Advanced Radiotherapy Techniques for Mediastinal Lymphomas: Results from an Italian Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
- Characteristics of the center;
- Total number of patients treated with external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) and number of patients with mediastinal lymphoma treated in 2017;
- Adoption of IMRT in clinical practice for the treatment of mediastinal lymphomas, image fusion with diagnostic imaging, frequency of the use of the IMRT technique and comparison of ‘rival’ plans during treatment planning procedures (personalized approach to OAR sparing);
- Use of specific dose constraints for the OARs; presence of differences with constraints used for solid tumors; contouring of cardiac sub-structures;
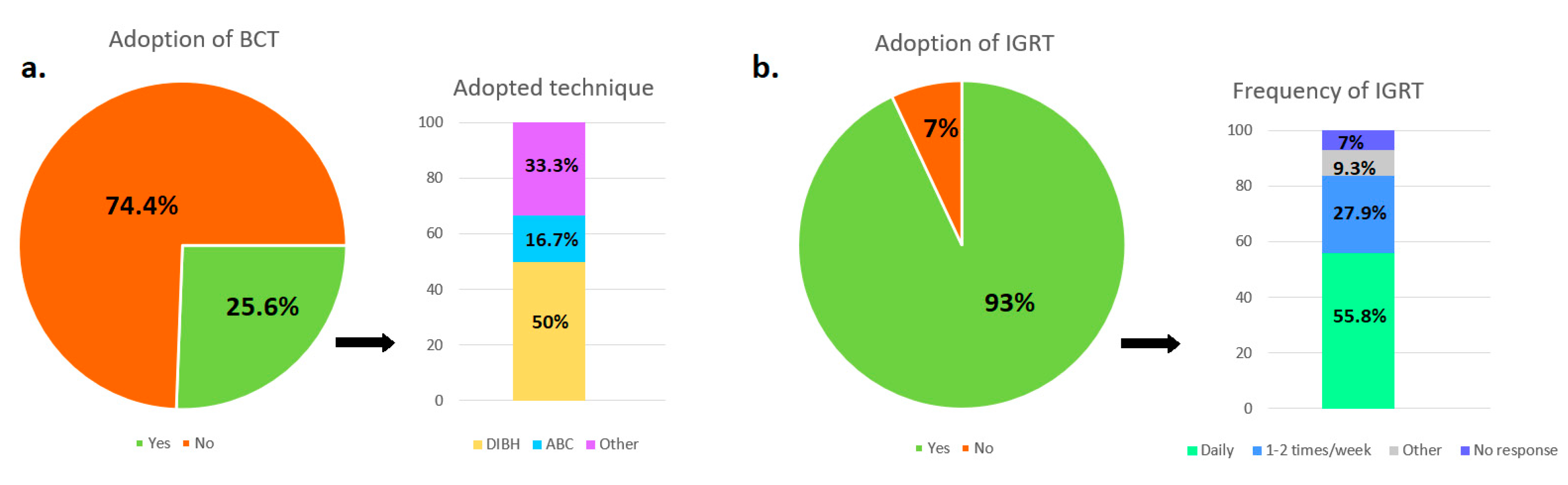
- Adoption of breathing control and/or gating techniques;
- Use and frequency of IGRT;
- Perceived necessity of standardization of techniques and dose constraints.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Treatment Volumes of Participating Centers
3.2. Use of IMRT for the Treatment of Mediastinal Lymphoma
3.3. Dose Constraints to the OARs for the Treatment of Mediastinal Lymphoma
3.4. Adoption of Breathing Control and/or Gating Techniques
3.5. Use and Frequency of IGRT Procedures
3.6. Perceived Necessity of Standardization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filippi, A.R.; Levis, M.; Parikh, R.; Hoppe, B. Optimal Therapy for Early-Stage Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Risk Adapting, Response Adapting, and Role of Radiotherapy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaeel, N.G.; Milgrom, S.A.; Terezakis, S.; Berthelsen, A.K.; Hodgson, D.; Eich, H.T.; Dieckmann, K.; Qi, S.N.; Yahalom, J.; Specht, L. The Optimal Use of Imaging in Radiation Therapy for Lymphoma: Guidelines from the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group (ILROG). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, A.K.; LaCasce, A.; Travis, L.B. Long-term complications of lymphoma and its treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.K.; Bernardo, M.V.; Weller, E.; Backstrand, K.; Silver, B.; Marcus, K.C.; Tarbell, N.J.; Stevenson, M.A.; Friedberg, J.W.; Mauch, P.M. Second malignancy after Hodgkin’s Disease treated with radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy: Long term risks and risk factors. Blood 2002, 100, 1096–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cellai, E.; Magrini, S.M.; Masala, G.; Alterini, R.; Costantini, A.S.; Rigacci, L.; Olmastroni, L.; Papi, M.G.; Spediacci, M.A.; Innocenti, F.; et al. The risk of second malignant tumors and its consequences for the overall survival of Hodgkin’s disease patients and for the choice of their treatment at presentation: Analysis of a series of 1524 cases consecutively treated at the Florence University Hospital. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 49, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasse, S.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Goergen, H.; Plütschow, A.; Müller, H.; Kreissl, S.; Buerkle, C.; Borchmann, S.; Fuchs, M.; Borchmann, P.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Contemporary Treatment in Early-Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma: Updated Analyses of the German Hodgkin Study Group HD7, HD8, HD10, and HD11 Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simontacchi, G.; Filippi, A.R.; Ciammella, P.; Buglione, M.; Saieva, C.; Magrini, S.M.; Ricardi, U. Interim PET After Two ABVD Cycles in Early-Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma: Outcomes Following the Continuation of Chemotherapy Plus Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciammella, P.; Filippi, A.R.; Simontacchi, G.; Buglione, M.; Botto, B.; Mangoni, M.; Iotti, C.; Merli, F.; Marcheselli, L.; Bisi, G.; et al. Post-ABVD/pre-radiotherapy (18)F-FDG-PET provides additional prognostic information for early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma: A retrospective analysis on 165 patients. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koeck, J.; Abo-Madyan, Y.; Lohr, F.; Stieler, F.; Kriz, J.; Mueller, R.P.; Wenz, F.; Eich, H.T. Radiotherapy for early mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma according to the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG): The roles of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and involved-node radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraldo, M.V.; Aznar, M.C.; Vogelius, I.R.; Petersen, P.M.; Specht, L. Involved node radiation therapy: An effective alternative in early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, A.R.; Ciammella, P.; Piva, C.; Ragona, R.; Botto, B.; Ricardi, U. Involved-site image-guided intensity modulated versus 3D conformal radiation therapy in early stage supradiaphragmatic Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, L.; Yahalom, J.; Illidge, T.; Berthelsen, A.K.; Constine, L.S.; Eich, H.T.; Girinsky, T.; Hoppe, R.T.; Mauch, P.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; et al. Modern radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma: Field and dose guidelines from the international lymphoma radiation oncology group (ILROG). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, A.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Aleman, B.M.P.; Pinnix, C.C.; Constine, L.S.; Ricardi, U.; Illidge, T.M.; TheodorEich, H.; Hoppe, B.S.; Dabaja, B.; et al. Involved Site Radiation Therapy in Adult Lymphomas: An Overview of International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group Guidelines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 909–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, A.R.; Meregalli, S.; DI Russo, A.; Levis, M.; Ciammella, P.; Buglione, M.; Guerini, A.E.; De Marco, G.; De Sanctis, V.; Vagge, S.; et al. Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL) expert consensus on the use of intensity-modulated and image-guided radiotherapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma involving the mediastinum. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buglione, M.; Guerini, A.E.; Filippi, A.R.; Spiazzi, L.; Pasinetti, N.; Magli, A.; Toraci, C.; Borghetti, P.; Triggiani, L.; Alghisi, A.; et al. A Systematic Review on Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Mediastinal Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, P.M.; Aznar, M.C.; Berthelsen, A.K.; Loft, A.; Schut, D.A.; Maraldo, M.; Josipovic, M.; Klausen, T.L.; Andersen, F.L.; Specht, L. Prospective Phase II Trial of Image-Guided Radiotherapy in Hodgkin Lymphoma: Benefit of Deep Inspiration Breath-Hold. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paumier, A.; Ghalibafian, M.; Gilmore, J.; Beaudre, A.; Blanchard, P.; Nemr, M.; Azoury, F.; Hamokles, H.; Lefkopoulos, D.; Girinsky, T.; et al. Dosimetric benefits of intensity-modulated radiotherapy combined with the deep-inspiration breath-hold technique in patients with mediastinal Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, A.S.; Hoppe, B.S.; Louis, D.; McDonald, A.M.; Morris, C.G.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Li, Z.; Flampouri, S. Comparison of Techniques for Involved-Site Radiation Therapy in Patients With Lower Mediastinal Lymphoma. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 9, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, L.; Sethugavalar, B.; Robertshaw, H.; Bayman, E.; Thomas, E.; Gilson, D.; Prestwich, R.J. Involved node, site, field and residual volume radiotherapy for lymphoma: A comparison of organ at risk dosimetry and second malignancy risks. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.L.; Connors, J.M.; Tyldesley, S.; Savage, K.J.; Campbell, B.A.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Hamm, J.; Pickles, T. Secondary breast cancer risk by radiation volume in women with Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cella, L.; Conson, M.; Pressello, M.C.; Molinelli, S.; Schneider, U.; Donato, V.; Orecchia, R.; Salvatore, M.; Pacelli, R. Hodgkin’s lymphoma emerging radiation treatment techniques: Trade-offs between late radio-induced toxicities and secondary malignant neoplasms. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, D.C.; Johanson, S.; Peguret, N.; Cozzi, L.; Olsen, D.R. Predicted risk of radiation-induced cancers after involved field and involved node radiotherapy with or without intensity modulation for early-stage hodgkin lymphoma in female patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, A.R.; Ragona, R.; Piva, C.; Scafa, D.; Fiandra, C.; Fusella, M.; Giglioli, F.R.; Lohr, F.; Ricardi, U. Optimized volumetric modulated arc therapy versus 3D-CRT for early stage mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma without axillary involvement: A comparison of second cancers and heart disease risk. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores, G.M.; Metayer, C.; Curtis, R.E.; Lynch, C.F.; Clarke, E.A.; Glimelius, B.; Storm, H.; Pukkala, E.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Holowaty, E.J.; et al. Second malignant neoplasms among long-term survivors of Hodgkin’s disease: A population-based evaluation over 25 years. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3484–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Gilbert, E.; Curtis, R.; Inskip, P.; Kleinerman, R.; Morton, L.; Rajaraman, P.; Little, M.P. Second solid cancers after radiation therapy: A systematic review of the epidemiologic studies on the radiation dose-response relationship. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omer, B.; Kadan-Lottick, N.S.; Roberts, K.B.; Wang, R.; Demsky, C.; Kupfer, G.M.; Cooper, D.; Seropian, S.; Ma, X. Patterns of subsequent malignancies after Hodgkin lymphoma in children and adults. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippi, A.R.; Ragona, R.; Fusella, M. Changes in breast cancer risk associated with different volumes, doses and techniques in female Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients treated with supra-diaphragmatic radiotherapy. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 3, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, A.Y.; Maraldo, M.V.; Brodin, N.P.; Aznar, M.C.; Vogelius, I.R.; Rosenschöld, P.M.; Petersen, P.M.; Specht, L. The effect on esophagus after different radiotherapy techniques for early stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, C.; Correa, C.; Duane, F.K.; Aznar, M.C.; Anderson, S.J.; Bergh, J.; Dodwell, D.; Ewertz, M.; Gray, R.; Jagsi, R. Estimating the risks of breast cancer radiotherapy: Evidence from modern radiation doses to the lungs and heart and from previous randomized trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, A.R.; Vanoni, V.; Meduri, B.; Cozzi, L.; Scorsetti, M.; Ricardi, U.; Lohr, F. Intensity Modulated Radiation therapy and second cancer risk in adults. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriz, J.; Spickermann, M.; Lehrich, P.; Schmidberger, H.; Reinartz, G.; Eich, H.; Haverkamp, U. Breath-hold technique in conventional APPA or intensity-modulated radiotherapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Comparison of ILROG IS-RT and the GHSG IF-RT. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2015, 191, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, M.C.; Maraldo, M.V.; Schut, D.A.; Lundemann, M.; Brodin, N.P.; Vogelius, I.R.; Berthelsen, A.K.; Specht, L.; Petersen, P.M. Minimizing late effects for patients with mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma: Deep inspiration breath-hold, IMRT, or both? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, J.M.; Crook, S.; Wan, K.; Scott, L.; Foroudi, F. A case study evaluating deep inspiration breath-hold and intensity-modulated radiotherapy to minimise long-term toxicity in a young patient with bulky mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2017, 64, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rechner, L.A.; Maraldo, M.V.; Vogelius, I.R.; Zhu, X.R.; Dabaja, B.S.; Brodin, N.P.; Petersen, P.M.; Specht, L.; Aznar, M.C. Life years lost attributable to late effects after radiotherapy for early stage Hodgkin lymphoma: The impact of proton therapy and/or deep inspiration breath hold. Radiother Oncol. 2017, 125, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Starke, A.; Bowden, J.; Lynn, R.; Hall, K.; Hudson, K.; Rato, A.; Aldridge, E.; Robb, D.; Steele, P.; Brady, J.; et al. Comparison of butterfly volumetric modulated arc therapy to full arc with or without deep inspiration breath hold for the treatment of mediastinal lymphoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 129, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, B.S.; Bates, J.E.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Morris, C.G.; Louis, D.; Ho, M.W.; Hoppe, R.T.; Shaikh, M.; Li, Z.; Flampouri, S. The Meaningless Meaning of Mean Heart Dose in Mediastinal Lymphoma in the Modern Radiation Therapy Era. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 10, e147–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levis, M.; Filippi, A.R.; Fiandra, C.; De Luca, V.; Bartoncini, S.; Vella, D.; Ragona, R.; Ricardi, U. Inclusion of heart substructures in the optimization process of volumetric modulated arc therapy techniques may reduce the risk of heart disease in Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 138, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| FIL Guidelines | ILROG Guidelines | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal | Required | Avoid | Optimal | Acceptable | If Necessary | Avoid | |
| Heart | Mean < 5 Gy | Mean, 5–15 Gy | Coronary vessels | Mean < 5Gy | Mean 5–10 Gy | Mean 10–18 Gy | Coronary artery and left ventricle |
| Left ventricle | Mean < 2 Gy | Mean, 5–10 Gy | Coronary vessels | / | / | / | |
| Breasts (whole breasts) | Mean dose < 4 Gy | V4 < 50% | Glandular tissue | Mean dose < 4 GyV4 < 10% | Mean dose 4–15 Gy; V4 10–20%; V10 < 10% | Mean dose > 15 Gy; V4 > 20%; V10 > 10% | Glandular tissue |
| Lungs (minus PTV) | V5 < 55% | V5 55–60% | V5 < 35% V20 < 20% Mean dose < 8 Gy | V5 35–45% V20 20–28% Man dose 8–12 Gy | V5 45–55% V20 28–35% Man dose 12–15 Gy | ||
| V20 < 30% | V20 < 35% | ||||||
| Mean dose < 10 Gy | Mean < 13.5 Gy | ||||||
| Thyroid | V5 < 93% V20 < 82% V25 < 63% V30 < 62% 2.2 mL < 25 Gy | V25 < 70% | Whole thyroid | V25 < 62.5% | Whole thyroid | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Russo, A.; Simontacchi, G.; Guerini, A.E.; Filippi, A.R.; Levis, M.; Ciammella, P.; De Sanctis, V.; Vagge, S.; Meregalli, S.; De Marco, G.; et al. Advanced Radiotherapy Techniques for Mediastinal Lymphomas: Results from an Italian Survey. Hemato 2021, 2, 496-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2030031
Di Russo A, Simontacchi G, Guerini AE, Filippi AR, Levis M, Ciammella P, De Sanctis V, Vagge S, Meregalli S, De Marco G, et al. Advanced Radiotherapy Techniques for Mediastinal Lymphomas: Results from an Italian Survey. Hemato. 2021; 2(3):496-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Russo, Anna, Gabriele Simontacchi, Andrea Emanuele Guerini, Andrea Riccardo Filippi, Mario Levis, Patrizia Ciammella, Vitaliana De Sanctis, Stefano Vagge, Sofia Meregalli, Giuseppina De Marco, and et al. 2021. "Advanced Radiotherapy Techniques for Mediastinal Lymphomas: Results from an Italian Survey" Hemato 2, no. 3: 496-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2030031
APA StyleDi Russo, A., Simontacchi, G., Guerini, A. E., Filippi, A. R., Levis, M., Ciammella, P., De Sanctis, V., Vagge, S., Meregalli, S., De Marco, G., Lanfranchi, B., Spiazzi, L., & Buglione, M. (2021). Advanced Radiotherapy Techniques for Mediastinal Lymphomas: Results from an Italian Survey. Hemato, 2(3), 496-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2030031







