Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Recognition of Markers for Targeted Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Alterations Defining Aggressive DLBCL
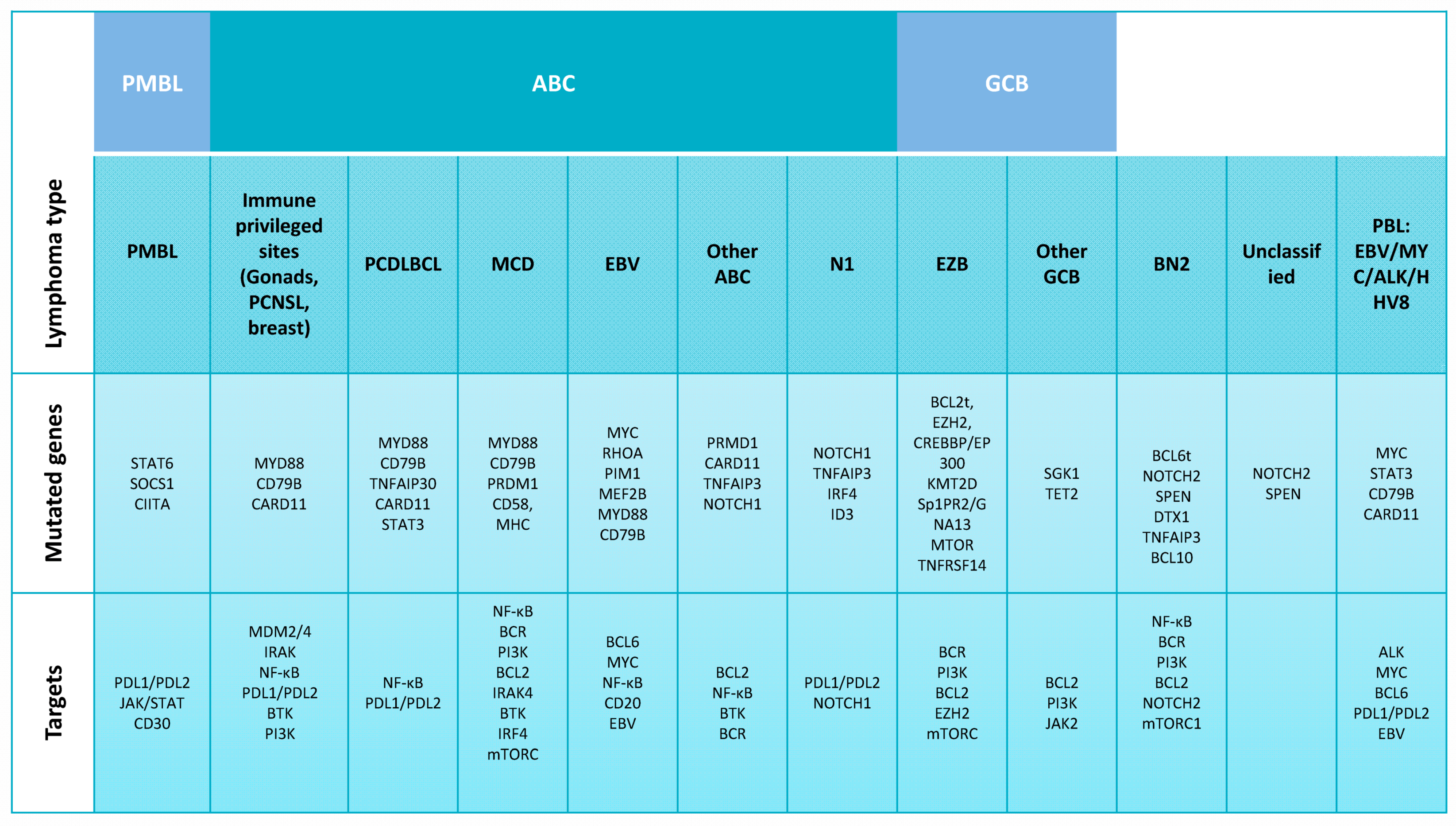
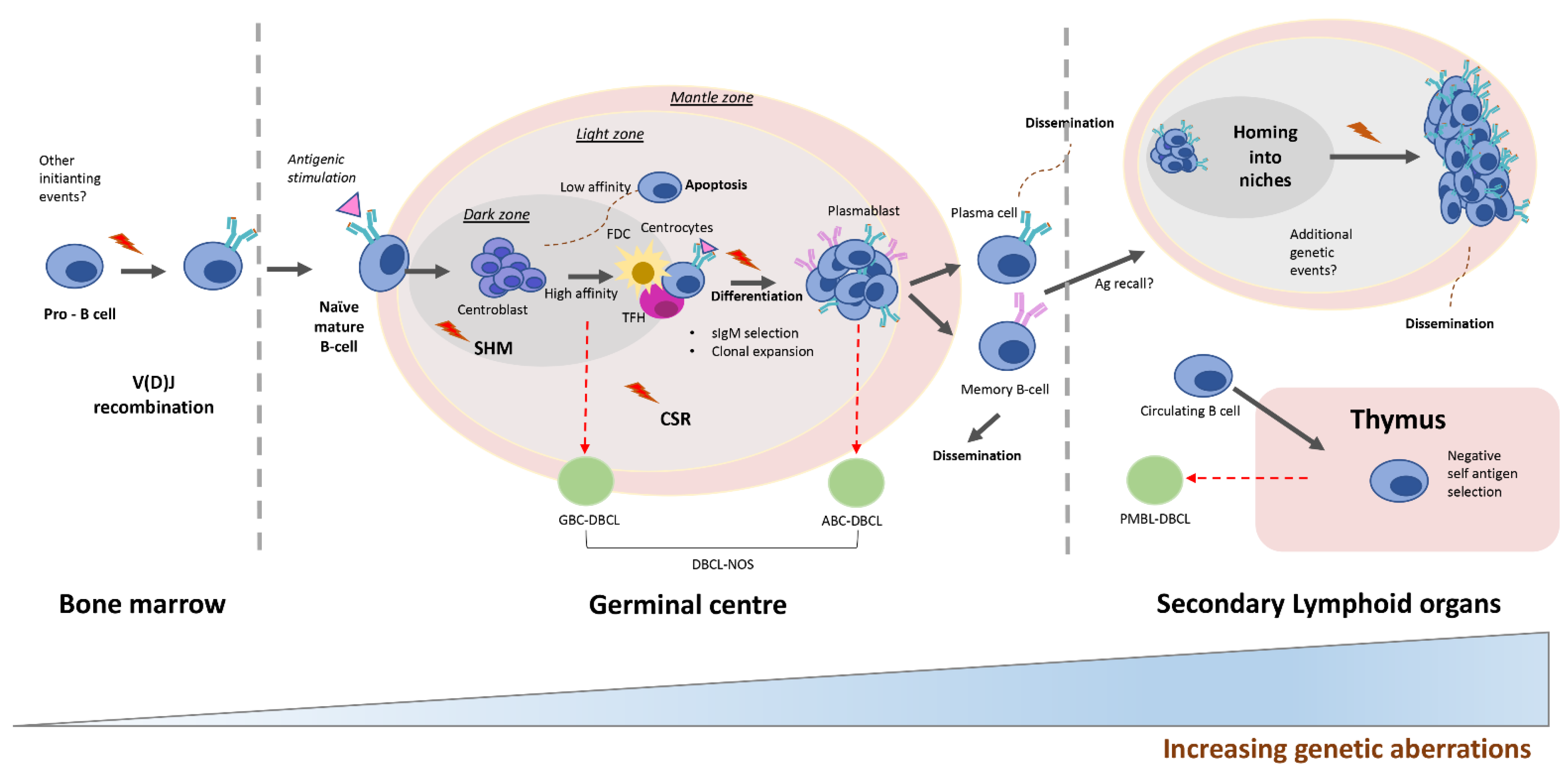
2.1. DLBCL Subclassification
2.2. Relevant Genes and Pathways
3. BCL6, MYC and BCL2
3.1. BCL6
3.2. MYC
- -
- B-cell lymphomas with concurrent MYC and BCL2 abnormalities other than translocations behave similarly to MYC/BCL2 double-hit lymphomas [74].
- -
- This group can be better defined through the recognition of the double-hit gene expression signature (27% of DLBCL-GC patients), which identifies a distinct subgroup of GC-like DLBCLs with a 5-year time to progression rate of 57% [75].
- -
- A molecular high grade, defined using GEP, identifies 9% of DLBCL cases with shorter PFS, in which an analysis of the treatment effects suggested a positive effect of bortezomib [17].
- -
- Double-hit MYC/BCL6 has different biological and clinical implications than the MYC/BCL2 combination.
3.3. BCL2
4. B-Cell Receptor Signaling and Toll-Like Receptor Pathways
4.1. BCR
4.2. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling
4.3. NF-κB Pathway
4.4. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway
5. Epigenetic Regulators Histone/Chromatin Modifiers Pathway
5.1. EZH2
5.2. CREBBP and EP300
5.3. Other Genes Associated with Epigenetics and Chromatin Regulation
6. p53 Pathway
7. Escape from Immune Surveillance
7.1. MHC Class
7.2. CD58
7.3. CD70
7.4. Other Genes Involved in Immune Escape
8. JAK-STAT Pathway
9. Others
10. Therapeutic Targeting of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
10.1. BCL6 Inhibitors
10.2. BCL2/MYC Inhibitors
10.3. BTK iInhibition
10.4. Toll-Like Receptor Inhibition
10.5. PI3K Inhibition
10.6. NF-κB Inhibition
10.7. JAK/STAT Inhibition
10.8. ICIs
11. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sujobert, P.; Salles, G.; Bachy, E. Molecular Classification of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma: What Is Clinically Relevant? Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hurt, E.H.; Wiestner, A.; Staudt, L.M. A gene expression-based method to diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9991–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.W.; Emre, N.C.T.; Kohlhammer, H.; Dave, S.S.; Davis, R.E.; Carty, S.; Lam, L.T.; Shaffer, A.L.; Xiao, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13520–13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; Campo, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Smeland, E.B.; Giltnane, J.M.; et al. The Use of Molecular Profiling to Predict Survival after Chemotherapy for Diffuse Large-B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, J.L.; Medeiros, L.J.; Huang, W.; Khoury, J.D.; McDonnell, T.J.; Tang, G.; Schlette, E.; Yin, C.C.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; et al. MYC rearrangement and MYC/BCL2 double expression but not cell-of-origin predict prognosis in R-CHOP treated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 104, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, M.; Hollander, P.; Pandzic, T.; Mansouri, L.; Ednersson, S.B.; Andersson, P.; Hultdin, M.; Fors, M.; Erlanson, M.; Degerman, S.; et al. Cell-of-origin determined by both gene expression profiling and immunohistochemistry is the strongest predictor of survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.W.; Mottok, A.; Ennishi, D.; Wright, G.W.; Farinha, P.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Kridel, R.; Barry, G.S.; Hother, C.; Abrisqueta, P.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell of Origin Determined by Digital Gene Expression in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Biopsies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Feldman, T.; Rimsza, L.M.; Westin, J.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Zinzani, P.L. Integrating precision medicine through evaluation of cell of origin in treatment planning for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staiger, A.M.; Ziepert, M.; Horn, H.; Scott, D.W.; Barth, T.F.; Bernd, H.W.; Feller, A.C.; Klapper, W.; Szczepanowski, M.; Hummel, M.; et al. Clinical Impact of the Cell-of-Origin Classification and the MYC/BCL2 Dual Expresser Status in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated Within Prospective Clinical Trials of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Sehn, L.H.; Johnson, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Patti, C.; Belada, D.; Samoilova, O.; Suh, C.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Ibrutinib and Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone in Non–Germinal Center B-Cell Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Chiappella, A.; Witzig, T.E.; Spina, M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Zhang, L.; Flament, J.; Repici, J.; Vitolo, U. ROBUST: Lenalidomide-R-CHOP versus placebo-R-CHOP in previously untreated ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, A.; Cummin, T.E.; Barrans, S.; Maishman, T.; Mamot, C.; Novak, U.; Caddy, J.; Stanton, L.; Kazmi-Stokes, S.; McMillan, A.; et al. Gene-expression profiling of bortezomib added to standard chemoimmunotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (REMoDL-B): An open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2019, 20, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sáez, A.I.; Sáez, A.J.; Artiga, M.J.; Pérez-Rosado, A.; Camacho, F.I.; Díez, A.; García, J.F.; Fraga, M.; Bosch, R.; Rodríguez-Pinilla, S.M.; et al. Building an outcome predictor model for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 63150–63151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, E.; Chacon, I.; Plaza, M.M.; Muñoz, E.; Cruz, M.A.; Martinez, B.; Lopez, L.; Martinez-Montero, J.C.; Orradre, J.L.; Saez, A.I.; et al. Clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is dependent on the relationship between different cell-cycle regulator proteins. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle-López, A.; de Villambrosía, S.G.; Francisco, M.; Malatxeberria, S.; Sáez, A.; Montalban, C.; Sánchez, L.; Garcia, J.F.; González-Barca, E.; López-Hernández, A.; et al. Stratifying diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy: GCB/non-GCB by immunohistochemistry is still a robust and feasible marker. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18036–18049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tzankov, A.; Green, T.; Wu, L.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Liu, W.-M.; Visco, C.; Li, Y.; Miranda, R.N.; et al. MYC/BCL2 protein coexpression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: A report from The International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Blood 2013, 121, 4021–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenwald, A.; Bens, S.; Advani, R.; Barrans, S.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Elsensohn, M.-H.; Natkunam, Y.; Calaminici, M.; Sander, B.; Baia, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of MYC Rearrangement and Translocation Partner in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Study by the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.W.; King, R.L.; Staiger, A.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Jiang, A.; Horn, H.; Mottok, A.; Farinha, P.; Slack, G.W.; Ennishi, D.; et al. High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma morphology. Blood 2018, 131, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.; Slack, G.W.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rogic, S.; Scott, D.W.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Sehn, L.H.; et al. Concurrent Expression of MYC and BCL2 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, B.E.; Castro, D.; Paredes, S.; Miranda, R.N.; Castillo, J.J. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tu, M.; Jabbar, K.J.; Cao, X.; Tzankov, A.; Visco, C.; Cai, Q.; Montes-Moreno, S.; An, Y.; Dybkaer, K.; et al. Clinical and biological significance of de novo CD5+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5615–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ok, C.Y.; Li, L.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybaer, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Prevalence and Clinical Implications of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in De Novo Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Western Countries. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montes-Moreno, S.; Odqvist, L.; Diaz-Perez, J.A.; Lopez, A.B.; de Villambrosía, S.G.; Mazorra, F.; Castillo, M.E.; Lopez, M.; Pajares, R.; García, J.F.; et al. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly is an aggressive post-germinal center B-cell neoplasm characterized by prominent nuclear factor-kB activation. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, T.; Bodmer-Haecki, A.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A. Evaluation of the diagnostic and prognostic value of PDL1 expression in Hodgkin and B-cell lymphomas. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 54, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravelle, P.; Burroni, B.; Péricart, S.; Rossi, C.; Bezombes, C.; Tosolini, M.; Damotte, D.; Brousset, P.; Fournié, J.-J.; Laurent, C. Mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 expression and prognostic relevance in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A summary of immunohistochemical studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44960–44975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Liu, W.-M.; Miranda, R.N.; Zhang, L.; Montes-Moreno, S.; et al. CD30 expression defines a novel subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with favorable prognosis and distinct gene expression signature: A report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 2013, 121, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottok, A.; Wright, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Ott, G.; Ramsower, C.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Delabie, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Song, J.Y.; et al. Molecular classification of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma using routinely available tissue specimens. Blood 2018, 132, 2401–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitteldorf, C.; Berisha, A.; Pfaltz, M.C.; Broekaert, S.M.; Schön, M.P.; Kerl, K.; Kempf, W. Tumor Microenvironment and Checkpoint Molecules in Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—New Therapeutic Targets. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mareschal, S.; Pham-Ledard, A.; Viailly, P.J.; Dubois, S.; Bertrand, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Fontanilles, M.; Bohers, E.; Ruminy, P.; Tournier, I.; et al. Identification of Somatic Mutations in Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Leg Type by Massive Parallel Sequencing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciocia, P.; Badat, M.; Cheesman, S.; D’Sa, S.; Joshi, R.; Lambert, J.; Mohamedbhai, S.; Pule, M.; Linch, D.; Ardeshna, K. Treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with secondary central nervous system involvement: Encouraging efficacy using CNS-penetrating R-IDARAM chemotherapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 172, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gebauer, N.; Gebauer, J.; Hardel, T.T.; Bernard, V.; Biersack, H.; Lehnert, H.; Rades, D.; Feller, A.C.; Thorns, C. Prevalence of targetable oncogenic mutations and genomic alterations in Epstein–Barr virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Aguilar, A.; Idbaih, A.; Boisselier, B.; Habbita, N.; Rossetto, M.; Laurenge, A.; Bruno, A.; Jouvet, A.; Polivka, M.; Adam, C.; et al. Recurrent Mutations of MYD88 and TBL1XR1 in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5203–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ollila, T.A.; Olszewski, A.J. Extranodal Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Molecular Features, Prognosis, and Risk of Central Nervous System Recurrence. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefnagel, J.J.; Dijkman, R.; Basso, K.; Jansen, P.M.; Hallermann, C.; Willemze, R.; Tensen, C.P.; Vermeer, M.H. Distinct types of primary cutaneous large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Blood 2005, 105, 3671–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Ledard, A.; Cappellen, D.; Martinez, F.; Vergier, B.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Merlio, J.-P. MYD88 Somatic Mutation Is a Genetic Feature of Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Leg Type. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2118–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambrosio, M.R.; Piccaluga, P.P.; Ponzoni, M.; Rocca, B.J.; Malagnino, V.; Onorati, M.; de Falco, G.; Calbi, V.; Ogwang, M.; Naresh, K.N.; et al. The Alteration of Lipid Metabolism in Burkitt Lymphoma Identifies a Novel Marker: Adipophilin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L. Molecular pathogenesis of germinal center-derived B cell lymphomas. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 288, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krull, J.E.; Wenzl, K.; Hartert, K.T.; Manske, M.K.; Sarangi, V.; Maurer, M.J.; Larson, M.C.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Ansell, S.M.; McPhail, E.; et al. Somatic copy number gains in MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 identifies a subset of aggressive alternative-DH/TH DLBCL patients. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küppers, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Mechanisms of chromosomal translocations in B cell lymphomas. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5580–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Neumeister, P.; Goossens, T.; Nanjangud, G.; Chaganti, R.S.K.; Küppers, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Hypermutation of multiple proto-oncogenes in B-cell diffuse large-cell lymphomas. Nature 2001, 412, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangault, C.; Amé-Thomas, P.; Rossille, D.; Dulong, J.; Caron, G.; Nonn, C.; Chatonnet, F.; Desmots, F.; Launay, V.; Lamy, T.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Cell Crosstalk within Follicular Lymphoma Cell Niche: Towards a Definition of the FL Supportive Synapse. Cancers 2020, 12, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Chiarenza, A.; Fabbri, G.; Grunn, A.; Trifonov, V.; Kasper, L.H.; Lerach, S.; Tang, H.; Ma, J.; et al. Inactivating mutations of acetyltransferase genes in B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2011, 471, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhshi, T.J.; Georgel, P.T. Genetic and epigenetic determinants of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.B.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppa, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cader, F.Z.; Schackmann, R.C.J.; Hu, X.; Wienand, K.; Redd, R.; Chapuy, B.; Ouyang, J.; Paul, N.; Gjini, E.; Lipschitz, M.; et al. Mass cytometry of Hodgkin lymphoma reveals a CD4+ regulatory T-cell–rich and exhausted T-effector microenvironment. Blood 2018, 132, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Ye, B.H.; Chaganti, R.S.; Dalla-Favera, R. BCL-6, a POZ/zinc-finger protein, is a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6947–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatzi, K.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, C.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.; Gearhart, M.D.; Giannopoulou, E.G.; Zumbo, P.; Kirouac, K.; Bhaskara, S.; Polo, J.M.; et al. A Hybrid Mechanism of Action for BCL6 in B Cells Defined by Formation of Functionally Distinct Complexes at Enhancers and Promoters. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, B.H.; Cattoretti, G.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hawe, N.; de Waard, R.; Leung, C.; Nouri-Shirazi, M.; Orazi, A.; Chaganti, R.; et al. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. BCL6: Master regulator of the germinal center reaction and key oncogene in B cell lymphomagenesis. Adv. Immunol. 2010, 105, 193–210. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, K.; Liso, A.; Tiacci, E.; Benedetti, R.; Pulsoni, A.; Foa, R.; di Raimondo, F.; Ambrosetti, A.; Califano, A.; Klein, U.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling of Hairy Cell Leukemia Reveals a Phenotype Related to Memory B Cells with Altered Expression of Chemokine and Adhesion Receptors. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls, E.; Lobry, C.; Geng, H.; Wang, L.; Cárdenas, M.; Rivas, M.; Cerchietti, L.; Oh, P.; Yang, S.N.; Oswald, E.; et al. BCL6 Antagonizes NOTCH2 to Maintain Survival of Human Follicular Lymphoma Cells. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tunyaplin, C.; Shaffer, A.L.; Angelin-Duclos, C.D.; Yu, X.; Staudt, L.M.; Calame, K.L. Direct repression of prdm1 by Bcl-6 inhibits plasmacytic differentiation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, B.; Lista, F.; Coco, F.L.; Knowles, D.; Offit, K.; Chaganti, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Alterations of a zinc finger-encoding gene, BCL-6, in diffuse large-cell lymphoma. Science 1993, 262, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tzankov, A.; Deng, L.; Wang, X.; Manyam, G.C.; Visco, C.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Zhang, L.; Dybkær, K.; et al. Prognostic impact of concurrent MYC and BCL6 rearrangements and expression in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 2401–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aukema, S.M.; Kreuz, M.; Kohler, C.W.; Rosolowski, M.; Hasenclever, D.; Hummel, M.; Kueppers, R.; Lenze, D.; Ott, G.; Pott, C.; et al. Biological characterization of adult MYC-translocation-positive mature B-cell lymphomas other than molecular Burkitt lymphoma. Haematology 2013, 99, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turakhia, S.K.; Hill, B.T.; Dufresne, S.D.; Nakashima, M.O.; Cotta, C.V. Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas with Translocations Involving BCL6 and MYC Have Distinct Clinical-Pathologic Characteristics. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, J.; Greiner, T.C.; Patel, K.; Dave, B.J.; Smith, L.; Ji, J.; Wright, G.; Sanger, W.G.; Pickering, D.L.; Jain, S.; et al. Distinctive patterns of BCL6 molecular alterations and their functional consequences in different subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin, R.D.; Mendez-Lago, M.; Mungall, A.J.; Goya, R.; Mungall, K.L.; Corbett, R.D.; Johnson, N.A.; Severson, T.M.; Chiu, R.; Field, M.; et al. Frequent mutation of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 476, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Cermak, L.; Pagan, J.K.; Rossi, M.; Martinengo, C.; di Celle, P.F.; Chapuy, B.; Shipp, M.; Chiarle, R.; Pagano, M. FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 481, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E. Understanding MYC-driven aggressive B-cell lymphomas: Pathogenesis and classification. Blood 2013, 122, 3884–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karube, K.; Campo, E. MYC Alterations in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.M.; Young, K.H.; Visco, C.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Orazi, A.; Go, R.S.; Nielsen, O.; Gadeberg, O.V.; Mourits-Andersen, T.; Frederiksen, M.; et al. Immunohistochemical Double-Hit Score Is a Strong Predictor of Outcome in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3460–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsburg, D.J.; Petrich, A.M.; Abramson, J.S.; Sohani, A.R.; Press, O.; Cassaday, R.D.; Chavez, J.C.; Song, K.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Gandhi, M.; et al. Impact of oncogene rearrangement patterns on outcomes in patients with double-hit non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer 2016, 122, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blombery, P.; Birkinshaw, R.W.; Nguyen, T.; Gong, J.; Thompson, E.R.; Xu, Z.; Westerman, D.A.; Czabotar, P.E.; Dickinson, M.; Huang, D.C.; et al. Characterization of a novel venetoclax resistance mutation (BCL2 Phe104Ile) observed in follicular lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, e188–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clipson, A.; Barrans, S.; Zeng, N.; Crouch, S.; Grigoropoulos, N.F.; Liu, H.; Kocialkowski, S.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Worrillow, L.; et al. The prognosis of MYC translocation positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma depends on the second hit. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2015, 1, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunleavy, K.; Fanale, M.A.; Abramson, J.S.; Noy, A.; Caimi, P.F.; Pittaluga, S.; Parekh, S.; Lacasce, A.; Hayslip, J.W.; Jagadeesh, D.; et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab) in untreated aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with MYC rearrangement: A prospective, multicentre, single-arm phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e609–e617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Seegmiller, A.C.; Lin, P.; Wang, X.J.; Miranda, R.N.; Bhagavathi, S.; Medeiros, L.J. B-cell lymphomas with concurrent MYC and BCL2 abnormalities other than translocations behave similarly to MYC/BCL2 double-hit lymphomas. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.; Younes, A. High grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6: Double hit and triple hit lymphomas and double expressing lymphoma. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monni, O.; Joensuu, H.; Franssila, K.; Klefstrom, J.; Alitalo, K.; Knuutila, S. BCL2 overexpression associated with chromosomal amplification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 1997, 90, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusumoto, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sekiguchi, N.; Tanimoto, K.; Onishi, Y.; Yokota, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Maeshima, A.M.; Ishida, T.; Inagaki, H.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with extra Bcl-2 gene signals detected by FISH analysis is associated with a “non-germinal center phenotype”. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, J.M.; Johnson, N.A.; Morin, R.D.; Scott, D.W.; Tan, K.; Ben-Nierah, S.; Boyle, M.J.; Slack, G.W.; Marra, M.A.; Connors, J.M.; et al. BCL2 mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L., III; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Compagno, M.; Houldsworth, J.; Monti, S.; Grunn, A.; Nandula, S.V.; Aster, J.C.; Murty, V.V.; Shipp, M.A.; Dalla-Favera, R. Inactivation of the PRDM1/BLIMP1 gene in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaffer, A.; Lin, K.-I.; Kuo, T.C.; Yu, X.; Hurt, E.M.; Rosenwald, A.; Giltnane, J.M.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Calame, K.; et al. Blimp-1 Orchestrates Plasma Cell Differentiation by Extinguishing the Mature B Cell Gene Expression Program. Immunology 2002, 17, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamason, R.L.; McCully, R.R.; Lew, S.M.; Pomerantz, J.L. Oncogenic CARD11 Mutations Induce Hyperactive Signaling by Disrupting Autoinhibition by the PKC-Responsive Inhibitory Domain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8240–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tibiletti, M.G.; Martin, V.; Bernasconi, B.; del Curto, B.; Pecciarini, L.; Uccella, S.; Pruneri, G.; Ponzoni, M.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Martinelli, G.; et al. BCL2, BCL6, MYC, MALT 1, and BCL10 rearrangements in nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas: A multicenter evaluation of a new set of fluorescent in situ hybridization probes and correlation with clinical outcome. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knies, N.; Alankus, B.; Weilemann, A.; Tzankov, A.; Brunner, K.; Ruff, T.; Kremer, M.; Keller, U.B.; Lenz, G.; Ruland, J. Lymphomagenic CARD11/BCL10/MALT1 signaling drives malignant B-cell proliferation via cooperative NF-κB and JNK activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E7230–E7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.-H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of Adaptive Immunity by the Innate Immune System. Science 2010, 327, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rovira, J.; Karube, K.; Valera, A.; Colomer, D.; Enjuanes, A.; Colomo, L.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Giné, E.; Dlouhy, I.; Magnano, L.; et al. MYD88 L265P Mutations, But No Other Variants, Identify a Subpopulation of DLBCL Patients of Activated B-cell Origin, Extranodal Involvement, and Poor Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.E.; Brown, K.D.; Siebenlist, U.; Staudt, L.M. Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lam, L.; George, T.C.; Wright, G.W.; Dave, S.S.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. Oncogenic CARD11 Mutations in Human Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Science 2008, 319, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, D.L.; Turer, E.E.; Lee, E.G.; Ahmad, R.-C.; Wheeler, M.T.; Tsui, C.; Hurley, P.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Hitotsumatsu, O.; et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, M.; Lim, W.K.; Grunn, A.; Nandula, S.V.; Brahmachary, M.; Shen, Q.; Bertoni, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Scandurra, M.; Califano, A.; et al. Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-kappaB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2009, 459, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.Q.; Jeelall, Y.S.; Beutler, B.; Horikawa, K.; Goodnow, C.C. Consequences of the recurrent MYD88L265P somatic mutation for B cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzl, K.; Manske, M.K.; Sarangi, V.; Asmann, Y.W.; Greipp, P.T.; Schoon, H.R.; Braggio, E.; Maurer, M.J.; Feldman, A.L.; Witzig, T.E.; et al. Loss of TNFAIP3 enhances MYD88L265P-driven signaling in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Phelan, J.D.; Staudt, L.M. B-Cell Receptor Signaling in Diffuse Large B-Cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, S.; Hussain, A.R.; Siraj, A.K.; Manogaran, P.S.; Al-Jomah, N.A.; Moorji, A.; Atizado, V.; Al-Dayel, F.; Belgaumi, A.; El-Solh, H.; et al. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival. Blood 2006, 108, 4178–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfeifer, M.; Grau, M.; Lenze, D.; Wenzel, S.-S.; Wolf, A.; Wollert-Wulf, B.; Dietze, K.; Nogai, H.; Storek, B.; Madle, H.; et al. PTEN loss defines a PI3K/AKT pathway-dependent germinal center subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12420–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kloo, B.; Nagel, D.; Pfeifer, M.; Grau, M.; Düwel, M.; Vincendeau, M.; Dörken, B.; Lenz, P.; Lenz, G.; Krappmann, D. Critical role of PI3K signaling for NF-kappaB-dependent survival in a subset of activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.W.; Hao, Z.; Hirao, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Lin, W.J.; Young, A.; Duncan, G.S.; Yoshida, H.; Wakeham, A.; Lang, P.A.; et al. 14-3-3sigma regulates B-cell homeostasis through stabilization of FOXO1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominguez-Sola, D.; Kung, J.; Holmes, A.B.; Wells, V.A.; Mo, T.; Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. The FOXO1 Transcription Factor Instructs the Germinal Center Dark Zone Program. Immunity 2015, 43, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caganova, M.; Carrisi, C.; Varano, G.; Mainoldi, F.; Zanardi, F.; Germain, P.-L.; George, L.; Alberghini, F.; Ferrarini, L.; Talukder, A.K.; et al. Germinal center dysregulation by histone methyltransferase EZH2 promotes lymphomagenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 5009–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velichutina, I.; Shaknovich, R.; Geng, H.; Johnson, N.A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Melnick, A.M.; Elemento, O. EZH2-mediated epigenetic silencing in germinal center B cells contributes to proliferation and lymphomagenesis. Blood 2010, 116, 5247–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Béguelin, W.; Popovic, R.; Teater, M.; Jiang, Y.; Bunting, K.L.; Rosen, M.; Shen, H.; Yang, S.N.; Wang, L.; Ezponda, T.; et al. EZH2 Is Required for Germinal Center Formation and Somatic EZH2 Mutations Promote Lymphoid Transformation. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobashi, A. Molecular Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2016, 56, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin, R.D.; Johnson, N.A.; Severson, T.M.; Mungall, A.J.; An, J.; Goya, R.; Paul, J.E.; Boyle, M.; Woolcock, B.W.; Kuchenbauer, F.; et al. Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.B.; Chu, J.; Berg, T.; Schapira, M.; Cheng, S.-W.G.; Moradian, A.; Morin, R.D.; Mungall, A.J.; Meissner, B.; Boyle, M.; et al. Somatic mutations at EZH2 Y641 act dominantly through a mechanism of selectively altered PRC2 catalytic activity, to increase H3K27 trimethylation. Blood 2011, 117, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grossman, S.R. p300/CBP/p53 interaction and regulation of the p53 response. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 268, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondello, P.; Tadros, S.; Teater, M.; Fontan, L.; Chang, A.Y.; Jain, N.; Yang, H.; Singh, S.; Ying, H.-Y.; Chu, C.-S.; et al. Selective Inhibition of HDAC3 Targets Synthetic Vulnerabilities and Activates Immune Surveillance in Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashwah, H.; Schmid, C.A.; Kasser, S.; Bertram, K.; Stelling, A.; Manz, M.G.; Müller, A. Inactivation of CREBBP expands the germinal center B cell compartment, down-regulates MHCII expression and promotes DLBCL growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9701–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Trifonov, V.; Fabbri, G.; Ma, J.; Rossi, D.; Chiarenza, A.; Wells, V.A.; Grunn, A.; Messina, M.; Elliot, O.; et al. Analysis of the coding genome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Hussein, S.; Lee, J.-E.; Holmes, A.B.; Bansal, M.; Vlasevska, S.; Mo, T.; Tang, H.; Basso, K.; et al. Disruption of KMT2D perturbs germinal center B cell development and promotes lymphomagenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R. Genetics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffie, R.; Zhou, N.; Rolland, D.; Önder, Ö.; Basrur, V.; Campbell, S.; Wellen, K.E.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Capell, B.C.; Busino, L. FBXW7 Triggers Degradation of KMT2D to Favor Growth of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2498–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Molina, A.; Boss, I.W.; Canela, A.; Pan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, M.; Hu, D.; Agirre, X.; Niesvizky, I.; et al. The histone lysine methyltransferase KMT2D sustains a gene expression program that represses B cell lymphoma development. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Wu, L.; Visco, C.; Tai, Y.C.; Tzankov, A.; Liu, W.-M.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybkær, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Mutational profile and prognostic significance of TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP: Report from an International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 2012, 120, 3986–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidano, G.; Ballerini, P.; Gong, J.Z.; Inghirami, G.; Neri, A.; Newcomb, E.W.; Magrath, I.T.; Knowles, D.M.; Dalla-Favera, R. p53 mutations in human lymphoid malignancies: Association with Burkitt lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5413–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebauer, N.; Bernard, V.; Gebauer, W.; Thorns, C.; Feller, A.C.; Merz, H. TP53 mutations are frequent events in double-hit B-cell lymphomas with MYC and BCL2 but not MYC and BCL6 translocations. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Medeiros, L.J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Young, K.H. Genetic alterations and their clinical implications in DLBCL. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steidl, C.; Shah, S.P.; Woolcock, B.W.; Rui, L.; Kawahara, M.; Farinha, P.; Johnson, N.A.; Zhao, Y.; Telenius, A.; Neriah, S.B.; et al. MHC class II transactivator CIITA is a recurrent gene fusion partner in lymphoid cancers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 471, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapuy, B.; Cheng, H.; Watahiki, A.; Ducar, M.D.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Ouyang, J.; Christie, A.L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patient-derived xenograft models capture the molecular and biological heterogeneity of the disease. Blood 2016, 127, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa-Malladi, M.; Lieu, Y.K.; Califano, O.; Holmes, A.B.; Bhagat, G.; Murty, V.V.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R. Combined Genetic Inactivation of β2-Microglobulin and CD58 Reveals Frequent Escape from Immune Recognition in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Ortega-Molina, A.; Geng, H.; Ying, H.-Y.; Hatzi, K.; Parsa, S.; McNally, D.; Wang, L.; Doane, A.S.; Agirre, X.; et al. CREBBP Inactivation Promotes the Development of HDAC3-Dependent Lymphomas. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cycon, K.A.; Rimsza, L.M.; Murphy, S.P. Alterations in CIITA constitute a common mechanism accounting for downregulation of MHC class II expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 184–194.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranheim, E.; Cantwell, M.; Kipps, T. Expression of CD27 and its ligand, CD70, on chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 1995, 85, 3556–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Agematsu, K. Involvement of CD27/CD70 interactions in antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity by perforin-mediated cytotoxicity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 130, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.; Chen, L.; Berglund, M.; Ren, W.; de Miranda, N.F.C.C.; Lisboa, S.; Fangazio, M.; Zhu, S.; Hou, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Genetic basis of PD-L1 overexpression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 3026–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, L.C.; Twa, D.D.W.; Mottok, A.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Woolcock, B.W.; Zhao, Y.; Savage, K.J.; Marra, M.A.; Scott, D.W.; Gascoyne, R.D.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of programmed death ligand structural rearrangements in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 2016, 128, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, M.R.; Monti, S.; Rodig, S.J.; Juszczynski, P.; Currie, T.; O’Donnell, E.; Chapuy, B.; Takeyama, K.; Neuberg, D.; Golub, T.R.; et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 3268–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wenzl, K.; Manske, M.K.; Asmann, Y.W.; Sarangi, V.; Greipp, P.T.; Krull, J.E.; Hartert, K.; He, R.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Amplification of 9p24.1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies a unique subset of cases that resemble primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, B.S.; Tan, K.B.; Ni, J.; Kwi-Ok-Oh, Z.H.L.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Wang, S.; Gentz, R.; Yu, G.-L.; Harrop, J.; et al. A Newly Identified Member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily with a Wide Tissue Distribution and Involvement in Lymphocyte Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 14272–14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boice, M.; Salloum, D.; Mourcin, F.; Sanghvi, V.; Amin, R.; Oricchio, E.; Jiang, M.; Mottok, A.; Denis-Lagache, N.; Ciriello, G.; et al. Loss of the HVEM Tumor Suppressor in Lymphoma and Restoration by Modified CAR-T Cells. Cell 2016, 167, 405–418.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afshar-Sterle, S.; Zotos, D.; Bernard, N.J.; Scherger, A.K.; Rödling, L.; Alsop, A.E.; Walker, J.; Masson, F.; Belz, G.T.; Corcoran, L.M.; et al. Fas ligand–mediated immune surveillance by T cells is essential for the control of spontaneous B cell lymphomas. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müschen, M.; Rajewsky, K.; Krönke, M.; Küppers, R. The origin of CD95-gene mutations in B-cell lymphoma. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kortylewski, M.; Pardoll, D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: Role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Song, Y.Q.; Shi, Y.F.; Zhu, J. High nuclear expression of STAT3 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Testoni, M.; Zucca, E.; Young, K.H.; Bertoni, F. Genetic lesions in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.B.; Yu, J.J.; Yu, R.Y.-L.; Mendez, L.M.; Shaknovich, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cattoretti, G.; Ye, B.H. Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2008, 111, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, L.T.; Wright, G.; Davis, R.E.; Lenz, G.; Farinha, P.; Dang, L.; Chan, J.W.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Staudt, L.M. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-{kappa}B pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3701–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karube, K.; Enjuanes, A.; Dlouhy, I.; Jares, P.; Martin-Garcia, D.; Nadeu, F.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Rovira, J.; Clot, G.; Royo, C.; et al. Integrating genomic alterations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies new relevant pathways and potential therapeutic targets. Leukemia 2018, 32, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juskevicius, D.; Lorberl, T.; Gsponer, J.; Perrina, V.; Ruiz, C.; Stenner-Liewen, F.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A. Distinct genetic evolution patterns of relapsing diffuse large B-cell lymphoma revealed by genome-wide copy number aberration and targeted sequencing analysis. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.Y.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Fabi, M.; Lorenz, I.C.; Hussein, S.; Bansal, M.; Califano, A.; Pasqualucci, L.; Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. MEF2B mutations lead to deregulated expression of the oncogene BCL6 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suk-youn, L.; Kumano, K.; Nakazaki, K.; Sanada, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Yamamoto, G.; Nannya, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Ota, S.; Izutsu, K.; et al. Gain of function mutations and copy number increases of Notch2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer science. 2009, 100, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muppidi, J.R.; Schmitz, R.; Green, J.A.; Xiao, W.; Larsen, A.B.; Braun, S.E.; An, J.; Xu, Y.; Rosenwald, A.; Ott, G.; et al. Loss of signalling via Gα13 in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma. Nature 2014, 516, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cattoretti, G.; Mandelbaum, J.; Lee, N.; Chaves, A.H.; Mahler, A.M.; Chadburn, A.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; MacLennan, A.J. Targeted Disruption of the S1P2 Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Gene Leads to Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Formation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8686–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerchietti, L.C.; Ghetu, A.F.; Zhu, X.; Da Silva, G.F.; Zhong, S.; Matthews, M.; Bunting, K.L.; Polo, J.M.; Fares, C.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of BCL6 kills DLBCL cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerchietti, L.C.; Lopes, E.C.; Yang, S.N.; Hatzi, K.; Bunting, K.L.; Tsikitas, L.A.; Malik, A.; Robles, A.I.; Walling, J.; Varticovski, L.; et al. A purine scaffold Hsp90 inhibitor destabilizes BCL-6 and has specific antitumor activity in BCL-6-dependent B cell lymphomas. Nat. Met. 2009, 12, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Kahl, B. Targeting BCL-2 in Hematologic Malignancies. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younes, A.; Ansell, S.; Fowler, N.; Wilson, W.; de Vos, S.; Seymour, J.; Advani, R.; Forero, A.; Morschhauser, F.; Kersten, M.J.; et al. The landscape of new drugs in lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roschewski, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Wilson, W.H. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma—Treatment approaches in the molecular era. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.; O’Connor, O.A.; Czuczman, S.; LaCasce, A.S.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Leonard, J.P.; Tulpule, A.; Dunleavy, K.; Xiong, H.; Chiu, Y.-L.; et al. Navitoclax, a targeted high-affinity inhibitor of BCL-2, in lymphoid malignancies: A phase 1 dose escalation study of safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and antitumour activity. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, M.C.; Pang, M.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.-T.; de Vos, S.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Said, J.; Baum, L.G. Galectin-3 binds to CD45 on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells to regulate susceptibility to cell death. Blood 2012, 120, 4635–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delmore, J.E.; Issa, G.C.; Lemieux, M.E.; Rahl, P.B.; Shi, J.; Jacobs, H.M.; Kastritis, E.; Gilpatrick, T.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; et al. BET Bromodomain Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy to Target c-Myc. Cell 2011, 146, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amorim, S.; Stathis, A.; Gleeson, M.; Iyengar, S.; Magarotto, V.; Leleu, X.; Morschhauser, F.; Karlin, L.; Broussais, F.; Rezai, K.; et al. Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or multiple myeloma: A dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e196–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boi, M.; Gaudio, E.; Bonetti, P.; Kwee, I.; Bernasconi, E.; Tarantelli, C.; Rinaldi, A.; Testoni, M.; Cascione, L.; Ponzoni, M.; et al. The BET Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 affects pathogenic pathways in preclinical B-cell tumor models and synergizes with targeted drugs. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2015, 21, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grommes, C.; Pastore, A.; Palaskas, N.; Tang, S.S.; Campos, C.; Schartz, D.; Codega, P.; Nichol, D.; Clark, O.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; et al. Ibrutinib Unmasks Critical Role of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieg, A.M. CpG Still Rocks! Update on an Accidental Drug. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012, 22, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahrsdorfer, B.; Mühlenhoff, L.; Blackwell, S.E.; Wagner, M.; Poeck, H.; Hartmann, E.; Jox, R.; Giese, T.; Emmerich, B.; Endres, S.; et al. B-Cell Lymphomas Differ in their Responsiveness to CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, P.N.; Romero, D.L.; Yang, Y.; Shaffer, A.L.; Chaudhary, D.; Robinson, S.; Miao, W.; Rui, L.; Westlin, W.F.; Kapeller, R.; et al. Selective interleukin-1 receptor–associated kinase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune disorders and lymphoid malignancy. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.S.; Degorce, S.L.; Anjum, R.; Culshaw, J.; Davies, R.D.; Davies, N.L.; Dillman, K.S.; Dowling, J.E.; Drew, L.; Ferguson, A.D.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of Pyrrolopyrimidine Inhibitors of Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4) for the Treatment of Mutant MYD88 L265P Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 10071–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.; Dasyam, N.; Giunti, G.; Mester, B.; Bauer, E.; Andrews, B.; Perera, T.; Ostapowicz, T.; Frampton, C.; Li, P.; et al. Third-generation anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cells incorporating a TLR2 domain for relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphoma: A phase I clinical trial protocol (ENABLE). BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdmann, T.; Klener, P.; Lynch, J.T.; Grau, M.; Vočková, P.; Molinsky, J.; Tuskova, D.; Hudson, K.; Polanska, U.M.; Grondine, M.; et al. Sensitivity to PI3K and AKT inhibitors is mediated by divergent molecular mechanisms in subtypes of DLBCL. Blood 2017, 130, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.R.; Hamadani, M.; Hayslip, J.; Janssens, A.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Ottmann, O.; Arnason, J.; Tilly, H.; Millenson, M.; Offner, F.; et al. Voxtalisib (XL765) in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e170–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Hawkes, E.; Verhoef, G.; Haioun, C.; Lim, S.T.; Heo, D.S.; Ardeshna, K.; Chong, G.; Haaber, J.; Shi, W.; et al. Single-agent activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition with copanlisib in patients with molecularly defined relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2184–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, L.T.; Davis, R.E.; Pierce, J.; Hepperle, M.; Xu, Y.; Hottelet, M.; Nong, Y.; Wen, D.; Adams, J.; Dang, L.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors of IkappaB kinase are selectively toxic for subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma defined by gene expression profiling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strauss, S.J.; Higginbottom, K.; Jüliger, S.; Maharaj, L.; Allen, P.; Schenkein, D.; Lister, T.A.; Joel, S.P. The Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib Acts Independently of p53 and Induces Cell Death via Apoptosis and Mitotic Catastrophe in B-Cell Lymphoma Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goy, A.; Younes, A.; McLaughlin, P.; Pro, B.; Romaguera, J.E.; Hagemeister, F.; Fayad, L.; Dang, N.H.; Samaniego, F.; Wang, M.; et al. Phase II study of proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Czuczman, M.S.; Dave, S.S.; Wright, G.; Grant, N.; Shovlin, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Janik, J.E.; Staudt, L.M.; et al. Differential efficacy of bortezomib plus chemotherapy within molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2009, 113, 6069–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-H.; Kosek, J.; Wang, M.; Heise, C.; Schafer, P.H.; Chopra, R. Lenalidomide efficacy in activated B-cell-like subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is dependent upon IRF4 and cereblon expression. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 160, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Sassone, M.; Angelillo, P.; Zaja, F.; Re, A.; di Rocco, A.; Spina, M.; Fabbri, A.; Stelitano, C.; Frezzato, M.; et al. Long-lasting efficacy and safety of lenalidomide maintenance in patients with relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who are not eligible for or failed autologous transplantation. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; LaPlant, B.; Macon, W.R.; Reeder, C.B.; Foran, J.M.; Nelson, G.D.; Thompson, C.A.; Rivera, C.E.; Inwards, D.J.; Micallef, I.N.; et al. Lenalidomide Combined With R-CHOP Overcomes Negative Prognostic Impact of Non–Germinal Center B-Cell Phenotype in Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Qing, K.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, J. Low dose of lenalidmide and PI3K/mTOR inhibitor trigger synergistic cytoxicity in activated B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.J.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J.; Kaufman, G.P.; Czuczman, N.M.; Mavis, C.; Skitzki, J.J.; Czuczman, M.S. The novel proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and potentiates the anti-tumour activity of chemotherapy in rituximab-resistant lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shaffer, A.L., III; Emre, N.T.; Ceribelli, M.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Platig, J.; Kohlhammer, H.; et al. Exploiting synthetic lethality for the therapy of ABC diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mascarenhas, J.; Hoffman, R. Ruxolitinib: The First FDA Approved Therapy for the Treatment of Myelofibrosis: Figure 1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3008–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younes, A.; Romaguera, J.; Fanale, M.; McLaughlin, P.; Hagemeister, F.; Copeland, A.; Neelapu, S.; Kwak, L.; Shah, J.; Faria, S.D.C.; et al. Phase I Study of a Novel Oral Janus Kinase 2 Inhibitor, SB1518, in Patients with Relapsed Lymphoma: Evidence of Clinical and Biologic Activity in Multiple Lymphoma Subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4161–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, P.-K.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Blocks the Anti-apoptotic Activity of IL-6 in Human Liver Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27429–27439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seth, P.P.; Vasquez, G.; Allerson, C.A.; Berdeja, A.; Gaus, H.; Kinberger, G.A.; Prakash, T.P.; Migawa, M.T.; Bhat, B.; Swayze, E.E. Synthesis and biophysical evaluation of 2′,4′-constrained 2′O-methoxyethyl and 2′,4′-constrained 2′O-ethyl nucleic acid analogues. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, Y.; Woessner, R.; Younes, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Fowler, N.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, J.; Jo, M.; et al. AZD9150, a next-generation antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of STAT3 with early evidence of clinical activity in lymphoma and lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 314ra185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reilley, M.J.; McCoon, P.; Cook, C.; Lyne, P.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, Y.; Woessner, R.; Younes, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Fowler, N.; et al. STAT3 antisense oligonucleotide AZD9150 in a subset of patients with heavily pretreated lymphoma: Results of a phase 1b trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansell, S.M.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Koenig, P.A.; La Plant, B.R.; Kabat, B.F.; Fernando, D.; Habermann, T.M.; Inwards, D.J.; Verma, M.; Yamada, R.; et al. Phase I Study of Ipilimumab, an Anti–CTLA-4 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6446–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Santoro, A.; Gritti, G.; Brice, P.; Barr, P.M.; Kuruvilla, J.; Cunningham, D.; Kline, J.; Johnson, N.A.; Mehta-Shah, N.; et al. Nivolumab Combined with Brentuximab Vedotin for Relapsed/Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Efficacy and Safety from the Phase II CheckMate 436 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bledsoe, J.R.; Redd, R.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Soumerai, J.D.; Nishino, H.T.; Boyer, D.F.; Ferry, J.A.; Zukerberg, L.R.; Harris, N.L.; Abramson, J.S.; et al. The immunophenotypic spectrum of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma reveals prognostic biomarkers associated with outcome. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, E436–E441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, M.G.; Advani, R.H.; Ligon, A.H.; Natkunam, Y.; Redd, R.A.; Homer, H.; Connelly, C.F.; Sun, H.H.; Daadi, S.E.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 Genetic Alterations Define Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Predict Outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2690–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiyasu, J.; Miyoshi, H.; Hirata, A.; Arakawa, F.; Ichikawa, A.; Niino, D.; Sugita, Y.; Yufu, Y.; Choi, I.; Abe, Y.; et al. Expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 is associated with poor overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stewart, C.; Tan, Y.; Abo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Dunford, A.J.; Meredith, D.M.; Thorner, A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armand, P.; Nagler, A.; Weller, E.A.; Devine, S.M.; Avigan, D.E.; Chen, Y.-B.; Kaminski, M.S.; Holland, H.K.; Winter, J.N.; Mason, J.R.; et al. Disabling Immune Tolerance by Programmed Death-1 Blockade with Pidilizumab after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results of an International Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4199–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Ribrag, V.; Moskowitz, C.H.; Michot, J.-M.; Kuruvilla, J.; Balakumaran, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chlosta, S.; Shipp, M.A.; Armand, P. Safety and tolerability of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayak, L.; Iwamoto, F.M.; La Casce, A.; Mukundan, S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Chapuy, B.; Armand, P.; Rodig, S.J.; Shipp, M.A. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system and testicular lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 3071–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesokhin, A.M.; Ansell, S.M.; Armand, P.; Scott, E.C.; Halwani, A.; Gutierrez, M.; Millenson, M.M.; Cohen, A.D.; Schuster, S.J.; Lebovic, D.; et al. Nivolumab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancy: Preliminary Results of a Phase Ib Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armand, P.; Engert, A.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Timmerman, J.M.; Collins, G.P.; Ramchandren, R.; Cohen, J.B.; et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma After Failure of Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Extended Follow-Up of the Multicohort Single-Arm Phase II CheckMate 205 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.; Schlafer, D.; Flowers, C.R.; Allen, P.B. Investigational PD-1 inhibitors in HL and NHL and biomarkers for predictors of response and outcome. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribrag, V.; Lee, S.T.; Rizzieri, D.; Dyer, M.J.; Fayad, L.; Kurzrock, R.; Andritsos, L.; Bouabdallah, R.; Hayat, A.; Bacon, L.; et al. A Phase 1b Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Durvalumab in Combination with Tremelimumab or Danvatirsen in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, 309–317.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomas-Roca, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Alonso-Alonso, R.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Piris, M.A. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Recognition of Markers for Targeted Therapy. Hemato 2021, 2, 281-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2020017
Tomas-Roca L, Rodriguez M, Alonso-Alonso R, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Piris MA. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Recognition of Markers for Targeted Therapy. Hemato. 2021; 2(2):281-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomas-Roca, Laura, Marta Rodriguez, Ruth Alonso-Alonso, Socorro M. Rodriguez-Pinilla, and Miguel Angel Piris. 2021. "Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Recognition of Markers for Targeted Therapy" Hemato 2, no. 2: 281-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2020017
APA StyleTomas-Roca, L., Rodriguez, M., Alonso-Alonso, R., Rodriguez-Pinilla, S. M., & Piris, M. A. (2021). Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Recognition of Markers for Targeted Therapy. Hemato, 2(2), 281-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2020017







