Abstract
We used density functional theory (DFT) calculations to investigate the structural, electronic, magnetic, mechanical, and thermodynamic properties of CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo and W) compounds. These are XYZ type half-Heusler alloys, which also exist in the face centred cubic MgAgAs-type structure and conform to space group. We computed these properties in three different atomic arrangements known as Type-I, Type-II, and Type-III phases. In all these phases, the alloys were found to be in the ferromagnetic state. Furthermore, the calculated electronic band structure and the total electronic density of states indicated a metallic behavior in CoWSb, nearly half-metallic behavior in CoMoSb, and half-metallic behavior in CoCrSb, with a minority-spin band gap of 0.81 eV. Furthermore, the calculated mechanical properties predicted an anisotropic behavior of these alloys in their stable phase. Finally, due to its high Debye temperature value, CoCrSb shows stronger covalent bonding than CoMoSb and CoWSb, respectively.
1. Introduction
Ternary half-Heusler (HH) compounds involving the Co atom have recently attracted attention due to their high Curie temperature and structural similarity with binary semiconductors with zinc-blende (ZB) structure that makes them potential candidates in optoelectronic and spintronic applications such as quantum sensors, resistors and computers devices [1,2,3,4], topological insulators [5,6], and thermoelectric devices [7,8]. The wide range of usage of HH in applications is due to its excellent electrical, mechanical, and electronic properties as well as thermal stability.
The crystal structure, C of any HH alloy is similar to the structure, of a full-Heusler alloy (YZ) but missing one X atom. The absence of inversion symmetry due to an empty X site and the low coordination number of the d-band metals in the HH alloys are believed to be essential for these materials novel electronic and magnetic properties. Some research groups have reported three possible distinct atomic arrangements, called Type-I, Type-II, and Type-III phases, due to this missing X atom in the HH alloy [1,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
Using density functional theory, some Co-based HH compounds have been predicted to be semiconductor, metallic, and half-metallic materials. The half-metallic material is material that behave like a semiconductor in the minority spin, while in the majority spin, it has the metallic character, as first reported by de Groot et al. [12] in 1983 for the NiMnSb alloy, which also depends on the valence electron counts (VEC) of the alloys [7,8,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Nanda and Dasgupta [14] reported CoMoSb to be metallic from the series of HH compounds XMZ (X = Fe, Co, Ni: M = Ti, V, Nb, Zr, Cr, Mo, Mn and Z = Sb, Sn) they investigated. Zhong-Yu et al. [16] studied the structural and electronic properties of CoCrZ (Z = Sb and Te) using the full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FP-LAPW) method. They showed that CoCrSb is half-metallic and has a spin-minority gap.
In this paper, we have investigated the structural, electronic, magnetic, mechanical, and thermodynamics properties of a series of half-Heusler compounds, CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W). We identify the most stable phases and investigate the impact of the lattice parameter on the magnetic properties for each stable phase of HH CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W). To shed some light on the metallic behavior, electronic transport, mechanical stability, and strength of chemical bonding between their atoms, we have computed and analyzed the electronic spin bands and spin density of states (DOS), the response to shear deformation and unidirectional compression and the Debye temperature, q.
2. Computational Details
Our calculations were performed using the Quantum Espresso Ab-Initio simulation package [19,20,21]. The generalized gradient approximation (GGA) within the Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof (PBE) formulation [22] was used to treat electronic exchange and correlation effects. The plane wave energy cutoff was set to 680 eV and a k-point mesh of the Monkhorst–Pack type [23] and with grid was used to sample the irreducible Brillouin zone. For electronic properties calculations (band structure and DOS), a denser mesh grid was used. The plane-waves pseudopotentials basis functions set consists of the 3d 4s, 3d 4s, 4d 5s, 5d 6s, and 5s 5p for Co, Cr, Mo, W, and Sb, respectively. The Thermo_pw code [24,25] was used to calculate the mechanical and thermodynamic properties.
3. Results
3.1. Structural Properties
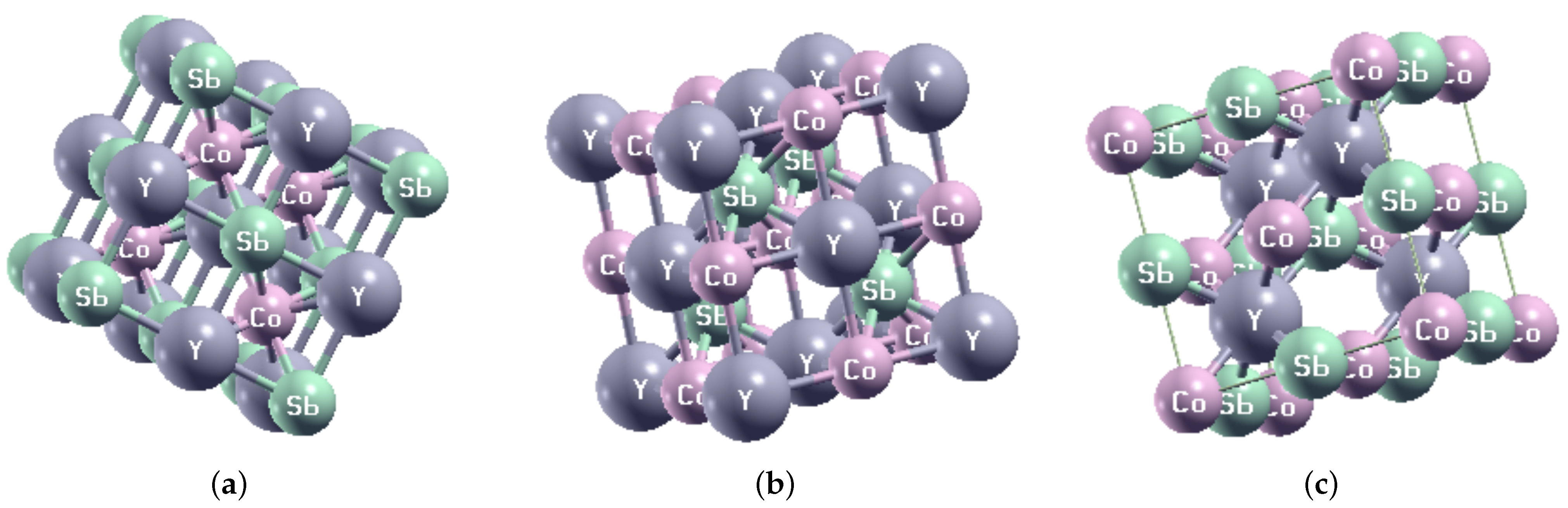
We started by calculating the equilibrium lattice constant of the HH compound CoYSb (Cr, Mo, W) considering the three possible site arrangement of X and Y atoms shown in Figure 1. In Table 1, the Wyckoff [26] positions of the three atoms and vacancy are given based on in Type-I, Type-II, and Type-III phases which conform to space group.
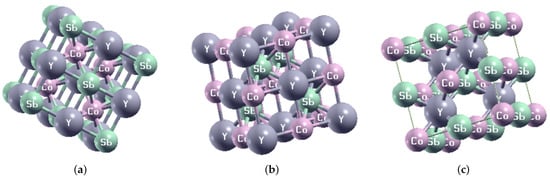
Figure 1.
The optimized crystal structure of CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, and W) for (a) Type-I, (b) Type-II, and (c) Type-III.

Table 1.
The Wyckoff positions of the three atoms, X, Y, and Z: 4a = (0, 0, 0) a, 4b = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) a and 4c = (0.25, 0.25, 0.25) a, with the 4d site vacant.
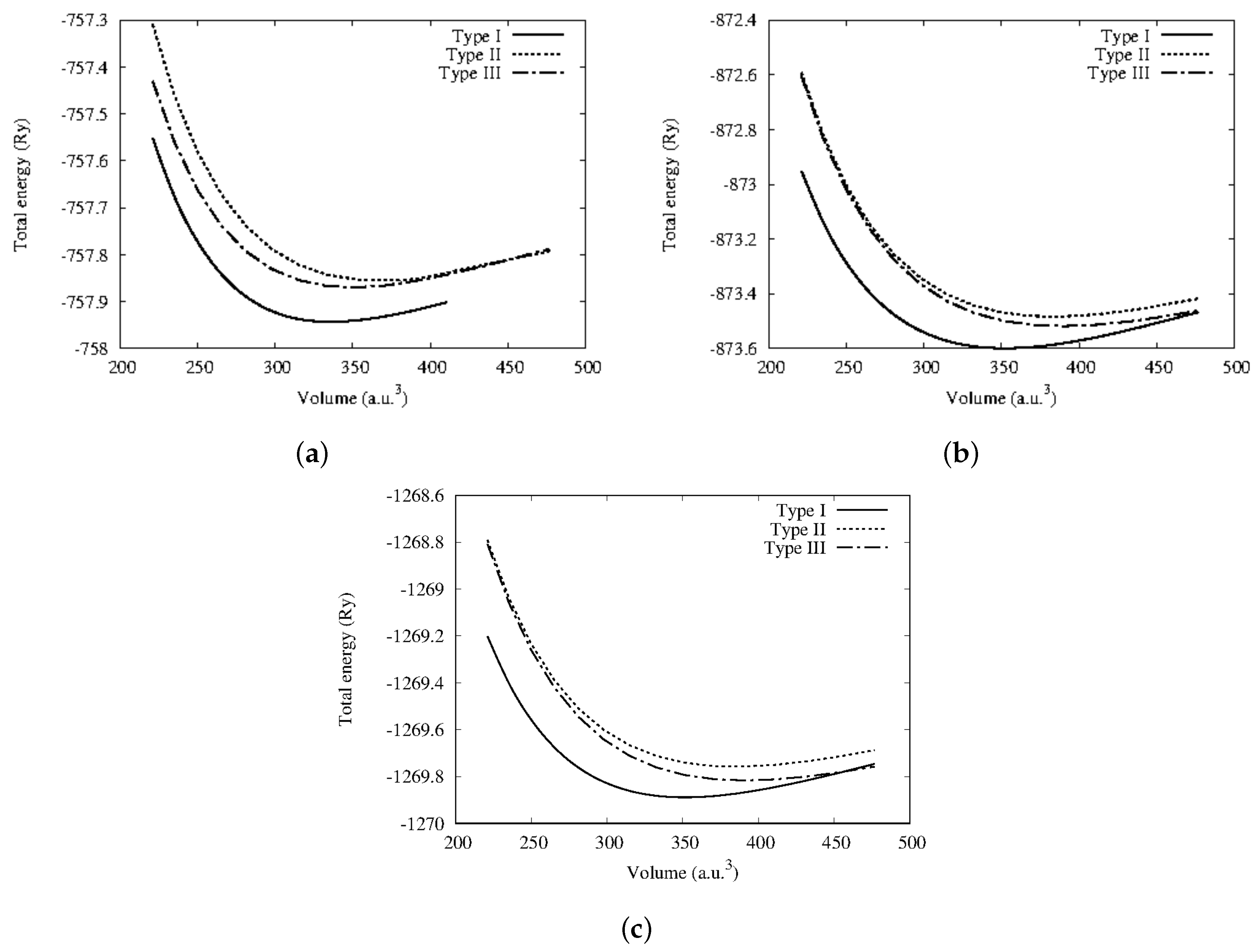
Figure 2 shows the energy–volume curves of the considered systems plotted by fitting to Murnaghan equation of states [27]. From there, the equilibrium lattice constant (), bulk modulus (B), the minimum energy (), and pressure derivative (B) were derived and are reported in Table 2. The minimum energies obtained from the fitted energy–volume curves of CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) alloys show that the Type-I phase is the most stable structural phase (Figure 1 and Table 2). The lattice constants are smaller in this phase and bulk moduli more significant than in other structural phases. However, large pressure derivatives of bulk moduli are observed in all structural phases, which indicates that these alloys display strong sensitivity against pressure change. Henceforth, all other results were obtained based on the stable state Type-I CoYSb phase apart from the magnetic properties.
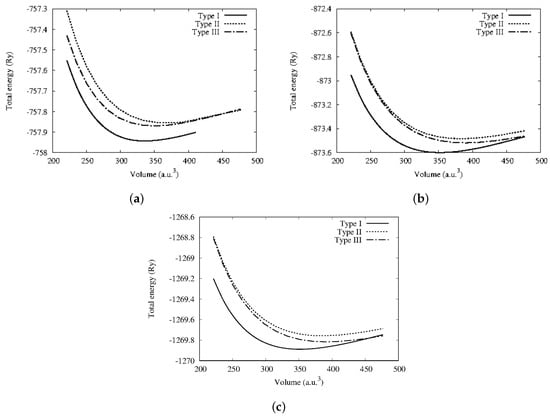
Figure 2.
Calculated total energy as a function of volume in ferromagnetic state for the three possible structural phases (a) CoCrSb, (b) CoMoSb, and (c) CoWSb, respectively.

Table 2.
The optimized lattice constants, (Å), equilibrium energies, (Ry), bulk modulus, B (GPa), and pressure derivative for the bulk modulus, B for CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) for the three possible structural phases.
3.2. Magnetic Properties
The calculated total and partial magnetic moments for all phases are listed in Table 3. It is seen that for CoCrSb, irrespective of the structural phase, the major contribution to the total magnetic moment comes from the Y (Cr) atom, whereas, for the other two materials, i.e., CoYSb (Y = Mo and W), it is only in the Type-I phase that the major contributors to the magnetic moment come from the Y atom. As shown in Table 3, their primary contributions come from Co-atom for the structural phases Type-II and Type-III phases. This discrepancy is attributed to the higher lattice parameters as well as unstable phases in the atomic positions for Type-II and Type-III used in the calculations. However, irrespective of the structural phase, the total magnetic moments for CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, and W) are greater than 1, which indicates that these materials have ferromagnetic properties.

Table 3.
The calculated spin magnetic moments in for CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) compounds for the three possible structural phases comparing with available data.
Many half-Heusler alloys follow the Slater–Pauling (SP) rule = −18 [28,29] where is the total number of valence electrons and 18 means that there are 9 electrons occupied spin-down states per unit cell. CoMoSb and CoWSb, just like CoCrSb alloy, have 20 valence electrons, indicating that the total magnetic moment should be 2 . For our calculated values, this is in accord only with Type-I alloys, although the magnetic moment increase by 0.1 and 0.49 for CoCrSb and CoWSb, respectively, whereas it is reduced by 0.21 for CoMoSb alloy. This slight discrepancy is attributed to the position at the Fermi level. For CoCrSb and CoWSb, the pseudogap is slightly below the Fermi level, while for CoMoSb, the pseudogap is slightly higher than the Fermi level. These results are compared with the work of Galanakis and Dederichs [29] where RhMnIn and RhMnTl also show similar trends. In general, our calculated values for the magnetic moments are in good agreement with other calculated values available for Type-I CoCrSb and CoMoSb [14,16] with a minimal deviation of less than 1%.
3.3. Electronic Band Structure
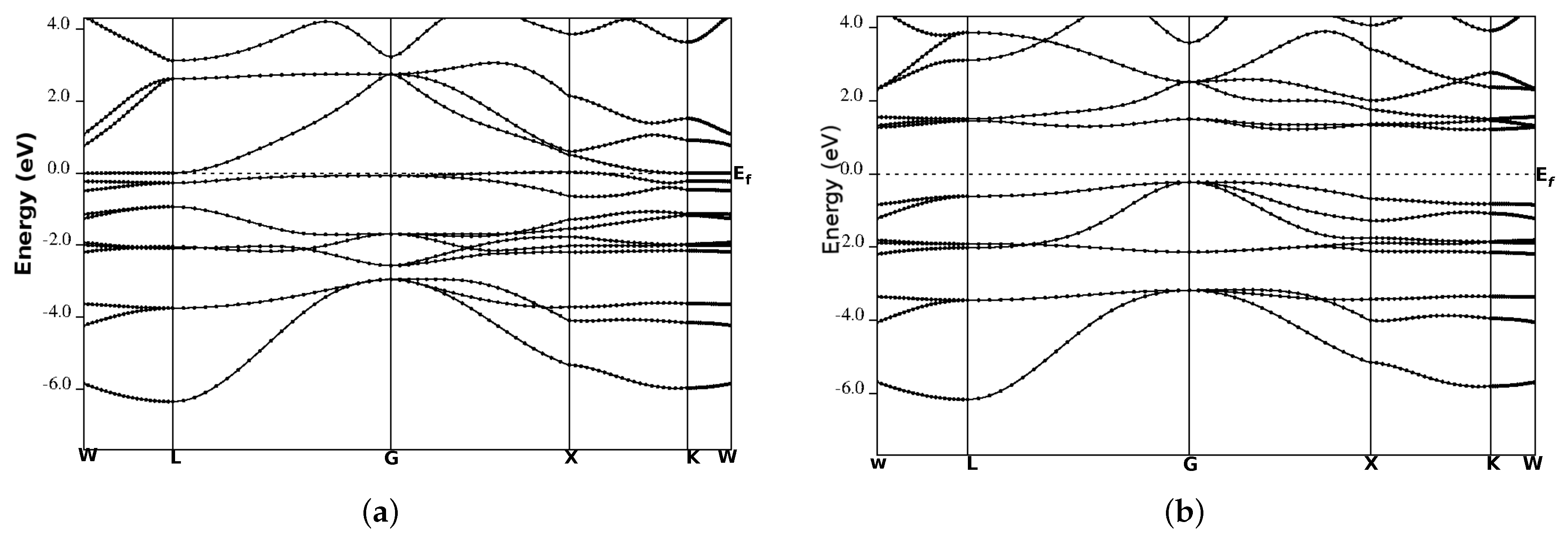
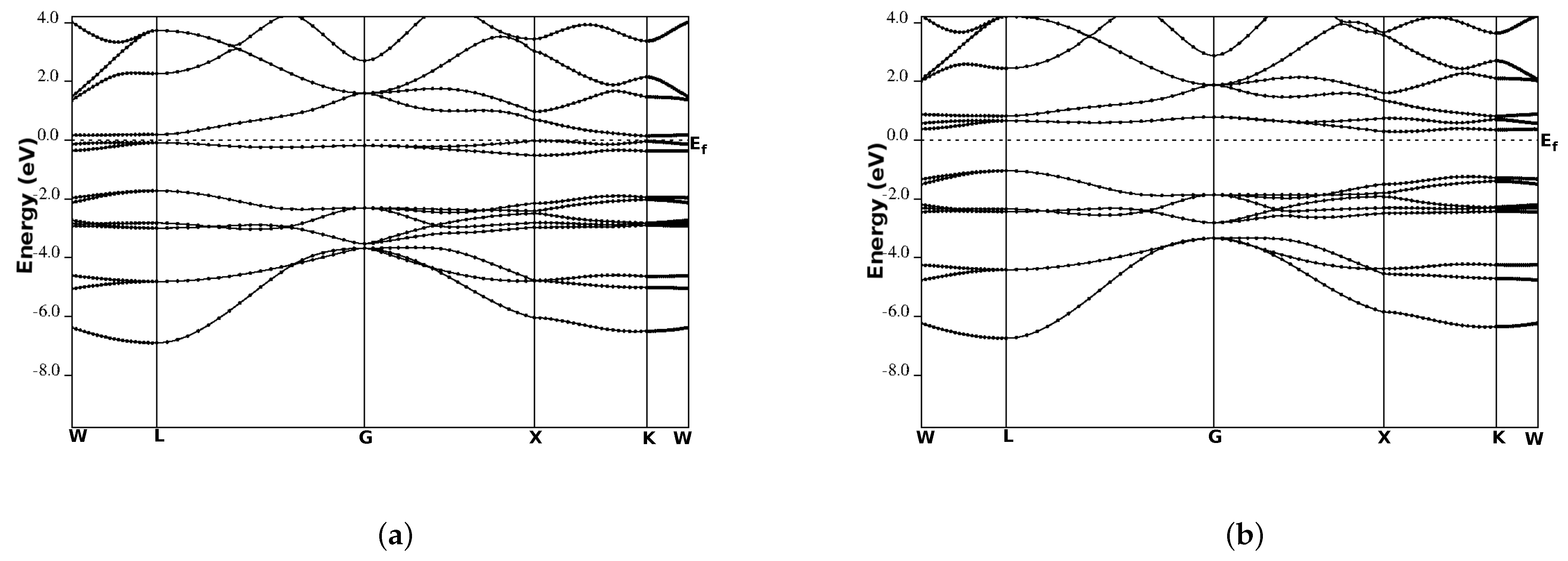
We performed the spin-polarized energy band structure calculations for structural phase Type-I in CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W). This was carried out using the calculated equilibrium lattice constants as well as the high symmetry directions in the first Brillouin zone, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. In both Figure 3 and Figure 4, the minority-spin (down) states lie within the semiconductor region and the majority (up) states in the metallic region. In Figure 3a and Figure 4a, the majority-spin channels energy bands exhibit metallic properties where orbitals overlap from the valence band to the conduction bands, whereas in the minority-spin, there is a gap separating the valence band from the conduction bands, as shown in Figure 3b and Figure 4b. These gaps in the minority spin revealed the half-metallic nature in CoCrSb and CoMoSb half-Heusler alloys. For CoCrSb alloy, the valence band maximum (VBM) occurs at the -point and the conduction band minimum (CBM) is located at the X-point, resulting in an energy band gap of 0.81 eV for this alloy. This band gap is in good agreement with the previously calculated value of 0.77 eV by Zhong-Yu et al. [16]. Meanwhile, for CoMoSb, minority-spin gaps become broader, and the Fermi level is pushed closer to the conduction bands of the minority-spin electrons. Here, the VBM is located at the L-point, and the CBM is at the X-point, which leads to an energy band gap of 0.32 eV, as presented in Figure 4b. This also indicates that CoMoSb is half-metallic since the alloy behaves like metal in the majority spin and shows semiconducting properties in the minority spin. We did not report on the metallic nature in CoWSb alloy because, at both majority and minority spin channels, the material has metallic properties.
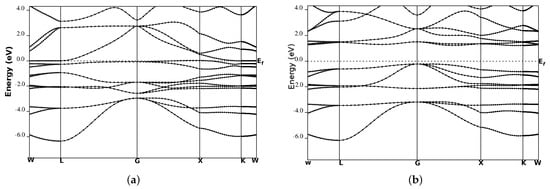
Figure 3.
Band structures for CoCrSb (a) majority-spin and (b) minority-spin. The Fermi level is indicated by the dashed horizontal line.
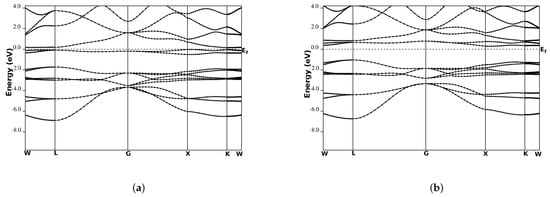
Figure 4.
Band structures for CoMoSb (a) majority-spin and (b) minority-spin. The Fermi level is indicated by the dashed horizontal line.
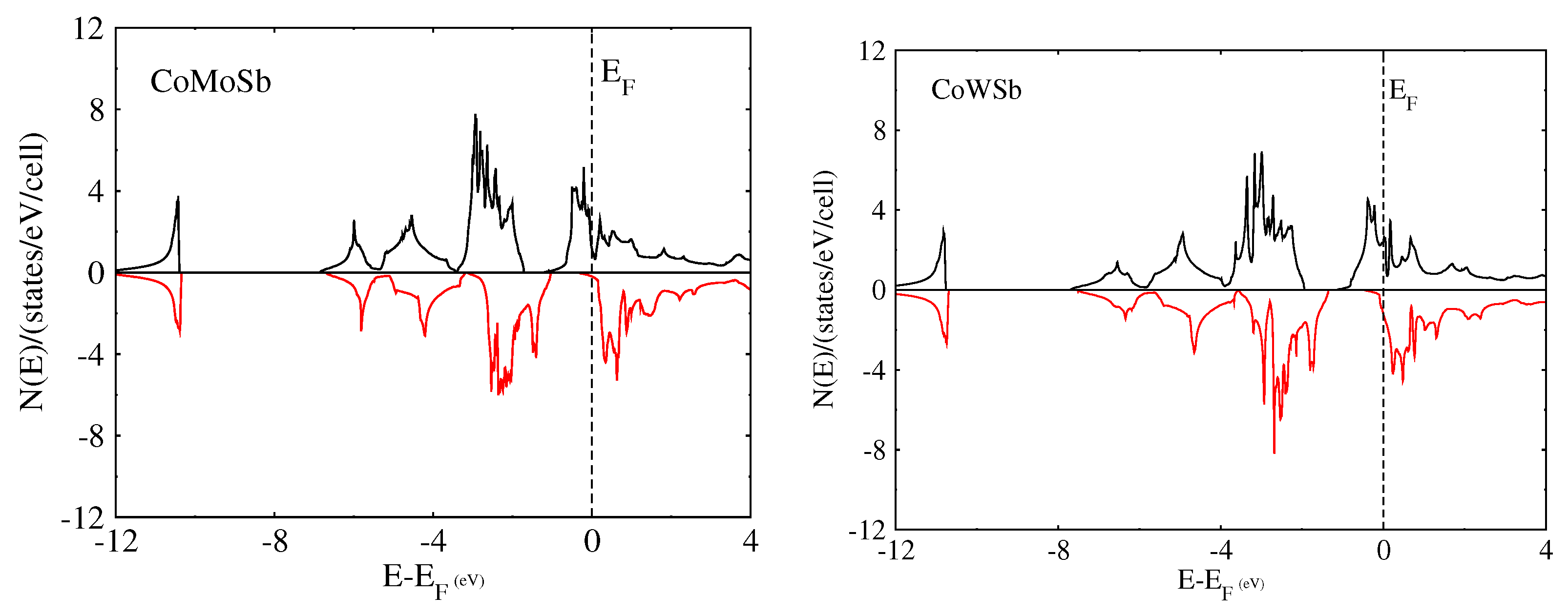
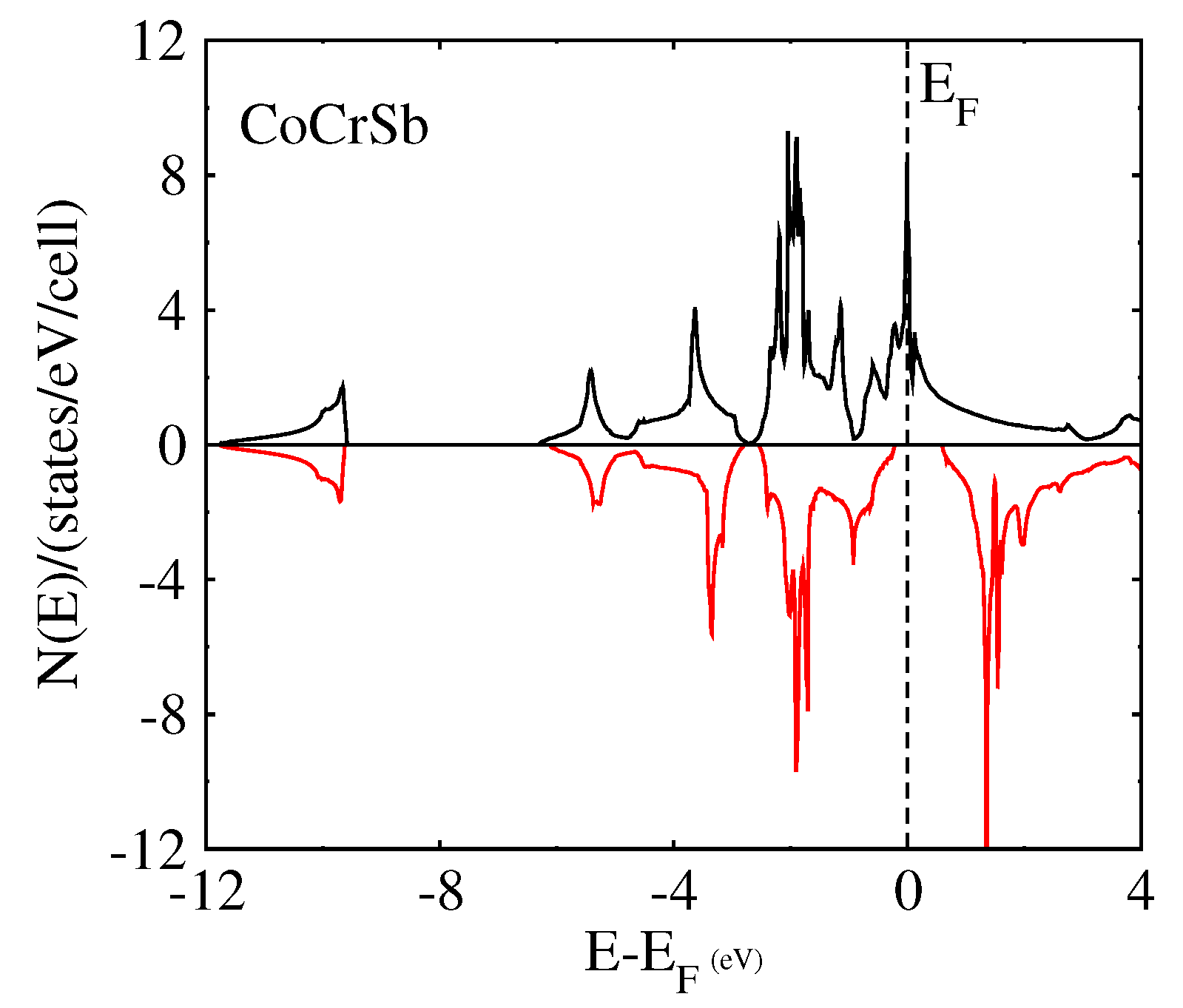
To further confirm the possibility of the half-metallicity of the CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) compounds, we calculated the total spin density of state (TDOS) and spin polarization percentage for CoCrSb, CoMoSb, and CoWSb, respectively. As a result, all these mentioned alloys show various degrees of half-metallic behaviors based on the spin-polarized calculation.
The half-metallicity decreases from 100% for CoCrSb to 33% for CoWSb and further confirm half-metallicity for CoCrSb, nearly half-metallic for CoMoSb, and metallic for CoWSb as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The calculated minority-spin band gap, half-metallic (HM) gap, and % spin polarization (SP) of Type I CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W).
The spin polarization (P) at the Fermi energy () was calculated via the following expression:
Figure 5 displays the total DOS in which for the majority-spin (up spin) channel, the energy bands exhibit a metallic overlap with the for all the alloys, whereas in the minority-spin (down spin) direction, an energy gap is opened and the locates within the gap for CoCrSb, slightly close to the conduction band for CoMoSb, and into the conduction band for CoWSb. Hence, CoCrSb is half-metallic (with spin polarized of 100%), CoMoSb is nearly half-metallic, and CoWSb is metallic, respectively.
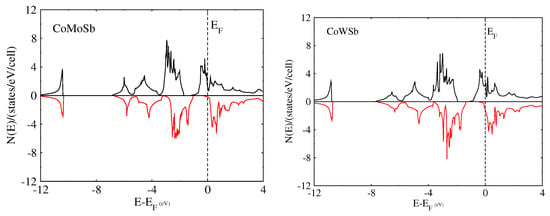
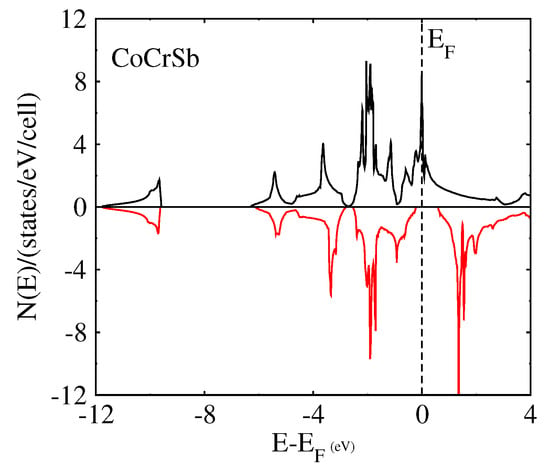
Figure 5.
Calculated total spin density of states (DOS) of Type-I CoYSb alloy.
3.4. Mechanical Properties
In this section, we discuss the mechanical properties and phase stability of the stable structure (Type-I), such as the elastic constants for a cubic structure, which are reduced into three independent elastic constants , , and , respectively. The link between mechanical and dynamic behavior of a material such as shear modulus (G), bulk modulus (B), and Young’s modulus (E) is usually obtained through the stress–strain method [30]. We test the mechanical stability of these compounds based on the durability of the crystal against external forces, which is a desirable property to ensure its sustainability in any application. The mechanical stability is evaluated according to the Born and Huang stability criteria for cubic structure [31].
The calculated elastic constants values for the stable Type-I structures of CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, and W) satisfy the above stability criteria. Hence, these compounds are mechanically stable, as shown from our results in Table 5. Furthermore, using the Voigt–Reuss–Hill approximation [32,33,34,35], the shear modulus (G), bulk modulus (B), Poisson’s ratio (), and Young’s modulus (E) were calculated using the following equations:

Table 5.
Various mechanical properties of CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) stable phase obtained from the calculated lattice.
The shear anisotropy (A), the Pugh’s [36] ratio, and the inverse, which is Frantsevich’s ratio, are given by the expression
The bulk (B) and shear (G) are important in alloy applications due to the empirical rule that materials with high B and G tend to have a high melting point and high Debye temperature. Generally, B and G show how resistive alloys are when subjected to fracture and plastic deformation, respectively. The higher the value B, the more its resistance to deformation due to pressure. CoWSb resistance to pressure is stronger than that of CoMoSb and CoCrSb alloy, respectively, as shown in Table 5. The value of shear modulus G shows the resistance of a material to deformation by shear stress. The higher the value G, the higher its resistance to shear stress. Hence, CoCrSb > CoMoSb > CoWSb. The Young’s modulus E characterizes the material’s stiffness, and the higher the value E, the stiffer is the material. Therefore, as shown in Table 5, CoCrSb is stiffer than CoMoSb, and CoWSb is the least stiffer. The unidirectional elastic constant is much higher than indicating that these compounds present weaker resistance to pure shear deformation compared to resistance to unidirectional compression.
The condition for Zener (anisotropy) to predict anisotropic and isotropic material is that when the cubic shear anisotropy factor is greater or less than 1, the material is said to be anisotropic, but when it is equal to unity, then isotropic [37]. Based on this, we deduced the cubic shear anisotropy factor [38] for these compounds using Equation (7). Our results were subject to the condition stated above. Our calculated result shows anisotropy factors as 0.49, 0.64, and 0.45 for CoCrSb, CoMoSb, and CoWSb, respectively. From these values, one can conclude that these compounds are substantially anisotropic in nature. The degree of ductility of a material is explained by the Pugh ratio, which is the ratio of the bulk and shear modulus of the material. The material is said to be more ductile if the Pugh’s ratio increases more and it is greater than 1.75 (G/B < 0.57) [39]; otherwise, it is brittle. As shown in Table 5, we can see that the compounds are ductile in nature because their values are greater than 1.75. The Poisson’s ratio () characterizes the bonding forces in material and its compression against external forces [40,41]. The alloys reported in this work are central-force solid ( is generally between 0.25 to 0.5) and incompressible because is due to their values that lie within this range. Hence, indicating that the metallic bonding contribution to the atomic bond is dominant.
3.5. Thermodynamic Properties
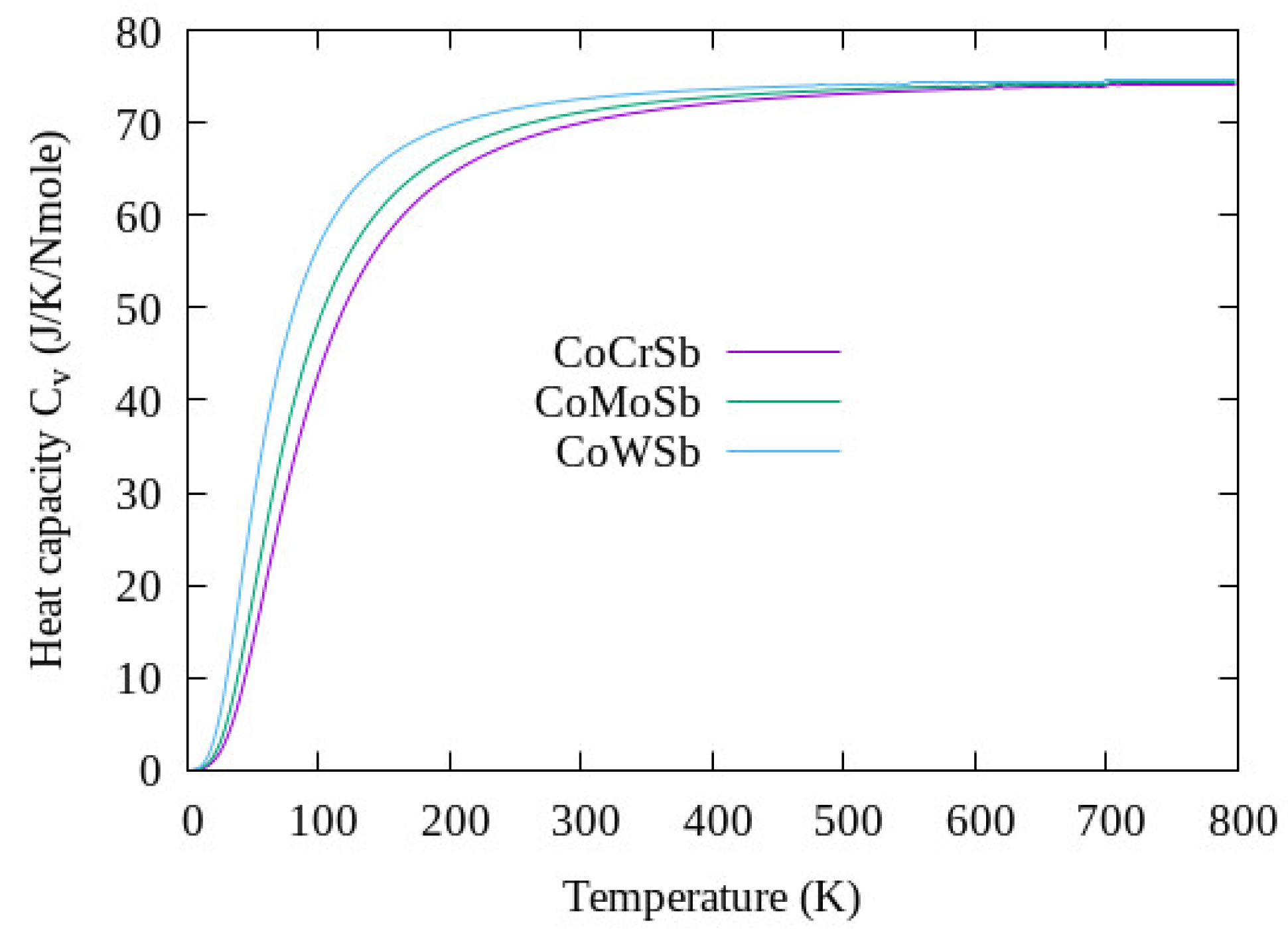
The effects of temperature at constant pressure on the thermodynamic properties of the CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) material from the state equation, considering the quasiharmonic approximation of the Debye model, were analyzed as presented below. Figure 6 shows the behavior of specific heat at constant volume, , as a temperature function, which varied from 0 K to 800 K at constant pressure.
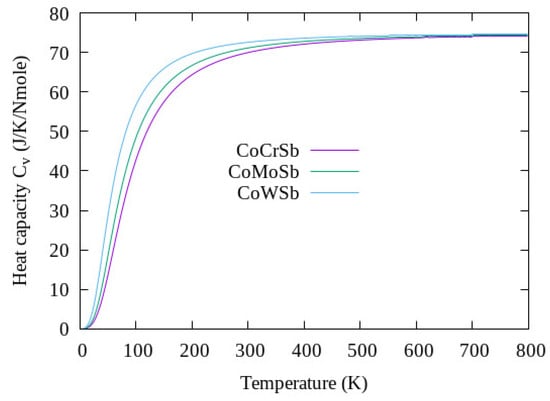
Figure 6.
Heat capacity against temperature for Type-I CoYSb alloy.
It can be seen from Figure 6 the trend of the specific heat toward the Dulong–Petit limit, which is the specific heat value independent of temperature. From this limit value of Dulong–Petit, as the temperature increases, each of the atoms in the material absorbs the same amount of energy proportional to the temperature increase. This value corresponds to 72.63 J/Nmol.K for CoCrSb and CoMoSb, respectively, while it reads 73.47 J/Nmol.K for CoWSb. The Debye temperature is a fundamental parameter of thermodynamic, which is linked with many physical properties of the material such as the melting temperature, lattice vibrations, and specific heat at low temperature [42]. These properties listed in Table 6 were obtained from the calculated elastic constants using the following equations
where () is the compressional velocity and () the shear sound velocity. The average sound velocity () is expressed in terms of compressional and shear sound velocities, as stated below.

Table 6.
Average sound velocity (), compressional velocity (), shear sound velocity (), Debye temperature (), and predicted melting temperature () for the stable phase CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W).
The Debye temperature is thus expressed as
where ℏ is the reduced Planck’s constant, is Boltzmann’s constant, is Avogadro’s number, M is the atomic mass of a unit cell, n is the number of atomic per formula unit, and is the density.
The covalence bonds strength in solids is characterized by Debye temperature, which is listed in the table above along with the predicted melting temperature estimated from our elastic constant calculated using the following expression [43].
Our analysis how that CoCrSb has stronger bonds than CoMoSb and CoWSb due to its higher Debye temperature.
4. Conclusions
We have investigated the structural, mechanical, electronic, and thermodynamic properties of Co-based half-Heusler CoYSb (Y = Cr, Mo, W) alloys. These alloys conform to space group in the three possible atomic arrangements—the so called Type-I, Type-II, and Type-III structural phases. We determined and reported the stable atomic positions of these alloys. The optimized structures and calculated total magnetic moments show that these alloys are ferromagnetic in all three phases. Electronic band structures analysis show that CoCrSb and CoMoSb are half-metallic and nearly half-metallic, respectively, in nature. This is complemented with their percentage of spin polarization and confer to these materials potential uses in spintronic. We also confirmed their mechanical stability and predicted their anisotropy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A.A. and O.T.U.; methodology, G.A.A.; validation, O.T.U., P.O.A., J.O.A., S.K. and G.A.A.; writing—O.T.U., and P.O.A.; writing—review and editing. J.O.A., S.K. and G.A.A.; supervision, G.A.A., J.O.A. and S.K.; project administration, G.A.A., J.O.A. and S.K.; funding acquisition, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Stephane Kenmoe gratefully acknowledges the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) for the funding 388390466–TRR 247.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kieven, D.; Klenk, R.; Naghavi, S.; Felser, C.; Gruhn, T. I-II-V half-Heusler compounds for optoelectronics: Ab initio calculations. Phys. Rev. 2010, B81, 075208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurmehl, S.; Fecher, G.H.; Kandpal, H.C.; Kseno-fontov, V.; Felser, C.; Lin, H.J.; Morais, J. Geometric, electronic, and magnetic structure of Co2FeSi: Curie temperature and magnetic moment measurements and calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 184434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, S.A.; Awschalom, D.D.; Buhrman, R.A.; Daughton, J.M.; von Molnar, S.; Roukes, M.L.; Chtchelkanova, A.Y.; Treger, D.M. Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 2001, 294, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Bennett, J.W.; Rabe, K.M.; Vanderbilt, D. Half-Heusler semiconductors as piezoelectrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 037602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, D.; Yao, Y.; Feng, W.; Wen, J.; Zhu, W.; Chen, X.Q.; Stocks, G.M.; Zhang, Z. Half-Heusler compounds as a new class of three-dimensional topological insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 096404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Wray, L.A.; Xia, Y.; Xu, S.; Jia, S.; Cava, R.J.; Bansil, A.; Hasan, M.Z. Half-Heusler ternary compounds as new multifunctional experimental platforms for topological quantum phenomena. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeeshan, M.; Singh, H.K.; den Brink, J.V.; Kandpal, H.C. Ab initio design of new cobalt based half-Heusler materials for thermoelectric application. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 075407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minami, S.; Fumiyuki, I.; Yo, M.P.; Mineo, S. First-Principle study on thermoelectric properties of half-Heusler compound CoMSb (M= Sc, Ti, V, Cr and Mn). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 032403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.D.; Yuan, Z.R.; Lu, L.Y.; Liu, M.M.; Huang, Z.G.; Zhang, F.M.; Du, Y.W. Effect of annealing on the magnetic entropy change of CoMnSb alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 428, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.; Mahanti, S.D.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Structural stability of Ni-containing half-Heusler compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancoff, F.B.; Bobo, J.F.; Richter, O.E.; Bessho, K.; Johnson, P.R.; Sinclair, R.; Nix, W.D.; White, R.; Clemens, B.M. Growth and characterization of epitaxial NiMnSb/PtMnSb C1b Heusler alloy superlattices. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.A.; Mueller, F.M.; van Engen, P.G.; Buschow, K.H.J. New class of materials: Half-metallic ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanakis, I.; Mavropoulos, P.; Dederichs, P.H. Electronic structure and Slater Pauling behaviour in half-metallic Heusler alloys calculated from first principles. J. Phys. D 2006, 39, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, B.R.K.; Dasgupta, J.I. Electronic structure and magnetism in half-Heusler compounds. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 73077323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanpal, H.C.; Felse, C.; Seshadri, R. Covalent bonding and the nature of band gaps in some half-Heusler compounds. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong-Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Meng-Mei, P.; Shu-Juan, S. First-principle studies of half-metallicities and magnetisms of the semi-Heusler alloys CoCrTe and CoCrSb. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 127501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobola, J.; Pierre, J. Electronic phase diagram of the XTZ (X= Fe, Co, Ni; T= Ti, V, Zr, Nb, Mn; Z= Sn, Sb) semi-Heusler compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 296, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkova, S.E.; Eremeev, S.V.; Kakeshita, T.; Kulkov, S.S.; Rudenski, G.E. The electronic structure and magnetic properties of full-and half-Heusler alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scandolo, S.; Giannozzi, P.; Cavaoni, C.; de Gironcoli, S.; Pasquarello, A.; Baroni, S. First-principles codes for computational crystallography in the Quantum-ESPRESSO package. Z. Krist. 2005, 220, 574579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Baroni, S.; Bonini, N.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Cococcioni, M.; Dabo, I.; et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: A modular and open-source software project for quantum. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Andreussi, O.; Brumme, T.; Bunau, O.; Nardelli, M.B.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Cococcioni, M.; et al. Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with Quantum ESPRESSO. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 465901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://dalcorso.github.io/thermopw (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Corso, A.D. Elastic constants of beryllium: A first-principles investigation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 075401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyckoff, R.W.G. Crystal Structures, Crystal Structures, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1963; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Murnaghan, F.D. The Compressibility of Media under Extreme Pressures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1944, 30, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubler, J. First principle theory of metallic magnetism. Phys. B+C 1984, 127, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I.; Dederichs, P.H.; Mavropoulous, P.H. Slater-Pauling behavior and origin of the half-metallicity of the full-Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 174429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, Y.L.; Saxe, P. Symmetry-general least-squares extraction of elastic data for strained materials from ab initio calculations of stress. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, M.; Huang, K. Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices. Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices; Oxford Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1956; pp. 120–156. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, W. Lehrbuck der Kristallphysik; B. B. Teubner: Leipzig, Germany, 1928; p. 739. [Google Scholar]
- Reuss, A.; Angew, Z. Calculation of the centrifugal limit of mixed crystals due to the plasticity condition for single crystals. Math. Mech. 1929, 9, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R. The elastic behaviour of a crystalline aggregate. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 1952, 65, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, H.B. Solid State Physics, F. Seitz and D. Properties of Engineering Ceramics; Kriegel, W., Palmour, H., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1958; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, S.F. Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Philos. Mag. 1954, 45, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, J.; Jain, V.k.; Chandra, A.R.; Jain, V.; Lakshmi, N. Joural of Superconductivity and Magnetism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zener, C. Elasticity and Anelasticity of Metals; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Degheidy, A.R.; Elkenany, E.B. Electronic, optical, and mechanical properties of BN, AlN, and InN with zinc-blende structure under pressure. Chin. Phys. 2017, 26, 086103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.C.; Ghosh, S.J. First-principal study of full Heusler alloys Co2VZ (Z = As, In). Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 435, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, D.; Peng, F.; Gao, T.; Cheng, X. Ab initio calculations of elastic constants and thermodynamic properties of NiAl under high pressures. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 44, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.L. A simplified method for calculating the Debye temperature from elastic constants. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1963, 24, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, M.E.; Brown, L.D.; Marcus, H.L. Elastic constants versus melting temperature in metals. Scr. Metall. 1984, 18, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).