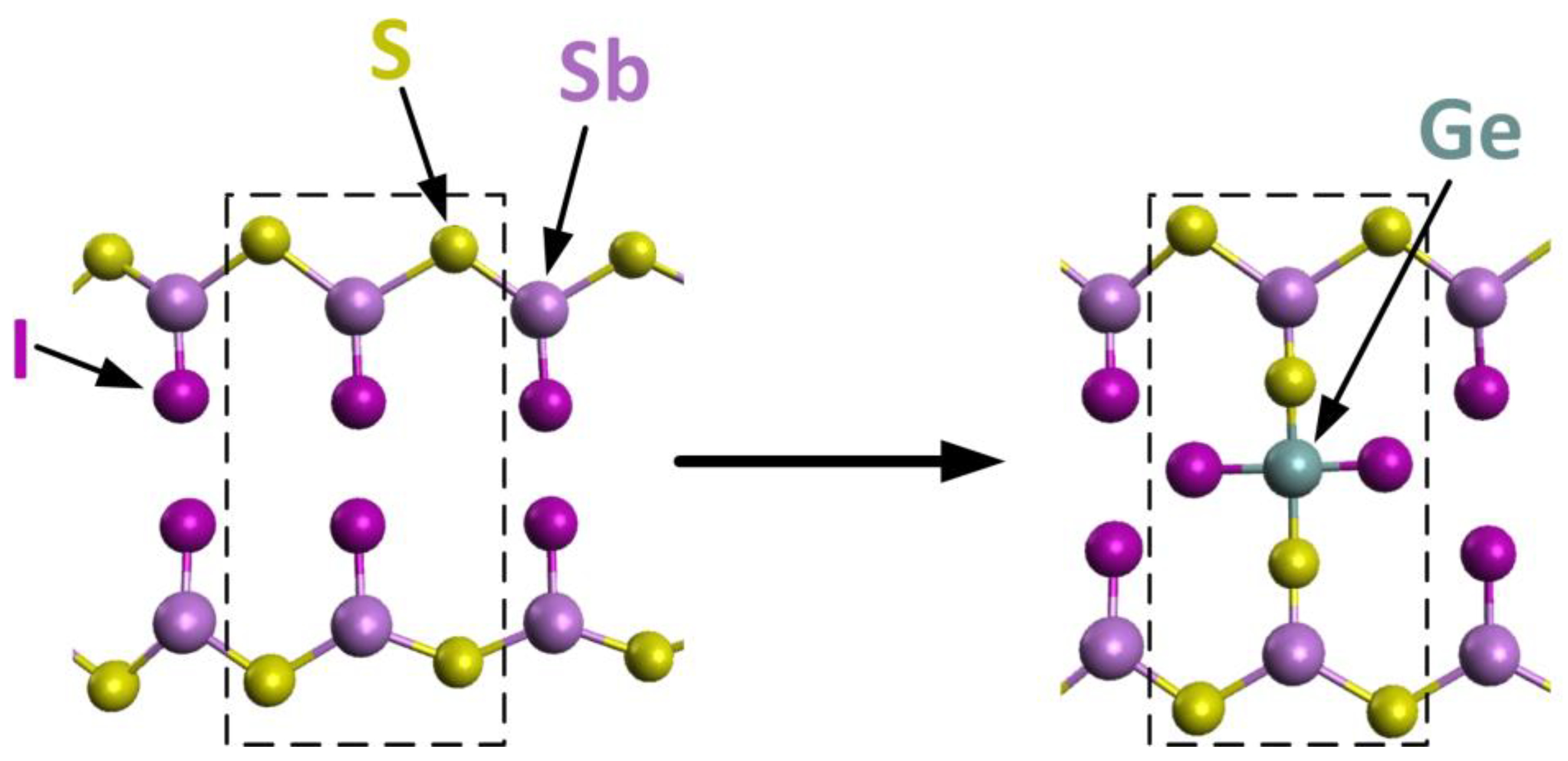
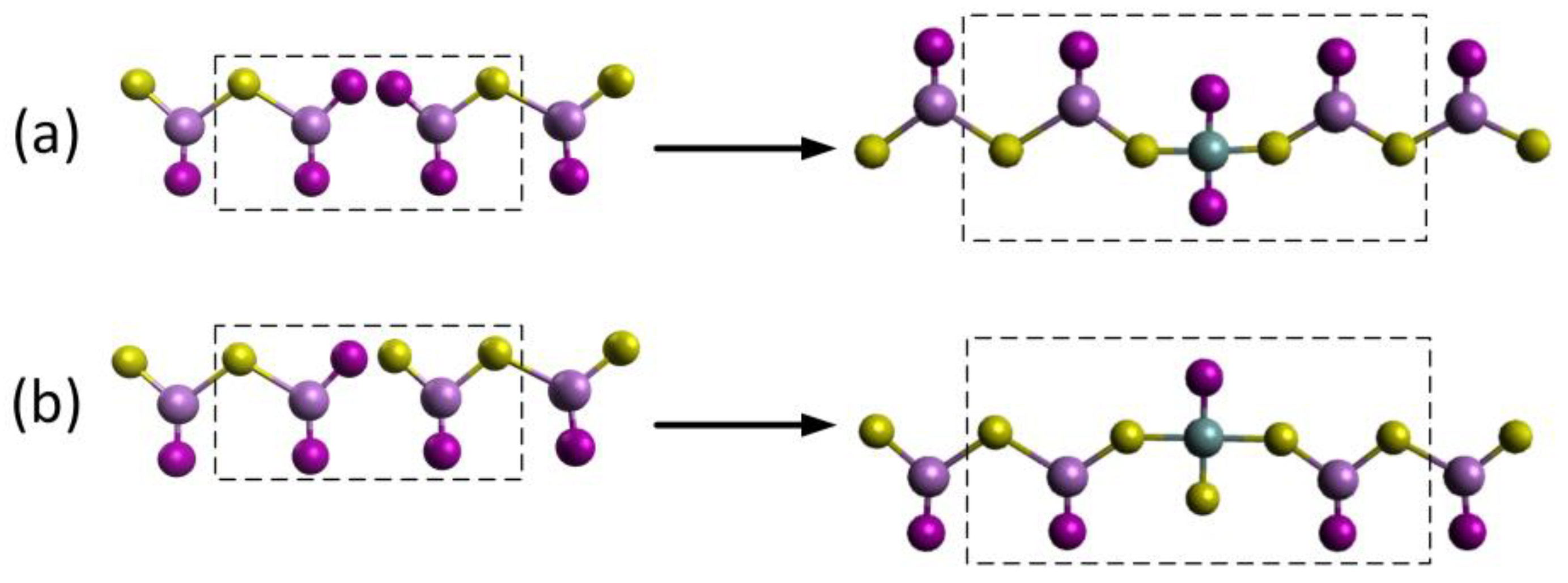


| Structural Element | Raman Shift, cm−1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| SbI3 | 38, 57, 70, 80,138, 165 | [13] |
| SbSI | 108, 115, 138, 139, 165, 290, 315 | [16] |
| Sb2S3 | 107, 138, 155, 162,280, 290, 300, 308, 310, 315, 319 | [15,17,18] |
| GeS2, S3Ge-GeS3, GeS4 | 101, 200, 255, 330, 340, 343, 365, 373 | [15,16,18,19,20,21,22] |
| Sample | Tg, °C | Tx, °C | Tc, °C | Tm, °C | KH | KW | KLL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5Ge | 199 | 219 | 232 | 329 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.41 |
| 7.5Ge | 225 | 265 | 283 | 338 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.47 |
| 12.5Ge | 235 | 280 | 294 | 343 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 0.48 |
| 17.5Ge | 259 | 299 | 314 | 344 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 0.50 |
| Sample | σRT·10−3, S/cm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ea, eV | |||||
| 2.5Ge | 2.75 | 0.127 | 0.18 | 0.066 | 5.85 |
| 7.5Ge | 1.96 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.064 | 6.33 |
| 12.5Ge | 1.33 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.070 | 6.39 |
| 17.5Ge | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.085 | 6.99 |
| Sample | ρ, g/cm3 | Vm, cm3/mol | NAg+·10−22, cm−3 | l, Å | Lnσ0exp | Lnσ0calc | ΔS, J·(K·mol)−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5Ge | 5.20 | 50.26 | 1.20 | 4.37 | 5.85 | 4.304 | 17.4 |
| 7.5Ge | 5.10 | 50.29 | 1.20 | 4.37 | 6.33 | 4.297 | 21.4 |
| 12.5Ge | 5.04 | 49.87 | 1.21 | 4.36 | 6.39 | 4.296 | 21.9 |
| 17.5Ge | 4.87 | 50.60 | 1.19 | 4.38 | 6.99 | 4.280 | 26.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markov, V.; Farziev, T.; Dybin, N. Influence of Germanium Sulfide on the Structure, Ag-Ion Conductivity and Stability of Glasses in the GeS2-Sb2S3-AgI System. Solids 2025, 6, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6020022
Markov V, Farziev T, Dybin N. Influence of Germanium Sulfide on the Structure, Ag-Ion Conductivity and Stability of Glasses in the GeS2-Sb2S3-AgI System. Solids. 2025; 6(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkov, Viktor, Talib Farziev, and Nikita Dybin. 2025. "Influence of Germanium Sulfide on the Structure, Ag-Ion Conductivity and Stability of Glasses in the GeS2-Sb2S3-AgI System" Solids 6, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6020022
APA StyleMarkov, V., Farziev, T., & Dybin, N. (2025). Influence of Germanium Sulfide on the Structure, Ag-Ion Conductivity and Stability of Glasses in the GeS2-Sb2S3-AgI System. Solids, 6(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids6020022







