The Cross-Talk between Microbiome and Metabolome in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
Research Methodology
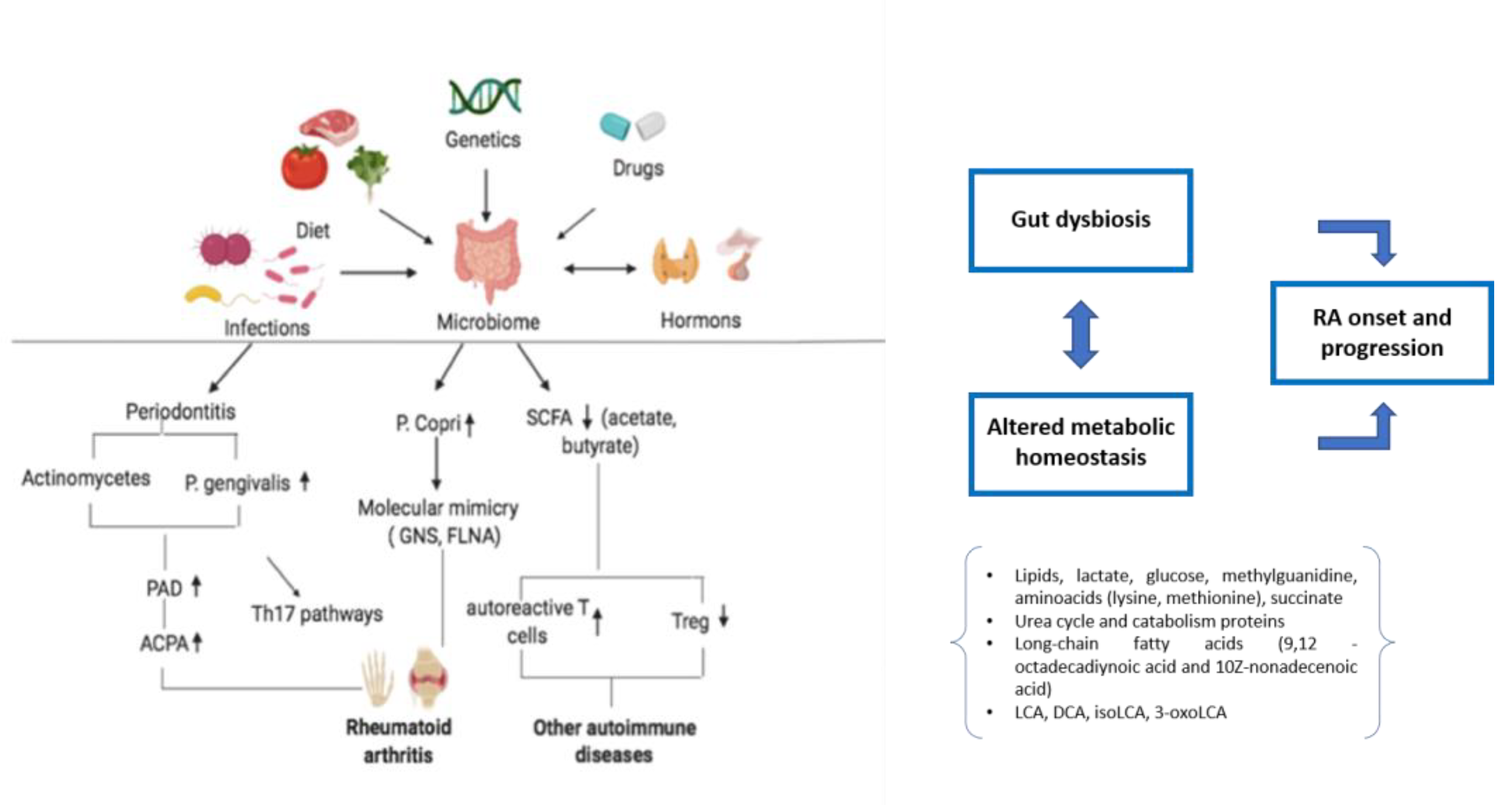
2. Metabolome in RA
3. Microbiome in RA
4. Metabolomics Applied to Treatment and Interference with Microbiome Pathological Dysfunction in RA
| Metabolites | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predisposing Bacteria | Collinsella, Eggerthella, and Faecalibacterium genera | [32] | |
| Verrucomicrobiaand Akkermansia | 9,12-octadecadiynoic acid and 10Z-nonadecenoic acid | [33] (animal study) | |
| Lactobacillus salivarius | [62] | ||
| P. copri | [63] | ||
| Prevotella sp. | [64] | ||
| Protective Bacteria | B. fragilis | Butyrate | [52] (animal study) |
| Escherichia coli and Bacteroides species | [53] (animal study), [54] (animal study) | ||
| Haemophilus spp. | [62] | ||
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarumLS/07 | [82] (animal study) | ||
| P. distasonis | LCA, DCA, isoLCA and 3-oxoLCA | [86] (animal study) | |
| Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum | unconjugated secondary BA | [87] (animal study) | |
| L. casei | [88,89] (animal study), [90] (animal study) | ||
| L. acidophilus | [89] (animal study) |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Buckley, C.D.; Isaacs, J.D. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis—Shaping the immunological landscape. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovská, N.; Prajzlerová, K.; Vencovský, J.; Šenolt, L.; Filková, M. The pre-clinical phase of rheumatoid arthritis: From risk factors to prevention of arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romão, V.C.; Fonseca, J.E. Disease mechanisms in preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: A narrative review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 689711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Immunometabolism in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 294, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edilova, M.I.; Akram, A.; Abdul-Sater, A.A. Innate immunity drives pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saferding, V.; Blüml, S. Innate immunity as the trigger of systemic autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siouti, E.; Andreakos, E. The many facets of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 165, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.-W.A.; Felson, D.T.; Yood, R.A.; Walker, A.M. The lag time between onset of symptoms and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, J.R. Treating rheumatoid arthritis early: A window of opportunity? Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chang, C.; Jiang, P.; Wei, K.; Zhang, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, S.; et al. Metabolomics in rheumatoid arthritis: Advances and review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 961708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coras, R.; Murillo-Saich, J.D.; Guma, M. Circulating Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Metabolites and Its Potential Role in Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, B.; Fang, Z.; Leng, Y.-F.; Wang, D.-W.; Chen, F.-Q.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.-L. Metabolomics in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Jt. Bone Spine 2020, 87, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, C.; Camarda, F.; Donzella, D.; La Barbera, L.; Guggino, G. Metabolomics: An Emerging Approach to Understand Pathogenesis and to Assess Diagnosis and Response to Treatment in Spondyloarthritis. Cells 2022, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutley, G.S.; Sahota, K.; Sahbudin, I.; Filer, A.; Arayssi, T.; Young, S.P.; Raza, K. Relationship Between Inflammation and Metabolism in Patients With Newly Presenting Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 676105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.P.; Kapoor, S.R.; Viant, M.R.; Byrne, J.J.; Filer, A.; Buckley, C.D.; Kitas, G.D.; Raza, K. The Impact of Inflammation on Metabolomic Profiles in Patients with Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietzner, M.; Kaul, A.; Henning, A.-K.; Kastenmüller, G.; Artati, A.; Lerch, M.M.; Adamski, J.; Nauck, M.; Friedrich, N. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of chronic low-grade inflammation among generally healthy individuals. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.R.; Filer, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.A.; Fisher, B.A.; Taylor, P.C.; Buckley, C.D.; McInnes, I.B.; Raza, K.; Young, S.P. Metabolic Profiling Predicts Response to Anti–Tumor Necrosis Factor α Therapy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; for the IMID Consortium; Julià, A.; Vinaixa, M.; Domènech, E.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Cañete, J.D.; Ferrándiz, C.; Tornero, J.; Gisbert, J.P. Urine metabolome profiling of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvã¡n-Peã±A, S.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Metabolic Reprograming in Macrophage Polarization. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.C.; O’Neill, L.A.J. A Role for the Krebs Cycle Intermediate Citrate in Metabolic Reprogramming in Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannahill, G.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Adamik, J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; McGettrick, A.F.; Goel, G.; Frezza, C.; Bernard, N.J.; Kelly, B.; Foley, N.H.; et al. Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. Nature 2013, 496, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucino, V.; Certo, M.; Bulusu, V.; Cucchi, D.; Goldmann, K.; Pontarini, E.; Haas, R.; Smith, J.; Headland, S.E.; Blighe, K.; et al. Lactate Buildup at the Site of Chronic Inflammation Promotes Disease by Inducing CD4+ T Cell Metabolic Rewiring. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 1055–1074.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Zeisbrich, M.; Goronzy, J.J. Metabolic signatures of T-cells and macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 46, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, J.; Tukiainen, T.; Sarin, A.-P.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Tikkanen, E.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Würtz, P.; Silander, K.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple loci influencing human serum metabolite levels. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, J.; Demirkan, A.; Würtz, P.; Draisma, H.H.; Haller, T.; Rawal, R.; Vaarhorst, A.; Kangas, A.J.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Pirinen, M.; et al. Genome-wide study for circulating metabolites identifies 62 loci and reveals novel systemic effects of LPA. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Wu, D.; Trynka, G.; Raj, T.; Terao, C.; Ikari, K.; Kochi, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 2014, 506, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.M.A.; Stevens, C.R.; Walsh, E.C.; De Jager, P.L.; Goyette, P.; Plenge, R.M.; Vyse, T.J.; Rioux, J.D. Defining the Role of the MHC in Autoimmunity: A Review and Pooled Analysis. PLOS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; de Jong, B.A.W.; Berglin, E.; Hallmans, G.; Wadell, G.; Stenlund, H.; Sundin, U.; van Venrooij, W.J. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delft, M.A.; Huizinga, T.W. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wright, K.; Davis, J.M.; Jeraldo, P.; Marietta, E.V.; Murray, J.; Nelson, H.; Matteson, E.L.; Taneja, V. An expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, F.; Dai, W.; Hong, X.; Liu, D.; Tang, D.; et al. Analysis of gut microbiota and metabolites in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and identification of potential biomarkers. Aging 2021, 13, 23689–23701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, D.; Wu, C.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Q. The role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, A.B.; Kopec, J.; Shrestha, L.; Thezenas, M.-L.; Burgess-Brown, N.A.; Fischer, R.; Yue, W.W.; Venables, P.J. Crystal structure of Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase: Implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Kurakawa, T.; Umemoto, E.; Motooka, D.; Ito, Y.; Gotoh, K.; Hirota, K.; Matsushita, M.; Furuta, Y.; Narazaki, M.; et al. Dysbiosis Contributes to Arthritis Development via Activation of Autoreactive T Cells in the Intestine. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2646–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, K.M.; Vissink, A.; de Smit, M.J.; Westra, J.; Brouwer, E. Lessons to be learned from periodontitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013, 25, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, N.; Wait, R.; Sroka, A.; Eick, S.; Nguyen, K.-A.; Lundberg, K.; Kinloch, A.; Culshaw, S.; Potempa, J.; Venables, P.J. Peptidylarginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis citrullinates human fibrinogen and α-enolase: Implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, J.T.; Gerow, E.A.; Schaff, R.; Taut, A.D.; Shin, S.-Y.; Sugai, J.; Brand, D.; Burberry, A.; Jorns, J.; Lundy, S.K.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis oral infection exacerbates the development and severity of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, M.F.; Abusleme, L.; Reinholdt, J.; Palmer, R.J.; Teles, R.P.; Sampson, K.; Rosen, A.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Sokolove, J.; Giles, J.T.; et al. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans—Induced hypercitrullination links periodontal infection to autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 369ra176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Beckler, M.D.; Amini, S.S.; Kesselman, M.M. Oral Microbiome in Pre-Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans in Bacterial Composition. Cureus 2022, 5, e32201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looh, S.C.; Soo, Z.M.P.; Wong, J.J.; Yam, H.C.; Chow, S.K.; Hwang, J.S. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans as the Aetiological Cause of Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Are the Unsolved Puzzles? Toxins 2022, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Mou, F.; Wang, H.; Zou, Q.; Zhong, B.; Wu, L.; Wei, H.; et al. Role of the Gut Microbiome in Modulating Arthritis Progression in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Bäckhed, F. Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Alipour, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Sharif, S.-K.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Zavvari, S. Probiotic supplementation improves inflammatory status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition 2014, 30, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, S.; Wang, D.; Wen, C.; Xu, G. Exploration of the serum metabolite signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 127, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishikawa, T.; Maeda, Y.; Nii, T.; Motooka, D.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsushita, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Kawada, S.; Teshigawara, S.; et al. Metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiome revealed novel aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, B.; Uitz, E.; Thonhofer, R.; Trummer, M.; Pestemer-Lach, I.; McCarty, M.; Krejs, G.J. ω-3 Fatty Acids Infusions as Adjuvant Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häger, J.; Bang, H.; Hagen, M.; Frech, M.; Träger, P.; Sokolova, M.; Steffen, U.; Tascilar, K.; Sarter, K.; Schett, G.; et al. The Role of Dietary Fiber in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Barbera, L.; Macaluso, F.; Fasano, S.; Grasso, G.; Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G. Microbiome Changes in Connective Tissue Diseases and Vasculitis: Focus on Metabolism and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, M.; Visekruna, A. Short-chain fatty acids: Bacterial messengers modulating the immunometabolism of T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Dong, C.; Zhao, B.; Lin, K.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, L.; Xu, H.; Yang, L. Bacteroides fragilis participates in the therapeutic effect of methotrexate on arthritis through metabolite regulation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1015130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohashi, O.; Kohashi, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Ozawa, A.; Shigematsu, N. Reverse Effect of Gram-Positive Bacteria vs. Gram-Negative Bacteria on Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Germfree Rats. Microbiol. Immunol. 1985, 29, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohashi, O.; Kohashi, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Ozawa, A.; Shigematsu, N. Suppressive effect ofEscherichia coli on adjuvant-induced arthritis in germ-free rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breban, M.A.; Moreau, M.C.; Fournier, C.; Ducluzeau, R.; Kahn, M.F. Influence of the bacterial flora on collagen-induced arthritis in susceptible and resistant strains of rats. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1993, 11, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, M.E.C.; Bengtsson, C.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L.; Saevarsdottir, S. Recent infections are associated with decreased risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based case-control study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.T.; Rooney, P.J.; Jones, D.B.; Bienenstock, J.; Goodacre, R.L. Increased intestinal permeability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A side-effect of oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy? Rheumatology 1987, 26, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, A.; Isenberg, D.; Hajirousou, V.; Tolfree, S.; Clark, J.; Snaith, M.L. Preliminary evidence for gut involvement in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatology 1986, 25, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaluso, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Ferrante, A.; Ciccia, F. Histopathology of the gut in rheumatic diseases. Reumatismo 2018, 70, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzio, V.; Biasi, G.; Corrado, A.; De Santi, M.; Vindigni, C.; Vrti, S.; Bayeli, P.F.; Marcolongo, R. Intestinal Histological and Ultrastructural Inflammatory Changes in Spondyloarthropathy and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 26, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielants, H.; De Vos, M.; Goemaere, S.; Schelstraete, K.; Cuvelier, C.; Goethals, K.; Maertens, M.; Ackerman, C.; Veys, E.M. Intestinal mucosal permeability in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. II. Role of disease. J. Rheumatol. 1991, 18, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, J.U.; Sczesnak, A.; Longman, R.S.; Segata, N.; Ubeda, C.; Bielski, C.; Rostron, T.; Cerundolo, V.; Pamer, E.G.; Abramson, S.B.; et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. eLife 2013, 2, e01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianta, A.; Arvikar, S.L.; Strle, K.; Drouin, E.E.; Wang, Q.; Costello, C.; Steere, A.C. Two rheumatoid arthritis–specific autoantigens correlate microbial immunity with autoimmune responses in joints. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2946–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G.; Negru, P.A.; Marcu, M.F.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L. In-depth bibliometric analysis and current scientific mapping research in the context of rheumatoid arthritis pharmacotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartikoski, B.J.; De Oliveira, M.S.; Santo, R.C.D.E.; Dos Santos, L.P.; Dos Santos, N.G.; Xavier, R.M. A Review of Metabolomic Profiling in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Bringing New Insights in Disease Pathogenesis, Treatment and Comorbidities. Metabolites 2022, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Plant, D.; Verstappen, S.M.; Isaacs, J.D.; Morgan, A.; Hyrich, K.L.; Barton, A.; Wilson, A.G. The MATURA investigators Differential DNA methylation correlates with response to methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, B.; Plewa, S.; Klupczynska, A.; Sikorska, D.; Samborski, W.; Kokot, Z.J. Serum free amino acid levels in rheumatoid arthritis according to therapy and physical disability. Cytokine 2019, 113, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Scrivo, R.; Brandt, J.; Valerio, M.; Casadei, L.; Valesini, G.; Manetti, C. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: The potential of an emerging methodology for improved patient diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment efficacy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, R.; Rao, M.; Zhang, C.; Agrati, C.; Ippolito, G.; Wang, F.-S.; Zumla, A.; Maeurer, M. Immunometabolism: New insights and lessons from antigen-directed cellular immune responses. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 279–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselt, H.R.; Muller, I.B.; Jansen, G.; Van Weeghel, M.; Vaz, F.M.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Heil, S.G.; De Jonge, R. Identification of Metabolic Biomarkers in Relation to Methotrexate Response in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamoun, Y.M.; Polireddy, K.; Cho, Y.K.; Medcalf, M.R.; Funk, R.S. Methotrexate Disposition, Anti-Folate Activity, and Metabolomic Profiling to Identify Molecular Markers of Disease Activity and Drug Response in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model. Metabolites 2021, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Fan, H.; He, D.; Zhao, S.; Shu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Lu, S.; Xiao, C.; et al. Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Combination of Methotrexate and Tripterygium Glycosides Tablets—A Quantitative Plasma Pharmacochemical and Pseudotargeted Metabolomic Approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artacho, A.; Isaac, S.; Nayak, R.; Flor-Duro, A.; Alexander, M.; Koo, I.; Manasson, J.; Smith, P.B.; Rosenthal, P.; Homsi, Y.; et al. The Pretreatment Gut Microbiome Is Associated With Lack of Response to Methotrexate in New-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Fan, J.; Su, Q.; Yang, Z. Cytokines and Abnormal Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Casadei, L.; Valerio, M.; Scrivo, R.; Valesini, G.; Manetti, C. 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomic Study for Identifying Serum Profiles Associated with the Response to Etanercept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, Z.; Migne, C.; Petera, M.; Gaudin, P.; Lequerre, T.; Marotte, H.; Tebib, J.; Guillot, E.P.; Soubrier, M. Variations in the metabolome in response to disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Saegusa, J.; Onishi, A.; Morinobu, A. Biomarkers identified by serum metabolomic analysis to predict biologic treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitsma, X.M.; Yang, W.; Jacobs, J.W.G.; Pethö-Schramm, A.; Borm, M.E.A.; Harms, A.C.; Hankemeier, T.; van Laar, J.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G. Baseline metabolic profiles of early rheumatoid arthritis patients achieving sustained drug-free remission after initiating treat-to-target tocilizumab, methotrexate, or the combination: Insights from systems biology. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Saich, J.D.; Diaz-Torne, C.; Ortiz, M.A.; Coras, R.; Gil-Alabarse, P.; Pedersen, A.; Corominas, H.; Vidal, S.; Guma, M. Metabolomics profiling predicts outcome of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: An exploratory study. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, S.R.; Kavanaugh, A.; Lodi, A.; Wang, B.; Boyle, D.; Tiziani, S.; Guma, M. Metabolomic profiling predicts outcome of rituximab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Naved, T.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Chakrabarti, P.; Aleya, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the role of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 108078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-K.; Chen, P.-K.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, D.-Y. Increased Levels of Omega-3 Fatty Acids and DHA Are Linked to Pain Reduction in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Janus Kinase Inhibitors. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuppen, B.V.J.; Fu, J.; van Wietmarschen, H.A.; Harms, A.C.; Koval, S.; Marijnissen, A.C.A.; Peeters, J.J.W.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Tekstra, J.; van Laar, J.M.; et al. Exploring the Inflammatory Metabolomic Profile to Predict Response to TNF-α Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, B.; Golkar, H.R.; Farshbaf, S.; Emadi-Baygi, M.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akhavan, R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic supplementation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 19, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, A.; Hu, J.; Yuan, T.; Zhou, S.; Xu, W.; Wei, P.; Yin, S.; et al. Gut commensal Parabacteroides distasonis alleviates inflammatory arthritis. Gut 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ren, H.; Yang, N.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; et al. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum-Mediated Bile Acid Metabolism to Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis via the Gut–Joint Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Sharif, S.K.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, L.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Nakhjavani, M.R.; Mohtadi-Nia, J. Effects of Lactobacillus casei supplementation on disease activity and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdekar, S.; Singh, V.; Kumari, A.; Sharma, P.; Singh, R.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Alipour, B.; Sharif, S.-K.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, L.; et al. Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus acidophilus Regulate Inflammatory Pathway and Improve Antioxidant Status in Collagen-Induced Arthritic Rats. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2013, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdekar, S.; Singh, V.; Singh, R.; Sharma, P.; Keshav, P.; Kumar, A. Lactobacillus casei reduces the Inflammatory Joint Damage Associated with Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) by Reducing the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Lactobacillus Casei: COX-2 Inhibitor. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pružinská, K.; Slovák, L.; Dráfi, F.; Poništ, S.; Juránek, I.; Chrastina, M.; Švík, K.; Strojný, L.; Ambro, L.; Bauerová, K. Enhanced Anti-Inflammatory Effect of the Combination of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LS/07 with Methotrexate Compared to Their Monotherapies Studied in Experimental Arthritis. Molecules 2022, 28, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Barbera, L.; Rizzo, C.; Grasso, G.; Macaluso, F.; Camarda, F.; Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G. The Cross-Talk between Microbiome and Metabolome in Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioChem 2023, 3, 47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem3010004
La Barbera L, Rizzo C, Grasso G, Macaluso F, Camarda F, Ciccia F, Guggino G. The Cross-Talk between Microbiome and Metabolome in Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioChem. 2023; 3(1):47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Barbera, Lidia, Chiara Rizzo, Giulia Grasso, Federica Macaluso, Federica Camarda, Francesco Ciccia, and Giuliana Guggino. 2023. "The Cross-Talk between Microbiome and Metabolome in Rheumatoid Arthritis" BioChem 3, no. 1: 47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem3010004
APA StyleLa Barbera, L., Rizzo, C., Grasso, G., Macaluso, F., Camarda, F., Ciccia, F., & Guggino, G. (2023). The Cross-Talk between Microbiome and Metabolome in Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioChem, 3(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem3010004









