Data-Driven Decision Support for Adult Autism Diagnosis Using Machine Learning †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Work
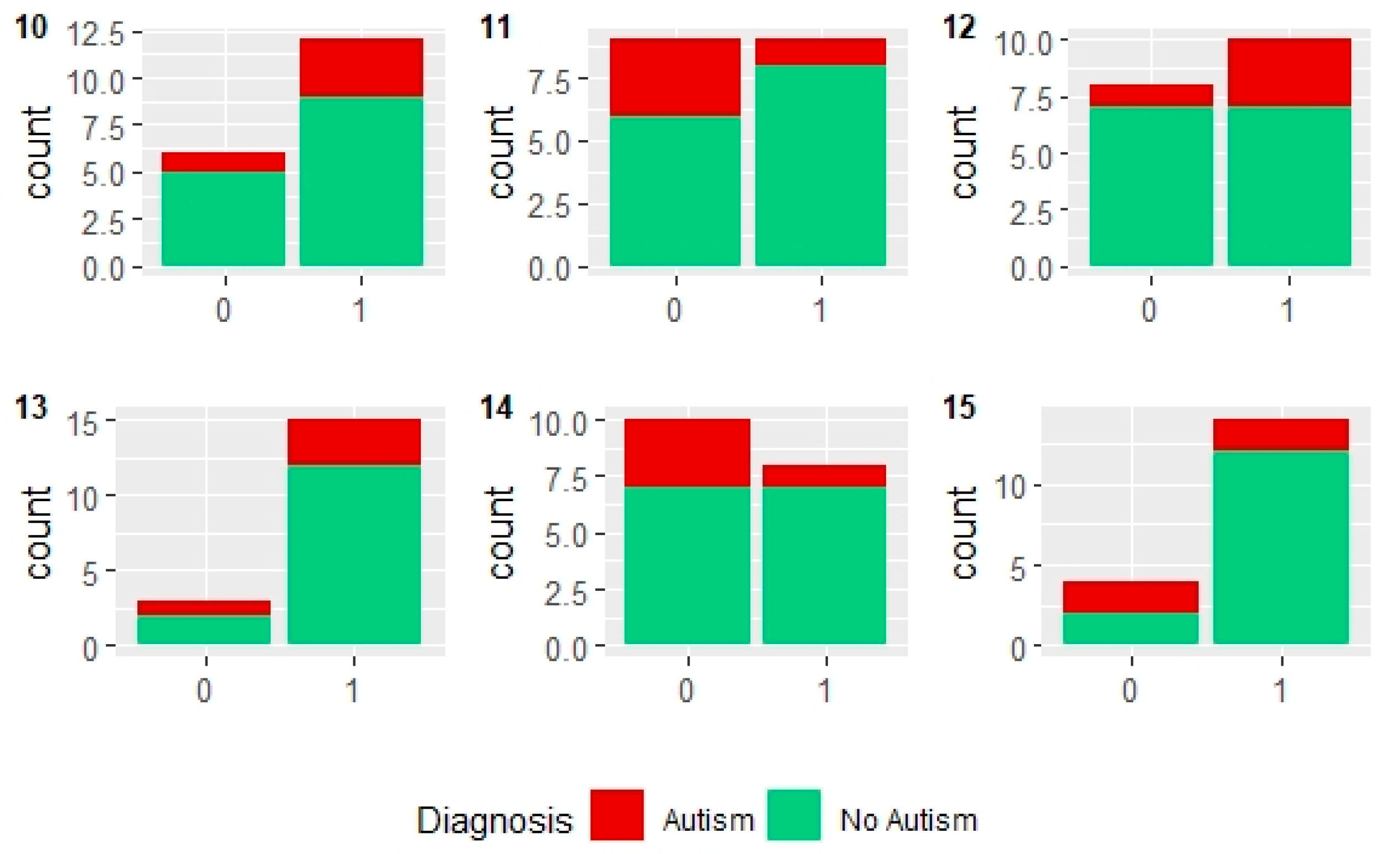
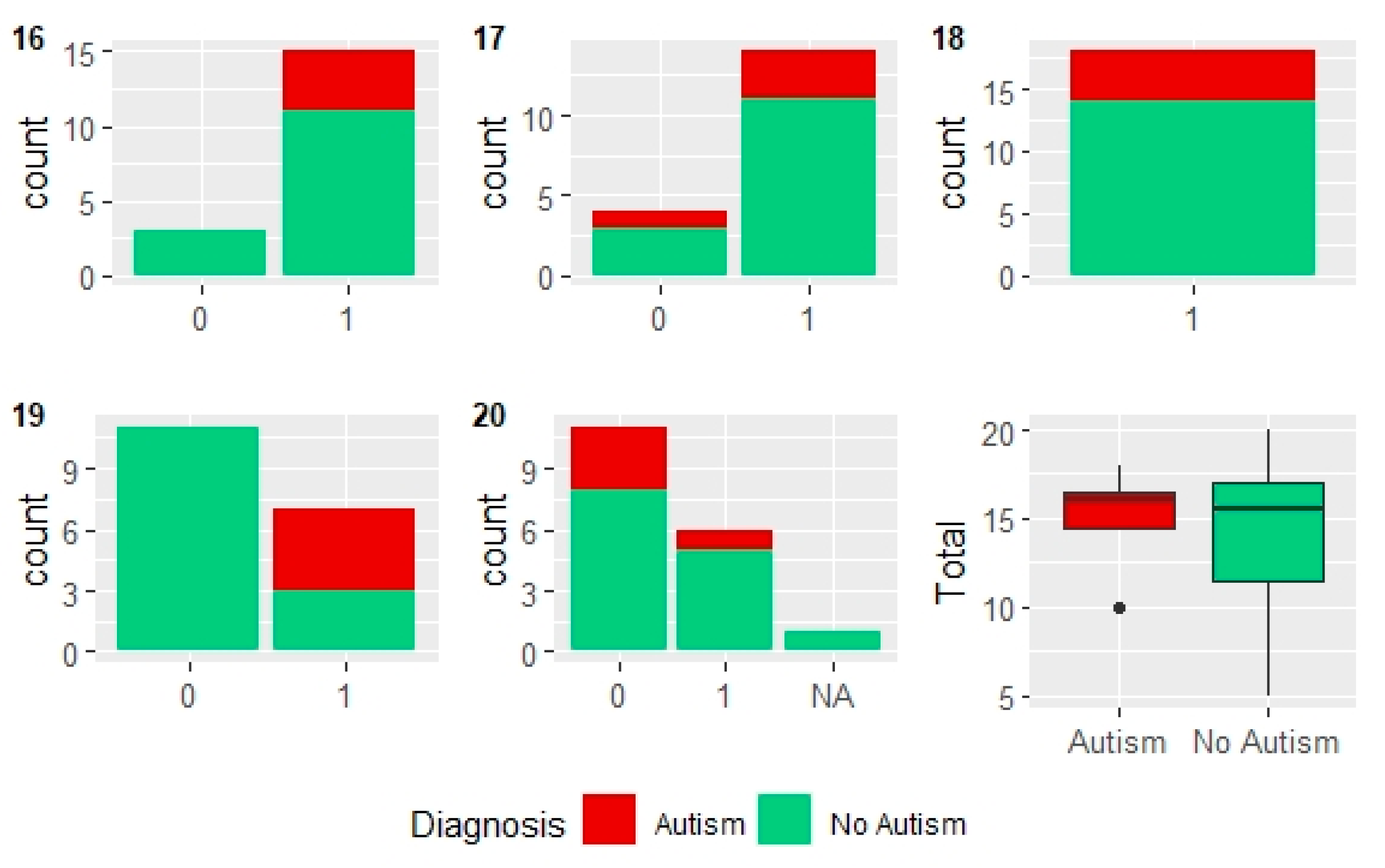
3. Data Analysis Using Machine Learning
3.1. Analysis Using Weka
3.2. Analysis Using JADBio
4. Autism Screening Questionnaire
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Press: Washington, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, C.; Cook, E.H.; Leventhal, B.L.; Amaral, D.G. Autism spectrum disorders. Neuron 2000, 28, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brugha, T.S.; McManus, S.; Bankart, J.; Scott, F.; Purdon, S.; Smith, J.; Bebbington, P.; Jenkins, R.; Meltzer, H. Epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders in adults in the community in England. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, C.M.; Wilson, C.E.; Robertson, D.M.; Ecker, C.; Daly, E.M.; Hammond, N.; Galanopoulos, A.; Dud, I.; Murphy, D.G.; McAlonan, G.M. Autism spectrum disorder in adults: Diagnosis, management, and health services development. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 1669–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, J.; Brugha, T.; McManus, S.; Meltzer, H.; Smith, J.; Scott, F.J.; Purdon, S.; Bankart, J. Autism Spectrum Disorders in Adults Living in Households Throughout England: Report from the Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey 2007; The NHS Information Centre for Health and Social Care: Teddington, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fombonne, E. Epidemiology of autistic disorder and other pervasive developmental disorders. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66 (Suppl. S10), 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, C.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Van Der Gaag, R.J. Autism spectrum disorders in adults. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2008, 152, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, L.; Potter, D. The epidemiology of autistic spectrum disorders: Is the prevalence rising? Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2002, 8, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritvo, R.A.; Ritvo, E.R.; Guthrie, D.; Ritvo, M.J.; Hufnagel, D.H.; McMahon, W.; Tonge, B.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Jassi, A.; Attwood, T.; et al. The Ritvo Autism Asperger Diagnostic Scale-Revised (RAADS-R): A scale to assist the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in adults: An international validation study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2011, 41, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnard, J.; Harvey, V.; Potter, D.; Prior, A. Ignored or Ineligible? The Reality for Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders; National Autistic Society: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Le Couteur, A.; Haden, G.; Hammal, D.; McConachie, H. Diagnosing autism spectrum disorders in pre-school children using two standardised assessment instruments: The ADI-R and the ADOS. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 38, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, C.A.; Murray, D.S.; Akers, R.; Mitchell, T.; Manning-Courtney, P. Use of the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) in a clinical setting. Autism 2011, 15, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Autism Spectrum Disorder in Adults: Diagnosis and Management (Guideline CG142); National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barlati, S.; Deste, G.; Gregorelli, M.; Vita, A. Autistic traits in a sample of adult patients with schizophrenia: Prevalence and correlates. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Crescenzo, F.; Postorino, V.; Siracusano, M.; Riccioni, A.; Armando, M.; Curatolo, P.; Mazzone, L. Autistic symptoms in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bastiaansen, J.A.; Meffert, H.; Hein, S.; Huizinga, P.; Ketelaars, C.; Pijnenborg, M.; Bartels, A.; Minderaa, R.; Keysers, C.; de Bildt, A. Diagnosing autism spectrum disorders in adults: The use of Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) module 4. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2011, 41, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berthoz, S.; Hill, E.L. The validity of using self-reports to assess emotion regulation abilities in adults with autism spectrum disorder. Eur. Psychiatry 2005, 20, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frith, U. Autism: Explaining the Enigma, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Leyfer, O.T.; Folstein, S.F.; Bacalman, S.; Davis, N.O.; Dinh, E.; Morgan, J.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Lainhart, J.E. Comorbid psychiatric disorders in children with autism: Interview development and rates of disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2006, 36, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillberg, C. A Guide to Asperger Syndrome; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fusar-Poli, L.; Brondino, N.; Politi, P.; Aguglia, E. Missed diagnoses and misdiagnoses of adults with autism spectrum disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 272, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.; Ashton-Smith, J. Missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis? Girls and women on the autism spectrum. Good Autism Pract. 2011, 12, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, L.; Petrides, K.V.; Allison, C.; Smith, P.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Lai, M.-C.; Mandy, W. “Putting on my best normal”: Social camouflaging in adults with autism spectrum conditions. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 2519–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glascoe, F.P. Screening for developmental and behavioral problems. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2005, 11, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, P.; Chavan, B.S. Development of a screening instrument for autism spectrum disorder: Chandigarh autism screening instrument. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 147, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Bhatia, T.; Sharma, V.; Antony, N.; Das, D.; Sahu, S.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, V.; Brar, J.S.; Iyengar, S.; et al. Protocol for development of the indian autism screening questionnaire: The screening version of the Indian scale for assessment of autism. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2020, 42 (Suppl. S6), S63–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabtah, F. An accessible and efficient autism screening method for behavioural data and predictive analyses. Health Inform. J. 2018, 25, 1739–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabtah, F.; Peebles, D. Early autism screening: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eaves, L.C.; Wingert, H.D.; Ho, H.H.; Mickelson, E.C.R. Screening for autism spectrum disorders with the social communication questionnaire. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatrics 2006, 27, S95–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodbury-Smith, M.R.; Robinson, J.; Wheelwright, S.; Baron-Cohen, S. Screening adults for asperger syndrome using the AQ: A preliminary study of its diagnostic validity in clinical practice. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2005, 35, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappok, T.; Heinrich, M.; Underwood, L. Screening tools for autism spectrum disorders. Adv. Autism 2015, 1, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Hoekstra, R.A.; Knickmeyer, R.; Wheelwright, S. The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2001, 31, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.M.; Andersen, L.M.J.; Bejerot, S. RAADS-14 screen: Validity of a screening tool for autism spectrum disorder in an adult psychiatric population. Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Robinson, J.; Woodbury-Smith, M. The Adult Asperger Assessment (AAA): A diagnostic method. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2005, 35, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizoo, B.B.; Horwitz, E.H.; Teunisse, J.P.; Kan, C.C.; Visser, C.T.W.M.; Forceville, E.J.M.; Van Voorst, A.J.P.; Van Voorst, H.M. Predictive validity of self-report questionnaires in the assessment of autism spectrum disorders in adults. Autism 2015, 19, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakabayashi, A.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Tojo, Y. The Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) in Japan: A cross-cultural comparison. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2006, 36, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, H.; Alison, J.S. How useful are the Adult Asperger Assessment and AQ-10 within an adult clinical population of all intellectual abilities? Adv. Autism 2016, 2, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusar-Poli, L.; Ciancio, A.; Gabbiadini, A.; Meo, V.; Patania, F.; Rodolico, A.; Saitta, G.; Vozza, L.; Petralia, A.; Signorelli, M.S.; et al. Self-reported autistic traits using the AQ: A comparison between individuals with ASD, psychosis, and non-clinical controls. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamou, M.; Jones, S.L.; Wetherhill, S. AAA Screening in Adults with ASD: A Retrospective Cohort Study; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwood, K.L.; Gillan, N.; Horder, J.; Hayward, H.; Woodhouse, E.; McEwen, F.S.; Findon, J.; Eklund, H.; Spain, D.; Wilson, C.E.; et al. Predicting the diagnosis of autism in adults using the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) questionnaire. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bishop, S.L.; Seltzer, M.M. Self-reported autism symptoms in adults with autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Booth, T.; Murray, A.L.; McKenzie, K.; Kuenssberg, R.; O’Donnell, M.; Burnett, H. Brief report: An evaluation of the AQ-10 as a brief screening instrument for ASD in adults. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 2997–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allison, C.; Auyeung, B.; Baron-Cohen, S. Toward brief “red flags” for autism screening: The short autism spectrum quotient and the short quantitative checklist in 1000 cases and 3000 controls. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 51, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, H.; Koyama, T.; Osada, H. Autism-Spectrum Quotient-Japanese version and its short forms for screening normally intelligent persons with pervasive developmental disorders. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2005, 59, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, J.-F.; Lortie, M.; Taschereau-Dumouchel, V.; Théoret, H. Validation of French-Canadian versions of the Empathy Quotient and Autism Spectrum Quotient. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 2009, 41, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ketelaars, C.; Horwitz, E.; Sytema, S.; Bos, J.; Wiersma, D.; Minderaa, R.; Hartman, C.A. Brief report: Adults with mild autism spectrum disorders (ASD): Scores on the autism spectrum quotient (AQ) and comorbid psychopathology. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 38, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, T.; So, R.; Kim, Y.S.; Leventhal, B.; Epstein, R.A. A systematic review of screening tools in non-young children and adults for autism spectrum disorder. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 80, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Brayne, C. Screening for autism spectrum disorders: What is the evidence? Autism 2006, 10, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posserud, M.-B.; Lundervold, A.J.; Gillberg, C. Validation of the autism spectrum screening questionnaire in a total population sample. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2009, 39, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritvo, R.A.; Ritvo, E.R.; Guthrie, D.; Yuwiler, A.; Ritvo, M.J.; Weisbender, L. A scale to assist the diagnosis of autism and Asperger’s disorder in adults (RAADS): A pilot study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 38, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.L.; Johnson, M.; Alty, B.; Adamou, M. The effectiveness of RAADS-R as a screening tool for adult ASD populations. Autism Res. Treat. 2021, 2021, 9974791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kember, S.M.; Williams, M.N. Autism in Aotearoa: Is the RAADS-14 a valid tool for a New Zealand population? Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2021, 37, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, C.M.; Cramer, R.D.; McGonigle, J.J. Examining the diagnostic validity of autism measures among adults in an outpatient clinic sample. Autism Adulthood 2019, 1, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picot, M.-C.; Michelon, C.; Bertet, H.; Pernon, E.; Fiard, D.; Coutelle, R.; Abbar, M.; Attal, J.; Amestoy, A.; Duverger, P.; et al. The French version of the revised ritvo autism and Asperger diagnostic scale: A psychometric validation and diagnostic accuracy study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugha, T.; Tyrer, F.; Leaver, A.; Lewis, S.; Seaton, S.; Morgan, Z.; Tromans, S.; van Rensburg, K. Testing adults by questionnaire for social and communication disorders, including autism spectrum disorders, in an adult mental health service population. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 29, e1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, E.H.; Schoevers, R.A.; Ketelaars, C.E.J.; Kan, C.C.; van Lammeren, A.M.D.; Meesters, Y.; Spek, A.A.; Wouters, S.; Teunisse, J.P.; Cuppen, L.; et al. Clinical assessment of ASD in adults using self- and other-report: Psychometric properties and validity of the Adult Social Behavior Questionnaire (ASBQ). Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2016, 24, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.M.J.; Näswall, K.; Manouilenko, I.; Nylander, L.; Edgar, J.; Ritvo, R.A.; Ritvo, E.; Bejerot, S. The Swedish version of the ritvo autism and Asperger diagnostic scale: Revised (RAADS-R). A Validation study of a rating scale for adults. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2011, 41, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westwood, H.; Eisler, I.; Mandy, W.; Leppanen, J.; Treasure, J.; Tchanturia, K. Using the autism-spectrum quotient to measure autistic traits in anorexia nervosa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romero, M.; Aguilar, J.M.; Del-Rey-Mejías, Á.; Mayoral, F.; Rapado, M.; Peciña, M.; Barbancho, M.Á.; Ruiz-Veguilla, M.; Lara, J.P. Psychiatric comorbidities in autism spectrum disorder: A comparative study between DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5 diagnosis. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2016, 16, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mannion, A.; Leader, G. Comorbidity in autism spectrum disorder: A literature review. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2013, 7, 1595–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, M.-C.; Kassee, C.; Besney, R.; Bonato, S.; Hull, L.; Mandy, W.; Szatmari, P.; Ameis, S.H. Prevalence of co-occurring mental health diagnoses in the autism population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugnegård, T.; Hallerbäck, M.U.; Gillberg, C. Asperger syndrome and schizophrenia: Overlap of self-reported autistic traits using the Autism-spectrum Quotient (AQ). Nord. J. Psychiatry 2015, 69, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebartz Van Elst, L.; Pick, M.; Biscaldi, M.; Fangmeier, T.; Riedel, A. High-functioning autism spectrum disorder as a basic disorder in adult psychiatry and psychotherapy: Psychopathological presentation, clinical relevance and therapeutic concepts. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 263 (Suppl. S2), S189–S196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigham, S.; Rodgers, J.; Berney, T.; Couteur, A.L.; Ingham, B.; Parr, J.R. Psychometric properties of questionnaires and diagnostic measures for autism spectrum disorders in adults: A systematic review. Autism 2018, 23, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happé, F.G.; Mansour, H.; Barrett, P.; Brown, T.; Abbott, P.; Charlton, R.A. Demographic and cognitive profile of individuals seeking a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in adulthood. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 3469–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sewani, H.; Kashef, R. An autoencoder-based deep learning classifier for efficient diagnosis of autism. Children 2020, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef, R. ECNN: Enhanced convolutional neural network for efficient diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2022, 71, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanimozhiselvi, C.S.; Jayaprakash, D. Machine learning based autism grading for clinical decision making. Int. J. Recet. Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 7443–7446. [Google Scholar]
- Eslami, T.; Almuqhim, F.; Raiker, J.S.; Saeed, F. Machine learning methods for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using functional and structural MRI: A survey. Front. Neuroinform. 2021, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, K.K.; Novack, M.N.; LaHaye, N.; Parlett-Pelleriti, C.; Anden, R.; Dixon, D.R.; Linstead, E. Applications of supervised machine learning in autism spectrum disorder research: A review. Review J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 6, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batsakis, S.; Adamou, M.; Tachmazidis, I.; Antoniou, G.; Kehagias, T. Data-driven decision support for autism diagnosis using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Management of Digital EcoSystems, Hammamet, Tunisia, 1–3 November 2021; pp. 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.; Frank, E.; Holmes, G.; Pfahringer, B.; Reutemann, P.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA data mining software: An update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2009, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsakis, S.; Tachmazidis, I.; Baryannis, G.; Antoniou, G. Semantic artificial neural networks. In European Semantic Web Conference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Došilović, F.K.; Brčić, M.; Hlupić, N. Explainable artificial intelligence: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Convention On Information And Communication Technology, Electronics And Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Shavlik, J.W.; Towell, G.G. An approach to combining explanation-based and neural learning algorithms. In Applications of Learning and Planning Methods; World Scientific: Singapore, 1991; pp. 71–98. [Google Scholar]
- Towell, G.G.; Shavlik, J.W. Knowledge-based artificial neural networks. Artif. Intell. 1994, 70, 119–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamardinos, I.; Charonyktakis, P.; Lakiotaki, K.; Borboudakis, G.; Zenklusen, J.C.; Juhl, H.; Chatzaki, E.; Lagani, V. Just Add Data: Automated Predictive Modeling and Biosignature Discovery; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Laurel Hollow, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tsamardinos, I.; Greasidou, E.; Borboudakis, G. Boot-strapping the out-of-sample predictions for efficient and accurate cross-validation. Mach. Learn. 2018, 107, 1895–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
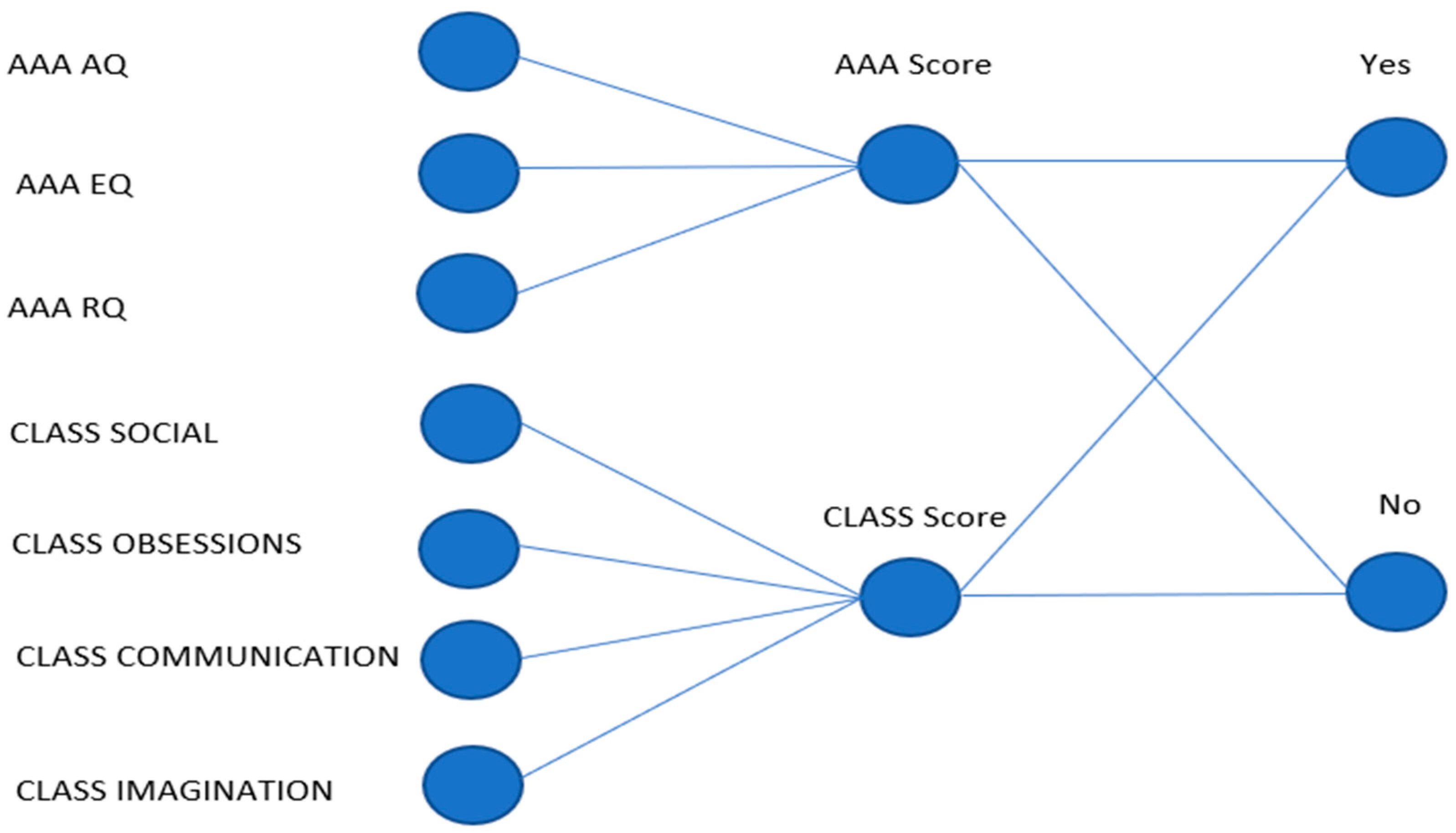



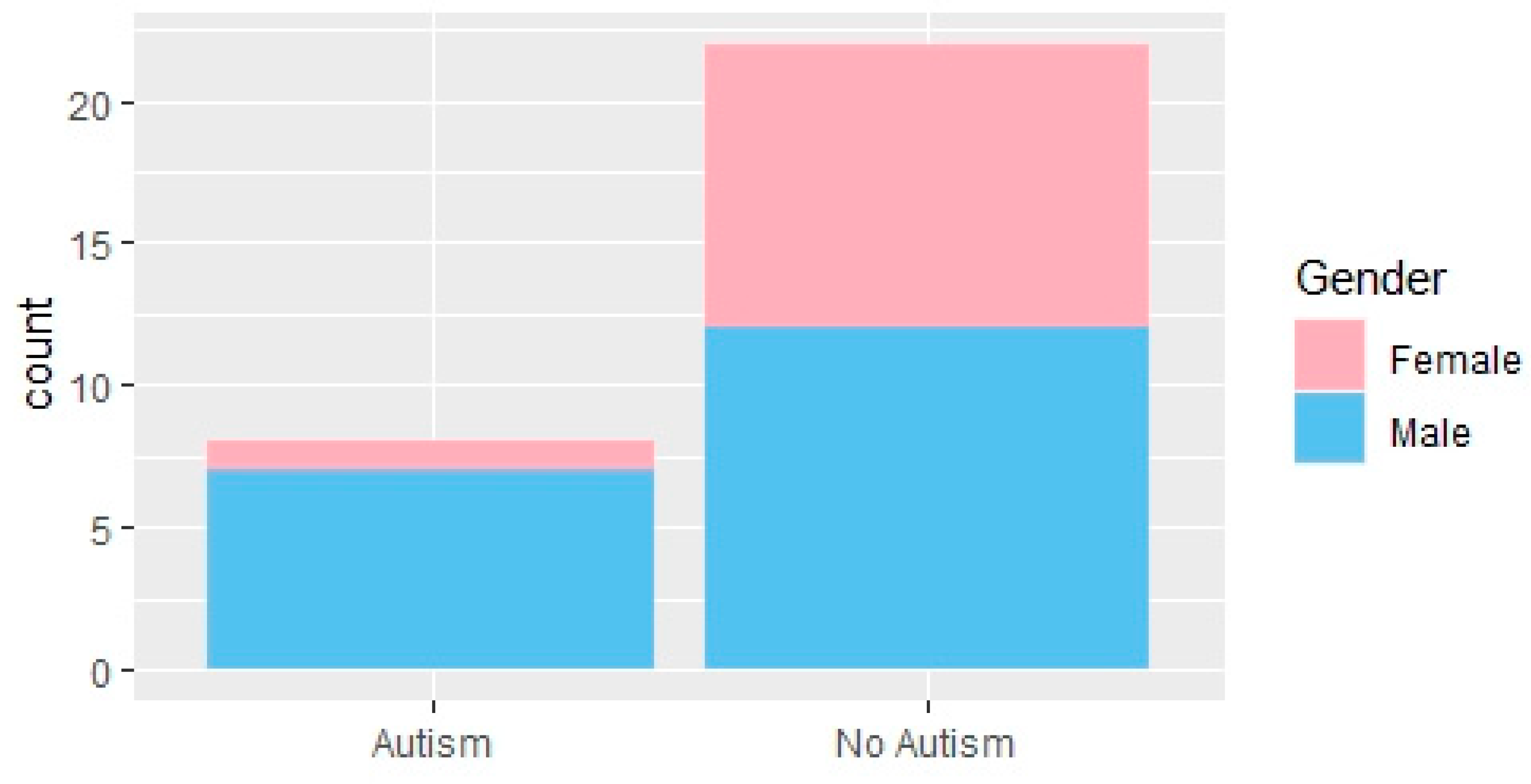






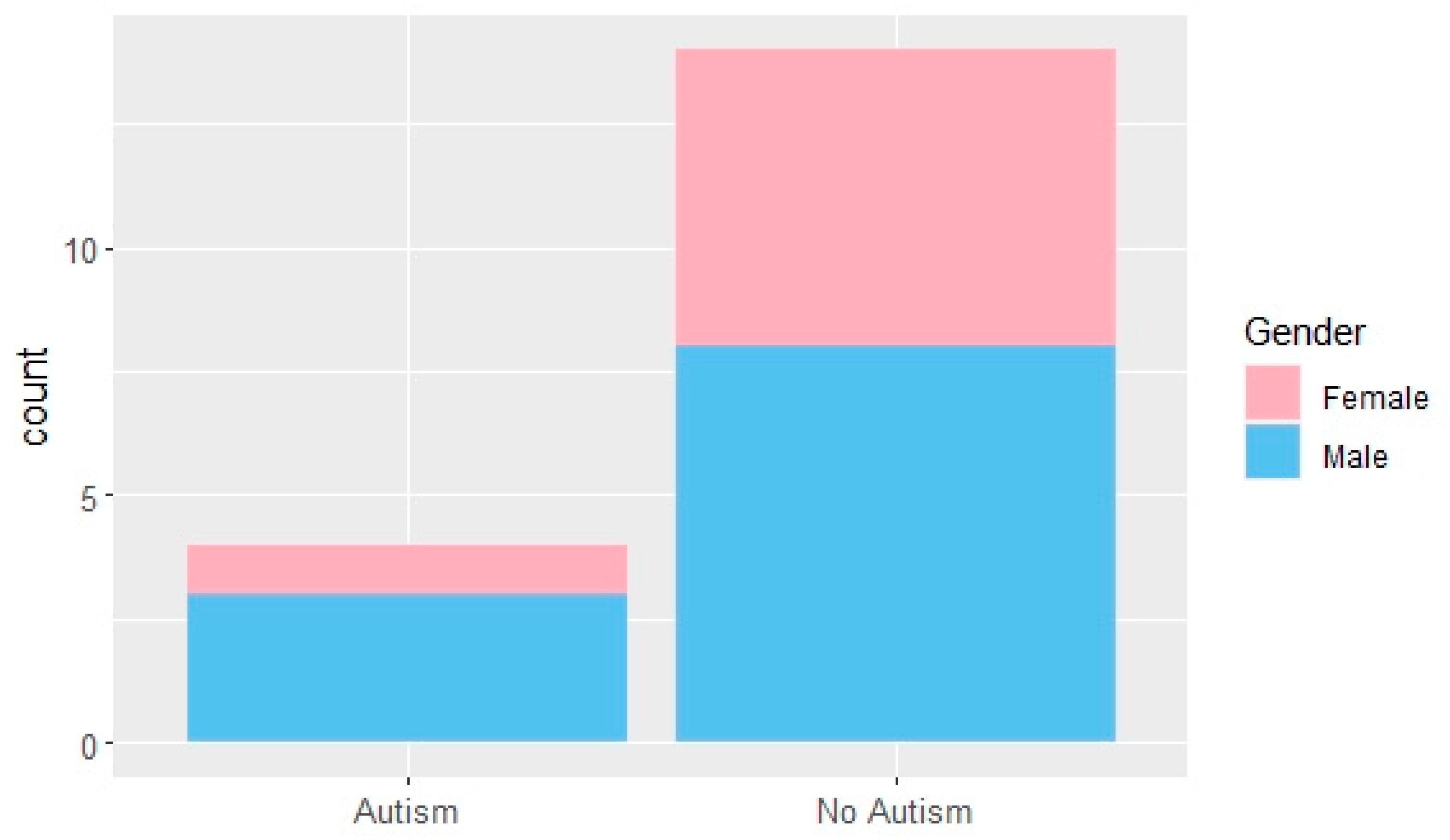
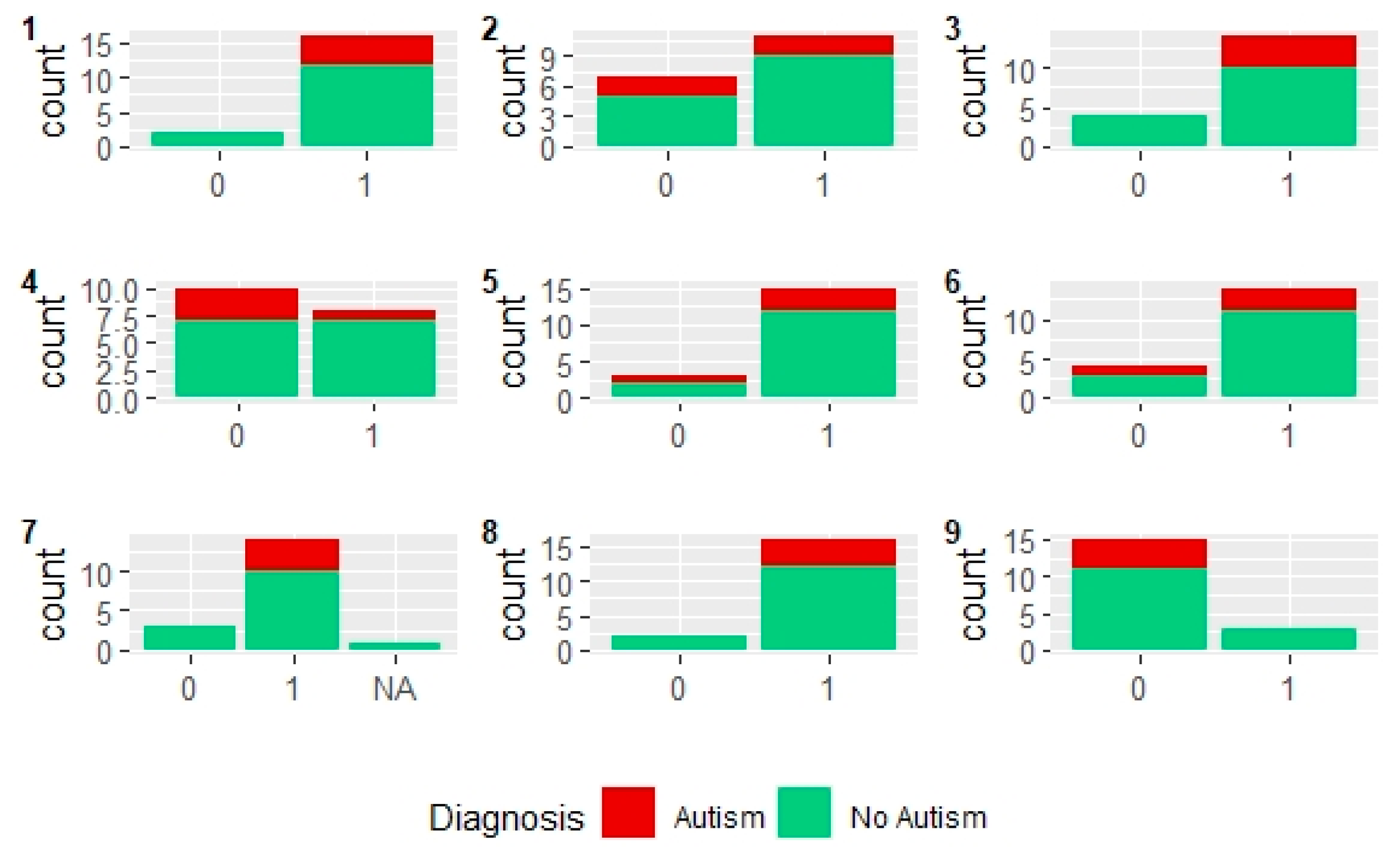


| Model | Total Positive Rate | ROC Area |
|---|---|---|
| Multilayer Perceptron | 0.885 | 0.805 |
| SMO | 0.854 | 0.500 |
| Random Forest | 0.859 | 0.870 |
| Model | Total Positive Rate | ROC Area |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.844 | 0.814 |
| Decision Tree (J48) | 0.870 | 0.775 |
| SANN | 0.875 | 0.870 |
| Analysis Type | Interpretability Required | Interpretability Not Required | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature Selection | No Feature Selection | Feature Selection | No Feature Selection | |
| Preliminary | 0.756 | 0.794 | 0.750 | 0.833 |
| Typical | 0.778 | 0.807 | 0.798 | 0.830 |
| Extensive | 0.794 | 0.806 | 0.833 | 0.823 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batsakis, S.; Adamou, M.; Tachmazidis, I.; Jones, S.; Titarenko, S.; Antoniou, G.; Kehagias, T. Data-Driven Decision Support for Adult Autism Diagnosis Using Machine Learning. Digital 2022, 2, 224-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital2020014
Batsakis S, Adamou M, Tachmazidis I, Jones S, Titarenko S, Antoniou G, Kehagias T. Data-Driven Decision Support for Adult Autism Diagnosis Using Machine Learning. Digital. 2022; 2(2):224-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital2020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatsakis, Sotirios, Marios Adamou, Ilias Tachmazidis, Sarah Jones, Sofya Titarenko, Grigoris Antoniou, and Thanasis Kehagias. 2022. "Data-Driven Decision Support for Adult Autism Diagnosis Using Machine Learning" Digital 2, no. 2: 224-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital2020014
APA StyleBatsakis, S., Adamou, M., Tachmazidis, I., Jones, S., Titarenko, S., Antoniou, G., & Kehagias, T. (2022). Data-Driven Decision Support for Adult Autism Diagnosis Using Machine Learning. Digital, 2(2), 224-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital2020014






