Emotions during the Pandemic’s First Wave: The Case of Greek Tweets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Mining
…contains 237M Tweet IDs for Twitter posts that mentioned “COVID” as a keyword or as part of a hashtag (e.g., COVID-19, COVID19) between March and July of 2020. Sampling Method: hourly requests sent to Twitter Search API using Social Feed Manager, an open-source software that harvests social media data and related content from Twitter and other platforms. NOTE: (1) In accordance with Twitter API Terms, only Tweet IDs are provided as part of this dataset. (2) To recollect tweets based on the list of Tweet IDs contained in these datasets, you will need to use tweet ‘rehydration’ programs like Hydrator (…) or Python library Twarc (…). (3) This dataset, like most datasets collected via the Twitter Search API, is a sample of the available tweets on this topic and is not meant to be comprehensive. Some COVID-related tweets might not be included in the dataset either because the tweets were collected using a standardized but intermittent (hourly) sampling protocol or because tweets used hashtags/keywords other than COVID (e.g., Coronavirus or #nCoV). (4) To broaden this sample, consider comparing/merging this dataset with other COVID-19 related public datasets…
3.2. The Enrichment of the Greek Corpus
- A selection of tweets identified as using the Greek language. The reconstruction of the network of hashtags used in those tweets;
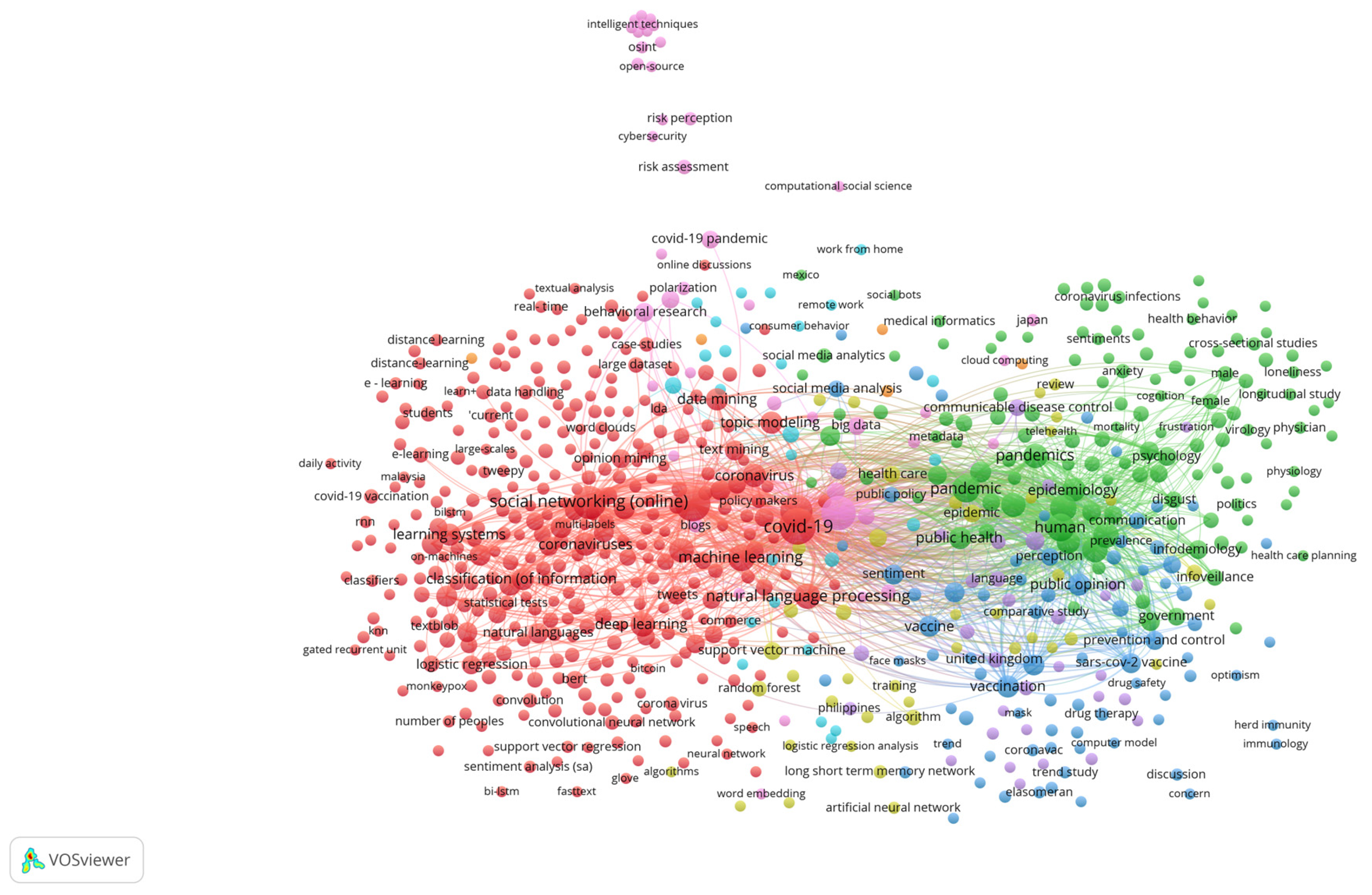
- Hashtag network analysis: This network is an undirected graph capturing the co-occurrence of hashtags in the same tweet, creating an edge for each pair of hashtags (Figure 2). We identified groups of hashtags appearing together more often, algorithmically organized into clusters (modularity classes) of strongly interconnected hashtags, shown in Figure 2 under different colors. Different attitudes towards the pandemic or containment policies are expected to use different hashtags. The nodes were ranked according to PageRank algorithm [17], which calculates both the degree of a node (i.e., the number of its connections to other nodes) and the connection to important nodes (highly influential nodes) [18].
- We selected hashtags with the highest PageRank, excluding those non-country-specific and including hashtags from various groups (modularity classes), to ensure diversity. This resulted to a list of 50–75 hashtags per month (Appendix A, Table A2).
- A search was conducted via Twitter API using the twarc2 library for the Python programming language querying for those hashtags to produce the final corpus of Greek tweets.
3.3. Restrictions
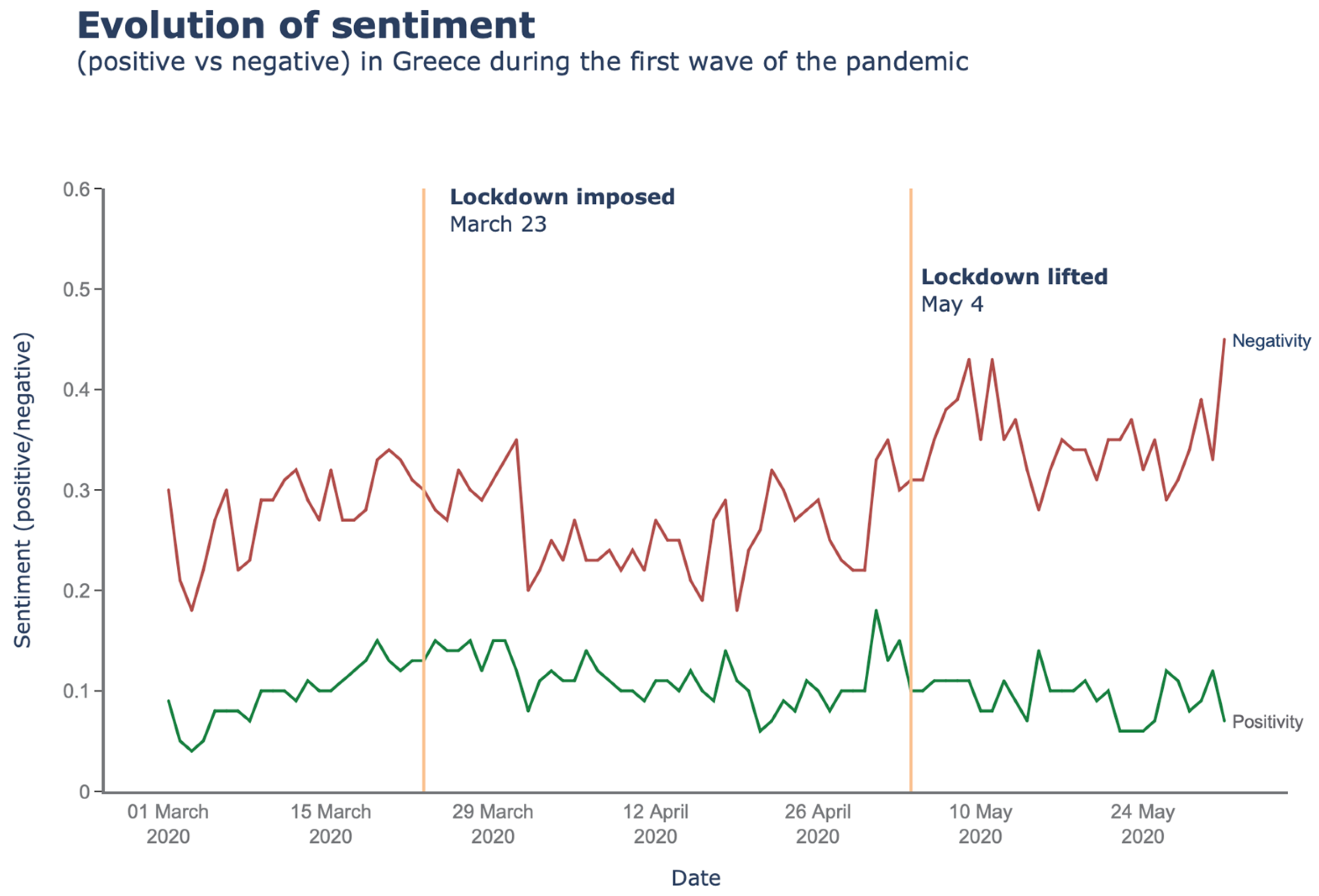
3.4. Sentiment Analysis
3.5. Social Network Analysis
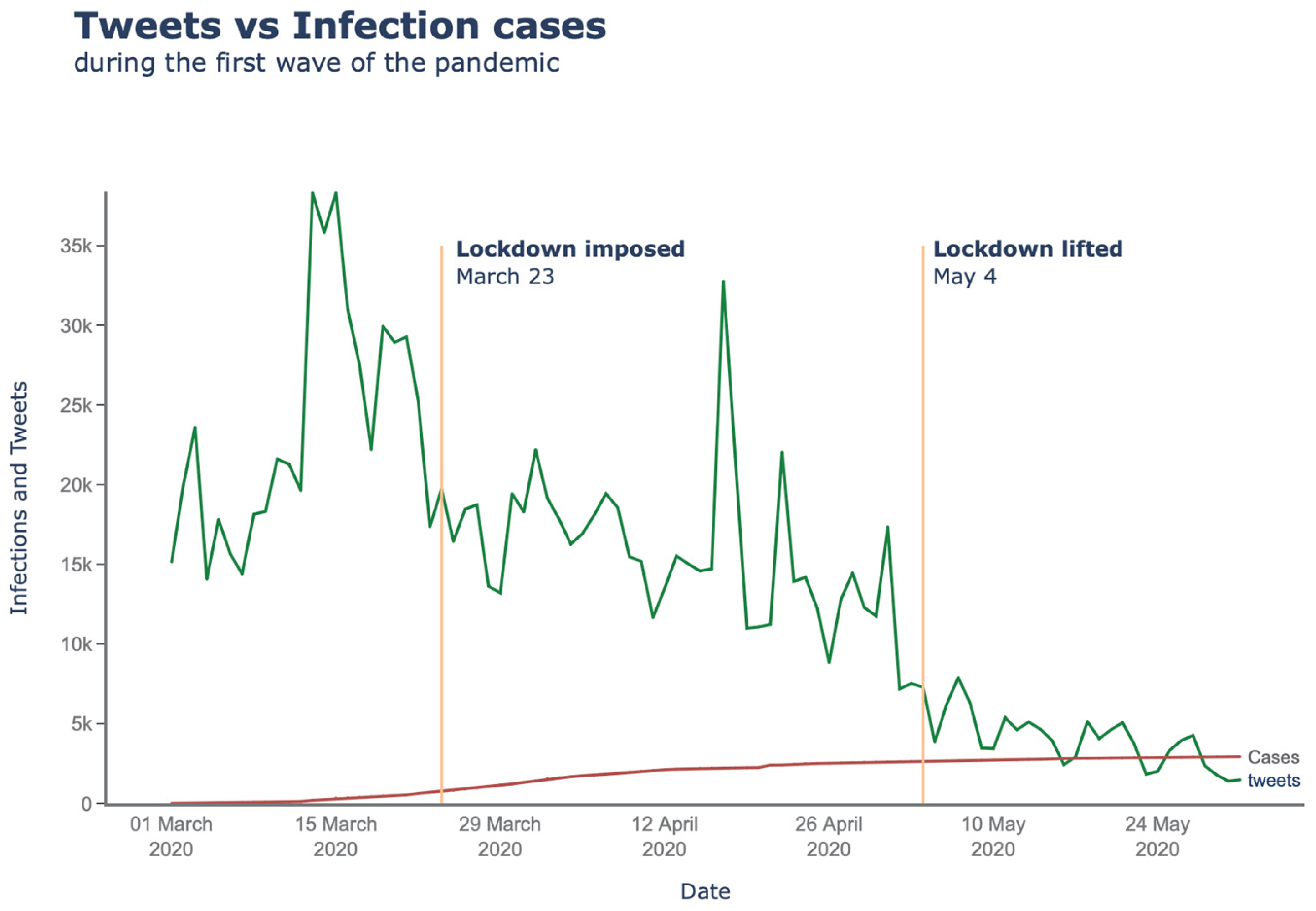
4. Results
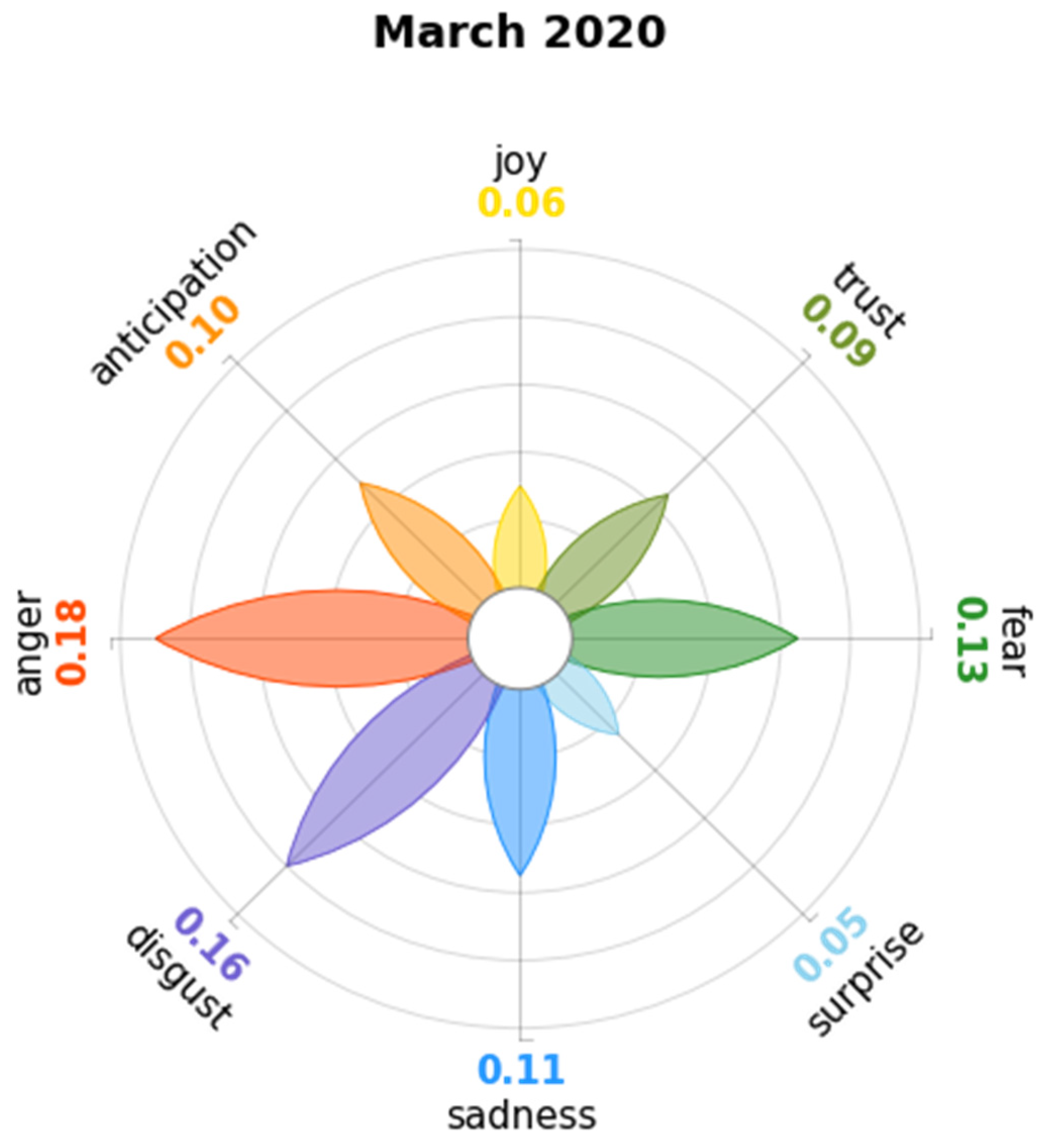
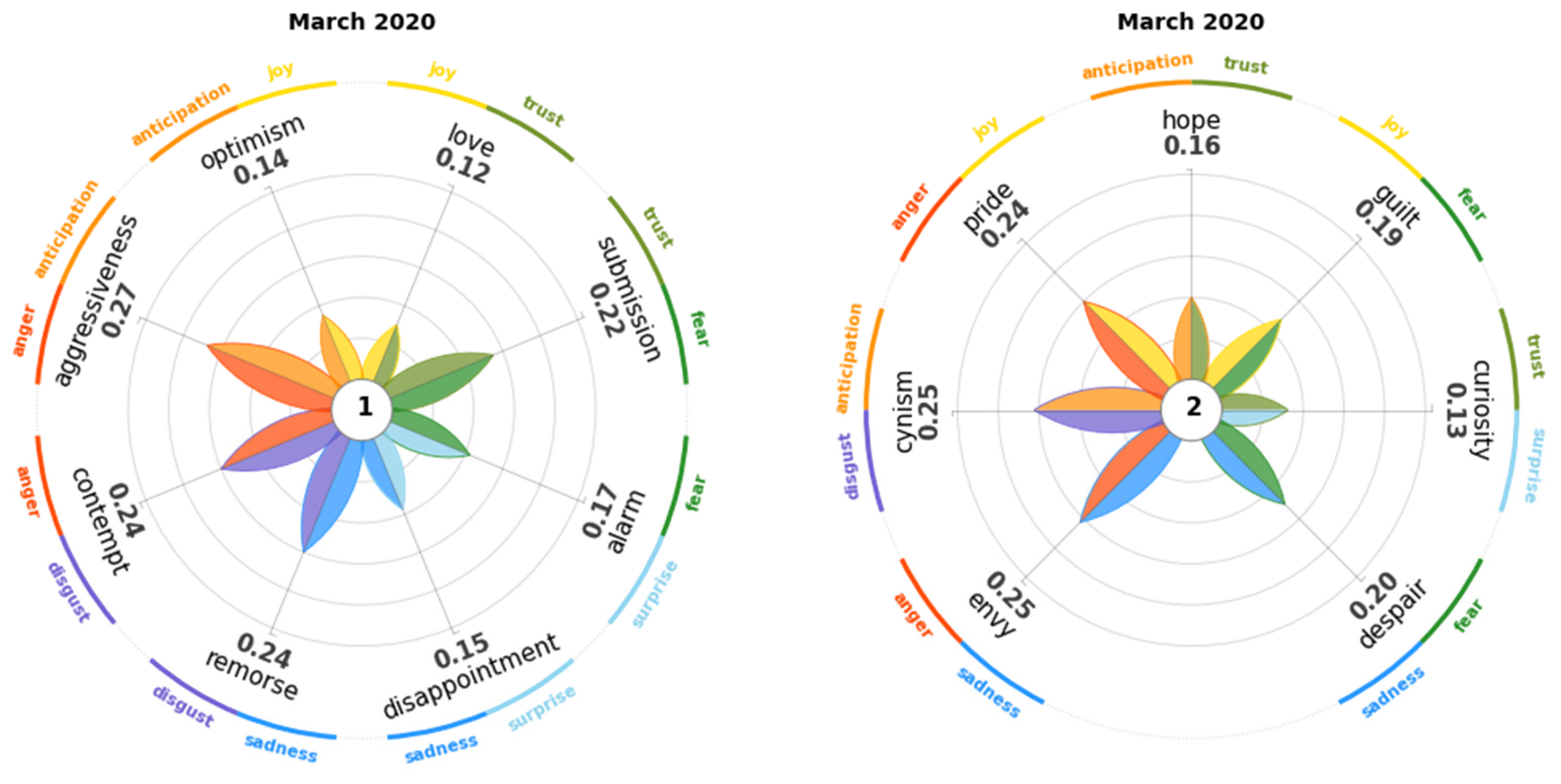
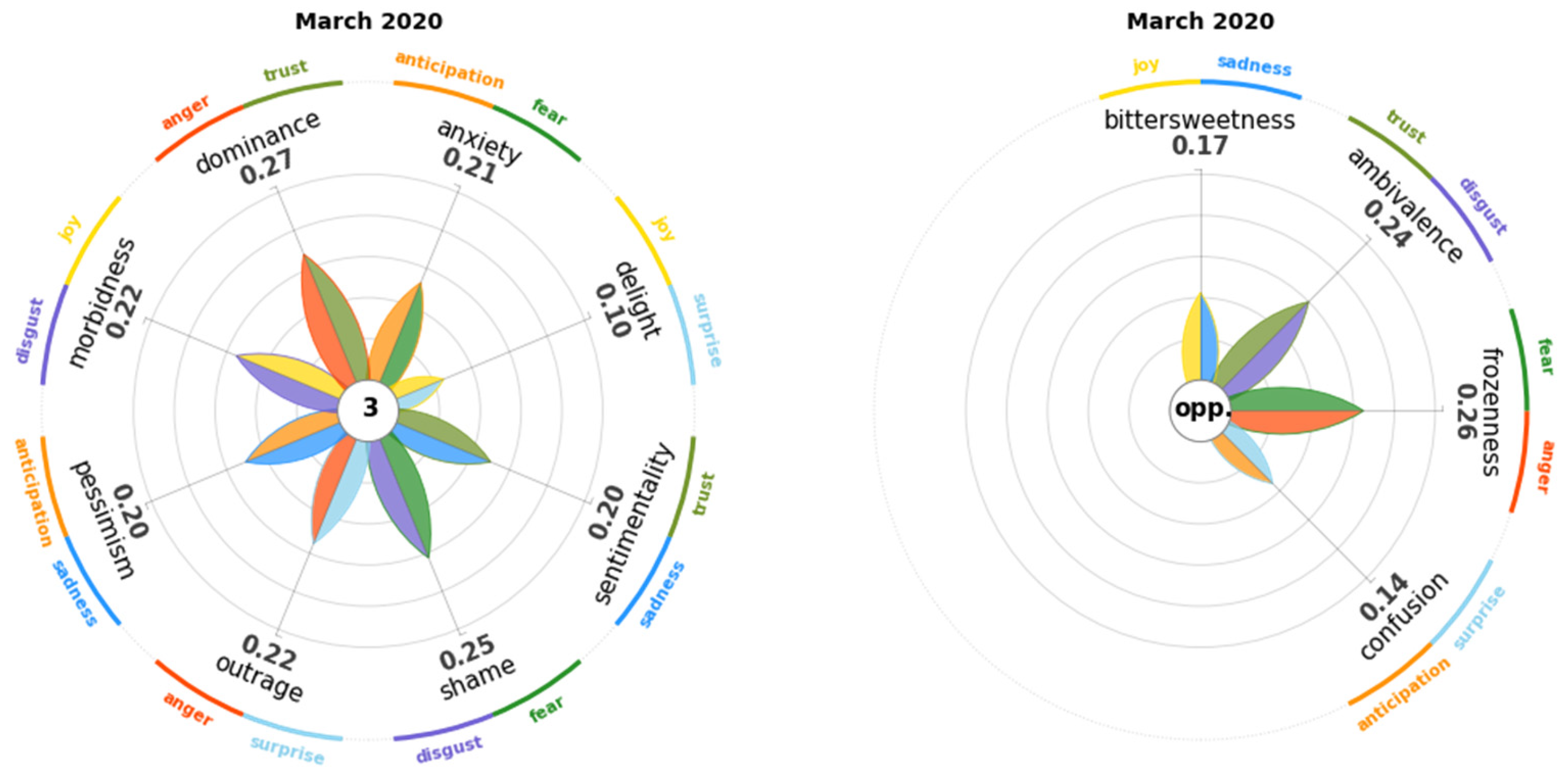
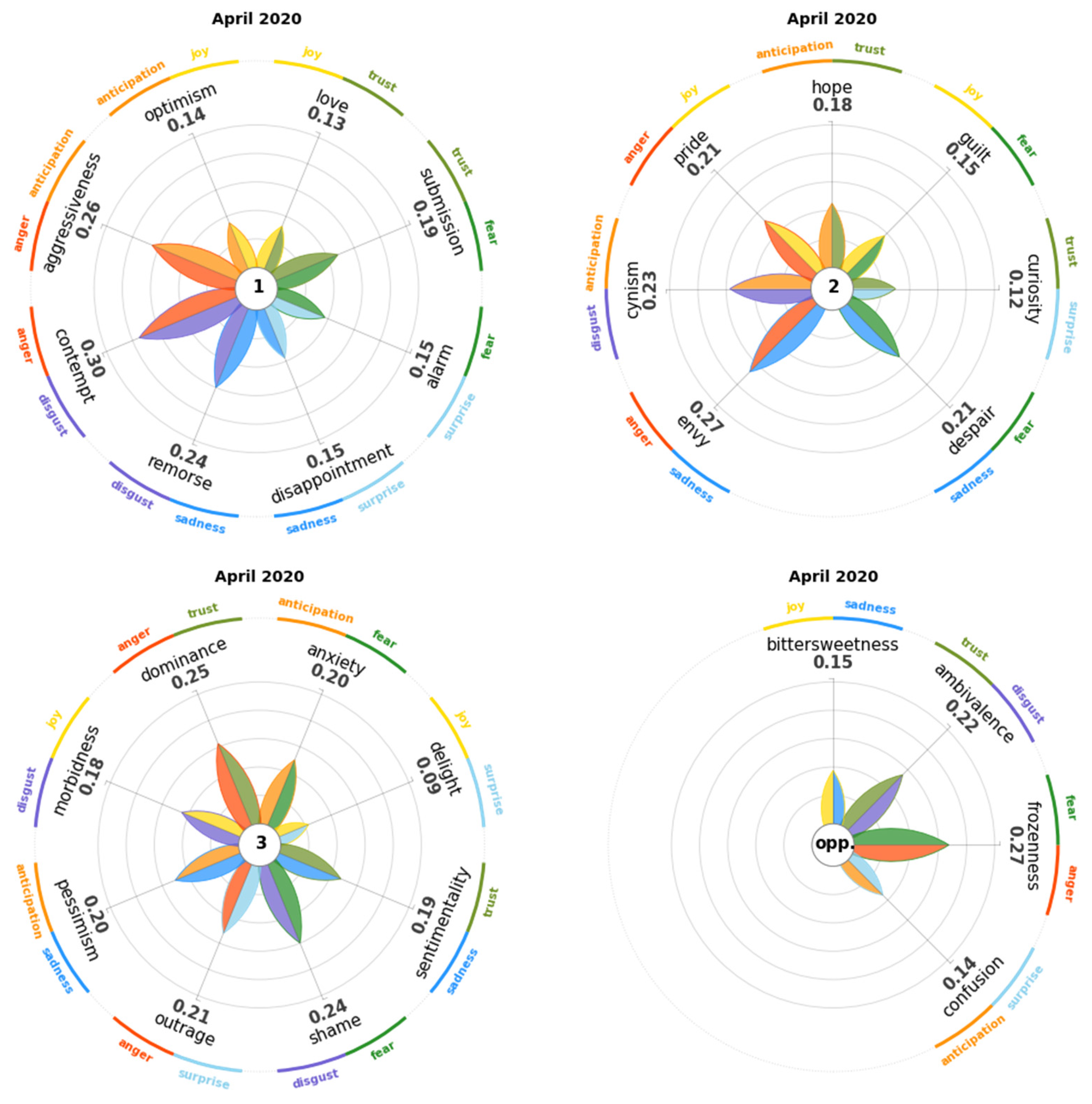
4.1. March 2020
- The French government has banned public gatherings of more than 5000 people indoors because of the new coronavirus, the health minister announced.
- Hey, don’t terrorize the Greeks, dumbasses!
- I have been through Measles, Chickenpox, Rubella, Lice, Chernobyl, Anthrax, Avian Influenza, Pig Influenza, Mad Cows, Ebola, Coxsackie, H1N1, economic crisis with 3–4 Memoranda, Referendum, two Mitsotakis, two Karamanlis, two Papandreou, one [Varoufakis]
- Arrests under the antiterrorism law for a publication. This is how you fight a pandemic when you hire cops instead of nurses and doctors.
- After the notorious ‘personal responsibility,’ today we learned that the government has done all right with the medical equipment in hospitals, but it is the fault of the workers who waste it. #Καλοφάγωτο #COVID_19.
- COVID-19-Italy: The victims of the coronet in Bergamo are more than the victims of World War II. The authorities are talking about a catastrophe, according to France 2’s correspondent in Rome.
- Who is afraid of “Makelio” [newspaper]? We’re dying, do you understand, you miserable bastards?
- Coronavirus: high risk for COVID-19 in Europe #OpenNews #OraEllados7 It has now hit 1/3 of the world’s countries and worldwide the number of victims has reached 3117 and the number of infections 90,912.
- during curfew staying at home is an order of the welfare state... and needless moving around entails a fine and maybe soon a prison sentence... so we either “#MENUMESPITI [i.e., Stay at home] or #PAMEPHILACY [i.e., We go to prison], therefore home and prison became identical...for our sake of course.
- #Government_Mitsotakis speaks about an ‘invisible war,’ but will we go mad? The #coronavirus or other VIRUS is the WEAPON the enemy is behind the weapon e.g., weapon #illegalimmigrants ENEMY #erdogan, everything has its origin why not refer to the origin or creation of the #coronavirus? Responsible = THEM.
- [An untranslatable derogatory term is used to describe the supporters of the Left party of major opposition] heckle the govt for delay (!!!) in taking measures for #COVID_19. When it banned carnivals 12 days ago, they were down on it for its “undemocratic” decision
. Decide exactly what the hell you want, you ideological opportunists!!!!
- When was the last time there was a curfew in Greece??? Um....During [German] OCCUPATION???? #Coronavirus, #Greece, #KyriakosMitsotakis, #HOAX, #Cases, #Scam, #Masons, #COVID
- The Turk is waiting for the right time to strike. That time is approaching. In 20 days, there will be queues outside hospitals waiting for hospitalization, people will be in panic. Then he will strike. Watch and pray #coronavirus #Evros #migration #Greece_under_attack.
- #Coronavirus epidemic of WORLDWIDE PSYCHOPATHS terrorizing, committing crimes with the DIRT of soul and body excretions!
- I can deal with #menume_spiti [i.e., We stay at home] for as long as it takes, but I can’t fight dumbass, indifference, selfishness and the criminal incompetence of the government and all politicians #coronavirus.
- It is smelling... death in Europe, as deaths from the new coronavirus are rising rapidly, with Spain surpassing China in the number of deaths.
- #Tsiodoras [i.e., the head of the Greek National Public Health Agency] “PLEASE keep what we tell you!” what a plea! curse the idiots who don’t #MENUMESPITI [i.e., We stay at home] #we_are_homeless! pleas are too weak! Use a whip!!!!
- #Coronavirus here is Balkans but the nudity of the ‘prosperous’ Europe who entangled our countries in memorandums, wars, and 69 innocent souls are considered as a detail, without underestimating the tragedy of death in the face of ethnic cleansing in Italy for example!
- These days that we are delaying the compulsory closure of the country at home—because that will happen eventually—bring more deaths. In a country where the very enforcement of the law is optional, the recommendation to stay home and a video add with Spyros Papadopoulos is not enough. #MENUMESPITI
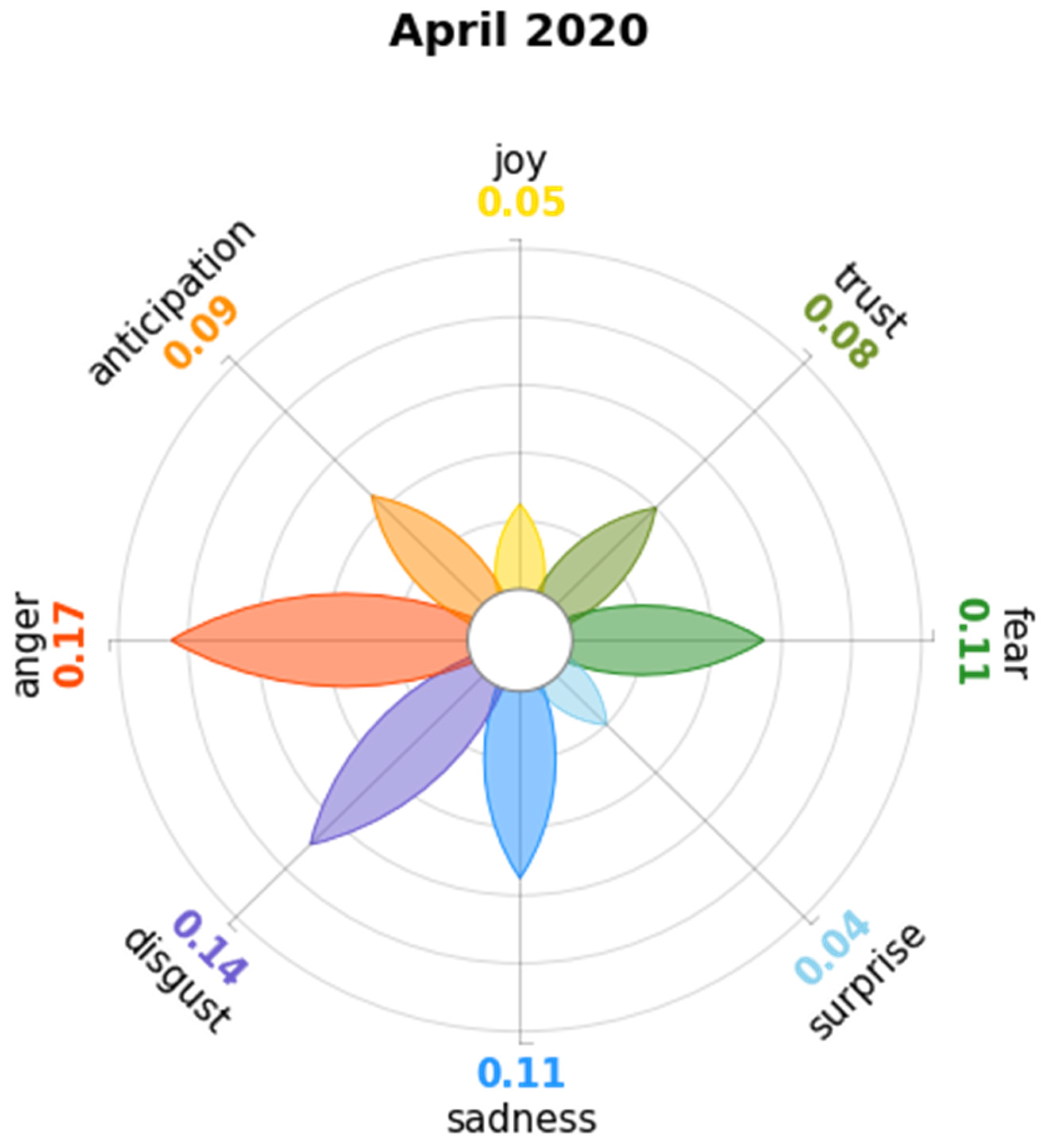
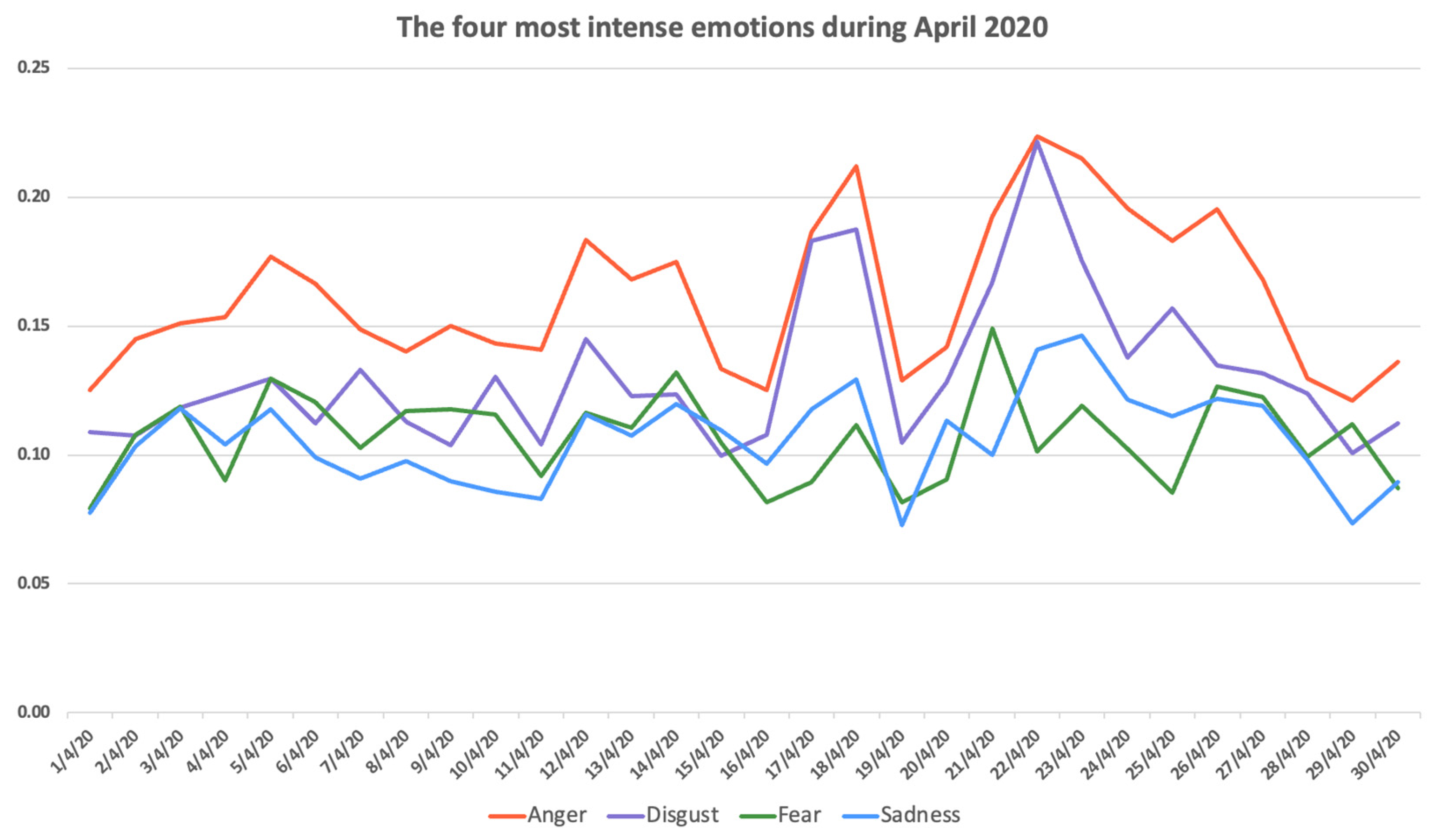
4.2. April 2020
- On 8 April, control over violating containment measures and mobility restrictions was upgraded, fines were doubled and churches were announced to remain closed until 28 April, in view of the Easter celebrations (19 April);
- On 14 April, the death toll exceeded one hundred deceased persons in Greece;
- On April 17, a decision to provide lifelong learning aiming at freelancers and professionals in fields like medicine or engineering, as a means to provide financial aid to them due to lockdown, was uncovered as a scandal when the content was proved to be machine-translated and of dubious quality;
- On 28 April, the end of the lockdown and the phasing out of the containment measures was announced.
- #antireport #COVID_19gr #curfew The following example shows how TV channels are presenting their shots so that the burden of responsibility continues to fall on the “undisciplined” people who are walking on beaches and parks...
- I don’t know about you, but I haven’t seen anyone from SYRIZA uploading proof of deposit of 50% of their salary, unlike the members of the New Democracy party..... It’s probably a coincidence
#SYRIZA_exploiters #curfew #carantine #Covid_19 #StayHome #lockdown
- We won’t die at home... Strengthen the National Health System... You are potential murderers @PrimeministerGR @Vkikilias #curfew #COVID_19 #MENUMESPITI
- What will be left after the “pandemic”? A new memorandum, massive unemployment and poverty, suicide attacks from fundamentalist Muslims and State terrorism with repeated quarantines.
- Tragic images from Ecuador under total collapse of the health system: woman whose husband died in her home and stayed there for two days, “I’m not afraid of death, but I don’t want to die like this” #COVID_19 #we_stay_at_home.
- The “scientific décor” of the Stalinist Junta #ND_deceptions should (1) release DEATH CERTIFICATES and (2) DO NECROPSY. Scammers with the FAKE #coronoius you are destroying the ECONOMY and SETTLE DOWN millions of baboon assassins #GoAway.
- For everyone else, political management is (a) fear mongering (b) incarceration (c) disappearance of any reaction to the Legislative Acts (d) broken health care system -→ regime incompetence. #Covid19gr.
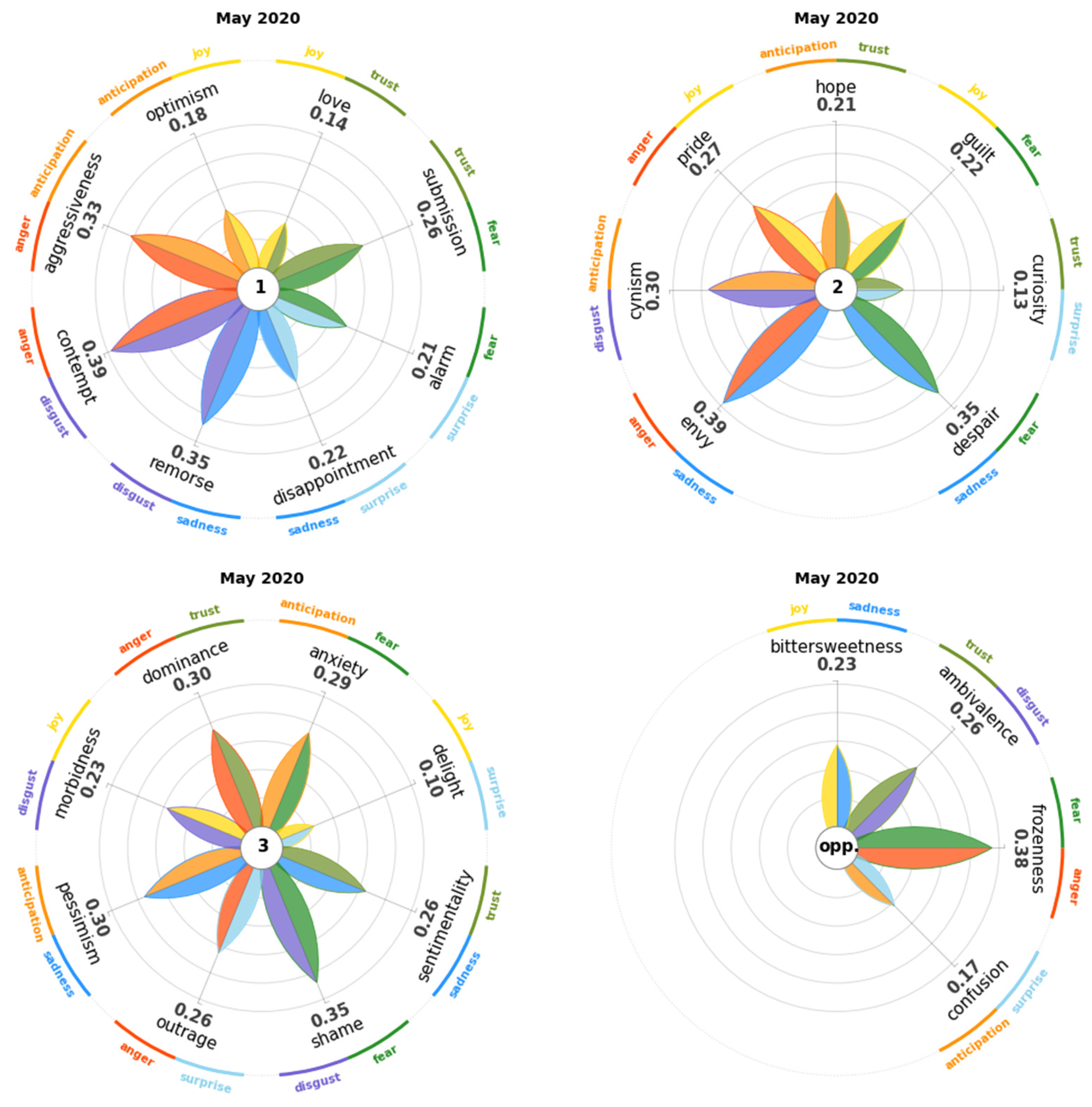
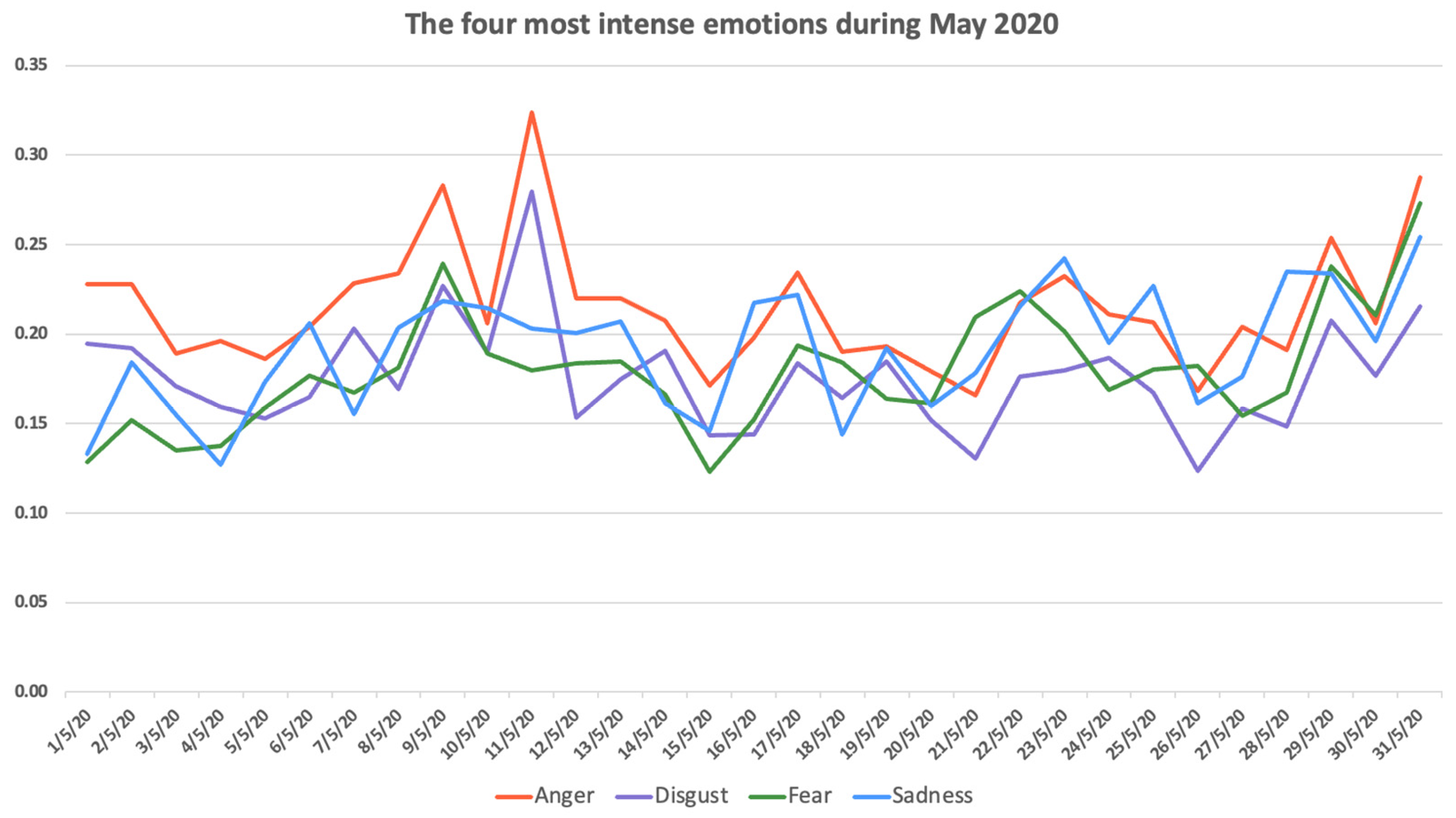
4.3. May 2020
- Imagine them updating us every evening at 6 pm (those left alive) on the evolution of #Covid_19 in Greece. A Nightmare on Elm Street
And then you tell me there are no miracles
.
- @Apotis4stis5 Brigand Davelis, Mitsotakis family and the “success story” with the masks #May_Day #coronavirus #mask #COVID19 #COVID_19 #Nordwest: The article...reads: “...behind all this is an effort to attract tourists...”
- So today I watched carefully the whole session of the Parliament, the briefing at six […] Conclusion: those who don’t have low income or a business of more than 200 people are screwed.
- “For flu we have a vaccine, for #covid_19GR we don’t. Do you understand the difference?” All the years we’ve had a flu vaccine did deaths cease, you idiot??? #Parliament #corona #Covid_19.
- Twitter allows access to our coronavirus-related tweets, to scientists and public crisis management and civil protection officials! The purpose, is to investigate misinformation, they say...
- Prosecutors and police authorities closed their eyes. They only know how to persecute Greek Orthodox citizens! #May_Day #left #anti-Greeks #PAME #Government_Mitsotakis #quarantine #corona #banning_traffic #Orthodoxy [For the Communist trade union’s May Day rally].
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Month | Tweets | Retweets | Replies | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| March | 147,311 | 348,368 | 9416 | 505,095 |
| April | 100,671 | 202,331 | 6380 | 309,382 |
| May | 52,051 | 51,677 | 1797 | 105,525 |
| Total | 300,033 | 602,376 | 17,593 | 920,002 |
| March 2020 | April 2020 | May 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| #κορωναιος #ειδήσεις #κορωνοιο #ελλάδα #μεταναστευτικό #coronavirusgreece #νδ_απατεωνες #καρναβαλι #κορονοιος_movies #κορονοιος_songs #koronaios #κοροναιος #ιταλια #κορονοϊός #κορωνοϊός #μένουμε_σπίτι #πανδημία #μένουμεσπίτι #κορωναϊός #υγεία #κοροναϊος #ιταλία #πνευμονία #επιδημία #κορονοϊού #κορωναϊος #κορονοϊό #ηπα #τουρκία #οικονομία #κύπρος #κορονοιος #κορωνοιος #menoumespiti #μενουμεστοσπιτι #κοροναϊός #menoume_spiti #κορονοϊος #θεσσαλονικη #κυσεα #refugeesgr #greece_turkey_borders #τουρκια #λεσβο #εβρο #greeks #καθαραδευτερα #greekborders #digitalsolidaritygr #συνορα #greekborder | #covid19gr #covid_19gr #menoumespiti #μενουμε_σπιτι #menoume_spiti #covid19greece #κορονοϊός #μενουμεσπιτι #απαγορευση_κυκλοφοριας #καραντινα #κοροναιος #κορονοιος #κορωνοιος #μενουμεστοσπιτι #θεσσαλονίκη #καλοπασχα #κορωνοΐος #μετζη_του_νεουκτη #πάσχα #σκοιλ_ελικικου #υπερβαση #υστερογραφα #apotis4stis5 #greek #staypositive #thessaloniki #ysterografa #γερμανία #εε #ελλάδα #κοροναϊός #κορωνοϊός #δντ #κορονοιός #μεθ #κορωναϊός #ειδήσεις #κυβέρνηση #ισπανία #σκαι #απάτη #μασόνοι #ηπα #κρούσματα #ευρώπη #υγεία #οικονομία #τεστ #koronoios #covid19cy #κύπρος #κυπρος #θατακαταφέρουμε #dimokritos #amarysia #antireport #κορονοϊος #menoume_dynatoi #κκε #μμε #μένουμεενεργοί #κουκάκι #στηριζουμετοεσυ #εβρος #ergnews #αλληλεγγύη #καη #παραιτηθειτε_ειστε_ανικανοι #μεταναστευτικό #κέρκυρα #κανενας_μονος #καμια_μονη #τωρα_λογαριαζομαστε #κλειστε_τις_εκκλησιες_τωρα #καμίαμόνη | #κορωνοιος #μενουμε_ασφαλεις #κορονοϊός #κορονοιος #πανδημια #μενουμεσπιτι #προσφυγικο #κρανιδι #koinoniamega #the2nightshow #κορωνοϊός #πανδημία #υγεία #ηπα #οικονομία #ειδήσεις #τουρισμός #πολιτική #κίνα #ηλιοθεραπεία #παραλία #ξαπλώστρες #περιβαλλοντικά #λουόμενοι #παθογόνοι #ιοί #επιστημονική #ευρωπαϊκή #επιβράδυνση #υπερβαση #εε #elefantaki #πρωτομαγια #αγια_παρασκευη #1μαη #refugeesgr #petralona #μερκούρη #φιλοπάππου #ανοιξη #μαπ #απαγόρευση_κυκλοφορίας #μένουμεασφαλείς #μένουμεσπίτι #κορώναφόβος #κορονάϊος #κοροδόϊος #ⲕⲟⲣⲱⲛⲁⲓⲟⲥ #κοροναϊού #καναλάρχες #κλινικάρχες #μένουμε_άνεργοι #4_μαΐου #ⲙⲉⲛⲟⲩⲙⲉⲥⲡⲓⲧⲓ #menoumeasfaleis #ιιβεαα #ευχαριστώ |
Appendix B

References
- Chukwuere, J.E. Social media and COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic literature review. J. Afr. Film. Diaspora Stud. 2022, 5, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Spiteri, G.; Fielding, J.; Diercke, M.; Campese, C.; Enouf, V.; Gaymard, A.; Bella, A.; Sognamiglio, P.; Moros, M.J.S.; Riutort, A.N. First cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the WHO European Region, 24 January to 21 February 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, A.; Vijayalakshmi, R. An automatic emotion analysis of real time corona tweets. In Advanced Informatics for Computing Research: 4th International Conference, ICAICR 2020, Gurugram, India, 26–27 December 2020; Revised Selected Papers, Part I 4; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzani, D.; Vergani, L.; Pizzoli, S.F.M.; Marton, G.; Pravettoni, G. Emotional tone, analytical thinking, and somatosensory processes of a sample of italian tweets during the first phases of the COVID-19 pandemic: Observational study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e29820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, K.; Aknin, L.B.; Lotun, S.; Sandstrom, G.M. Brief exposure to social media during the COVID-19 pandemic: Doom-scrolling has negative emotional consequences, but kindness-scrolling does not. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, J.; Moctezuma, D.; Fernández-Isabel, A.; Martin de Diego, I. Detecting emotional evolution on twitter during the COVID-19 pandemic using text analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Noh, E.B.; Choi, S.H.; Zhao, B.; Nam, E.W. Determining public opinion of the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea and Japan: Social network mining on twitter. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2020, 26, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M. Arabic sentiment analysis about online learning to mitigate COVID-19. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 30, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerald, O.; Eslen-Ziya, H. From discontent to action:# Quarantinehotel as not just a hashtag. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2022, 8, 2051806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuzali, H.; Zhang, T.; Ananiadou, S. Emotions and Topics Expressed on Twitter During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United Kingdom: Comparative Geolocation and Text Mining Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e40323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydros, D.; Argyropoulou, M.; Vrana, V. A content and sentiment analysis of Greek tweets during the pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geronikolou, S.; Drosatos, G.; Chrousos, G. Emotional analysis of twitter posts during the first phase of the COVID-19 pandemic in Greece: Infoveillance study. JMIR Form. Res. 2021, 5, e27741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, L.; García-Barriocanal, E.; Sicilia, M.A. Sentiment analysis of COVID-19 cases in Greece using Twitter data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 230, 120577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katika, A.; Zoulias, E.; Koufi, V.; Malamateniou, F. Mining Greek Tweets on Long COVID Using Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modeling. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2023, 305, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoteli, E.; Koukaras, P.; Tjortjis, C. Social media sentiment analysis related to COVID-19 vaccines: Case studies in English and Greek language. In IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; Maglogiannis, I., Iliadis, L., Macintyre, J., Cortez, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzd, A.; Mai, P. Going viral: How a single tweet spawned a COVID-19 conspiracy theory on Twitter. Big Data Soc. 2020, 7, 2053951720938405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, L.; Brin, S.; Motwani, R.; Winograd, T. The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web; Technical Report; Stanford InfoLab: Stanford, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cherven, K. Mastering Gephi Network Visualization; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Godard, R.; Holtzman, S. COVID-19 Misinformation and Polarization on Twitter: #StayHome, #Plandemic, and Health Communication. Int. J. Soc. Media Online Communities (IJSMOC) 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, G.; Wiebelt, L.; Weisser, C.; Kis-Katos, K.; Luber, M.; Säfken, B. An iterative topic model filtering framework for short and noisy user-generated data: Analyzing conspiracy theories on twitter. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ramahi, M.; Elnoshokaty, A.; El-Gayar, O.; Nasralah, T.; Wahbeh, A. Public discourse against masks in the COVID-19 era: Infodemiology study of Twitter data. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021, 7, e26780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzberg, B.H.; Tsou, M.H.; Gawron, M. Social Media Surveillance and (Dis) Misinformation in the COVID-19 Pandemic. In Communicating Science in Times of Crisis: The COVID-19 Pandemic; O’Hair, H.D., O’Hair, M.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 262–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohey, J.S. An analysis of newspaper opinion on war issues. Public Opin. Q. 1941, 5, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found. Trends® Inf. Retr. 2008, 2, 1–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Turney, P. Emotions evoked by common words and phrases: Using mechanical turk to create an emotion lexicon. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2010 Workshop on Computational Approaches to Analysis and Generation of Emotion in Text, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5 June 2010; pp. 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Turney, P.D. Crowdsourcing a word–emotion association lexicon. Comput. Intell. 2013, 29, 436–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutchik, R.; Kellerman, H. (Eds.) Theories of Emotion; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Plutchik, R.; Kellerman, H. (Eds.) The Measurement of Emotions; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Plutchik, R.E.; Conte, H.R. (Eds.) Circumplex Models of Personality and Emotions; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Plutchik, R. The nature of emotions: Human emotions have deep evolutionary roots, a fact that may explain their complexity and provide tools for clinical practice. Am. Sci. 2001, 89, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, A.; Vilella, S.; Ruffo, G. PyPlutchik: Visualising and comparing emotion-annotated corpora. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, A.; Kubde, P.; Vaidya, S. Emotional analysis using twitter data during pandemic situation: COVID-19. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 10–12 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemprala, N.; Bhatt, P.; Valecha, R.; Rao, H.R. Emotions during the COVID-19 crisis: A health versus economy analysis of public responses. Am. Behav. Sci. 2021, 65, 1972–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathayomchan, B.; Taecharungroj, V.; Wattanacharoensil, W. Evolution of COVID-19 tweets about Southeast Asian Countries: Topic modelling and sentiment analyses. Place Brand. Public Dipl. 2023, 19, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hagen, L.; Patel, M.; Falling, M. Evolution of the plandemic communication network among serial participants on Twitter. New Media Soc. 2023, 25, 3676–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, I.; Carter, P.; Sutch, H.; Lally, H. Online extremism and Islamophobic language and sentiment when discussing the COVID-19 pandemic and misinformation on Twitter. Ethn. Racial Stud. 2023, 46, 1407–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljedaani, W.; Saad, E.; Rustam, F.; de la Torre Díez, I.; Ashraf, I. Role of artificial intelligence for analysis of covid-19 vaccination-related tweets: Opportunities, challenges, and future trends. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocamo, C.; Viviani, M.; Famiglini, L.; Bartoli, F.; Pasi, G.; Carrà, G. Surveilling COVID-19 emotional contagion on Twitter by sentiment analysis. Eur. Psychiatry 2021, 64, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdaoui, A.; Azé, J.; Bringay, S.; Poncelet, P. Feel: A french expanded emotion lexicon. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2017, 51, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, H.S.; Beg, M.O.; Qamar, S. Domain specific emotion lexicon expansion. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Islamabad, Pakistan, 21–22 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabasi, A.L. Network Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barabási, A.L. Linked: The New Science of Networks; Perseus: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Piontti, A.P.; Perra, N.; Rossi, L.; Samay, N.; Vespignani, A. Charting the Next Pandemic: Modeling Infectious Disease Spreading in the Data Science Age; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Monaci, S.; Persico, S. Who’s fuelling Twitter disinformation on the COVID-19 vaccination campaign? Evidence from a computational analysis of the green pass debate. Contemp. Ital. Politics 2023, 15, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, L. An entropy-based method to control COVID-19 rumors in online social networks using opinion leaders. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tous-Rovirosa, A.; Dergacheva, D. #EsteVirusloParamosUnidos: Comunicación política de guerra en Twitter. Creación de comunidades homogéneas en la crisis de COVID-19. Estud. Sobre Mensaje Periodis. 2021, 27, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yang, Y. Cross-platform comparative study of public concern on social media during the COVID-19 pandemic: An empirical study based on Twitter and Weibo. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shargabi, A.A.; Selmi, A. Social network analysis and visualization of Arabic tweets during the COVID-19 pandemic. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 90616–90630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, M.R.; Jinich-Diamant, A.; Li, J.; Nali, M.; Mackey, T.K. Characterizing twitter user topics and communication network dynamics of the “Liberate” movement during COVID-19 using unsupervised machine learning and social network analysis. Online Soc. Netw. Media 2021, 21, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahja, M.; Safdar, G.A. Unlink the link between COVID-19 and 5G networks: An NLP and SNA based approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 209127–209137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.C.; Cornelson, K.; Benham, J.L.; Fullerton, M.M.; Tang, T.; Constantinescu, C.; Mourali, M.; Oxoby, R.J.; Marshall, D.A.; Hemmati, H. Analyzing social media to explore the attitudes and behaviors following the announcement of successful COVID-19 vaccine trials: Infodemiology study. JMIR Infodemiology 2021, 1, e28800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiotte, R.; Delvenne, J.C.; Barahona, M. Laplacian dynamics and multiscale modular structure in networks. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0812.1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, M.; Smith-Lovin, L.; Cook, J.M. Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2001, 27, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakis, N.A.; Fowler, J.H. Connected: The Surprising Power of Our Social Networks and How They Shape Our Lives; Little, Brown Spark: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelfel, J.; Haller, A.O. Significant others, the self-reflexive act and the attitude formation process. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1971, 36, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Limassol, Cyprus, 5–8 June 2023; 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomy, M.; Venturini, T.; Heymann, S.; Bastian, M. ForceAtlas2, a continuous graph layout algorithm for handy network visualization designed for the Gephi software. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Brown, W.M.; Klavans, R.; Boyack, K.W. OpenOrd: An open-source toolbox for large graph layout. In Visualization and Data Analysis 2011; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 7868, pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Efficient, high-quality force-directed graph drawing. Math. J. 2005, 10, 37–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Dai, G.; Wang, H. Visualization of large hierarchical data by circle packing. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montreal, QU, Canada, 22–27 April 2006; pp. 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratoudaki, H. At the Gates: Borders, National Identity, and Social Media During the “Evros Incident”. J. Borderl. Stud. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraamidou, M.; Eftychiou, E. Migrant Racialization on Twitter during a border and a pandemic crisis. Int. Commun. Gaz. 2022, 84, 227–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, D.; Kokkinaki, F.; Kounalaki, X.; Maragidou, M.; Papagiannakis, L.; Sakellariou, A.; Haramis, P. Borders and Coronavirus: Refugee Policy and Public Discourse in a time of a dual crisis in Greece. Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung. 2021. Available online: https://www.antigone.gr/wp-content/uploads/library/selected-publications-on-migration-and-asylum/greece/en/17365.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Durkheim, É. On Suicide; Penguin Books: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skarpelos, Y.; Messini, S.; Roinioti, E.; Karpouzis, K.; Kaperonis, S.; Marazoti, M.-G. Emotions during the Pandemic’s First Wave: The Case of Greek Tweets. Digital 2024, 4, 126-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4010006
Skarpelos Y, Messini S, Roinioti E, Karpouzis K, Kaperonis S, Marazoti M-G. Emotions during the Pandemic’s First Wave: The Case of Greek Tweets. Digital. 2024; 4(1):126-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkarpelos, Yannis, Sophia Messini, Elina Roinioti, Kostas Karpouzis, Stavros Kaperonis, and Michaela-Gavriela Marazoti. 2024. "Emotions during the Pandemic’s First Wave: The Case of Greek Tweets" Digital 4, no. 1: 126-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4010006
APA StyleSkarpelos, Y., Messini, S., Roinioti, E., Karpouzis, K., Kaperonis, S., & Marazoti, M.-G. (2024). Emotions during the Pandemic’s First Wave: The Case of Greek Tweets. Digital, 4(1), 126-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4010006















