Biopolymers in Biotechnology and Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Polysaccharides
2.1. Hyaluronic Acid
Applications
2.2. Alginate
Applications
2.3. Chitosan
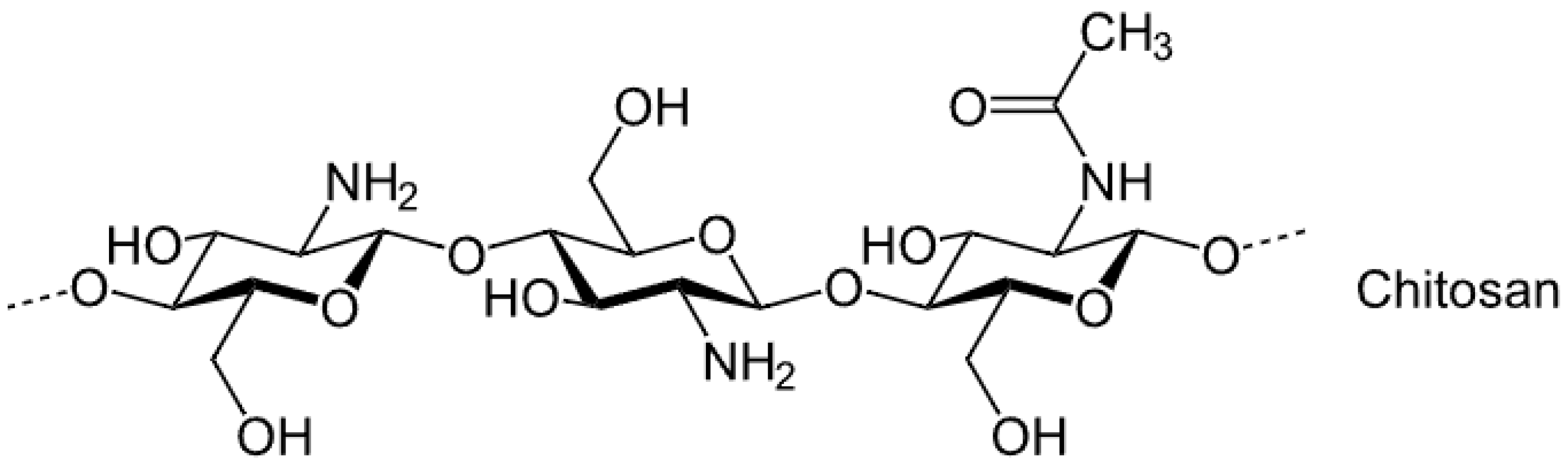
Applications
2.4. Agarose

Applications
2.5. Carrageenan
Applications
2.6. Bacterial Cellulose
Applications
2.7. Dextran
Applications
3. Proteins
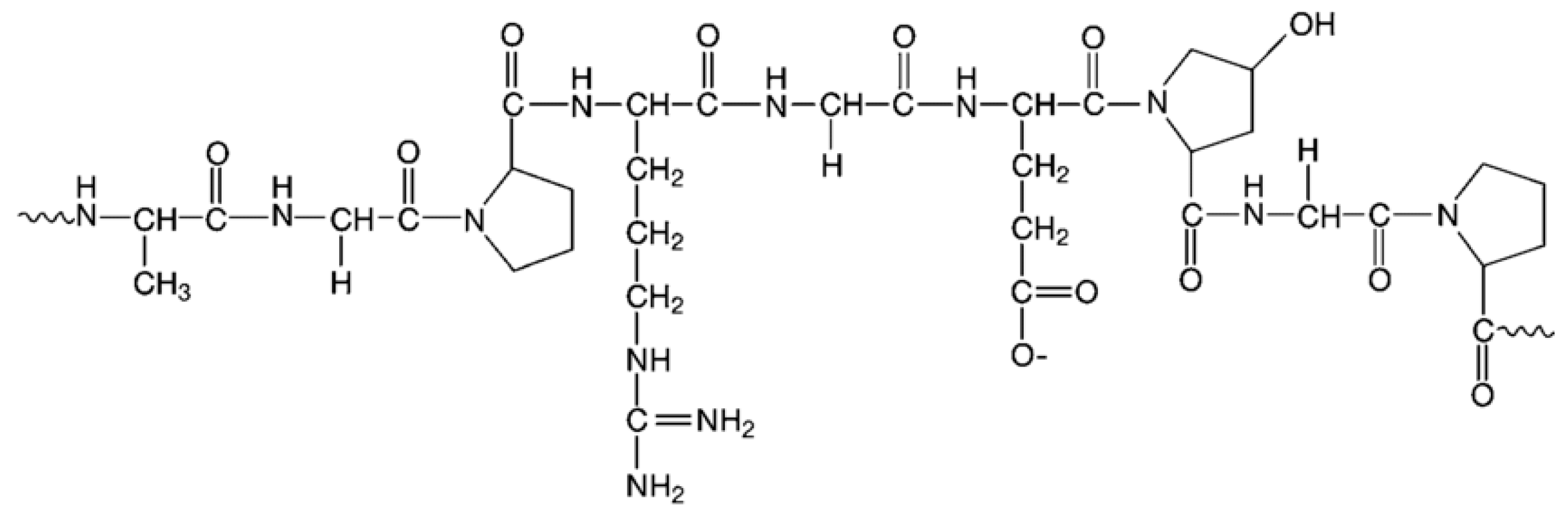
3.1. Collagen
Applications
3.2. Gelatin
Applications
3.3. Silk Fibroin
Application
3.4. Albumin
Application
4. Others
4.1. Polycaprolactone
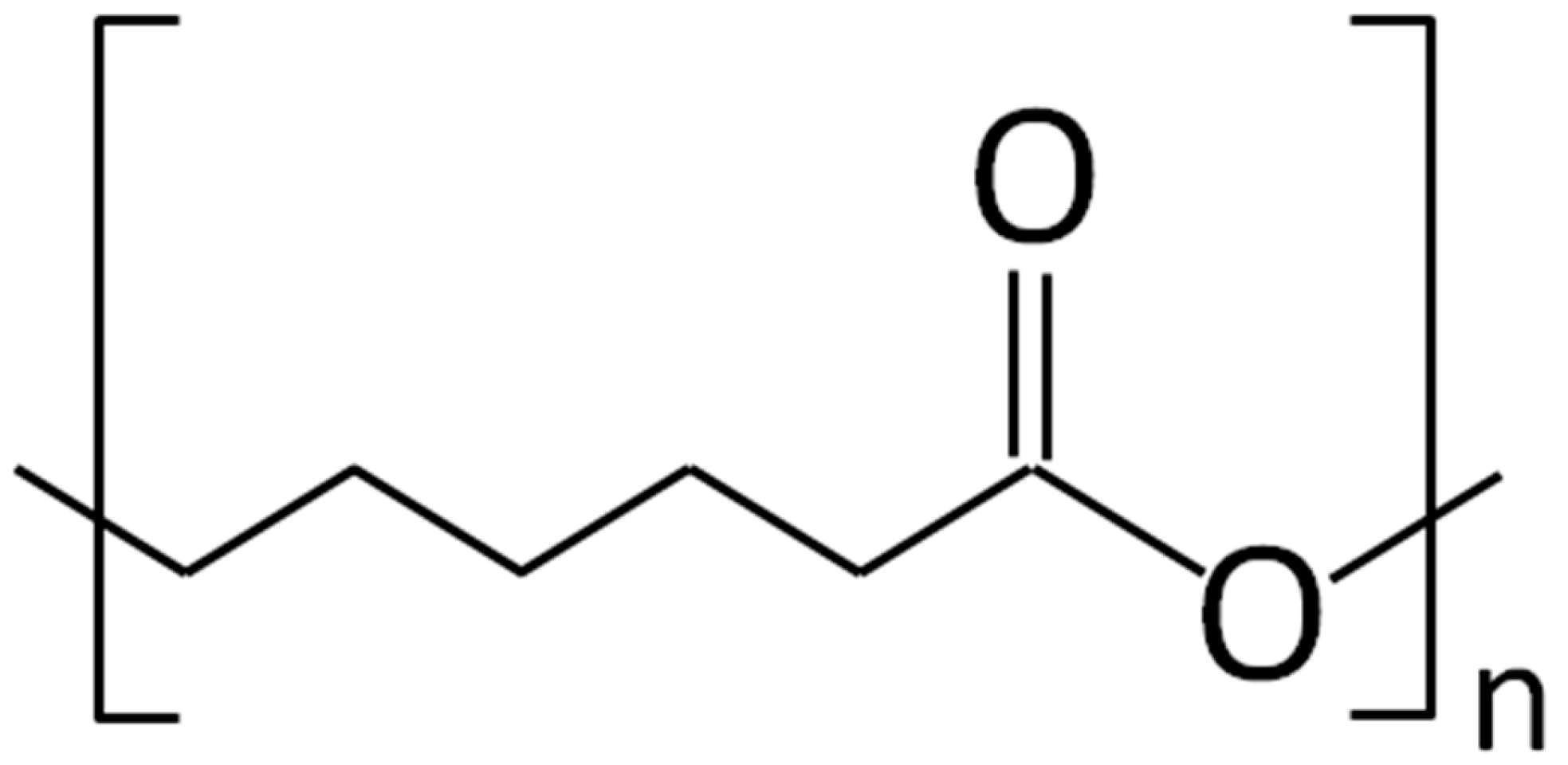
Application
4.2. Polyhydroxybutyrate
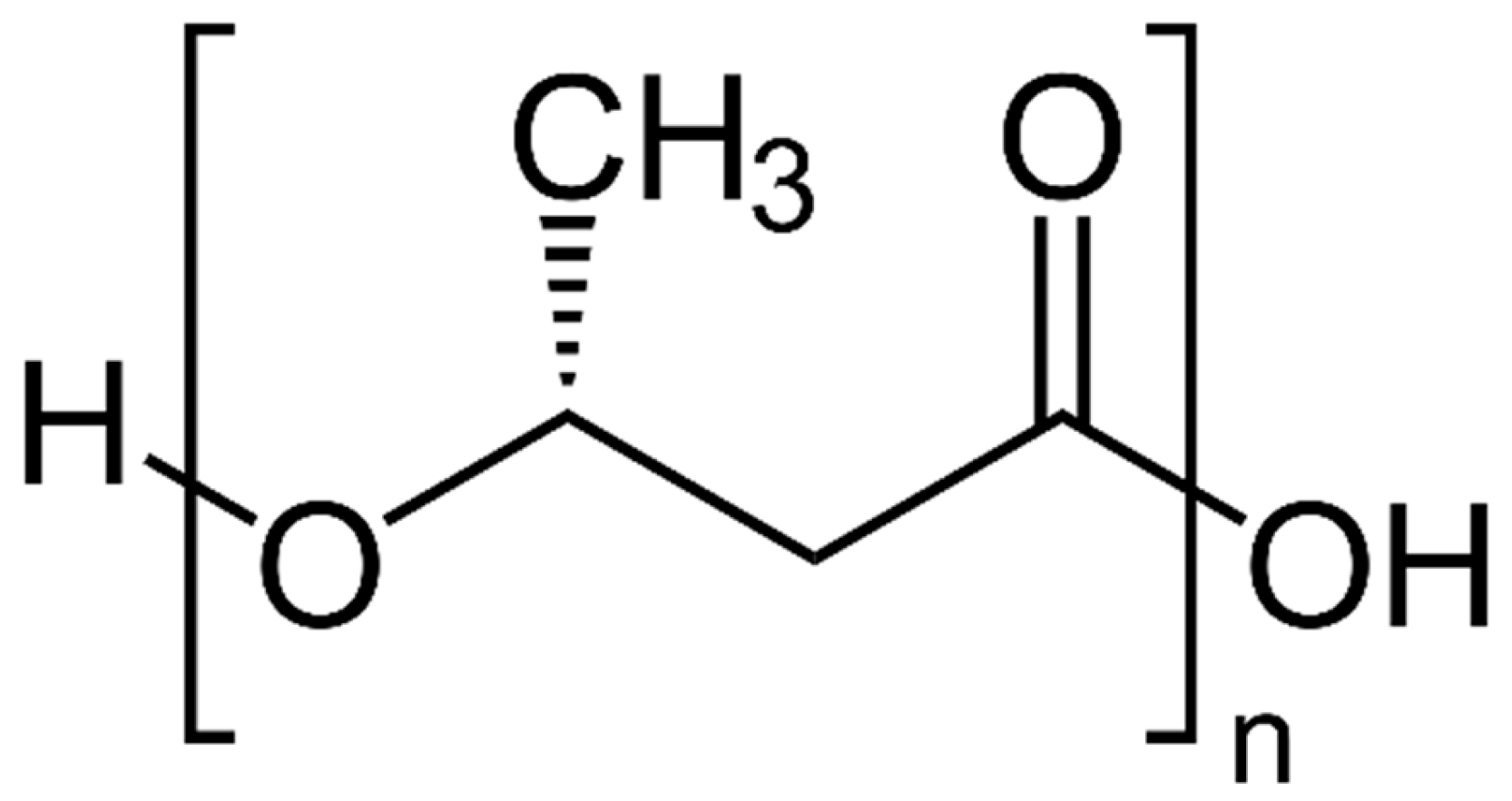
Application
4.3. Polylactic Acid

Applications
5. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, A.; Ringu, T.; Ghosh, S.; Pramanik, N. A comprehensive review on recent advances in preparation, physicochemical characterization, and bioengineering applications of biopolymers. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 7247–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Hasan, M.R. Synthetic Biopolymer’s. In Functional Biopolymer’s; Jafar Mazumder, M.A., Sheardown, H., Al-Ahmed, A., Eds.; Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, G.I.; Ndudi, W.; Ali, A.; Yousif, E.; Jikah, A.N.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Mafe, A.N.; Opiti, R.A.; Madueke, C.J.; et al. Biopolymers: An inclusive review. Hybrid Adv. 2025, 9, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, N.; Atif, M. Polysaccharides based biopolymers for biomedical applications: A review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 35, e6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Nie, S.; Yu, Q.; Xie, M.; Jia, Z. Reviews on Mechanisms of In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5692852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaith, A.; Jain, N.; Kaul, S.; Nagaich, U. Polysaccharide-infused bio-fabrication: Advancements in 3D bioprinting for tissue engineering and bone regeneration. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboulis, A.; Michailidou, G.; Koumentakou, I.; Bikiaris, D.N. Polysaccharide 3D Printing for Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.E.; Cummings, C.; Brass, A.; Chen, Y. Secondary and tertiary structures of hyaluronan in aqueous solution, investigated by rotary shadowing-electron microscopy and computer simulation. Hyaluronan is a very efficient network-forming polymer. Biochem. J. 1991, 274, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, C.; Stellavato, A.; D’AGostino, M.; D’AGostino, A.; Schiraldi, C.; La Gatta, A. Hyaluronan size and concentration: Effect on key biophysical and biochemical features. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, S.; Pirrung, M. The Fallacy of Hyaluronic Acid Binding a Thousand Times Its Weight in Water. Mat. Chem. 2023, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Kjøniksen, A.; Nyström, B. Effect of pH on the Behavior of Hyaluronic Acid in Dilute and Semidilute Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 274, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolar, J. Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan): A review. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyaluronic Acid Market Analysis. May 2025. Available online: https://markwideresearch.com/hyaluronic-acid-market/#:~:text=The%20global%20hyaluronic%20acid%20market%20was%20valued%20at,growth%20rate%20%28CAGR%29%20of%2010.4%25%20during%20this%20period (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Nosenko, T.N.; Sitnikova, V.E.; Uspenskaya, M.V. Sorption of human serum albumin on surface IPN acrylic hydrogels filled with sodium hyaluronate. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Peng, X.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, X. The application of hyaluronic acid in bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.; Silva, A.C.; Marques, A.C.; Lobo, J.S.; Amaral, M.H. Biotechnology Applied to Cosmetics and Aesthetic Medicines. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwowska, N.M.; Bebenek, K.A.; Żądło, D.A.; Wcisło-Dziadecka, D.L. Physiochemical properties and application of hyaluronic acid: A systematic review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzillo, R.; Schiraldi, C.; Corsuto, L.; D’agostino, A.; Filosa, R.; De Rosa, M.; La Gatta, A. Optimization of hyaluronan-based eye drop formulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, A.; Priefer, R. Hyaluronic acid applications in ophthalmology, rheumatology, and dermatology. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 489, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Goltsche, K.; Cheng, L.; Xie, F.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Zhong, Z.; Haag, R. Hyaluronic acid-shelled acid-activatable paclitaxel prodrug micelles effectively target and treat CD44-overexpressing human breast tumor xenografts in vivo. Biomaterials 2016, 84, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, A.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhang, K. Advances in Hyaluronic Acid for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 910290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Moon, M.J.; Surendran, S.P.; Jeong, Y.Y. Biomedical Applications of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanomaterials in Hyperthermic Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, J. Hydrogel Preparation Methods and Biomaterials for Wound Dressing. Life 2021, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasvani, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D. Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery, route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshidfar, N.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Alginate-Based Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoux, M.A.; Guilak, F.; Setton, L.A. Compressive and shear properties of alginate gel: Effects of sodium ions and alginate concentration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 47, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.-J.; Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Decoupling the dependence of rheological/mechanical properties of hydrogels from solids concentration. Polymer 2002, 43, 6239–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Smith, M.K.; Mooney, D.J. Designing alginate hydrogels to maintain viability of immobilized cells. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4023–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkakula, J.R.; Gujarathi, P.; Pansare, P.; Tripathi, S. A comprehensive review on alginate-based delivery systems for the delivery of chemotherapeutic agent: Doxorubicin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X. Alginate hydrogel dressings for advanced wound management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdiri, K.; Cayla, A.; Elamri, A.; Erard, A.; Salaun, F. Alginate-Based Bio-Composites and Their Potential Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alginate Market Value. Available online: https://www.futuredatastats.com/alginate-market#:~:text=The%20global%20Alginate%20Market%20size%20was%20valued%20at,a%20value%20of%20USD%201.47%20Billion%20by%202032 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, K. Preparation and dye filtration property of electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate–calcium alginate/carbon nanotubes composite nanofibrous filtration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 161, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Hu, Z.-C. The development of an alginate/polycaprolactone composite scaffold for in situ transfection application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.; Kievit, F.M.; Florczyk, S.J.; Veiseh, O.; Wu, J.; Park, J.O.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Alginate Scaffold Culture System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Increases Malignancy and Drug Resistance. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel Kou, S.; Peters, L.M.; Mucalo, M.R. Chitosan: A review of sources and preparation methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan Preparation from Marine Sources. Structure, Properties and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- No, H.K.; Meyers, S.P.; Lee, K.S. Isolation and characterization of chitin from crawfish shell waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Hajji, S.; Frachet, V.; Rinaudo, M.; Jellouli, K.; Nasri, M. Chitin extraction from shrimp shell using enzymatic treatment. Antitumor, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitosan Structure. Available online: https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chitozan (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a Wound Dressing Starting Material: Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janvikul, W.; Uppanan, P.; Thavornyutikarn, B.; Krewraing, J.; Prateepasen, R. In vitro comparative hemostatic studies of chitin, chitosan, and their derivatives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Yano, R.; Miyatake, K.; Tomohiro, I.; Shigemasa, Y.; Minami, S. Effects of chitin and chitosan on blood coagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitosan Market Value. Available online: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/chitosan-market#:~:text=The%20global%20chitosan%20market%20stood%20at%20a%20value,by%20the%20increasing%20product%20demand%20for%20treating%20wastewater (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Chicea, D.; Nicolae-Maranciuc, A. A Review of Chitosan-Based Materials for Biomedical, Food, and Water Treatment Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croisier, F.; Jérôme, C. Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriente, A.; Fasolino, I.; Gomez-Sánchez, A.; Prokhorov, E.; Buonocore, G.G.; Luna-Barcenas, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Raucci, M.G. Chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite scaffolds to modulate osteogenic and inflammatory response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 110, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.N.; Veeresh, V.; Mallick, S.P.; Jain, Y.; Sinha, S.; Rastogi, A.; Srivastava, P. Design and evaluation of chitosan/chondroitin sulfate/nano-bioglass based composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thambiliyagodage, C.; Jayanetti, M.; Mendis, A.; Ekanayake, G.; Liyanaarachchi, H.; Vigneswaran, S. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Applications—A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Lee, D.S. Chitosan-based composite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motshekga, S.C.; Ray, S.S.; Onyango, M.S.; Momba, M.N. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan-based nanocomposites containing bentonite-supported silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles for water disinfection. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, T.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Adsorption and photocatalyst assisted dye removal and bactericidal performance of ZnO/chitosan coating layer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaye, M. Developments on gelling algal galactans, their structure and physico-chemistry. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Algae-Based Agarose Biomaterials: Production and Applications. In Algae-Based Biomaterials for Sustainable Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Xu, X.-W.; Chen, F.-Q.; Weng, H.-F.; Chen, J.; Ru, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, A.-F. Extraction, Modification and Biomedical Application of Agarose Hydrogels: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucca, P.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Sanjust, E. Agarose and Its Derivatives as Supports for Enzyme Immobilization. Molecules 2016, 21, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MarketWatch Global Agarose Market Analysis and Business Growth Outlook [2023–2030]. Available online: https://www.marketwatch.com/ (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Zarrintaj, P.; Manouchehri, S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Saeb, M.R.; Urbanska, A.M.; Kaplan, D.L.; Mozafari, M. Agarose-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 187, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garakani, S.S.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Atoufi, Z.; Kamrava, S.K.; Setayeshmehr, M.; Alizadeh, R.; Faghihi, F.; Bagher, Z.; Davachi, S.M.; Abbaspourrad, A. Fabrication of chitosan/agarose scaffolds containing extracellular matrix for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Khattab, A.; Islam, M.A.; Hweij, K.A.; Zeitouny, J.; Waters, R.; Sayegh, M.; Hossain, M.; Paul, A. Injectable Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Repair after Myocardial Infarction. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Kumar, C.U.; Jewrajka, S.K. Degradable/cytocompatible and pH responsive amphiphilic conetwork gels based on agarose-graft copolymers and polycaprolactone. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8548–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupert, R.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Thien, V.Y.; Yong, W.T.L. Carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Solieriaceae): Metabolism, Structure, Production, and Application. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 859635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; Da Silva, D.B., Jr.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; van de Velde, F. Portuguese carrageenophytes: Carrageenan composition and geographic distribution of eight species (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappa-Carrageenan (YC30039) Cas No: 11114-20-8—Chemical Structure. Available online: https://www.biosynth.com/p/YC30039/11114-20-8-kappa-carrageenan (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Noralian, Z.; Gashti, M.P.; Moghaddam, M.R.; Tayyeb, H.; Erfanian, I. Ultrasonically developed silver/iota-carrageenan/cotton bionanocomposite as an efficient material for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrageenan Market Value. Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/carrageenan-market#:~:text=The%20global%20carrageenan%20market%20is%20estimated%20to%20account,thickening%20and%20gelling%20agent%20derived%20from%20red%20seaweed (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Frediansyah, A. The antiviral activity of iota-, kappa-, and lambda-carrageenan against COVID-19: A critical review. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 12, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C. Carrageenans as Broad-Spectrum Microbicides: Current Status and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianculli, R.H.; Mase, J.D.; Schulz, M.D. Antiviral Polymers: Past Approaches and Future Possibilities. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 9158–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Farahani, M.; Sedighi, M.; Rabiee, N.; Savoji, H. Carrageenans for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 281, 119045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Quito, E.-M.; Ruiz-Caro, R.; Veiga, M.-D. Carrageenan: Drug Delivery Systems and Other Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Q.; Fan, G.; Luo, T.; McClements, D.J. Controlling lipid digestion profiles using mixtures of different types of microgel: Alginate beads and carrageenan beads. J. Food Eng. 2018, 238, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piard, C.; Luthcke, R.; Kamalitdinov, T.; Fisher, J. Sustained delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor from mesoporous calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite microparticles promotes in vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, E.G.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Chondrogenic potential of injectable κ-carrageenan hydrogel with encapsulated adipose stem cells for cartilage tissue-engineering applications. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ding, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Fan, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, D. Bacterial cellulose-based biomaterials: From fabrication to application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgieva, S. Bacterial Cellulose as a Versatile Platform for Research and Development of Biomedical Materials. Processes 2020, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lanot, A.; Mao, N. The relationship between molecular weight of bacterial cellulose and the viscosity of its copper (II) ethylenediamine solutions. Cellulose 2024, 31, 7973–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupașcu, R.E.; Ghica, M.V.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.-E.; Popa, L.; Velescu, B.Ș.; Arsene, A.L. An Overview Regarding Microbial Aspects of Production and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose. Materials 2022, 15, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rol, F.; Belgacem, M.N.; Gandini, A.; Bras, J. Recent advances in surface-modified cellulose nanofibrils. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohite, B.V.; Patil, S.V. A novel biomaterial: Bacterial cellulose and its new era applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2014, 61, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BC Market Value. Available online: https://www.businessresearchinsights.com/market-reports/microbial-and-bacterial-cellulose-market-100001#:~:text=The%20global%20microbial%20and%20bacterial%20cellulose (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Berglund, L.; Squinca, P.; Baş, Y.; Zattarin, E.; Aili, D.; Rakar, J.; Junker, J.; Starkenberg, A.; Diamanti, M.; Sivlér, P.; et al. Self-Assembly of Nanocellulose Hydrogels Mimicking Bacterial Cellulose for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 2264–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, A.; Umamaheswari, S.; Vassou, M.C. Bacterial cellulose: A versatile biomaterial for biomedical application. Carbohydr. Res. 2025, 552, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacicedo, M.; Islan, G.; León, I.; Álvarez, V.; Chourpa, I.; Allard-Vannier, E.; García-Aranda, N.; Díaz-Riascos, Z.; Fernández, Y.; Schwartz, S.; et al. Bacterial cellulose hydrogel loaded with lipid nanoparticles for localized cancer treatment. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Xi, X.; Li, R.; Sun, G. Engineering Polysaccharides for Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozzi, F. Lactic acid bacteria. In Encyclopedia of Food Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 501–508. ISBN 9780123849533. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Montes, E. Dextran: Sources, Structures, and Properties. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dextran Structure. Available online: https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dekstran (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Hu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Luo, Y. Recent advances in dextran-based drug delivery systems: From fabrication strategies to applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 117999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jalili, S. Dextran, as a biological macromolecule for the development of bioactive wound dressing materials: A review of recent progress and future perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luanda, A.; Badalamoole, V. Past, present and future of biomedical applications of dextran-based hydrogels: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 228, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dextran Market Value. Available online: https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com/market-reports/dextran-market-107093#:~:text=The%20Dextran%20market%20was%20valued%20at%20USD%20229.29,during%20the%20forecast%20period%20from%202025%20to%202033 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Sun, G.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.-I.; Sebastian, R.; Dickinson, L.E.; Fox-Talbot, K.; Reinblatt, M.; Steenbergen, C.; Harmon, J.W.; Gerecht, S. Dextran hydrogel scaffolds enhance angiogenic responses and promote complete skin regeneration during burn wound healing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20976–20981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, C.I.W.; Garcea, G.; Strickland, A.; Maddern, G.J. Use of a Modified Chitosan–Dextran Gel to Prevent Peritoneal Adhesions in a Rat Model. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 171, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, T.P.; Peters, M.C.; Ennett, A.B.; Mooney, D.J. Polymeric system for dual growth factor delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, S.P.; Langer, R.; Fink, G.R.; Kohane, D.S. Injectable in situ cross-linking hydrogels for local antifungal therapy. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, J.; Evangelista, M.B.; Ferreira, L.; Gil, M.H. (Eds.) Carbohydrates Applications in Medicine; Research Signpost: Trivandrum, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Bazaka, K.; Crawford, R.J. Advanced synthetic polymer biomaterials derived from organic sources. In New Functional Biomaterials for Medicine and Healthcare; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 71–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Williams, D.F. Biomaterial Types. In Definitions of Biomaterials for the Twenty-First Century; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviello, G.; Connor, B.; McBrearty, J.; Rodriguez, G.; Hu, X. Protein and Polysaccharide-Based Optical Materials for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, S.S.; Mahmood, A. Biopolymers: An Introduction and Biomedical Applications. J. Phys. Chem. Funct. Mater. 2024, 7, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen Structure and Stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, M.; Abdul, N.S.; Qamar, Z.; Al Bahri, B.M.; Al Ghalayini, K.Z.K.; Kakti, A. Collagen Structure, Synthesis, and Its Applications: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e24856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbese, Z.; Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Collagen-Based Nanofibers for Skin Regeneration and Wound Dressing Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Pei, Y.; Tang, K.; Albu-Kaya, M.G. Structure, extraction, processing, and applications of collagen as an ideal component for biomaterials—A review. Collagen Leather 2023, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collagen Market Value. Available online: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/collagen-market#:~:text=The%20global%20collagen%20market%20size%20attained%20a%20value,and%20reach%20around%20USD%2015.37%20Billion%20by%202034 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Rütsche, D.; Nanni, M.; Rüdisser, S.; Biedermann, T.; Zenobi-Wong, M. Enzymatically Crosslinked Collagen as a Versatile Matrix for In Vitro and In Vivo Co-Engineering of Blood and Lymphatic Vasculature. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2209476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshanbinfar, K.; Evans, A.D.; Samanta, S.; Kolesnik-Gray, M.; Fiedler, M.; Krstic, V.; Engel, F.B.; Oommen, O.P. Enhancing biofabrication: Shrink-resistant collagen-hyaluronan composite hydrogel for tissue engineering and 3D bioprinting applications. Biomaterials 2025, 318, 123174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbaresso, R.C.; Rău, I.; Zgârian, R.G.; Meghea, A.; Ghica, M.V. Niflumic acid-collagen delivery systems used as anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics in dentistry. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2013, 17, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobaraki, M.; Ghaffari, M.; Yazdanpanah, A.; Luo, Y.; Mills, D. Bioinks and bioprinting: A focused review. Bioprinting 2020, 18, e00080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G. Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, J.A.; Akhter, N.; Ashraf, Q.S.; Mir, S.A.; Makroo, H.A.; Majid, D.; Barba, F.J.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Dar, B. A comprehensive review on gelatin: Understanding impact of the sources, extraction methods, and modifications on potential packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, M.C.; Hernáez-Moya, R.; Iturriaga, L.; Pedraz, J.L.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Taebnia, N.; Orive, G. Recent advances in gelatin-based therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommareddy, S.; Shenoy, D.B.; Amiji, M.M. Gelatin Nanoparticles and Their Biofunctionalization. In Nanotechnologies for the Life Sciences, 1st ed.; Kumar, C.S.S.R., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelatin Market Value. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/gelatin-market-107012 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Mohanto, S.; Narayana, S.; Merai, K.P.; Kumar, J.A.; Bhunia, A.; Hani, U.; Al Fatease, A.; Gowda, B.J.; Nag, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; et al. Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutmacher, D.W. Scaffold design and fabrication technologies for engineering tissues—State of the art and future perspectives. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’BRien, F.J. Biomaterials & scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchels, F.P.W.; Feijen, J.; Grijpma, D.W. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, H.-T.; Zhao, J.-M.; Cao, M.; Wang, S.-D. Review on Fabrication and Application of Regenerated Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin Materials. Autex Res. J. 2023, 23, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q. Advances in Preparation and Properties of Regenerated Silk Fibroin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Ki, C.S.; Oh, H.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C. Molecular weight distribution and solution properties of silk fibroins with different dissolution conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.R. Self-Assembled Protein–Drug Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. In Advanced and Modern Approaches for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, K.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, R.-Y.; Kim, I.S.; Zhang, K.-Q. A Review of Structure Construction of Silk Fibroin Biomaterials from Single Structures to Multi-Level Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.L.; Dhanya, B.; Sukriti; Rani, V.; Thakur, M.; Jeslin, J.; Kushwaha, R. Carbohydrate and protein based biopolymeric nanoparticles: Current status and biotechnological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán, F.R.; Gaspar, G.; Chomachayi, M.D.; Jalali-Arani, A.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; Cenis, J.L.; de la Orden, M.U.; Pérez, E.; Urreaga, J.M.M. Influence of addition of organic fillers on the properties of mechanically recycled PLA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24291–24304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SF Market Value. Available online: https://www.cognitivemarketresearch.com/silk-fibroin-sf-market-report (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Agostinacchio, F.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Dirè, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Motta, A. Silk fibroin-based inks for in situ 3D printing using a double crosslinking process. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, D.; Shokat, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Javaid, A.; Khurshid, M.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Nashwan, A.J. Exploring the recent developments of alginate silk fibroin material for hydrogel wound dressing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.U.D.; Gautam, S.P.; Qadrie, Z.L.; Gangadharappa, H. Silk fibroin as a natural polymeric based bio-material for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems-A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, E.; Moghaddam, M.M.; Kazemi-Lomedasht, F. Use of Albumin for Drug Delivery as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2024, 25, 676–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoufinia, R.; Mota, A.; Keyhanvar, N.; Safari, F.; Shamekhi, S.; Abdolalizadeh, J. Overview of Albumin and Its Purification Methods. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutapea, T.P.H.; Madurani, K.A.; Syahputra, M.Y.; Hudha, M.N.; Asriana, A.N.; Suprapto; Kurniawan, F. Albumin: Source, preparation, determination, applications, and prospects. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2023, 8, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzazy, H.M.E.; Christenson, R.H. All About Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics, and Medical Applications. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 2014–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanapala, P.; De Silva, C.; Doran, T.; Suphioglu, C. Cracking the egg: An insight into egg hypersensitivity. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albumin Market Value. Available online: https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/albumin-market/37220/#:~:text=The%20Albumin%20Market%20size%20was%20valued%20at%20USD,liver%20accounting%20for%2050%25%20of%20blood%20plasma%20proteins (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Shastri, D.; Raj, V.; Lee, S. Revolutionizing Alzheimer’s treatment: Harnessing human serum albumin for targeted drug delivery and therapy advancements. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 99, 102379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoukian, O.S.; Sardashti, N.; Stedman, T.; Gailiunas, K.; Ojha, A.; Penalosa, A.; Mancuso, C.; Hobert, M.; Kumbar, S.G. Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. In Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 462–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, M.-O.; Vercesi, F. Polycaprolactone: How a Well-Known and Futuristic Polymer Has Become an Innovative Collagen-Stimulator in Esthetics. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G.K.; Yadav, K.S. Fabrication and Characterization of Polycaprolactone-Based Green Materials for Drug Delivery. In Applications of Advanced Green Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 395–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cai, T.; Jin, Q.; Ji, J. Design and fabrication of functional polycaprolactone. e-Polymers 2015, 15, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Natta, F.J.; Hill, J.W.; Carothers, W.H. Studies of Polymerization and Ring Formation. XXIII.1 ε-Caprolactone and its Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The return of a forgotten polymer—Polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Gentile, G.; Sorrentino, L.; Ambrosio, L. Polycaprolactone: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; Mark, H.F., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labet, M.; Thielemans, W. Synthesis of polycaprolactone: A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3484–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.Y.; Kim, B.C.; Yoon, K.J. The Effect of Molecular Weight of Polycaprolactone on the Ester Interchange Reactions during Melt Blending with Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. J. 2002, 34, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnikowski, M.; Dargaville, T.R.; Ivanovski, S.; Hutmacher, D.W. Degradation mechanisms of polycaprolactone in the context of chemistry, geometry and environment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 96, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimowska, A.; Morawska, M.; Bocho-Janiszewska, A. Biodegradation of poly(ε-caprolactone) in natural water environments. PJCT 2017, 19, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polycaprolactone Structure. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polycaprolactone#/media/File:Polycaprolactone_structure.png (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- PCL Market Value. Available online: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-polycaprolactone-pcl-market#:~:text=The%20global%20polycaprolactone%20PCL%20market%20size%20was%20valued,during%20the%20forecast%20period%20of%202024%20to%202031 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Azimi, B.; Nourpanah, P.; Rabiee, M.; Arbab, S. Poly (∊-caprolactone) Fiber: An Overview. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2014, 9, 155892501400900309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, C.K.; DeForest, C.A. Polymer Design and Development. In Biology and Engineering of Stem Cell Niches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, R.; Mahajan, A.; Nandana, D.; Katti, D.S.; Mehrotra, D. Polycaprolactone as biomaterial for bone scaffolds: Review of literature. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 10, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonartsev, A.P.; Bonartseva, G.A.; Reshetov, I.V.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Shaitan, K.V. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates in medicine and the biological activity of natural poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Acta Nat. 2019, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdam, B.; Fournet, M.B.; McDonald, P.; Mojicevic, M. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Factors Impacting Its Chemical and Mechanical Characteristics. Polymers 2020, 12, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanrasu, K. Microbial Bio-Based Polymer Nanocomposite for Food Industry Applications. In Handbook of Microbial Nanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezcano, M.F.; Álvarez, G.; Chuhuaicura, P.; Godoy, K.; Alarcón, J.; Acevedo, F.; Gareis, I.; Dias, F.J. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Scaffolds for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: A Systematic Review of Animal Models. Biology 2022, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Gupta, N.S.; Bezek, L.B.; Linn, J.; Bejagam, K.K.; Banerjee, S.; Dumont, J.H.; Nam, S.Y.; Kang, H.W.; Park, C.H.; et al. Biodegradation Studies of Polyhydroxybutyrate and Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-Polyhydroxyvalerate Films in Soil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleksy, M.; Dynarowicz, K.; Aebisher, D. Polymer and composite materials used in medicine. Polimery 2023, 68, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyhydroxybutyrate Structure. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polyhydroxybutyrate#/media/File:Poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrat.svg (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- PHB Market Value. Available online: https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/polyhydroxybutyrate-phb-market/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Israni, N.; Shivakumar, S. Polyhydroxybutyrate. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 405–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, N.G.; Bahú, J.O.; Blanco-Llamero, C.; Severino, P.; Concha, V.O.; Souto, E.B. Polylactic acid (PLA): Properties, synthesis, and biomedical applications—A review of the literature. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1309, 138243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in modern medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranakoti, L.; Gangil, B.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, T.; Sharma, S.; Ilyas, R.; El-Khatib, S. Critical Review on Polylactic Acid: Properties, Structure, Processing, Biocomposites, and Nanocomposites. Materials 2022, 15, 4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aniśko, J.; Barczewski, M. Polylactide: From Synthesis and Modification to Final Properties. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2021, 15, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, H.R.; Ebrahimi, F. Synthesis, properties, and applications of polylactic acid-based polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butbunchu, N.; Pathom-Aree, W. Actinobacteria as Promising Candidate for Polylactic Acid Type Bioplastic Degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Albuquerque, T.L.; Marques, J.E., Jr.; De Queiroz, L.P.; Ricardo, A.D.S.; Rocha, M.V.P. Polylactic acid production from biotechnological routes: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polylactic_Acid Structure. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polylactic_acid#/media/File:Polylactid_sceletal.svg (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- PLA Market Value. Available online: https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com/market-reports/polylactic-acid-pla-market-111310#:~:text=The%20global%20Polylactic%20Acid%20%28PLA%29%20market%20was%20valued,CAGR%20of%2017.96%25%20during%20the%20forecast%20period%202025%E2%80%932033 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Yang, Z.; Yin, G.; Sun, S.; Xu, P. Medical applications and prospects of polylactic acid materials. iScience 2024, 27, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhao, M.; Xu, F.; Yang, B.; Li, X.; Meng, X.; Teng, L.; Sun, F.; Li, Y. Synthesis and Biological Application of Polylactic Acid. Molecules 2020, 25, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
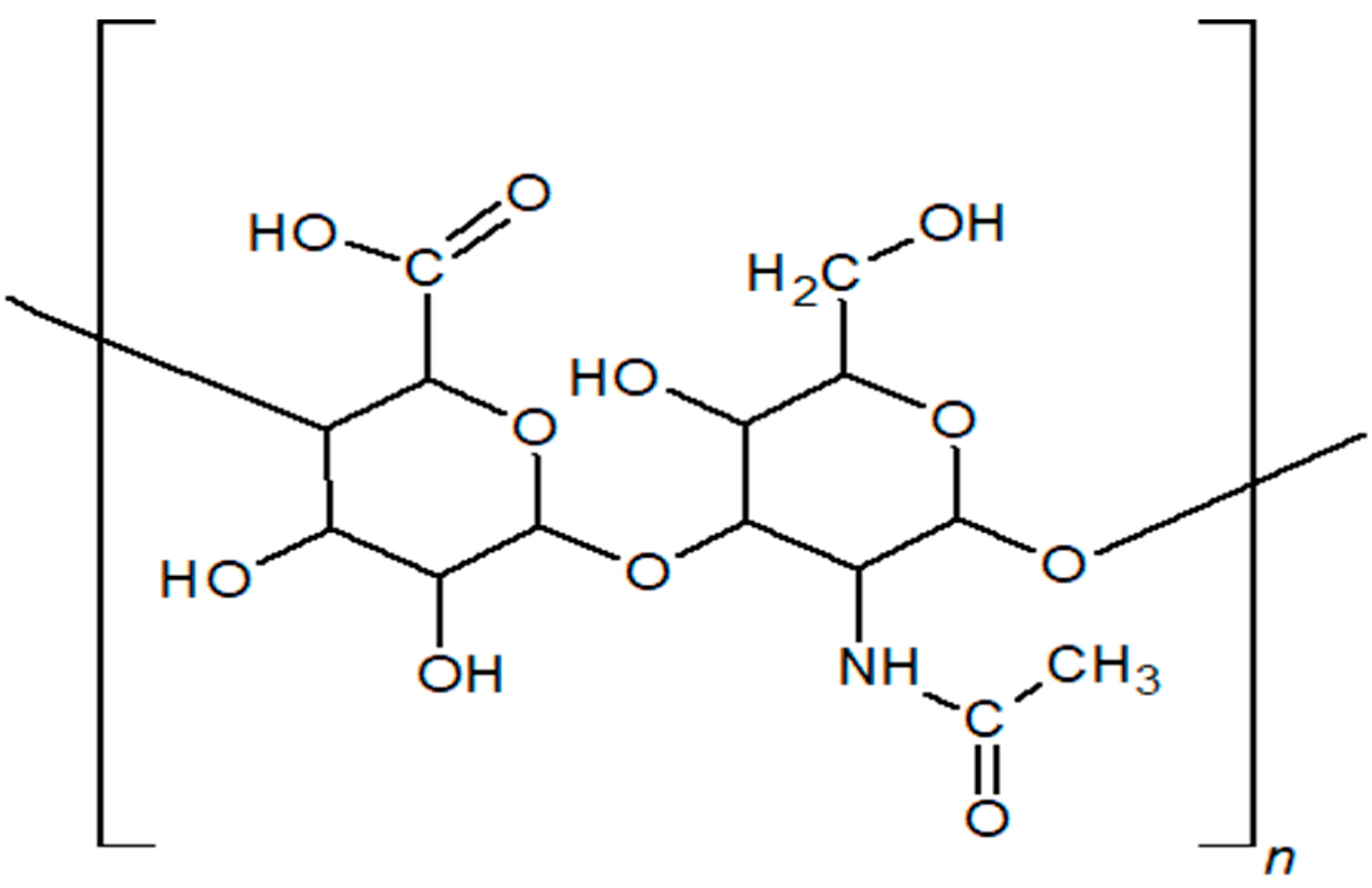
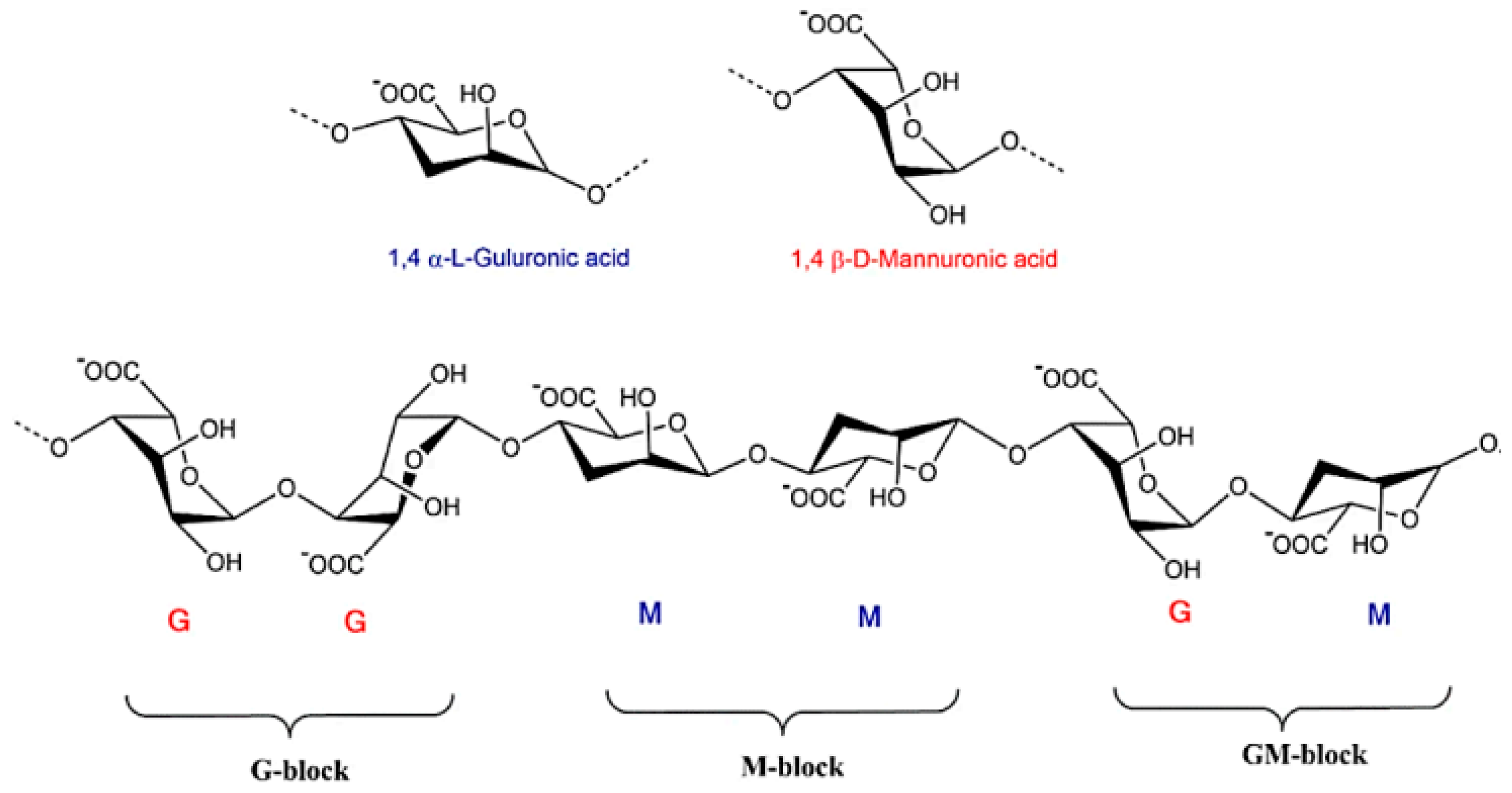




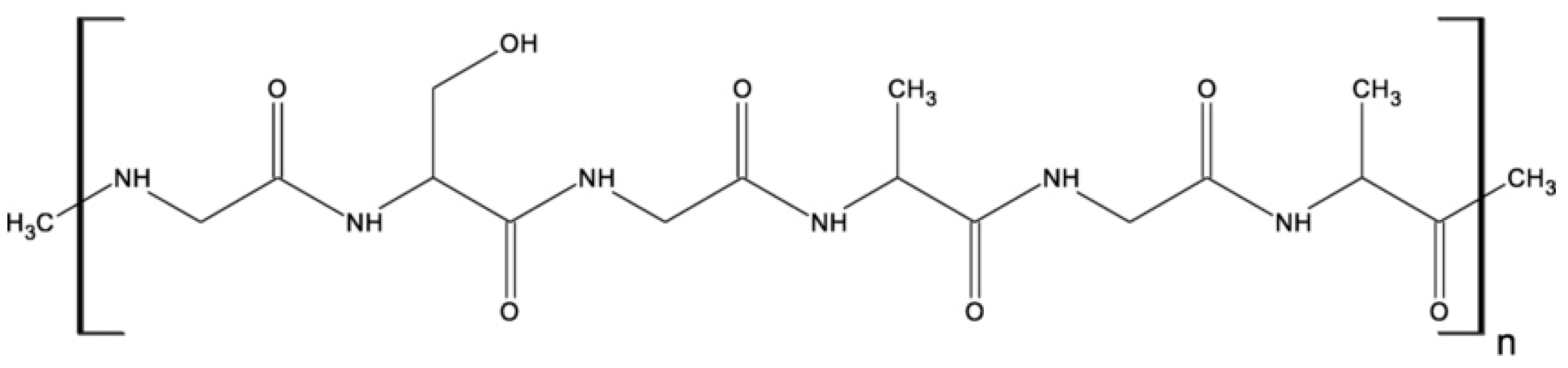
| Biopolymer | Type/Structure | Origin | Key Properties | Applications | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyaluronic Acid (HA) | Linear macromolecular mucopolysaccharide consisting of alternately linked D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine monomers | Rooster combs, Pig umbilical cord, Bovine vitreous body, Bovine synovial fluid, Streptococci, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bacillus subtilis, Lactococcus lactis | Non-immunogenicity, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, high water retention, pseudoplasticity, and viscoelasticity | Diagnostics, therapeutics, drug delivery, tissue engineering, cosmetics, ophthalmology, cancer treatment, wound healing | [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,23,24] |
| Alginate (ALG) | Anionic polysaccharide composed of β-D-mannuronic acid (M) and α-L-guluronic acid (G) monomers | Brown seaweed, specific bacterial genera (Pseudomonas, Azotobacter), and marine macroalgae species | Hydrophilic, non-toxic, inert, non-immunogenic, high absorbency, biodegradability, and biocompatibility | Tissue engineering (hydrogels, scaffolds), wound dressings | [25,34,35,36] |
| Chitosan (CH) | Linear, semi-crystalline polysaccharide consisting of (N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine units | Partial deacetylation of chitin | Biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, non-immunogenic hemostatic activity, antimicrobial | Tissue engineering (hydrogels, scaffolds), wound healing, drug delivery | [43,45,47,48,49,50,51,53,54] |
| Agarose (AGR) | Linear polymer composed of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose units | Red algae | numerous hydroxyl groups, | Tissue engineering, drug delivery, and dental applications | [60,61,62,63] |
| Carrageenan (CG) | Anionic sulfated polysaccharide, various types: kappa (κ), iota (ι), mu (μ), nu (ν), theta (θ), lambda (λ) | Red seaweeds (Rhodophyceae) | Bioactive properties (antibacterial, antiviral, anticoagulant) | Drug delivery, tissue engineering | [70,71,72,73,76,77] |
| Bacterial Cellulose (BC) | Nanostructure | Gram-negative bacteria (Gluconacetobacter, Acetobacter, Agrobacterium, Achromobacter, Aerobacter, Sarcina, Azobacter, Rhizobium, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, and Alcaligenes) | High mechanical strength, high purity, and biocompatibility | Tissue repairing, drug-controlled release, and wound healing | [78,79,85,86,87] |
| Dextran (DX) | Linear a-1,6-linked D-glucopyranose residues | Bacterial secretion | Solubility in various solvents, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility | Skin regeneration, prevention of intra-abdominal adhesions, and drug delivery | [88,92,93,96,97] |
| Biopolymer | Type/Structure | Origin | Key Properties | Applications | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen (CL) | Fibrous protein, triple right-handed helical structure | Animal tissues | Tensile strength, biocompatibility, and biodegradability | Tissue engineering, drug carrier | [103,104,105,110,111,112] |
| Gelatin (GL) | Fibrous protein, amphoteric properties | Acid or alkaline hydrolysis of collagen | Biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-cytotoxicity, and cell adhesion | Tissue engineering, 3D cell growth scaffolds | [113,114,117,120,121,122,123] |
| Silk Fibroin (SF) | glycoprotein, anti-parallel beta-sheet structure | Silkworms (Bombyx mori) | Non-toxic degradation products, mechanical strength, low immunogenicity, water-insoluble | Tissue engineering, drug carriers, wound healing | [127,128,129,132,133,134] |
| Albumin (ALB) | Globular protein | Blood plasma | Biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-immunogenicity, and versatile binding | Drug delivery systems | [121,135,141] |
| Biopolymer | Type/Structure | Origin | Key Properties | Applications | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | ε-caprolactone units | Chemical synthesis | Biocompatible, biodegradable, bioresorbable | Sutures, drug-release systems, tissue scaffolds | [7,143,144,155,156,157] |
| Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) | linear polymer built from 3-hydroxybutyrate units | Bacteria | Biocompatible, biodegradable, thermoplastic | Orthopaedic engineering, nerve regeneration, drug delivery, tissue regeneration | [159,160,161,162,166] |
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | aliphatic polyester built from lactic acid units | Chemical synthesis or bacterial fermentation | Biocompatible, biodegradable, hydrophobic, short degradation time | Tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, implants, sutures | [167,168,169,171,176,177] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grabowski, M.; Gmyrek, D.; Żurawska, M.; Trusek, A. Biopolymers in Biotechnology and Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review. Macromol 2025, 5, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030034
Grabowski M, Gmyrek D, Żurawska M, Trusek A. Biopolymers in Biotechnology and Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review. Macromol. 2025; 5(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrabowski, Maciej, Dominika Gmyrek, Maria Żurawska, and Anna Trusek. 2025. "Biopolymers in Biotechnology and Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review" Macromol 5, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030034
APA StyleGrabowski, M., Gmyrek, D., Żurawska, M., & Trusek, A. (2025). Biopolymers in Biotechnology and Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review. Macromol, 5(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030034






