From Agro-Industrial Waste to Gold Lixiviant: Evaluating Cassava Wastewater Applications in Artisanal Mining
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Leaching with Manipueira in Natura
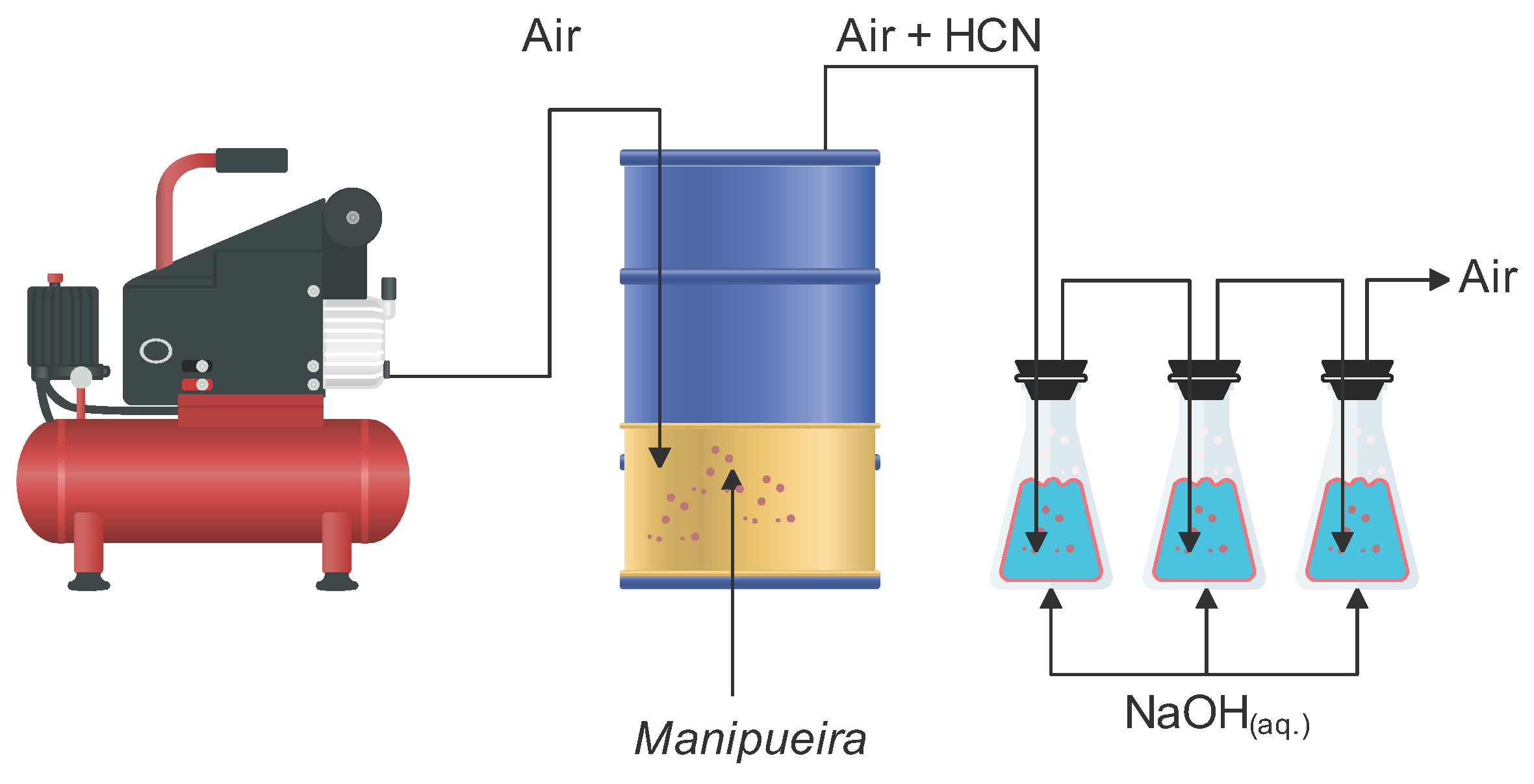
3.2. Concentrating Cyanide from Manipueira
3.3. Laboratory Analysis and Metallurgical Balance of Au
3.4. Data Analysis and Experimental Limitations
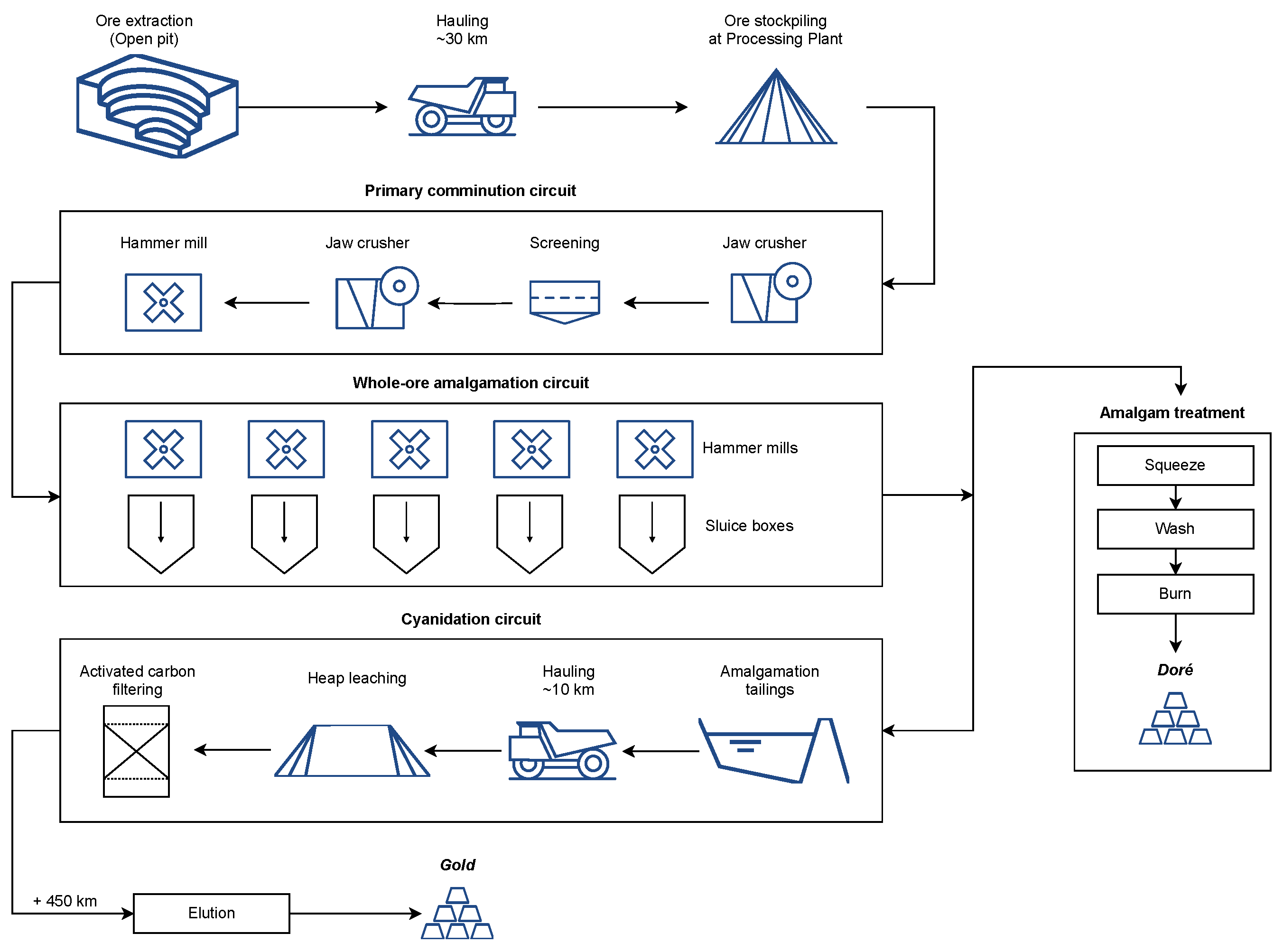
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Lixiviant and Ore Characterization
4.2. Gold Leaching Performance
4.3. Interpretation of Leaching Behavior
4.4. Cyanide Consumption and pH Control
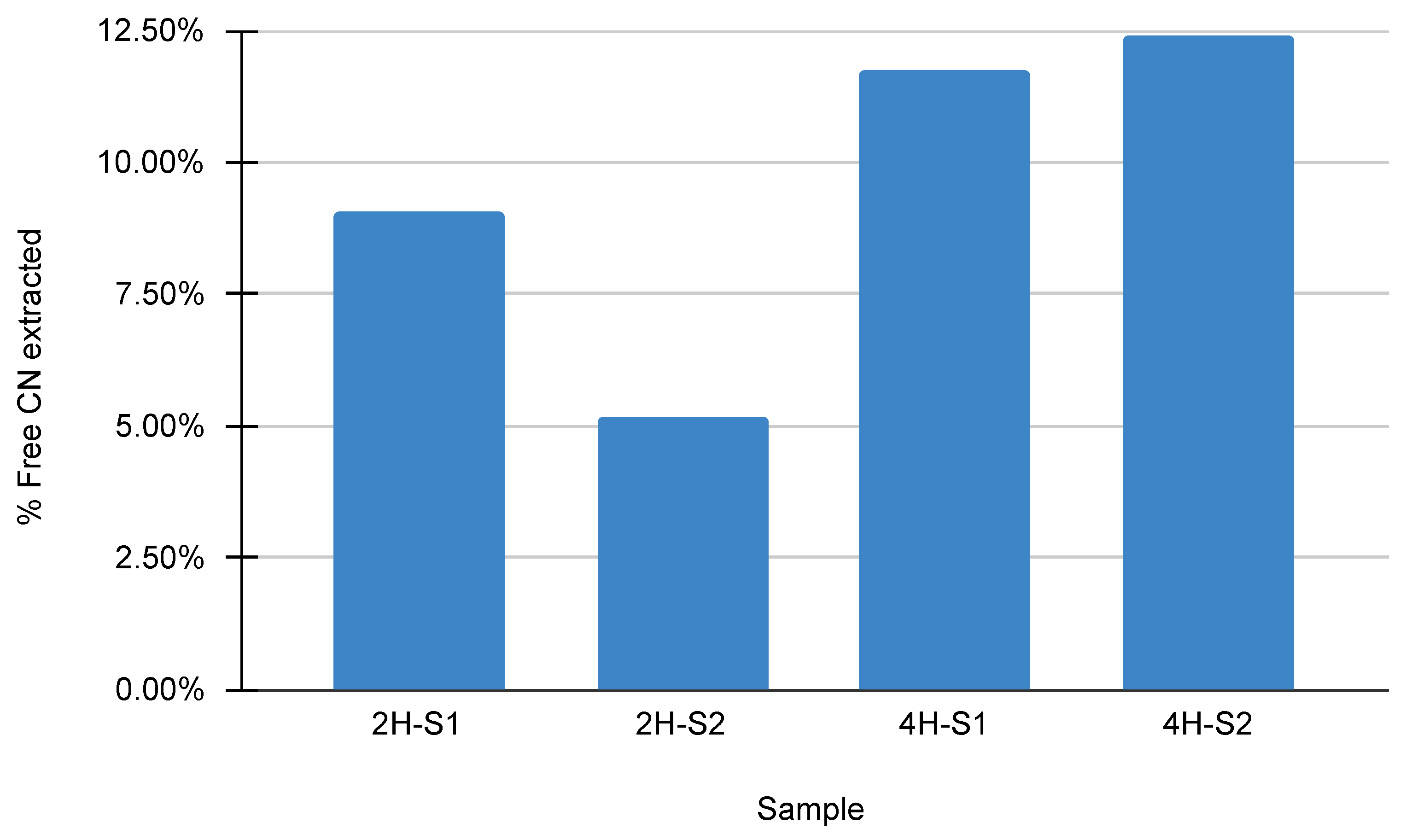
4.5. Cyanide Stripping and Concentration Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esdaile, L.J.; Chalker, J.M. The Mercury Problem in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6905–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Smits, K.; Phelan, T. Quantifying mercury use in artisanal and small-scale gold mining for the Minamata Convention on Mercury’s national action plans: Approaches and policy implications. Environ. Sci. Policy 2023, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, H.; O’Leary, K.G. Mercury Exposure and Health Impacts among Individuals in the Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Community: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Elbel, J.; Nordberg, G.; Lucchini, R.; Bartrem, C.; Grandjean, P.; Mergler, D.; Moyo, D.; Nemery, B.; et al. Reducing disease and death from Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM)-the urgent need for responsible mining in the context of growing global demand for minerals and metals for climate change mitigation. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G. Abatement of mercury pollution in the small-scale gold mining industry: Restructuring the policy and research agendas. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Watari, T.; Seccatore, J.; Nakajima, K.; Nansai, K.; Takaoka, M. A review of gold production, mercury consumption, and emission in artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASGM). Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Global Mercury Assessment 2018; Technical Report; United Nations Environment Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- World Bank. 2023 State of the Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining Sector; Technical Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel, T.; Hruschka, F.; Priester, M. Global Report on Artisanal & Small-Scale Mining; Technical Report; International Institute for Environment and Development: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Meutia, A.A.; Bachriadi, D.; Gafur, N.A. Environment Degradation, Health Threats, and Legality at the Artisanal Small-Scale Gold Mining Sites in Indonesia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, A.K.; Ghoveisi, H.; Bonzongo, J.C.J. Use of Metallic Mercury in Artisanal Gold Mining by Amalgamation: A Review of Temporal and Spatial Trends and Environmental Pollution. Minerals 2024, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seney, C.S.; Bridges, C.C.; Aljic, S.; Moore, M.E.; Orr, S.E.; Barnes, M.C.; Joshee, L.; Uchakina, O.N.; Bellott, B.J.; McKallip, R.J.; et al. Reaction of Cyanide with Hg0 -Contaminated Gold Mining Tailings Produces Soluble Mercuric Cyanide Complexes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2834–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Fytas, K. Mercury Management in Small-Scale Mining. Int. J. Surf. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2002, 16, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vásquez, R.; García-Martínez, M.J.; Bolonio, D. Investigation of Gold Recovery and Mercury Losses in Whole Ore Amalgamation: Artisanal Gold Mining in Nambija, Ecuador. Minerals 2023, 13, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro de Tecnologia Mineral (CETEM). Mineral Data; Centro de Tecnologia Mineral: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Manzolli, B.; Rajão, R.; Bragança, A.C.H.; de Alcântara, G.K.; Nunes, F.; Filho, B.S. Legalidade da Produção de Ouro no Brasil; Editora IGC/UFMG: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cleary, D. Anatomy of the Amazon Gold Rush; Palgrave Macmillan UK: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzino, M.; Seccatore, J.; Marin, T.; De Tomi, G.; Veiga, M.M. Gold losses and mercury recovery in artisanal gold mining on the Madeira River, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 102, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, M.M.; Hinton, J.J. Abandoned artisanal gold mines in the Brazilian Amazon: A legacy of mercury pollution. Nat. Resour. Forum 2002, 26, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.C.; Souza, J.D.; D rea, J.G.; Jardim, W.F.; Fadini, P.S. Mercury Biomagnification in a Tropical Black Water, Rio Negro, Brazil. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 45, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, J.R.D. Mercury in the Amazon: Problem or opportunity? A commentary on 30 years of research on the subject. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2020, 8, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulet, M. Methylmercury in water, seston, and epiphyton of an Amazonian river and its floodplain, Tapajos River, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 261, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.O.; Marshall, B.G.; Kaplan, R.J.; Moreno-Chavez, J.; Veiga, M.M. Evidence of reduced mercury loss and increased use of cyanidation at gold processing centers in southern Ecuador. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbrugge, B.; Lanzano, C.; Libassi, M. The cyanide revolution: Efficiency gains and exclusion in artisanal- and small-scale gold mining. Geoforum 2021, 126, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, A.; Figueroa, L.; Wang, W.; Smith, N.M.; Ranville, J.F.; Vuono, D.C.; Alejo Zapata, F.D.; Morales Paredes, L.; Sharp, J.O.; Bellona, C. Transitional dynamics from mercury to cyanide-based processing in artisanal and small-scale gold mining: Social, economic, geochemical, and environmental considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosai, S.; Nakajima, K.; Yamasue, E. Mercury mitigation and unintended consequences in artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, M.M.; Angeloci, G.; Hitch, M.; Colon Velasquez-Lopez, P. Processing centres in artisanal gold mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youpoungam, A.A.; Kantarcı, S.; Alp, İ. Characterization and Reprocessing of Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mine Tailings. Min. Metall. Explor. 2024, 41, 2603–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nheta, W.; Nkwinika, M.; Mailula, M. Optimisation of gold recovery from small scale custom mills. In Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM’20), Virtual Conference, 16–18 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, D.; Adiansyah, J.S.; Matrani, B.F.A.; Johari, H.I. Mercury Reduction on Gold Extraction in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining. A Case Study in Pelangan Village, West Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1175, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, H.A.M.; Guimarães, J.R.D. Mercury cyanide complexes and their relevance as environmental contaminants. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drace, K.; Kiefer, A.M.; Veiga, M.M. Cyanidation of Mercury-Contaminated Tailings: Potential Health Effects and Environmental Justice. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi, D.; Fajon, V.; Kotnik, J.; Shlyapnikov, Y.; Adotey, D.K.; Serfor-Armah, Y.; Horvat, M. Mercury methylation in cyanide influenced river sediments: A comparative study in Southwestern Ghana. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.N.; Veiga, M.M.; Klein, B.; Telmer, K.; Gunson, A.J.; Bernaudat, L. Strategies for reducing the environmental impact of reprocessing mercury-contaminated tailings in the artisanal and small-scale gold mining sector: Insights from Tapajos River Basin, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzila, A.N.; Moyo, T.; Petersen, J. A Study on the Applicability of Agitated Cyanide Leaching and Thiosulphate Leaching for Gold Extraction in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining. Minerals 2022, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohio, E.N.; Sossou, S.K.; Karoui, H.; Yacouba, H. Environmental Cyanide Pollution from Artisanal Gold Mining in Burkina Faso: Human Exposure Risk Analysis Based on a Conceptual Site Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, T. International cyanide management code. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15, pp. 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. Gold–An historical introduction. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15, pp. xxv–xlvii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müezzinogˇlu, A. A Review of Environmental Considerations on Gold Mining and Production. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 33, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüger, A.; Fafilek, G.; Restrepo B., O.J.; Rojas-Mendoza, L. On the volatilisation and decomposition of cyanide contaminations from gold mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, J.O. The Chemistry of Gold Extraction, 2nd ed.; SME: Littleton, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.D. Summary of gold plants and processes. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Massaro, L.; De Theije, M. Understanding small-scale gold mining practices: An anthropological study on technological innovation in the Vale do Rio Peixoto (Mato Grosso, Brazil). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 618–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, J.; Torres, R. Prospects for thiourea as a leaching agent in Colombian gold small-scale mining: A comprehensive review. J. Sustain. Min. 2022, 21, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzombak, D.A.; Ghosh, R.S.; Wong-Chong, G.M. (Eds.) Cyanide in Water and Soil, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botz, M.; Mudder, T.; Akcil, A. Cyanide treatment: Physical, chemical and biological processes. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15, pp. 672–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillison, D. Cyanide Remediation: Current and Past Technologies. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on Hazardous Waste Research, Manhattan, KS, USA, 23–24 May 1995. [Google Scholar]
- The Cyanide Code. The International Cyanide Management Institute (ICMI). The Cyanide Code. Available online: https://cyanidecode.org/becoming-a-signatory/becoming-a-participant/document-library/ (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Fleming, C.A. The Economic and Environmental Case for Recovering Cyanide from Gold Plant Tailings; SGS Minerals Services Technical Paper 2003-02; SGS Minerals Services: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, C. Cyanide recovery. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15, pp. 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulvianti, M.; Zidorn, C. Chemical Diversity of Plant Cyanogenic Glycosides: An Overview of Reported Natural Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piršelová, B.; Jakubčinová, J. Plant cyanogenic glycosides: From structure to properties and potential applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1612132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.A. Why are so many food plants cyanogenic? Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, I.A.; Pinotti, M.H.P. Cyanogenic glycosides in plants. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2000, 43, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolarinwa, I.F.; Oke, M.O.; Olaniyan, S.A.; Ajala, A.S. A Review of Cyanogenic Glycosides in Edible Plants. In Toxicology—New Aspects to This Scientific Conundrum; Soloneski, S., Larramendy, M., Eds.; InTech: Houston, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attahdaniel, B.E.; Ebisike, K.; Adeeyinwo, C.E.; Adetunji, A.R.; Olusunle, S.O.O.; Adewoye, O.O. Production of Sodium Cyanide from Cassava Wastes. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 707–709. [Google Scholar]
- Monga, I.; Paul, V.; Muniyasamy, S.; Zinyemba, O. Green Synthesis of Sodium Cyanide Using Hydrogen Cyanide Extracted under Vacuum from Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) Leaves. Sustain. Chem. 2022, 3, 312–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndubuisi, N.D.; Chidiebere, A.C.U. Cyanide in Cassava: A Review. Int. J. Genom. Data Min. 2018, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Gleadow, R.; Cliff, J.; Zacarias, A.; Cavagnaro, T. Cassava: The Drought, War and Famine Crop in a Changing World. Sustainability 2010, 2, 3572–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.; Mirione, E.; Ernesto, M.; Massaza, F.; Cliff, J.; Rezaul Haque, M.; Bradbury, J. Processing of cassava roots to remove cyanogens. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 18, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.L.R.; Bradbury, J.H. Bitterness of cassava: Identification of a new apiosyl glucoside and other compounds that affect its bitter taste. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1995, 68, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiwona-Karltun, L.; Brimer, L.; Kalenga Saka, J.D.; Mhone, A.R.; Mkumbira, J.; Johansson, L.; Bokanga, M.; Mahungu, N.M.; Rosling, H. Bitter taste in cassava roots correlates with cyanogenic glucoside levels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, P.; Veiga, M.; De Andrade Lima, L.; Oliveira, L.; Motta, J.; Jesus, J.; Lavkulich, L. Leaching gold with cassava: An option to eliminate mercury use in artisanal gold mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, P.; Veiga, M. Comparing cyanidation with amalgamation of a Colombian artisanal gold mining sample: Suggestion of a simplified zinc precipitation process. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2023, 13, 101208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anene, N.C.; Dangulbi, B.M.; Veiga, M.M. Assessment of Gold and Mercury Losses in an Artisanal Gold Mining Site in Nigeria and Its Implication on the Local Economy and the Environment. Minerals 2024, 14, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Wan, R.Y.; Díaz, X. Preg-robbing gold ores. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 15, pp. 937–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Rosales, E.; Camporredondo Saucedo, J.; Kudriavtsev, Y.; Mamani Maron, G.; Rojas Venegas, F.; Castruita Avila, L. Study of Preg-Robbing with Quicklime in Gold Cyanide Solutions Analyzed by Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry. Metals 2024, 14, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönen, N.; Kabasakal, O.; Özdil, G. Recovery of cyanide in gold leach waste solution by volatilization and absorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 113, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Cyanide (ppm) | pH Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Mid-Cycle | Final | Initial | Final |
| 250 | <10 | 20 | 4.1 | 9.9–10.4 |
| 250 | 30 | 20 | 4.1–4.4 | 10.3–10.8 |
| 250 | 30 | 20 | 5.9 | 10.4–10.5 |
| 250 | 30 | 20 | 4.4–5.9 | 10.3–10.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, E.M.; Barreto, M.d.C.S.; Veiga, M.M.; De Tomi, G. From Agro-Industrial Waste to Gold Lixiviant: Evaluating Cassava Wastewater Applications in Artisanal Mining. Mining 2025, 5, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040064
Silva EM, Barreto MdCS, Veiga MM, De Tomi G. From Agro-Industrial Waste to Gold Lixiviant: Evaluating Cassava Wastewater Applications in Artisanal Mining. Mining. 2025; 5(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Emiliano Mendonça, Maria do Carmo S. Barreto, Marcello M. Veiga, and Giorgio De Tomi. 2025. "From Agro-Industrial Waste to Gold Lixiviant: Evaluating Cassava Wastewater Applications in Artisanal Mining" Mining 5, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040064
APA StyleSilva, E. M., Barreto, M. d. C. S., Veiga, M. M., & De Tomi, G. (2025). From Agro-Industrial Waste to Gold Lixiviant: Evaluating Cassava Wastewater Applications in Artisanal Mining. Mining, 5(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040064







