Supramolecular Structure and Complexation of Gum Arabic in Aqueous Solutions: What Determines Its Protective Functions in Nature and Technologies?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
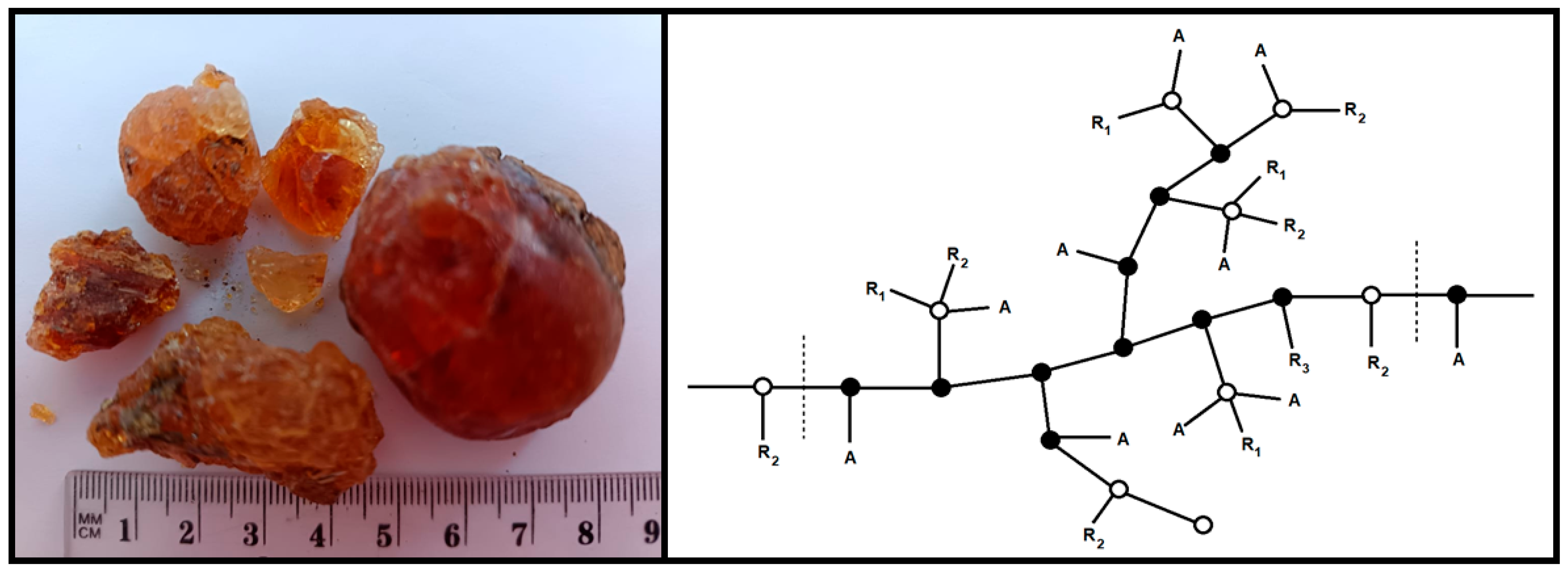
2.1. Material
2.2. Dynamic Light Scattering
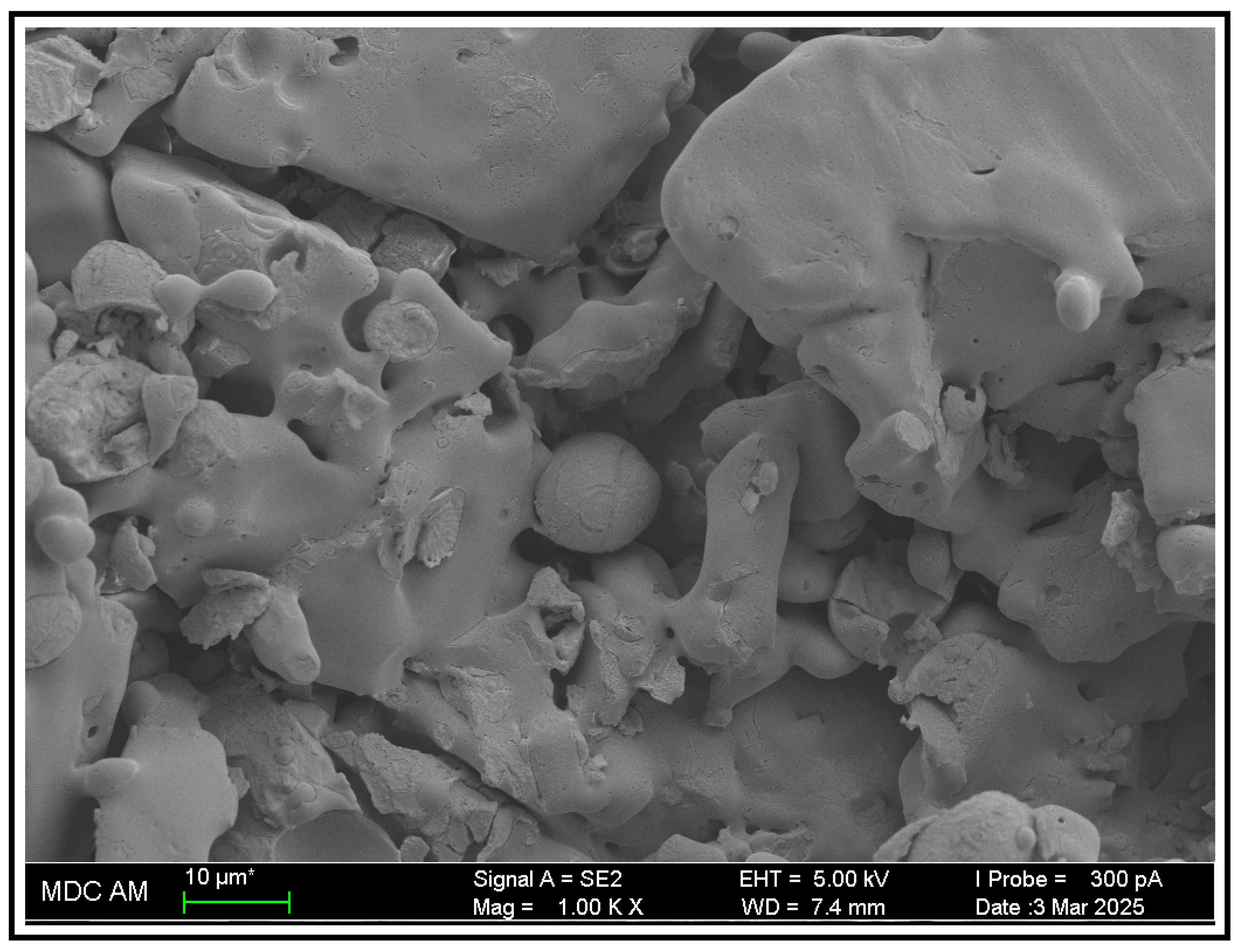
2.3. Electron Microscopy
2.4. NMR Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
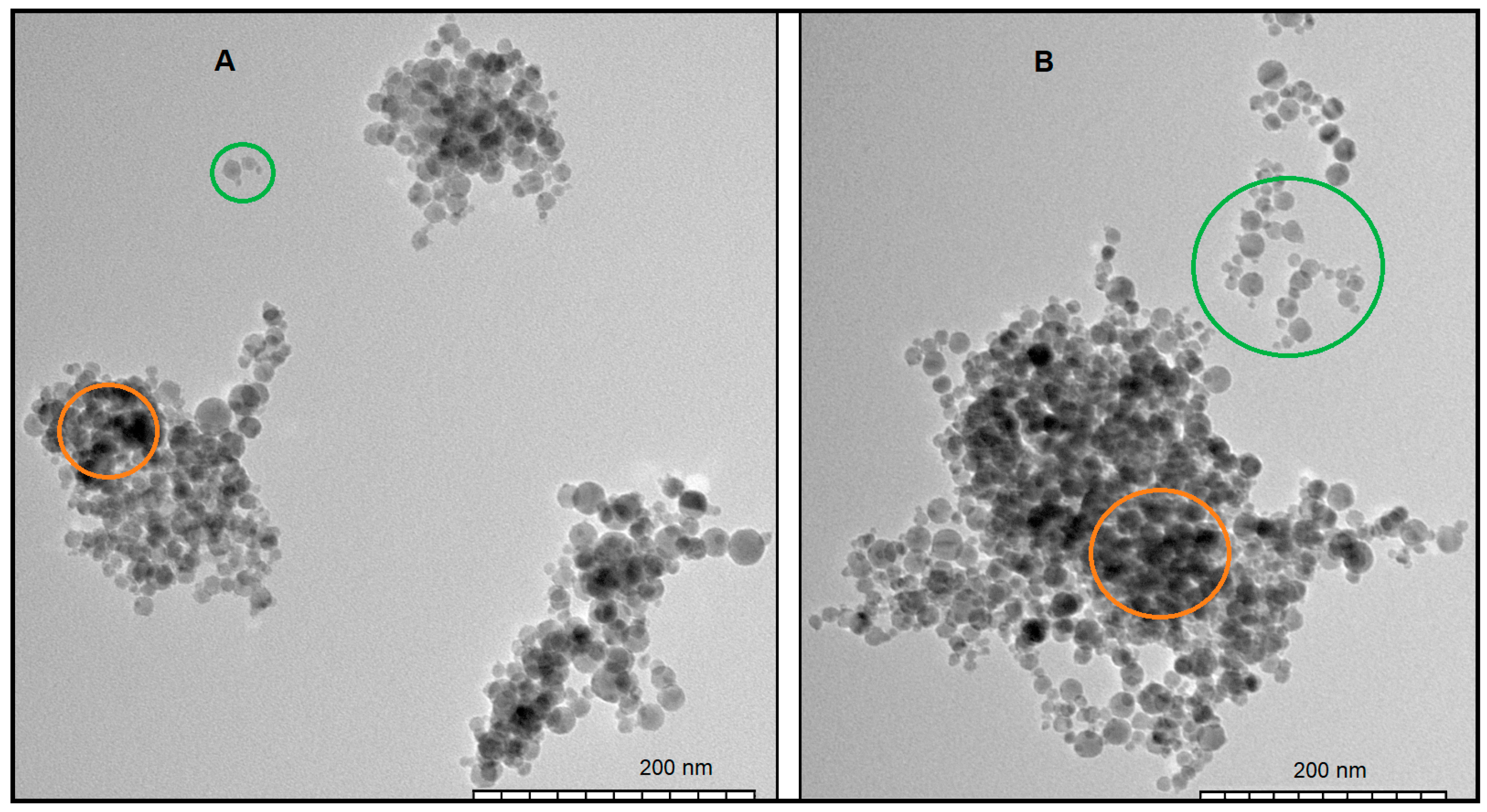
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.3. NMR Experiments
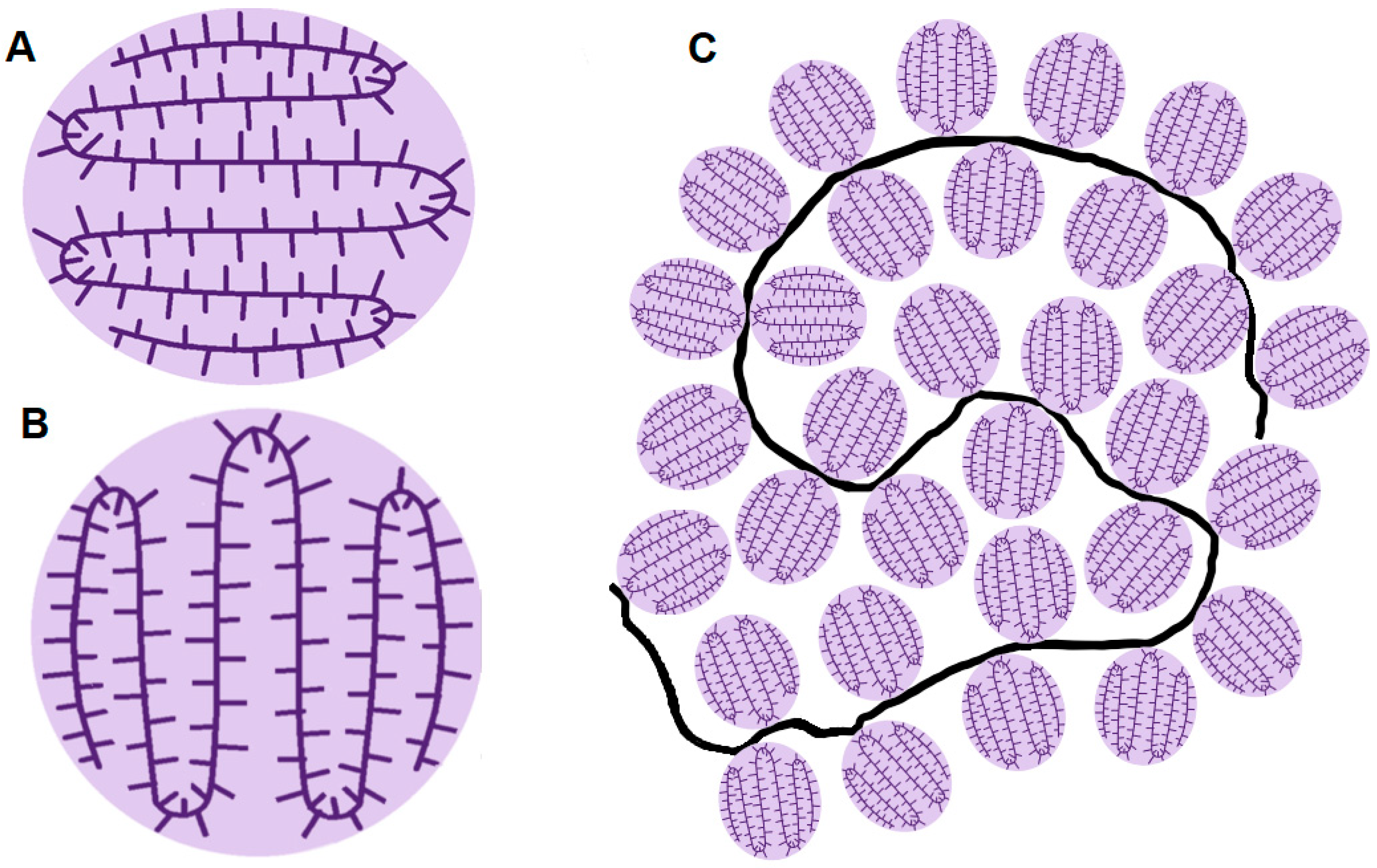
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Structural features of the amphiphilic GA molecule, which is a colloidal structure of hydrophilic anionic polysaccharide blocks linked together by a polypeptide chain that includes hydrophobic fragments (“wattle blossom” model);
- Mobility of parts of the GA molecule and their tendency to form associates and complexes both among themselves and with surfaces;
- Structural features of the polysaccharide blocks (“crown” model), allowing for rapid swelling and local gelation emergence with an increase in their local concentration while maintaining low solution viscosity up to fairly high GA concentrations;
- Interfacial activity of amphiphilic GA molecules, creating the possibility of forming viscous layers on interfacial surfaces.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whistler, R.L. Exudate gums. In Industrial Gums: Polysaccharides and Their Derivatives, 3rd ed.; Whistler, R.L., BeMiller, J.N., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.A.; Phillips, G.O. 11—Gum Arabic. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Saskatoon, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, H.H.; Ahmed, A.A.; Musa, T.H. Chemistry, Biological, and Pharmacological Properties of Gum Arabic. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J.-M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alftrén, J.; Peñarrieta, J.M.; Bergenståhl, B.; Nilsson, L. Comparison of molecular and emulsifying properties of gum arabic and mesquite gum using asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.M.; Phillips, G.O.; Sljivo, A.; Snowden, M.J.; Williams, P.A. A review of recent developments on the regulatory, structural and functional aspects of gum Arabic. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Ziada, A.; Blunden, G. Biological effects of gum arabic: A review of some recent research. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeken, D.; Dierckx, K.; Dewettinck, S. Exudate gums: Occurrence, production, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 63, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Kadyirov, A.I.; Ziganshina, S.A.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zueva, O.S.; Gubaidullin, A.T.; Zuev, Y.F. Supramolecular Structure and Mechanical Performance of κ-Carrageenan–Gelatin Gel. Polymers 2022, 14, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubaidullin, A.T.; Galeeva, A.I.; Galyametdinov, Y.G.; Ageev, G.G.; Piryazev, A.A.; Ivanov, D.A.; Ermakova, E.A.; Nikiforova, A.A.; Derkach, S.R.; Zueva, O.S.; et al. Modulation of Structural and Physical-Chemical Properties of Fish Gelatin Hydrogel by Natural Polysaccharides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zueva, O.S.; Gubaidullin, A.T.; Makarova, A.O.; Bogdanova, L.R.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zuev, Y.F. Structural features of composite protein-polysaccharide hydrogel in the presence of a carbon nanomaterial. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubaidullin, A.T.; Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kadyirov, A.I.; Ziganshina, S.A.; Salnikov, V.V.; Zueva, O.S.; Zuev, Y.F. Modulation of Molecular Structure and Mechanical Properties of κ-Carrageenan-Gelatin Hydrogel with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers 2022, 14, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Taneja, S. Exudate gums: Chemistry, properties and food applications—A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padil, V.V.T.; Senan, C.; Cerník, M. “Green” polymeric electrospun fibers based on tree-gum hydrocolloids: Fabrication, characterization and applications. Mater. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 5, 127–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.E.; Williams, P.A.; Menzies, A.R.; Phillips, G.O. Characterization of commercial samples of gum arabic. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Nigen, M.; Mejia Tamayo, V.; Doco, T.; Williams, P.; Amine, C.; Renard, D. Acacia gum: History of the future. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 78, 140–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawy, A.; Rodrigues, A.E. Plant gums in Pickering emulsions: A review of sources, properties, applications, and future perspectives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 332, 121900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipkin, A.M.; Wagner, M.; McGrath, K.; Brooks, A.S.; Lucas, P.W. An experimental study of hafting adhesives and the implications for compound tool technology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jubori, Y.; Ahmed, N.T.B.; Albusaidi, R.; Madden, J.; Das, S.; Sirasanagandla, S.R. The Efficacy of Gum Arabic in Managing Diseases: A Systematic Review of Evidence-Based Clinical Trials. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidi, S. Therapeutic Potential of Gum Arabic (Acacia senegal) in Chronic Kidney Disease Management: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.A. 16—Health Benefits of Gum Arabic and Medical Use. In Gum Arabic Structure, Properties, Application and Economics; Mariod, A.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Chen, D.; Ye, L.; Peng, P.; Wang, H.; Al Saleh, N.; Al-Kenani, N.S.; Guo, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, L. Pharmacological targets and therapeutic mechanisms of Arabic gum in treating diabetic wounds: Insights from network pharmacology and experimental validation. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1528880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Alrefaey, H.R.; Adelrahman, K.; Moustafa, A.; Egodawaththa, N.M.; Crawford, K.E.; Nesnas, N.; Sabra, S.A. Gum Arabic: A Commodity with Versatile Formulations and Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelon, J.K.; Jumba, I.O.; Keter, J.K.; Chemuku, W.; Oduor, F.D.O. Assessment of physical properties of gum arabic from Acacia senegal varieties in Baringo District, Kenya. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 4, 95–98. Available online: https://academicjournals.org/journal/AJPS/article-full-text-pdf/417951A11473 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Mbugua, R.; Salim, R.; Ndambuki, J. Effect of Gum Arabic Karroo as a water-reducing admixture in cement mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2016, 5, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinwa, A.U.; Abdulbasir, G.; Abdulkadir, G. Gum Arabic as an admixture for cement concrete production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzyski, P. The Influence of Gum Arabic Admixture on the Mechanical Properties of Lime-Metakaolin Paste Used as Binder in Hemp Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, A.; Biswas, D.; Siracusa, V.; Roy, S. Natural Gum-Based Functional Bioactive Films and Coatings: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morodi, V.; Kaseke, T.; Fawole, O.A. Impact of Gum Arabic Coating Pretreatment on Quality Attributes of Oven-Dried Red Raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.). Fruit. Process. 2022, 10, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, H.; Buksh, K.; Noreen, S.; Pervaiz, F.; Maqbool, I. Hydrogels as potential drug-delivery systems: Network design and applications. Ther. Deliv. 2021, 12, 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olabode, O.; Akinsanya, O.; Daramola, O.; Sowunmi, A.; Osakwe, C.; Benjamin, S.; Samuel, I. Effect of Salt Concentration on Oil Recovery During Polymer Flooding: Simulation Studies on Xanthan Gum and Gum Arabic. Polymers 2023, 15, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timothy, U.J.; Umoren, P.S.; Solomon, M.M.; Igwe, I.O.; Umoren, S.A. An appraisal of the utilization of natural gums as corrosion inhibitors: Prospects, challenges, and future perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, S.A.; Obot, I.B.; Ebenso, E.E.; Okafor, P.C.; Ogbobe, O.; Oguzie, E.E. Gum arabic as a potential corrosion inhibitor for aluminium in alkaline medium and its adsorption characteristics. Anti Corros. Methods Mater. 2006, 53, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, S.A. Inhibition of aluminium and mild steel corrosion in acidic medium using Gum Arabic. Cellulose 2008, 15, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaoui, K.; Mejdoubi, E.; Jodeh, S.; Lamhamdi, A.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; Algarra, M.; Zarrouk, A.; Errich, A.; Salghi, R.; Lgaz, H. Eco friendly green inhibitor Gum Arabic (GA) for the corrosion control of mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Corros. Sci. 2017, 129, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Alvarez, V.; Koenig, J.D.; Luo, J.-L. Gum Arabic as corrosion inhibitor in the oil industry: Experimental and theoretical studies. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, B.; Youssouf, R.; Abdelouahad, C. Gum Arabic as an eco-friendly inhibitor for API 5L X42 pipeline steel in HCl medium. Corros. Sci. 2014, 82, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dalo, M.A.; Othman, A.A.; Al-Rawashdeh, N.A.F. Exudate gum from Acacia trees as green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic media. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 9303–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khair, T.; Abakumova, Y.; Zueva, O. Inhibitive behaviour of Gum Arabic on corrosion process of pipeline steel in acidic environment. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 592, 04011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajadisastra, J.; Sutriyo, P.P.; Pujiyanto, A. Antioxidant activity of gold nanoparticles using gum arabic as a stabilizing agent. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 462–465. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, M.M.; Gerengi, H.; Umoren, S.A.; Essien, N.B.; Essien, U.B.; Kaya, E. Gum Arabic-silver nanoparticles composite as a green anticorrosive formulation for steel corrosion in strong acid media. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, U.J.; Mamudu, U.; Solomon, M.M.; Umoren, P.S.; Igwe, I.O.; Anyanwu, P.I.; Aharanwa, B.C.; Lim, R.C.; Uchechukwu, T.O.; Umoren, S.A. In-situ biosynthesized plant exudate gums-silver nanocomposites as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 132065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gashua, I.B.; Williams, P.A.; Yadav, M.P.; Baldwin, T.C. Characterisation and molecular association of Nigerian and Sudanese Acacia gum exudates. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.C.; Phillips, G.O.; Williams, P.A. The role of the proteinaceous component on the emulsifying properties of gum Arabic. Food Hydrocoll. 1988, 2, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.-P.; Wang, C.; Cui, S.W.; Wang, Q.; Xie, M.-Y.; Phillips, G.O. A further amendment to the classical core structure of gum Arabic (Acacia senegal). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.A.; Phillips, G.O.; Stephen, A.M.; Churms, S.C. Gums and Mucilages. In Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications; Stephen, A.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kersten, F.; Martin, D.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Wefers, D. Gum Arabic—Same but different: Comparative analysis of structural characteristics and emulsifying properties of 20 Acacia senegal samples of various qualities. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 165, 111231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevelde, M.-C.; Fenyo, J.-C. Macromolecular distribution of Acacia senegal gum (gum arabic) by size-exclusion chromatography. Carbohydr. Polym. 1985, 5, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defaye, J.; Wong, E. Structural studies of gum arabic, the exudate polysaccharide from Acacia senegal. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 150, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, T.; Williams, P.A.; Phillips, G.O.; Al-Assaf, S.; Baldwin, T.C. New insights into the structural characteristics of the arabinogalactan-protein (AGP) fraction of gum arabic. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9269–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashua, I.B.; Williams, P.A.; Baldwin, T.C. Molecular characteristics, association and interfacial properties of gum Arabic harvested from both Acacia senegal and Acacia seyal. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.C.; Phillips, G.O.; Williams, P.A. Fractionation and characterization of gum from Acacia senegal. Food Hydrocoll. 1989, 3, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, D.; Lavenant-Gourgeon, L.; Ralet, M.C.; Sanchez, C. Acacia senegal Gum: Continuum of Molecular Species Differing by Their Protein to Sugar Ratio, Molecular Weight, and Charges. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2637–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Fong, C.; Lamport, D.T.A. Gum arabic glycoprotein is a twisted hairy rope. A new model based on O-galactosyl hydroxyproline as the polysaccharide attachment site. Plant Physiol. 1991, 96, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atgié, M.; Garrigues, J.C.; Chennevière, A.; Masbernat, O.; Roger, K. Gum Arabic in solution: Composition and multi-scale structures. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, Y.; Al-Assaf, S.; Phillips, G.O.; Nishinari, K.; Zhang, H. Rheological study of gum Arabic solutions: Interpretation based on molecular self-association. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. The Role of Structure in Polymer Rheology: Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, O.S.; Makarova, A.O.; Zvereva, E.R.; Kurbanov, R.K.; Salnikov, V.V.; Turanov, A.N.; Zuev, Y.F. Industrial block copolymer surfactants: Diversity of associative forms and interaction with carbon nanomaterial. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuev, Y.F.; Kurbanov, R.K.; Idiyatullin, B.Z.; Us’yarov, O.G. Sodium dodecyl sulfate self-diffusion in premicellar and low-concentrated micellar solutions in the presence of a back-ground electrolyte. Colloid. J. 2007, 69, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.N.; Neiss, T.G. Solution NMR Spectroscopy of Food Polysaccharides. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziej, S.; Scherb-Forster, J.; Schlicht, C.; Eisenreich, W. Fast Identification of Food Thickeners by Nontargeted NMR Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3761–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincher, G.B.; Stone, B.A.; Clarke, A.E. Arabinogalactan-proteins: Structure, biosynthesis and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1983, 34, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, selfassembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beevers, C.A.; McDonald, T.R.R.; Robertson, J.H.; Stern, F. The crystal structure of sucrose. Acta Crystallogr. 1952, 5, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Lapp, A.; Schmitt, C.; Gaillard, C.; Kolodziejczyk, C.E.; Renard, D. The Acacia gum arabinogalactan fraction is a thin oblate ellipsoid: A new model based on SANS and ab initio calculation. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Huan, S.; Li, Z.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of emulsifying properties of food-grade polysaccharides in oil-in-water emulsions: Gum Arabic, beet pectin, and corn fiber gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; McClements, D.J. Progress in natural emulsifiers for utilization in food emulsions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, O.S.; Rukhlov, V.S.; Zuev, Y.F. Morphology of ionic micelles as studied by numerical solution of Poisson equation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6174–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zueva, O.S.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zuev, Y.F. Nanosized Being of Ionic Surfactant Micelles: An Advanced View on Micellization Process. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
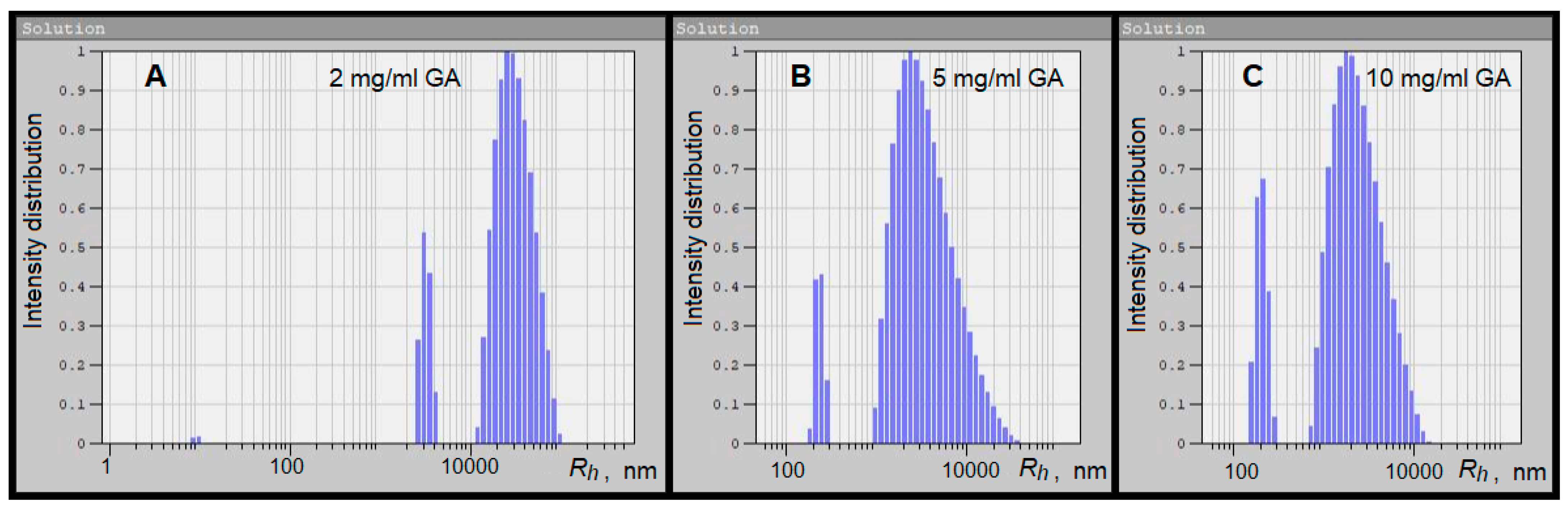




| Concentration of GA | Maxima of Particle Size Distribution by Intensity Rhmax, nm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | |
| 2 mg/mL | 9 ± 0.8 | 3246 ± 464 | 34,000 ± 16,000 |
| 5 mg/mL | – | 240 ± 324 | 4593 ± 4160 |
| 10 mg/mL | – | 209 ± 344 | 2894 ± 2004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zueva, O.S.; Klimovitskaya, M.A.; Skvortsova, P.V.; Khair, T.; Kazantseva, D.A.; Abakumova, Y.; Gromova, N.R. Supramolecular Structure and Complexation of Gum Arabic in Aqueous Solutions: What Determines Its Protective Functions in Nature and Technologies? Macromol 2025, 5, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040049
Zueva OS, Klimovitskaya MA, Skvortsova PV, Khair T, Kazantseva DA, Abakumova Y, Gromova NR. Supramolecular Structure and Complexation of Gum Arabic in Aqueous Solutions: What Determines Its Protective Functions in Nature and Technologies? Macromol. 2025; 5(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleZueva, Olga S., Mariya A. Klimovitskaya, Polina V. Skvortsova, Tahar Khair, Daria A. Kazantseva, Yuliya Abakumova, and Naira R. Gromova. 2025. "Supramolecular Structure and Complexation of Gum Arabic in Aqueous Solutions: What Determines Its Protective Functions in Nature and Technologies?" Macromol 5, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040049
APA StyleZueva, O. S., Klimovitskaya, M. A., Skvortsova, P. V., Khair, T., Kazantseva, D. A., Abakumova, Y., & Gromova, N. R. (2025). Supramolecular Structure and Complexation of Gum Arabic in Aqueous Solutions: What Determines Its Protective Functions in Nature and Technologies? Macromol, 5(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040049







