Cathepsin B: Plasma Expression and Concentration in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients
Abstract
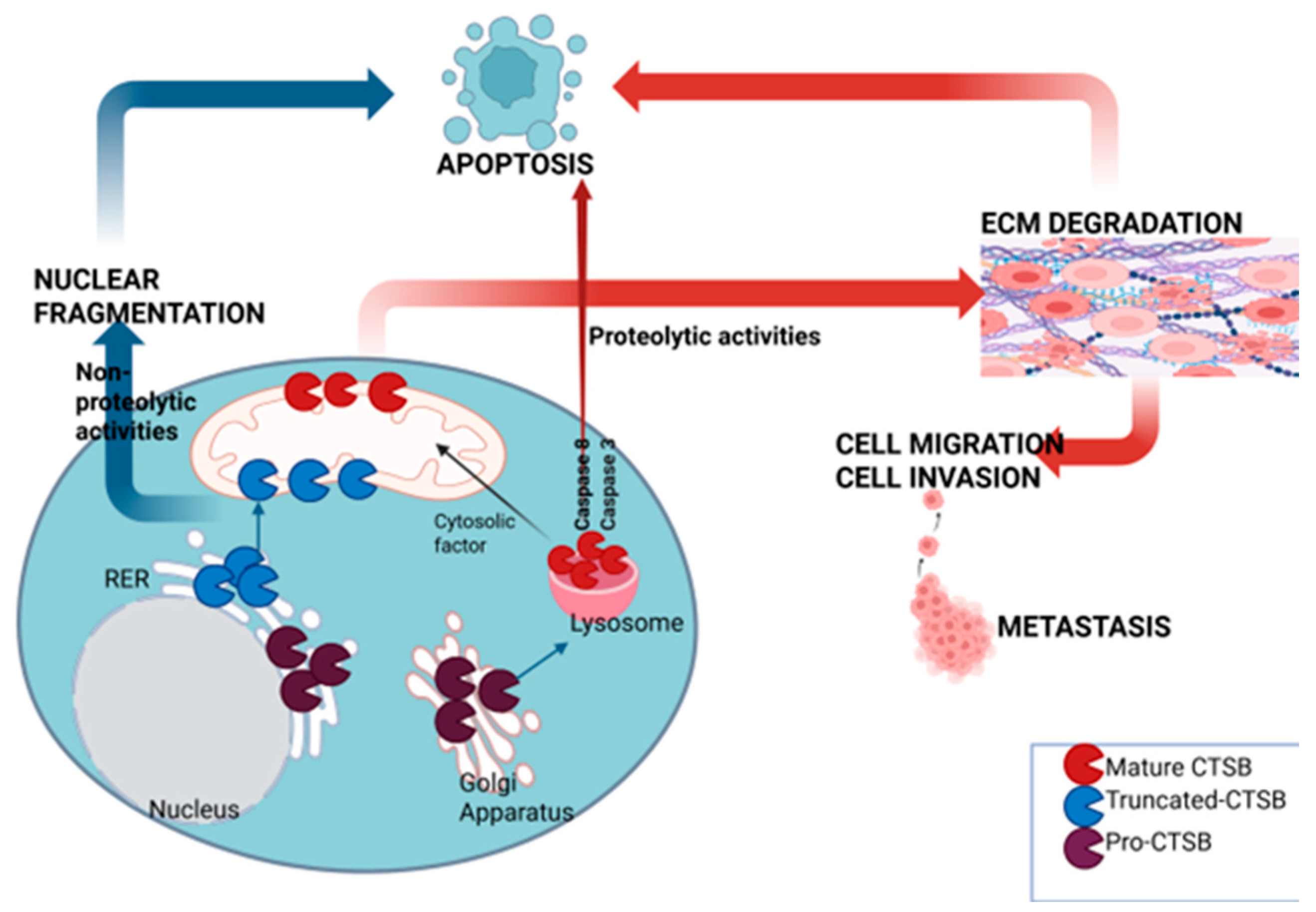
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Data of NHL Patients and Controls
3.2. Plasma Cathepsin B, Cystatin C and Redox Parameters in NHL Patients and Control Groups
3.3. The Association Between CTSB Plasma Concentration and NHL Subtype
3.4. Plasma CTSB mRNA Levels and CTSB Levels in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients
3.5. The Correlation of Plasma CTSB with the CTSB mRNA Level and Redox Parameters in NHL Patients Before and After Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NHL | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| CTSB | Cathepsin B |
| RER | Rough endoplasmatic reticulum |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Cys C | Cystatin C |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| TAS | Total antioxidant status |
| TOS | Total oxidant status |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
References
- Mugnaini, E.N.; Ghosh, N. Lymphoma. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2016, 43, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Pimenta, M.; Estevinho, M.M.; Sousa Dias, M.; Martins, Â.; Estevinho, L.M. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in B-Cell Lymphomas. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, S. The Role of Cathepsin B in Pathophysiologies of Non-Tumor and Tumor Tissues: A Systematic Review. J. Cancer 2023, 14, 2344–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yan, C.; Kong, W.; Lan, F.; Narengaowa; Zhao, S.; Yang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Qing, H.; et al. Cathepsin B in Programmed Cell Death Machinery: Mechanisms of Execution and Regulatory Pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Featherston, T.; Marsh, R.W.; Van Schaijik, B.; Brasch, H.D.; Tan, S.T.; Itinteang, T. Expression and Localization of Cathepsins B, D, and G in Two Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulations in Moderately Differentiated Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronina, M.V.; Frolova, A.S.; Kolesova, E.P.; Kuldyushev, N.A.; Parodi, A.; Zamyatnin, A.A. The Intricate Balance between Life and Death: ROS, Cathepsins, and Their Interplay in Cell Death and Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalmanach, G.; Saidi, A.; Bigot, P.; Chazeirat, T.; Lecaille, F.; Wartenberg, M. Regulation of the Proteolytic Activity of Cysteine Cathepsins by Oxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.A.; Ackerman, S.L. Oxidative Stress, Cell Cycle, and Neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, X. Cathepsin B as a Target in Cancer Therapy and Imaging. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19593–19611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, S.M.; Chua, S.X.S.; Venkatachalam, G.; Shen, L.; Luo, L.; Clement, M.-V. Sub-Lethal Oxidative Stress Induces Lysosome Biogenesis via a Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization-Cathepsin-Caspase 3-Transcription Factor EB-Dependent Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16170–16189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, P.; Zhang, N. CTSB Knockdown Inhibits Proliferation and Tumorigenesis in HL-60 Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, L.; Gocheva, V.; Quick, M.L.; Kester, J.C.; Spencer, A.K.; Garfall, A.L.; Bowman, R.L.; Joyce, J.A. Combined Deletion of Cathepsin Protease Family Members Reveals Compensatory Mechanisms in Cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.; Lin, Y.; Liton, P.B. Cathepsin B Is Up-Regulated and Mediates Extracellular Matrix Degradation in Trabecular Meshwork Cells Following Phagocytic Challenge. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, C.S.; Rao, J.S. Cathepsin B as a Cancer Target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsouvanh, A.; Proungvitaya, T.; Limpaiboon, T.; Wongkham, C.; Wongkham, S.; Luvira, V.; Proungvitaya, S. Serum Cathepsin B to Cystatin C Ratio as a Potential Marker for the Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 9511–9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Asano, G.; Tanaka, S. Expression of Cathepsin B and Cystatin C in Human Colorectal Cancer. Human Pathol. 1999, 30, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, T.; Gao, X.; Lou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Q.; Tan, J.; Huang, J. Relationship between Cathepsins and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mendelian Randomized Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1370350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundelöf, J.; Sundström, J.; Hansson, O.; Eriksdotter-Jönhagen, M.; Giedraitis, V.; Larsson, A.; Degerman-Gunnarsson, M.; Ingelsson, M.; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K.; et al. Higher Cathepsin B Levels in Plasma in Alzheimer’s Disease Compared to Healthy Controls. JAD 2011, 22, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, X. Cystatin C Is a Disease-associated Protein Subject to Multiple Regulation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekic, J.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasic, S.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Topic, A.; Zeljkovic, A.; Stefanovic, A.; Zunic, G. Association of Oxidative Stress and PON1 with LDL and HDL Particle Size in Middle-Aged Subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 37, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.M.; Effer, B.; Costa-Silva, T.A.; Chen, C.; Ciccone, M.F.; Pessoa, A.; Dos Santos, C.O.; Monteiro, G. Cathepsin B Is Not an Intrinsic Factor Related to Asparaginase Resistance of the Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia REH Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, A.; Završnik, J.; Mikhaylov, G.; Knez, D.; Pečar Fonović, U.; Matjan Štefin, P.; Butinar, M.; Gobec, S.; Turk, B.; Kos, J. Evaluation of Novel Cathepsin-X Inhibitors in Vitro and in Vivo and Their Ability to Improve Cathepsin-B-Directed Antitumor Therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, K.; Ciccone, A.; Peters, C.; Yagita, H.; Bird, P.I.; Villadangos, J.A.; Trapani, J.A. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes from Cathepsin B-Deficient Mice Survive Normally in Vitro and in Vivo after Encountering and Killing Target Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 30485–30491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoš, T.; Pišlar, A.; Jewett, A.; Kos, J. Cysteine Cathepsins in Tumor-Associated Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, B.; Mongrain, S.; Cagnol, S.; Langlois, M.-J.; Boulanger, J.; Bernatchez, G.; Carrier, J.C.; Boudreau, F.; Rivard, N. Cathepsin B Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis, Cell Invasion, and Metastasis: Cathepsin B Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Liu, Q.; Tang, X.; Kang, T.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhao, X.; Tang, F. Diagnostic Values of Serum Cathepsin B and D in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Sloane, B.F. Cathepsin B: Multiple Roles in Cancer. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devetzi, M.; Scorilas, A.; Tsiambas, E.; Sameni, M.; Fotiou, S.; Sloane, B.F.; Talieri, M. Cathepsin B Protein Levels in Endometrial Cancer: Potential Value as a Tumour Biomarker. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Fan, Q. Clinical Significance of Serum Cathepsin B and Cystatin C Levels and Their Ratio in the Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Cancer. OTT 2017, 10, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Peng, X.; Luo, C.; Shen, G.; Zhao, C.; Zou, L.; Li, L.; Sang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. Cathepsin B as a Potential Prognostic and Therapeutic Marker for Human Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Miao, Z.; Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; et al. Cathepsin B S-Nitrosylation Promotes ADAR1-Mediated Editing of Its Own mRNA Transcript via an ADD1/MATR3 Regulatory Axis. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berquin, I.M.; Sloane, B.F. Cathepsin B Expression in Human Tumors. In Intracellular Protein Catabolism; Suzuki, K., Bond, J.S., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; Volume 389, pp. 281–294. ISBN 978-1-4613-8003-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nagakannan, P.; Eftekharpour, E. Differential Redox Sensitivity of Cathepsin B and L Holds the Key to Autophagy-Apoptosis Interplay after Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibition in Nutritionally Stressed SH-SY5Y Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Okamura, N.; Yagi, M.; Omatsu, H.; Yamamori, M.; Kuwahara, A.; Nishiguchi, K.; Horinouchi, M.; Okumura, K.; Sakaeda, T. Effects of ABCB1 3435C>T Genotype on Serum Levels of Cortisol and Aldosterone in Women with Normal Menstrual Cycles. Genet. Mol. Res. 2009, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhout, J.; Peeters, M.; Bogaerts, A.; Smits, E.; Deben, C. Oxidative Stress-Inducing Anticancer Therapies: Taking a Closer Look at Their Immunomodulating Effects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, M.; Mahjoub, S.; Moslemi, D.; Karkhah, A. Three Cycles of AC Chemotherapy Regimen Increased Oxidative Stress in Breast Cancer Patients: A Clinical Hint. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 8, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Xiong, Z.; Ihsan, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez, M.; Lopez-Torres, B.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Anadón, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Cancer Metabolism: The Role of ROS in DNA Damage and Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2023, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cai, Z.; Hu, T.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, L. Cathepsin B Aggravated Doxorubicin-induced Myocardial Injury via NF-κB Signalling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4848–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Softić, A.; Begić, L.; Halilbašić, A.; Vižin, T.; Kos, J. The Predictive Value of Cystatin C in Monitoring of B Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Relation to Biochemical and Clinical Parameters. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 2013, 52792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, N.; Salah El-Din, M.; El-Shishtawy, M.; El-Gayar, A. Serum Cystatin C as a Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staun-Ram, E.; Miller, A. Cathepsins (S and B) and Their Inhibitor Cystatin C in Immune Cells: Modulation by Interferon-β and Role Played in Cell Migration. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 232, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Controls, n = 35 | NHL Patients, n = 44 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTSB (ng/mL) | 11.57 (10.12–13.41) | 15.28 (11.68–17.23) | 0.003 |
| Cys C (mg/L) | 0.82 (0.74–0.90) | 1.03 (0.88–1.24) | <0.001 |
| TAS (mmol/L) | 1147 (1002–1222) | 998 (818–1144) | 0.014 |
| TOS (mmol/L) | 9.30 (5.6–12.80) | 12.60 (8.2–17.40) | 0.025 |
| High-Grade NHL, n = 18 | Low-Grade NHL, n = 26 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTSB (ng/mL) | 14.27 (11.65–15.62) | 15.99 (11.64–18.67) | 0.122 |
| CTSB mRNA r (p) | TAS mmol/L r (p) | TOS mmol/L r (p) | Cys C mg/L r (p) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTSB (ng/mL) n = 18 | 0.591 (0.026) | −0.499 (0.035) | 0.576 (0.012) | −0.687 (0.002) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savic, Z.R.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Malcic-Zanic, D.; Stankovic, S.; Egeljic-Mihailovic, N.; Stojisavljević, Đ.; Sopić, M.; Mirjanic-Azaric, B. Cathepsin B: Plasma Expression and Concentration in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients. Hemato 2025, 6, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato6020013
Savic ZR, Bogavac-Stanojevic N, Malcic-Zanic D, Stankovic S, Egeljic-Mihailovic N, Stojisavljević Đ, Sopić M, Mirjanic-Azaric B. Cathepsin B: Plasma Expression and Concentration in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients. Hemato. 2025; 6(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato6020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavic, Zana Radic, Natasa Bogavac-Stanojevic, Dragana Malcic-Zanic, Sinisa Stankovic, Natasa Egeljic-Mihailovic, Đorđe Stojisavljević, Miron Sopić, and Bosa Mirjanic-Azaric. 2025. "Cathepsin B: Plasma Expression and Concentration in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients" Hemato 6, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato6020013
APA StyleSavic, Z. R., Bogavac-Stanojevic, N., Malcic-Zanic, D., Stankovic, S., Egeljic-Mihailovic, N., Stojisavljević, Đ., Sopić, M., & Mirjanic-Azaric, B. (2025). Cathepsin B: Plasma Expression and Concentration in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients. Hemato, 6(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato6020013







